A Novel Probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
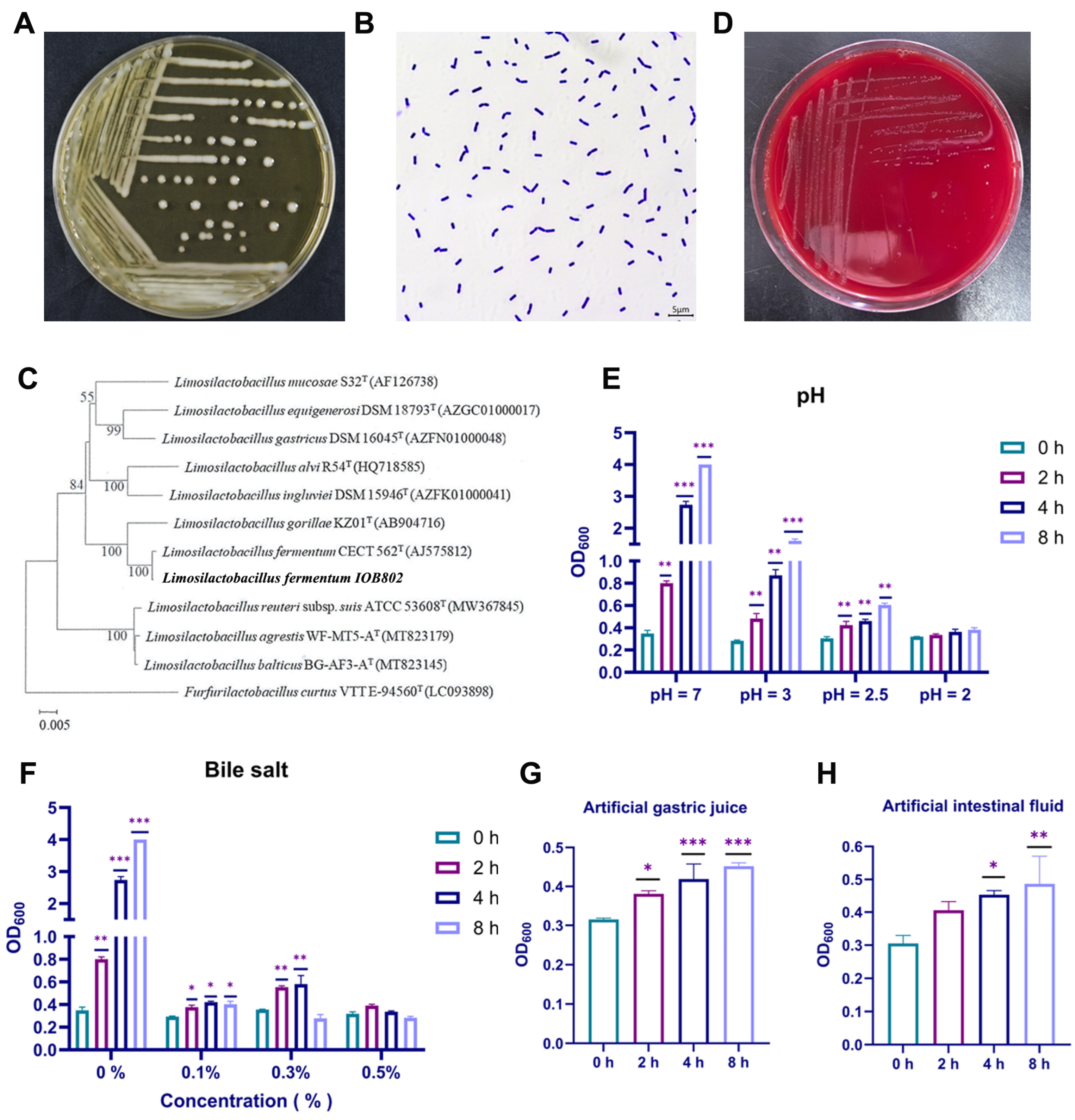
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Strain
2.2. Acid and Bile Tolerance Test
2.3. Simulated Gastric and Intestinal Fluids Tolerance Test
2.4. Safety Assessment
2.5. Preparation of Probiotic Postbiotics
2.6. Animals and Group Allocation
2.7. Memory Assessment of KM Mice
2.7.1. The Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
2.7.2. The Step-Down Test
2.8. Elisa
2.9. The Detection of Neurochemical Indicators
2.10. HE Staining
2.11. Nissl Staining
2.12. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.13. Measurement of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.14. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplification
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. L. fermentum IOB802 Exhibited Favorable Probiotic Properties
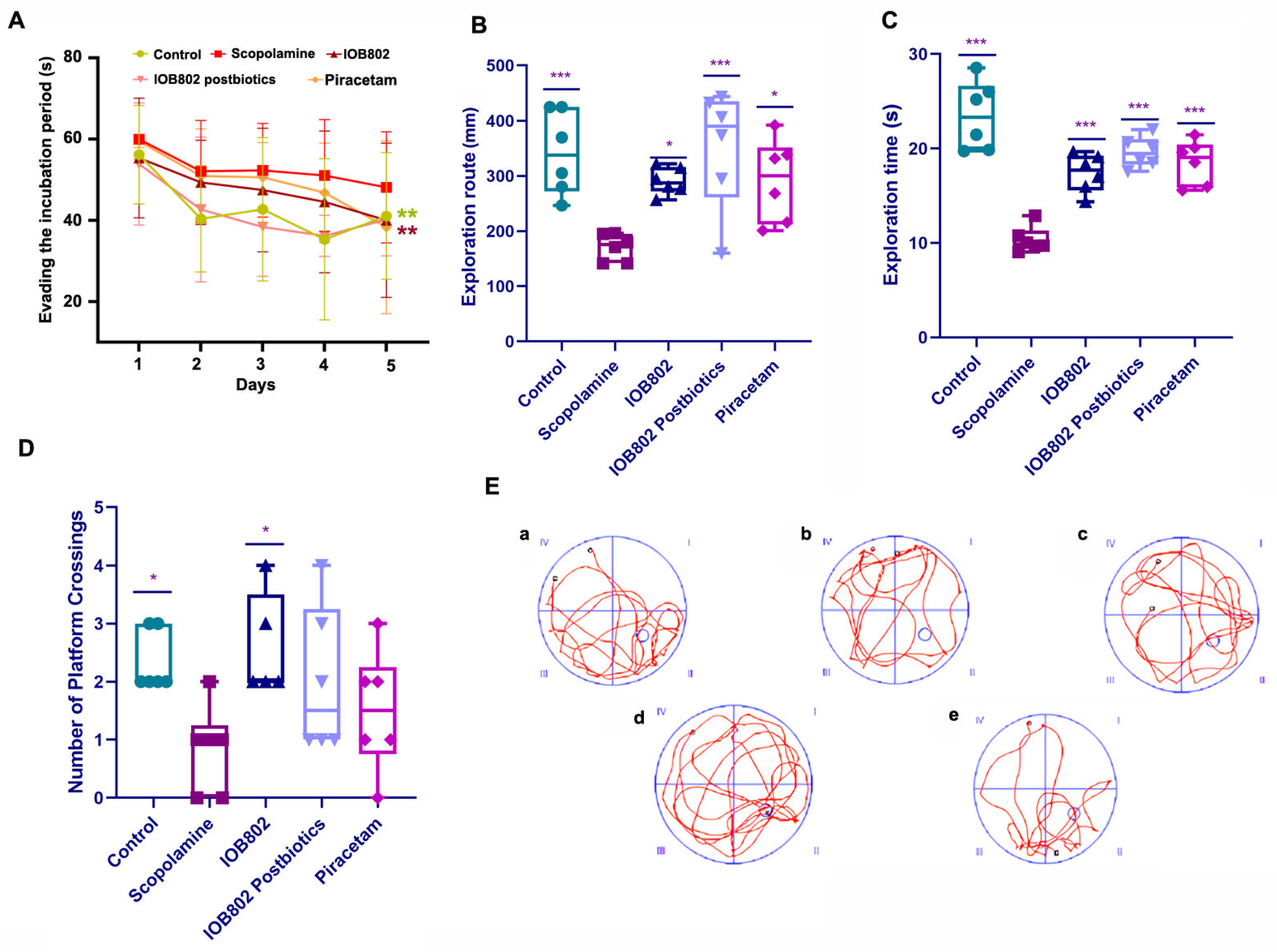
3.2. IOB802 and Its Postbiotics Improve Memory Performance in the Step-Down Test
3.3. IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Enhance Spatial Learning and Memory in the Morris Water Maze
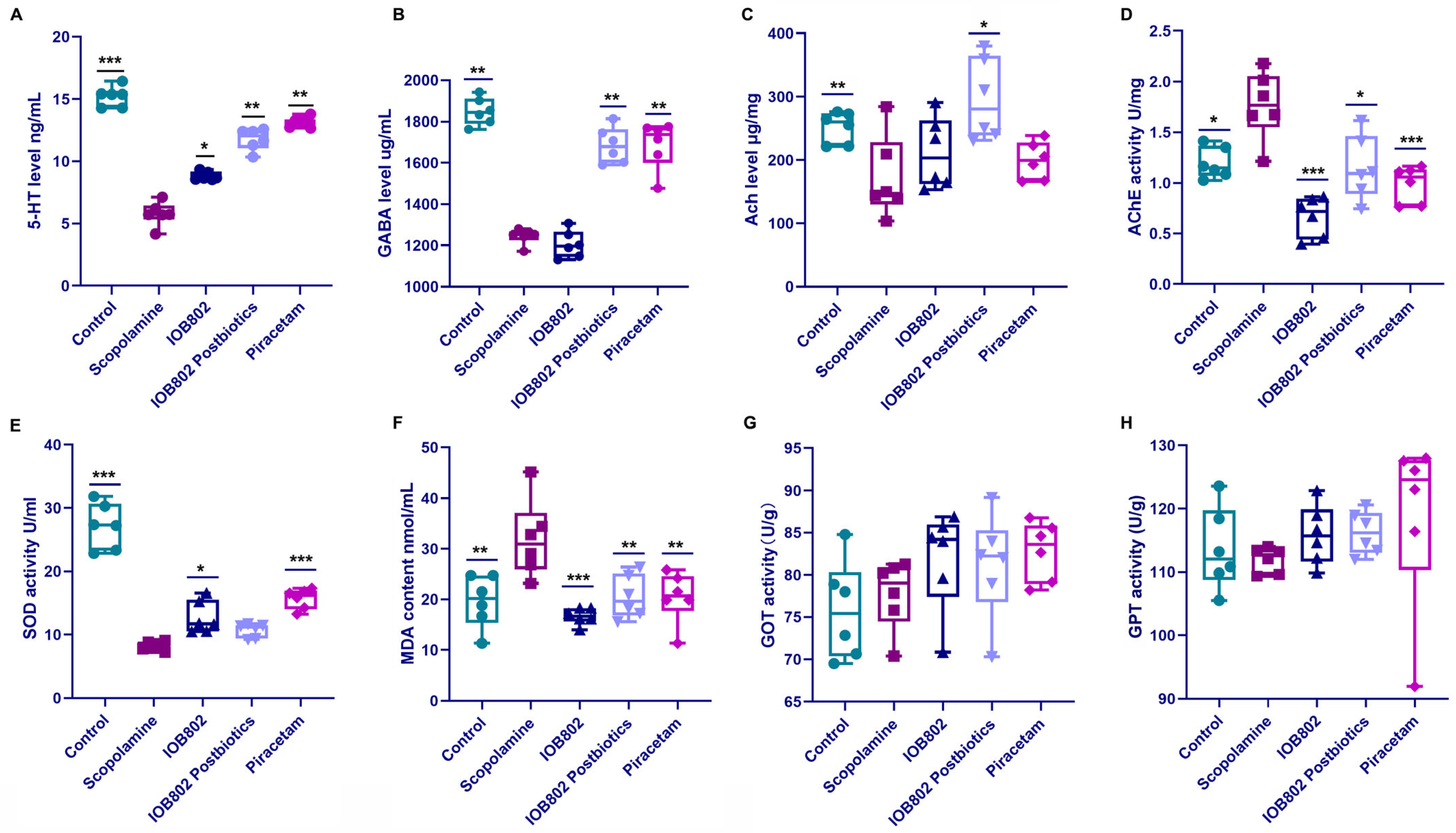
3.4. IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Normalize Neurochemical Markers Associated with Cognitive Function
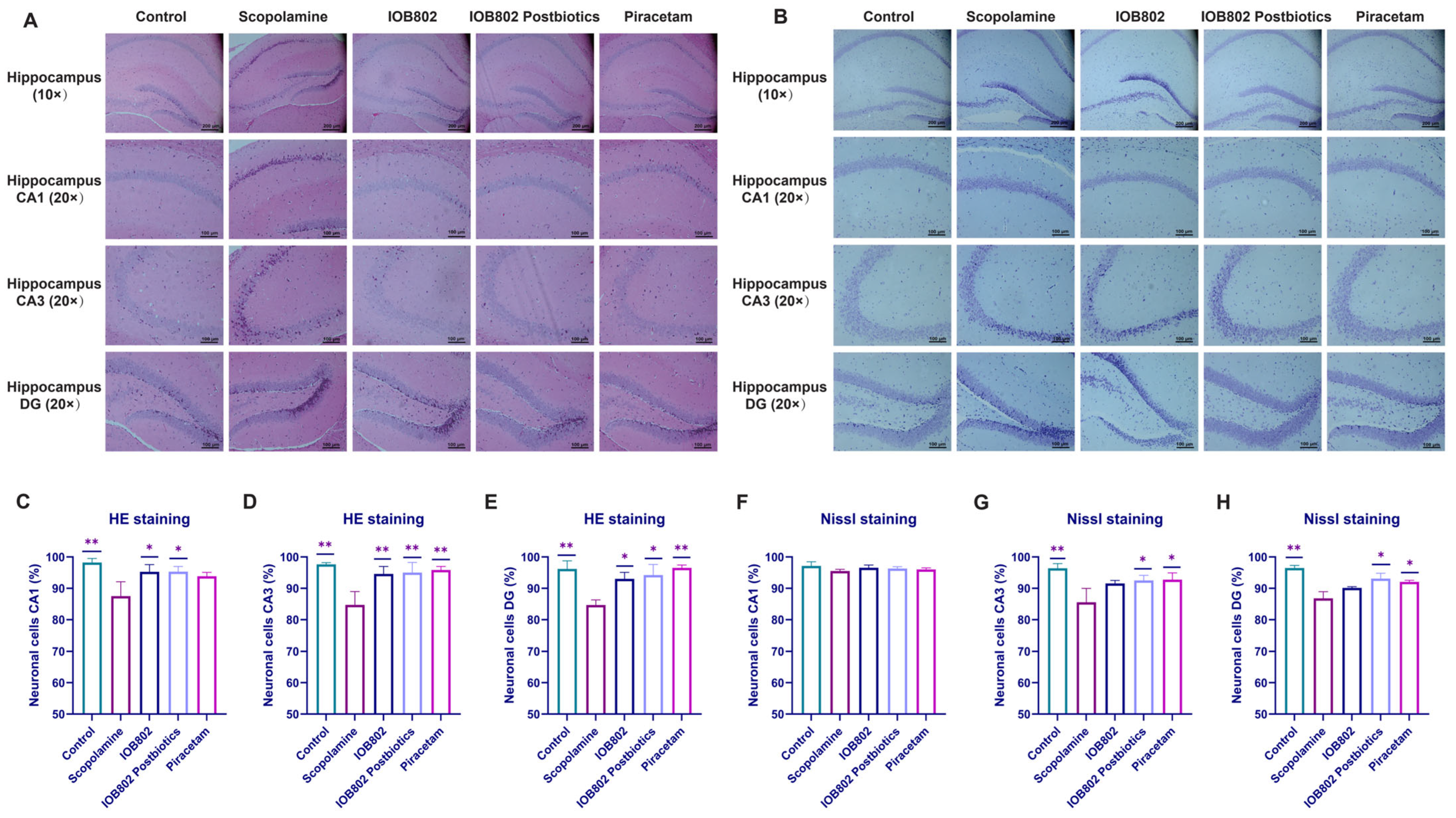
3.5. IOB802 and Its Postbiotics Attenuate Hippocampal Neuronal Damage
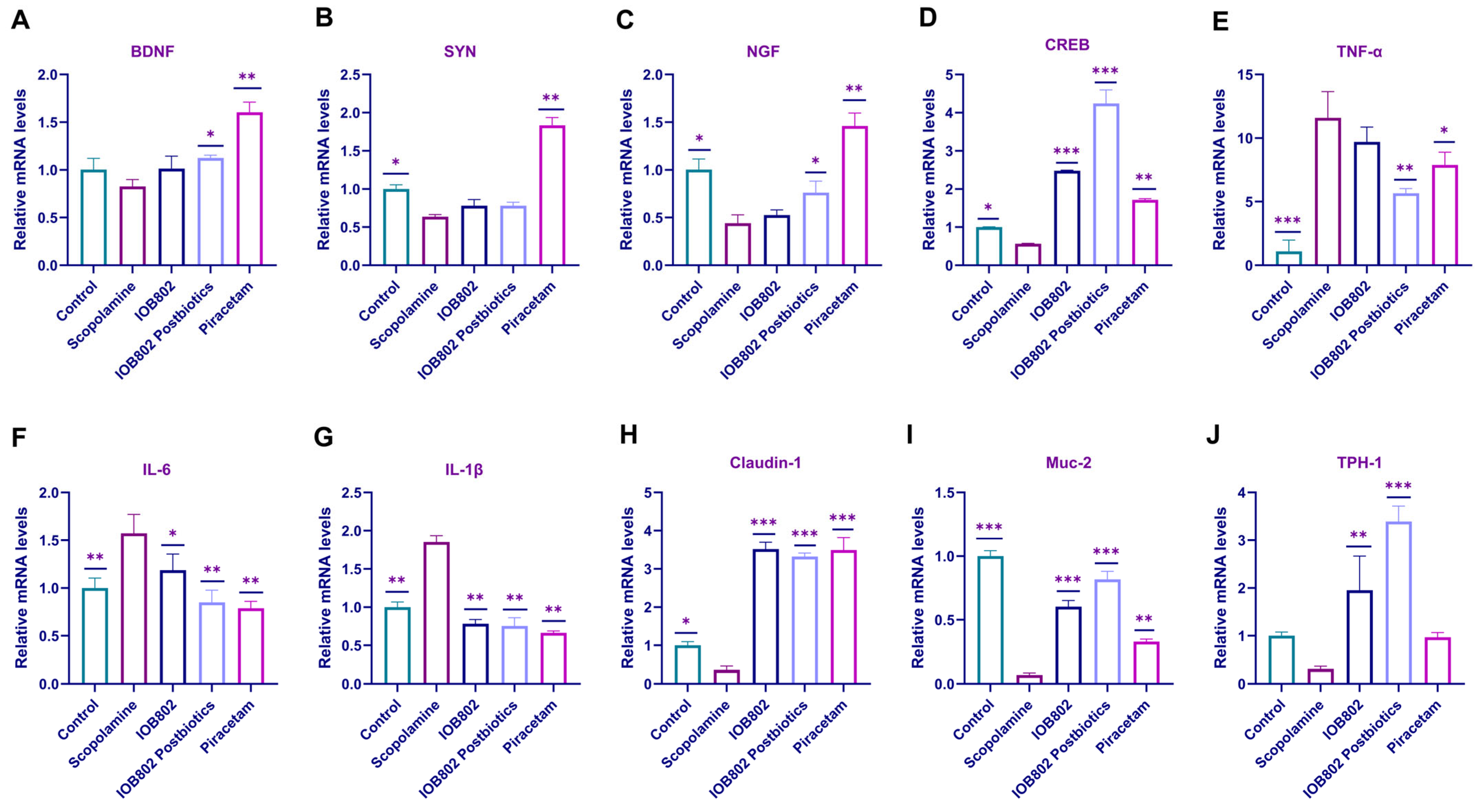
3.6. IOB802 and Its Probiotics Affect the Expression Level of Neurotrophic Factors, Pro-Inflammatory Genes, and Intestinal Tight Junction Component
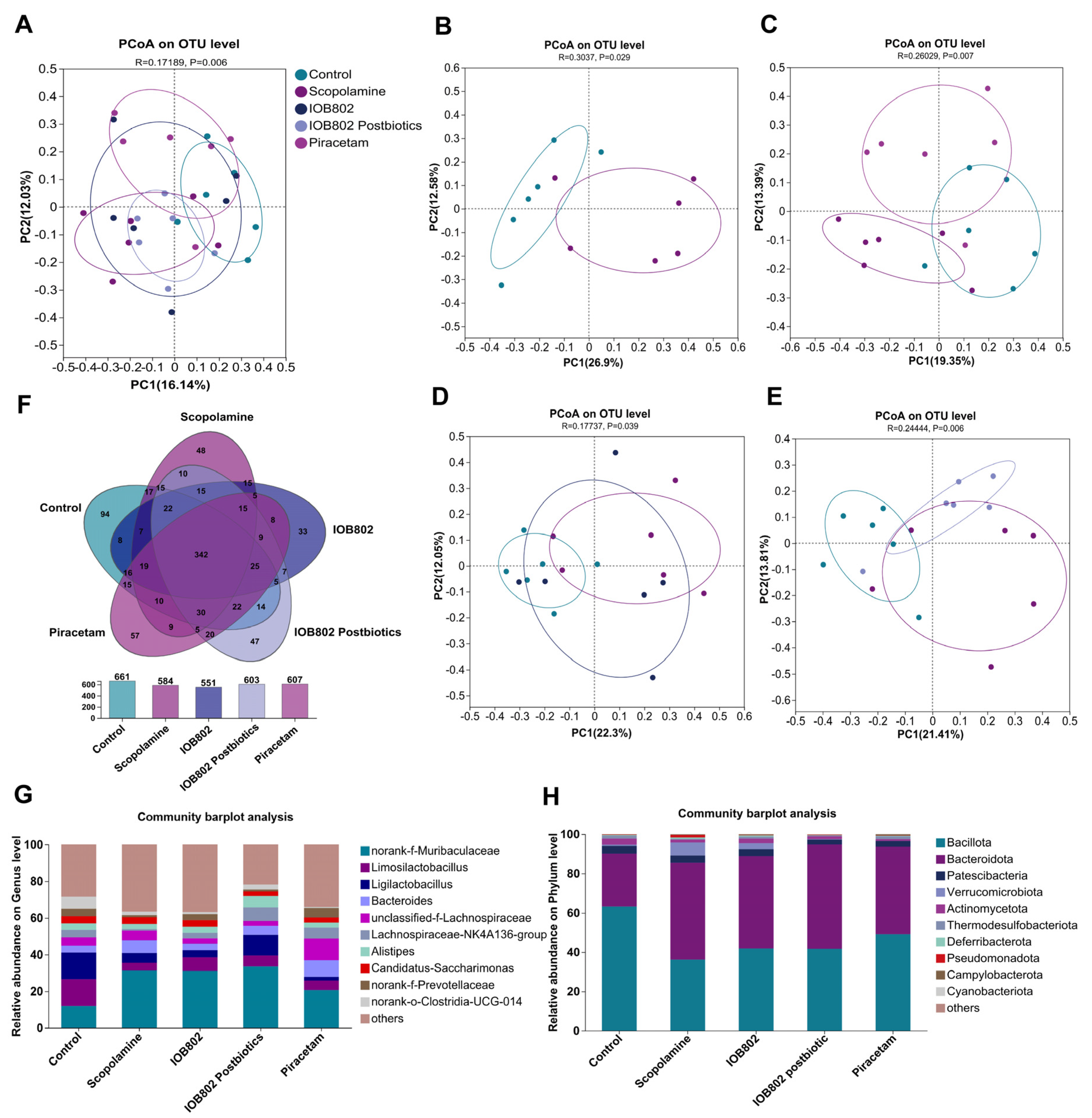
3.7. IOB802 and Its Postbiotics Affected Gut Microbial Diversity in Mice
3.8. IOB802 and Its Postbiotics Have an Effect on the Gut Microbial Composition
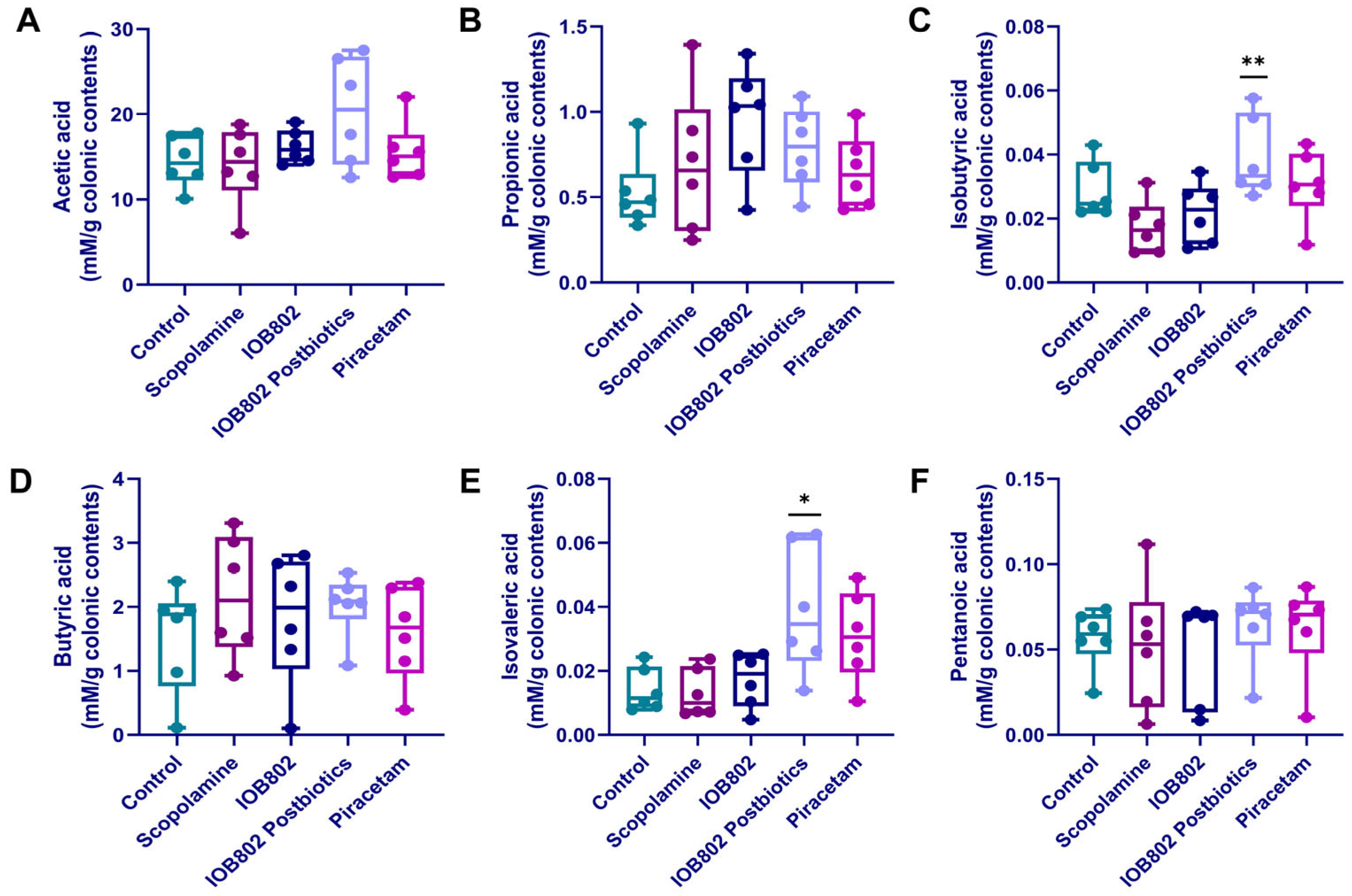
3.9. IOB802 and Its Postbiotics Affect Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Metabolic Profiling
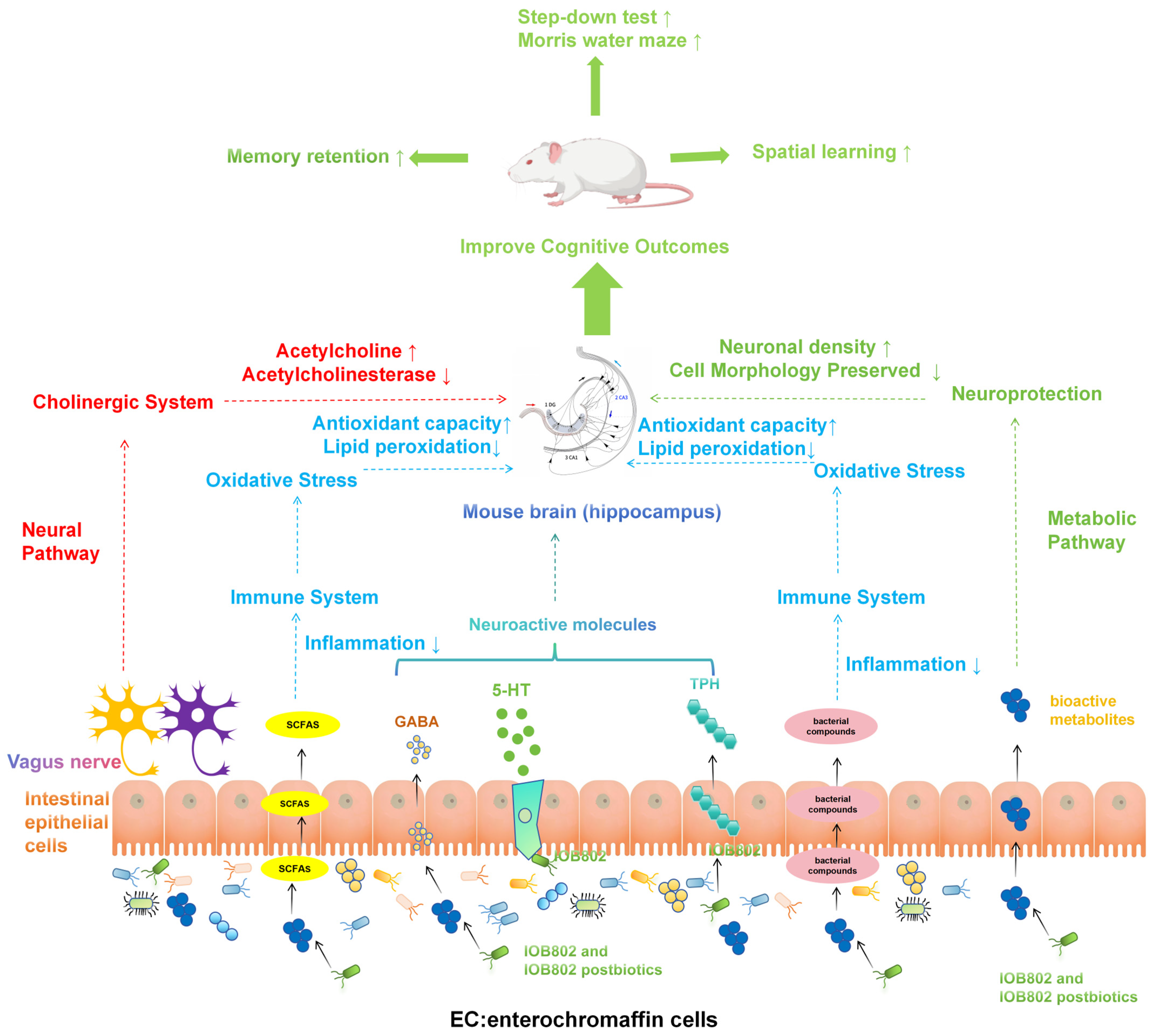
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rock, P.L.; Roiser, J.P.; Riedel, W.J.; Blackwell, A.D. Cognitive impairment in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisano, G.; Montagne, A.; Kisler, K.; Schneider, J.A.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier link to human cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 1, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, B.; Miller, R.; McAfoose, J.; Johnson, M.; Quirk, F.; Mitchell, D. The role of cognitive impairment in general functioning in major depression. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 176, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; DiBenedetti, D.; Perez, V. Cognitive dysfunction and work productivity in major depressive disorder. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2016, 16, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Luo, C.; Lv, D.; Tian, L.; Qu, C. Risk Factors Affecting Cognitive Impairment of the Elderly Aged 65 and Over: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 903794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Keefe, R.S.E.; McGuire, P.K. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: Aetiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1902–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, H.; Momenabadi, S.; Vafaei, A.A.; Bandegi, A.R.; Mazaheri, Z.; Vakili, A. Probiotic supplementation attenuates hippocampus injury and spatial learning and memory impairments in a cerebral hypoperfusion mouse model. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4985–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Hart, A.L.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J.; Knight, S.C. Mechanisms of action of probiotics: Recent advances. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, K.V.; Sherwin, E.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Feeding the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Diet, microbiome, and neuropsychiatry. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.O.; Holtzman, D.M. Gut Microbiota: From the Forgotten Organ to a Potential Key Player in the Pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, V.; Giardina, S.; Puoci, F. The Effect of a Probiotic Complex on the Gut-Brain Axis: A Translational Study. Neuropsychobiology 2022, 81, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuinness, A.J.; Davis, J.A.; Dawson, S.L.; Loughman, A.; Collier, F.; O’Hely, M.; Simpson, C.A.; Green, J.; Marx, W.; Hair, C.; et al. A systematic review of gut microbiota composition in observational studies of major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith, M.R.B.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in Gut Microbiota Composition in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; Asemi, Z.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Hamidi, G.A.; Salami, M. Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Metabolic Status in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind and Controlled Trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.R.; Shin, M.; Mun, D.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeong, D.Y.; Song, M.; Ko, G.; Unno, T.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S. Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum strain JDFM216 improves cognitive behavior and modulates immune response with gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Ye, M.; Luo, F.; Hu, B.; Wang, A.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; He, Z.; Chen, F.; Qian, C.; et al. Probiotics treatment improves cognitive impairment in patients and animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, M.; Guzzetta, K.E.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; van de Wouw, M.; Moloney, G.M.; Gual-Grau, A.; Spichak, S.; Olavarría-Ramírez, L.; Fitzgerald, P.; Morillas, E.; et al. Microbiota from young mice counteracts selective age-associated behavioral deficits. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Yin, L.; et al. Age-related shifts in gut microbiota contribute to cognitive decline in aged rats. Aging 2020, 12, 7801–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ding, N.; Feng, X.; Liao, W. The gut microbiome, immune modulation, and cognitive decline: Insights on the gut-brain axis. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1529958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Inslicht, S.S.; Bhargava, A. Gut-Brain Axis: Role of Microbiome, Metabolomics, Hormones, and Stress in Mental Health Disorders. Cells 2024, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna Freire, M.O.; Cruz Neto, J.P.R.; de Albuquerque Lemos, D.E.; de Albuquerque, T.M.R.; Garcia, E.F.; de Souza, E.L.; de Brito Alves, J.L. Limosilactobacillus fermentum Strains as Novel Probiotic Candidates to Promote Host Health Benefits and Development of Biotherapeutics: A Comprehensive Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Mei, M.; Wang, H.; Huang, A. Probiotic potential and safety properties of Limosilactobacillus fermentum A51 with high exopolysaccharide production. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1498352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Y.; Ding, J.; Shen, J.; Xue, Z.; Qi, W.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Protective effects of a novel probiotic strain, Lactococcus lactis ML2018, in colitis: In vivo and in vitro evidence. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y. Enriched Environment Promotes Cognitive Function Recovery following Cerebral Ischemic Injury via Upregulating GABAergic and Glutamatergic Systems in the Contralateral Hippocampus. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 8850119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Song, W.; Cai, C.F.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, Q.; Yan, X.; Cao, Y.; Fang, M. Neuroprotective effects of the aerial parts of Polygala tenuifolia Willd extract on scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments in mice. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Chang, L.; Kwon, H.K.; Im, S.H. Beyond the gut: Decoding the gut-immune-brain axis in health and disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadan, A.S.; El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Ellakwa, D.E. The microbiota-gut-brain-axis theory: Role of gut microbiota modulators (GMMs) in gastrointestinal, neurological, and mental health disorders. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 13397–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzynska, B.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A.; Kruk-Slomka, M.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Michalak, A.; Musik, I.; Biala, G. Effects of imperatorin on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in mice. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreta, M.P.; Burgos-Alonso, N.; Torrecilla, M.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Bruzos-Cidón, C. Efficacy of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors on Cognitive Function in Alzheimer’s Disease. Review of Reviews. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krok, A.C.; Maltese, M.; Mistry, P.; Miao, X.; Li, Y.; Tritsch, N.X. Intrinsic dopamine and acetylcholine dynamics in the striatum of mice. Nature 2023, 621, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Amenta, F. Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.S.; Liang, J.H.; Yang, M.J.; Ren, Y.R.; Cheng, D.H.; Wu, Q.H.; He, Y.; Yin, J. Low Serum Superoxide Dismutase Is Associated with a High Risk of Cognitive Impairment After Mild Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 834114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.R.; Ahmed, I.; Moktadir, A.A.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Shahid, S.F.B.; Islam, S.N.; Islam, M.S.; Hasnat, A. Elevated serum levels of malondialdehyde and cortisol are associated with major depressive disorder: A case-control study. SAGE Open Med. 2018, 6, 2050312118773953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Pande, S.; Acharya, S. Potentiation of anti-Alzheimer activity of curcumin by probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toader, C.; Serban, M.; Munteanu, O.; Covache-Busuioc, R.A.; Enyedi, M.; Ciurea, A.V.; Tataru, C.P. From Synaptic Plasticity to Neurodegeneration: BDNF as a Transformative Target in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. Promoting cognitive health through the nexus of gut microbiota and dietary phytochemicals. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1636131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakroo, S.; Soltani, S.; Tarrah, A.; LaPointe, G. The effect of dietary transition on infant microbiota composition and metabolic activity captured with the simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (SHIME). Gut Microbiome 2025, 6, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Ge, Y.; Gao, J. Role of gut microbiota in neuroinflammation: A focus on perioperative neurocognitive disorders. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1582909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, S.; Tremblay, A.; Iqbal, U.H.; Kassem, O.; Le Barz, M.; Thomas, V.; Bronner, S.; Perrot, T.; Ismail, N.; Parker, J.A. Psychobiotics and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Where Do We Go from Here? Microorganisms 2024, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohesara, S.; Mostafavi Abdolmaleky, H.; Pirani, A.; Thiagalingam, S. Therapeutic Horizons: Gut Microbiome, Neuroinflammation, and Epigenetics in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cells 2025, 14, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, D.; Meng, X.; Jiang, P.; Shi, H.; Ge, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, M.; et al. Dimethyl itaconate ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by a high-fat diet via the gut-brain axis in mice. Microbiome 2023, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-Araiza, A.; Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G.; Galván, E.J.; Hernández-Frausto, M.; Herrera-López, G.; Romo-Parra, H.; García-Contreras, V.; Fernández-Presas, A.M.; Jasso-Chávez, R.; Borlongan, C.V.; et al. Probiotics and Prebiotics as a Therapeutic Strategy to Improve Memory in a Model of Middle-Aged Rats. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobielska, M.; Bartosik, N.K.; Zyzik, K.A.; Kowalczyk, E.; Karbownik, M.S. Mechanisms of Cognitive Impairment in Depression. May Probiotics Help? Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 904426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Chen, N.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, L.; He, H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Hong, G. The gut microbiota-brain axis in neurological disorders. MedComm 2024, 5, e656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.Y.; Shen, W.; Zheng, L.; Guo, X.; Cline, H.T. Excitatory synaptic dysfunction cell-autonomously decreases inhibitory inputs and disrupts structural and functional plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Efficacy of a postbiotic and its components in promoting colonic transit and alleviating chronic constipation in humans and mice. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhowail, A.H.; Alharbi, A.M. Exploring how levetiracetam mitigates toxicity and ameliorates memory impairment. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1651414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Hritcu, L.; Stoica, B.; Bild, W.; Stefanescu, C. Changes of some oxidative stress markers in the serum of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.G.; Schuff, N.; Yaffe, K.; Madison, C.; Miller, B.; Weiner, M.W. Hippocampal atrophy patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowler, J.V. Vascular cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76 (Suppl. S5), v35–v44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanek, J.; Prasko, J.; Genzor, S.; Ociskova, M.; Kantor, K.; Holubova, M.; Slepecky, M.; Nesnidal, V.; Kolek, A.; Sova, M. Obstructive sleep apnea, depression and cognitive impairment. Sleep Med. 2020, 72, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.J.; Greverus, D.; Dellani, P.R.; Weibrich, C.; Wille, P.R.; Scheurich, A.; Stoeter, P.; Fellgiebel, A. Functional implications of hippocampal volume and diffusivity in mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 2005, 28, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, F. Emerging Insights into Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders: The Role of Signaling Across the Gut-Brain Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 10861–10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolfi, C.; Maresca, C.; Monteleone, G.; Laudisi, F. Implication of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Gut Dysbiosis and Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucientes, A.; Lisbona-Montañez, J.M.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Ruiz-Limón, P.; Manrique-Arija, S.; García-Studer, A.; Ortiz-Márquez, F.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Intestinal Dysbiosis, Tight Junction Proteins, and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GenBank Accession Number | Primer | Sequences (5′→3′) | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| NM_001289726.2 | GAPDH | Forward: GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | 154 |
| Reverse: CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT | |||
| NM_001278601.1 | TNF-α | Forward: GACGTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG | 228 |
| Reverse: TTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAG | |||
| NM_001314054.1 | IL-6 | Forward: CCAAGAGGTGAGTGCTTCCC | 118 |
| Reverse: CTGTTGTTCAGACTCTCTCCCT | |||
| NM_008361.4 | IL-1β | Forward: GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | 89 |
| Reverse: ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT | |||
| NM_001048139.1 | BDNF | Forward: TCATACTTCGGTTGCATGAAGG | 137 |
| Reverse: AGACCTCTCGAACCTGCCC | |||
| NM_009305.2 | SYN | Forward: CAGTTCCGGGTGGTCAAGG | 138 |
| Reverse: ACTCTCCGTCTTGTTGGCAC | |||
| NM_001112698.2 | NGF | Forward: CCAGTGAAATTAGGCTCCCTG | 142 |
| Reverse: CCTTGGCAAAACCTTTATTGGG | |||
| NM_001037726.1 | CREB | Forward: CAGGGGTCGCAAGGATTGAAG | 125 |
| Reverse: ATCGCCTGAGGCAGTGTACT | |||
| NM_001136084.2 | TPH1 | Forward: AACAAAGACCATTCCTCCGAAAG | 119 |
| Reverse: TGTAACAGGCTCACATGATTCTC | |||
| NM_016674.4 | Claudin-1 | Reverse: CCGGATAAAAAGAGTACGCTGG | 100 |
| Forward: GGGGACAACATCGTGACCG | |||
| NM_023566.4 | Muc-2 | Reverse: AGGAGTCGAAGACTTTGCACT | 106 |
| Forward: AGGGCTCGGAACTCCAGAAA |
| Group | Incubation Period (s) | Number of Errors |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 114.61 ± 4.62 * | 0.71 ± 0.49 * |
| Scopolamine | 81.52 ± 21.99 | 2.40 ± 1.14 |
| IOB802 | 105.96 ± 12.20 * | 0.88 ± 0.35 * |
| IOB802 postbiotic | 108.39 ± 9.80 * | 1.00 ± 0.63 * |
| Piracetam | 105.27 ± 11.36 * | 0.90 ± 0.32 * |
| Group | Chao 1 | Ace | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 324.12 ± 48.16 | 325.81 ± 52.12 | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 3.28 ± 0.75 | 0.9993 |
| Scopolamine | 305.68 ± 52.27 | 307.92 ± 53.05 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 3.24 ± 0.32 | 0.9992 |
| IOB802 | 281.04 ± 47.52 | 285.82 ± 51.70 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 3.15 ± 0.53 | 0.9993 |
| IOB802 Postbiotics | 362.67 ± 44.24 | 362.69 ± 47.73 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 3.53 ± 0.62 | 0.9993 |
| Piracetam | 317.42 ± 42.93 | 321.37 ± 41.77 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 3.51 ± 0.29 | 0.9992 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Pan, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, H.; Li, B.; Han, X.; Fu, T.; Liang, W.; Zhou, S.; Ma, W. A Novel Probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234037
Song Y, Pan W, Meng L, Wu H, Li B, Han X, Fu T, Liang W, Zhou S, Ma W. A Novel Probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yuxuan, Wenjing Pan, Linlin Meng, Hengyu Wu, Boyang Li, Xuemei Han, Tianmin Fu, Wu Liang, Sa Zhou, and Wenjian Ma. 2025. "A Novel Probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice" Foods 14, no. 23: 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234037
APA StyleSong, Y., Pan, W., Meng, L., Wu, H., Li, B., Han, X., Fu, T., Liang, W., Zhou, S., & Ma, W. (2025). A Novel Probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum IOB802 and Its Postbiotic Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice. Foods, 14(23), 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234037







