Advances of MXene in Detection and Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. MXene Applied in Foodborne Pathogen Detection
| Material-Based Substrate | Target Bacteria | Limit of Detection (LOD) (CFU/mL) | Linear Detection Range (CFU/mL) | Recovery (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) (%) | R2 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG@MXene | S. Typhimurium | 160 | 1.6 × 102–1.6 × 107 | 100.46–106.37 | 4.56–7.28 | 0.99 | [37] |
| MXene-Hemin-Au@mAb-based biosensor | L. monocytogenes | 23 | 10–106 | 91.19–102.98 | - | 0.991 | [54] |
| PDA@ZnMoO4/MXen | L. monocytogenes | 12 | 10–107 | 98–126 | 1.63–5.85 | 0.991 | [55] |
| DNAzyme-Fc-MXene@AuNBPs | V. parahaemolyticus | 6 | 10–108 | 94.0–106.0 | 4.26–8.51 | 0.995 | [56] |
| LAP-MXene@AuNPs-ssDNA MRS | V. parahaemolyticus | 10 | 102–108 | 97.4–103.2 | 1.8–5.6 | 0.998 | [57] |
| cDNA-POSS-PQDs | V. parahaemolyticus | 10 | 102–106 | 93–108 | 1.9–7.4 | 0.9981 | [58] |
| MXene/polypyrrole | Salmonella | 23 | 103–107 | 96–109.4 | 1.33–2.87 | - | [59] |
| Ag@TiO2/MXene | E. coli O157:H7 | 1 | 1–17 | - | - | - | [60] |
| MXene@MB | Salmonella | 5 | 2.4 × 101–2.4 × 107 | 98.3–102.2 | - | 0.9958 | [61] |
2.1. Application of MXene-Based Electrochemical Sensor in the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens
2.2. Application of MXene-Based SERS Substrate in the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens
2.3. Application of MXene-Based Fluorescence Platform for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens
2.4. Application of Mxene-Based Dual-Mode Sensing System in the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens
| Detection Method | Materials | Target Bacteria | Limit of Detection (LOD) (CFU/mL) | Linear Detection Range (CFU/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical detection | Ag@TiO2/MXene | E. coli O157:H7 | 1 | 1–17 | [60] |
| Electrochemical detection | MXene@MB | Salmonella | 5 | 2.4 × 101–2.4 × 107 | [61] |
| SERS | HfTe2-Au | Salmonella | 10 | [90] | |
| Fluorescence platform | GO-QD | L. monocytogenes | 100 | 102–106 | [91] |
| Chemiluminescence biosensing platform | HRP-Ab-CaHPO4 | Salmonella enteritidis | 10 | 10–105 | [92] |
| Electrochemical detection | rGO-CNT | S. Typhimurium | 10 | 10–108 | [93] |
| SERS | rGOPE/AuNPS | E. coli O157:H7 | 150 | 1.5 × 102–1.5 × 107 | [94] |
| Electrochemical detection | ssDNA-Au/CuMOF | S. aureus | 5 | 10–108 | [95] |
3. MXene Applied in Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens
3.1. Antibacterial Mechanism
3.1.1. Photothermal Effect
3.1.2. Chemical Antibacterial Action
3.1.3. Physical Barriers and Contact Killers
3.2. Application of MXene in Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens
3.2.1. Active Food Packaging Materials
3.2.2. Surface Modification of Food Processing Equipment
3.2.3. Immediate Sterilization Technology
4. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, B. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, T.; Andjelković, U.; Gajdošik, M.Š.; Rešetar, D.; Josić, D. Foodborne pathogens and their toxins. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladhadh, M. A Review of Modern Methods for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme, R.E.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Allard, M.W. Utilizing the Public GenomeTrakr Database for Foodborne Pathogen Traceback. In Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens: Methods and Protocols; Bridier, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Foddai, A.C.G.; Grant, I.R. Methods for detection of viable foodborne pathogens: Current state-of-art and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4281–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, W.; Ding, W.; Han, R.; Shen, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W. A multiplex PCR assay with a common primer for the detection of eleven foodborne pathogens. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiraz, M.P.; Majumdar, P.R.; Mahmud, M.M.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Ali, A. Conventional and advanced detection techniques of foodborne pathogens: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Microfluidic-Based Approaches for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.J.; An, H. Photothermal-Based Multiplex Nested Digital PCR System for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Micromachines 2024, 15, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Wei, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Enhanced sandwich immunoassay based on bivalent nanobody as an efficient immobilization approach for foodborne pathogens detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1289, 342209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Oh, S.-W. Combination of filtration and immunomagnetic separation based on real-time PCR to detect foodborne pathogens in fresh-cut apple. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 201, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, H.P.; Jaykus, L.-A. Detection of pathogens in foods: The current state-of-the-art and future directions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, B.; Patil, R.K.; Dwarakanath, S. A review on detection methods used for foodborne pathogens. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 144, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jeevanantham, S.; Kamalesh, R.; Sneha, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Methods of detection of food-borne pathogens: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Hoffmann, M.R. Rapid Detection Methods for Bacterial Pathogens in Ambient Waters at the Point of Sample Collection: A Brief Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, S84–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, J.; Mirhosseini, S.A.; Fooladi, A.A.I. A Review Approaches to Identify Enteric Bacterial Pathogens. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e17473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Bhardwaj, K.; Kaur, T.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K.; Kumar, V.; Bhatia, S.K.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Chopra, C.; Singh, R.; et al. Detection of Bacterial Pathogens and Antibiotic Residues in Chicken Meat: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Nie, X.; Fan, S.; Feng, M.; Fan, Z.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; He, G. Construction of atomically dispersed Cu-N4 sites via engineered coordination environment for high-efficient CO2 electroreduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Q.Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, T.Y.; Yan, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q.Z. Lychee-like plasmonic nanocomplex with programmable hierarchical structure: A high-performance SERS platform for monitoring diazepam in aquatic products. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Li, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, K.; Gao, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W. Dual-plasmonic metals functionalized MXene synergistic enhanced SERS biosensor for sensitive and selective detection of S. aureus in milk. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.-C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z. Recent advances in MXene: Preparation, properties, and applications. Front. Phys. 2015, 10, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Mashtalir, O.; Carle, J.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Carbides. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashtalir, O.; Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V.N.; Dall’Agnese, Y.; Heon, M.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Intercalation and delamination of layered carbides and carbonitrides. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V.N.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Gogotsi, Y. Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Materials by Selective Extraction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Ten Years of Progress in the Synthesis and Development of MXenes. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchi, R.M.; Arantes, J.T.; Santos, S.F. Synthesis, structure, properties and applications of MXenes: Current status and perspectives. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 18167–18188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwal, S.S.; Sheoran, K.; Mishra, K.; Kaur, H.; Saini, A.K.; Saini, V.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Nezhad, H.Y.; Thakur, V.K. Novel synthesis methods and applications of MXene-based nanomaterials (MBNs) for hazardous pollutants degradation: Future perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.R.G.; Shekhirev, M.; Wyatt, B.C.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Seh, Z.W. Fundamentals of MXene synthesis. Nat. Synth. 2022, 1, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, O.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Pant, K.K.; Joshi, R.K. Introduction to MXenes: Synthesis and characteristics. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 14, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhabeb, M.; Maleski, K.; Anasori, B.; Lelyukh, P.; Clark, L.; Sin, S.; Gogotsi, Y. Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7633–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Koo, S.; Obeng, E.; Sharma, A.; Shen, J.; Kim, J.S. Emerging 2D MXenes for antibacterial applications: Current status, challenges, and prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 492, 215275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Peng, J.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Y. Amorphous MXene Opens New Perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hui, Z.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, G.; Huang, W. Ti3C2TX MXene for Sensing Applications: Recent Progress, Design Principles, and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3996–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zou, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; et al. A CG@MXene nanocomposite-driven E-CRISPR biosensor for the rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in food. Talanta 2024, 266, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhen, X.; Feng, Q.; Gu, Y.; Yang, G.; Qu, L.; Zhu, J.-J. PEC-SERS Dual-Mode Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Based on Binding-Induced DNA Walker and C3N4/MXene-Au NPs Accelerator. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 14297–14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, K.; Helal, M.; Ali, A.; Ren, C.E.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Antibacterial Activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3674–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Covalent stabilization and functionalization of MXene via silylation reactions with improved surface properties. FlatChem 2019, 17, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, S.; Yu, S.; Johnson, H.M.; Chan, Y.K.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Y. MXene-Decorated Nanofibrous Membrane with Programmed Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects via Steering NF-κB Pathway for Infectious Cutaneous Regeneration. Small 2024, 20, 2304119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajavel, K.; Shen, S.Y.; Ke, T.; Lin, D.H. Achieving high bactericidal and antibiofouling activities of 2D titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) by delamination and intercalation. 2D Mater. 2019, 6, 035040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi Shamsabadi, A.; Sharifian Gh, M.; Anasori, B.; Soroush, M. Antimicrobial Mode-of-Action of Colloidal Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16586–16596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymaniha, M.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Rafieerad, A.R.; Maleki, A.; Amiri, A. Promoting Role of MXene Nanosheets in Biomedical Sciences: Therapeutic and Biosensing Innovations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Li, A.; Zhang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, D. Efficient visible-light-photocatalytic sterilization by novel Z-scheme MXene/TiO2/Bi2S3. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, T.S.; Maleski, K.; Goad, A.; Sarycheva, A.; Anayee, M.; Foucher, A.C.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Shuck, C.E.; Stach, E.A.; Gogotsi, Y. Modified MAX Phase Synthesis for Environmentally Stable and Highly Conductive Ti3C2 MXene. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6420–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayesteh Zeraati, A.; Mirkhani, S.A.; Sun, P.; Naguib, M.; Braun, P.V.; Sundararaj, U. Improved synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXenes resulting in exceptional electrical conductivity, high synthesis yield, and enhanced capacitance. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, K.; Kovářík, T.; Khadheer Pasha, S.K. State of the art recent progress in two dimensional MXenes based gas sensors and biosensors: A comprehensive review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 424, 213514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, D.; Dhinakaran, V.; Byun, H.-S. MXenes: An emerging 2D material. Carbon 2022, 192, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Huang, Q. MXenes: Two-Dimensional Building Blocks for Future Materials and Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5775–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Shang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. MXenes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications in Ultrafast Photonics. Small 2021, 17, 2006054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezen, S.; Zarepour, A.; Zarrabi, A.; Iravani, S. MXene-based biosensors for selective detection of pathogenic viruses and bacteria. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Fan, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H. POD-like nanozyme constructed from perspective of charge transfer engineering for biosensing of magnetic separation treated Listeria monocytogenes. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, N.; Sakthivel, R.; Karthik, C.S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Liu, X.; Wen, H.-W.; Yang, W.; Chung, R.-J. Polydopamine-modified 3D flower-like ZnMoO4 integrated MXene-based label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenes detection in milk and seafood. Talanta 2025, 282, 127008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Xiao, S.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Jia, Z.; Yu, Z.; Gan, N. Fluorescent/electrochemical dual-signal response biosensing strategy mediated by DNAzyme-ferrocene-triggered click chemistry for simultaneous rapid screening and quantitative detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Yang, F.; Shi, X.; Jiang, X.; Hao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z. Magnetic relaxation switch biosensor for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus based on photocleavable hydrogel. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1336, 343516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hong, J.; Wang, W.; Xiao, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Q.; Gan, N. Fluorescent aptasensor for detection of live foodborne pathogens based on multicolor perovskite-quantum-dot-encoded DNA probes and dual-stirring-bar-assisted signal amplification. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, O.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, M.; Wu, J. Rapid and simple preparation of an MXene/polypyrrole-based bacteria imprinted sensor for ultrasensitive Salmonella detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 918, 116513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobana, B.; Renugadevi, K.; Prakash, P. Transformative microbe (E. Coli O157:H7) detection: Advancing microbial surveillance in food matrices with a photosensor of silver doped titanium dioxide/MXene nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Wu, W.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Deng, C. An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of live Salmonella in food via MXene amplified methylene blue signals and electrostatic immobilization of bacteriophages. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Cao, K.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chai, C.; Dai, P. A novel electrochemical sensor for glucose detection based on a Ti3C2Tx/ZIF-67 nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 20138–20146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-L.; Deng, H.-M.; Cheng, M.-L.; Li, H.-L.; Yuan, R.; Wei, S.-P. A photoelectrochemical biosensor based on Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ag2S as a novel photoelectric material for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA-141. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 394, 134343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipour, M.; Ahmadipour, M.; Pal, U.; Satgunam, M. Recent advancement in MXene-based electrochemical biosensor for early cancer detection. Microchem. J. 2025, 216, 114765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, A.; Xue, J. Novel Ti3C2Tx MXene nanozyme with manageable catalytic activity and application to electrochemical biosensor. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zahid, S.; Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Farooq, N.; Rao, K.A.; Taj, M.B.; Manzoor, S.; Voskressensky, L.G.; Luque, R. Direct electron transfer chemistry of redox-active enzymes: Applications in biosensor development. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2025, 19, 963–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, S.A.; Palaniyandy, N.; Sigalas, I.; Iyuke, S.E.; Ozoemena, K.I. Probing the electrochemistry of MXene (Ti2CTx)/electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD) composites as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 297, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damirchi, Z.; Firoozbakhtian, A.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R. Ti3C2/Ni/Sm-based electrochemical glucose sensor for sweat analysis using bipolar electrochemistry. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Kang, S.; Lu, W.Q. Ge Nanoparticles in MXene Sheets: One-step Synthesis and Highly Improved Electrochemical Property in Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.Q.; Han, X.H.; Yang, X.H.; Zhao, J.; Chai, C.P. Detection of Hydrazine at MXene/ZIF-8 Nanocomposite Modified Electrode. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Wu, T.; Gu, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Che, X.L.; Sun, D.; Huang, F.Q. Nb2Se2C: A new compound as a combination of transition metal dichalcogenide and MXene for oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9036–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.Z.; Xie, X.Q.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Song, J.J.; Wu, W.J.; Su, D.W.; Wang, G.X. Confined Sulfur in 3D MXene/Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybrid Nanosheets for Lithium-Sulfur Battery. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12613–12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Chen, Z.R.; Fu, N.; Yang, Z.L. Hexaazatriphenylene-doped MXene films for the high-performance micro-supercapacitors and wearable pressure sensor system. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.W.; Dong, J.D.; Fang, X.J.; Zheng, W.H.; Sun, Y.T.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, Z.X.; Huang, Y.D. Ti3C2Tx MXene/polyaniline (PANI) sandwich intercalation structure composites constructed for microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 169, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahil; Jaryal, V.B.; Sharma, R.; Thakur, K.K.; Ataya, F.S.; Gupta, N.; Singh, D. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Fe3O4―MoS2@MXene Nanocomposite as an Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Levofloxacin. Chemistryselect 2025, 10, e202405959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Lin, S.; Ding, W.; Zhu, X.G.; Sheng, Z.G.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.B.; Sun, Y.P. 2D/2D 1T-MoS2/Ti3C2 MXene Heterostructure with Excellent Supercapacitor Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 0190302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lian, S.S.; Li, X.Z.; Kuai, Z.Y.; Jiang, D.L.; Chen, S.; Peng, C. Photoreversible control of coumarin driven hydrophobic Ti3C2Tx MXene composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
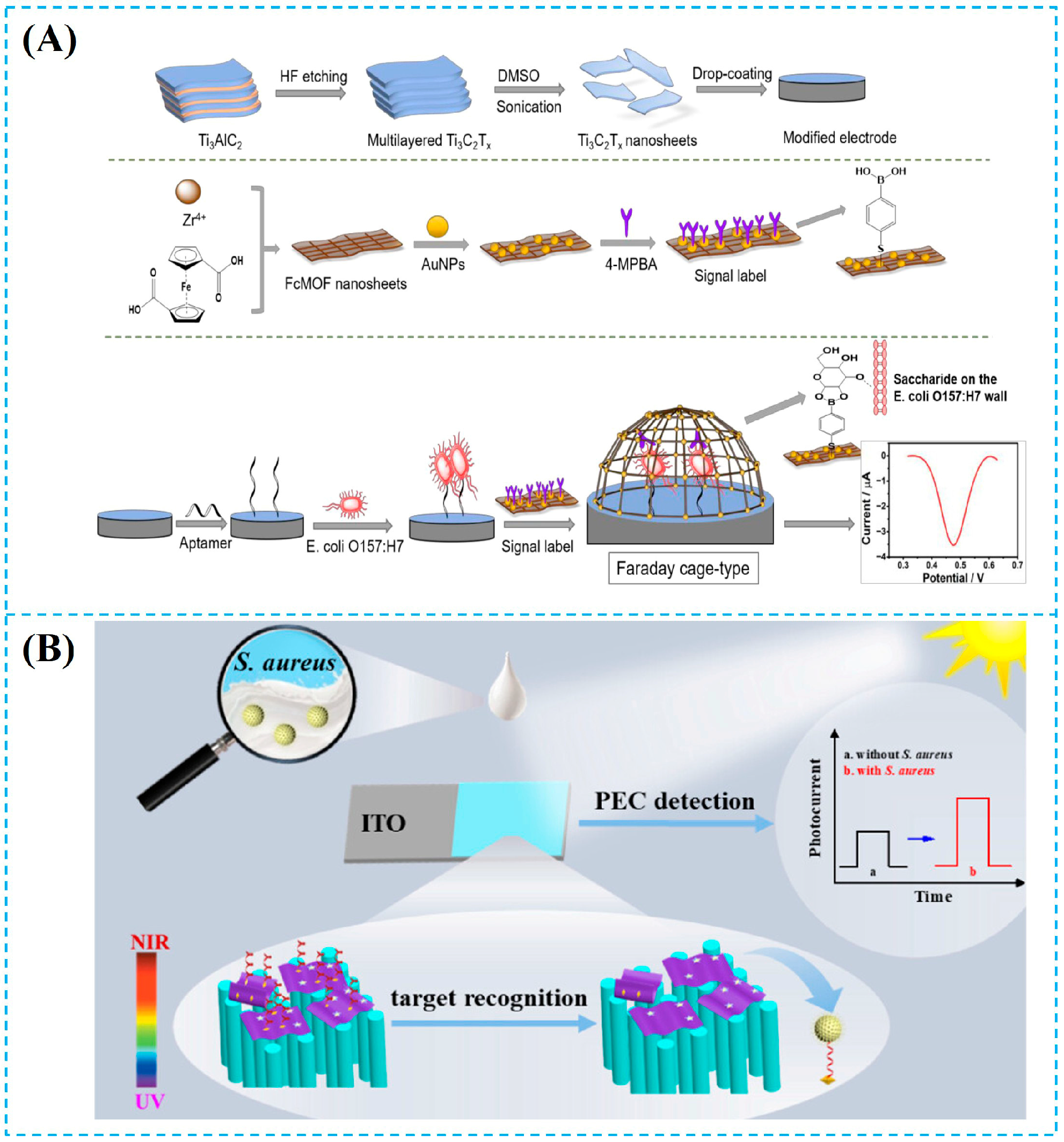
- Dai, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Geng, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; He, P. Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework and Ti3C2Tx Nanosheet-Based Faraday Cage-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor for Escherichia coli Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 9201–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Dong, X.; Shen, G.; He, L.; Cai, C.; Liu, Q.; Niu, Q.; Xu, C. Target Recognition-Triggered Interfacial Electron Transfer Model: Toward Signal-On Photoelectrochemical Aptasensing for Efficient Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Using Ti3C2Tx-Au NBPs/ZnO NR Composites. Langmuir 2024, 40, 20526–20536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, N.N.; Azmi, F.S.N.; Abu Bakar, N.; Aziz, T.; Shapter, J.G. Titanium carbide MXene/silver nanostars composite as SERS substrate for thiram pesticide detection. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, S.; Park, E.; Sun, Y.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, L.; Jung, Y.M. Decoration of Ag nanoparticle on MXene sheets for SERS studies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 316, 124382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.L.; Yang, S.; Li, G.Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Qu, Z.W.; Gao, J.; Fan, X.C.; et al. Direct writing of flexible two-dimensional MXene arrays for SERS sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 12115–12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.L.; Zhao, C.Y.; Tang, X.; Gao, J.; Li, G.Q.; Cai, H.Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Qu, Z.W.; Fan, X.C.; et al. Charge-transfer-driven ultrasensitive SERS sensing in a two-dimensional titanium carbonitride MXene. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 2405–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, L. Photocatalytic Deposition of Au Nanoparticles on Ti3C2Tx MXene Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Molecules 2024, 29, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, W.D.; Shi, B.; Qu, X.W.; Zheng, Y.K.; Zhou, P.W. Nb2C MXene self-assembled Au nanoparticles simultaneously based on electromagnetic enhancement and charge transfer for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 299, 122843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
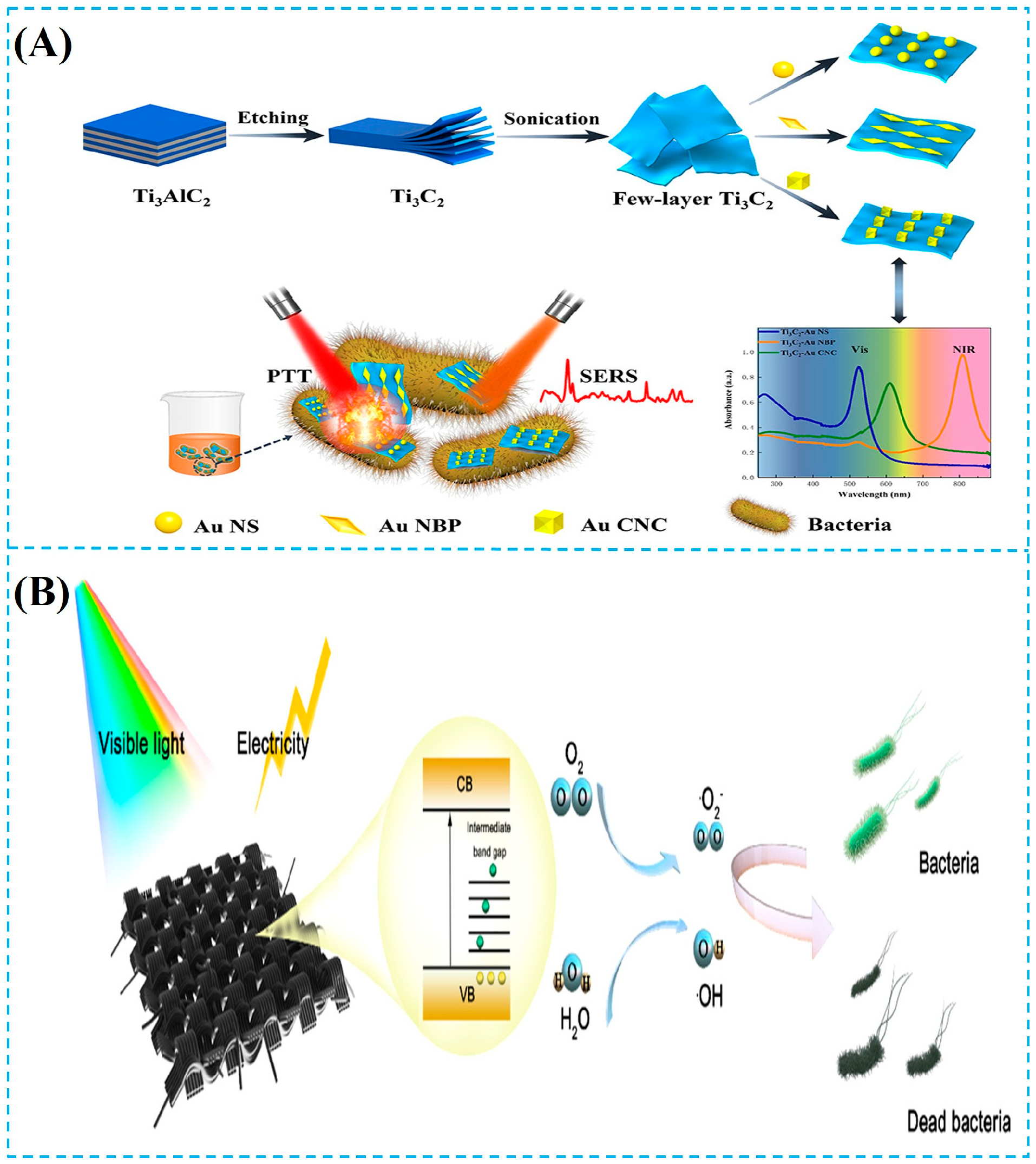
- Yu, Z.Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhao, W.D.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jin, S.Z. Versatile self-assembled MXene-Au nanocomposites for SERS detection of bacteria, antibacterial and photothermal sterilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.D.; Yang, Z.H.; Jiang, L.; Lou, X.C.; Cui, D.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y. Dual-functional Nb2C-Au nanostructure for rapid SERS detection and NIR-I/II photothermal sterilization of bacteria. Microchem. J. 2025, 217, 115135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.W.; Zhou, P.W.; Zhao, W.D.; Shi, B.Y.; Zheng, Y.K.; Jiang, L. Efficient capture and ultra-sensitive detection of drug-resistant bacteria ESBL-E. coli based on self-assembled Au NPs and MXene-Au SERS platform. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ye, B.; Zhuang, Z.; Lan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z. Rapid label-free SERS detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria based on hafnium ditelluride-Au nanocomposites. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2020, 13, 2041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D. Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide Fluorescent Switch Based Multivariate Testing Strategy for Reliable Detection of Listeria monocytogenes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9988–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.C.; Ye, R.F. One-Pot Synthesis of Enzyme and Antibody/CaHPO4 Nanoflowers for Magnetic Chemiluminescence Immunoassay of Salmonella enteritidis. Sensors 2023, 23, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appaturi, J.N.; Pulingam, T.; Thong, K.L.; Muniandy, S.; Ahmad, N.; Leo, B.F. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella with reduced graphene oxide-carbon nanotube based electrochemical aptasensor. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 589, 113489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ping, J.F.; Ye, Z.Z.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y.B. Impedimetric immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles modified graphene paper for label-free detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yi, H.C.; Gu, H.W.; Yin, X.L.; Xiang, D.L.; Zou, P. An electrochemical and colorimetric dual-mode aptasensor for Staphylococcus aureus based on a multifunctional MOF and magnetic separation technique. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkawa, T.; Uchida, K.; Daimon, S.; Shiomi, Y.; Adachi, H.; Qiu, Z.; Hou, D.; Jin, X.F.; Maekawa, S.; Saitoh, E. Separation of longitudinal spin Seebeck effect from anomalous Nernst effect: Determination of origin of transverse thermoelectric voltage in metal/insulator junctions. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 214403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledialidusti, R.; Anasori, B.; Barnoush, A. Temperature-dependent mechanical properties of Tin+1CnO2 (n=1, 2) MXene monolayers: A first-principles study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 3414–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzi, A.; Fusco, L.; Khan, A.; Bedognetti, D.; Zavan, B.; Vitale, F.; Yilmazer, A.; Delogu, L.G. Photodynamic Therapy Based on Graphene and MXene in Cancer Theranostics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Luo, Y.; Lin, H.; Ge, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Niobium Carbide MXene Augmented Medical Implant Elicits Bacterial Infection Elimination and Tissue Regeneration. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Insights into 2D MXenes for Versatile Biomedical Applications: Current Advances and Challenges Ahead. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, R.; Feng, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Recent development and prospects of surface modification and biomedical applications of MXenes. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lin, L.; He, Q.; Hu, H.; Luo, R.; Xian, D.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, F.; et al. Titanium carbide MXene-based hybrid hydrogel for chemo-photothermal combinational treatment of localized bacterial infection. Acta Biomater. 2022, 142, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.F.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhuo, J.C.; Du, T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Duan, J.Y.; Dong, H.L.; Wang, J.L. Engineering of Schottky heterojunction in Ru@Bi2S3/Nb2C MXene based on work function with enhanced carrier separation for promoted sterilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, X.; Jin, S. Self-Assembled MXene-Au Multifunctional Nanomaterials with Various Shapes for Label-free SERS Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Photothermal Sterilization. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. Photoelectrochemical Antibacterial Platform Based on Rationally Designed Black TiO2–x Nanowires for Efficient Inactivation against Bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Kong, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Q. Conductive Antibacterial Hemostatic Multifunctional Scaffolds Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets for Promoting Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2468–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qi, Z.; Gou, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.Z. Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional materials and biomedical applications for reactive oxygen species generation and scavenging. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 19516–19535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Guo, J.; Du, S.; Qiu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, T.; et al. Tailored Hydrogel Delivering Niobium Carbide Boosts ROS-Scavenging and Antimicrobial Activities for Diabetic Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, 2201300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Deng, C.; Li, D. MXene/zinc ion embedded agar/sodium alginate hydrogel for rapid and efficient sterilization with photothermal and chemical synergetic therapy. Talanta 2024, 266, 125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.L.; Gao, W.Z.; Liu, L.Z.; Luo, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Yue, T.L.; Sun, J.; Zhu, M.Q.; Wang, J.L. Work function mediated interface charge kinetics for boosting photocatalytic water sterilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Feng, G.; Wei, L.; Weng, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Wang, X. Multifunctional sandwich-like composite film based on superhydrophobic MXene for self-cleaning, photodynamic and antimicrobial applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, S.Y.; Wei, H.X.; Luo, Y.Z.; Cong, F.; Li, W.D.; Hong, L.Z.; Su, J.Y. Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy Based on Borneol-Containing Polymer-Modified MXene Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 45178–45188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
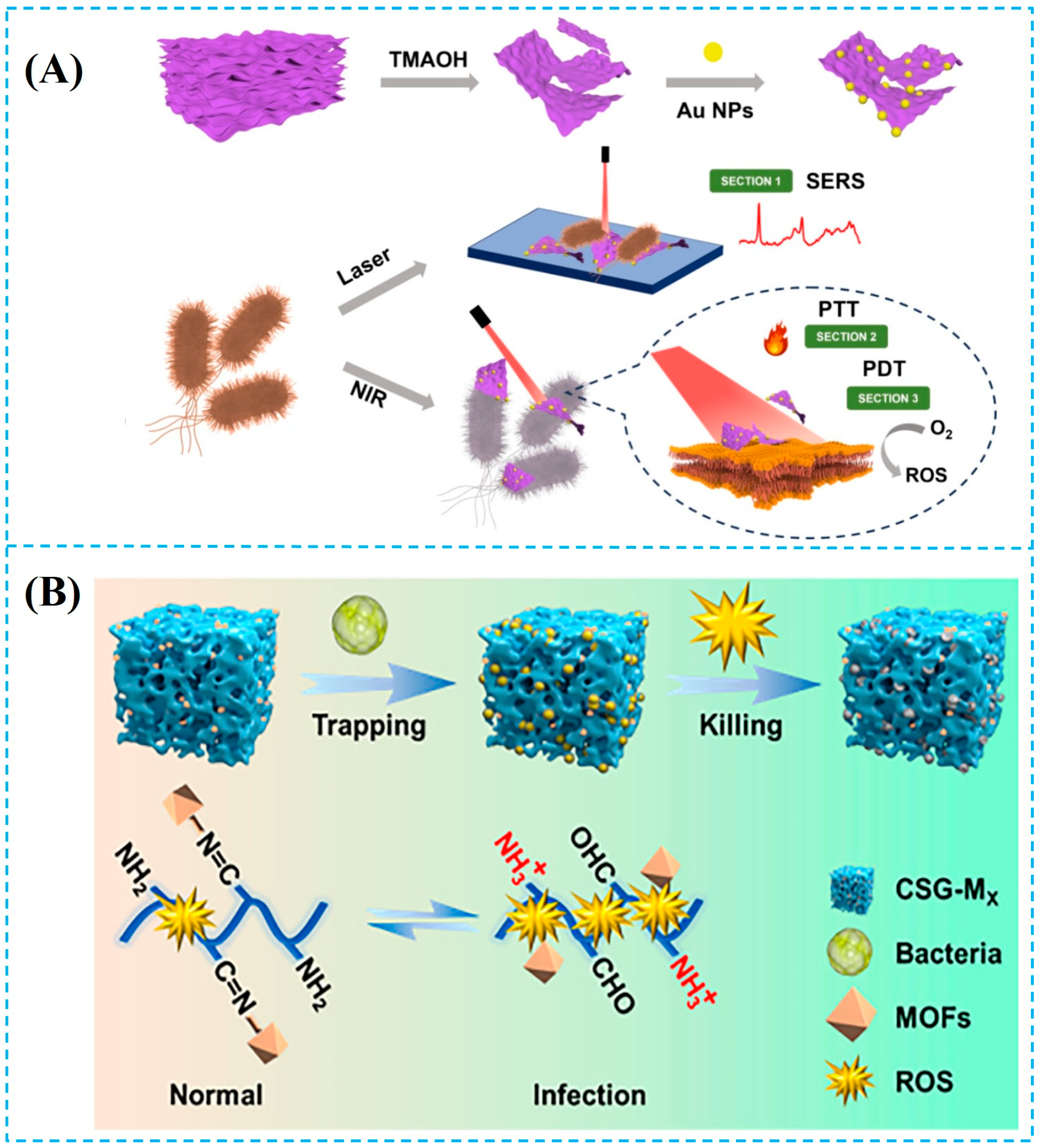
- Zhao, W.; Jiang, L.; Pan, W.; Li, D.; Duan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L. V2CTx-Au Nanostructures for Rapid Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection of Bacteria and Synergistic Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 14673–14683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wen, J.; Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Chu, H. Chemically Grafted Nanozyme Composite Cryogels to Enhance Antibacterial and Biocompatible Performance for Bioliquid Regulation and Adaptive Bacteria Trapping. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19672–19683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, K.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Helal, M.; Berdiyorov, G.R.; Gogotsi, Y. Efficient Antibacterial Membrane based on Two-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Nanosheets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Gomez, T.; Rasool, K.; Ponraj, J.; Prenger, K.; Naguib, M.; Mahmoud, K.A. Effect of Sheet Size and Atomic Structure on the Antibacterial Activity of Nb-MXene Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11372–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerberger, E.A.; Street, R.M.; McDaniel, R.M.; Barsoum, M.W.; Schauer, C.L. Antibacterial properties of electrospun Ti3C2Tz (MXene)/chitosan nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35386–35394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Perini, G.; Aguilar-Hurtado, J.Y.; Zambrano, D.F.; Wang, B.; Niccolini, B.; Henriques, P.C.; Rosa, E.; De Maio, F.; Delogu, G.; et al. Laser-Mediated antibacterial effects of Few- and Multi-Layer Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 567, 150795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Hu, H.; Han, J.; Zhao, Z. Double transition-metal TiVCTX MXene with dual-functional antibacterial capability. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria: Current trends and future perspectives. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9665–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Dang, A.; Li, T.; Sun, Y.; Deng, W.; Lee, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Zada, A.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Efficient multiplexed label-free detection by flexible MXene/graphene oxide fibers with enhanced charge transfer and hot spots effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 133888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, W.; Yan, H.; Wang, R.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q. Advances of MXene in Detection and Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens. Foods 2025, 14, 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223807
Gao W, Yan H, Wang R, Wu W, Wang Q. Advances of MXene in Detection and Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223807
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Wenjie, Han Yan, Rui Wang, Wei Wu, and Qinzhi Wang. 2025. "Advances of MXene in Detection and Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens" Foods 14, no. 22: 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223807
APA StyleGao, W., Yan, H., Wang, R., Wu, W., & Wang, Q. (2025). Advances of MXene in Detection and Sterilization of Foodborne Pathogens. Foods, 14(22), 3807. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223807







