Tracking Cadmium Transfer from Soil to Cup: An Electrochemical Sensing Strategy Based on Bi3+-Rich MOFs for Tea Safety Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of MOF(Bi)
2.4. Preparation of Sensing Interface
2.5. Electrochemical Measurement
2.6. Preparation of Samples
3. Results and Discussion
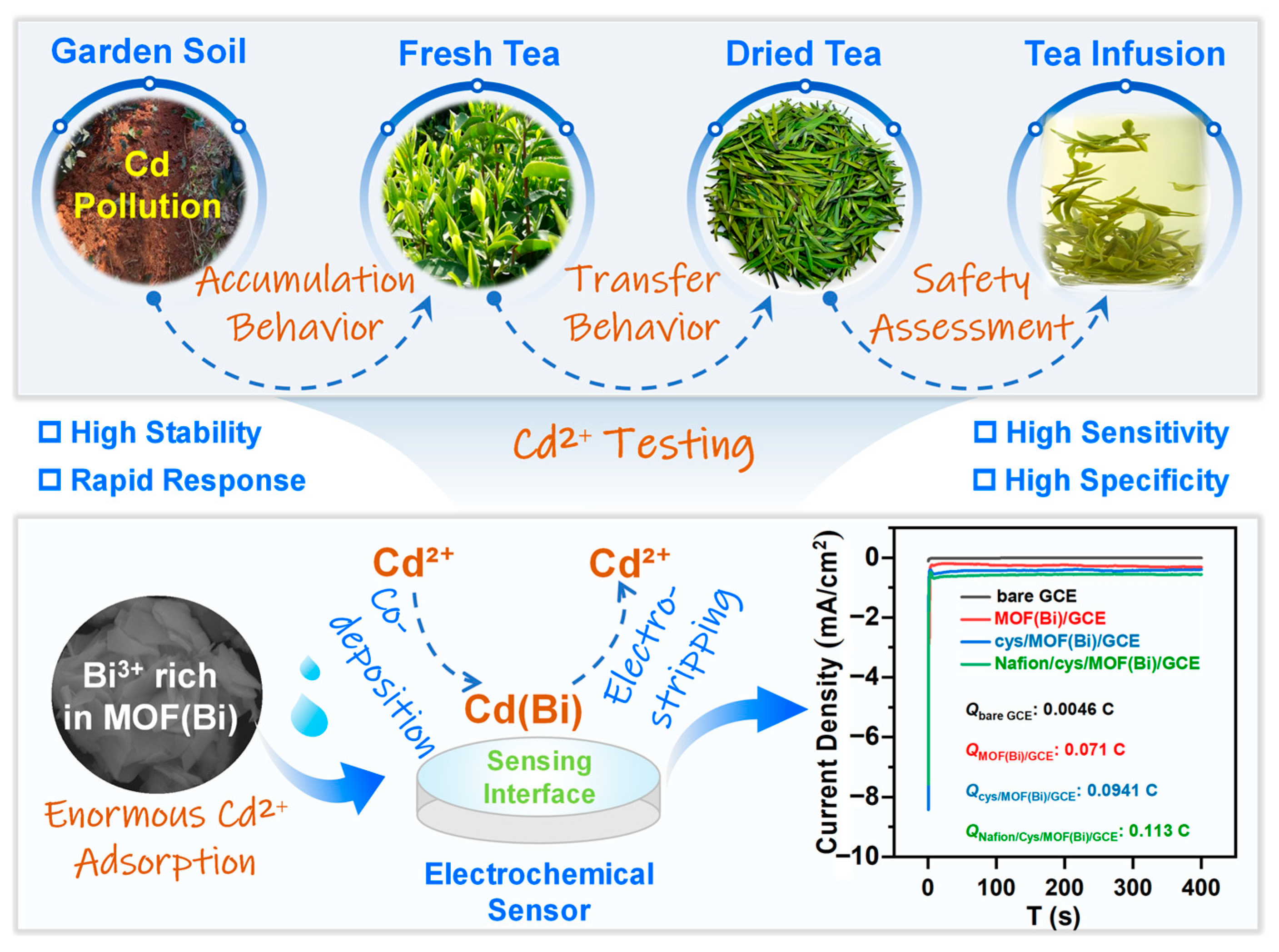
3.1. Principle of Electrochemical Sensing Toward Cd2+ Testing
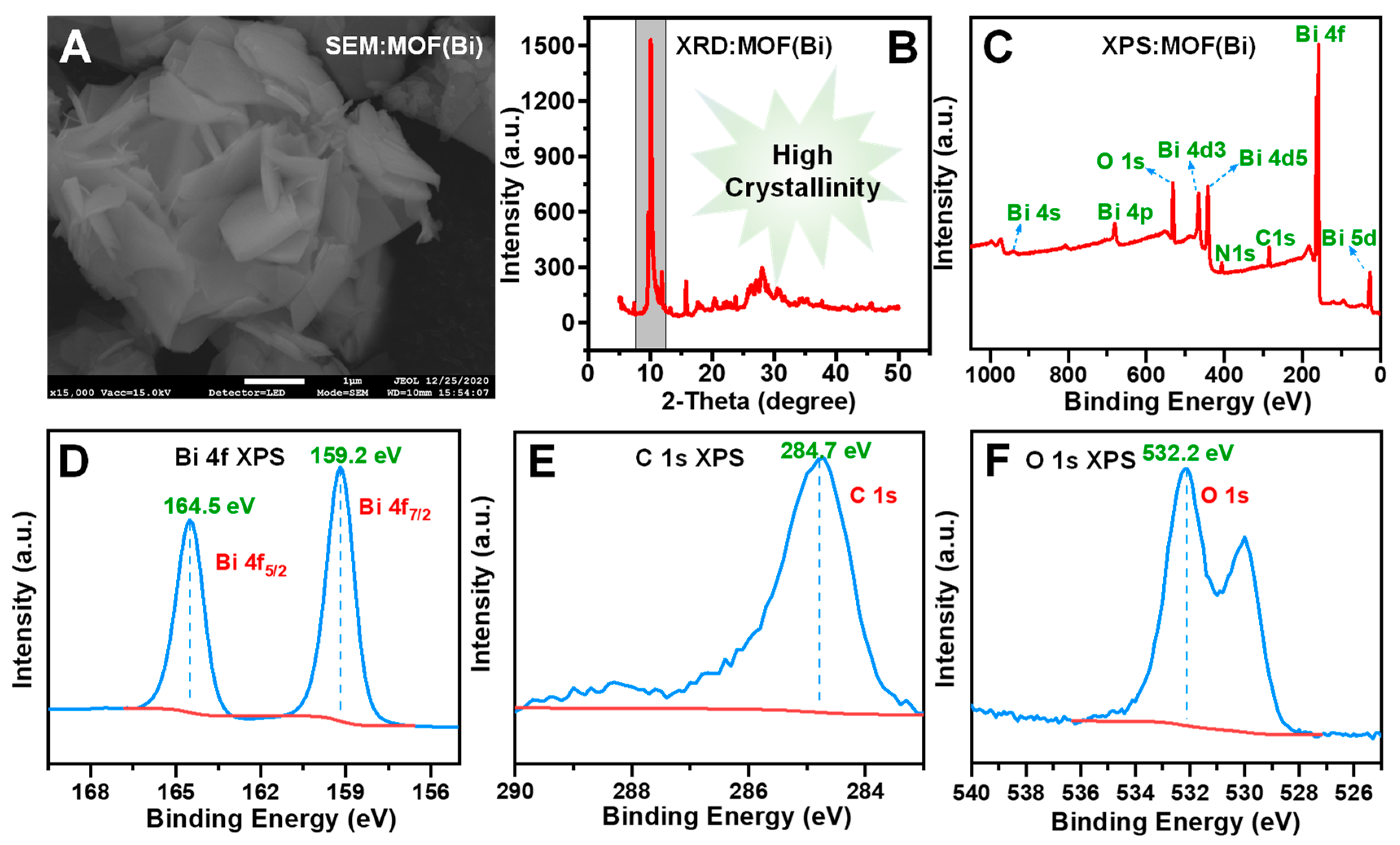
3.2. Characterization of MOF(Bi)
3.3. Electrochemical Properties of MOF(Bi)-Anchored Interface
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
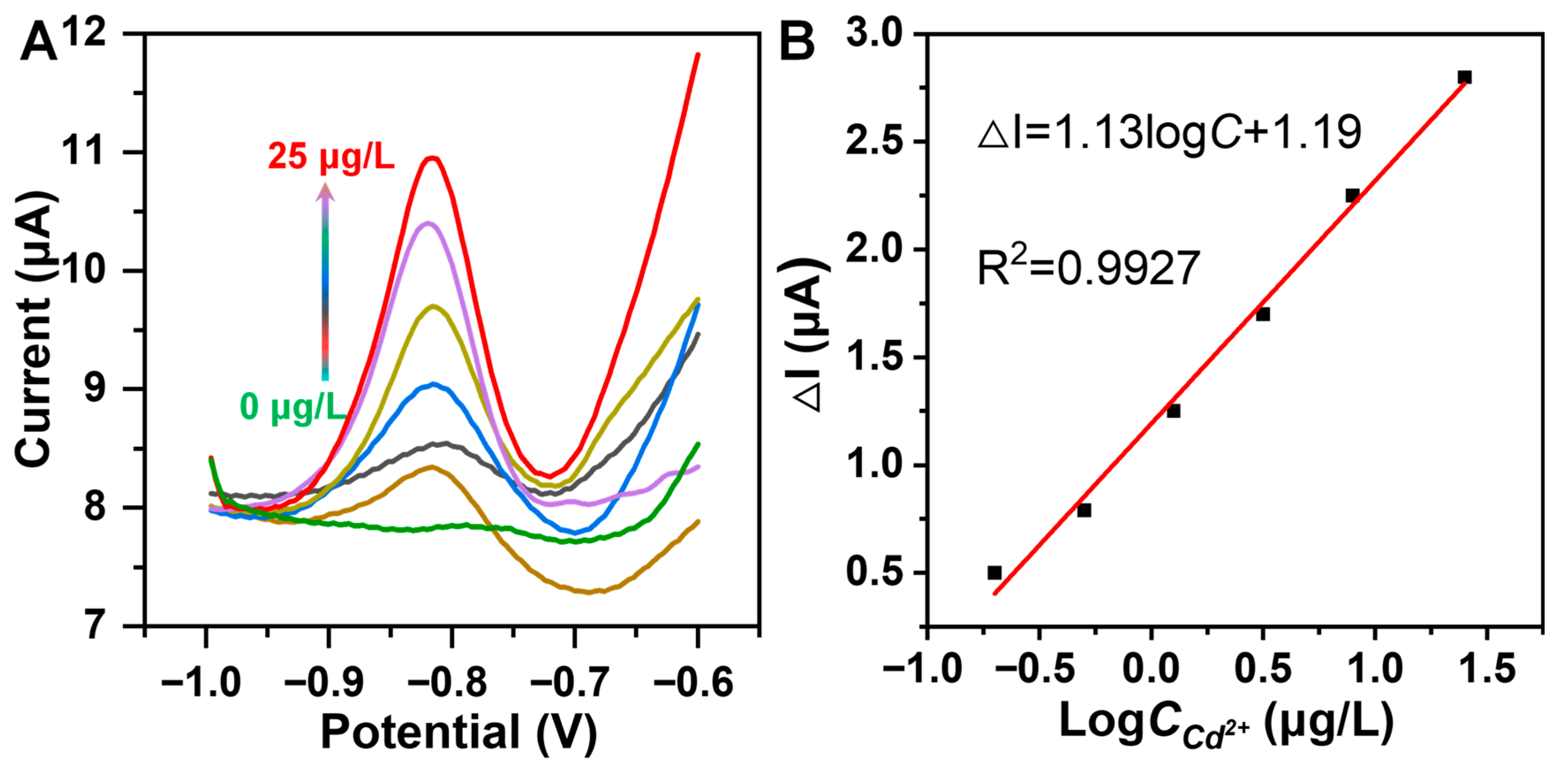
3.5. Electrochemical Sensing Toward Cd2+
3.6. Stability, Reproducibility, Specificity
3.7. Detection of Cd2+ in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marco, A.; Aguirre, M.Á.; Quijada, C.; Hidalgo, M. Electrochemically controlled liquid-liquid microextraction: An innovative methodology for heavy metal extraction from tea using non-toxic menthol-based eutectic mixture. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1375, 344542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Huang, X.W.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zou, Y.C.; Li, Z.H.; Shi, J.Y.; et al. Highly catalytic Ce-based MOF for powering electrochemical aptasensing toward evaluating dissolution rate of microelement copper from tea-leaves. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Qin, C.; Hu, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Manufacturing Process Analysis and Tea Chemical Component Characterization on Ann Tea Quality Formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 22714–22723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.W.; Zhu, H.K.; Wang, J.J.; Yuan, H.B.; Zhao, J.W.; Chen, Q.S. Prediction of black tea fermentation quality indices using NIRS and nonlinear tools. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T.T.; Zhao, G.S.; Qian, F.; Huang, J.B.; Wang, H.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.J. Green tea infusion protects against alcoholic liver injury by attenuating inflammation and regulating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3165–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sui, Y.; Wisniewski, M. Current and future perspectives on tea production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 235, 121663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.; Islam, M.U.; Jiang, X.; Wang, B.; He, S.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Selenium levels in soil and tea as affected by soil properties in Jiangxi Province, China. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Dai, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Fenton-like catalytic MOFs driving electrochemical aptasensing toward tracking lead pollution in pomegranate fruit. Food Control 2025, 169, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Recent Advances in Food Safety: Nanostructure-Sensitized Surface-Enhanced Raman Sensing. Foods 2025, 14, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Q.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Lu, W.; Dai, X.; Xu, R. Advances in Nanozyme Catalysis for Food Safety Detection: A Comprehensive Review on Progress and Challenges. Foods 2025, 14, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.W.; Zou, X.B. Rapid determination of cadmium in rice using an all-solid RGO-enhanced light addressable potentiometric sensor. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhassan, Z.; Ali, S.; Kaleem, Z.; Shahbaz, H.; He, D.; Khan, A.R.; Salam, A.; Hamid, Y.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Zhou, W.J.; et al. Effects of nanosilica priming on rapeseed (Brassica napus) tolerance to cadmium and arsenic stress by regulating cellular metabolism and antioxidant defense. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4518–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, M.M.; Hang, Y.Y.; Lu, B.; Wu, X.H.; Chen, Q.S. Estimating cadmium content in lettuce leaves based on deep brief network and hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tian, Y.; Yao, K.S.; Xu, M. Visualization of heavy metal cadmium in lettuce leaves based on wavelet support vector machine regression model and visible-near infrared hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sun, J.; Cong, S.L.; Ji, X.Y.; Yao, K.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, X. Fluorescence hyperspectral imaging for detection of selenium content in lettuce leaves under cadmium-free and cadmium environments. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 144055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.S.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.M.; Fu, L. Hyperspectral technique combined with stacking and blending ensemble learning method for detection of cadmium content in oilseed rape leaves. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Peng, Z.; Cui, F.J.; Zhou, Q.; Man, Z.W.; Guo, J.; Sun, W.J. Can cadmium-contaminated rice be used to produce food additive sodium erythorbate? Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.J.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Cong, S.L. Nondestructive detection of cadmium content in oilseed rape leaves under different silicon environments using deep transfer learning and Vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barimah, A.O.; Guo, Z.M.; Agyekum, A.A.; Guo, C.; Chen, P.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.B.; Chen, Q.S. Sensitive label-free Cu2O/Ag fused chemometrics SERS sensor for rapid detection of total arsenic in tea. Food Control 2021, 130, 108341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barimah, A.O.; Chen, P.; Yin, L.M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.B.; Guo, Z.M. SERS nanosensor of 3-aminobenzeneboronic acid labeled Ag for detecting total arsenic in black tea combined with chemometric algorithms. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulak, A.; Bodur, S.E.; Bakırdere, S. Microwave synthesis method for dandelion-like copper cobaltite nanoparticles and its usage for the preconcentration of cadmium at trace levels in tap water and Za’atar tea samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 146, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, T.A.R.; de Carvalho, D.T.; Gorup, L.F.; Tarley, C.R.T.; Figueiredo, E.C. Determination of cadmium and lead in tea and coffee beverages by direct magnetic sorbent sampling flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2025, 487, 144709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.J.M. Heavy Metals in Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.-Z.; Sun, R.; Du, Z.-Y.; Yang, W.-B.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, T.-Q. A sustainable agricultural strategy integrating Cd-contaminated soils remediation and bioethanol production using sorghum cultivars. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, W.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, L. Effects of exogenous additives on wheat Cd accumulation, soil Cd availability and physicochemical properties in Cd-contaminated agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (Trial). China Environmental Publishing Group Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Vieira, D.C.S.; Yunta, F.; Baragaño, D.; Evrard, O.; Reiff, T.; Silva, V.; de la Torre, A.; Zhang, C.; Panagos, P.; Jones, A.; et al. Soil pollution in the European Union—An outlook. Environ. Sci. Policy 2024, 161, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, C.; Öner, M.; Çetin, G.; Bakırdere, S. A simple and effective graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanocomposite based solid phase extraction method for the determination of cadmium in tea matrix at trace levels by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 127, 105968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC No 1881/2006; Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- GB 2762-2017; National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission & China Food and Drug Administration; China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhong, W.-S.; Ren, T.; Zhao, L.-J. Determination of Pb (Lead), Cd (Cadmium), Cr (Chromium), Cu (Copper), and Ni (Nickel) in Chinese tea with high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.C.; Peng, Y.; Wen, X.; Ni, X. Distribution, accumulation, and potential risks of heavy metals in soil and tea leaves from geologically different plantations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.A.; Sohail, A.; Sanaullah, M.; Ahmad, W.; Iqbal, D.N.; Khalid, K.; Wani, T.A.; Zargar, S. Assessment of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk of exposure to potentially toxic elements in tea infusions: Determination by ICP-OES and multivariate statistical data analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 84, 127454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.J.M.; Brooks, R.R.W. Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements. a review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery 1989, 1, 81–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.X.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y.; Huang, X.W.; Liu, C.; et al. Rapid detection of cadmium ions in meat by a multi-walled carbon nanotubes enhanced metal-organic framework modified electrochemical sensor. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amr, A.; Abd El-Wahed, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Augustyniak, M.; El-Samad, L.M.; Karim, A.A.E.; El Wakil, A. UPLC-MS/MS analysis of naturally derived apis mellifera products and their promising effects against cadmium-induced adverse effects in female rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, T.H.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, Q.M.; Chen, Q.S. Inner filter effect-based upconversion nanosensor for rapid detection of thiram pesticides using upconversion nanoparticles and dithizone-cadmium-cadmium complexes. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jun, S.; Yan, T.; Bing, L.; Hang, Y.Y.; Quansheng, C. Hyperspectral technique combined with deep learning algorithm for detection of compound heavy metals in lettuce. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Lu, W.; Dai, X.; Xu, R. Nanostructure-engineered optical and electrochemical biosensing toward food safety assurance. Foods 2025, 14, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Lu, W.; Dai, X.; Xu, R. Electrochemical Biosensors Driving Model Transformation for Food Testing. Foods 2025, 14, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, C.; Zhou, L.; Hou, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X. Allosteric switch for electrochemical aptasensor toward heavy metals pollution of Lentinus edodes sensitized with porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1278, 341752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.C.; Huang, X.W.; Zhang, X.N.; Gao, S.J.; Chen, H.L.; Li, Z.H.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Shi, J.Y.; Zou, X.B. Unveiling rheological behavior of hydrogels toward Magic 3D printing patterns. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 168, 111505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Aljuhani, E.H.; Alwael, H.; Assirey, E.A.; Nassef, H.M.; El-Shahawi, M.S. Redox impulse, computational calculation of molecular energy potentials and ultra-trace determination of the food colorant erythrosine b in fruit jams, soft drinks and water. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.H.; Zou, X.B.; Xu, Y.W.; Xu, X.C. A smart-phone-based electrochemical platform with programmable solid-state-microwave flow digestion for determination of heavy metals in liquid food. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.S.; Li, C.H.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.D. Simultaneously determination of trace Cd2+ and Pb2+ based on L-cysteine/graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.; Oh, T.H. Progress in electrochemical sensing of lead, cadmium and mercury based on graphene and MXenes. Talanta 2026, 297, 128671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keawkim, K.; Chuanuwatanakul, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Motomizu, S. Determination of lead and cadmium in rice samples by sequential injection/anodic stripping voltammetry using a bismuth film/crown ether/Nafion modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Food Control 2013, 31, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Rao, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Duan, X.; Wen, Y.; Kong, Z.; Xu, J. Smartphone-based portable sensor with Bi-MOF nanocomposite for Cd (II) in vegetable samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2024, 973, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, J.; Sivalingam, S.; Sriman Narayanan, S. Novel synthesized SABA/MWCNTs composite to detect Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions in real samples of rice water, tobacco extract and raw milk. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 387, 122586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pu, Y.; Xu, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, H. A ratiometric electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of multiple heavy metal ions in water and herbal medicines based on methylene blue-functionalized metal–organic framework. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, P.; Liu, H.; Teng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L.; Jiang, L. Development of an electrochemical immunoassay for rapid detection of E. coli using anodic stripping voltammetry based on Cu@Au nanoparticles as antibody labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Basto, M.C.; España-Sánchez, C.A.; Ágreda, J.A.; Sandoval-Rojas, A.d.P. Improving precision and trueness in the quantification of cadmium using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry and bismuth film electrodes. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Huang, X.W.; Shi, Y.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Tan, W.L.; Zhang, X.A.; Zou, Y.C.; Wang, T.X.; Shi, J.Y.; Zou, X.B. Electrochemical Sensing toward Noninvasive Evaluation of High-Starch Food Digestion via Point-of-Use Monitoring Glucose Level in Saliva. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 11422–11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.A.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Huang, X.W.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zou, Y.C.; Li, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Shi, J.Y.; et al. Simple-easy electrochemical sensing mode assisted with integrative carbon-based gel electrolyte for in-situ monitoring of plant hormone indole acetic acid. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.N.; Wang, Z.L.; Huang, X.W.; Hu, X.T.; Li, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.J.; Wei, X.O.; Zhai, X.D.; et al. H-Bond Modulation Mechanism for Moisture-driven Bacteriostat Evolved from Phytochemical Formulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2312053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Feng, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Meng, X.; Zhai, W.; Pang, H. Emerging insights into the application of metal-organic framework (MOF)-based materials for electrochemical heavy metal ion detection. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Noureen, B.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, A.; Zhou, L.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, W.; et al. An electrochemical sensor using nickel-based metal-organic framework towards highly-sensitive detection of multiple heavy metal ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 444, 138352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.A.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Hu, X.T.; Huang, X.W.; Yin, L.M.; Huang, Q.L.; Wen, Y.B.; Li, B.; Shi, J.Y.; et al. Switchable aptamer-fueled colorimetric sensing toward agricultural fipronil exposure sensitized with affiliative metal-organic framework. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.X.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; You, T.Y. Label-free ratiometric homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor based on hybridization chain reaction for facile and rapid detection of aflatoxin B1 in cereal crops. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.Y.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.Y.; Dong, N.; Chen, T.; You, T.Y. Engineering the Signal Transduction between CdTe and CdSe Quantum Dots for In Situ Ratiometric Photoelectrochemical Immunoassay of Cry1Ab Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13583–13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.J.; Liu, X.H.; Ma, S.; Li, L.B.; You, T.Y. Quantification of zearalenone in mildewing cereal crops using an innovative photoelectrochemical aptamer sensing strategy based on ZnO-NGQDs composites. Food Chem. 2020, 322, 126778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.A.; Huang, C.Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.X.; Shen, J.Z.; Han, E. Structure-Switching Electrochemical Aptasensor for Single-Step and Specific Detection of Trace Mercury in Dairy Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10106–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Meng, S.Y.; Liu, D.; Dong, D.M.; You, T.Y. Electric Field-Induced Specific Preconcentration to Enhance DNA-Based Electrochemical Sensing of Hg2+ via the Synergy of Enrichment and Self-Cleaning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Zhao, X.; Gu, C.D.; Xu, F.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Huang, X.Y.; Qian, J. Fabrication of a Versatile Aptasensing Chip for Aflatoxin B1 in Photothermal and Electrochemical Dual Modes. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 3390–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.D.; Meng, S.Y.; Wang, M.; Li, W.J.; Dong, N.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.Y.; You, T.Y. In-depth interpretation of aptamer-based sensing on electrode: Dual-mode electrochemical-photoelectrochemical sensor for the ratiometric detection of patulin. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.M.; Lu, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.G. Influences of Sprinkler Frost Protection on Air and Soil Temperature and Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Tea Plants in Tea Gardens. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.Y.; Yan, H.F.; Ullah, I.; Zuo, Z.Y.; Li, L.L.; Yu, J.J. Effects of irrigation quantity and biochar on soil physical properties, growth characteristics, yield and quality of greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.H.; Yu, J.G.; Xue, L.H.; Li, H.B.; Yang, L.Z. Roles of bulk and rhizosphere denitrifying bacteria in denitrification from paddy soils under straw return condition. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.C. Long-term fertilization with high nitrogen rates decreased diversity and stability of diazotroph communities in soils of sweet potato. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, L.K.; Miao, W.J.; Wu, Q.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Gao, C. Thermal versus Microwave Inactivation Kinetics of Lipase and Lipoxygenase from Wheat Germ. J. Food Process Eng. 2016, 39, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, L.K.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, K.K.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Evaluation of the possible non-thermal effect of microwave radiation on the inactivation of wheat germ lipase. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.W.; Xiao, H.W.; Ma, H.L.; Zhou, C.S. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Drying Kinetics and Color Changes of Ginkgo Biloba Seeds during Microwave Drying Process. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 3278595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Xu, B.; Deng, B.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y. Rice bran real-time stabilisation technology with flowing microwave radiation: Its impact on rancidity and some bioactive compounds. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2018, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.X.; Hu, B.Y.; Pan, Y.N.; Feng, X.Y.; Yan, A.R.; Guo, H.W.; Wei, Y.L.; Chen, T.Y.; Ruan, Y.Q.; et al. Uncovering the formation of black tea cream: Focusing on the self-assembly process of infusion nanoparticles with different brewing times. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.; Zhang, E.; Ihtisham, M.; Ilyas, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Guo, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D.J.; et al. Metabolic profiling, pigment component responses to foliar application of Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn for tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 319, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.G.; Li, P.P. Consistency of electrical and physiological properties of tea leaves on indicating critical cold temperature. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 159, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Ho, W.K. Noble Metal-Like Behavior of Plasmonic Bi Particles as a Cocatalyst Deposited on (BiO)2CO3 Microspheres for Efficient Visible Light Photocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 4341–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Dai, C. Quantitative analysis of cadmium content in tomato leaves based on hyperspectral image and feature selection. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.W.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.Y.; Zou, X.B.; Li, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.D. Microfabricated interdigitated Au electrode for voltammetric determination of lead and cadmium in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem. 2016, 201, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Fang, Z.G.; Shi, G.L.; Lou, L.Q.; Ren, K.D.; Cai, Q.S. Italian ryegrass-rice rotation system for biomass production and cadmium removal from contaminated paddy fields. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Li, J.; Kamal, N.; Mahmoud, E.; Omara, A.E.D.; Du, D.L. Assessing and Predicting soil quality in heavy metal-contaminated soils: Statistical and ANN-based techniques. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 6510–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.Y.; Xu, S.Y.; Zang, X.J.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Z.Q.; He, S.B.; Du, D.L.; Li, J. Effects of combined pollution of high-density polyethylene and cadmium on carbon and nitrogen storage and forms in coastal wetland soil. Agriculture 2025, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.W.; Pan, G.J.; Qi, W.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xing, J.C.; Gao, Y. Ball-milling-modified biochar with additives enhances soil Cd passivation, increases plant growth and restrains Cd uptake by Chinese cabbage. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soils | Measured Value in Soil (mg/kg) | Measured Value in Fresh Tea (mg/kg) | Measured Value in Dried Tea (mg/kg) | Measured Value in Tea Infusion (mg/kg) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-MS | Sensor | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ICP-MS | Sensor | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ICP-MS | Sensor | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ICP-MS | Sensor | RSD (%) | RE (%) | |
| C10 | 11.07 | 10.18 | 4.6 | 8.04 | 2.72 | 2.58 | 5.0 | 5.15 | 4.62 | 4.39 | 5.1 | 4.98 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 4.7 | 8.57 |
| C15 | 14.4 | 15.12 | 5.6 | 5.00 | 3.29 | 3.45 | 4.8 | 4.86 | 4.98 | 4.62 | 5.4 | 7.23 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 4.9 | 8.11 |
| C20 | 22.8 | 21.56 | 5.2 | 5.44 | 3.57 | 3.49 | 5.3 | 2.24 | 6.23 | 6.47 | 4.5 | 3.85 | 0.41 | 0.39 | 5.5 | 4.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ding, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X. Tracking Cadmium Transfer from Soil to Cup: An Electrochemical Sensing Strategy Based on Bi3+-Rich MOFs for Tea Safety Monitoring. Foods 2025, 14, 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213779
Wang J, Ding Z, Wu X, Wang X, Li H, Zhu M, Zhang X. Tracking Cadmium Transfer from Soil to Cup: An Electrochemical Sensing Strategy Based on Bi3+-Rich MOFs for Tea Safety Monitoring. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213779
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiaoling, Zhengyin Ding, Xinxin Wu, Xindong Wang, Hao Li, Minchen Zhu, and Xinai Zhang. 2025. "Tracking Cadmium Transfer from Soil to Cup: An Electrochemical Sensing Strategy Based on Bi3+-Rich MOFs for Tea Safety Monitoring" Foods 14, no. 21: 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213779
APA StyleWang, J., Ding, Z., Wu, X., Wang, X., Li, H., Zhu, M., & Zhang, X. (2025). Tracking Cadmium Transfer from Soil to Cup: An Electrochemical Sensing Strategy Based on Bi3+-Rich MOFs for Tea Safety Monitoring. Foods, 14(21), 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213779






