Structure and Functional Characteristics of Soybean Protein from Different Northeast Cultivars and Their Effects on the Quality of Soymilk Gel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soybean Samples
2.2. Compositional Analysis of Soybeans
2.2.1. Protein Content
2.2.2. Fat Content
2.2.3. Isoflavone Content
2.2.4. Selenium Content
2.2.5. Phytic Acid Content
2.3. Protein Extraction
2.4. Protein Characterization
2.4.1. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.4.4. Protein Solubility
2.4.5. Water and Oil Retention Capacity
2.4.6. Gelation Capacity Assessment
2.5. Soymilk Gel Preparation
2.6. Soymilk Gel Quality Evaluation
2.6.1. Gel Yield
2.6.2. Water Holding Capacity
2.6.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.6.4. Rheological Analysis
2.6.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protein, Fat, and Bioactive Compound Profiles Across Soybean Germplasm
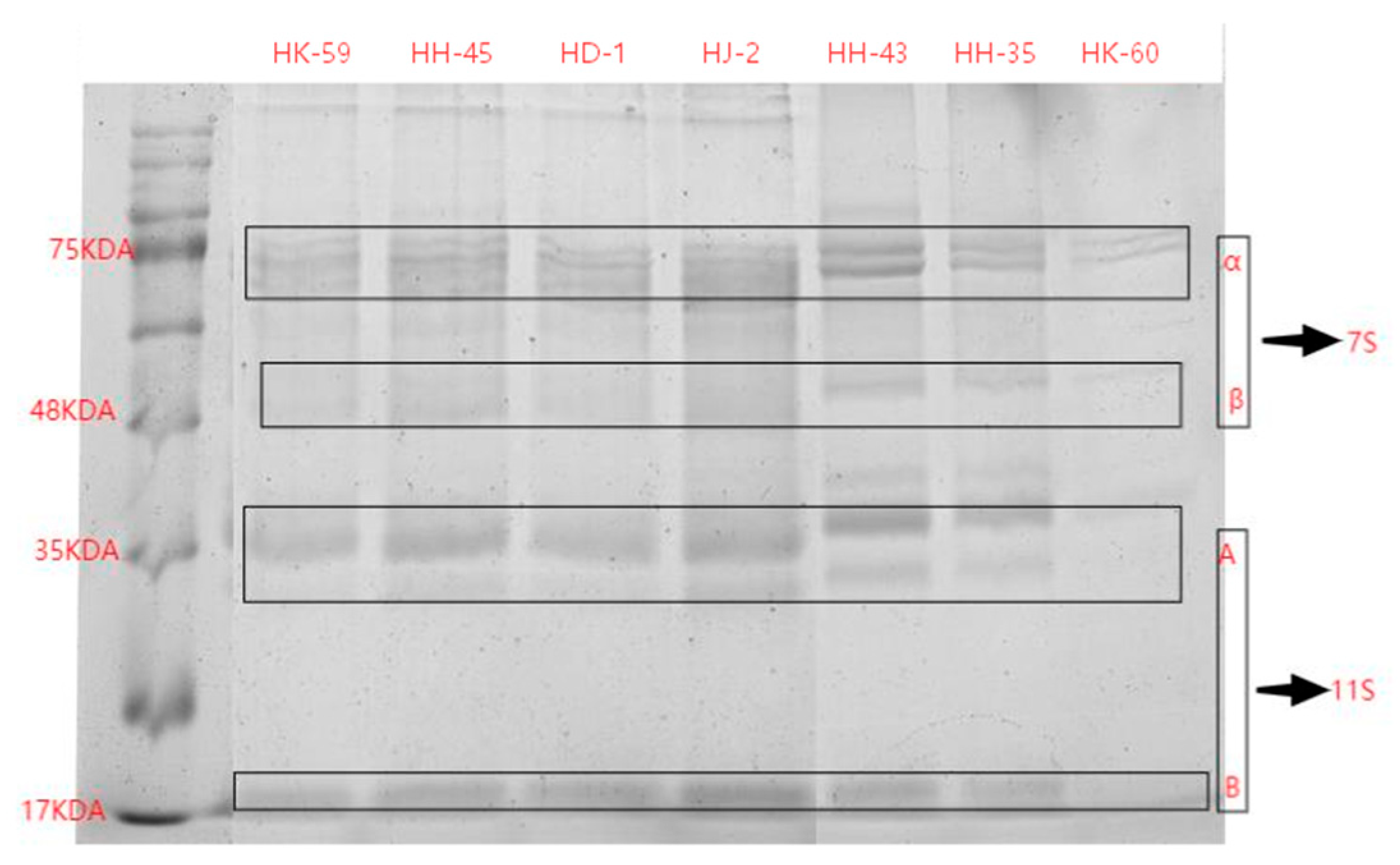
3.2. Protein Composition by SDS-PAGE
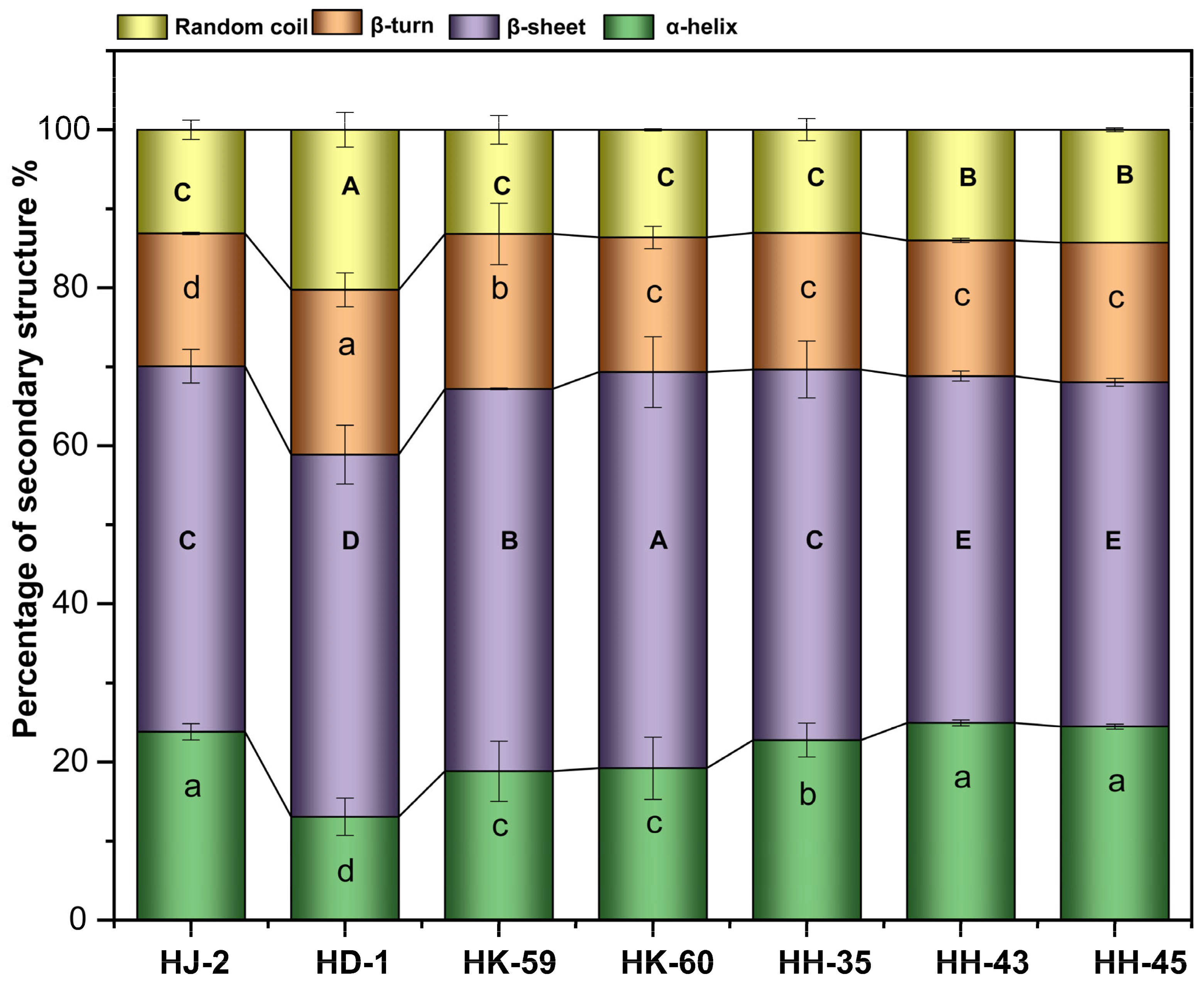
3.3. Secondary Structure Analysis by FTIR Spectroscopy
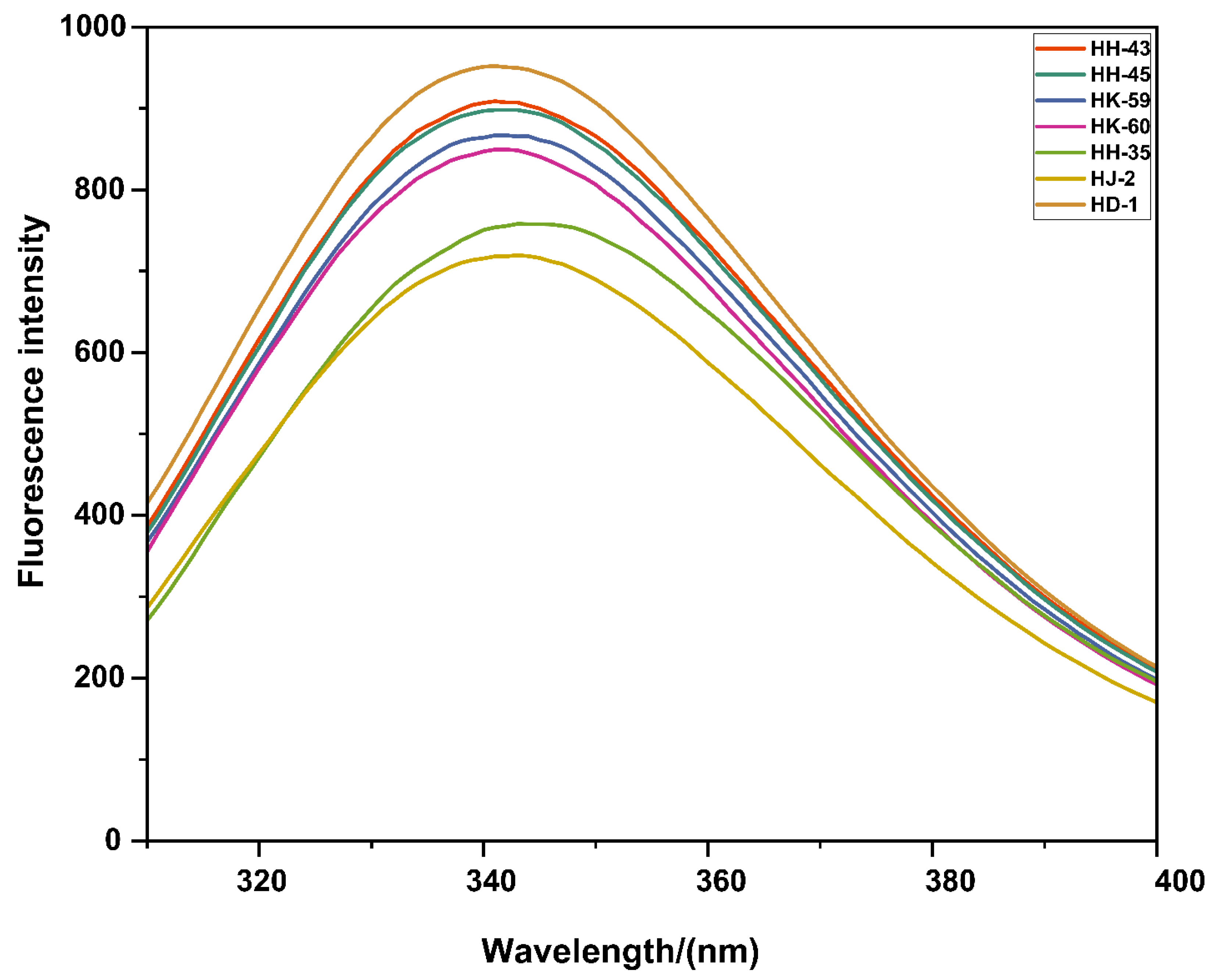
3.4. Tertiary Structure Assessment by Fluorescence Spectroscopy
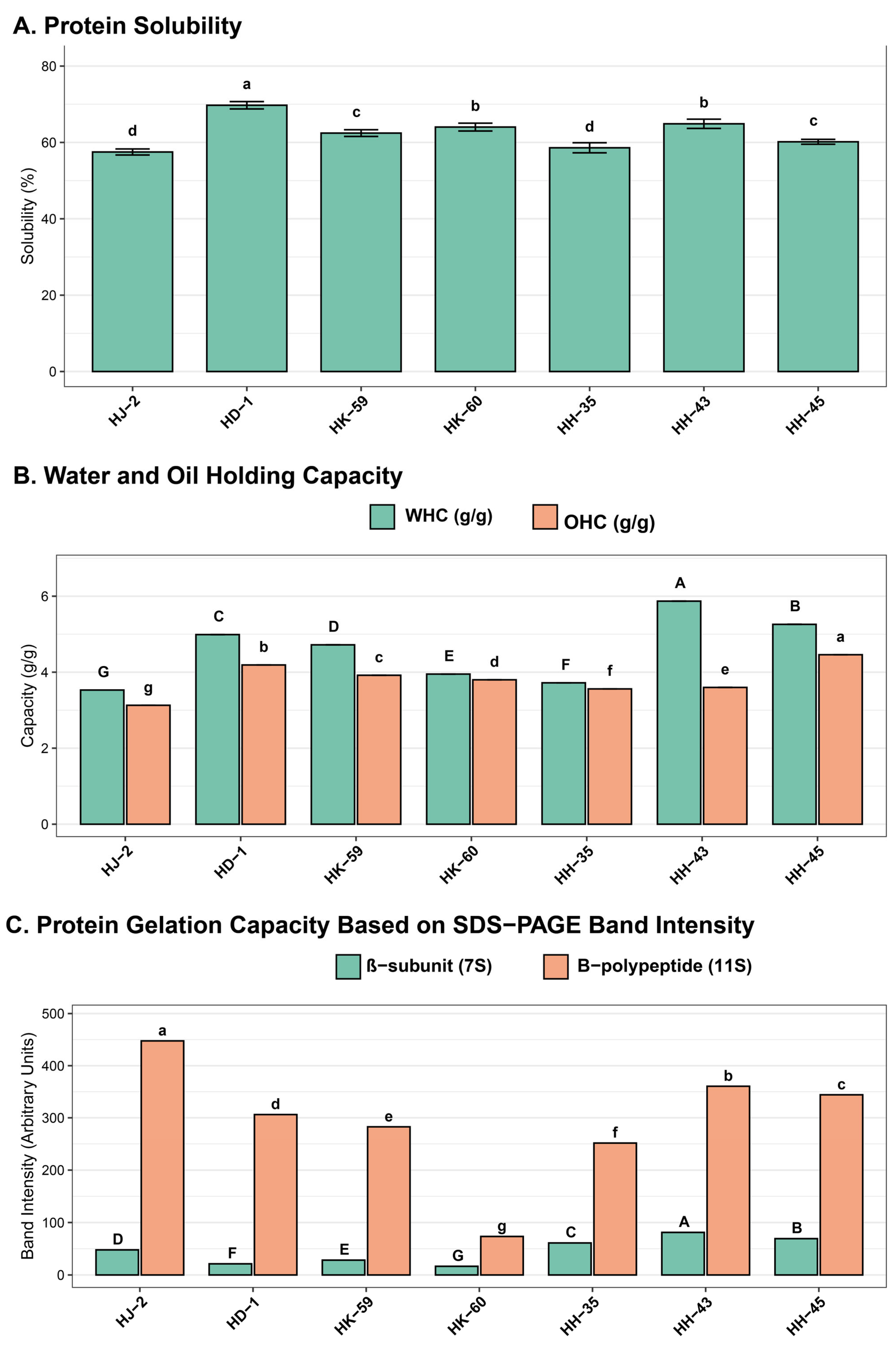
3.5. Functional Properties of Soybean Protein Isolates
3.6. Soymilk Yield and Gel-Forming Properties
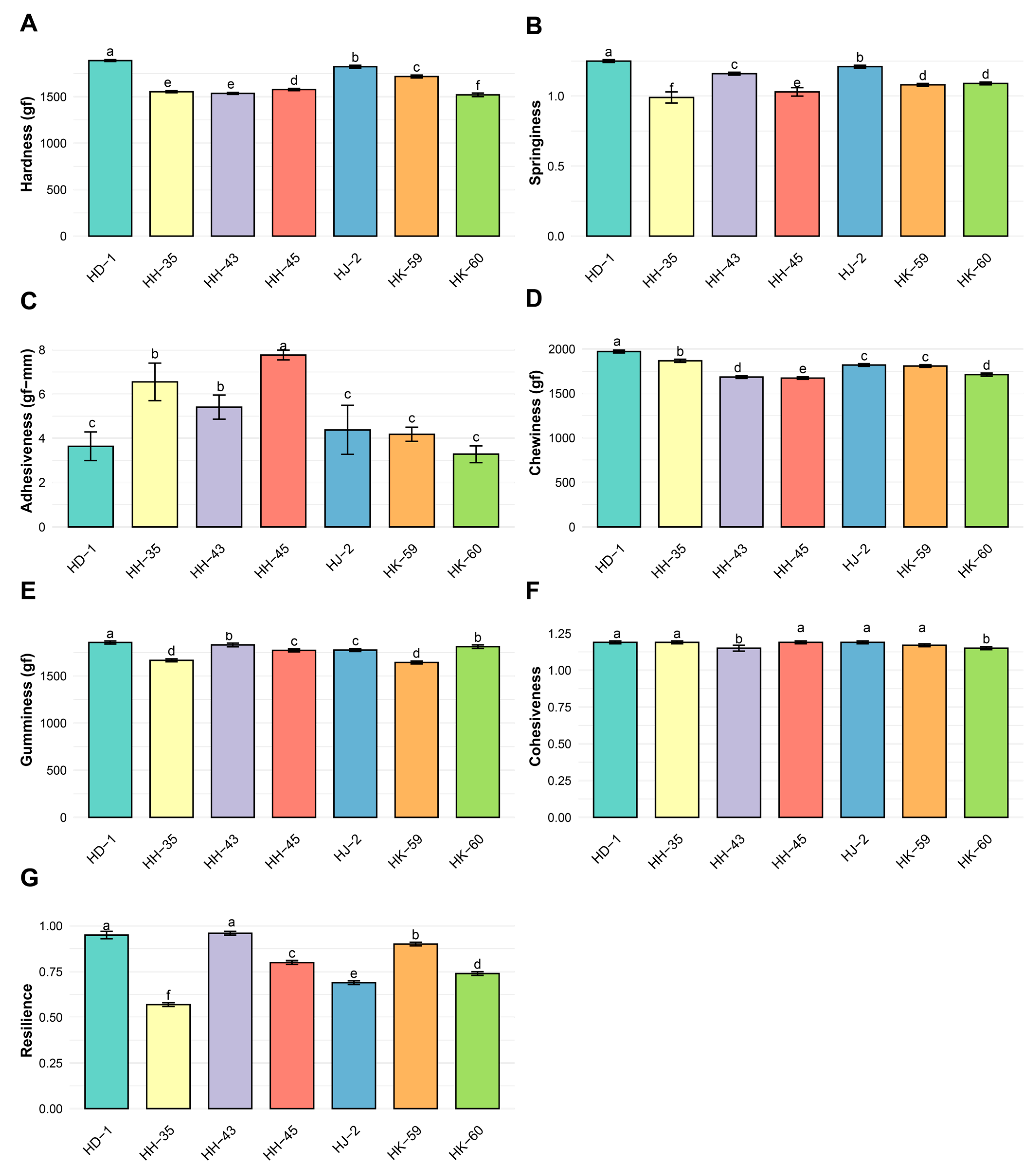
3.7. Texture Profile Analysis
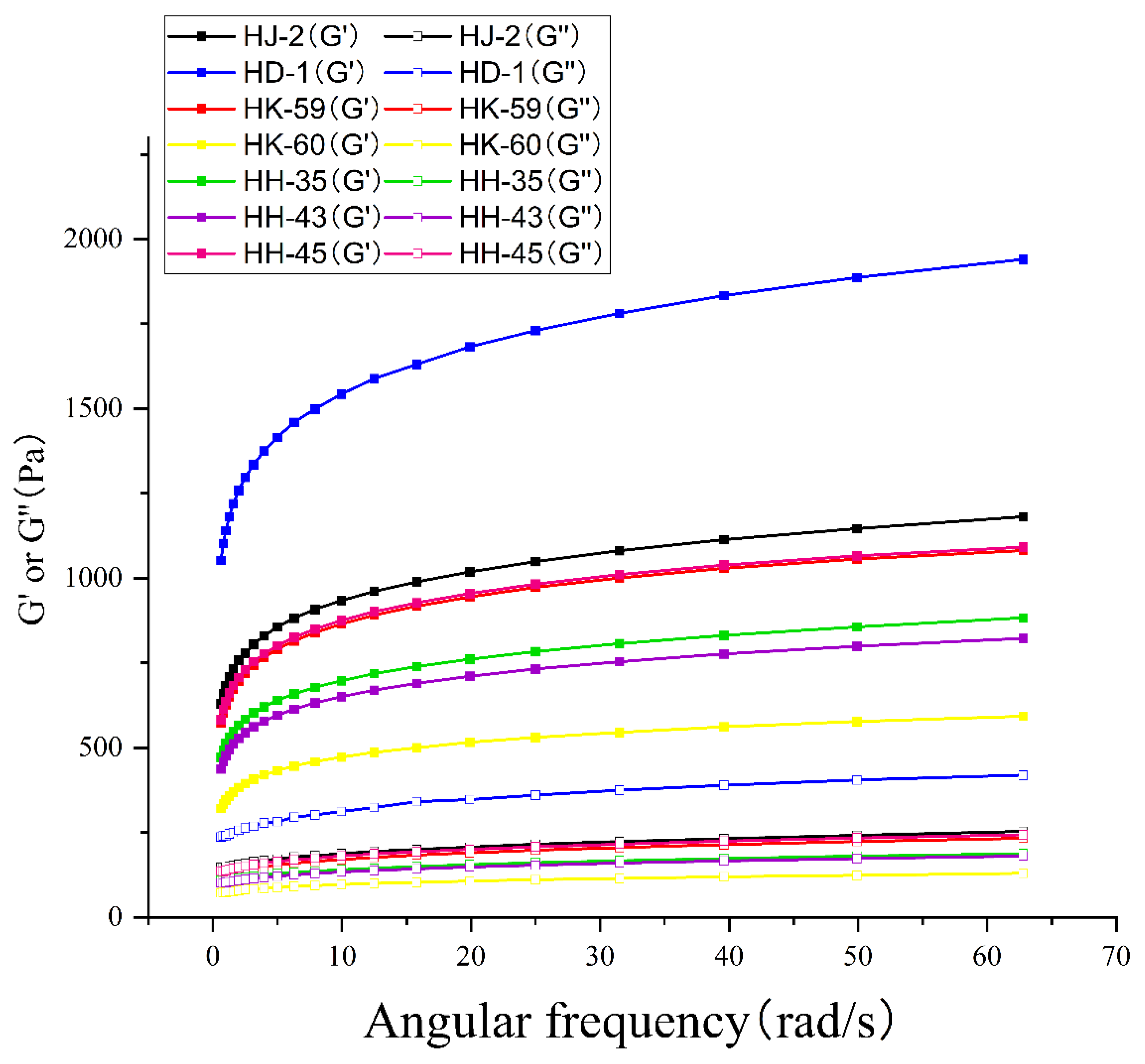
3.8. Rheological Properties
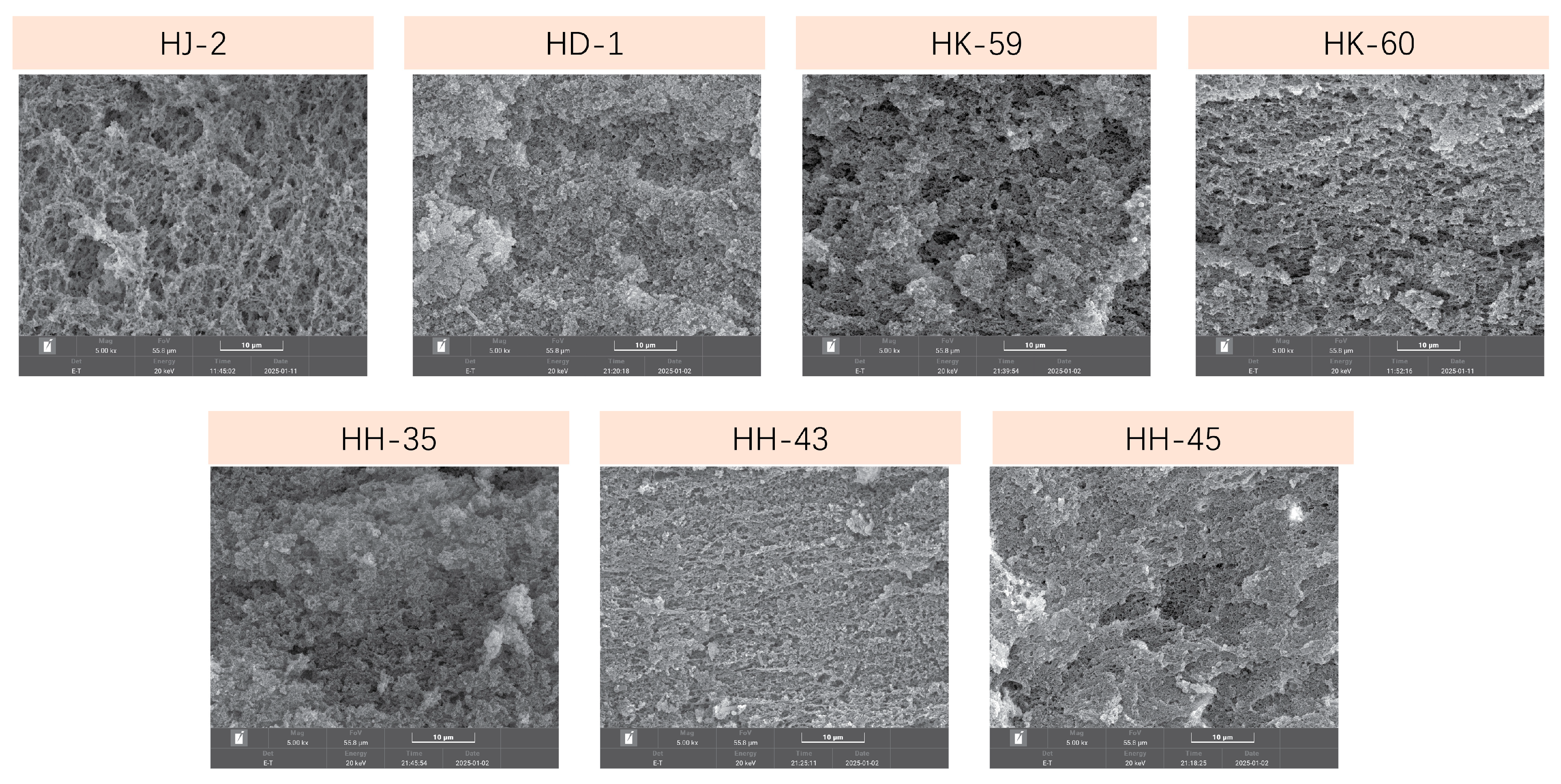
3.9. Gel Microstructure by Scanning Electron Microscopy
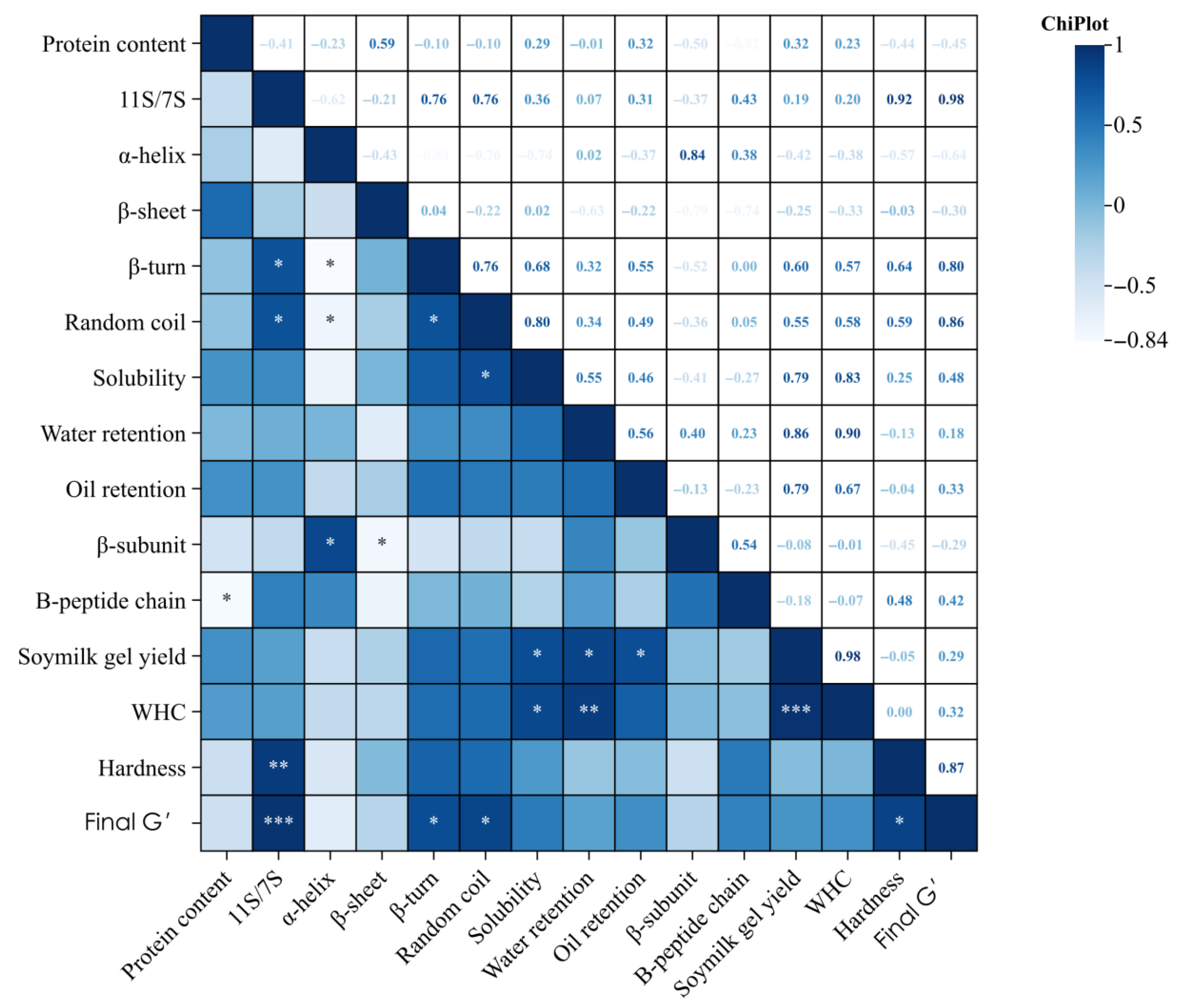
3.10. Correlation Analysis Between Protein Characteristics and Gel Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Protein Composition on Gelation Performance
4.2. Structural Basis of Gel Network Formation
4.3. Relationship Between Secondary and Tertiary Structures and Gel Texture
4.4. Solubility and Microstructure as Predictors of Water-Holding Capacity
4.5. Rheological Indicators of Network Stability
4.6. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, P.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. A review on plant-based proteins from soybean: Health benefits and soy product development. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M. Perspective: Soybeans can help address the caloric and protein needs of a growing global population. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 909464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Hao, X.; Ji, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y. A systematic review of black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.): Nutritional composition, bioactive compounds, health benefits, and processing to application. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1188–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wu, N.; Jiang, L.; Wu, F.; Yu, D.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Effect of electrochemical treatment on the formation and characteristics of induced soybean milk gel. J. Food Eng. 2022, 323, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L. Soy protein: Molecular structure revisited and recent advances in processing technologies. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Han, T.; Song, Y.; Zhu, X. Impact of freeze-thaw cycles on the structural and quality characteristics of soy protein gels with different 11S/7S protein ratios. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Deng, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X. Soy protein gels based on ultrasonic treatment: Effects of Ca2+ and 11S/7S ratio on gel structures and digestive properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 111, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, L.; Lv, M.; Huang, Y.; Sun, B.; Qu, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and properties of soy protein gels prepared with different 11S/7S ratios. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Qing, M.; Chi, Y.; Chi, Y. Egg white protein under thermal stress: Thermal aggregation orientation and gel properties decline. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, P.; Xu, B. Modulating the aggregation of myofibrillar protein to alleviate the textural deterioration of protein gels at high temperature: The effect of hydrophobic interactions. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, Z. Fabrication and Characterization of Composite Hydrogels for Efficient Wound Healing. Master’s Thesis, Department of Chemistry, COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus, Lahore, Pakistan, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Teng, D.; Yu, C.; Yao, L.; Ma, X.; Wu, T. Increased sulfur-containing amino acid content and altered conformational characteristics of soybean proteins by rebalancing 11S and 7S compositions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 828153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Feng, L.; Lei, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Soybean phenological changes in response to climate warming in three northeastern provinces of China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Sun, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, R.; Tian, S.; Xu, C.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, S.; Hou, W.; Wu, C. Geographic distributions and the regionalization of soybean seed compositions across China. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yan, X.; Li, W.; Jia, H.; Ren, H.; Lu, W. Multi-Environment Evaluation of Soybean Variety Heike 88: Transgressive Segregation and Regional Adaptation in Northern China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Hou, H. Science and technology of tofu making. In Handbook of Vegetable Preservation and Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 530–572. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Huang, L.; Xing, G.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Dai, D.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Xue, C. Structure and Functional Properties of Proteins from Different Soybean Varieties as Affected by the 11S/7S Globulin Ratio. Foods 2025, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Ren, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, R.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; Du, S.-k. Structural, functional properties of protein and characteristics of tofu from small-seeded soybeans grown in the Loess Plateau of China. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Roos, Y.H.; Miao, S. Comparative studies of structural and thermal gelation behaviours of soy, lentil and whey protein: A pH-dependency evaluation. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Swallah, M.S.; Gong, H.; Ji, L.; Meng, X.; Lyu, B.; Yu, H. The heated-induced gelation of soy protein isolate at subunit level: Exploring the impacts of α and α′ subunits on SPI gelation based on natural hybrid breeding varieties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-B.; Feng, B.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhang, H.-T.; Li, Z.-L.; Meng, L.; Zhang, J.-J.; Bai, X.-S.; Gao, F. A novel approach has been developed to produce pure plant-based gel soy yogurt by combining soy proteins (7S/11S), high pressure homogenization, and glycation reaction. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Hsieh, J.-F.; Kuo, M.-I. Insight into the processing, gelation and functional components of tofu: A review. Processes 2023, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Khoder, R.M.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S. Gelation properties of tofu induced by different coagulants: Effects of molecular interactions between nano-sized okara dietary fiber and soybean proteins. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Chen, S.; Fang, X.; Wu, J. Recent advance in modification strategies and applications of soy protein gel properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, P.; Florez-Palacios, S.L.; Shi, A.; Hou, A.; Ishibashi, T. Seed quality attributes of food-grade soybeans from the US and Asia. Euphytica 2010, 173, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard. Determination of Protein in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.6-2016; Fat: National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Fat in Foods (Method 2). National Health Commission of PRC: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T23788-2009; Determination of Soybean Isoflavone in Health-Care Food by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB5009.93-2017; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Selenium in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB5009.153; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Phytic Acid in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J. The Bradford method for protein quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, F.S.; de Souza, N.C.S.A.; de Moraes, M.V.; Abreu, B.J.; de Oliveira, M.F. CmyoSize: An ImageJ macro for automated analysis of cardiomyocyte size in images of routine histology staining. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2022, 241, 151892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Feng, Z.; Yang, J.; Hu, W.; Liang, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Mi, B.; Liu, Z. Investigating the co-firing characteristics of bamboo wastes and coal through cone calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis coupled with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Dai, S.; Gu, B. Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias-Junior, O.; Souza-Gabriel, A.E.; Miranda, C.E.S.; Pécora, J.D.; Silva-Sousa, Y.T.C.; Sousa-Neto, M.D. Solubility of Epiphany endodontic sealer prepared with resinous solvent. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valencia, J.; Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Martinez, I.; Careche, M. Estimation of frozen storage time or temperature by kinetic modeling of the Kramer shear resistance and water holding capacity (WHC) of hake (Merluccius merluccius L.) muscle. J. Food Eng. 2014, 120, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Mamu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, S. Protein aggregation and Ca2+-induced gelation of soymilk after heat treatment under slightly alkaline conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poysa, V.; Woodrow, L. Stability of soybean seed composition and its effect on soymilk and tofu yield and quality. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Deng, T.; Wang, C.; Mi, H.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effect of hydrocolloids on gel properties and protein secondary structure of silver carp surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.-H.; Hu, Z.-X.; Yu, Z.; An, H.-Z. Texture and rehydration properties of texturised soy protein: Analysis based on soybean 7S and 11S proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, A.; Shah, F. Rheology instruments for food quality evaluation. In Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 465–490. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Tong, Q.; Shehzad, Q.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M.; Riaz, T.; Jafari, S.M. Rheological analysis of solid-like nanoencapsulated food ingredients by rheometers. In Characterization of Nanoencapsulated Food Ingredients; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 547–583. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Choi, M.-J.; Xiong, Y.L. Comparative effects of micro vs. submicron emulsions on textural properties of myofibrillar protein composite gels. Food Struct. 2023, 38, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Cao, Y.; Lei, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H. Protein structure and sulfhydryl group changes affected by protein gel properties: Process of thermal-induced gel formation of myofibrillar protein. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Texture characteristics, protein solubility, and sulfhydryl group/disulfide bond contents of heat-induced gels of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulivarthi, M.K.; Buenavista, R.M.; Bangar, S.P.; Li, Y.; Pordesimo, L.O.; Bean, S.R.; Siliveru, K. Dry fractionation process operations in the production of protein concentrates: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4670–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanilla-Valdez, M.L.; Ma, Z.; Mondor, M.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J. Decoding the duality of Antinutrients: Assessing the impact of protein extraction methods on plant-based protein sources. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 12319–12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Pal, A.; Kumar, S.; Saharan, V. Protein chemistry and gelation. In Advances in Food Chemistry: Food Components, Processing and Preservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Ming, J. Effects of ionic strength and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on physicochemical characteristics of soybean 11S and 7S proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, T.; Uversky, V.N. The Three Functional States of Proteins: Structured, Intrinsically Disordered, and Phase Separated; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lankinen, T. Characterizing Spontaneous Secondary Structure Changes by Solute Minispidroins Within Distinct Phase Regions. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Armen, R.; Alonso, D.O.; Daggett, V. The role of α-, 310-, and π-helix in helix → coil transitions. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Logan, D.T.; Danielsson, J.; Oliveberg, M. Exposing the distinctive modular behavior of β-strands and α-helices in folded proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28775–28783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S. Alkaline-heat induced the conformationally flexible regions of soy protein and their effect on subunit aggregation. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, M.; Diao, X.; Sun, S.; Wen, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Lv, P.; Li, B. The Heat-Induced Gel–Sol Transition in Coated Tofu: A Study on Protein Conformation and Microstructural Changes. Gels 2025, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, S. Gliadin nanoparticles stabilized by a combination of thermally denatured ovalbumin with gemini dodecyl O-glucoside: The modulating effect of cosurfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 516, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Ji, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, G. Characterization of thermal denaturation structure and morphology of soy glycinin by FTIR and SEM. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. A novel process for peanut tofu gel: Its texture, microstructure and protein behavioral changes affected by processing conditions. LWT 2018, 96, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, J.E. Functional properties of soy proteins. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, L.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, L. Effect of cavitation jet technology on instant solubility characteristics of soymilk flour: Based on the change of protein conformation in soymilk. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 96, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, A.; Chang, H.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Feng, Z. Mechanism of change of the physicochemical characteristics, gelation process, water state, and microstructure of okara tofu analogues induced by high-intensity ultrasound treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhong, X.; Lu, Y.; Du, X.; Jia, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, M. Changes of soybean protein during tofu processing. Foods 2021, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J. Gel Formation Mechanism and Application in Dysphagia: Based on Peach Matrix-Soy Protein Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Liege, Liège, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Bui, K.; Akkutlu, I.Y. Capillary pressure in nanopores: Deviation from Young-Laplace equation. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec Featured at EAGE Conference and Exhibition, Paris, France, 12–15 June 2017; p. D031S007R008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Luo, K.; Liu, S.; Zeng, M.; Adhikari, B.; He, Z.; Chen, J. Textural and rheological properties of soy protein isolate tofu-type emulsion gels: Influence of soybean variety and coagulant type. Food Biophys. 2018, 13, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Varieties | Protein Content (g/100 g) | Fat Content (g/100 g) | Isoflavone Content (μg/g) | Phytic Acid Content (mg/g) | Selenium Content (μg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HJ-2 | 35.56 ± 0.05 d | 16.04 ± 0.10 e | 112.85 ± 1.04 e | 18.78 ± 0.04 a | 16.87 ± 0.04 a |
| HD-1 | 36.63 ± 0.47 c | 21.43 ± 0.98 a | 116.88 ± 1.01 d | 18.04 ± 0.08 c | 12.91 ± 0.01 e |
| HK-59 | 37.62 ± 0.37 b | 20.92 ± 0.21 b | 139.75 ± 1.01 b | 15.65 ± 0.01 e | 13.69 ± 0.02 d |
| HK-60 | 41.39 ± 0.01 a | 19.21 ± 0.30 c | 84.51 ± 1.02 f | 17.04 ± 0.10 d | 7.33 ± 0.02 g |
| HH-35 | 35.69 ± 0.01 d | 18.24 ± 0.10 d | 136.85 ± 1.02 b | 18.04 ± 0.08 c | 14.82 ± 0.02 b |
| HH-43 | 36.77 ± 0.01 c | 22.36 ± 0.99 a | 154.40 ± 1.16 a | 18.26 ± 0.07 b | 14.50 ± 0.01 c |
| HH-45 | 37.61 ± 0.14 b | 19.66 ± 1.00b c | 130.81 ± 1.09 c | 18.30 ± 0.05 b | 11.40 ± 0.02 f |
| Average | 37.32 ± 2.18 | 19.69 ± 2.09 | 125.15 ± 22.67 | 17.73 ± 0.99 | 13.07 ± 2.95 |
| Varieties | 11S | 7S | 11S/7S |
|---|---|---|---|
| HJ-2 | 603.43 ± 0.01 b | 219.38 ± 0.01 d | 2.7506 b |
| HD-1 | 473.18 ± 0.04 e | 115.51 ± 0.01 g | 4.0966 a |
| HK-59 | 423.20 ± 0.02 f | 175.07 ± 0.02 e | 2.4174 c |
| HK-60 | 141.22 ± 0.05 g | 123.92 ± 0.04 f | 1.1396 g |
| HH-35 | 490.64 ± 0.03 d | 314.92 ± 0.01 b | 1.5580 e |
| HH-43 | 817.01 ± 0.01 a | 639.46 ± 0.03 a | 1.2777 f |
| HH-45 | 566.75 ± 0.03 c | 242.64 ± 0.02 c | 2.3357 d |
| Average | 502.20 ± 206.40 | 261.56 ± 174.91 | 2.225 ± 0.99 |
| Varieties | Soymilk Yield (%) | Soymilk Gel Yield (%) | WHC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HJ-2 | 77.33 ± 2.12 b | 193.25 ± 4.18 c | 42.09 ± 0.38 c |
| HD-1 | 71.81 ± 2.10 c | 236.12 ± 2.30 a | 60.23 ± 3.14 a |
| HK-59 | 77.32 ± 1.02 b | 227.36 ± 2.64 a | 54.69 ± 6.84 a |
| HK-60 | 77.33 ± 1.01 b | 219.58 ± 7.63 b | 51.48 ± 3.54 b |
| HH-35 | 82.86 ± 3.02 a | 203.77 ± 3.53 c | 44.62 ± 0.96 c |
| HH-43 | 69.04 ± 1.02 c | 231.61 ± 1.96 a | 60.11 ± 8.24 a |
| HH-45 | 77.33 ± 2.11 b | 229.35 ± 2.11 b | 55.16 ± 2.33 a |
| Average | 76.15 ± 4.26 | 220.15 ± 16.12 | 52.36 ± 7.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, T.; Yan, S.; Zhu, X.; Kang, J.; Zhao, G.; Lamlom, S.F.; Ren, H.; et al. Structure and Functional Characteristics of Soybean Protein from Different Northeast Cultivars and Their Effects on the Quality of Soymilk Gel. Foods 2025, 14, 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234029
Xia X, Zhang C, Zhang S, Gao T, Yan S, Zhu X, Kang J, Zhao G, Lamlom SF, Ren H, et al. Structure and Functional Characteristics of Soybean Protein from Different Northeast Cultivars and Their Effects on the Quality of Soymilk Gel. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234029
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xiaoyu, Chunlei Zhang, Shiyao Zhang, Tianjiao Gao, Shuping Yan, Xiuqing Zhu, Jiaxin Kang, Guixing Zhao, Sobhi F. Lamlom, Honglei Ren, and et al. 2025. "Structure and Functional Characteristics of Soybean Protein from Different Northeast Cultivars and Their Effects on the Quality of Soymilk Gel" Foods 14, no. 23: 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234029
APA StyleXia, X., Zhang, C., Zhang, S., Gao, T., Yan, S., Zhu, X., Kang, J., Zhao, G., Lamlom, S. F., Ren, H., & Wang, J. (2025). Structure and Functional Characteristics of Soybean Protein from Different Northeast Cultivars and Their Effects on the Quality of Soymilk Gel. Foods, 14(23), 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234029






