Salting-Out Effect Behavior of Protein/λ-Carrageenan Composite Gels Enhanced by Enzymatic Pretreatment: Focusing on Microstructure, Interactions and the Potential for Dysphagia Food
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of SPI
2.3. Hydrolysis of SPI
2.4. Characterization of Hydrolyzed SPI
2.4.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
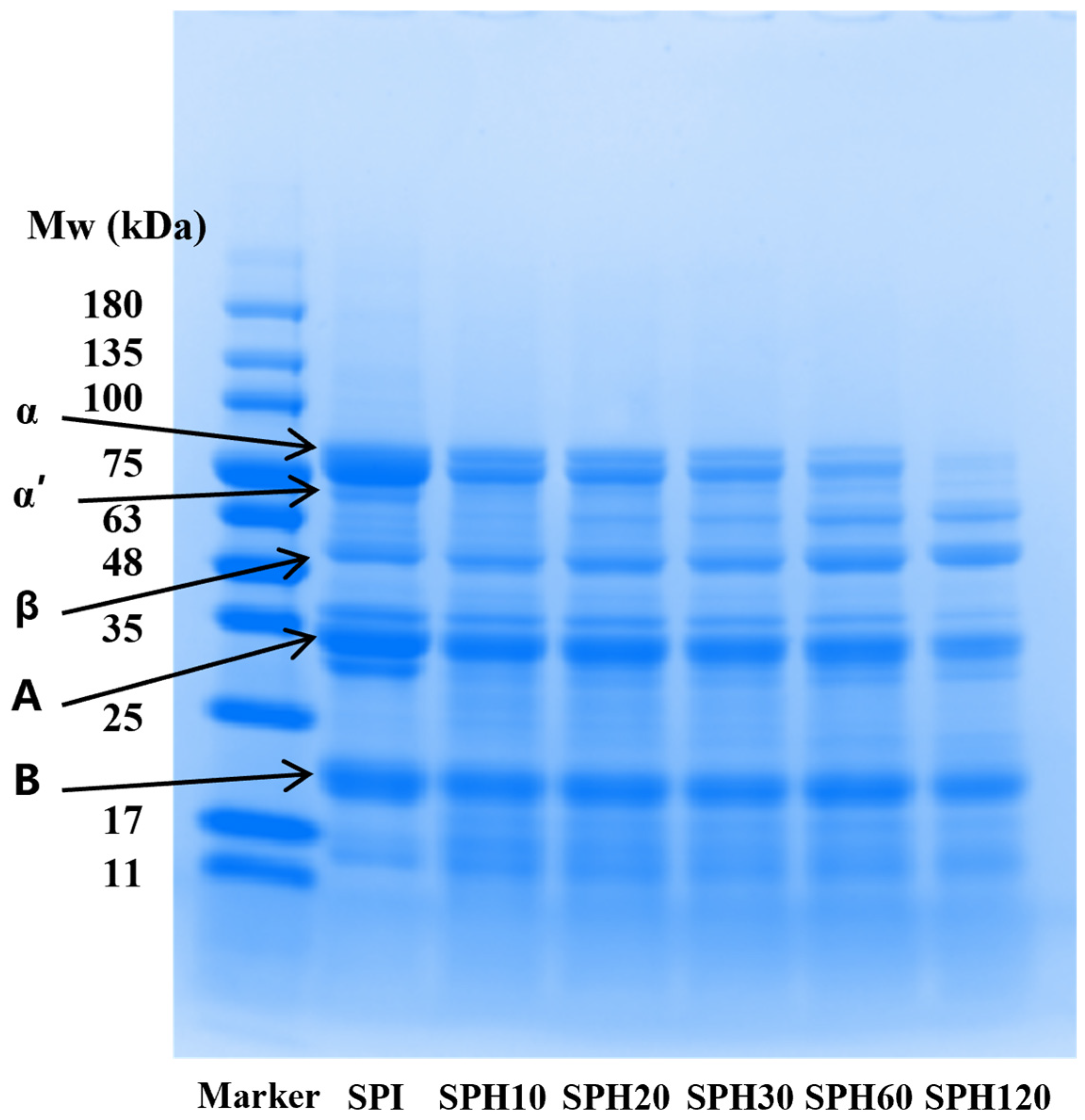
2.4.2. SDS-PAGE
2.5. Preparation of λ/SPI Hydrogels and K-λ/SPI Hydrogels After Immersion
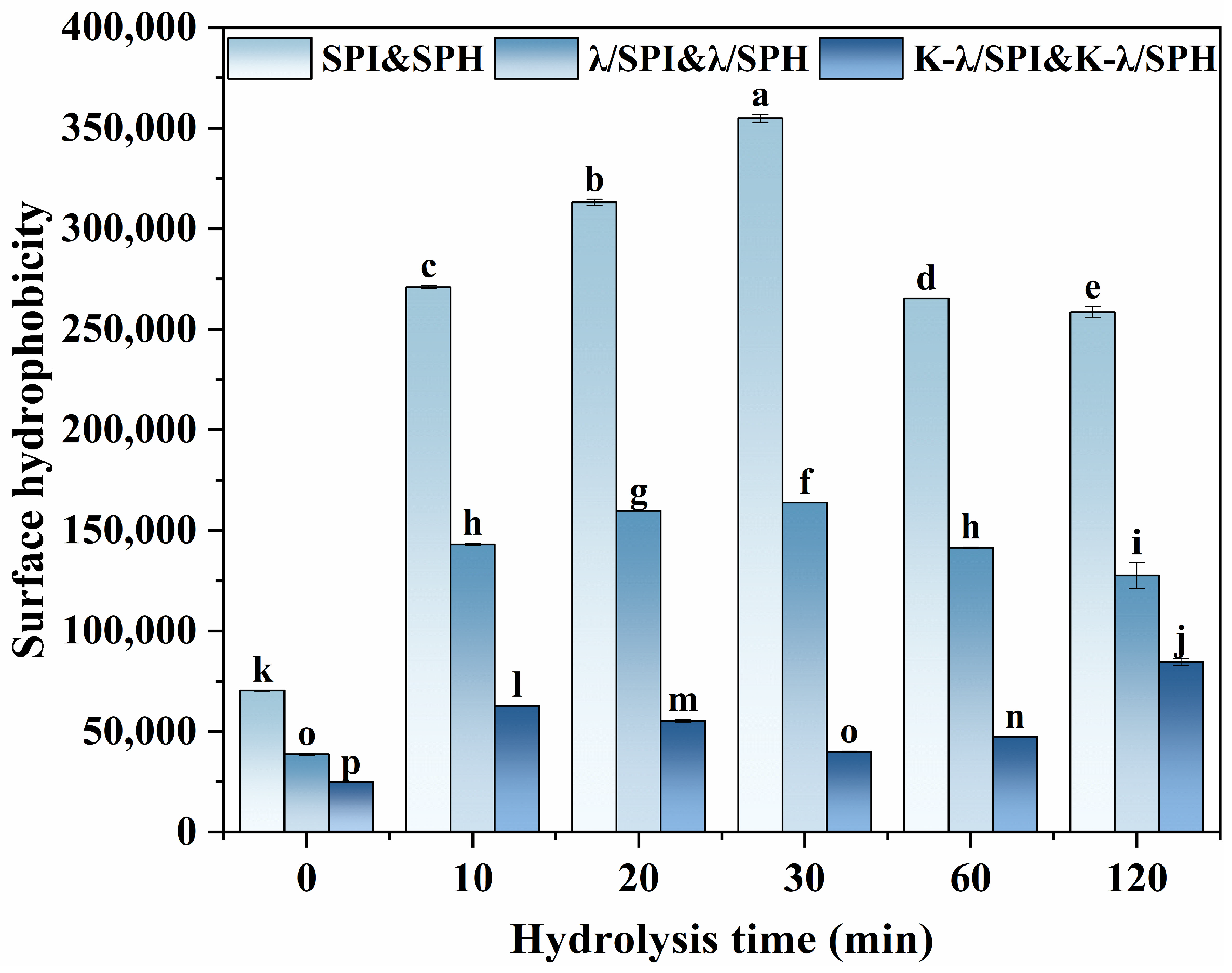
2.6. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.7. Water Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.8. Color Test
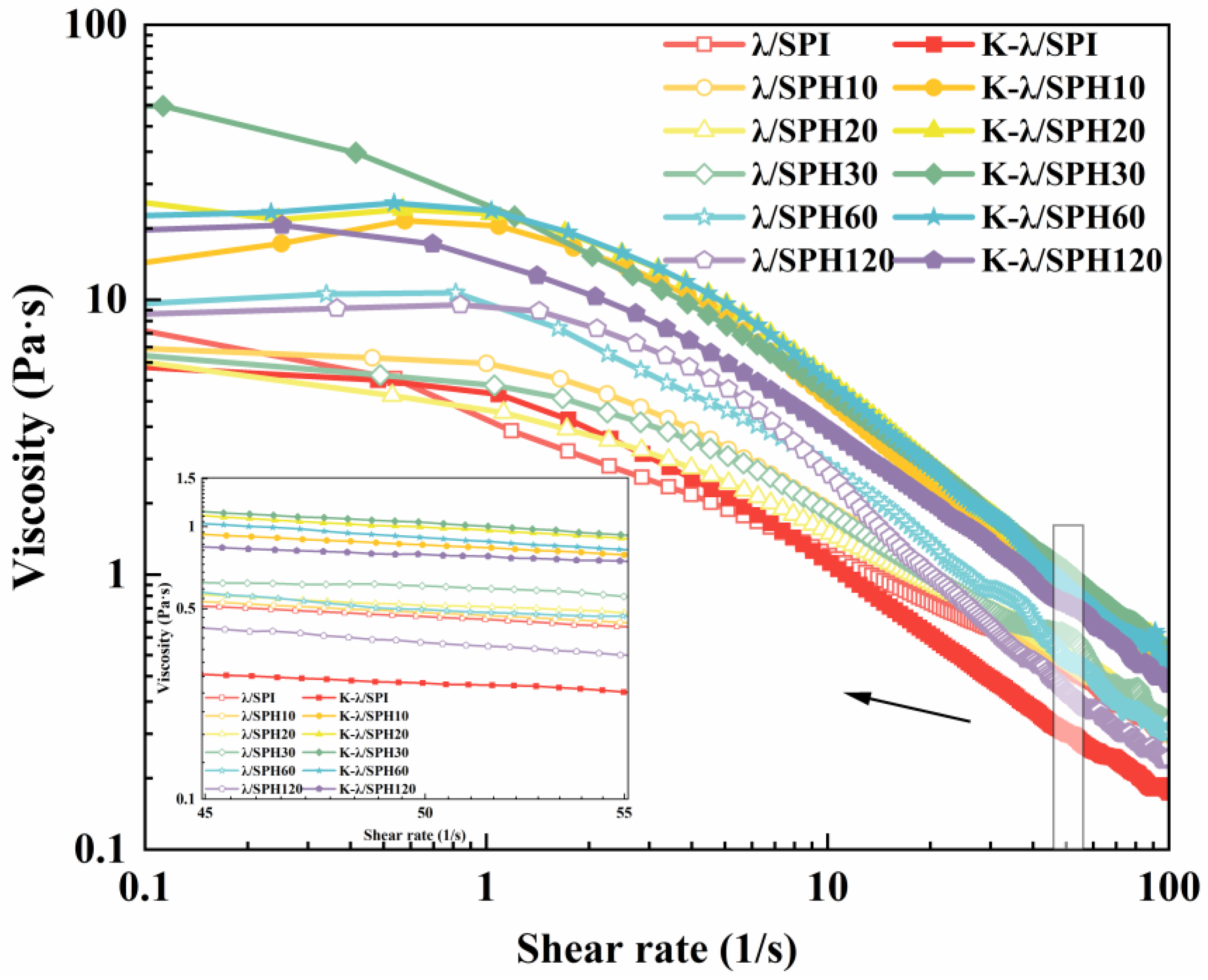
2.9. Rheology of Gels
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
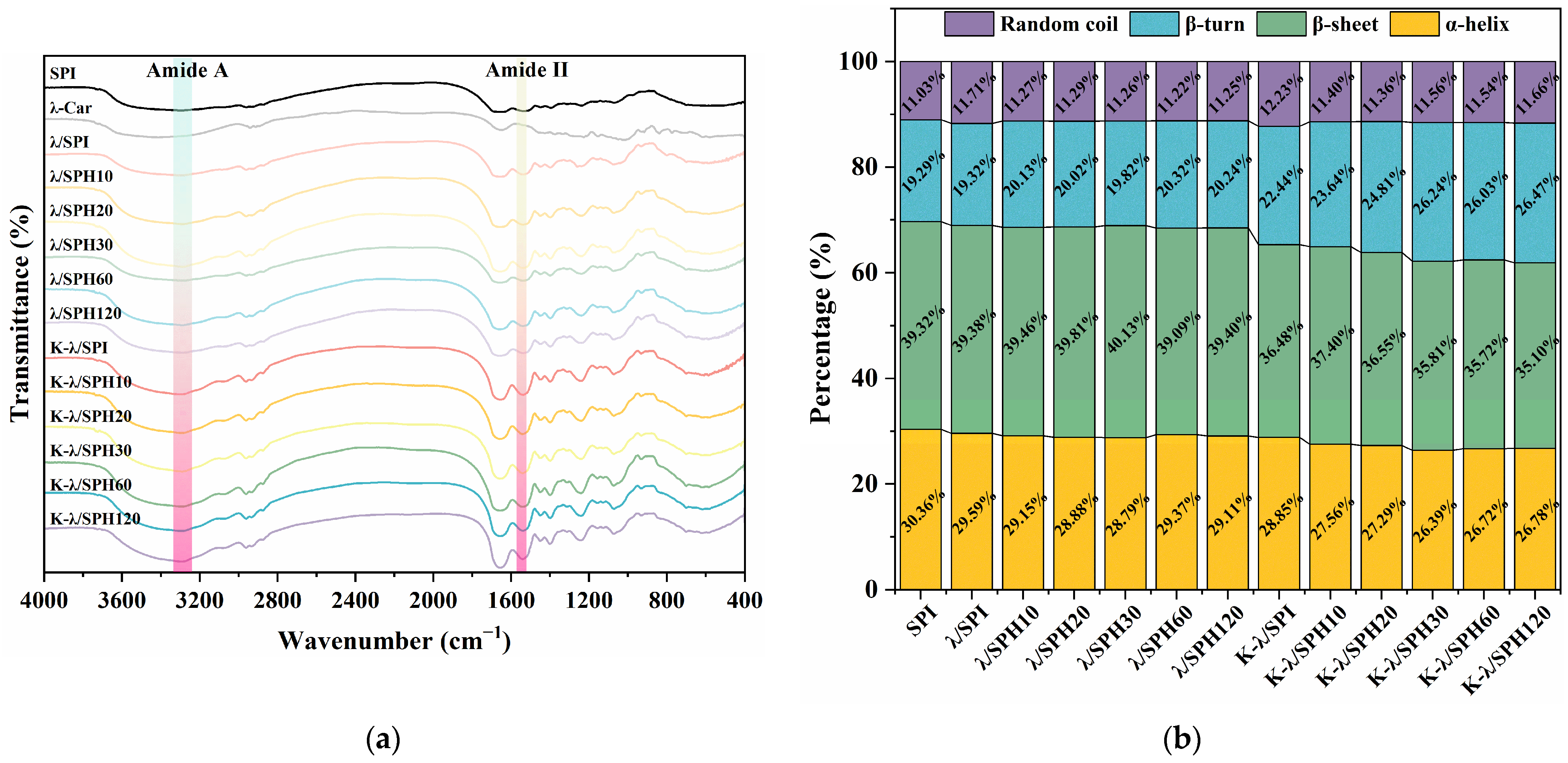
2.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.12. Determination of Intermolecular Forces
2.13. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
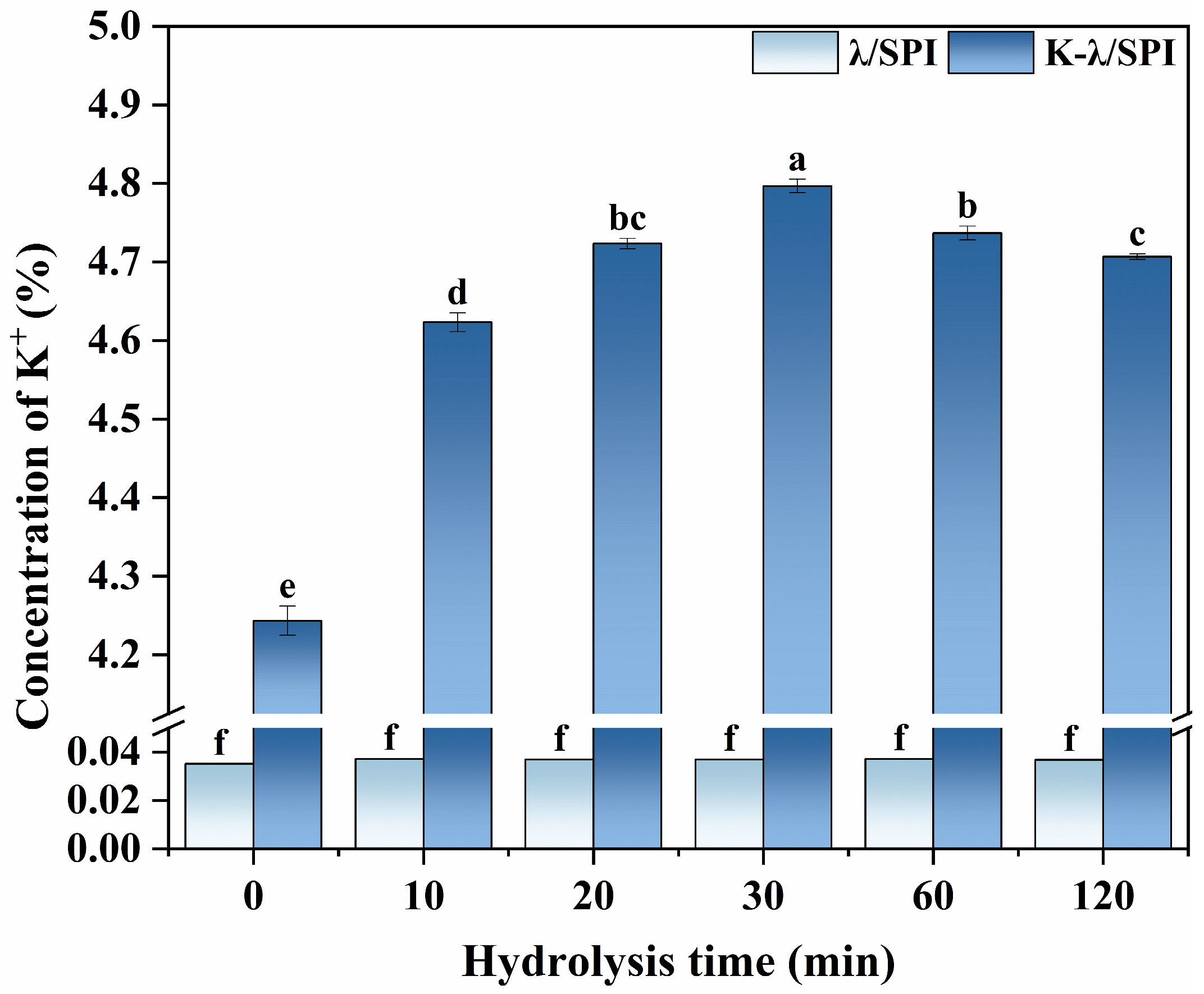
2.14. Microwave Digestion
2.15. Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
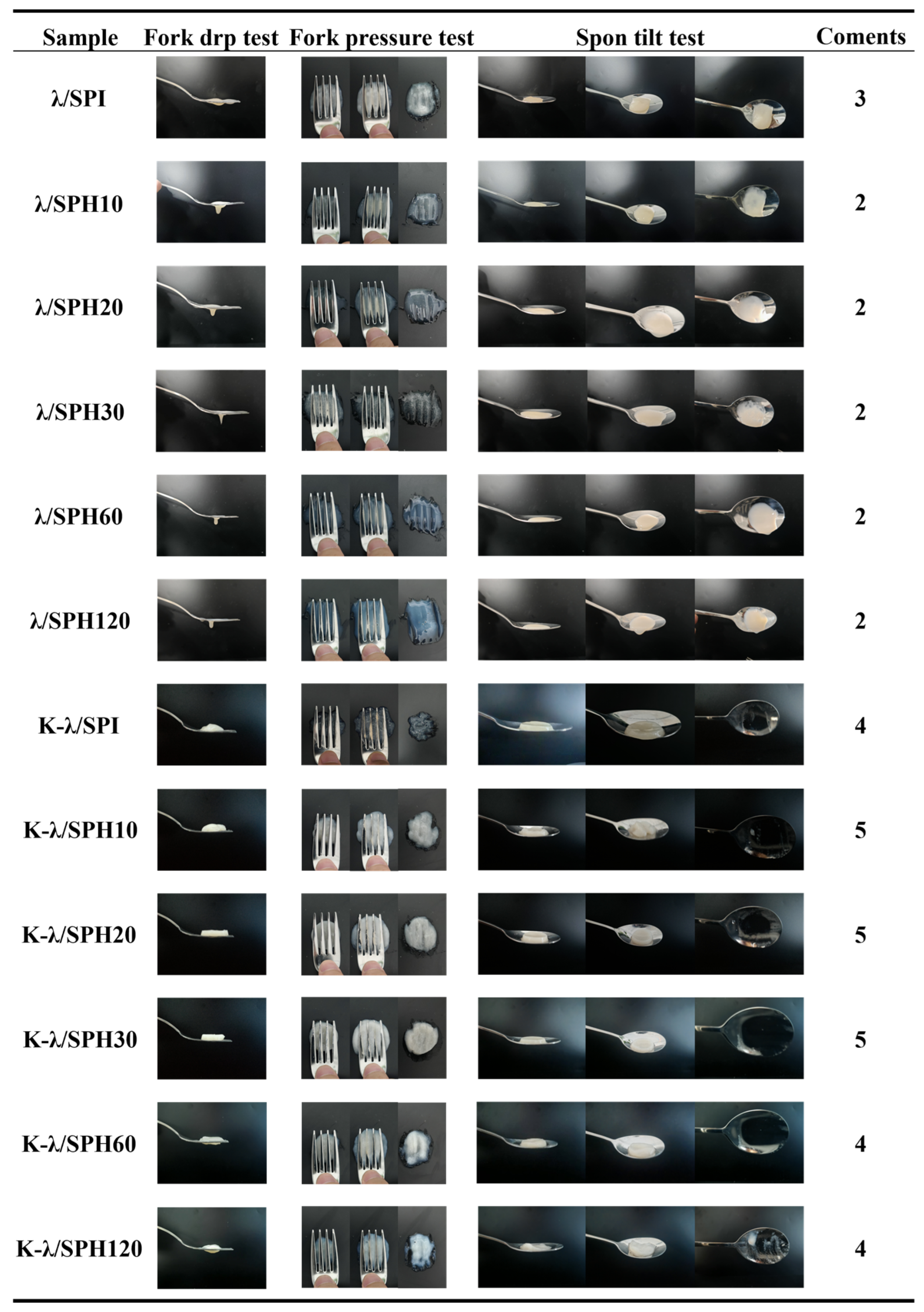
2.16. IDDSI Test
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Protein Hydrolysis
3.1.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH) Analysis
3.1.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis
3.2. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0) Analysis
3.3. Water Holding Capacity (WHC) Analysis
3.4. Color Analysis
3.5. Rheological Analysis
3.5.1. Dynamic Rheological Analysis
3.5.2. Apparent Viscosity Analysis
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
3.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.8. Intermolecular Forces Analysis
3.9. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.10. Elemental Analysis
3.11. IDDSI Analysis
3.12. Mechanisms Proposed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.; Qu, Y.; Hua, X.; Wang, F.; Jia, X.; Yin, L. Recent advances in soybean protein processing technologies: A review of preparation, alterations in the conformational and functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, W. Effects of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on Structure, Properties, and Enzymolysis of Soy Protein Isolate. Molecules 2019, 24, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Gantriis, R.F.; Fraga, P.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Plant-based food and protein trend from a business perspective: Markets, consumers, and the challenges and opportunities in the future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, R.J.S.; Sato, H.H. Antioxidant activities and functional properties of soy protein isolate hydrolysates obtained using microbial proteases. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Boateng, I.D.; Xu, J. How does ultrasound-assisted ionic liquids (UA-ILs) pretreatment affect the functional properties of soy protein hydrolysates? A critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, Z.; Huang, M.; Fan, Q.; Cui, L.; Xie, P.; Liu, L.; Guan, X.; Jin, J.; Jin, Q.; et al. Static stability of partially crystalline emulsions stabilized by milk proteins: Effects of κ-carrageenan, λ-carrageenan, ι-carrageenan, and their blends. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 147, 109387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.; Vilardell, N.; Clavé, P.; Speyer, R. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia 2016, 31, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Kang, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Xu, H. Effect and mechanism of calcium ions on the gelation properties of cellulose nanocrystals-whey protein isolate composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, W.; Henle, J.; Ninham, B.W. ‘Zur Lehre von der Wirkung der Salze’ (about the science of the effect of salts): Franz Hofmeister’s historical papers. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Feng, S.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yu, W.; Ye, Y.N.; An, M.; Qian, J.; Wu, Z.L.; et al. Co-Ion Specific Effect Aided Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Hydrogels toward Extreme Strengthening and Toughening. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 5881–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.; Beaney, T.E. Potassium-enriched salt: A new era for UK salt reduction? Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e436–e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Buren, L.; Dötsch-Klerk, M.; Seewi, G.; Newson, R. Dietary Impact of Adding Potassium Chloride to Foods as a Sodium Reduction Technique. Nutrients 2016, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X. Hydration of Hofmeister ions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 268, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, C.A.; Falshaw, R.; Janaswamy, S. Trivalent Iron Induced Gelation in Lambda-Carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2735–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiong, W. Tailoring the high-protein texture-modified foods for the dysphagia elderly by heating whey protein isolate-pectin complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, C.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Clave, P.; Costa, A.; Assegehegn, G. Nutritional Aspects of Dysphagia Management. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 271–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drudi, F.; Oey, I.; Leong, S.Y.; King, J.; Sutton, K.; Tylewicz, U. New opportunity of using pulsed electric field (PEF) technology to produce texture-modified chickpea flour-based gels for people with dysphagia. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 168, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munialo, C.D.; Kontogiorgos, V.; Euston, S.R.; Nyambayo, I. Rheological, tribological and sensory attributes of texture-modified foods for dysphagia patients and the elderly: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Xu, T.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, Q.; Lian, Z.; Tian, T.; Tong, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Combination and precipitation mechanism of soy protein and tea polyphenols. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved Method for Determining Food Protein Degree of Hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Liao, P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, T.; Tong, X.; Lyu, B.; Cheng, L.; Miao, L.; Qi, W.; Jiang, L.; et al. Soy protein isolate-catechin non-covalent and covalent complexes: Focus on structure, aggregation, stability and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of flexibility and surface hydrophobicity on emulsifying properties: Ultrasound-treated soybean protein isolate. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 142, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Zeng, Z.; Xiang, C.; Huang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, R. Solar-driven scalable hygroscopic gel for recycling water from passive plant transpiration and soil evaporation. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Xue, H.; Hu, X.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Combined effects of NaOH, NaCl, and heat on the gel characteristics of duck egg white. LWT 2022, 159, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Xu, T.; Su, R.; Dai, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Yang, B.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Composite gel based on κ-carrageenan-soybean isolate protein/soy protein fibrils: Focus on structural differences and gel properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, X.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Soy glycinin-carboxymethyl cellulose “chain bead-like” nanocomplexes: Focus on formation mechanism, functional characteristics and stability properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Lian, Z.; Qi, W.; Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Tian, T.; Lyu, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Non-covalent interaction of soy protein isolate and catechin: Mechanism and effects on protein conformation. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, K.; Zhu, F.; Wang, G.; Xi, G.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, B.; Xie, F. Revealing the role of λ-carrageenan on the enhancement of gel-related properties of acid-induced soy protein isolate/λ-carrageenan system. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Zainudin, B.H.; Yaakob, A.S. Method validation and determination of heavy metals in cocoa beans and cocoa products by microwave assisted digestion technique with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.Y.; Lam, P.; Steele, C.M.; Hanson, B.; Chen, J.; Dantas, R.O.; Duivestein, J.; Kayashita, J.; Lecko, C.; Murray, J.; et al. Development of International Terminology and Definitions for Texture-Modified Foods and Thickened Fluids Used in Dysphagia Management: The IDDSI Framework. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bi, J.; Nicolas, J.; Christophe, B.; Wang, F.; Lyu, J. Dysphagia food: Impact of soy protein isolate (SPI) addition on textural, physicochemical and microstructural properties of peach complex gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, N.; Ren, K.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, S.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Utilization of self-assembled soy protein nanoparticles as carriers for natural pigments: Examining non-interaction mechanisms and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Xu, F.; Zhong, F. Improvement of the encapsulation capacity and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate through controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Kong, Y.; Kang, Z.; Xie, F.; Sun, L. Formation of thermal-induced microgels from soy protein hydrolysates: Effects of selective proteolysis on glycinin/(3-conglycinin (3-conglycinin)). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Structural insights into acidic heating-induced amyloid fibrils derived from soy protein as a function of protein concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Romero, H.M. Exploring the structure-function relationship of Great Northern and navy bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein hydrolysates: A study on the effect of enzymatic hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, M.; Sathe, S.K. Interactions with 8-Anilinonaphthalene-1-Sulfoniac Acid (ANS) and Surface Hydrophobicity of Black Gram (Vigna mungo) Phaseolin. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Lv, D. Effects of pH-shifting combined with ion immersion on gel properties and protein aggregation behavior of soybean protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Mu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Ran, R. Strong Tough Conductive Hydrogels via the Synergy of Ion-Induced Cross-Linking and Salting-Out. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Nakajima, T.; Hisamatsu, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Phase-Separation-Induced Anomalous Stiffening, Toughening, and Self-Healing of Polyacrylamide Gels. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6990–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.L.; Mawad, D.; Dokos, S.; Sorrell, C.C. Comparative Bioactivities of Chemically Modified Fucoidan and λ-Carrageenan toward Cells Encapsulated in Covalently Cross-Linked Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 3131–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; Din, Z.-u.; Huang, Q.; Liu, R. Influence of okara dietary fiber with varying particle sizes on gelling properties, water state and microstructure of tofu gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wu, S.; Fang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bilal, M.; Shen, S.; Xie, C.; Wang, P.; Yang, R. Glucono-δ-lactone-induced gel fabrication of soybean protein isolate derived from germinated soybean: Focusing on protein aggregation and gelation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 169, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.K.W.; Chung, C.; Ogren, T.; Mutilangi, W.; McClements, D.J. Extending protein functionality: Microfluidization of heat denatured whey protein fibrils. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Bai, Q.; Qin, Y.; Liang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Luan, G. Film-forming properties and mechanisms of soy protein: Insights from β-conglycinin and glycinin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Yi, S.; Li, J. Improvement of the gel properties and flavor adsorption capacity of fish myosin upon yeast ß-glucan incorporation. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Wu, D.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Meng, D.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Q. Rheological and textural properties of acid-induced soybean protein isolate gel in the presence of soybean protein isolate hydrolysates or their glycosylated products. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shi, P.; Fan, F.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Corrigendum to “Hofmeister effect-assisted one step fabrication of fish gelatin hydrogels” [Food Science and Technology, 121 (2020) 108973]. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, O.; Bolivar-Prados, M.; Arreola, V.; Nascimento, W.V.; Tomsen, N.; Gallegos, C.; Brito-de La Fuente, E.; Clave, P. Therapeutic Effect, Rheological Properties and α-Amylase Resistance of a New Mixed Starch and Xanthan Gum Thickener on Four Different Phenotypes of Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Lou, F.; Sun, F.; Gong, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Soy protein isolate gel improved with carrageenan-assisted limited enzymatic hydrolysis: Gelation properties and binding abilities with selected flavour compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, Y. A review of inhibition mechanisms of surimi protein hydrolysis by different exogenous additives and their application in improving surimi gel quality. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 140002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Xia, N.; Chuang, R.; Rayan, A.M.; et al. Elucidating the mechanism by which hofmeister anions influence rheological properties and microstructure of egg yolk low-density lipoprotein/κ-carrageenan double-network hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Yanxin, L.; Xie, X.-a.; Li, P.; Du, B.; Li, L. Effect of different valence metal cations on the gel characteristics and microstructure of Inca peanut albumin gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Teng, Q.; Qian, S.; Liu, T.; Long, S.; Li, Z.; Tao, J.; Li, X. Synergistically Toughening Non-Neutral Polyampholyte Hydrogels by Ionic and Coordination Bonds at Low Metal-Ion Contents. Small 2025, 21, 2500258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lian, Z.; Cheng, L.; Liu, X.; Dai, S.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Insight into succinylated modified soy protein isolate-sodium alginate emulsion gels: Structural properties, interactions and quercetin release behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Elucidating the effect of the Hofmeister effect on formation and rheological properties of soy protein/κ-carrageenan hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Tu, Y. Effects of copper ions on the characteristics of egg white gel induced by strong alkali. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 4116–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Ho, H.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, M. Effects of ultrafine comminution treatment on gelling properties of myofibrillar proteins from chicken breast. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilloni, C.; Bonetti, D.; Morrone, A.; Giri, R.; Dobson, C.M.; Brunori, M.; Gianni, S.; Vendruscolo, M. Towards a structural biology of the hydrophobic effect in protein folding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ratcliffe, I.; Williams, P.A.; Luo, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. The influence of pH and monovalent ions on the gelation of pectin from the fruit seeds of the creeping fig plant. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Lv, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Sun, B. Effect of Na+ and Ca2+on the texture, structure and microstructure of composite protein gel of mung bean protein and wheat gluten. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.A.; Anema, S.G.; Havea, P.; Guyomarc’h, F.; Wong, M. Effect of adding low levels of β-mercaptoethanol on the disulphide bonds of κ-casein and β-lactoglobulin solutions. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 26, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xia, J.; Wei, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, N. Preparation, characterization, and foaming properties of soy protein nanoparticles by the cross-linking reaction induced by microbial transglutaminase. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Filho, G.; de Assuncao, R.M.N.; Vieira, J.G.; da Silva Meireles, C.; Cerqueira, D.A.; da Silva Barud, H.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Messaddeq, Y. Characterization of methylcellulose produced from sugar cane bagasse cellulose:: Crystallinity and thermal properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kang, H.; Feng, X.; Lian, X.; Li, L. The interaction of sweet potato amylose/amylopectin and KCl during drying. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hu, O.; Hou, L.; Ye, D.; Weng, S.; Jiang, X. Highly tough and ionic conductive starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels based on a universal soaking strategy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.-F.; Pan, M.-K.; Liu, Y.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.-H. Effects of Na+ on the cold gelation between a low-methoxyl pectin extracted from Premna microphylla turcz and soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Dao, L.-P.; Guo, Q.-Y.; Chen, T.-L.; Fu, L.-J.; Zhou, F.-C.; Yuan, Y. Investigation on the influence of AC electric filed and KCl on the structure and gel properties of Konjac glucomannan. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, T.; Theiner, S.; Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Vanhaecke, F.; Koellensperger, G. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xia, F. Role of a high calcium ion content in extending the properties of alginate dual-crosslinked hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25390–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Niu, G.; Gao, K.; Liu, X. Effects of hsian-tsao polysaccharide on myosin gel structure and its binding capacity to flavor compounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.-S.; Girard, M.; Therriault, D.; Heuzey, M.-C. 3D printed protein/polysaccharide food simulant for dysphagia diet: Impact of cellulose nanocrystals. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| GEL | L* | a* | b* | WI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ/SPI | 29.07 ± 0.49 g | −0.3 ± 0.056 a′ | 2.53 ± 0.533 C | 29.02 ± 0.493 G′ |
| λ/SPH10 | 31.23 ± 1.714 f | −0.82 ± 0.06 b′c′d′ | 2.91 ± 0.106 B | 31.17 ± 1.71 F′ |
| λ/SPH20 | 30.44 ± 0.638 f | −0.79 ± 0.04 b′c′ | 2.16 ± 0.132 D | 30.4 ± 0.642 F′ |
| λ/SPH30 | 30.59 ± 0.964 f | −0.21 ± 0.537 a′ | 5.37 ± 0.122 A | 30.38 ± 0.957 F′ |
| λ/SPH60 | 34.89 ± 0.182 d | −0.97 ± 0.006 c′d′ | 1.30 ± 0.076 F | 34.87 ± 0.181 D′ |
| λ/SPH120 | 40.67 ± 1.247 a | −1.98 ± 0.015 g′ | −0.73 ± 0.102 H | 40.63 ± 1.245 A′ |
| K-λ/SPI | 33.57 ± 0.346 e | −0.62 ± 0.015 b′ | 1.71 ± 0.087 E | 33.55 ± 0.344 E′ |
| K-λ/SPH10 | 35.04 ± 0.346 d | −1.24 ± 0.012 e′f′ | −0.56 ± 0.118 H | 35.02 ± 0.346 D′ |
| K-λ/SPH20 | 34.98 ± 0.410 d | −1.38 ± 0.026 f′ | −1.25 ± 0.060 IJ | 34.95 ± 0.409 D′ |
| K-λ/SPH30 | 38.02 ± 0.455 c | −1.05 ± 0.055 d′e′ | 0.78 ± 0.078 G | 38.01 ± 0.457 D′ |
| K-λ/SPH60 | 35.84 ± 0.201 d | −1.41 ± 0.035 f′ | −1.16 ± 0.049 I | 35.82 ± 0.200 D′ |
| K-λ/SPH120 | 39.40 ± 0.682 b | −2.07 ± 0.067 g′ | −1.49 ± 0.121 J | 39.35 ± 0.682 B′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Dai, S.; Tang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Xie, J.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Salting-Out Effect Behavior of Protein/λ-Carrageenan Composite Gels Enhanced by Enzymatic Pretreatment: Focusing on Microstructure, Interactions and the Potential for Dysphagia Food. Foods 2025, 14, 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213662
Yang B, Dai S, Tang Y, Xu T, Wang J, Zhu W, Xie J, Tong X, Wang H, Jiang L. Salting-Out Effect Behavior of Protein/λ-Carrageenan Composite Gels Enhanced by Enzymatic Pretreatment: Focusing on Microstructure, Interactions and the Potential for Dysphagia Food. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213662
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bowen, Shicheng Dai, Yaqi Tang, Tianhe Xu, Junzheng Wang, Weixiang Zhu, Junfeng Xie, Xiaohong Tong, Huan Wang, and Lianzhou Jiang. 2025. "Salting-Out Effect Behavior of Protein/λ-Carrageenan Composite Gels Enhanced by Enzymatic Pretreatment: Focusing on Microstructure, Interactions and the Potential for Dysphagia Food" Foods 14, no. 21: 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213662
APA StyleYang, B., Dai, S., Tang, Y., Xu, T., Wang, J., Zhu, W., Xie, J., Tong, X., Wang, H., & Jiang, L. (2025). Salting-Out Effect Behavior of Protein/λ-Carrageenan Composite Gels Enhanced by Enzymatic Pretreatment: Focusing on Microstructure, Interactions and the Potential for Dysphagia Food. Foods, 14(21), 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213662