Inactivated Akkermansia muciniphila AKK PROBIO Preserves Intestinal Homeostasis and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of Akkermansia muciniphila and Postbiotic Production
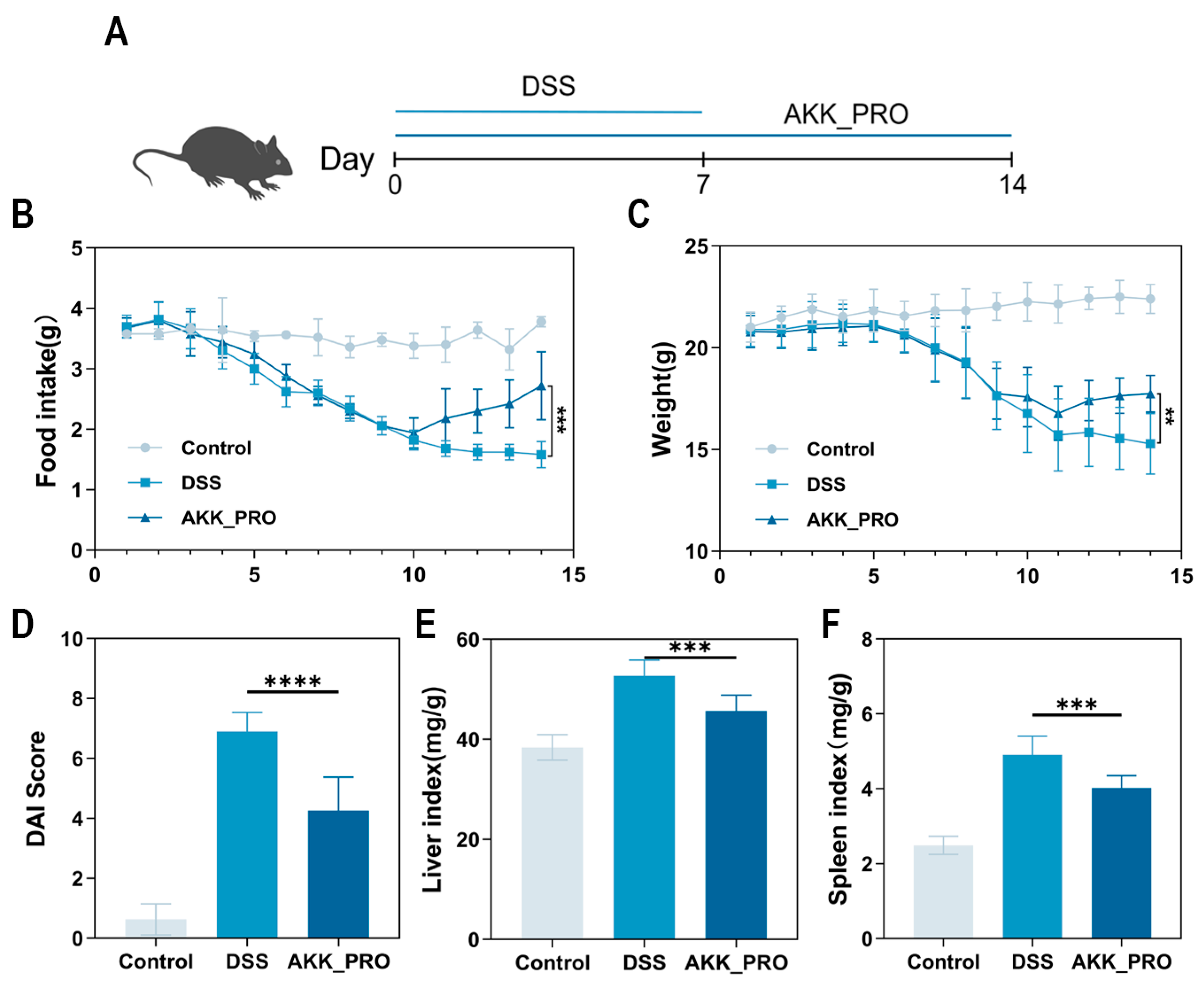
2.2. Design of Animal Experiments
2.3. Assessment of Disease Activity Index
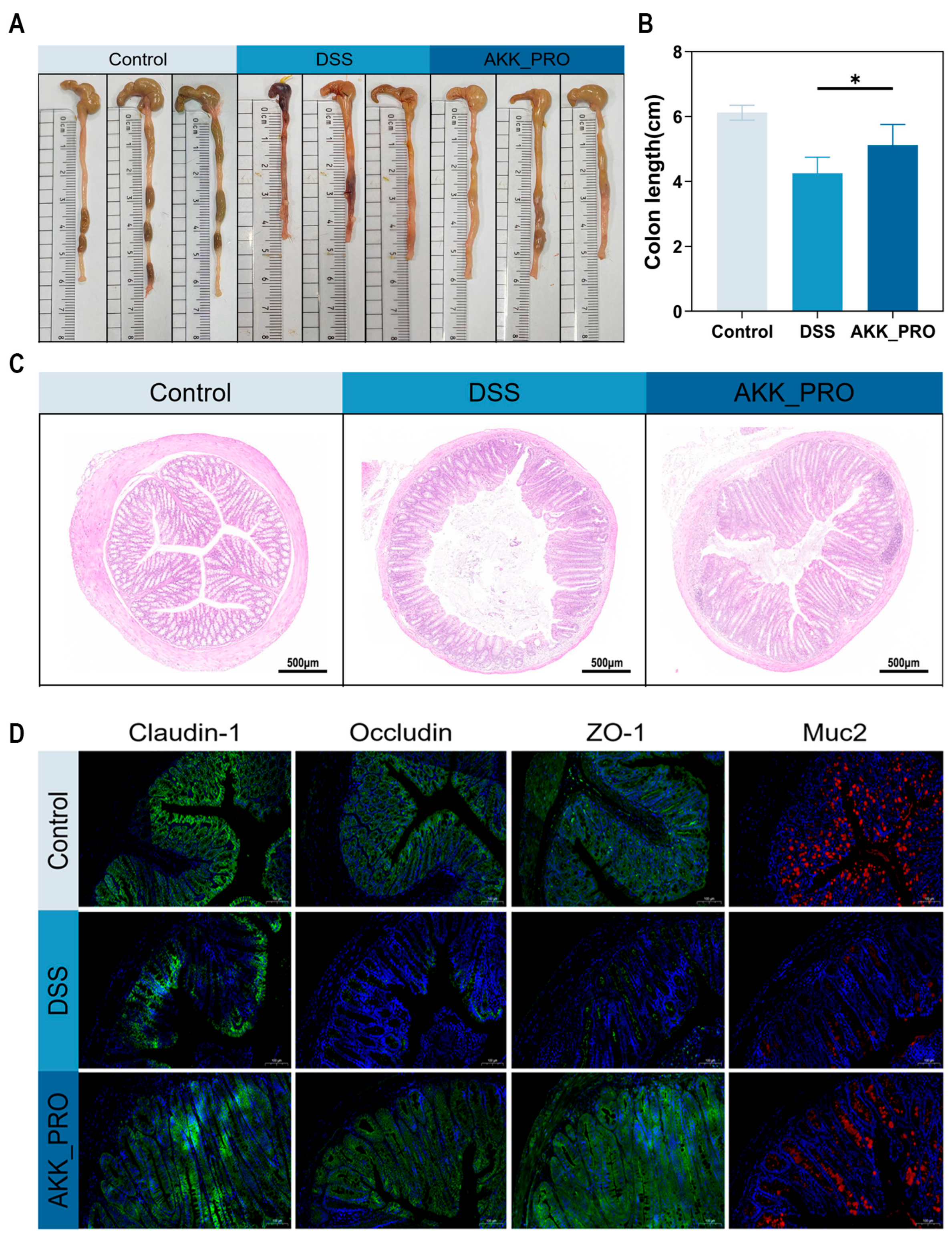
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
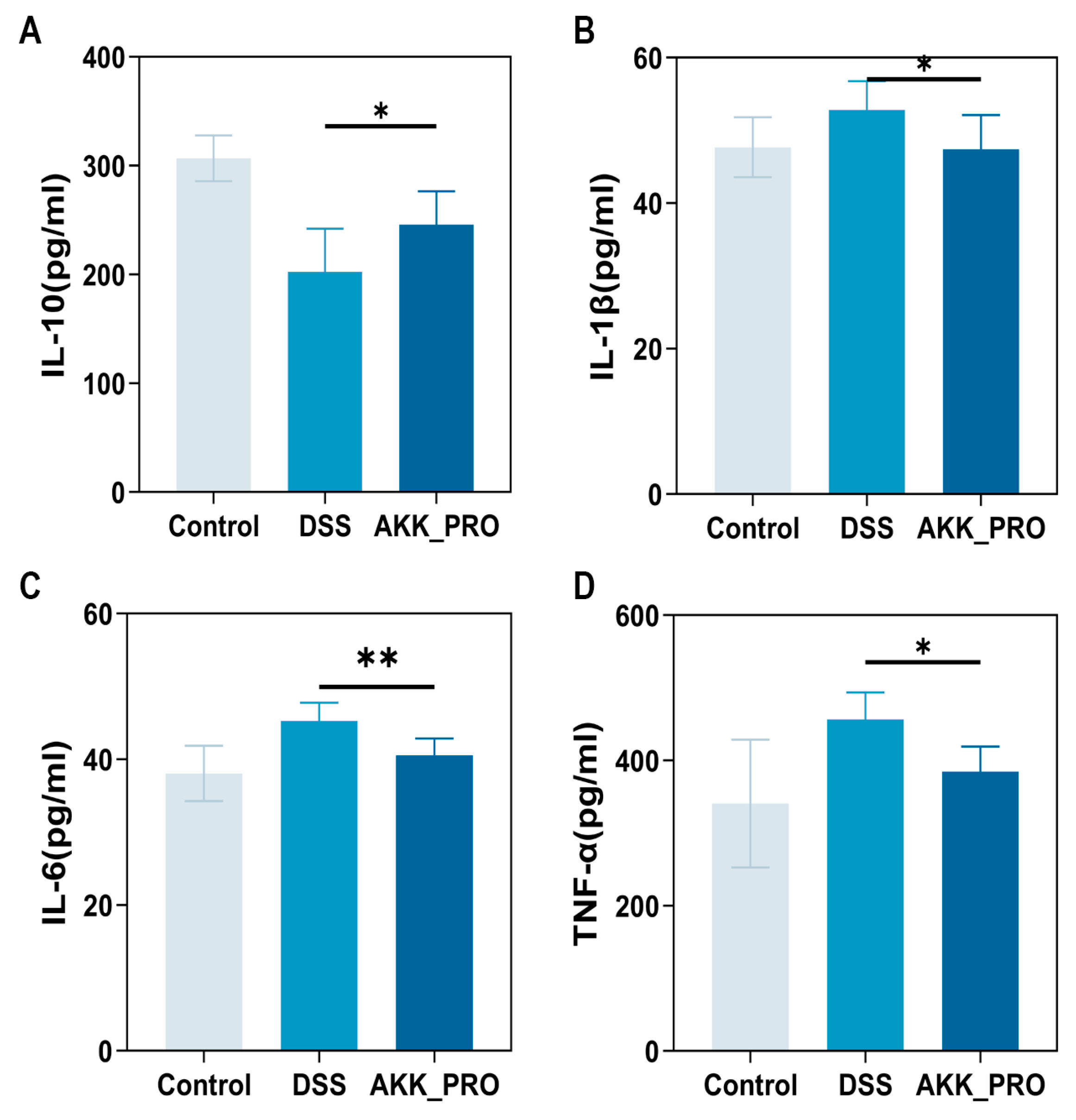
2.5. Measurement of Cytokine Levels in Colon Tissue
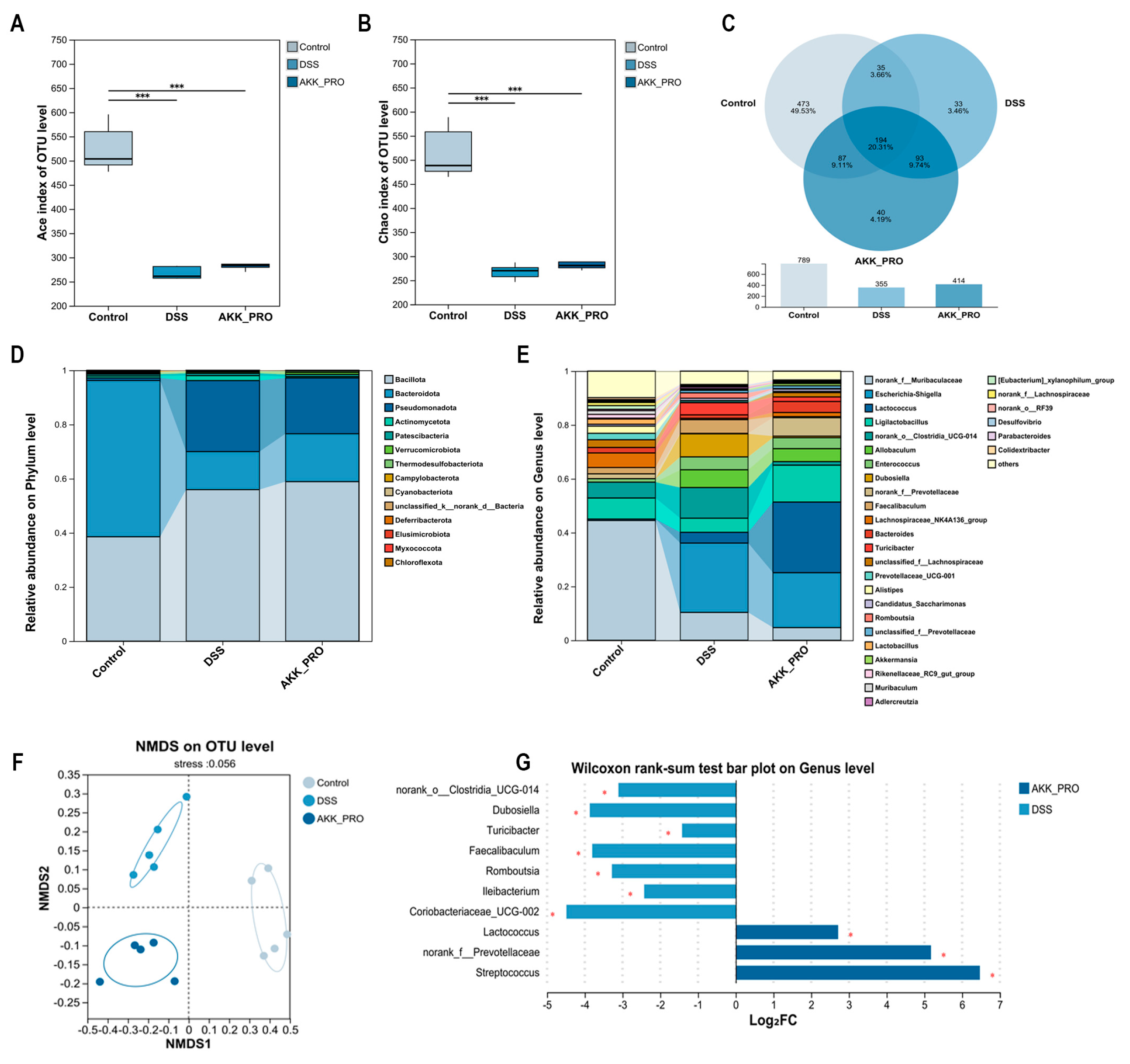
2.6. Compositional Analysis of Gut Microbiota
2.7. Quantification of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ingestion of Inactivated AKK PROBIO Alleviates Physiological Damage in DSS-Induced Mouse UC
3.2. Ingestion of Inactivated AKK PROBIO Alleviates Colonic Damage in DSS-Induced Mouse UC
3.3. Ingestion of Inactivated AKK PROBIO Reduces Inflammatory Cytokines and Alters Gut Microbiota Composition in DSS-Induced UC in Mice
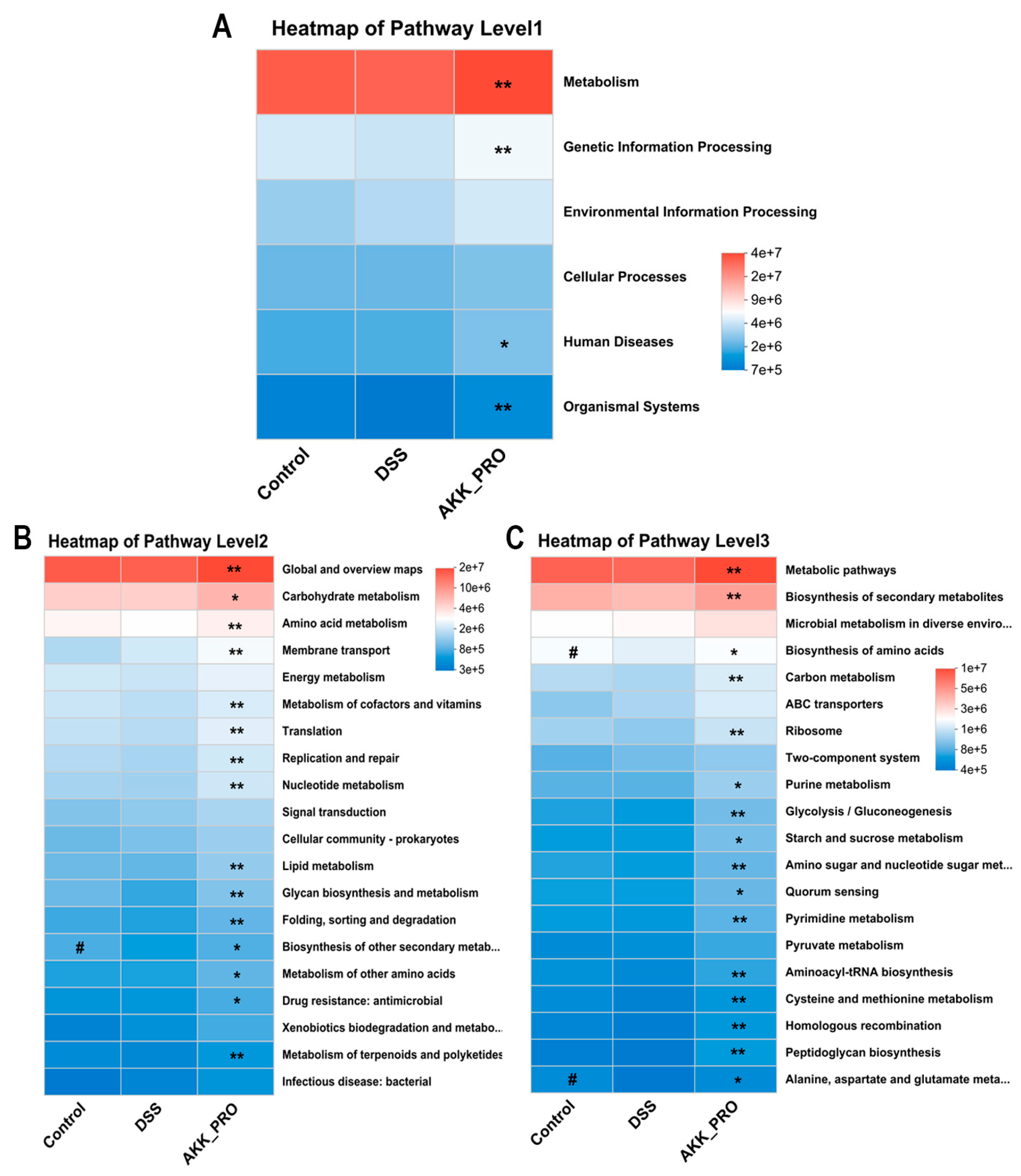
3.4. Functional Remodeling of Gut Microbial Metabolism Through Inactivated AKK PROBIO Administration
3.5. Intake of Inactivated AKK PROBIO Increased SCFA Levels in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Mice
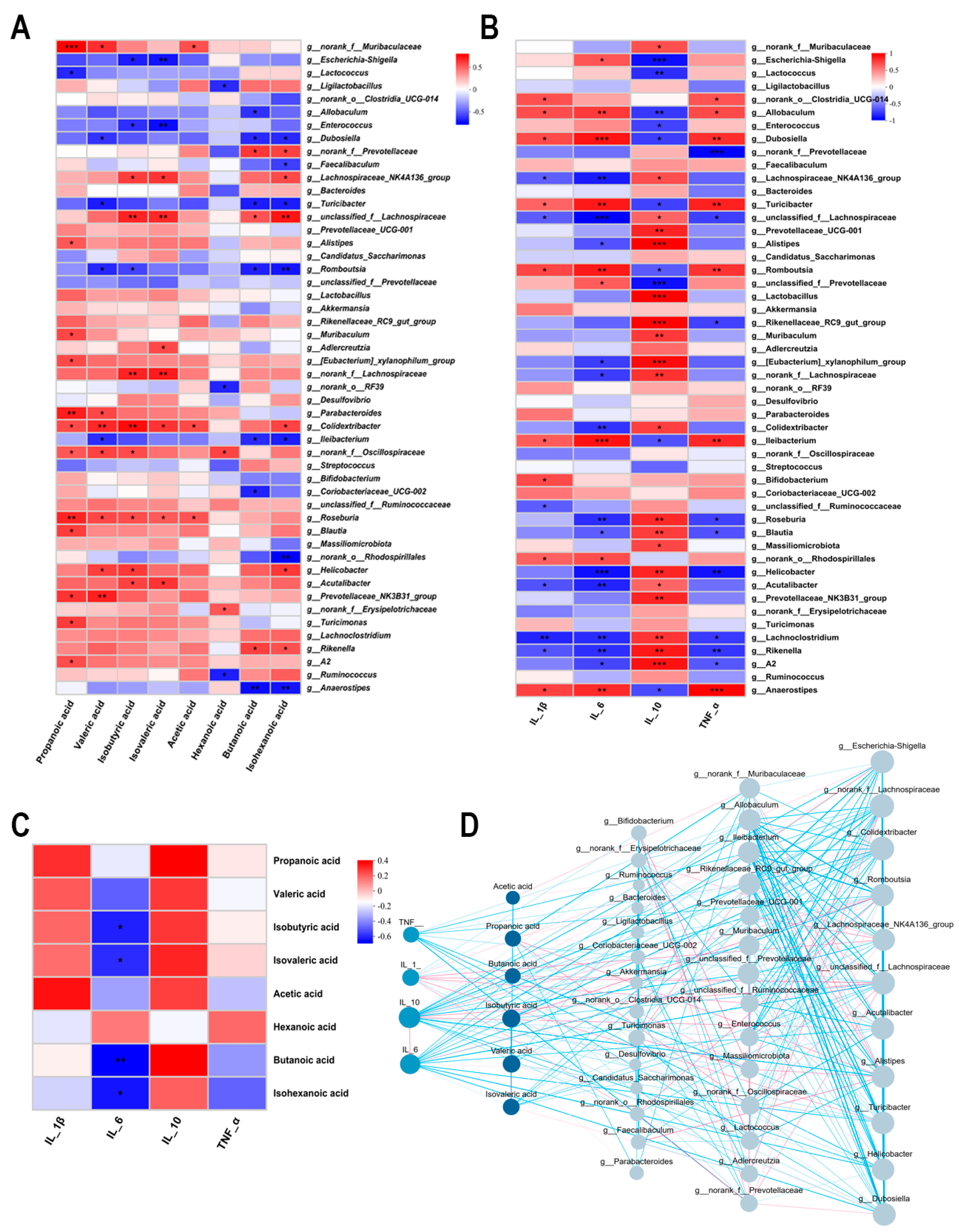
3.6. Interrelationship Analysis Between Gut Microbiota, SCFAs, and Inflammatory Factors
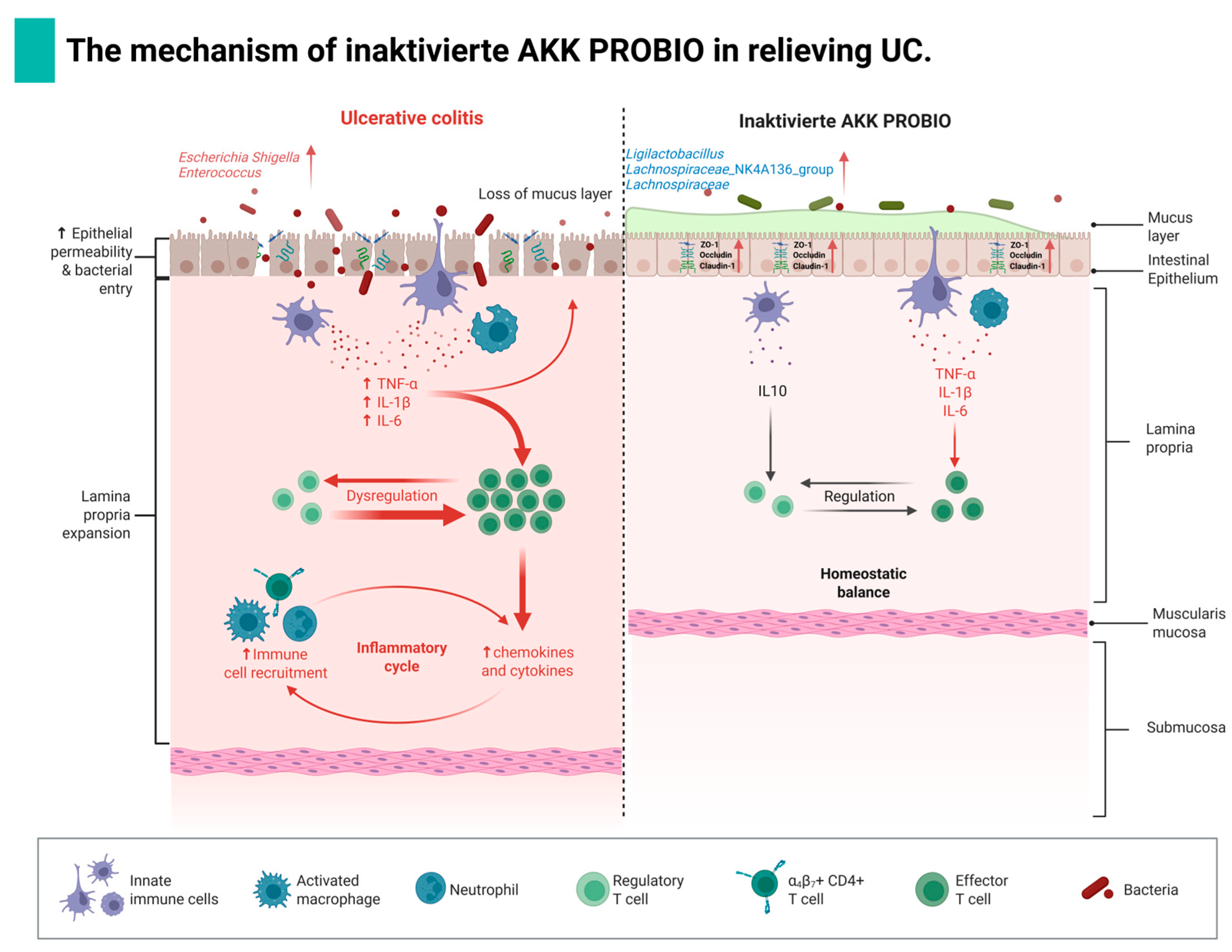
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Shen, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Postbiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Efficacy, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Implications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Feng, C.; Kwok, L.Y.; He, Q.; Sun, Z. Stronger Gut Microbiome Modulatory Effects by Postbiotics Than Probiotics in a Mouse Colitis Model. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; He, Q.; Kwok, L.Y.; Zhang, H. Postbiotic Administration Ameliorates Colitis and Inflammation in Rats Possibly through Gut Microbiota Modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 9054–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Luo, P.; Zhan, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. The Prophylaxis Functions of Lactobacillus fermentum Glf-217 and Lactobacillus plantarum Flp-215 on Ulcerative Colitis via Modulating Gut Microbiota of Mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5816–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Lactobacillus paracei Jy062 Postbiotic on Intestinal Barrier, Immunity, and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, H.; Lennon, G.; Balfe, Á.; Coffey, J.C.; Winter, D.C.; O’Connell, P.R. The Abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and Its Relationship with Sulphated Colonic Mucins in Health and Ulcerative Colitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, W.; Din, A.U.; Khan, T.M.; Rehman, M.U.; Hassan, A.; Aziz, T.; Alharbi, M.; Wu, J. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Bncc345679 Revolutionizes Dss-Induced Colitis and Modulates Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1433891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q. Programmable Probiotics Modulate Inflammation and Gut Microbiota for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment after Effective Oral Delivery. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besselink, M.G.H.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Buskens, E.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Goor, H.; Timmerman, H.M.; Nieuwenhuijs, V.B.; Bollen, T.L.; van Ramshorst, B.; Witteman, B.J.M.; et al. Probiotic Prophylaxis in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, A.; Mantel, M.; Marchix, J.; Bodinier, M.; Jan, G.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapeutic Strategies by Modulation of the Microbiota: How and When to Introduce Pre-, Pro-, Syn-, or Postbiotics? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G523–G553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Jin, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Z. Both Saccharomyces boulardii and Its Postbiotics Alleviate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice, Association with Modulating Inflammation and Intestinal Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yang, S.; Han, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, W.; Du, P. Progress of Research on the Alleviation of Intestinal Inflammation by Regulating Intestinal Mucosal Function with Postbiotics. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Yue, Y.; Ma, C.; Dong, L.; Chen, F. Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila Ameliorate the Lps-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction Via Modulating Ampk and Nf-Κb through Tlr2 in Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Tian, M.; Yu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Ren, D.; Wang, W. Characterization and Preliminary Safety Evaluation of Akkermansia muciniphila Probio. Foods 2024, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; He, Y.; Wen, S.; Yu, T.; Wang, W. The Alleviating Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila Probio on Aom/Dss-Induced Colorectal Cancer in Mice and Its Regulatory Effect on Gut Microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 114, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhu, N.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, W. Research on Preventive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila Akk probio on Acute Gouty Arthritis in Mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 7644–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q.; Xu, T.; Chen, W.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila Probio Ameliorates Overweight Via Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025, 10, 9250659. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, J.; Feng, S.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Huo, F.; Liu, H. Akkermansia muciniphila, Which Is Enriched in the Gut Microbiota by Metformin, Improves Cognitive Function in Aged Mice by Reducing the Proinflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-6. Microbiome 2023, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tan, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, N.; Zhu, S.; Tian, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q. Akkermansia muciniphila Supplementation Prevents Cognitive Impairment in Sleep-Deprived Mice by Modulating Microglial Engulfment of Synapses. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2252764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-Talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and Intestinal Epithelium Controls Diet-Induced Obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Jin, Y.L.; Pei, W.L.; Li, J.C.; Zhang, R.L.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, W. Amuc_1100 Pretreatment Alleviates Acute Pancreatitis in a Mouse Model through Regulating Gut Microbiota and Inhibiting Inflammatory Infiltration. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A Purified Membrane Protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the Pasteurized Bacterium Improves Metabolism in Obese and Diabetic Mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Xiong, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Kou, J.; Yi, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, H.; Qiao, J. Pasteurized Akkermansia Muciniphila Timepie001 Ameliorates Dss-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Alleviating Intestinal Injury and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1542522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Duan, X.; Chen, X.; Qian, S.; Ma, J.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Lactobacillus rhamnosus 1.0320 Postbiotics Ameliorate Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colonic Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Regulating the Intestinal Barrier and Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 25078–25093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Yu, X.; Ren, D.; Jiang, B. Akkermansia muciniphila One Effectively Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium (Dss)-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. NPJ Sci. Food 2024, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, J.; Guo, J. Abelmoschus Manihot Polysaccharide Fortifies Intestinal Mucus Barrier to Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation by Modulating Akkermansia muciniphila Abundance. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 3901–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Cui, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Man, C.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, Y. Branched-Chain Fatty Acids from Goat Milk Alleviate Ulcerative Colitis Via the Tlr4/Nf-Κb/Nlrp3 Pathway. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Kumar, N.; Chawla, M.; Philpott, D.J.; Basak, S. The Nf-Κb Signaling System in the Immunopathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Sci. Signal. 2024, 17, eadh1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, J.; Rey, N.B.; Fernández-García, R. Microbiota and Gut Inflammatory Markers (Zonulin and Fecal Calprotectin) Exhibit Age-Dependent Variation in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Life 2025, 15, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusainova, G.; Genkel, V.; Kuznetsova, A.; Nikushkina, K.; Saenko, A.; Abramovskikh, O.; Dolgushina, A. The Relationship between Serum Zonulin and Innate Immunity in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, K.; Liang, Z. Heat-Killed Saccharomyces boulardii Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Restoring the Intestinal Barrier, Reducing Inflammation, and Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Mao, K.; Shen, G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R. Limosilactobacillus fermentum Hf06-Derived Paraprobiotic and Postbiotic Alleviate Intestinal Barrier Damage and Gut Microbiota Disruption in Mice with Ulcerative Colitis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palrasu, M.; Marudamuthu, A.; Kakar, K.; Hamida, H.; Thada, S.; Gupta, R.; Wilson, K.; Carter, T.; Zhong, Y.; Saxena, A.; et al. Ahr-Dependent Induction of Β-Defensin 1 in Colonic Epithelial Cells Regulates Cross-Talk between Gut Microbiota and Immune Response Leading to Attenuation of Colitis. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2416324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, P.; Lv, Z.; Liu, H.; Zou, H.; et al. Honeysuckle-Derived Nanovesicles Regulate Gut Microbiota for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Adv. Sci. 2025, e05208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Tang, F.; Pi, Y.; Zhong, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, C. Lactobacillus vaginalis Alleviates Dss Induced Colitis by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Increasing the Production of 3-Indoleacrylic. Acid. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 213, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J.; Sun, L.; Dong, N.; Liu, B. Β-1,3-Glucans from Euglena Gracilis Protects against Ulcerative Colitis Via Modulating the Gut Barrier, T-Cell Immunity and Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305 Pt 2, 141288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynier, M.; Daugey, V.; Mallaret, G.; Gervason, S.; Meleine, M.; Barbier, J.; Aissouni, Y.; Lolignier, S.; Bonnet, M.; Ardid, D.; et al. Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila Improves Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Like Symptoms and Related Behavioral Disorders in Mice. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2298026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, L.M.; Torres, L.; Matos, I.D.; Miranda, V.C.; de Jesus, L.C.L.; Cavalcante, G.; de Souza Oliveira, J.J.; Cassali, G.D.; Mancha-Agresti, P.; de Carvalho Azevedo, V.A.; et al. Paraprobiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Protects Intestinal Damage in an Experimental Murine Model of Mucositis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ullah, H.; Ling, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Feng, P.; Ji, J.; Li, X. The Probiotic Enhances Donor Microbiota Stability and Improves the Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Treating Colitis. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.A.F.; Castelucci, P. Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Gut Health and Possible Therapeutic Approaches in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 9985–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visekruna, A.; Luu, M. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Bile Acids in Intestinal and Liver Function, Inflammation, and Carcinogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 703218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hays, K.E.; Pfaffinger, J.M.; Ryznar, R. The Interplay between Gut Microbiota, Short-Chain Fatty Acids, and Implications for Host Health and Disease. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2393270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Zhai, Q. Lactobacillus acidophilus Fcqhc4l1 Strengthens the Intestinal Mucus Barrier and Inhibits Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025, 14, 9250005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Score | Weight Loss (%) | Food Intake Decrease (g) | Fecal Consistency and Occult Blood |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0–5 | 0–0.5 | normal feces |
| 1 | 5–10 | 0.5–1 | loose stool |
| 2 | 10–15 | 1–1.5 | watery diarrhea |
| 3 | 15–20 | 1.5–2 | diarrhea with blood |
| 4 | over 20 | over 2 | watery diarrhea, with a lot of blood |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ren, D. Inactivated Akkermansia muciniphila AKK PROBIO Preserves Intestinal Homeostasis and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234063
Zhang H, Liu C, Huang Y, Ma X, Ren D. Inactivated Akkermansia muciniphila AKK PROBIO Preserves Intestinal Homeostasis and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234063
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongyan, Chunwen Liu, Yutian Huang, Xin Ma, and Dayong Ren. 2025. "Inactivated Akkermansia muciniphila AKK PROBIO Preserves Intestinal Homeostasis and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice" Foods 14, no. 23: 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234063
APA StyleZhang, H., Liu, C., Huang, Y., Ma, X., & Ren, D. (2025). Inactivated Akkermansia muciniphila AKK PROBIO Preserves Intestinal Homeostasis and Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Foods, 14(23), 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234063






