Molecular Evidence of Clonal Salmonella Enteritidis Persistence in Poultry Cold-Chain Environments Under Environmental Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. Primary Culture and Bacterial Enrichment
2.3. Selective and Differential Media Culturing
2.4. Bacterial Identification
2.5. Molecular Characterization
2.6. Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) Analysis
2.7. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Analysis
3. Results
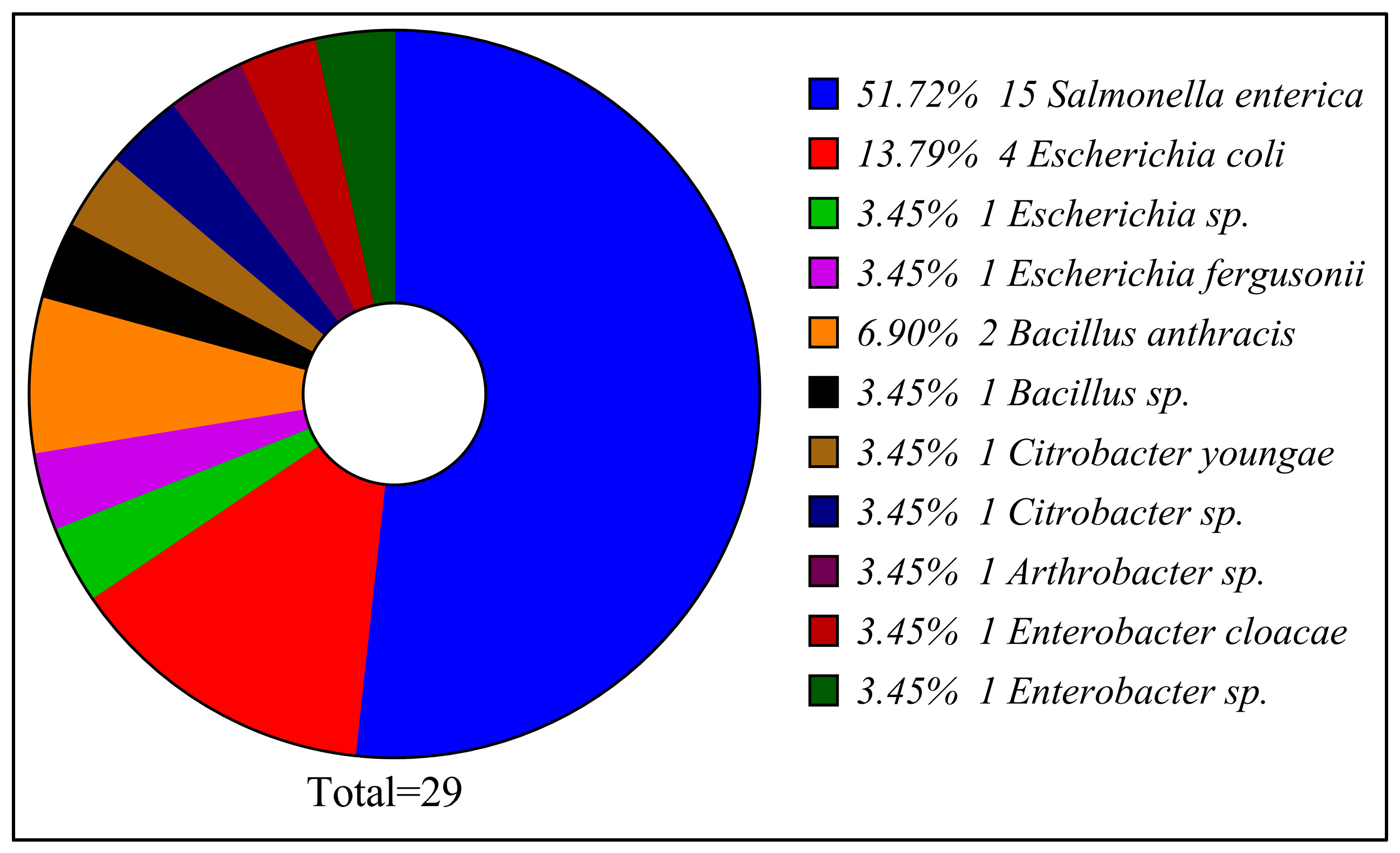
3.1. Bacterial Contamination of Poultry Refrigeration
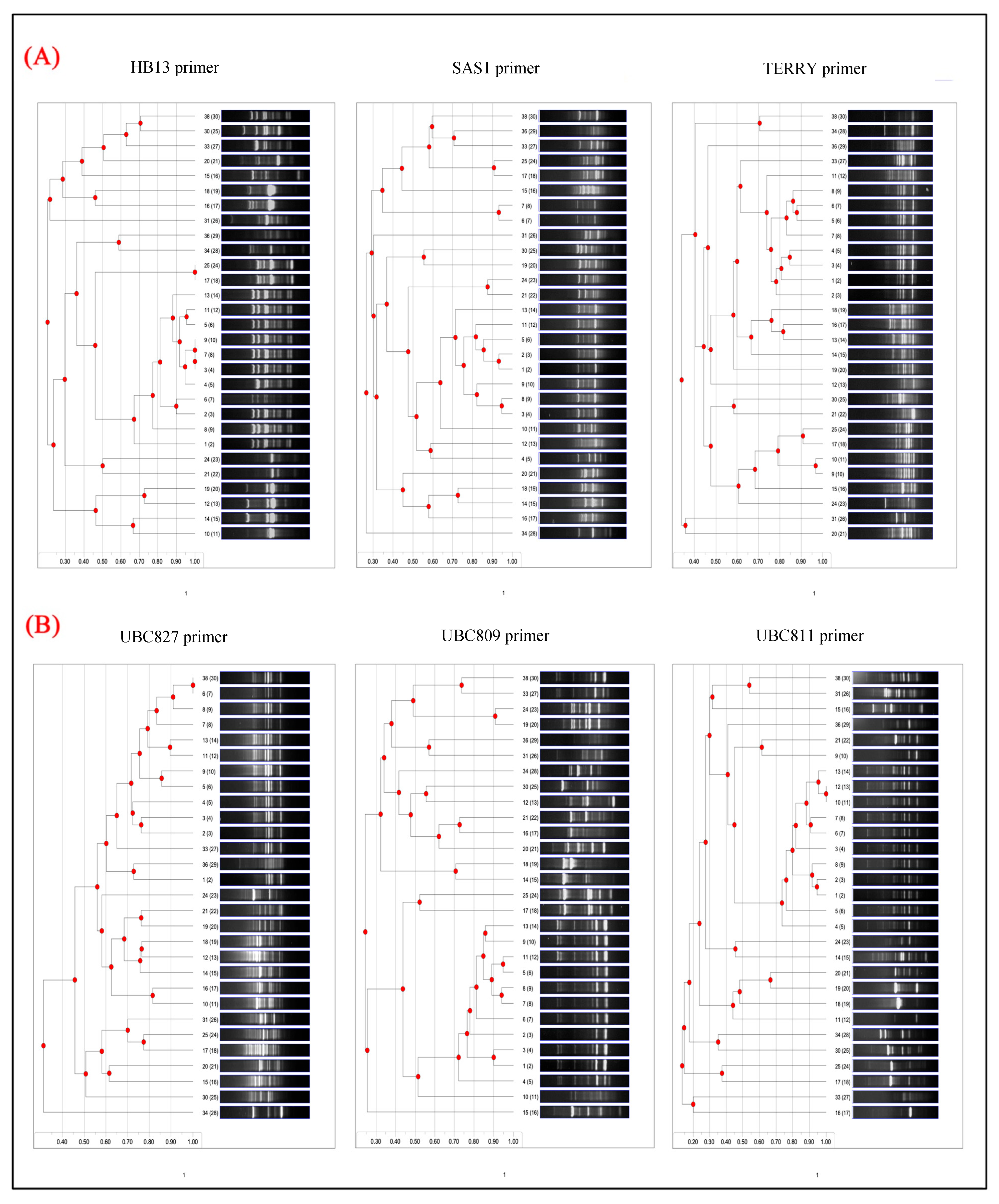
3.2. ISSR Investigation Between Isolates
Primer-Specific Amplification and Polymorphism Profiles
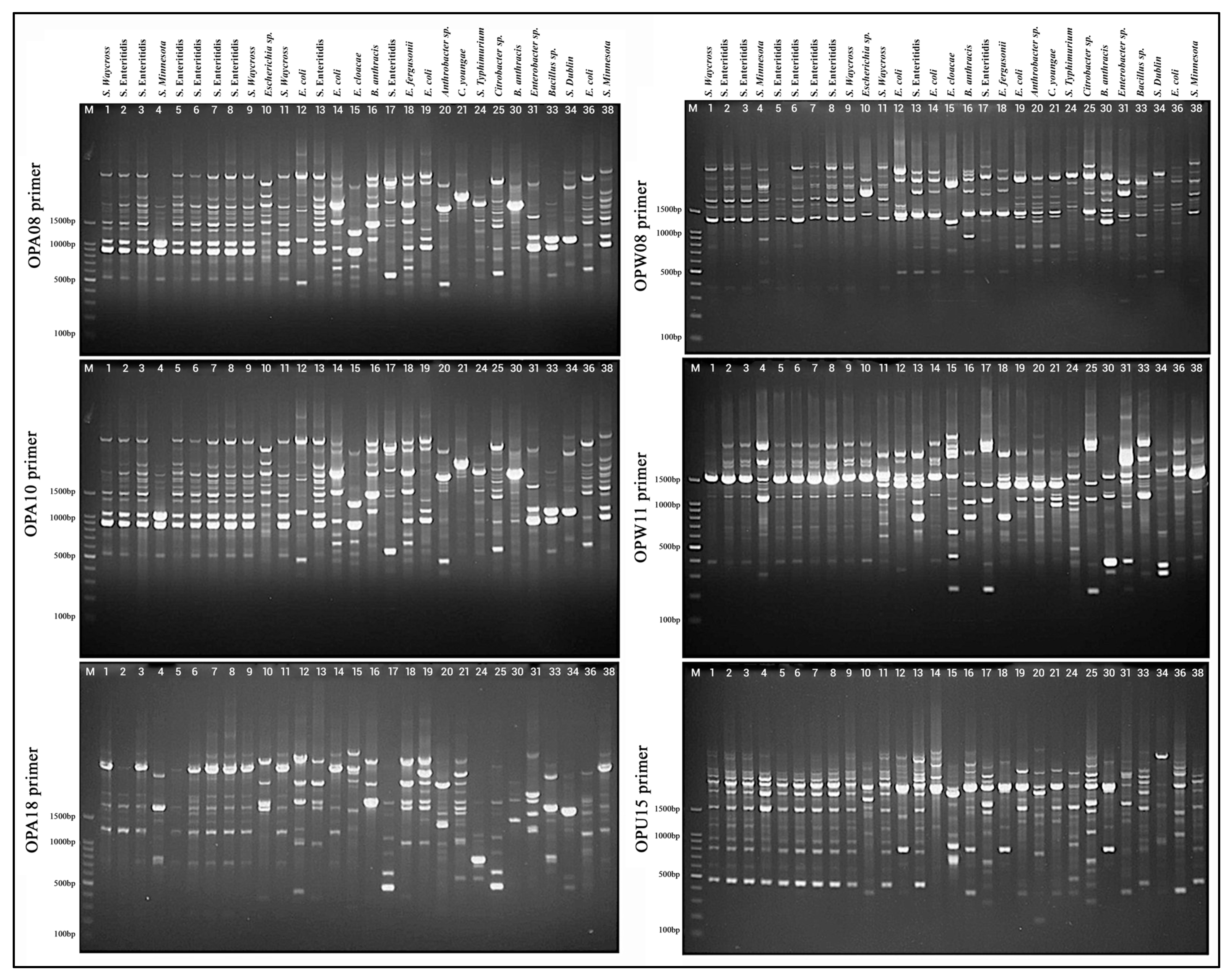
3.3. RAPD Investigation Between Isolates
3.3.1. RAPD-PCR Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
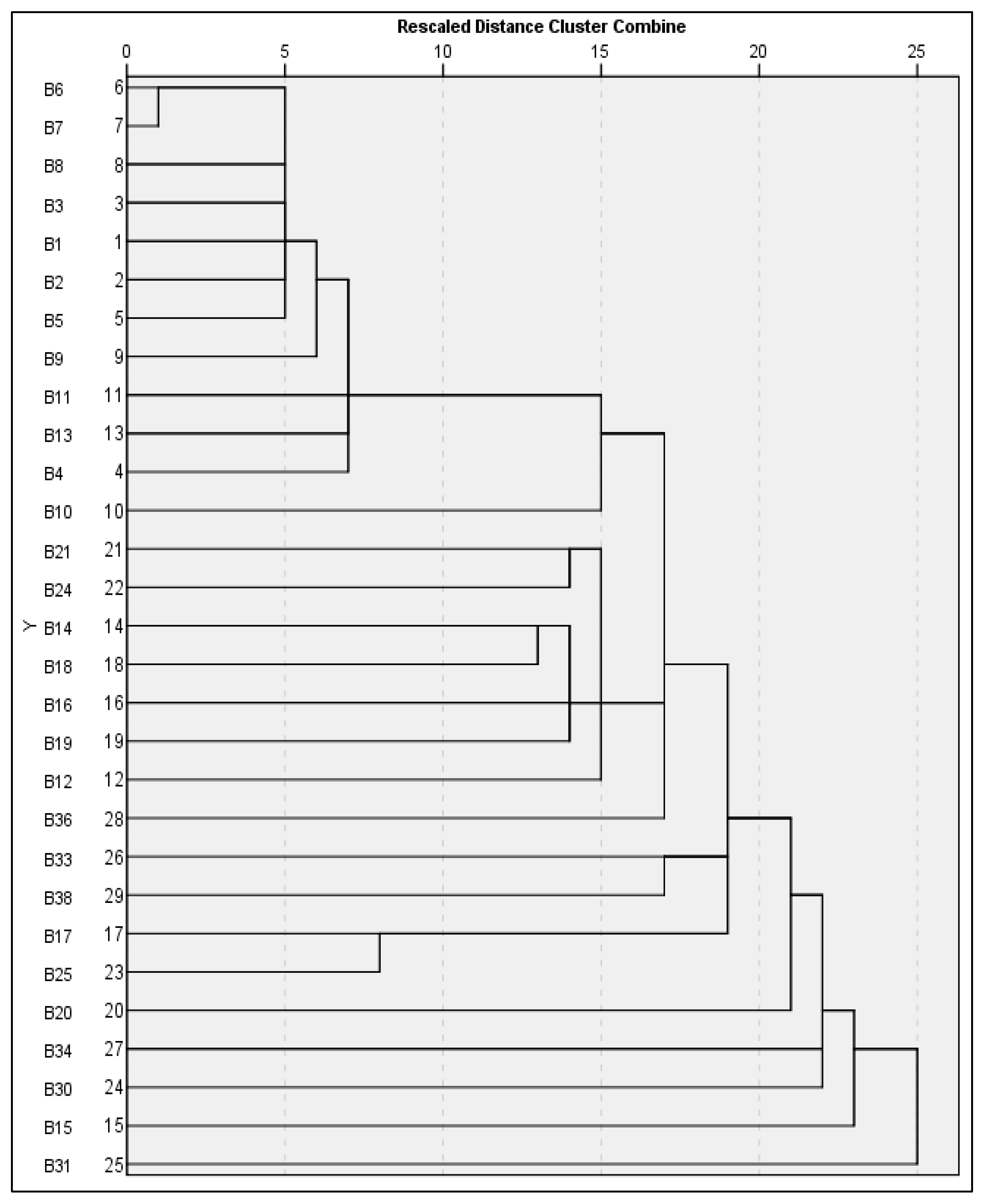
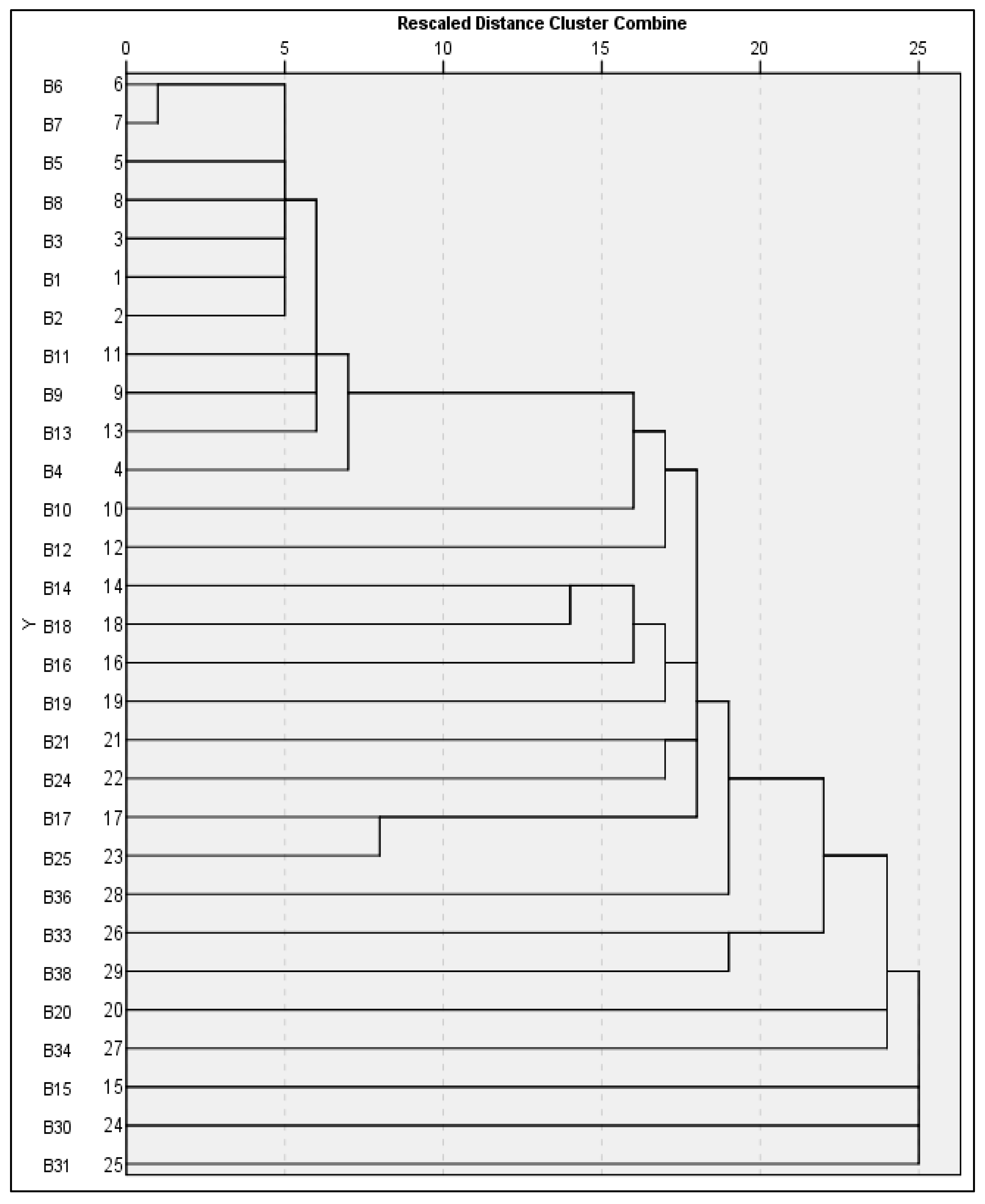
3.3.2. RAPD-Based Dendrogram Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mottet, A.; Tempio, G. Global poultry production: Current state and future outlook and challenges. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 73, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025–2034; OECD Publishing: Paris, France; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyn, F.; Ciacciariello, M. Future demands of the poultry industry: Will we meet our commitments sustainably in developed and developing economies? World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2021, 77, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, S.-M.; Dam, S.-M.; Truong, H.-D.; Le, D.-A.; Le, T.-A.D.; Nguyen, D.-V. Consumer’s Attitudes and Consumption Patterns of Meat Products, in Healthier Meat Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kathiravan, G.; Chitrambigai, K. Consumer preferences for native chicken meat in India: Implications for sustainable production and household dynamics. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2024, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiilholma, J. Food-safety concerns in the poultry sector of developing countries. In Poultry in the 21st Century, Proceedings of the International Poultry Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 5–7 November 2007; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2007; p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, H.M.; Attia, Y.A. Challenges to the Poultry Industry: Current Perspectives and Strategic Future After the COVID-19 Outbreak. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.H.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Mevo, S.I.U.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Current and future interventions for improving poultry health and poultry food safety and security: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1555–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouger, A.; Tresse, O.; Zagorec, M. Bacterial Contaminants of Poultry Meat: Sources, Species, and Dynamics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, K.; Singh, P.; Wani, A.A. Chapter 4—Safety of Meat and Poultry. In Regulating Safety of Traditional and Ethnic Foods; Prakash, V., Martín-Belloso, O., Keener, L., Astley, S., Braun, S., McMahon, H., Lelieveld, H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Vlad, S.T.; Bordei, S.I.; Magdalena, G.; Ianitchi, D.; Maftei, M.L.; Grigore, D.-M.; Moise, E.A.; Custura, I.; Tudorache, M. Factors Influencing the Quality of Chicken Meat: A Review. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 58, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Tashiguano, V. Assessing Spoilage Risks in Raw Chicken Breast: A Convergence Approach Using Microbiological Analysis, Volatile Profiling, Metagenomics, and Data Analytics for Microbial Growth and Shelf-Life Prediction. Master’s Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Donelan, A.K. Consumer Poultry Handling Behaviors. Doctoral Dissertation, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mafe, A.N.; Edo, G.I.; Makia, R.S.; Joshua, O.A.; Akpoghelie, P.O.; Gaaz, T.S.; Jikah, A.N.; Yousif, E.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A. A review on food spoilage mechanisms, food borne diseases and commercial aspects of food preservation and processing. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 5, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhana, D.K.; Haskito, A.E.P.; Purnama, M.T.E.; Safitri, D.A.; Annisa, S. Detection of microbial contamination in chicken meat from local markets in Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia. Vet. World 2021, 14, 3138–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaharn, K.; Pichpol, D.; Meeyam, T.; Harintharanon, T.; Lohaanukul, P.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Bacterial contamination of chicken meat in slaughterhouses and the associated risk factors: A nationwide study in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risalvato, J.; Sewid, A.H.; Eda, S.; Gerhold, R.W.; Wu, J.J. Strategic Detection of Escherichia coli in the Poultry Industry: Food Safety Challenges, One Health Approaches, and Advances in Biosensor Technologies. Biosensors 2025, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasijević, I.; Lakićević, B.; Petrović, Z. Cold chain management in meat storage, distribution and retail: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- James, S. Refrigeration and the Safety of Poultry Meat. Food Safety Control in the Poultry Industry; CPC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- López-Gómez, A.; Castano-Villar, A.M.; Palop, A.; Marín-Iniesta, F. Hygienic design and microbial control of refrigeration and air conditioning systems for food processing and packaging plants. Food Eng. Rev. 2013, 5, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A. Antimicrobial resistance: A growing serious threat for global public health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifedinezi, O.V.; Nnaji, N.D.; Anumudu, C.K.; Ekwueme, C.T.; Uhegwu, C.C.; Ihenetu, F.C.; Obioha, P.; Simon, B.O.; Ezechukwu, P.S.; Onyeaka, H. Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications for Food Safety and Public Health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endale, H.; Mathewos, M.; Abdeta, D. Potential Causes of Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance and Preventive Measures in One Health Perspective-A Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7515–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmigid, H.M. Efficiency of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) markers for genotype fingerprinting and genetic diversity studies in canola. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6409–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, W.A.; Techen, N.; Elsayed, K.N.M.; Essawy, E.A.; Tawfik, E.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Abdelhameed, M.S.; Hammouda, O.; Ross, S.A. Applying an internal transcribed spacer as a single molecular marker to differentiate between Tetraselmis and Chlorella species. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1228869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayar, J.K.; Arif, M.; Singh, U.S. Relative efficiency of RAPD and ISSR markers in assessment of DNA polymorphism and genetic diversity among Pseudomonas strains. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.S.; ul Haq, S.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S. RAPD and ISSR marker assessment of genetic diversity in Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: A unique source of germplasm highly adapted to drought and high-temperature stress. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghaith, T.; Almoteiry, K.; Alamri, A.; Alluhidan, M.; Alharf, A.; Al-Hammad, B.; Aliafali, I.; Seiter, A.; Pisani, E.; Herbst, C.H. Strengthening the Pharmaceutical System in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Towards a Medicine Policy to Support Vision 2030; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, L.J.; Noble-Wang, J.; Arduino, M.J. Surface sampling. In Manual of Environmental Microbiology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Chapter 2.6.2. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.J.; Graf, E.H. Sample Selection, Preservation, Transport, and Storage. In Manual of Molecular Microbiology: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, E.; Al-Ghamd, M.; Alsubaie, A.; Fadlelmula, A. The effect of seasonal variation on the hygienic standard of beef carcasses in Al Baha region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2013, 4, 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, E.J.O.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Smah, A.C.; Faith, E.O. Emerging Infectious Food System Related Zoonotic Foodborne Disease–A Threat to Global Food Safety and Nutrition Security, in Foodborne Pathogens-Recent Advances in Control and Detection; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, E.; Gugsa, G.; Ahmed, M. Review on Major Food-Borne Zoonotic Bacterial Pathogens. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 2020, 4674235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesewu, G.; Quaynor, E.; Olu-Taiwo, M.; Anim-Baidoo, I.; Asmah, R. Bacterial contaminants of raw broiler meat sold at Korle-Gonno, Accra, Ghana. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.B.; Seo, K.W.; Jeon, H.Y.; Lim, S.K.; Lee, Y.J. Characteristics of the antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from chicken meat produced by different integrated broiler operations in Korea. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savariraj, W.R.; Ravindran, N.B.; Kannan, P.; Rao, V.A. Occurrence and enterotoxin gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from retail chicken meat. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2021, 27, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Tiburzi, M.; Salsi, M.; Moguilevsky, M.; Pirovani, M. Survival of Salmonella on refrigerated chicken carcasses and subsequent transfer to cutting board. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smadi, H.; Sargeant, J.M.; Shannon, H.S.; Raina, P. Growth and inactivation of Salmonella at low refrigerated storage temperatures and thermal inactivation on raw chicken meat and laboratory media: Mixed effect meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2012, 2, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.L.d.; Vieira, B.S.; Carvalho, F.T.; Carvalho, R.C.T.; Figueiredo, E.E.d.S. Salmonella Behavior in Meat during Cool Storage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals 2022, 12, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, F.A.; Mohamed, H.A.; Munir, M.; Al Otaibi, M.M.; Kamel, S.M.; Alsaif, O.M.; Alqahtani, A.A.; AlDabal, M.A. Comprehensive risk assessment and control measures in the food service chain of hospitals nutrition department: A case study in Al-Ahsa Governorate, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1551446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M. Escherichia coli (E. coli) as an Indicator of Fecal Contamination in Water: A Review. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, A. ISSR Marker Based Linkage Mapping of Salinity Tolerance Using a Segregating Population in Rice; Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University: Haryana, India, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tarinejad, A.; Sofalian, O.; Valizadeh, R.; Shams, K. Efficiency of anchored and non-anchored ISSR markers to estimate genetic diversity among bread wheat cultivars. Iran. J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2015, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbrunner, N.J.; Gupta, A.P.; Young, K.K.; Will, S.G. Covalent modification of primers improves PCR amplification specificity and yield. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2017, 2, bpx011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, H.K. Assessment of genetic diversity in Lepidium sativum L. using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) marker. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2019, 25, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mint Abdelaziz, S.; Medraoui, L.; Alami, M.; Pakhrou, O.; Makkaoui, M.; Ould Mohamed Salem Boukhary, A.; Filali-Maltouf, A. Inter simple sequence repeat markers to assess genetic diversity of the desert date (Balanites aegyptiaca Del.) for Sahelian ecosystem restoration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, L.; Khan, M.A.; Zhu, F. Popular molecular markers in bacteria. Mol. Gen. Mikrobiol. Virusol. 2012, 27, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, V.P.; de Carli, S.; Lehmann, F.K.M.; Lunge, V.R.; Sobral, F.d.O.S.; Ikuta, N. Avaliação do duplex PCR em tempo real iss/iutA na identificação de Escherichia coli patogênica das Aves (APEC). In XIX Salão de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica; 2013; Available online: http://www.conferencias.ulbra.br/index.php/sic/xix/paper/view/1965 (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Simpson, S. Species Identification of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolates from Raw Poultry Products by MALDI-TOF MS and rRNA Sequence Analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, C.; Hess, M. Detection and identification of food-borne pathogens of the genera Campylobacter, Arcobacter and Helicobacter by multiplex PCR in poultry and poultry products. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Z.; Feng, S.-G.; Lu, J.-J.; Shi, N.-N.; Liu, J.-J. Phylogenetic study and molecular identification of 31 Dendrobium species using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F.; Huda, N.; Ali, G.R. Molecular techniques for detecting and typing of bacteria, advantages and application to foodborne pathogens isolated from ducks. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, T.O.; Lafta, I.J.; Ahmed, E.A.; Jassam, S.A. Application of RAPD-PCR and phylogenetic analysis for accurate characterization of Salmonella spp. isolated from chicken and their feed and drinking water. Iraqi J. Vet. Med. 2023, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, S.S.; Gaurav, A.; Joseph, B.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, N. Random amplified polymorphic DNA-based molecular heterogeneity analysis of Salmonella enterica isolates from foods of animal origin. Vet. World 2019, 12, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, J.; Rapp, D.; Dhawan, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Gupta, T.B.; Brightwell, G. Molecular detection and characterization of foodborne bacteria: Recent progresses and remaining challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 2433–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No. | Name of Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HB13 | GAGGAGGAGGC |
| 2 | SAS1 | GTGGTGGTGGTGGC |
| 3 | TERRY | GTGGTGGTGGGTGRC |
| 4 | UBC827 | ACACACACACACACACG |
| 5 | UBC809 | AGAGAGAGAGAG AGAGG |
| 6 | UBC811 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAC |
| No. | Name of Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | OPA-08 | GTGACGTAGG |
| 2 | OPA-10 | GTGATCGCAG |
| 3 | OPA-18 | AGGTGACCGT |
| 4 | OPW-08 | GACTGCCTCT |
| 5 | OPW-11 | CTGATGCGTG |
| 6 | OPU-15 | ACGGGCCAGT |
| Number on the Gel | Supermarket ID | Closest Bacterial Strain from NCBI Blast | NCBI Submitted Accession Number | Ident. % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Waycross | PX021782 | 95.95 |
| 2 | 3 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021784 | 97.04 |
| 3 | 4 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021779 | 96.47 |
| 4 | 5 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Minnesota | PX021775 | 100 |
| 5 | 7 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021772 | 91.42 |
| 6 | 10 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021787 | 91.97 |
| 7 | 17 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021776 | 97.81 |
| 8 | 20 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021774 | 95.99 |
| 9 | 27 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Waycross | PX021786 | 96.76 |
| 10 | 29 | Escherichia sp. | PX021773 | 99.91 |
| 11 | 30 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Waycross | PX021767 | 96.99 |
| 12 | 35 | E. coli | PX021785 | 100 |
| 13 | 40 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021792 | 96.38 |
| 14 | 41 | Escherichia coli | PX021788 | 99.72 |
| 15 | 51 | Enterobacter cloacae | PX021790 | 100 |
| 16 | 55 | Bacillus anthracis | PX021791 | 99.47 |
| 17 | 59 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis | PX021777 | 100 |
| 18 | 63 | Escherichia fergusonii | PX021771 | 99.82 |
| 19 | 69 | E. coli | PX021770 | 99.56 |
| 20 | 72 | Arthrobacter sp. | PX021768 | 99.91 |
| 21 | 78 | Citrobacter youngae | PX021778 | 99.64 |
| 24 | 84 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium | PX021765 | 92.52 |
| 25 | 89 | Citrobacter sp. | PX021793 | 99.47 |
| 30 | 99 | Bacillus anthracis | PX021783 | 97.77 |
| 31 | 113 | Enterobacter sp. | PX021781 | 100 |
| 33 | 119 | Bacillus sp. | PX021780 | 96.51 |
| 34 | 120 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Dublin | PX021766 | 95.78 |
| 36 | 133 | E. coli | PX021769 | 99.29 |
| 38 | 142 | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Minnesota | PX021789 | 99.64 |
| Primer | Total Bands | Polymorphic Bands | Polymorphism % |
|---|---|---|---|
| UBC827 | 22 | 20 | 90.9% |
| UBC809 | 19 | 17 | 89.5% |
| SAS1 | 18 | 16 | 88.9% |
| UBC811 | 17 | 15 | 88.2% |
| HB13 | 15 | 13 | 86.7% |
| TERRY | 12 | 8 | 66.7% |
| OPW-08 | 20 | 17 | 85.0% |
| OPU-15 | 13 | 11 | 84.6% |
| OPA-10 | 18 | 15 | 83.3% |
| OPW-11 | 17 | 14 | 82.4% |
| OPA-08 | 16 | 13 | 81.2% |
| OPA-18 | 14 | 10 | 71.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazi, K.S.; Alshehri, W.A.; Alkhammash, A.M.; Alqadri, N.; Bahwerth, F.S.; Baty, R.S.; Albakri, N.N.; Khalel, A.F.; Alpakistany, T.A.; Melebari, M. Molecular Evidence of Clonal Salmonella Enteritidis Persistence in Poultry Cold-Chain Environments Under Environmental Stress. Foods 2025, 14, 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223943
Gazi KS, Alshehri WA, Alkhammash AM, Alqadri N, Bahwerth FS, Baty RS, Albakri NN, Khalel AF, Alpakistany TA, Melebari M. Molecular Evidence of Clonal Salmonella Enteritidis Persistence in Poultry Cold-Chain Environments Under Environmental Stress. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223943
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazi, Khaled S., Wafa A. Alshehri, Alhanouf M. Alkhammash, Nada Alqadri, Fayez Saeed Bahwerth, Roua S. Baty, Nahlah N. Albakri, Ashjan F. Khalel, Tariq Abdulmutaleb Alpakistany, and Mohammad Melebari. 2025. "Molecular Evidence of Clonal Salmonella Enteritidis Persistence in Poultry Cold-Chain Environments Under Environmental Stress" Foods 14, no. 22: 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223943
APA StyleGazi, K. S., Alshehri, W. A., Alkhammash, A. M., Alqadri, N., Bahwerth, F. S., Baty, R. S., Albakri, N. N., Khalel, A. F., Alpakistany, T. A., & Melebari, M. (2025). Molecular Evidence of Clonal Salmonella Enteritidis Persistence in Poultry Cold-Chain Environments Under Environmental Stress. Foods, 14(22), 3943. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223943





