Extraction and Functional Properties of Crude Prolamin from Amaranth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Pre-Treatment
2.2. Extraction of Amaranth Crude Prolamin (ACP)
2.3. Structural Characterization
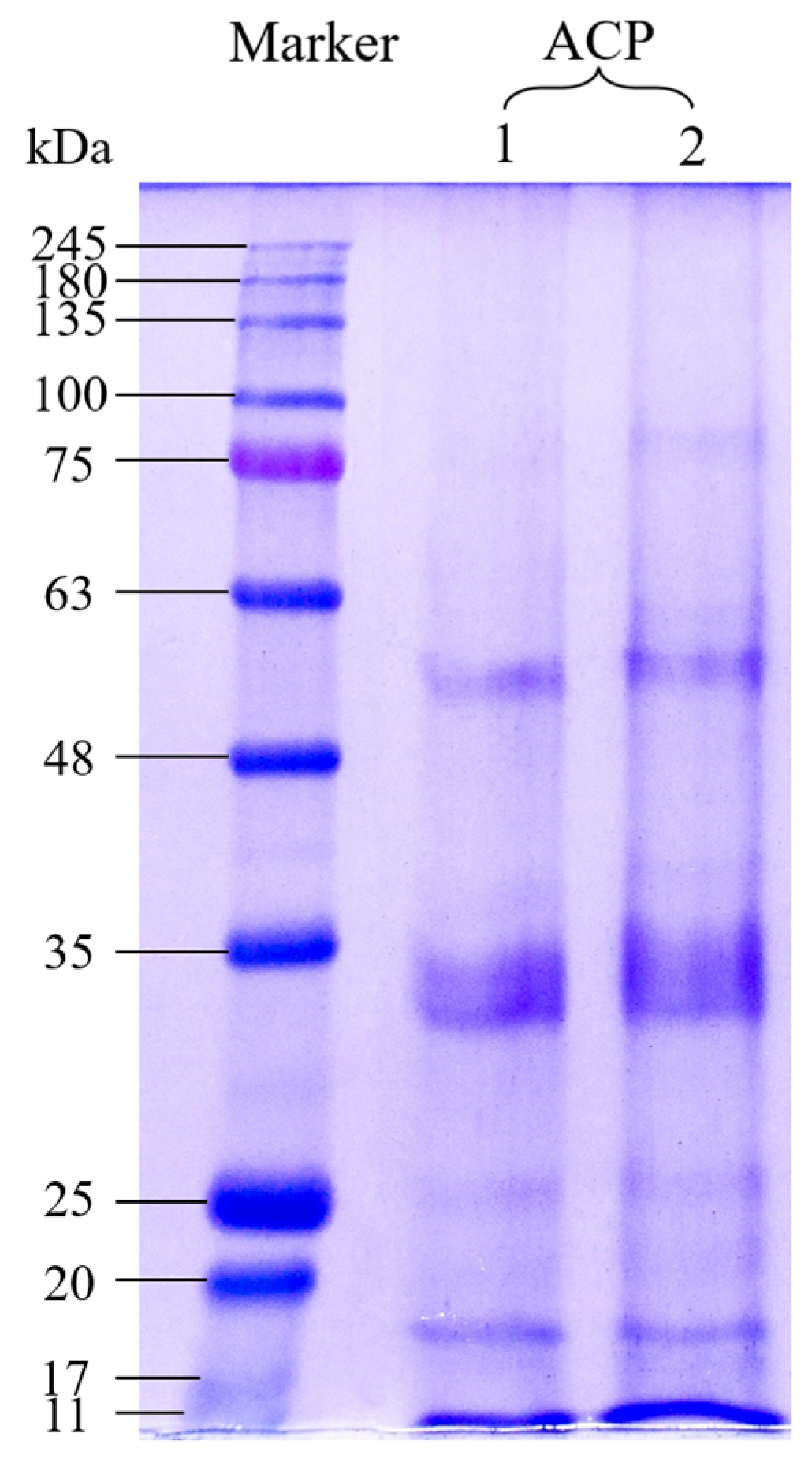
2.3.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
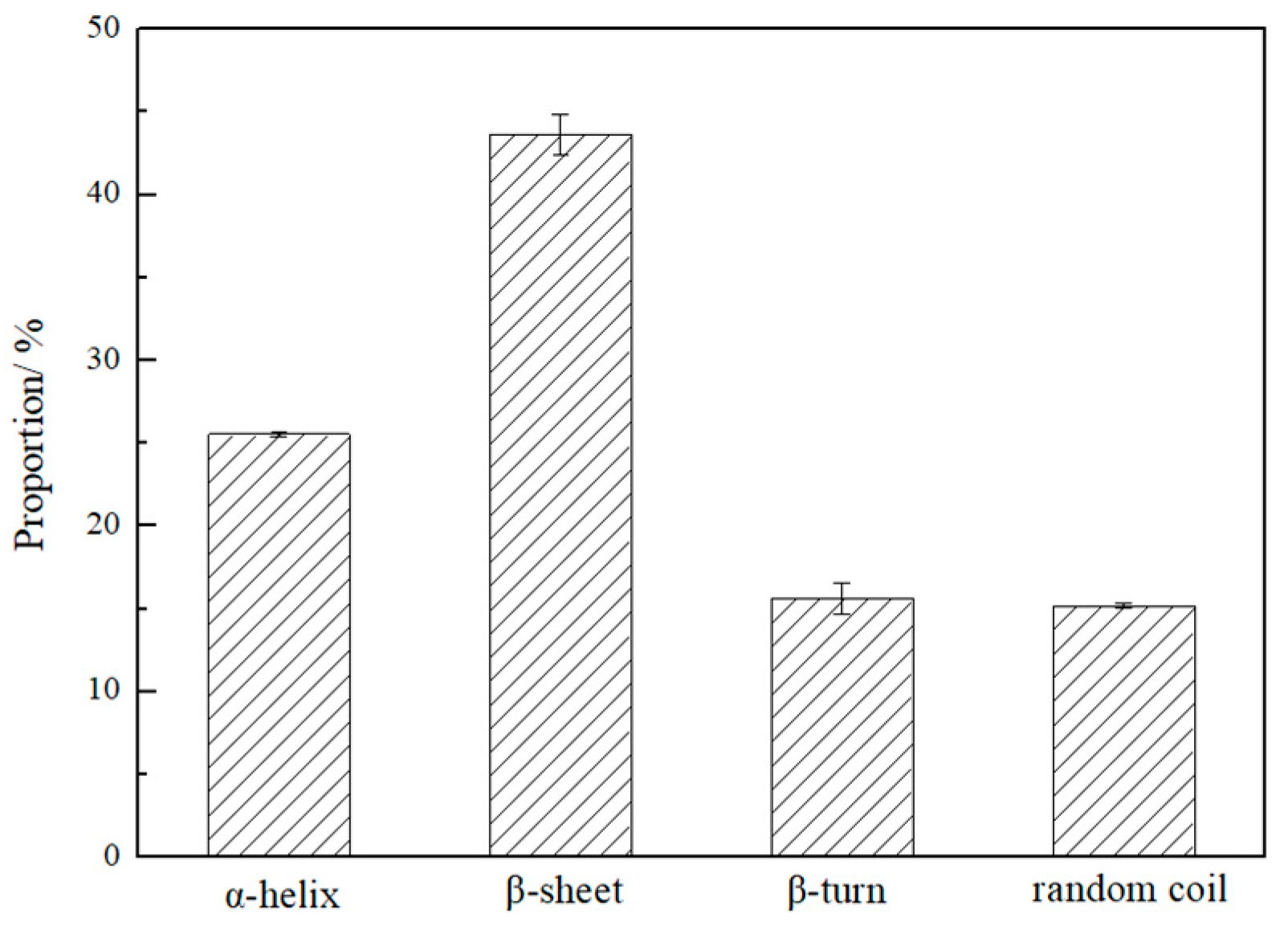
2.3.2. FTIR and Protein Secondary Structure
2.3.3. Sulfhydryl Group Content
2.3.4. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.3.5. Particle Size Distribution and ζ-Potential
2.4. Functional Properties of ACP
2.4.1. Water- and Oil-Holding Capacity
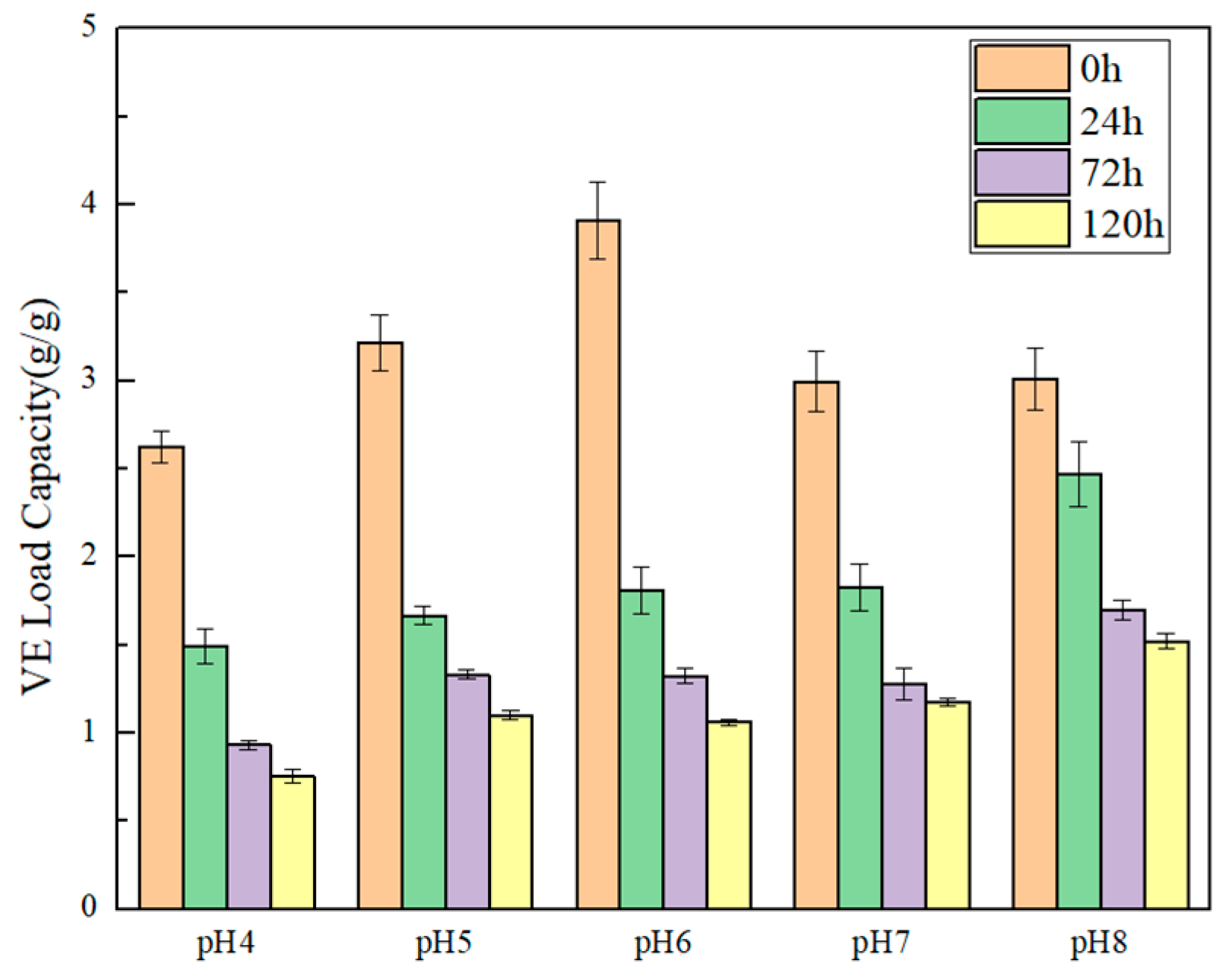
2.4.2. Emulsifying Capacity for Vitamin E
2.5. Morphological Properties
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of ACP Extraction
3.2. SDS-PAGE
3.3. Secondary Structure
3.4. Sulfhydryl Content and WCA Analysis
3.5. Particle Size and ζ-Potential Analysis
3.6. Oil- and Water-Holding Capacity
3.7. Emulsifying Capacity and Storage Stability
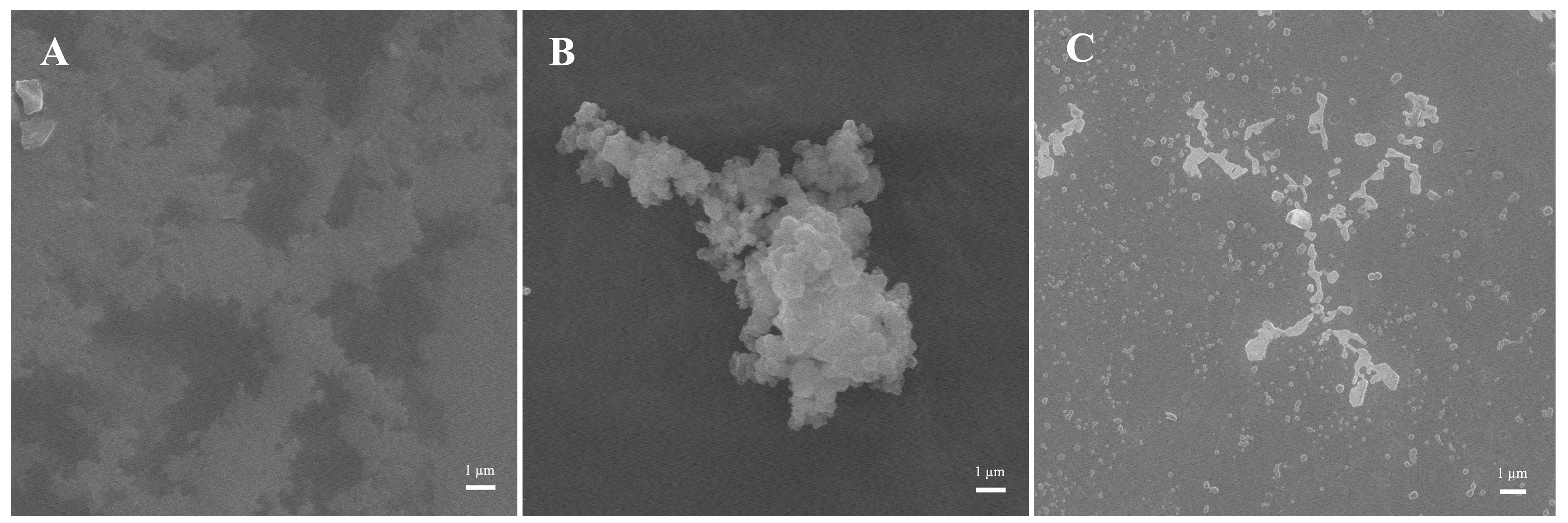
3.8. Microscopic Morphology Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamel, T.H.; Linssen, J.P.; Mesallam, A.S.; Damir, A.A.; Shekib, L.A. Effect of seed treatments on the chemical composition of two amaranth species: Oil, sugars, fibres, minerals and vitamins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Suryadi, E.; Ruswandi, D. Chemical Composition and Genetics of Indonesian Maize Hybrids. Am. J. Food Technol. 2017, 12, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palavecino, P.M.; Penci, M.C.; Calderón-Dominguez, G.; Ribotta, P.D. Chemical composition and physical properties of sorghum flour prepared from different sorghum hybrids grown in Argentina. Starch-Starke 2016, 68, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, M.; Gresta, F.; Costale, A.; Lo Presti, V.; Meineri, G.; Chiofalo, B. Amaranthus (hypochondriacus L.) as a Sustainable Source of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds for Animal Feeding. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.N.; Galante, M.; Robson, M.; Boeris, V.; Spelzini, D. Amaranth, quinoa and chia protein isolates: Physicochemical and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Peñas, E.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Pseudocereal grains: Nutritional value, health benefits and current applications for the development of gluten-free foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 137, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, A.B.T.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Modifications of physicochemical and functional properties of amaranth protein isolate (BRS Alegria) treated with high-intensity ultrasound. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorinstein, S.; Pawelzik, E.; Delgado-Licon, E.; Yamamoto, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Taniguchi, H.; Haruenkit, R.; Park, Y.S.; Jung, S.T.; Drzewiecki, J.; et al. Use of scanning electron microscopy to indicate the similarities and differences in pseudocereal and cereal proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyiam, P.N.; Tangjaidee, P.; Zhang, W.; Rawdkuen, S. A comparative study on novel-assisted extraction techniques for retrieving protein from Moringa oleifera seeds. Foods 2025, 14, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Khaksar, F.B.; Pagan, J.; Ibarz, A. Application of Ultrasound-Ultrafiltration-Assisted alkaline isoelectric precipitation (UUAAIP) technique for producing alfalfa protein isolate for human consumption: Optimization, comparison, physicochemical, and functional properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.R.; Zhang, W.X.; Yan, D.G.; Ma, L.X.; Ma, H.L. Solubility and aggregation of soy protein isolate induced by different ionic liquids with the assistance of ultrasound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, D.; Rohm, H.; Struck, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Protein from Pumpkin Seed Press Cake: Impact on Protein Yield and Techno-Functionality. Foods 2022, 11, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Karabulut, G.; Mundada, V.; Feng, H. Non-thermal ultrasonic contact drying of pea protein isolate suspensions: Effects on physicochemical and functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.F.; He, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Cao, X.D.; Ye, Y.K.; Sun, H.J. Comparison of crude prolamins from seven kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) based on composition, structure and functionality. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhiwa, P.J.; Taylor, J.; Taylor, J.R.N. Extraction and Film Properties of Kafirin from Coarse Sorghum and Sorghum DDGS by Percolation. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.L.; Orellana-Palacios, J.C.; Garcia, S.R.; Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Moreno, A.; Hadidi, M. Olive leaf protein: Extraction optimization, digestibility, structural and techno-functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Ehmke, L.; Sharma, C.; Miller, R.; Faa, P.; Smith, G.; Li, Y.H. Physicochemical properties and gluten structures of hard wheat flour doughs as affected by salt. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Kokini, J.L.; Huang, Q.R. Engineering Zein Films with Controlled Surface Morphology and Hydrophilicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.N.; Zhou, Y.H.; Song, B.; Wu, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, C.B.; Liu, J.S. Effect of Microwave Intermittent Drying on the Structural and Functional Properties of Zein in Corn Kernels. Foods 2024, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Tang, X.; Li, Y.H. Drying methods affect physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa protein isolate. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.C. Formation of Vitamin E Emulsion Stabilized by Octenylsuccinic Starch: Factors Affecting Particle Size and Oil Load. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C680–C686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Qiu, D.; He, L. Comparison of Prolamins From Different Cereals Based on Structure and Functionality. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 120, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojórquez-Velázquez, E.; Talamantes-Herrera, F.A.; Valles, S.; Cerritos-Castro, I.T.; de la Rosa, A.P.B. Molecular Characterisation of Seed Storage Proteins (SSPs) in Grain Amaranth. In The Amaranth Genome; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 55–79. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, F.; Pauly, A.; Rombouts, I.; Jansens, K.J.A.; Deleu, L.J.; Delcour, J.A. Proteins of Amaranth (Amaranthus spp.), Buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp.), and Quinoa (Chenopodium spp.): A Food Science and Technology Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Lopez, N.E.; Vasco, N.; Barba de la Rosa, A.P.; Paredes-Lopez, O. Amaranth seed proteins: Effect of defatting on extraction yield and on electrophoretic patterns. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1995, 47, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, Q.R. Physicochemical properties of kafirin protein and its applications as building blocks of functional delivery systems. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.K.; Xu, J.Z.; Yu, Y.S.; Wang, D.P.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Xu, X.X. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on the structural and functional properties of proteins in housefly larvae (Musca demestica). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 101, 106673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Hernandez, J.A.; Rodriguez-Felix, F.; Juarez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Robles-Garcia, M.A.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Castro-Enriquez, D.D.; Del-Toro-Sanchez, C.L. Zein-polysaccharide nanoparticles as matrices for antioxidant compounds: A strategy for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, J.; Pojic, M.; Torbica, A.; Rakita, S.; Zivancev, D.; Hajnal, E.J.; Hadnadev, T.D.; Hadnadev, M. Changes in the content of free sulphydryl groups during postharvest wheat and flour maturation and their influence on technological quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Zhang, S.; Bai, L.; Tang, H.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Meng, W.H.; Zhang, D.J. Flexible processing technology of coix seed prolamins by combined heat-ultrasound: Effects on their enzymatic hydrolysis characteristics and the hypoglycemic activities of derived peptides. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, S.; Liu, F.; Khin, M.N.; Yokoyama, W.H.; Zhong, F. Improvement of the water resistance and ductility of gelatin film by zein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, O.; Shin, M. Preparation and stability of resistant starch nanoparticles, using acid hydrolysis and cross-linking of waxy rice starch. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbour, M.; Jiang, H.; Mintah, B.K.; Wahia, H.; He, R.H. Ultrasonic-assisted protein extraction from sunflower meal: Kinetic modeling, functional, and structural traits. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Shen, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Schilling, M.W.; Li, Y.H. Parallel comparison of functional and physicochemical properties of common pulse proteins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.R.; Sun, C.X.; Gul, K.; Mata, A.; Fang, Y.P. Prolamin-based complexes: Structure design and food-related applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1120–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.M.; Huang, S.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Shi, W.Z.; Wang, X.C.; Zhong, J. Effects of antioxidant types on the stabilization and in vitro digestion behaviors of silver carp scale gelatin-stabilized fish oil-loaded emulsions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, B.G.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Foaming Properties of Wheat Gliadin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fan, F.J.; Chen, H.; Ma, W.C.; Du, M. Effects of high pressure homogenize treatment on the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of proteins from scallop (Chlamys farreri). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.Z.; Wu, X.C.; Li, M.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, F.; Yan, X.F.; Wang, J.L.; Li, C.X.; Brennan, C. Hydrophobicity-modulating self-assembled morphologies of α-zein in aqueous ethanol. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Xie, Q.H.; Chao, T.Y.; Cui, L.; Wang, P.; Yu, Y.Y.; Wang, Q. Construction of rough surface based on zein and rosin to hydrophobically functionalize cotton fabric with antibacterial activity. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 184, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | ACP | Zein |
|---|---|---|
| SHfree (μmol/g) | 19.51 ± 0.27 | 6.2 ± 0.19 |
| WCA (°) | 77.11 ± 0.21 | 53.91 ± 0.24 |
| ζ-potential (mV) | 18.92 ± 1.08 | 6.40 ± 0.58 |
| OHC (g/g) | 6.34 ± 0.11 | 8.63 ± 0.20 |
| WHC (g/g) | 7.45 ± 0.32 | 2.21 ± 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, L. Extraction and Functional Properties of Crude Prolamin from Amaranth. Foods 2025, 14, 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223926
Dong Y, Hu X, Wang Y, He L. Extraction and Functional Properties of Crude Prolamin from Amaranth. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223926
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yujun, Xiaojun Hu, Yajuan Wang, and Li He. 2025. "Extraction and Functional Properties of Crude Prolamin from Amaranth" Foods 14, no. 22: 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223926
APA StyleDong, Y., Hu, X., Wang, Y., & He, L. (2025). Extraction and Functional Properties of Crude Prolamin from Amaranth. Foods, 14(22), 3926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223926





