Anti-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Hepatic Steatosis Effects of Pickering Emulsion-Encapsulated Curcumin via Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulation in High-Fat-Diet Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Reagents and Diets
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) and Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT)
2.4. Biochemical Assays
2.5. Oil Red O Staining
2.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.7. 16S rDNA Sequencing
2.8. Assessment of SCFAs Concentrations
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
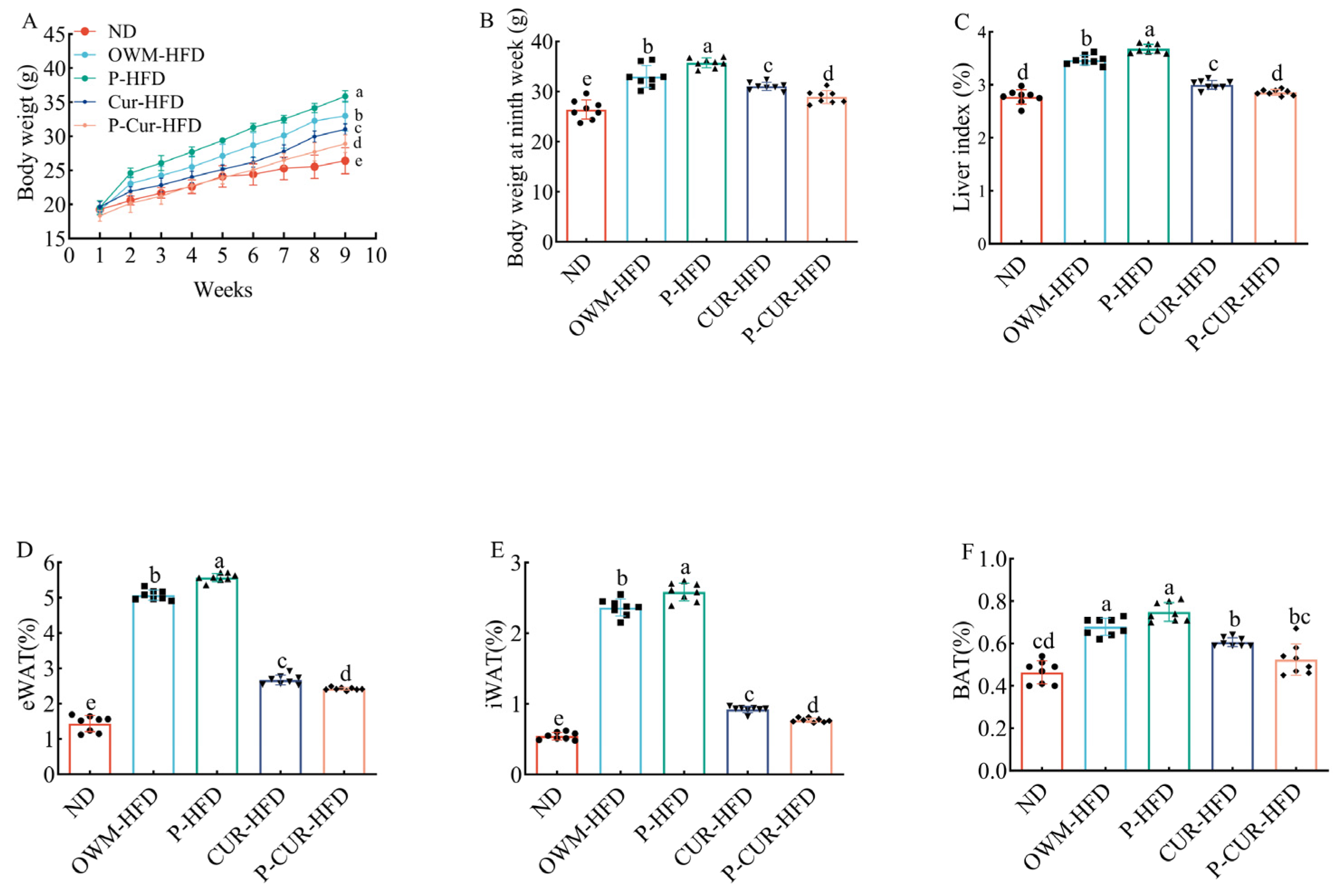
3.1. PE-Cur Attenuated High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity Phenotype
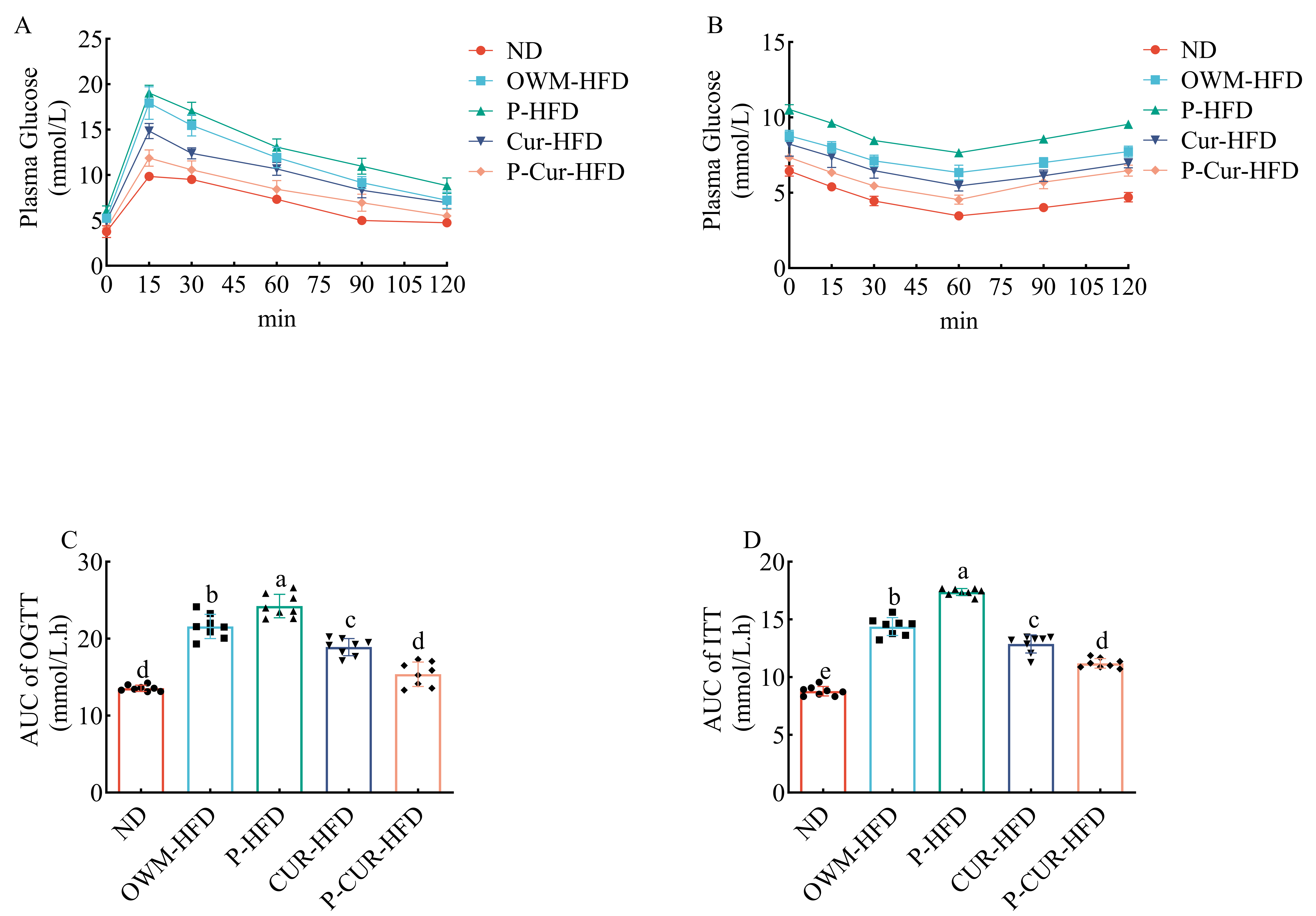
3.2. PE-Cur Alleviated Glucose Intolerance and IR
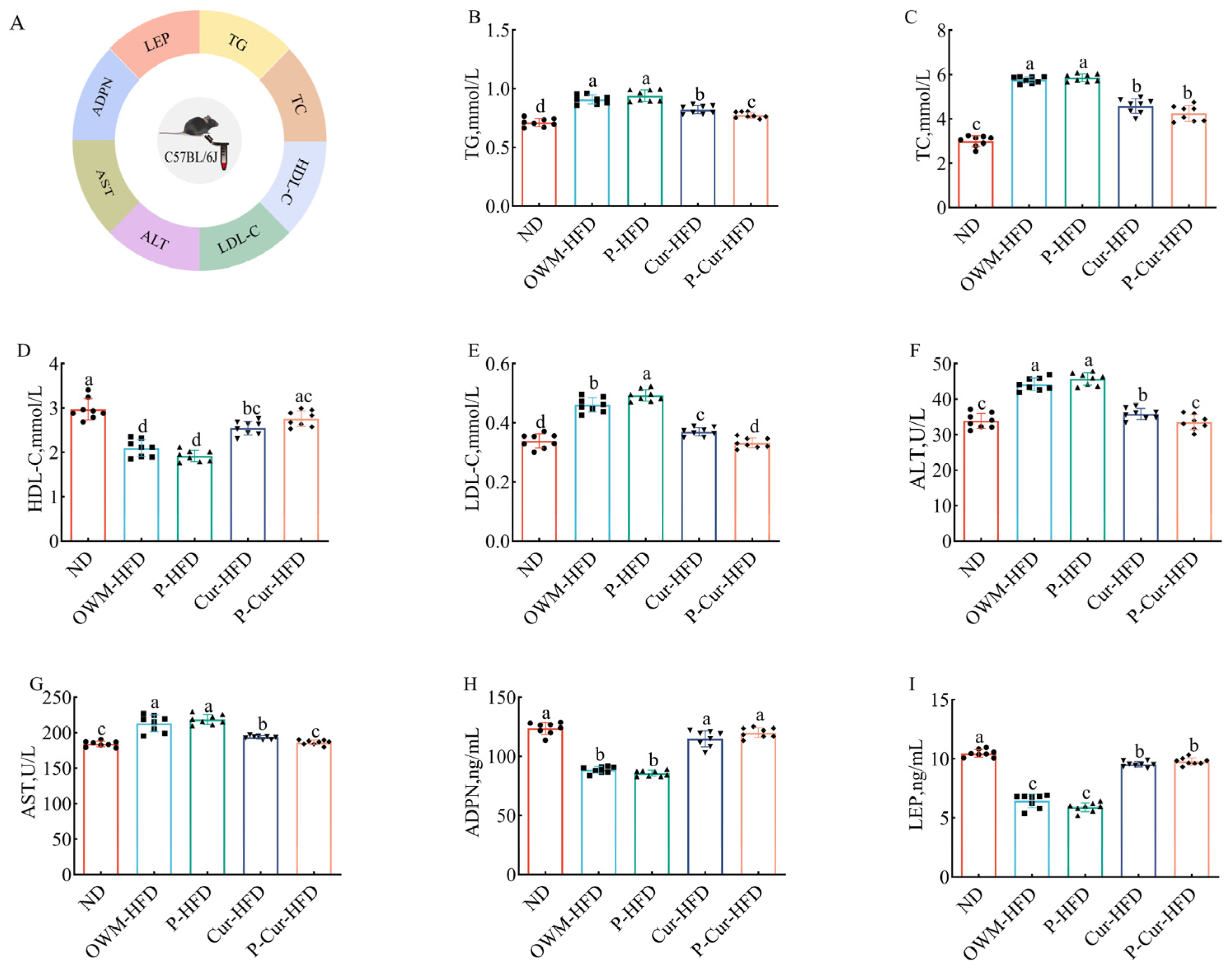
3.3. PE-Cur Alleviated Serum Metabolic Disorders in LMD Mice
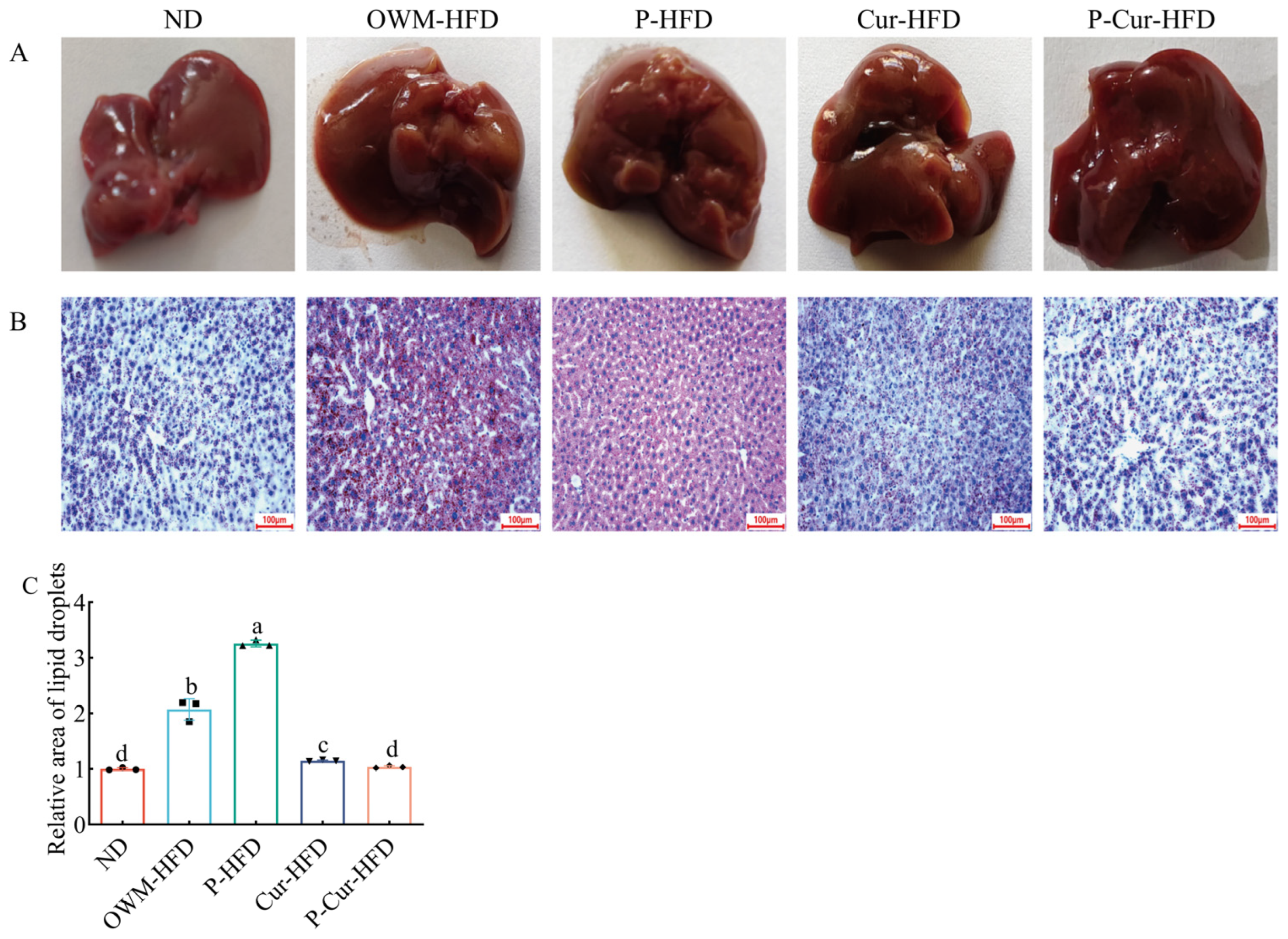
3.4. PE-Cur Alleviated Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
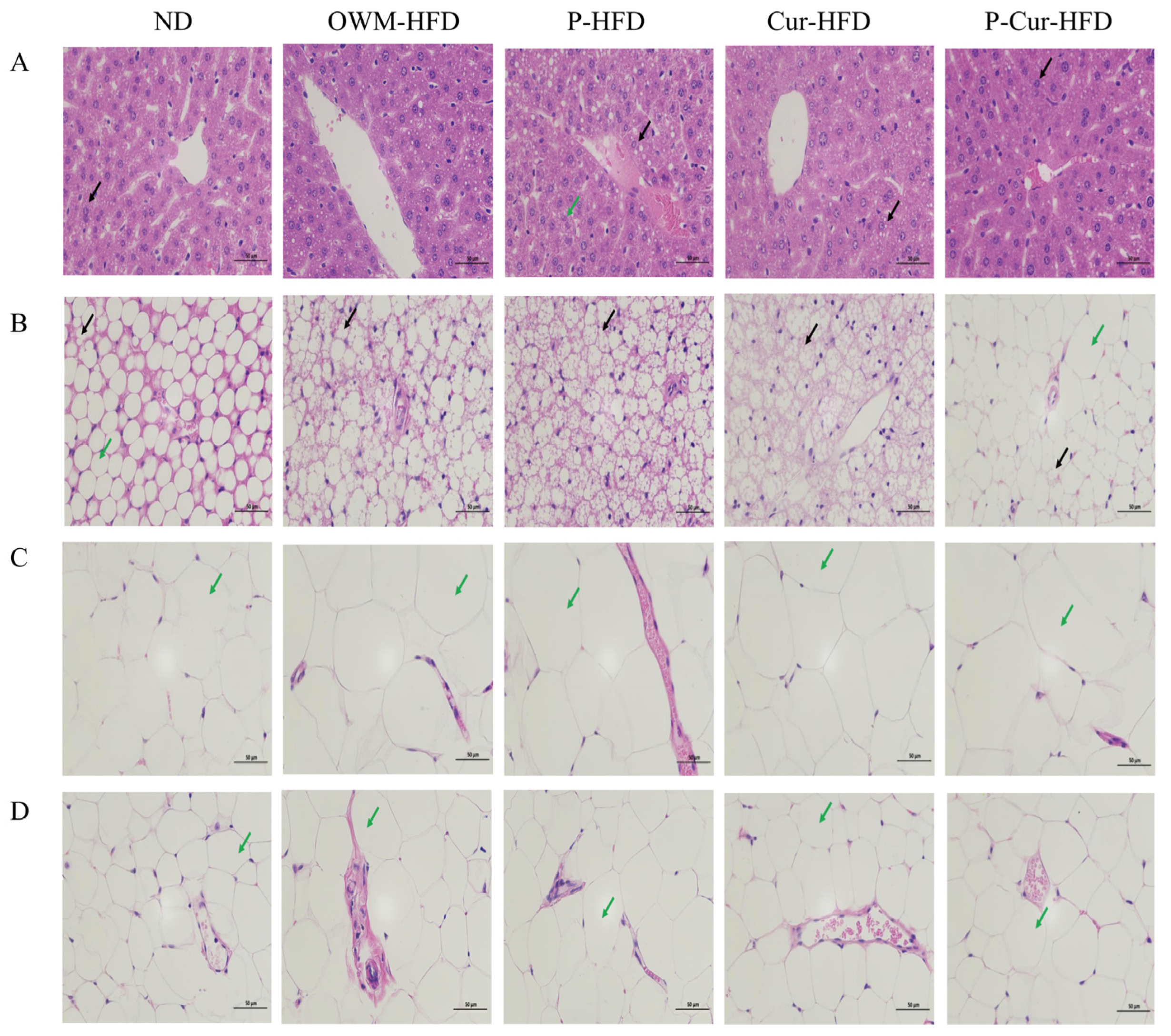
3.5. PE-Cur Improved Histopathological Changes in Liver, BAT, eWAT, and iWAT
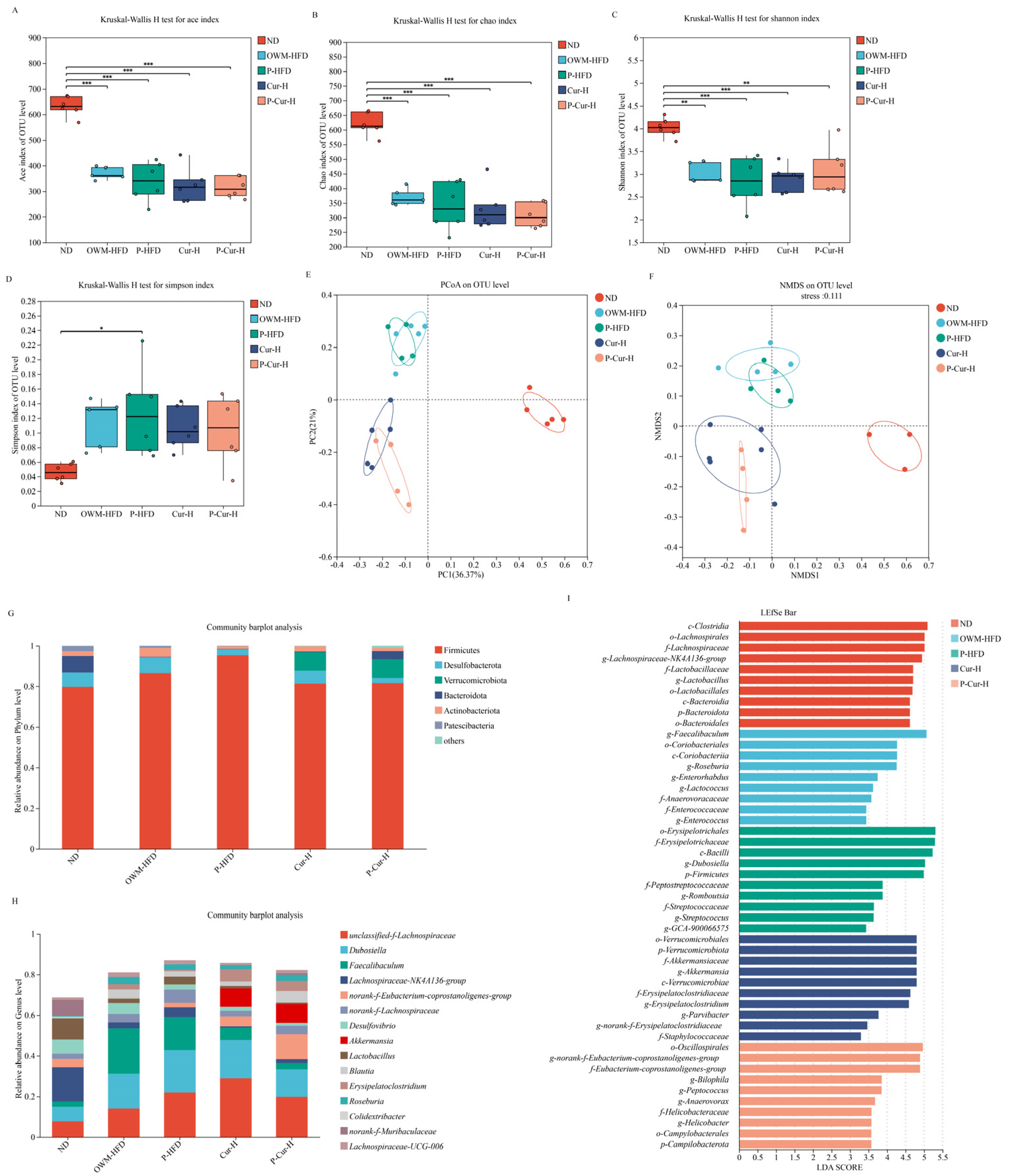
3.6. PE-Cur Effectively Improved the Structure of the Gut Microbiota
3.7. The Effects of PE-Cur on SCFAs Levels
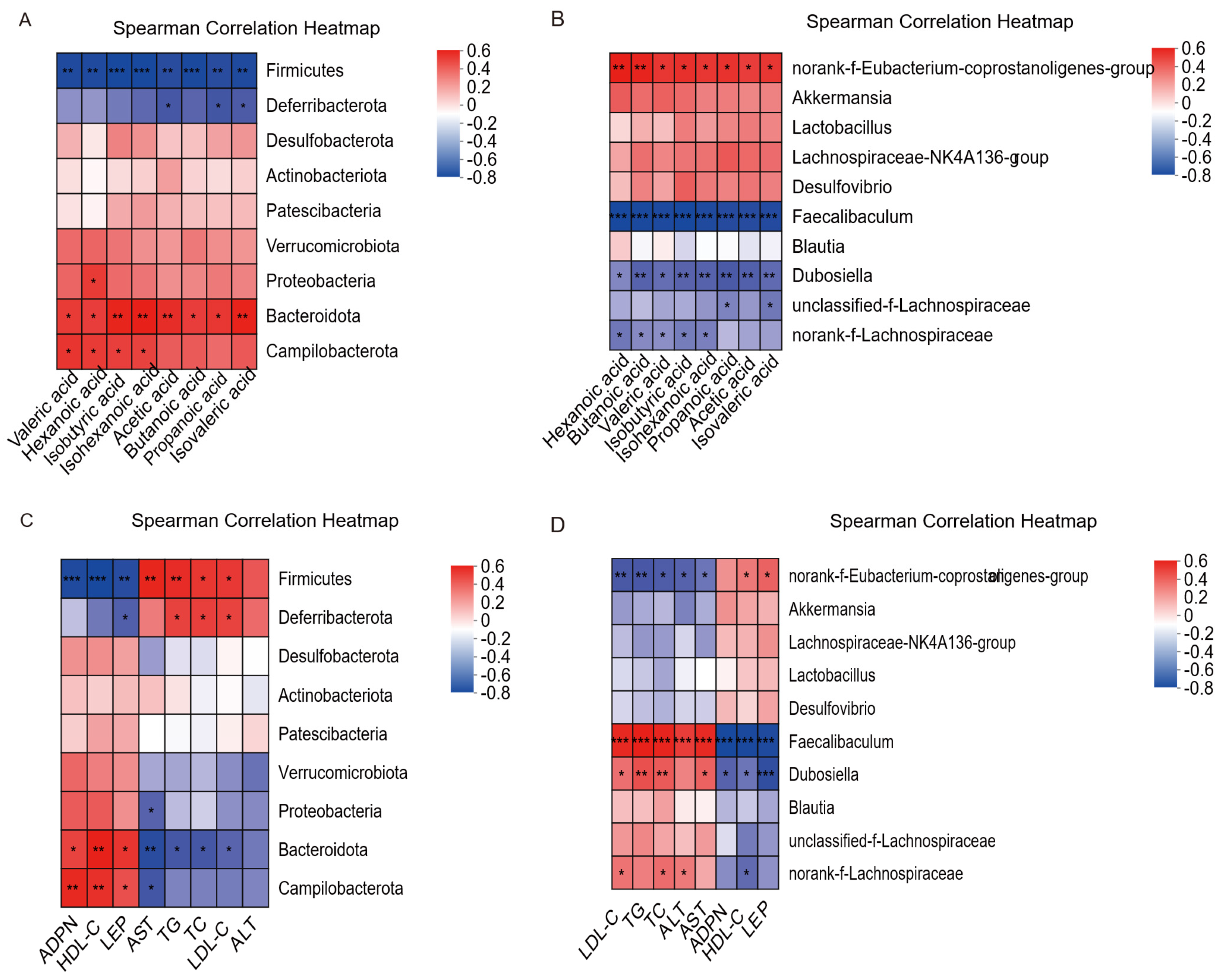
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiota-Serum Biochemical Factors and Gut Microbiota-SCFAs
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Haneishi, Y.; Furuya, Y.; Tanioka, Y.; Miyamoto, J. Polyunsaturated fatty acids-rich dietary lipid prevents high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 13, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, B.; Chen, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Hong, J. FBXO28 reduces high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in mice by alleviating abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Fan, D.; Deng, J.; Yang, H. Ginsenoside Rk3 Ameliorates Obesity-Induced Colitis by Modulating Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, F.; Gao, X.; Qin, L.; Yang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, G.; et al. Exercise ameliorates lipid droplet metabolism disorder by the PLIN2–LIPA axis-mediated lipophagy in mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Han, R.; Ma, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. ONOO—Activatable and LD-traced NIR fluorescent probe for mechanism study and early diagnosis of NAFLD and diabetes induced liver injury. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 412, 135806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alappat, L.; Awad, A.B. Curcumin and obesity: Evidence and mechanisms. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaadam, B.; Sanlier, N. Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. Curcumin attenuates cadmium-induced atherosclerosis by regulating trimethylamine-N-oxide synthesis and macrophage polarization through remodeling the gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; You, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Du, M.; Zou, T. Curcumin alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and obesity in association with modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Yang, X.; Jing, G.; Zhaozheng, Z.; Ziheng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Dongmin, L.I. Curcumin improves insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-fed mice through gut microbiota. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorantla, S.; Wadhwa, G.; Jain, S.; Sankar, S.; Nuwal, K.; Mahmood, A.; Dubey, S.K.; Taliyan, R.; Kesharwani, P.; Singhvi, G. Recent advances in nanocarriers for nutrient delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 2359–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jiang, Y.J.; Shi, J. Novel Pickering emulsion stabilized by glycosylated whey protein isolate: Characterization, stability, and curcumin bioaccessibility. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Shi, J. Novel Pickering emulsion stabilized by glycated casein embedding curcumin: Stability, bioaccessibility and antioxidant properties. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 194, 115796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L. Improved curcumin bioaccessibility in Pickering emulsion fabricated by rice glutelin fibrils. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Peng, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. Multi-responsive Pickering emulsions stabilized by amphiphilic cellulose nanocrystals for building smart release systems of hydrophobic drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 355, 123348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Z.; Ramzan, R.; Abdullah; Abbas, H.M.K.; Sun, W.; Zhang, G. Integrating the modified amphiphilic Eleocharis tuberosa starch to stabilize curcuminoid-enriched Pickering emulsions for enhanced bioavailability, thermal stability, and retention of the hydrophobic bioactive compound. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 352, 123199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, W.-K.; Chang, L.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Wu, M.-S.; Kuo, C.-H. Evaluation and Optimization of Sample Handling Methods for Quantification of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Human Fecal Samples by GC-MS. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Butera, M.A.; Zhou, C.; Maurizi, G.; Chen, B.; Ling, L.; Shawkat, A.; Patlolla, L.; Thakker, K.; Calle, V.; et al. Overnutrition causes insulin resistance and metabolic disorder through increased sympathetic nervous system activity. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hong, T.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z.; Mai, H.; Yao, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Curcumin supplementation alleviates hepatic fat content associated with modulation of gut microbiota-dependent bile acid metabolism in patients with nonalcoholic simple fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servida, S.; Panzeri, E.; Tomaino, L.; Marfia, G.; Garzia, E.; Appiani, G.C.; Moroncini, G.; De Gennaro Colonna, V.; La Vecchia, C.; Vigna, L. Overview of Curcumin and Piperine Effects on Glucose Metabolism: The Case of an Insulinoma Patient’s Loss of Consciousness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Hu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, K.; Pan, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y. Microglia Sirt6 modulates the transcriptional activity of NRF2 to ameliorate high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiao, B.; Li, S.; Faisal, S.; Shi, A.; Fu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q. Recent Advances on Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Diverse Edible Particles: Stability Mechanism and Applications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 864943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Yi, T.; Lu, Y. Pickering Emulsions Enhance Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin Nanocrystals: The Effect of Oil Types. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Dong, W.; Li, S.; Huang, A.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of Pickering emulsion gel stabilized by WPI/SPI composite particles and encapsulation of milk-derived peptide FDRPFL. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 199, 116093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.R.; Hsieh, W.T.; Chou, L.S.; Lin, C.S.; Wu, C.F.; Lin, J.W.; Lin, W.L.; Lin, T.C.; Liao, H.J.; Kao, C.Y.; et al. Curcumin Improved Glucose Intolerance, Renal Injury, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Decreased Chromium Loss through Urine in Obese Mice. Process 2021, 9, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, X. Consumption of dietary turmeric promotes fat browning and thermogenesis in association with gut microbiota regulation in high-fat diet-fed mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8153–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaikwawong, M.; Jansarikit, L.; Jirawatnotai, S.; Chuengsamarn, S. Curcumin extract improves beta cell functions in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2024, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Chou, W.L.; Ko, M.C.; Liao, J.C.; Huang, T.H. Curcumin mitigates obesity-driven dysbiosis and liver steatosis while promoting browning and thermogenesis in white adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 143, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.; Zou, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.; He, Y.; Feng, D. Curcumin protects against bisphenol A-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis in CD-1 mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 5091–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zou, J.; Mai, H.; Hong, T.; Liu, H.; Feng, D. Curcumin protects against high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic simple fatty liver by inhibiting intestinal and hepatic NPC1L1 expression via down-regulation of SREBP-2/HNF1α pathway in hamsters. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 119, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, M.Y.; Hwang, K.H.; Ahn, J.; Ha, T.Y. Curcumin attenuates diet-induced hepatic steatosis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 113, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Zou, J.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z.; He, Y.; Feng, D. Curcumin Supplementation Ameliorates Bile Cholesterol Supersaturation in Hamsters by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Cholesterol Absorption. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, G.; Olawale, F.; Liu, J.; Lee, D.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Chaffin, N.; Alake, S.; Lucas, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Egan, J.M.; et al. Curcumin Mitigates Gut Dysbiosis and Enhances Gut Barrier Function to Alleviate Metabolic Dysfunction in Obese, Aged Mice. Biology 2024, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servida, S.; Piontini, A.; Gori, F.; Tomaino, L.; Moroncini, G.; Colonna, V.D.G.; La Vecchia, C.; Vigna, L. Curcumin and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Overview with Focus on Glycemic Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; He, L. The Modulatory Effects of Curcumin on the Gut Microbiota: A Potential Strategy for Disease Treatment and Health Promotion. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, S.; Chang, S.; et al. Gut microbiota mediates the effects of curcumin on enhancing Ucp1-dependent thermogenesis and improving high-fat diet-induced obesity. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6558–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Tian, W.N.; Zhuang, M.M.; Shang, H.Y.; Gong, Z.Y.; Li, J.R. Green Radish Polysaccharides Ameliorate Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice via Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production and Gut Microbiota Regulation. Foods 2024, 13, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; Bleeker, A.; Gerding, A.; van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; van Dijk, T.H.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Protect Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity via a PPAR-Dependent Switch from Lipogenesis to Fat Oxidation. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; He, L.H.; Xu, L.J.; Li, S.B. Short-chain fatty acids: Bridges between diet, gut microbiota, and health. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Qiu, X.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Changes of Gut Microbiota and Its Correlation with Short Chain Fatty Acids and Bioamine in Piglets at the Early Growth Stage. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 617259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Aecal Digesta (μg/100 mg) | ND | OWM-HFD | P-HFD | Cur-H | P-Cur-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | 242.19 ± 1.95 a | 169.35 ± 4.34 d | 165.28 ± 3.88 d | 194.27 ± 3.95 c | 224.06 ± 4.60 b |
| Propanoic acid | 59.03 ± 1.92 a | 41.88 ± 1.89 d | 39.92 ± 1.88 d | 48.13 ± 2.57 c | 54.16 ± 1.80 b |
| Isobutyric acid | 6.76 ± 0.15 a | 5.49 ± 0.24 d | 5.40 ± 0.19 d | 6.11 ± 0.17 c | 6.44 ± 0.11 b |
| Butanoic acid | 50.45 ± 1.42 a | 41.86 ± 1.47 d | 40.61 ± 1.24 d | 45.66 ± 0.83 c | 48.86 ± 1.02 b |
| Isovaleric acid | 6.60 ± 0.23 a | 5.25 ± 0.18 d | 5.07 ± 0.15 d | 6.00 ± 0.10 c | 6.23 ± 0.12 b |
| Valeric acid | 8.27 ± 0.19 a | 7.36 ± 0.16d | 7.22 ± 0.13 d | 8.00 ± 0.10 c | 8.13 ± 0.06 ab |
| Isohexanoic acid | 1.47 ± 0.13 a | 0.79 ± 0.02 d | 0.66 ± 0.02 c | 1.09 ± 0.11 b | 1.17 ± 0.11 b |
| Hexanoic acid | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 c | 0.28 ± 0.01 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 a |
| Total SCFAs | 375.08 ± 1.00 a | 272.20 ± 1.39 b | 264.38 ± 1.25 c | 309.54 ± 1.31 d | 349.36 ± 1.31 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, L.; Wu, F.; Jiao, Y.; Ren, C.; Shu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Rao, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Anti-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Hepatic Steatosis Effects of Pickering Emulsion-Encapsulated Curcumin via Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulation in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234009
Niu L, Wu F, Jiao Y, Ren C, Shu Y, Liu Y, Zhao K, Rao W, Wang L, Zhang Z, et al. Anti-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Hepatic Steatosis Effects of Pickering Emulsion-Encapsulated Curcumin via Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulation in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Lisha, Fengyang Wu, Yingxue Jiao, Chi Ren, Ying Shu, Yi Liu, Kaixuan Zhao, Weili Rao, Liwen Wang, Zhisheng Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Anti-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Hepatic Steatosis Effects of Pickering Emulsion-Encapsulated Curcumin via Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulation in High-Fat-Diet Mice" Foods 14, no. 23: 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234009
APA StyleNiu, L., Wu, F., Jiao, Y., Ren, C., Shu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, K., Rao, W., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., & Qi, W. (2025). Anti-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Hepatic Steatosis Effects of Pickering Emulsion-Encapsulated Curcumin via Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Modulation in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods, 14(23), 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234009





