Lipidomic Profiling of Sweetpotato During Different Developmental Stages Using LC-ESI-MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Growing Conditions
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.4. HPLC Conditions
2.5. ESI-MS/MS Conditions
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lipid Composition of Sweetpotato G79
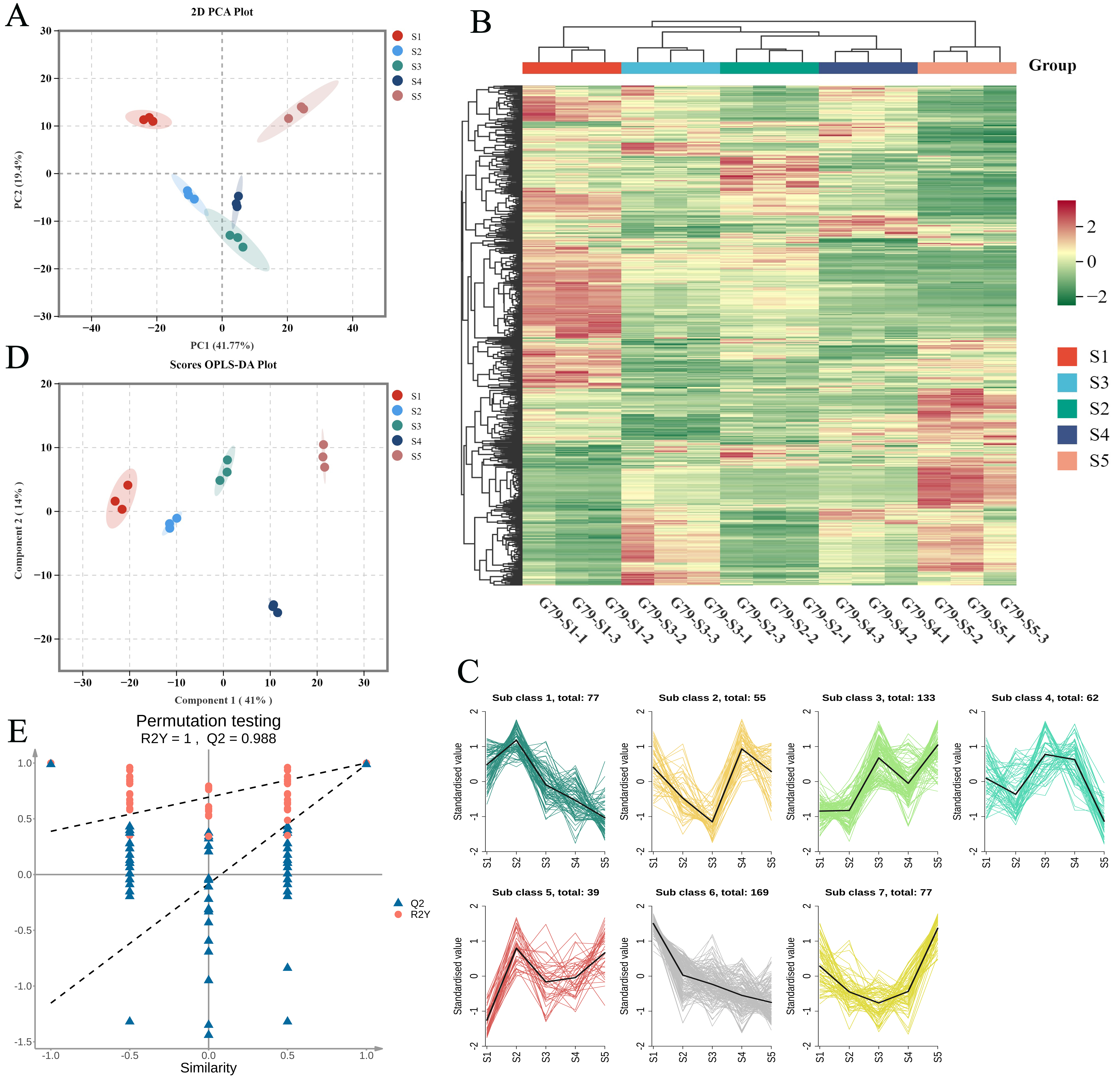
3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Lipids in G79 Across Different Developmental Stages
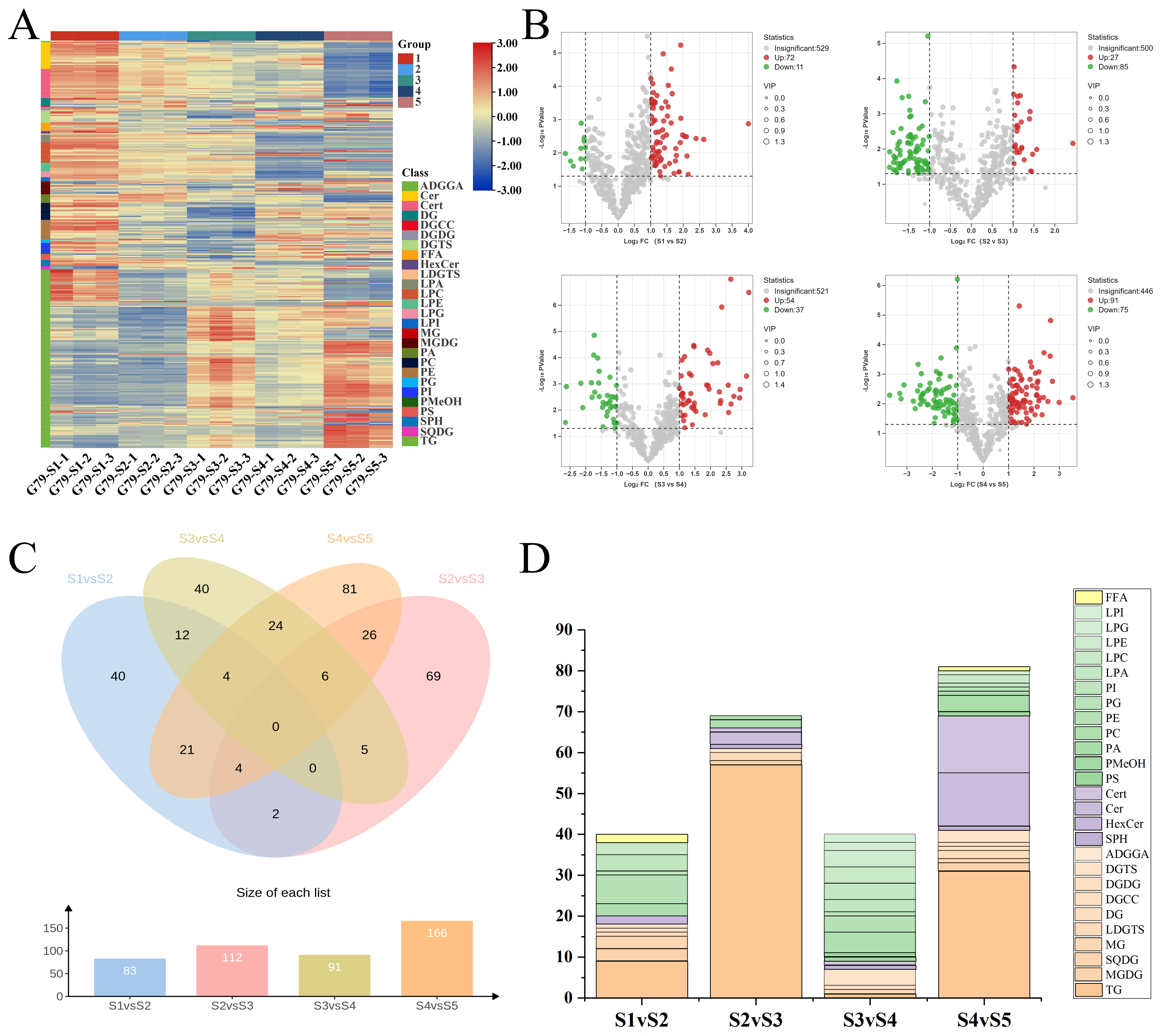
3.3. Identification and Characterization of Stage-Specific Differential Lipids in G79 Across Developmental Stages
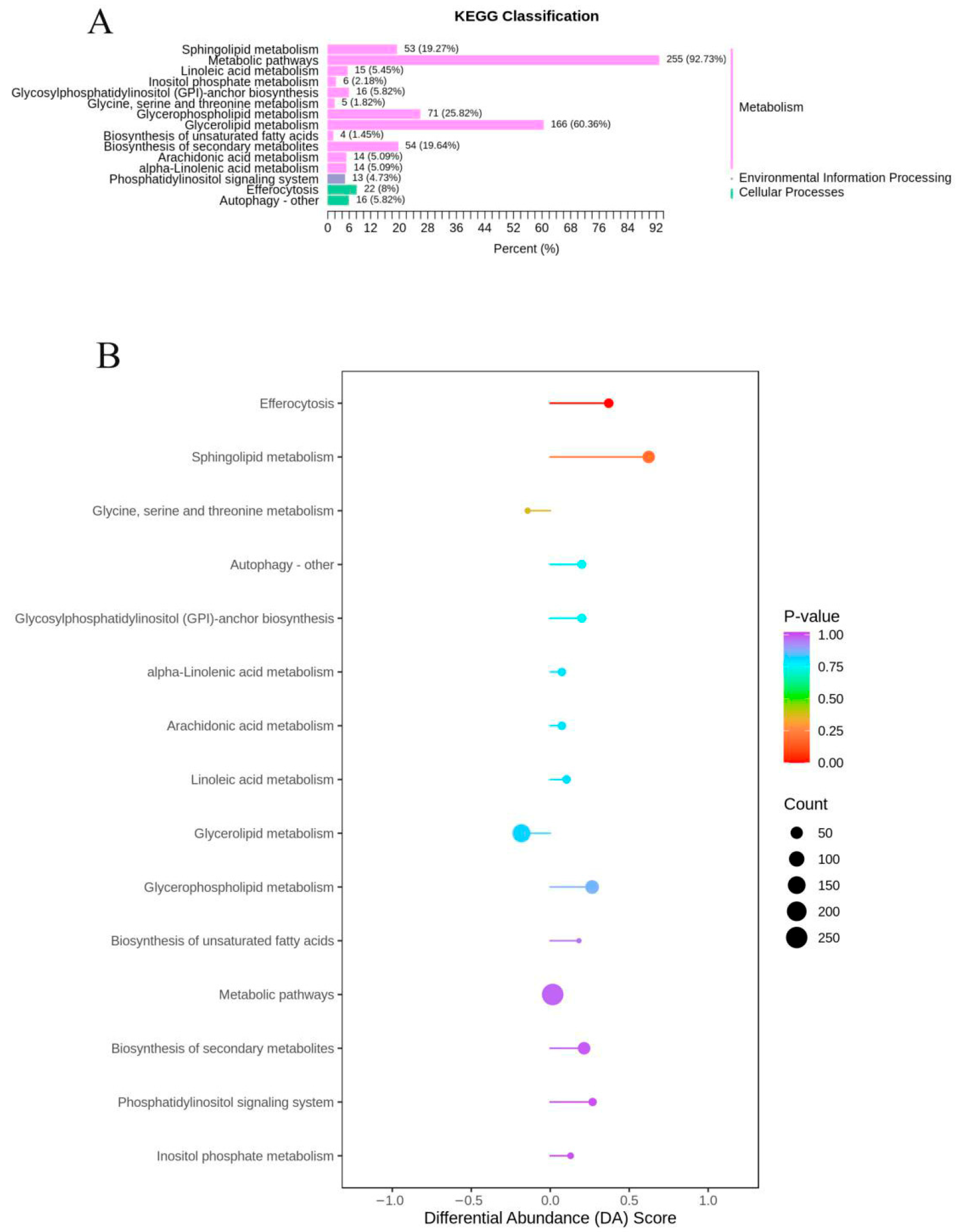
3.4. Lipid Metabolism Pathways Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.K. A comprehensive review of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam): Revisiting the associated health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.A.; Nie, S.P.; Zhu, F. Chemical constituents and health effects of sweet potato. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 90–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartabiano Leite, C.E.; Porcu, O.M.; De Casas, A.F. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L. Lam) nutritional potential and social relevance: A review. History 2020, 11, 23–40. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S. Sweetpotatoes [Ipomoea batatas (L.) lam]: The super food of the Next Century? An intensive review on their potential as a sustainable and versatile food source for future generations. CyTA-J. Food 2024, 22, 2397553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Huang, Y.M.; Li, H.F.; Chen, T.Y.; Yin, J. Breeding and adaptability analysis of new fresh-eating sweet potato variety Guishu No. 15. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2025, 46, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Sun, L.; Kong, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Dong, T. Progress on physiological and molecular mechanisms of storage root formation and development in sweetpotato. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 308, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, C.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, S. UPLC-MS-MS-based lipidomics for the evaluation of changes in lipids during dry-cured mutton ham processing. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; OuYang, B.; Wang, W.F.; Lan, D.M.; Wang, Y.H. Lipidomics analysis of rice bran during storage unveils mechanisms behind dynamic changes in functional lipid molecular species. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Singer, S.D.; Chen, G.Q. The role of triacylglycerol in plant stress response. Plants 2020, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.C.; Zhang, Y.; Kumar, A.; Francis, T.; Giblin, E.M.; Barton, D.L.; Ferrie, J.R.; Laroche, A.; Shah, S.; Zhu, W.; et al. Molecular modification of triacylglycerol accumulation by over-expression of DGAT1 to produce canola with increased seed oil content under field conditions. Botany 2009, 87, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.D.; Wang, Q.L.; Yan, X.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, C.X.; Meng, Q.; Xu, F.; Luo, M. The disruptions of sphingolipid and sterol metabolism in the short fiber of Ligon-Lintless-1 mutant revealed obesity impeded cotton fiber elongation and secondary cell wall deposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Li, C.M.; Hu, M.M.; He, X.M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wu, C.Y.; Duan, Q.; Peng, L.G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Evaluating rice lipid content, yield, and quality in response to nitrogen application rate and planting density. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1469264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.X.; Wang, Q.F.; He, Y.; Yu, H.M.; Lin, L.M.; Zhang, Z.W. Lipidomic Profiling and Storage-Induced Changes in Cassava Flour Using LC-MS/MS. Foods 2024, 13, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado Souza, L.; David, L.C.; Drapal, M.; Fraser, P.D.; Hofmann, J.; Klemens, P.A.; Perez-Fons, L. Cassava metabolomics and starch quality. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2019, 4, e20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reszczyńska, E.; Hanaka, A. Lipids composition in plant membranes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 78, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.D.; Zou, J.; Weselake, R.J. Abiotic factors influence plant storage lipid accumulation and composition. Plant Sci. 2016, 243, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, T.; Asija, S.; Umar, S.; Gupta, R. The intricate role of lipids in orchestrating plant defense responses. Plant Sci. 2024, 338, 111904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Lin, Q.H.; Xia, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.P.; Ouyang, Z.; Xia, Y. LipidOA: A machine-learning and prior-knowledge-based tool for structural annotation of glycerophospholipids. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 16759–16767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.B.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.T.; Hu, Y.C. Evaluation of lipidomics profile of quinoa flour and changes during storage based on ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole exactive orbitrap mass spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Corbacho, M.J.; Salama, M.F.; Canals, D.; Senkal, C.E.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingolipids in mitochondria. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadyro, O.; Samovich, S.; Edimecheva, I. Free-radical and biochemical reactions involving polar part of glycerophospholipids. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.X.; Yao, Y.Q.; Yang, J.L.; Zheng, R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.Y. Quality dynamic changes of nine sweetpotato varieties in different developmental stages. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2025, 41, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Buslaev, P.; Gordeliy, V.; Grudinin, S.; Gushchin, I. Principal component analysis of lipid molecule conformational changes in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.C.; Shanklin, J. Triacylglycerol metabolism, function, and accumulation in plant vegetative tissues. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. The ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: Stress encounters of the lipid kind. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25847–25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehelpannala, C.; Rupasinghe, T.; Pasha, A.; Esteban, E.; Hennessy, T.; Bradley, D.; Ebert, B.; Provart, N.J.; Roessner, U. An Arabidopsis lipid map reveals differences between tissues and dynamic changes throughout development. Plant J. 2021, 107, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayama, T.; Riezman, H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölzl, G.; Dörmann, P. Chloroplast lipids and their biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Hardré-Liénard, H.; Miras, S.; Miège, C.; Block, M.A.; Revah, F.; Maréchal, E. Refolding from denatured inclusion bodies, purification to homogeneity and simplified assay of MGDG synthases from land plants. Protein Expr. Purif. 2023, 31, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.X.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, B.B.; Yu, W.; Xiao, Y.S.; Peng, F.T. Lipid metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal that phosphatidylcholine enhanced the resistance of peach seedlings to salt stress through phosphatidic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8846–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.J.; Huo, Y.W.; Yang, N.; Wei, T.T. Phosphatidic acid: From biophysical properties to diverse functions. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 1870–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, D.C.; Aguilera Albesa, S.; Pujol, A. Ceramide signalling in inherited and multifactorial brain metabolic diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 143, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, F.; Zhao, M.J.; Zhang, M.H.; Liu, J.K.; Marchioni, E. Determination and comparison of phospholipid profiles in eggs from seven different species using UHPLC-ESI-Triple TOF-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, C.C.; Caramujo, M.J. The various roles of fatty acids. Molecules 2018, 23, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.J.; Wu, Q.; Feng, M.L.; Li, R.; Zhou, L.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Cao, H.X. Lipidomic profiles of lipid biosynthesis in oil palm during fruit development. Metabolites 2023, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, C.; Sakane, F. Sphingomyelin synthase-related protein generates diacylglycerol via the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids in the absence of ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
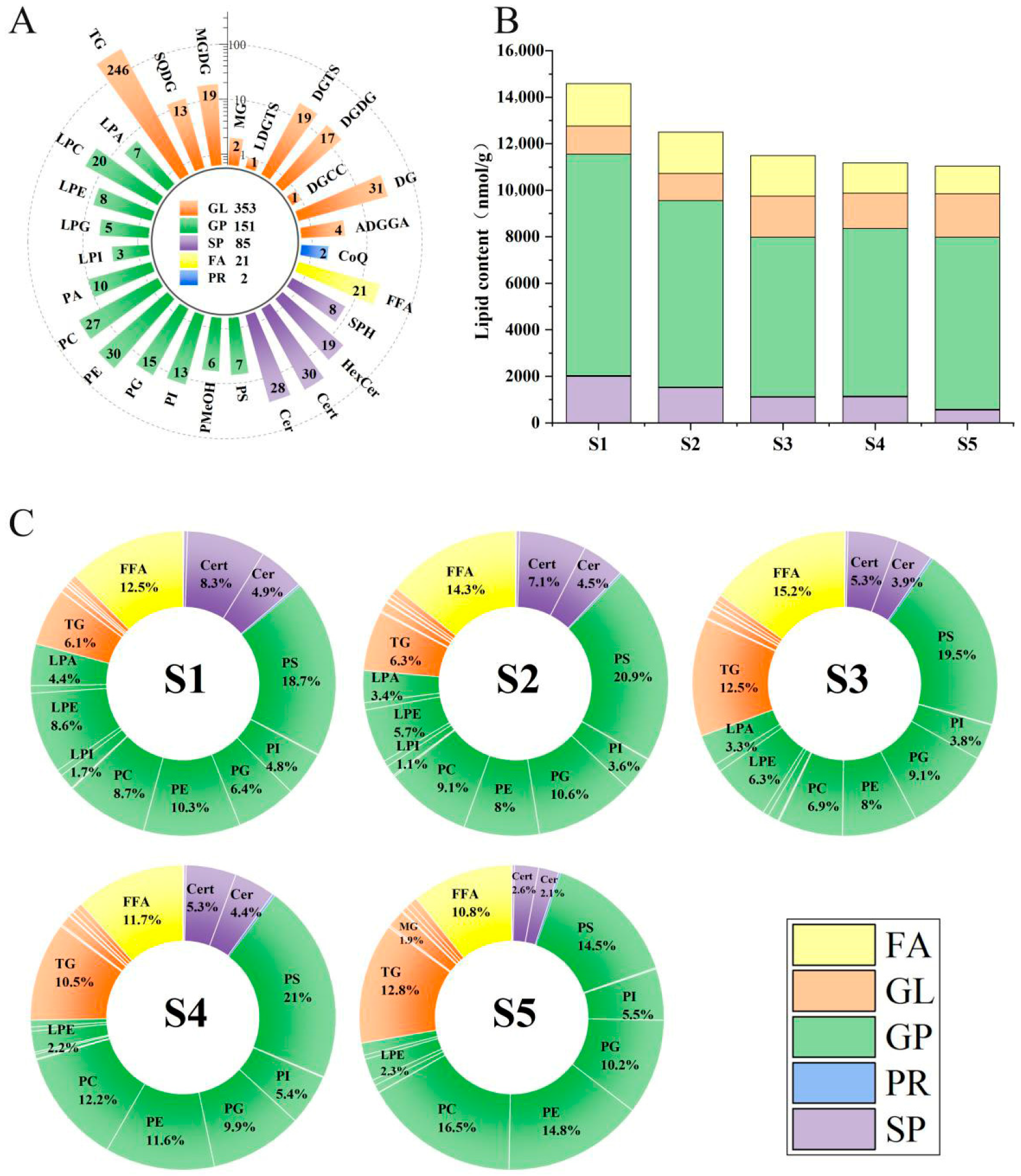
| Lipids | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphingosine (SPH) | 11.98 ± 1.12 b | 14.98 ± 0.65 a | 9.49 ± 0.53 c | 11.61 ± 0.57 b | 7.75 ± 0.34 d |
| Hexosylceramide (HexCer) | 56.29 ± 9.21 a | 38.59 ± 4.7 b | 29.17 ± 4.02 bc | 25.37 ± 5.73 c | 26.11 ± 2.84 c |
| Phytoceramide (Cert) | 1216.61 ± 53.24 a | 890.62 ± 90.95 b | 614.24 ± 90.5 c | 594.03 ± 79.22 c | 281.5 ± 47.84 d |
| Ceramide (Cer) | 719.58 ± 38.89 a | 566.83 ± 67.15 b | 444.94 ± 79.36 c | 487.18 ± 65.09 bc | 237.06 ± 36.07 d |
| Coenzyme Q (CoQ) | 33.83 ± 0.54 a | 29.7 ± 1.16 b | 34.05 ± 1.51 a | 33.68 ± 1.1 a | 27.21 ± 0.6 c |
| Phosphatidylserine (PS) | 2728.87 ± 461.76 a | 2613.84 ± 103.78 a | 2237.67 ± 550.92 ab | 2352.6 ± 341.32 ab | 1595 ± 389.82 b |
| Phosphatidylmethanol (PMeOH) | 9.94 ± 0.13 bc | 8.38 ± 0.29 c | 8.34 ± 0.31 c | 10.89 ± 1.25 b | 14.17 ± 1.49 a |
| Phosphatidylinositol (PI) | 692.95 ± 41.72 a | 454.85 ± 18.57 c | 434.99 ± 25.97 c | 603.01 ± 50.94 b | 601.71 ± 36.8 b |
| Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) | 934.52 ± 33.44 c | 1319.98 ± 92.31 a | 1047.75 ± 53.87 b | 1101.32 ± 68.28 b | 1120.93 ± 33.59 b |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) | 1495.08 ± 72.29 a | 1000.44 ± 109.46 c | 914.32 ± 125.76 c | 1297.8 ± 51.36 b | 1637.73 ± 71.56 a |
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 1274.27 ± 56.27 bc | 1136.51 ± 61.78 c | 787.7 ± 100.06 d | 1363.59 ± 90.22 b | 1824.61 ± 81.63 a |
| Phosphatidic acid (PA) | 17.39 ± 1.22 b | 21.33 ± 0.97 a | 15.3 ± 1.53 c | 13.35 ± 0.69 d | 3.45 ± 0.26 e |
| Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) | 243.2 ± 6.98 a | 140.67 ± 9.92 b | 129.76 ± 9.25 b | 54.27 ± 0.9 d | 89.8 ± 10 c |
| Lysophosphatidylglycerol (LPG) | 95.42 ± 2.77 a | 79.5 ± 12.37 b | 71.99 ± 5.88 b | 26.23 ± 0.17 c | 67.33 ± 9.74 b |
| Lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) | 1257.76 ± 42.9 a | 716.13 ± 39.92 b | 719.35 ± 18.08 b | 246.89 ± 12.73 c | 254.87 ± 14.33 c |
| Lysophophatidylcholine (LPC) | 118.11 ± 3.22 a | 96.41 ± 0.17 b | 95.61 ± 3.17 b | 49.91 ± 3.4 c | 48.96 ± 2.1 c |
| Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) | 647.17 ± 17.78 a | 426.26 ± 16.49 b | 384.07 ± 26.75 c | 80.58 ± 1.07 e | 142.86 ± 10.72 d |
| Triacylglycerol (TG) | 883.79 ± 140.7 b | 792.15 ± 59.16 b | 1439.3 ± 181.8 a | 1173.57 ± 120.99 a | 1409.97 ± 181.33 a |
| Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG) | 3.54 ± 0.34 c | 4.65 ± 0.27 ab | 4.05 ± 0.5 bc | 3.89 ± 0.47 bc | 5.03 ± 0.82 a |
| Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) | 9.33 ± 0.65 c | 16.09 ± 2.57 ab | 13.78 ± 0.66 b | 16.41 ± 1.68 ab | 18.85 ± 1.35 a |
| Monoacylglycerol (MG) | 97.04 ± 6.99 c | 123.51 ± 23.94 b | 112.71 ± 11.55 bc | 131.73 ± 8.21 b | 208.38 ± 9.58 a |
| Trimethylhomoserine (LDGTS) | 2.17 ± 0.08 c | 3.29 ± 0.38 b | 5.66 ± 0.54 a | 1.13 ± 0.06 d | 1.14 ± 0.05 d |
| Trimethylhomoserine (DGTS) | 11.35 ± 0.67 ab | 10.44 ± 0.86 bc | 8.75 ± 1.21 c | 11.86 ± 1.03 ab | 13.49 ± 2.23 a |
| Digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG) | 38.71 ± 4.28 c | 57.92 ± 3.79 ab | 50.25 ± 9.88 abc | 46.37 ± 6.43 bc | 60.35 ± 4.57 a |
| Diacylglyceryl-3-0-carboxyhydroxymethylcholine (DGCC) | 8.3 ± 0.66 b | 11.67 ± 2.91 a | 8.64 ± 0.57 b | 7.38 ± 0.71 b | 3.56 ± 0.24 c |
| Diacylglycerol (DG) | 46.86 ± 4.18 b | 53.49 ± 8.61 ab | 59.11 ± 11.46 ab | 64.17 ± 4 a | 61.79 ± 5.31 a |
| Acyl diacylglyceryl glucuronide (ADGGA) | 104.96 ± 14.97 a | 93.42 ± 9.54 a | 67.89 ± 14.38 b | 66.74 ± 8.97 b | 84.84 ± 8.05 ab |
| Free fatty acid (FFA) | 1824.42 ± 106.28 a | 1784.99 ± 154.44 a | 1745.47 ± 114.18 a | 1302.86 ± 151.13 b | 1189.25 ± 156.37 b |
| Stage | Length (cm) | Diameter (mm) | Fresh Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 9.30 ± 1.3 a | 15.36 ± 0.13 a | 12.13 ± 0.06 a |
| S2 | 13.16 ± 0.55 b | 26.13 ± 0.53 b | 39.91 ± 0.80 b |
| S3 | 15.97 ± 0.53 c | 37.55 ± 1.34 c | 117.03 ± 1.52 c |
| S4 | 16.48 ± 0.13 c | 42.03 ± 0.56 d | 140.76 ± 1.45 d |
| S5 | 16.77 ± 1.03 c | 48.38 ± 0.77 e | 149.97 ± 1.67 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Lipidomic Profiling of Sweetpotato During Different Developmental Stages Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Foods 2025, 14, 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234109
Li Z, Zhang R, Jiang X, Liu Y, Wang Z. Lipidomic Profiling of Sweetpotato During Different Developmental Stages Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234109
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zaisu, Rong Zhang, Xia Jiang, Ying Liu, and Zhangying Wang. 2025. "Lipidomic Profiling of Sweetpotato During Different Developmental Stages Using LC-ESI-MS/MS" Foods 14, no. 23: 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234109
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhang, R., Jiang, X., Liu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2025). Lipidomic Profiling of Sweetpotato During Different Developmental Stages Using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Foods, 14(23), 4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234109





