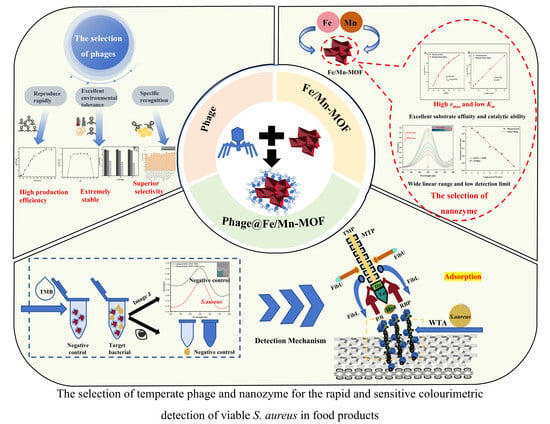
Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF Provides Insight into the Selection of Temperate Phage and Nanozyme for the Rapid and Sensitive Colourimetric Detection of Viable Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
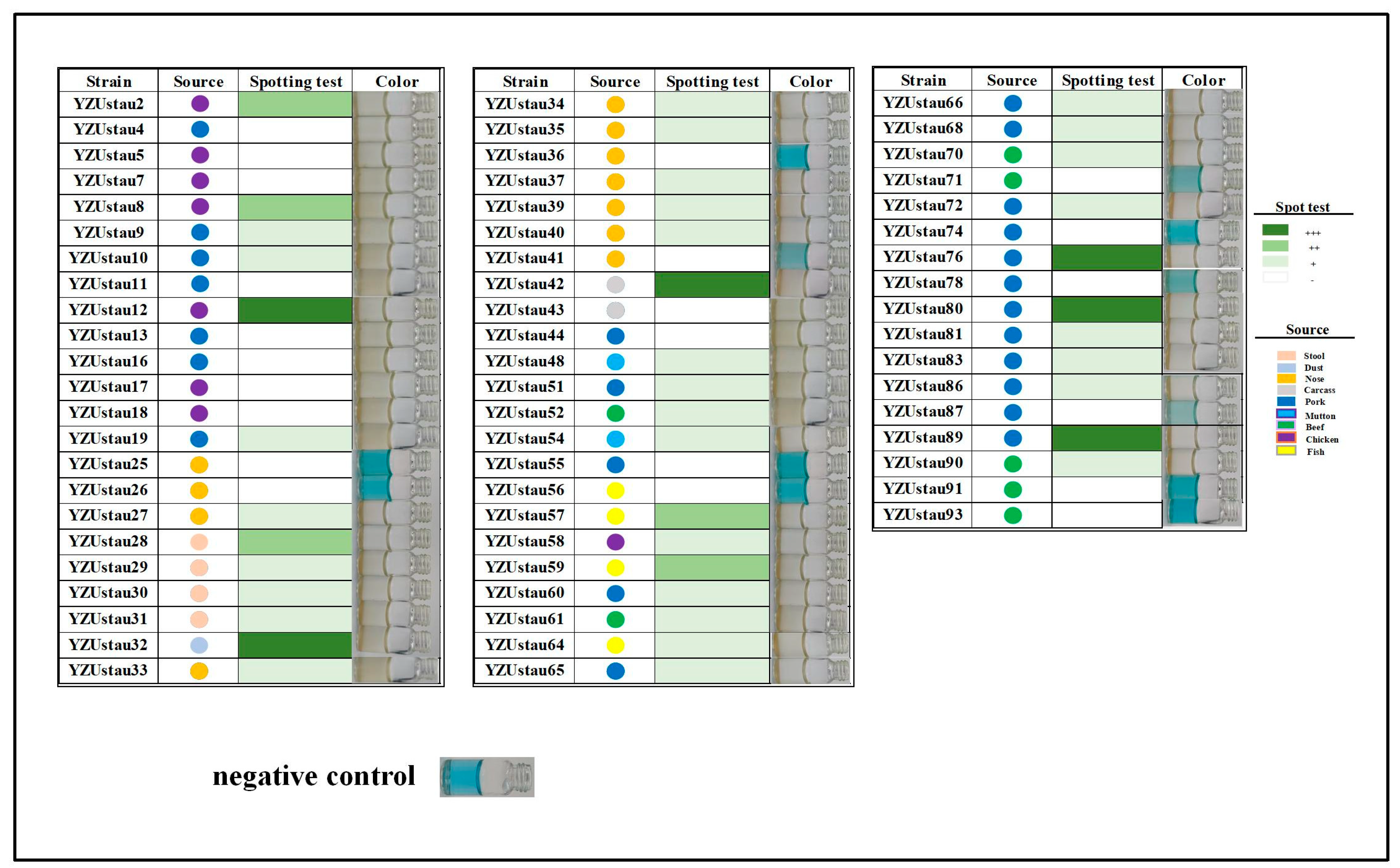
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Phage SapYZUs891 Isolation
2.4. Biological and Genomic Characterisation of the Isolated S. aureus Temperate Phage
2.5. Protein Modeling and Molecular Docking of Phage Tail Proteins ORF3 and ORF65
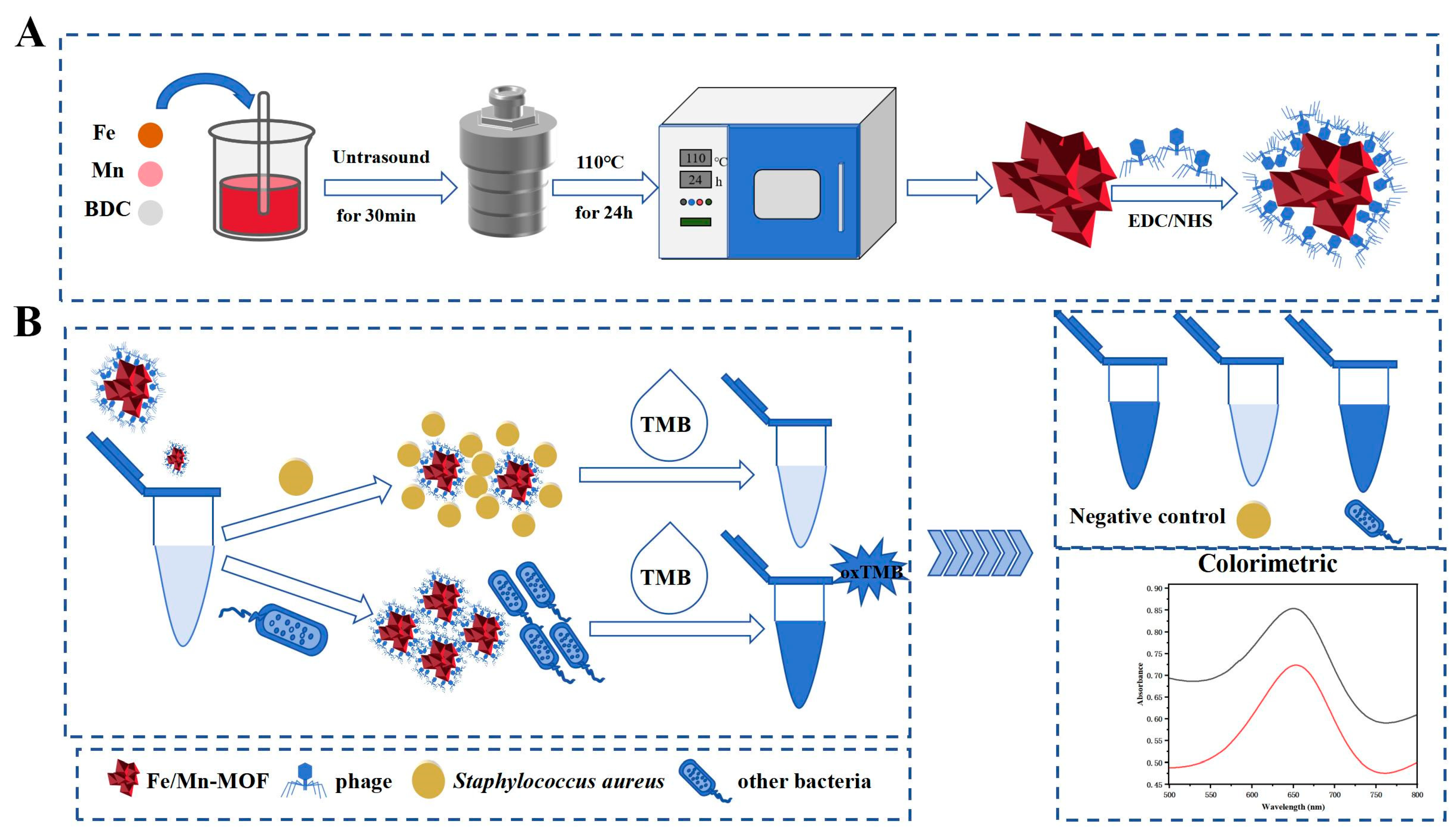
2.6. Immobilisation of SapYZUs891 on the Nanozymes
2.7. Utility of SapYZUs891@nanozymes in S. aureus Detection
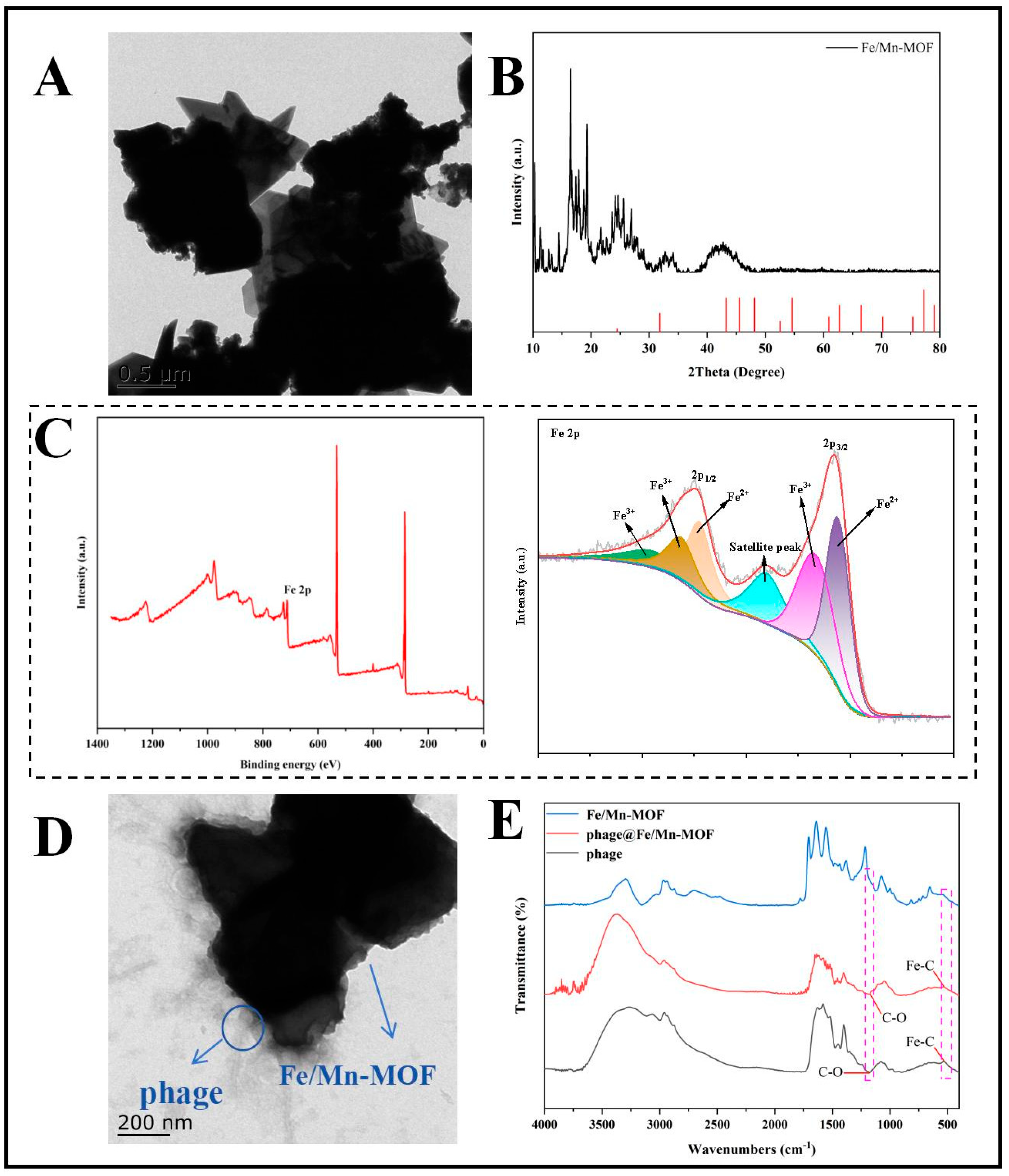
2.8. Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
2.9. Oxidase-like Activity of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
2.10. Selectivity, Anti-Interference, and Live/Dead Cell Discrimination
2.11. Effects of Food Preservatives, NaCl, and pH on SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
2.12. Application of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF for Testing RTE Food Samples
2.13. The Detection Mechanisms of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
2.14. Adsorption Rate
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Characterisation of Temperate Phage SapYZUs891
3.2. Characterisation of Materials
3.3. The Successful Immobilisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF via Covalent Bonding
3.4. Biological Activity and Oxidase-Mimicking Ability of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
3.5. Optimisation of the Testing Conditions
3.6. Sensitivity, Specificity, Anti-Interference, and Ability to Differentiate Live/Dead Bacteria of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
3.7. The Detection Performance of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF in Real Food Samples
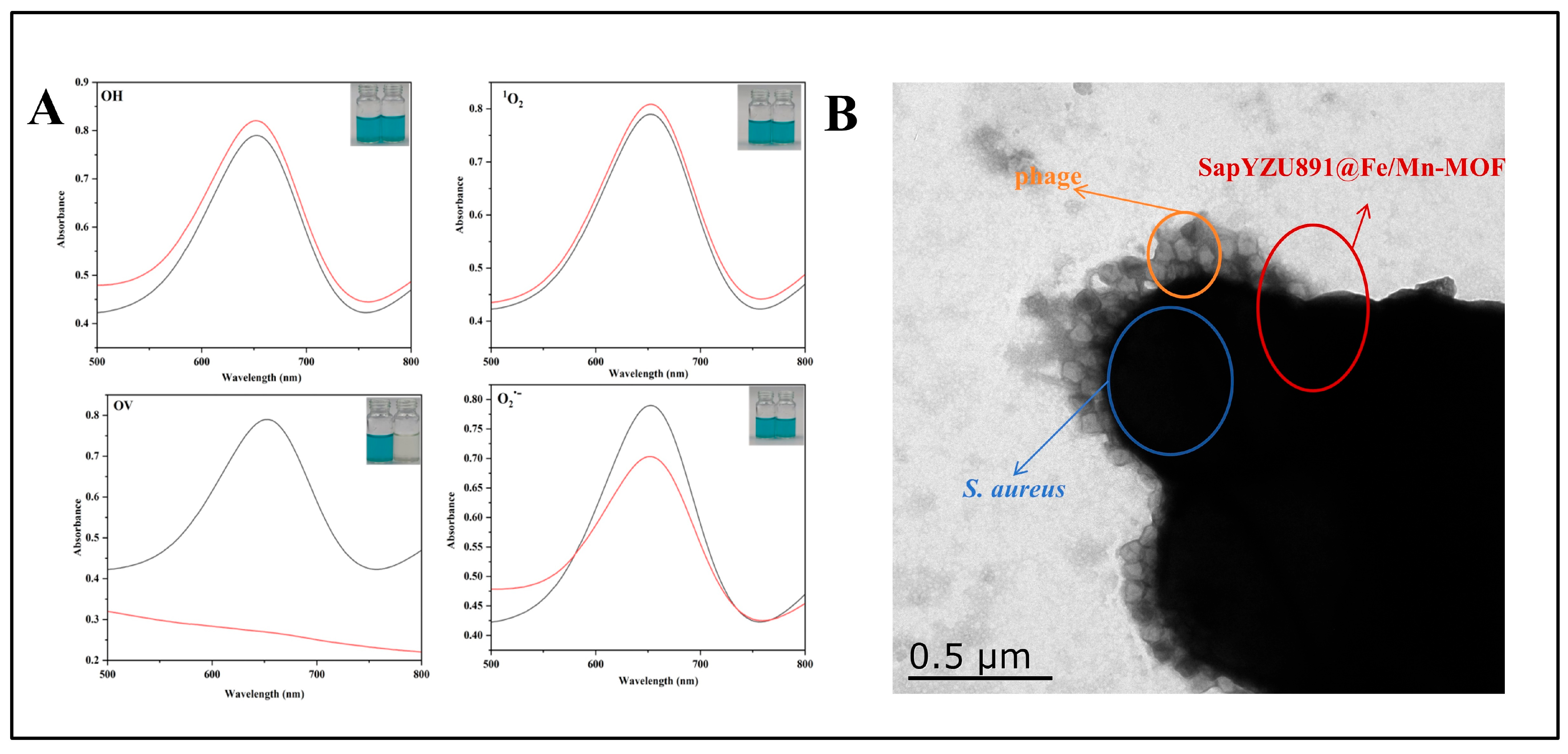
3.8. The Detection Mechanism of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Qin, D.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, Z.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Shen, J.; et al. Development and validation of an ELISA kit for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin A, B, C1, C2, C3, D, E from food samples. Food Control 2024, 166, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.M.; Jeong, K.B.; Luo, K.; Park, J.S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.R. Paper-based colorimetric detection of pathogenic bacteria in food through magnetic separation and enzyme-mediated signal amplification on paper disc. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1151, 338252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, G.; Gu, X.; Yang, Z. Nanozyme colourimetry based on temperate bacteriophage for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food matrices. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 416, 110657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H.; Jiang, C.; Geng, Y.; Sun, X.; Jing, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Dong, C. Recombinase polymerase amplification with polymer flocculation sedimentation for rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 331, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubab, M.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Olaimat, A.N.; Oh, D.H. Biosensors for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, H.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. A comprehensive review on the detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in food samples. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Sheen, Y.J.; Huang, T.P.; Kao, S.H.; Cheng, C.L.; Hwang, C.A.; Sheen, S.; Huang, L.; Sheen, L.Y. Effect of temperature on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in ready-to-eat cooked rice with pork floss. Food Microbiol. 2020, 89, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Lu, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Y.; Xing, X.; Yao, L. A rapid reduction of Au (I→0) strategy for the colorimetric detection and discrimination of proteins. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Sang, Z.; Liu, K.; Du, C.; Ma, L. Sub-10-nm multicolored gold nanoparticles for colorimetric determination of antibiotics via formation of interlocking rings. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ye, S.; Iqbal, K.; Liu, L.; Qiu, G.; Ye, W. Pt/NiCo2O4 nanocomposite with extremely low Pt loading as an oxidase-like nanozyme for colorimetric detection of acetaminophen in natural water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 152, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, Z.; Ye, K.; Zou, X.; Niu, X.; Pan, J. One-pot construction of acid phosphatase and hemin loaded multifunctional metal-organic framework nanosheets for ratiometric fluorescent arsenate sensing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 124407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qian, W.; Lei, F.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, F. Recent advances in MOF-based nanozymes: Synthesis, activities, and bioapplications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 263, 116593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Pena, J. Siderophore-mediated mobilization of manganese limits iron solubility in mixed mineral systems. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2023, 7, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Zhao, H. Bimetallic Fe/Mn metal-organic-frameworks and Au nanoparticles anchored carbon nanotubes as a peroxidase-like detection platform with increased active sites and enhanced electron transfer. Talanta 2020, 210, 120678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Y.; Deng, A.; Yuan, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhu, G. Characterisation of a colourimetric biosensor SapYZUM13@Mn3O4-NH2 reveals the mechanisms underlying its rapid and sensitive detection of viable Staphylococcus aureus in food. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sheng, L.; Lu, X.; Ye, Y.; Sun, J.; Ji, J.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Screening of bio-recognition elements by phage display and their application in the detection of foodborne pathogens. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 171, 117481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Tan, M.; Zhou, W.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z. Directional immobilization of phage on the palladium-based nanozyme for colorimetric detection of Cronobacter sakazakii in powdered infant formula. LWT 2023, 186, 115260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wen, H.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yang, J.; Gao, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Z.Q.; Xu, X. Surface engineering of magnetic peroxidase mimic using bacteriophage for high-sensitivity/specificity colorimetric determination of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Guo, J.; Li, T.; Tian, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Majeed, U.; Song, W.; Xiao, J.; Luo, Y. Phage-based technologies for highly sensitive luminescent detection of foodborne pathogens and microbial toxins: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1843–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Ye, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W. Isolation and characterization of a broad-spectrum phage SapYZU11 and its potential application for biological control of Staphylococcus aureus. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2023, 15, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xu, X.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Gu, X. High-sensitivity and high-specificity colorimetric detection of viable Staphylococcus aureus in ready-to-eat foods using a temperate-bacteriophage-based system with peroxidase-like activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 399, 134810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, F.; Toyofuku, M.; Menzi, C.; Kalawong, R.; Mairpady, S.S.; Francois, P.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Eberl, L. Antibiotics stimulate formation of vesicles in Staphylococcus aureus in both phage-dependent and -independent fashions and via different routes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01439-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.A.; Carrasco, S.T.; Brandolisio, F.; Abatangelo, V.; Boncompain, C.A.; Peresutti-Bacci, N.; Morbidoni, H.R. Bioinformatic analysis of a set of 14 temperate bacteriophages isolated from Staphylococcus aureus strains highlights their massive genetic diversity. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0033422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Rao, S.; Wen, H.; Han, Y.; Deng, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, G. Whole-genome analysis showed the promotion of genetic diversity and coevolution in Staphylococcus aureus lytic bacteriophages and their hosts mediated by prophages via worldwide recombination events. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1088125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Singh, G.; Vats, A.; Parmanand; Roshan, M.; Gautam, D.; Rana, C.; Kesharwani, R.K.; De, S.; Ghorai, S.M. Expression and characterization of novel chimeric endolysin CHAPk-SH3bk against biofilm-forming methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuz, S.; Tasdurmazli, S.; Acar, T.; Duran, G.N.; Ozdemir, C.; Ozbey, U.; Ozbil, M.; Karadayi, S.; Bayrak, O.F.; Derman, S.; et al. Evaluation of bacteriophage Φ11 host recognition protein and its host-binding peptides for diagnosing/targeting Staphylococcus aureus infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Kang, Y.; Cui, X.; Tang, R.; Yang, X. Metal-organic framework composite Mn/Fe-MOF@Pd with peroxidase-like activities for sensitive colorimetric detection of hydroquinone. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1279, 341797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Constructing difunctional histidine-modified magnetic hybrid nanozymes as capture probes and signal amplifiers for the sensitive colorimetric detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food. Microchem. J. 2022, 182, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yao, S. Polyoxometalate nanostructures decorated with CuO nanoparticles for sensing ascorbic acid and Fe2+ ions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 8302–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Ge, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Jia, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z. Ultrathin iron-cobalt oxide nanosheets with abundant oxygen vacancies for the oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Ye, F. Magnetic bead-sensing-platform-based chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer and its immunoassay application. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2708–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Cui, X.; Kong, F.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Li, X. Fe-N/C single-atom nanozyme-based colorimetric sensor array for discriminating multiple biological antioxidants. Analyst 2021, 146, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isho, R.D.; Sher, M.N.; Omer, K.M. Enhancing enzymatic activity of Mn@Co3O4 nanosheets as mimetic nanozyme for colorimetric assay of ascorbic acid. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, U.; Ullah, M.W.; Yang, Q.; Aziz, A.; Xu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S. High-density phage particles immobilization in surface-modified bacterial cellulose for ultra-sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 157, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Sun, S.F.; Zhang, Y.S.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, X.F.; Yang, Z.Q.; Jiao, X.A. Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage for controlling Salmonella enteritidis growth in ready-to-eat mixed-ingredient salads. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Qiao, C.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.; Hou, C.; Huo, D. A dual-functional single-atom Fe nanozyme-based sensitive colorimetric sensor for tannins quantification in brandy. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.N.; Bhima, B.; Kumar, P.U.; Ghosh, S. Bio-control of Salmonella spp. in carrot salad and raw chicken skin using lytic bacteriophages. LWT 2020, 122, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Bai, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, S. Mutation of a Staphylococcus aureus temperate bacteriophage to a virulent one and evaluation of its application. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, S.; Sun, E.; Chen, Y.; Hua, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, R.; Chen, H.; Peng, Z.; Wu, B. A temperate Siphoviridae bacteriophage isolate from Siberian tiger enhances the virulence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus through distinct mechanisms. Virulence 2022, 13, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Ning, Y.; Wan, Q.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Bacteriophages LSA2308 and LSA2366 infecting drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Isolation, characterization and potential application for milk safety. LWT 2021, 152, 112298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Lin, L.; Hua, L.; Liang, W.; Wu, B.; et al. Biocontrol of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using a virulent bacteriophage derived from a temperate one. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 267, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Leptihn, S.; Dong, K.; Loh, B.; Zhang, Y.; Stefan, M.I.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Cui, Z. JD419, a Staphylococcus aureus phage with a unique morphology and broad host range. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 602902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullor, K.; Postoak, B.; Rahman, M.; King, C.; McShan, W.M. Genomic sequencing of high-efficiency transducing Streptococcal bacteriophage A25: Consequences of escape from lysogeny. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00358-e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dalen, R.; Peschel, A.; van Sorge, N.M. Wall teichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus host interaction. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Osada, K.; Azam, A.H.; Asakawa, H.; Miyanaga, K.; Tanji, Y. The presence of two receptor-binding proteins contributes to the wide host range of staphylococcal Twort-Like Phages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5763–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusche, J.; Beck, C.; Lehmann, E.; Gerlach, D.; Daiber, E.; Mayer, C.; Müller, J.; Onallah, H.; Würstle, S.; Wolz, C.; et al. Characterization and host range prediction of Staphylococcus aureus phages through receptor-binding protein analysis. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Wen, H.; Li, Y.J.; Gao, Y.J.; Zheng, X.F.; Li, H.X.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, Z.Q. WGS analysis of two Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages from sewage in China provides insights into the genetic feature of highly efficient lytic phages. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.; Brennan, B.; McCoy, A.P.; Bogan, J.; Brady, A.; Hughes, G. In situ XPS chemical analysis of MnSiO3 copper diffusion barrier layer formation and simultaneous fabrication of metal oxide semiconductor electrical yest MOS structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; Wei, J.; Qiu, F.; Liu, Y. Fe-Mn bimetallic catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for efficient degradation of tetracycline: Mechanism insights and application for pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 445, 141365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xiao, J.; Lan, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Song, X.; Zeng, L. Metal ions-doped carbon dots: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Gupta, P.K.; Tran, V.K.; Son, S.E.; Hur, W.; Lee, H.B.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.N.; Seong, G.H. PVP-stabilized PtRu nanozymes with peroxidase-like activity and its application for colorimetric and fluorometric glucose detection. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, B.; Yang, H.; Lin, F.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.Q. Immobilization of a broad host range phage on the peroxidase-like Fe-MOF for colorimetric determination of multiple Salmonella enterica strains in food. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Long, Q.; Cen, B.; Gao, Q.; Tan, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.Q. Immobilization of a novel bacteriophage PpZDSS02 onto the peroxidase-mimicking Cu-MOF for colorimetric sensing of Proteus penneri encompassing both promotion and inhibition mechanisms. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, P.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Wu, C.; Yu, X.; He, Y. Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus using a novel multienzyme isothermal rapid amplification technique. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1027785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H. Poly-l-lysine-functionalized magnetic beads combined with polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J. Dairy. Sci. 2021, 104, 12342–12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, A.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Guan, T.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W. Rapid and interference-resistant colorimetric detection of viable Staphylococcus aureus in food using a broad host range phage SapYZU04 and MnFeO nanozyme. Food Control 2025, 171, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.L.; Wu, D.; Aziz, A.; Deng, S.S.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Asif, M.; Wang, S.Q. Colorimetric platform based on synergistic effect between bacteriophage and AuPt nanozyme for determination of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Wang, X. A visual colorimetric assay based on phage T156 and gold nanoparticles for the sensitive detection of Salmonella in lettuce. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1272, 341501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yao, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yin, X.; Su, L.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Lan, Q.; et al. Antibiotic and mammal IgG based lateral flow assay for simple and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Tao, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Rao, S.Q.; Gao, L.; Pan, Z.M.; Jiao, X.A. Isolation and characterization of virulent phages infecting Shewanella baltica and Shewanella putrefaciens, and their application for biopreservation of chilled channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Xiong, J.; Yue, H.; Fu, Z. Sandwich fluorimetric method for specific detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on antibiotic-affinity strategy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9864–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gu, J.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Zhang, C.; Ji, X.; Lv, H.; Muyldermans, S.; Wang, S. Selection of specific nanobodies to develop an immuno-assay detecting Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.J.; Suk, H.J.; Sung, H.Y.; Li, T.; Poo, H.; Kim, M.G. Novel antibody/gold nanoparticle/magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposites for immunomagnetic separation and rapid colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Pei, Y.; Wei, X.; Dong, H.; et al. Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus from food samples and food poisoning outbreaks in Shijiazhuang, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 652276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, H.H.; Yan, H. Novel SCCmec type XII methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates identified from a swine production and processing chain. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 225, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, D.; Guo, Y.; De Castro, C.; Kim, S.; Schlatterer, K.; Xu, F.; Pereira, C.; Seeberger, P.H.; Ali, S.; Codée, J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus alters cell wall glycosylation to evade immunity. Nature 2018, 563, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Nandi, A.; Mitra, P.; Saha, K.; Patel, P.; Jha, E.; Panda, P.K.; Singh, S.K.; Dutt, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; et al. Theragnostic application of nanoparticle and CRISPR against food-borne multi-drug resistant pathogens. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 15, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Dong, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, G.; Man, S.; Ma, L. CRISPR-Cas13a based bacterial detection platform: Sensing pathogen Staphylococcus aureus in food samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, S.; Zhao, S.; Ye, F. Analyte-induced laccase-mimicking activity inhibition and conductivity enhancement of electroactive nanozymes for ratiometric electrochemical detection of thiram. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Hao, G.; Wang, B.; Ma, T.; Zhu, S.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z. Three in one: A multifunctional oxidase-mimicking Ag/Mn3O4 nanozyme for colorimetric determination, precise identification, and broad-spectrum inactivation of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, M.; Chen, S.; Tu, Q.; Wang, J. Gold nanosensor for the selective identification of Escherichia coli in foodstuff and its antibacterial ability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Bai, M.; Wang, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. An ultrasensitive sandwich chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay based on phage-mediated double-nanobody for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W.; Ullah, M.W.; Farooq, U.; Aziz, A.; Wang, S. Bacteriophage-based advanced bacterial detection: Concept, mechanisms, and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Deng, A.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Z. Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF Provides Insight into the Selection of Temperate Phage and Nanozyme for the Rapid and Sensitive Colourimetric Detection of Viable Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products. Foods 2025, 14, 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213726
Zhou W, Li W, Han Y, Deng A, Li Y, Hu Q, Yuan L, Zhu G, Yang Z. Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF Provides Insight into the Selection of Temperate Phage and Nanozyme for the Rapid and Sensitive Colourimetric Detection of Viable Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wenyuan, Wenjuan Li, Yeling Han, Aiping Deng, Yajie Li, Qin Hu, Lei Yuan, Guoqiang Zhu, and Zhenquan Yang. 2025. "Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF Provides Insight into the Selection of Temperate Phage and Nanozyme for the Rapid and Sensitive Colourimetric Detection of Viable Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products" Foods 14, no. 21: 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213726
APA StyleZhou, W., Li, W., Han, Y., Deng, A., Li, Y., Hu, Q., Yuan, L., Zhu, G., & Yang, Z. (2025). Characterisation of SapYZUs891@Fe/Mn-MOF Provides Insight into the Selection of Temperate Phage and Nanozyme for the Rapid and Sensitive Colourimetric Detection of Viable Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products. Foods, 14(21), 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213726