Development and Structural Characterization of Pullulan/Lecithin/Zein Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Mountain Germander (Teucrium montanum) Polyphenolic Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Characterization of Mountain Germander Polyphenolic Extract
2.3.1. Extract Preparation
2.3.2. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.3.3. HPLC-UV-DAD Quantification of Phenylethanoid Glycosides (PGs)
2.4. Preparation of Solutions and Electrospinning Performance
2.5. Physical Properties of Polymer Solutions
2.6. Viscosity Curve and Rheological Tests of Polymer Solutions
2.7. Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers
2.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.7.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FT-IR) Analysis
2.7.3. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.7.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7.5. Encapsulation Efficiency (%)
2.7.6. Zeta Potential
2.7.7. In Vitro Digestion
2.7.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Properties of Polymer Solutions
3.2. Viscosity Curves and Rheological Characterization of Polymer Solutions
3.3. Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibers
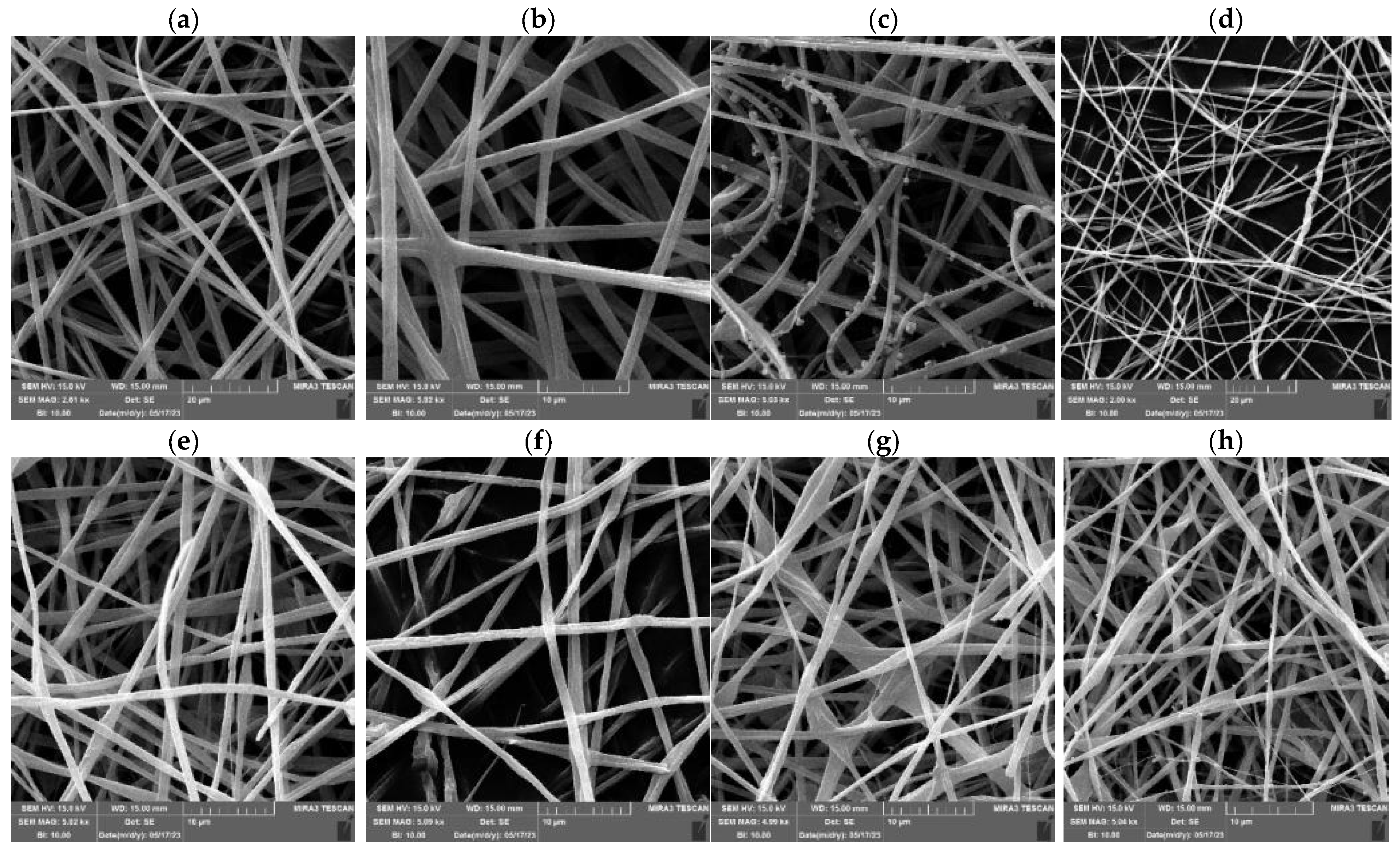
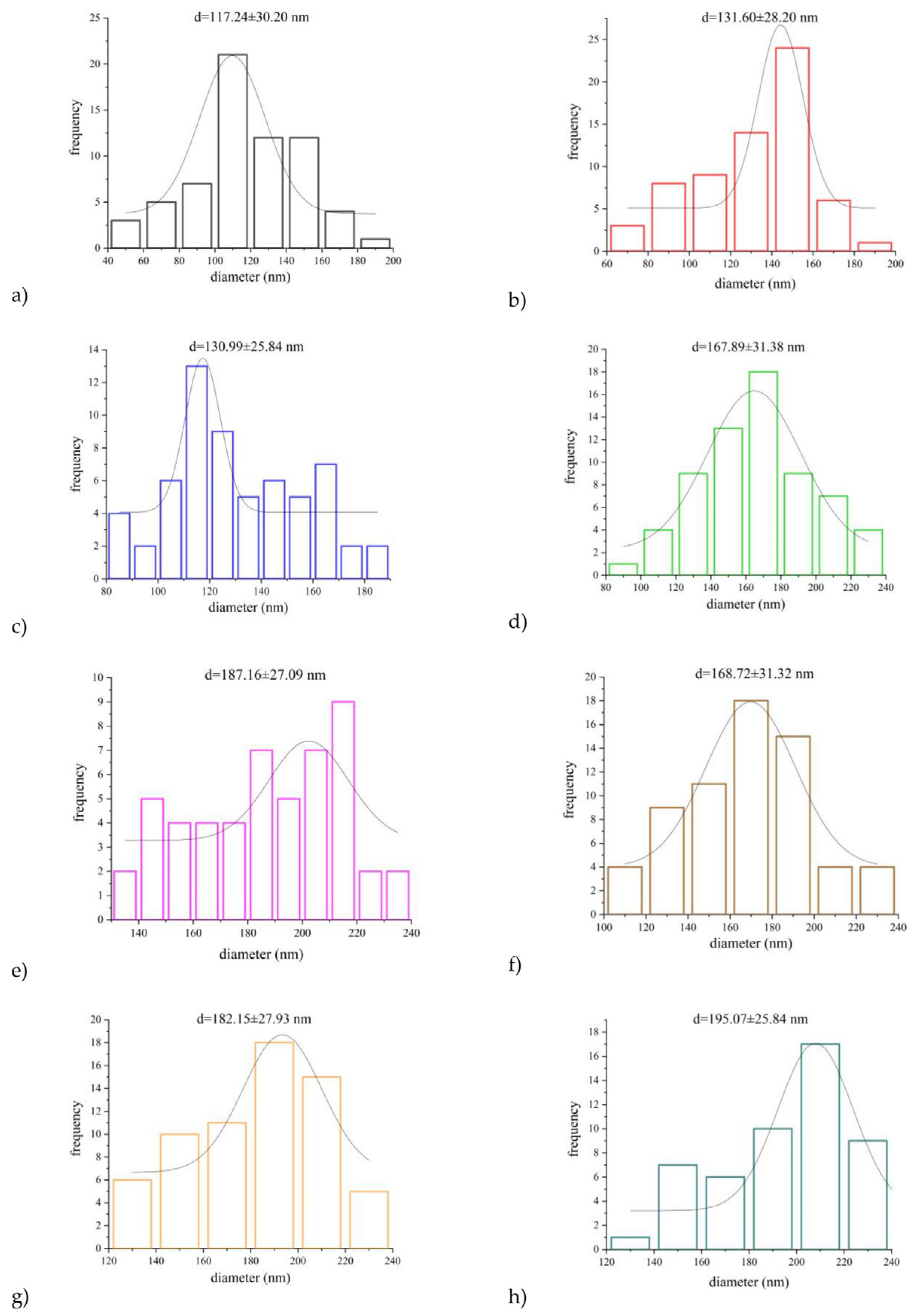
3.3.1. The Effect of the PUL:ZE Ratio on Nanofibers’ Morphology
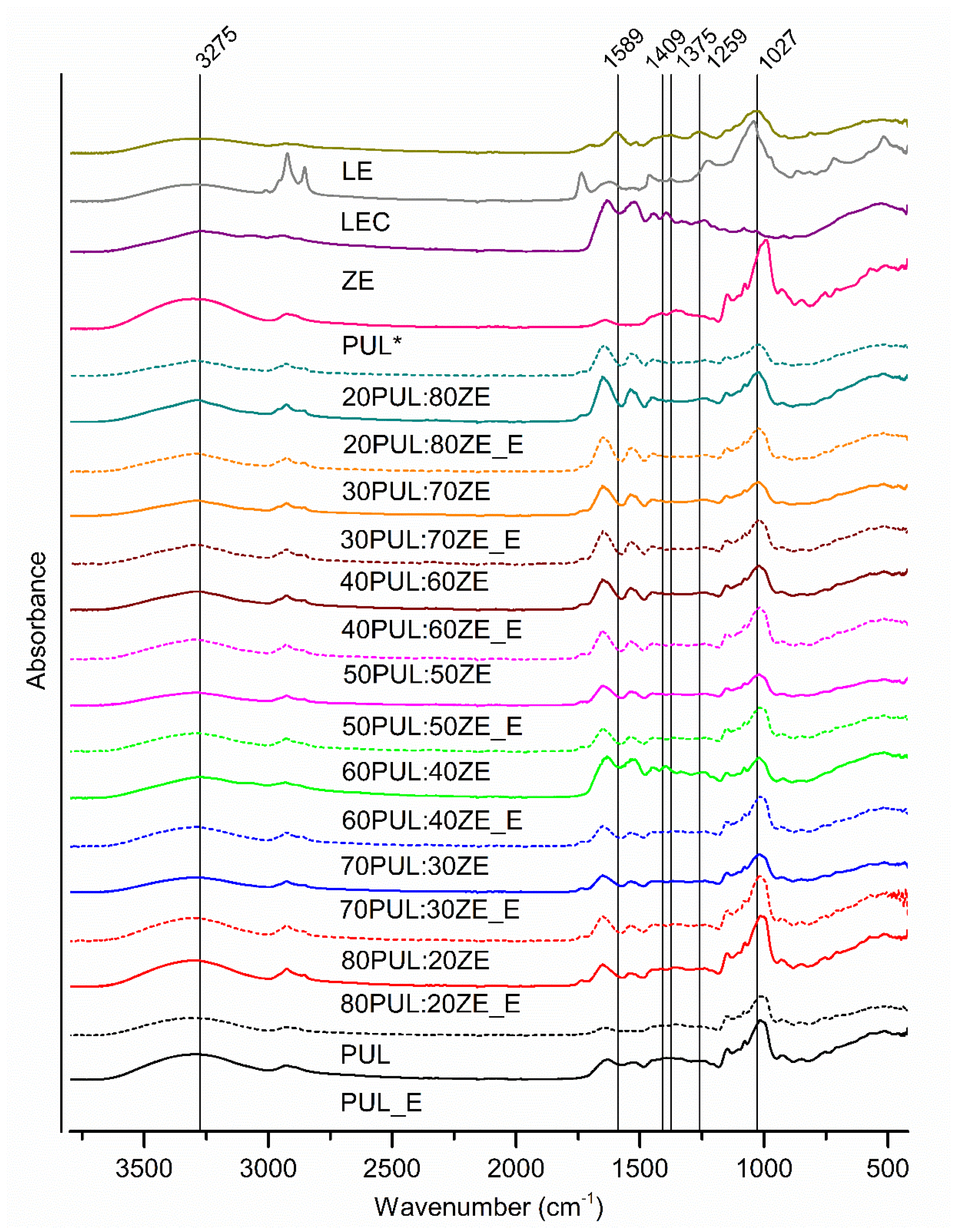
3.3.2. Characterization of Functional Groups and Their Interactions
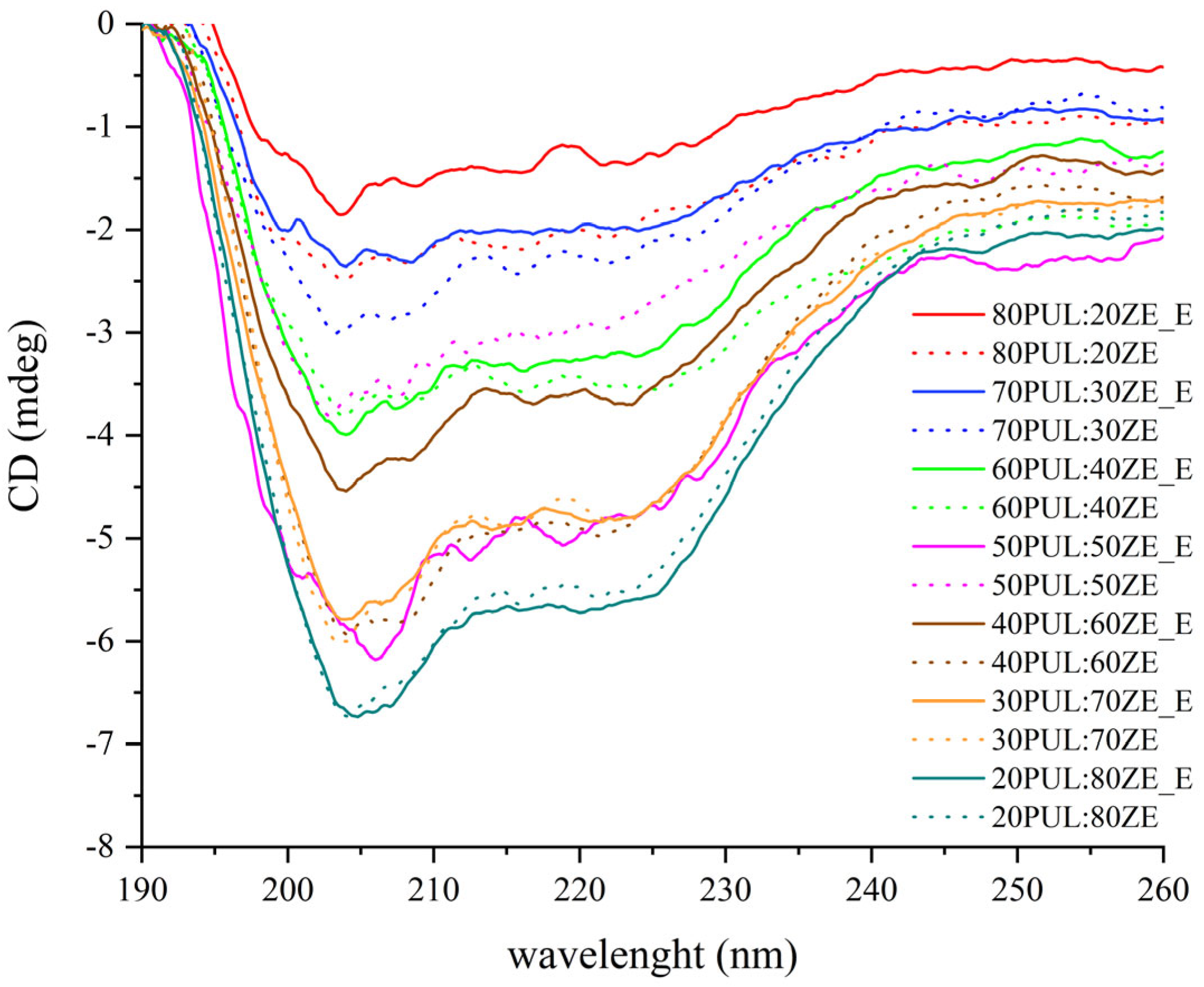
3.3.3. The Effect of Polyphenolic Extract on Secondary Conformation Change
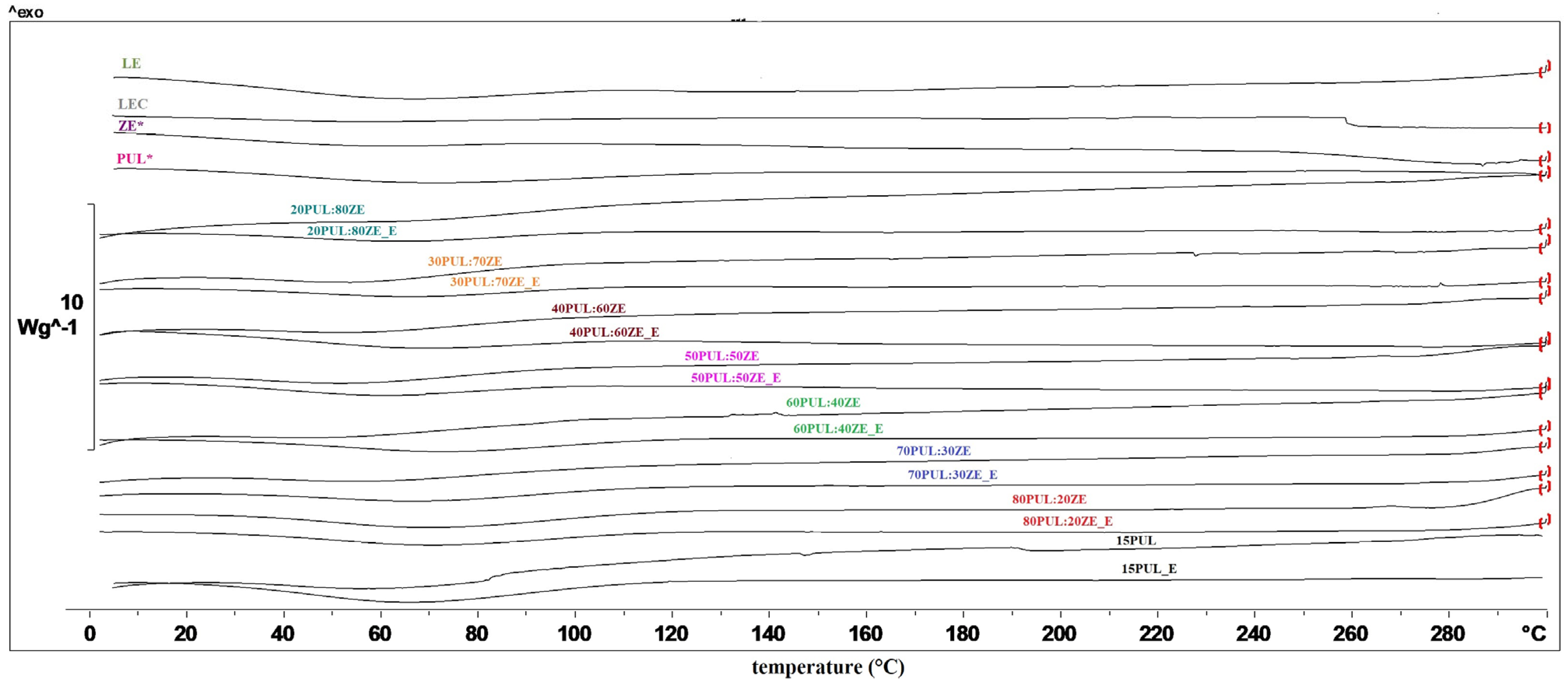
3.3.4. Thermal Properties of Electrospun Nanofibers
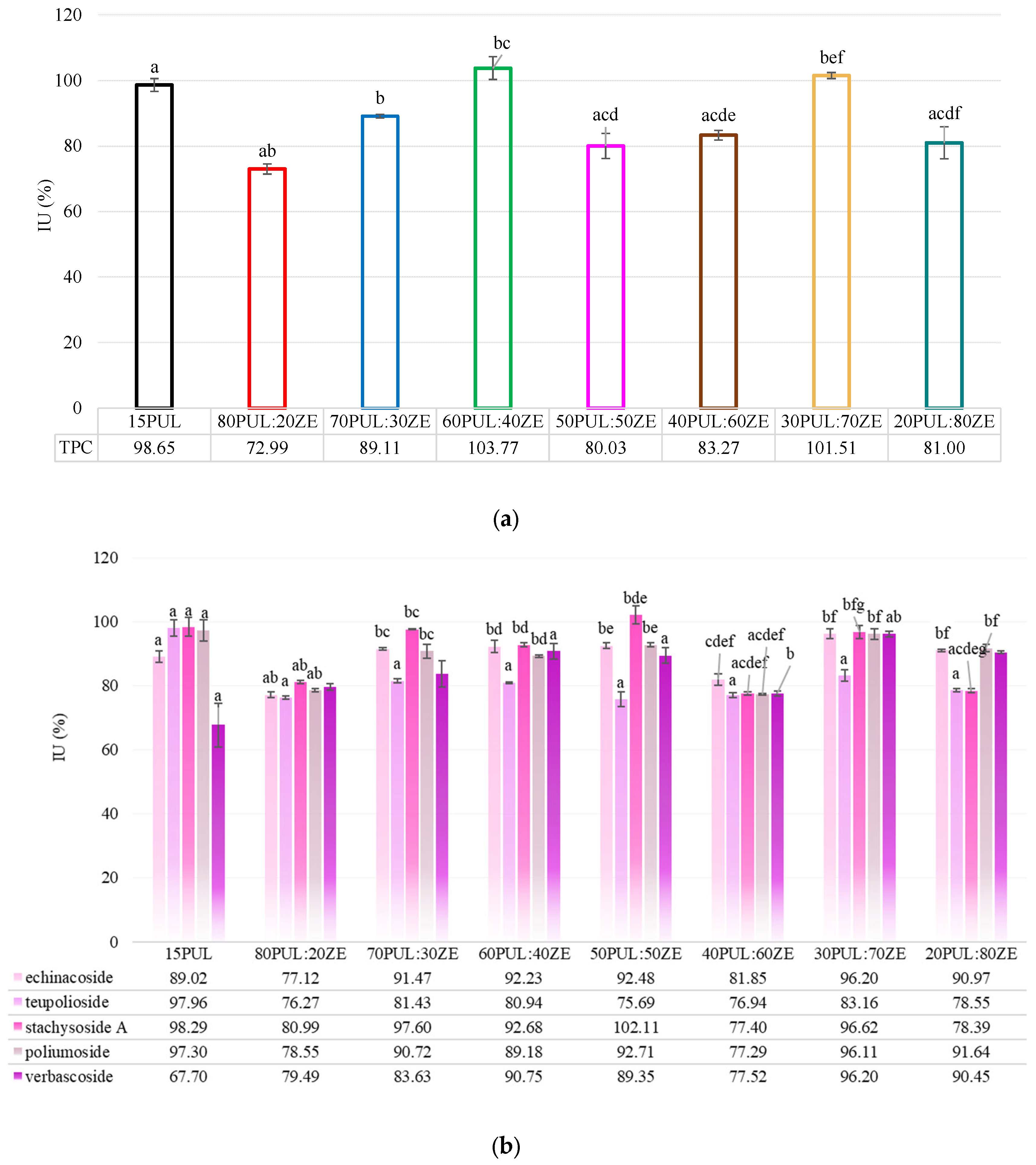
3.3.5. Encapsulation Efficiency of Electrospun Nanofibers
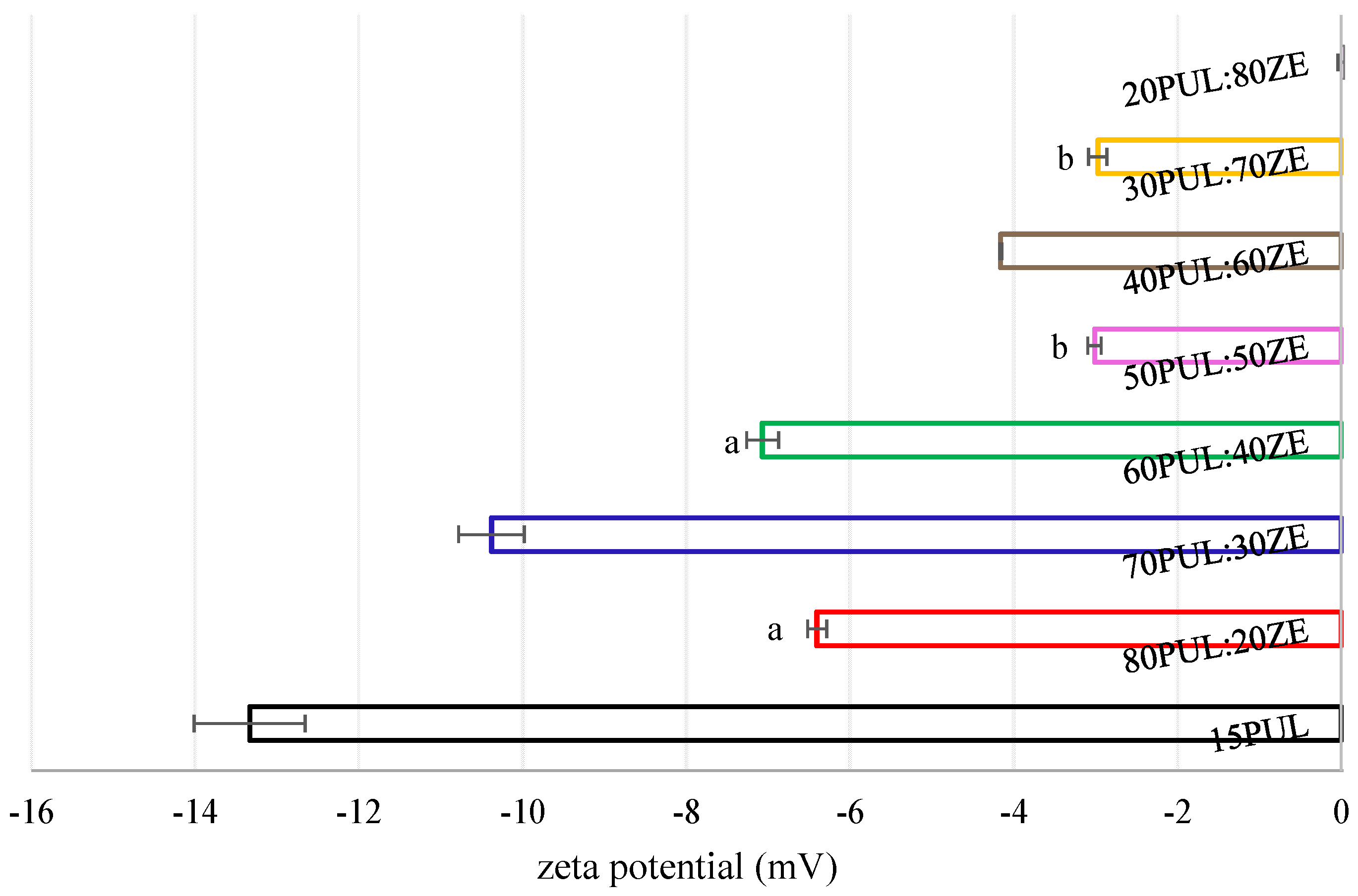
3.3.6. Zeta Potential of Electrospun Nanofibers
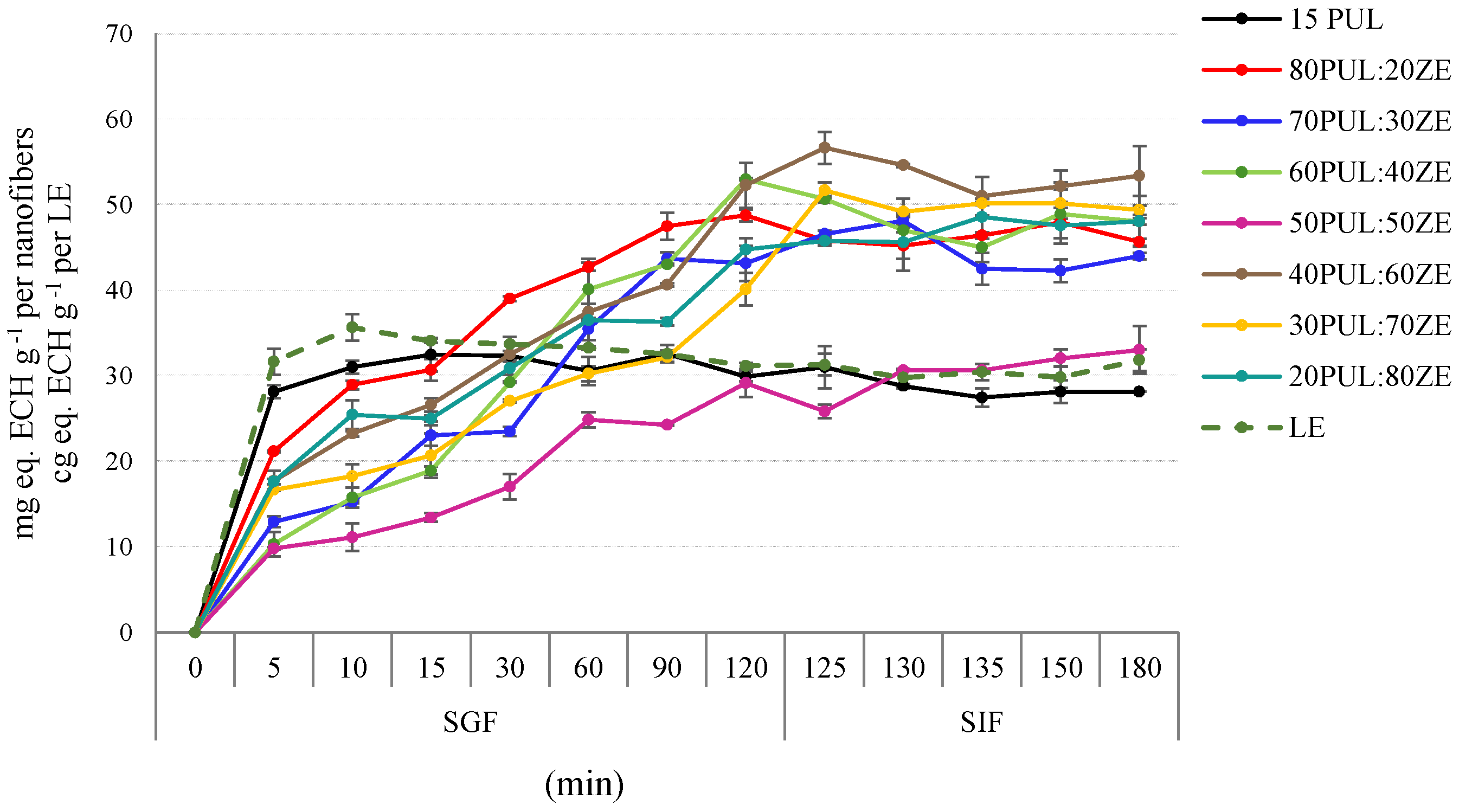
3.3.7. In Vitro Kinetic Release of Polyphenols
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Research and Markets. Plant Extracts Industry Report 2025–2034|Market Growth, Competitive Landscape, Opportunities, and Challenges—Clean-Label Trends Boost Adoption of Nutraceuticals and Supplements. GlobeNewswire. 2025. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/06/30/3107279/0/en/Plant-Extracts-Industry-Report-2025-2034-Market-Growth-Competitive-Landscape-Opportunities-and-Challenges-Clean-Label-Trends-Boost-Adoption-of-Nutraceuticals-and-Supplements.html (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Jafari, S.M.; McClements, D.J. Nanotechnology Approaches for Increasing Nutrient Bioavailability. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Potentials and Perspectives for Active Food Packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.; Xu, C.; Yu, W.; Yu, H.; Feng, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Hou, J.; et al. Enhanced Viability of Probiotics Encapsulated within Synthetic/Natural Biopolymers by the Addition of Gum Arabic via Electrohydrodynamic Processing. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, A.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning of Bilayer Emulsions: The Role of Gum Arabic as a Coating Layer in the Gelatin-Stabilized Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kang, S.; Yu, D.G.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. A Sequential Electrospinning of a Coaxial and Blending Process for Creating Double-Layer Hybrid Films to Sense Glucose. Sensors 2023, 23, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwesh, A.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Aghda, N.H.; Alkadi, F.; Maniruzzaman, M. Advanced 3D Electrospinning “Xspin” System: Fabrication of Bifiber Floating Oral Pharmaceutical Scaffolds for Controlled Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, L.; Xia, T.; Dong, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, C.; Xia, H. Janus Silk Fibroin/Polycaprolactone-Based Scaffold with Directionally Aligned Fibers and Porous Structure for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129927. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, Q.; Gao, J.; Luo, X.; Song, Y.; Li, T.; Luo, Z. Effects of Zein–Lecithin–EGCG Nanoparticle Coatings on Postharvest Quality and Shelf Life of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica). LWT 2023, 182, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Jiang, Y.; Junejo, S.A.; Jia, X.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q. Metal-Anchored Oxidized Starch–Pullulan Nanofiber Films Enhance Ethylene Adsorption and Banana Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Yu, Y.T.; Chang, K.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Hsieh, L.S. Enhanced Stability of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase via Electrospinning for Enzyme Immobilization. Polymers 2025, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghaee, R.; Ariaii, P. Development of Electrospun Whey Protein Isolate Nanofiber Mat for Omega-3 Nanoencapsulation: Microstructural and Physical Property Analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Han, J.; Zhang, L. Improvement in Probiotic Intestinal Survival by Electrospun Milk Fat Globule Membrane–Pullulan Nanofibers: Fabrication and Structural Characterization. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.M.; Siqueira, N.M.; Prabhakaram, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning and Electrospray of Bio-Based and Natural Polymers for Biomaterials Development. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovatti, E.; Fernandes, S.C.; Rubatat, L.; da Silva Perez, D.; Freire, C.S.; Silvestre, A.J.; Neto, C.P. Pullulan–Nanofibrillated Cellulose Composite Films with Improved Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S.; Saini, G.K.; Kennedy, J.F. Pullulan Production in Stirred Tank Reactor by a Colour-Variant Strain of Aureobasidium pullulans FB-1. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Gao, Q. Effect of Amylose Content on the Preparation for Carboxymethyl Starch/Pullulan Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Properties as Encapsulants of Thymol. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Kong, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Fabrication and Characterization of Crosslinked Pea Protein Isolate/Pullulan/Allicin Electrospun Nanofiber Films as Potential Active Packaging Material. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Gholizadeh, S.; Ebrahimi, A.; Almasi, H.; Hamishehkar, H.; Taheri, R.A. Development and Characterization of the Carvone-Loaded Zein/Pullulan Hybrid Electrospun Nanofibers for Food and Medical Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Dietary Protein–Phenolic Interactions: Characterization, Biochemical–Physiological Consequences, and Potential Food Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3589–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, Y.; Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Tea Polyphenols Coating on Zein Nanoparticles to Encapsulate β-Carotene by Anti-Solvent Precipitation Method. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, S.; Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. A Novel Bilayer Zein/MMT Nanocomposite Incorporated with Hypericum perforatum Oil for Wound Healing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumedi, F.; Aran, M.; Miri, M.A.; Seyedabadi, E. Preparation and Characterization of Zein Electrospun Fibers Loaded with Savory Essential Oil for Fruit Preservation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 203, 117121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Surendhiran, D.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Biodegradable Zein Active Film Containing Chitosan Nanoparticle Encapsulated with Pomegranate Peel Extract for Food Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, X.; Cao, C.; Lv, Z.; Han, C.; Guo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, J. Improved Antioxidant Activities of Edible Films by Curcumin-Containing with Zein/Polysaccharide. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhan, L.; Shao, P.; Xiang, N.; Sun, P.; Chen, H.; Gao, H. Electrospinning of Zein–Ethyl Cellulose Hybrid Nanofibers with Improved Water Resistance for Food Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, K.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Xia, G. Effects of the Acetic Acid–Water Ratio and Zein Concentration on Solution Blow Spinning: Influence on Solution Properties and Film Characterization. Food Chem. 2025, 492, 145545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Feng, B.; Du, S. Effect of Emulsifier on Formation of Zein-Based Composite Nanoparticles: Structure and Stability. LWT 2024, 214, 117094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.C.; Razzak, M.A.; Ho, T.C.; Surendhiran, D.; Park, J.S.; Chun, B.S. Fabrication of Zein and κ-Carrageenan Colloidal Particles for Encapsulation of Quercetin: In vitro Digestibility and Bio-Potential Activities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 111, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Han, W.; Han, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Q. Fabrication and Characterization of Zein–Sodium Alginate Complex Nanoparticles as an Effective Naringenin Delivery System: Physicochemical Stability, Solubility, and Antioxidant Activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 386, 122569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Luo, X.; Fan, F.; Sun, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Fang, Y. Zein and Gum Arabic Nanoparticles: Potential Enhancers of Immunomodulatory Functional Activity of Selenium-Containing Peptides. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 9972–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Y.; Cai, W.Q.; Luo, X.T.; Su, B.L.; Xiao, J.W.; Zhang, G.R.; Zhang, B.B. Delivery of Natural Monascus Yellow Pigment Using Zein–Lecithin Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Characterization, and In vitro Release Properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 197, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Zein–Lecithin–Total Flavonoids from Smilax glabra Complex Nanoparticles and the Study of Their Antioxidant Activity on HepG2 Cells. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, J.; Tian, Q.; Zang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, B. Improved Uptake of Anthocyanins-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Phenolic Acid–Grafted Zein and Lecithin. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Ni, F.; Luo, X.; Luo, Z. Fabrication of Zein–Lecithin–EGCG Complex Nanoparticles: Characterization and Controlled Release in Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savić, J.; Mačukanović-Jocić, M.; Jarić, S. Medical Ethnobotany on the Javor Mountain (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 27, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatković, B.K.; Bogosavljević, S.S.; Radivojević, A.R.; Pavlović, M.A. Traditional Use of the Native Medicinal Plant Resource of Mt. Rtanj (Eastern Serbia): Ethnobotanical Evaluation and Comparison. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šarić-Kundalić, B.; Dobeš, C.; Klatte-Asselmeyer, V.; Saukel, J. Ethnobotanical Study on Medicinal Use of Wild and Cultivated Plants in Middle, South and West Bosnia and Herzegovina. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatiha, B.A.; Ouafae, B.; Souad, S.; Fatima, E.H.; Jamila, D.; Allal, D.; Lahcen, Z. Ethnobotany Study of Medicinal Plants Used in the Treatment of Respiratory Diseases in the Middle Region of Oum Rbai. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 238815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Riguera, R. Phenylethanoid Glycosides in Plants: Structure and Biological Activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1994, 11, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shen, L.; Contreras, J.M.; Liu, Z.; Ma, K.; Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. New Potential Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators in Traditional Chinese Medicine for Treating Menopausal Syndrome. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 4736–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.B.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.Z. Chemical Profiling and Tyrosinase Inhibition Mechanism of Phenylethanoid Glycosides from Corallodiscus flabellatus. Molecules 2025, 30, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongkitwitoon, B.; Putalun, W.; Triwitayakorn, K.; Kitisripanya, T.; Kanchanapoom, T.; Boonsnongcheep, P. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Verbascoside- and Isoverbascoside-Rich Lamiales Medicinal Plants. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.A.; Fernandes, D.A.; da Fonseca, T.S.; Campos, M.F.; Jural, P.A.; Toledo e Silva, M.V.; Constant, L.E.C.; da Veiga, A.A.S.; Ferreira, B.R.; Magalhães, E.S.; et al. Plant Metabolites as In vitro Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Targets: A Systematic Review and Computational Analysis. Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, M.; El-Newary, S.A.; Aati, H.Y.; Wei, B.; Seif, M.; Ibrahim, A.Y. Anti-Alzheimer’s Potency of Rich Phenylethanoid Glycosides Extract from Marrubium vulgare L.: In vitro and In Silico Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Georgiev, M.I.; Cao, H.; Nahar, L.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Sarker, S.D.; Lu, B. Therapeutic Potential of Phenylethanoid Glycosides: A Systematic Review. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2605–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandura Jarić, A.; Šeremet, D.; Vojvodić Cebin, A.; Jokić, S.; Komes, D. The Multiple-Response Modeling of Heat-Assisted, Microwave-Assisted and Subcritical Water Extraction on Selected Phenolics from Traditional Plant Species Teucrium montanum. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 52, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandura Jarić, A.; Čikoš, A.; Pocrnić, M.; Aladić, K.; Jokić, S.; Šeremet, D.; Vojvodić Cebin, A.; Komes, D. Teucrium montanum L.—Unrecognized Source of Phenylethanoid Glycosides: Green Extraction Approach and Elucidation of Phenolic Compounds via NMR and UHPLC-HR MS/MS. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmore, J.M. Animal Polymer—AOAC Official Method 930.15—Moisture in Animal Polymer. In Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Helrich, K., Ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static In vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Luo, C.J. Monoaxial Electrospinning. In Nanofibers in Drug Delivery; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 60–96. [Google Scholar]
- Seethu, B.G.; Pushpadass, H.A.; Emerald, F.M.E.; Nath, B.S.; Naik, N.L.; Subramanian, K.S. Electrohydrodynamic Encapsulation of Resveratrol Using Food-Grade Nanofibers: Process Optimization, Characterization and Fortification. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2020, 13, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ahmed, I.; Rudd, C.; Liu, X. Rheological, Surface Tension and Conductivity Insights on the Electrospinnability of Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid)-Hyaluronic Acid Solutions and Their Correlations with the Nanofiber Morphological Characteristics. Polymers 2022, 14, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceituno-Medina, M.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Mendoza, S.; Lagaron, J.M. Development of Novel Ultrathin Structures Based in Amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) Protein Isolate through Electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Lim, T.C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, A. A Novel Electrospun Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose/Polyethylene Oxide Blend Nanofibers: Morphology and Physicochemical Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 181, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradzielski, M. Polymer–Surfactant Interaction for Controlling the Rheological Properties of Aqueous Surfactant Solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 63, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Saadi, A.; Fu, K.; Taxipalati, M.; Deng, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Dextran/Zein Hybrid Electrospun Fibers with Tailored Properties for Controlled Release of Curcumin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6355–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Que, F.; Kang, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Characterization of Gelatin/Zein Nanofibers by Hybrid Electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.; Reneker, D.H. Flat Polymer Ribbons and Other Shapes by Electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Vázquez, G.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Mendoza, S. Electrospun Fibers from Blends of Pea (Pisum sativum) Protein and Pullulan. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Barker, S.A.; Belton, P.S.; Craig, D.Q.M. A Spectroscopic and Thermal Investigation into the Relationship between Composition, Secondary Structure and Physical Characteristics of Electrospun Zein Nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. Electrospinning of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Boger Fluids to Understand the Role of Elasticity on Morphology of Nanofibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Hernandez, D.R.; Cardenas-Benitez, B.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Bonilla-Rios, J. Tailoring the Diameters of Electro-Mechanically Spun Fibers by Controlling Their Deborah Numbers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Yeum, J.H. Electrospun Pullulan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Silver Hybrid Nanofibers: Preparation and Property Characterization for Antibacterial Activity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 36, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, H.; Feng, Z.; Yu, W.; Gu, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Electro-Encapsulation of Probiotics in Gum Arabic-Pullulan Blend Nanofibers Using Electrospinning Technology. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 111, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Y.; Jia, X.W.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H.; Wang, H. Fast Dissolving Oral Films for Drug Delivery Prepared from Chitosan/Pullulan Electrospinning Nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Xiao, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and Thermal Stability of β-Cyclodextrin/Soybean Lecithin Inclusion Complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, T.; Uka, D.; Holló, B.B.; Jović, B.; Kordić, B.; Popović, B.M. Comprehensive Physicochemical Evaluation of Choline Chloride-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 116968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Non-Covalent Interactions between Proteins and Polysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râpă, M.; Gaidau, C.; Mititelu-Tartau, L.; Berechet, M.D.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Rosca, I.; Chiriac, A.P.; Matei, E.; Predescu, A.M.; Predescu, C. Bioactive Collagen Hydrolysate-Chitosan/Essential Oil Electrospun Nanofibers Designed for Medical Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M.; Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C. Protein–Polysaccharide Interactions: Phase-Ordering Kinetics, Thermodynamic and Structural Aspects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K. Significant Effect of Polar Head Group of Surfactants on the Solubilization of Zein in Mixed Micellar (SDS–DDAB) Media. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Calderon-Dominguez, G.; Chanona-Perez, J.J.; Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; Andraca-Adame, J.A.; Arzate-Vazquez, I.; Mendez-Mendez, J.V.; Moreno-Ruiz, L.A. Physical and Structural Characterization of Zein and Chitosan Edible Films Using Nanotechnology Tools. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. A Comparative Study of Covalent and Non-Covalent Interactions between Zein and Polyphenols in Ethanol-Water Solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Jian, L.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Fabrication, Characterization, and Physicochemical Stability of Zein–Chitosan Nanocomplex for Co-Encapsulating Curcumin and Resveratrol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, Z.; Avci, E.; Erdem, Y.K. Characterization of Binding Interactions between Green Tea Flavonoids and Milk Proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naczk, M.; Grant, S.; Zadernowski, R.; Barre, E. Protein Precipitating Capacity of Phenolics of Wild Blueberry Leaves and Fruits. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelitli, E.P.; Janiak, M.A.; Amarowicz, R.; Alasalvar, C. Protein Precipitating Capacity and Antioxidant Activity of Turkish Tombul Hazelnut Phenolic Extract and Its Fractions. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Guo, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W. Effect of Interaction between Tea Polyphenols with Soymilk Protein on Inactivation of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ma, H. Effects of Collagen and Casein with Phenolic Compounds Interactions on Protein In vitro Digestion and Antioxidation. LWT 2020, 124, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S.; Kaur, N.; Singh, D.; Kennedy, J.F. Investigating Aqueous Phase Separation of Pullulan from Aureobasidium pullulans and Its Characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Niu, B.; Chen, H.; Sun, P. Fabrication and Characterization of Tea Polyphenols Loaded Pullulan-CMC Electrospun Nanofiber for Fruit Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Shi, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Ni, F.; He, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Huang, M.; et al. The Fabrication of Novel Zein and Resveratrol Covalent Conjugates: Enhanced Thermal Stability, Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Qin, C.; Liu, N.; Han, J. The Preparation of Cistanche Phenylethanoid Glycosides Liquid Proliposomes: Optimized Formulation, Characterization and Proliposome Dripping Pills In vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Huang, W.; Peng, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lu, B. Enhancing the Stability, BBB Permeability and Neuroprotective Activity of Verbascoside In vitro Using Lipid Nanocapsules in Combination with Menthol. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attama, A.A.; Schicke, B.C.; Paepenmüller, T.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Solid Lipid Nanodispersions Containing Mixed Lipid Core and a Polar Heterolipid: Characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnan-Çınkır, N.; Ağçam, E.; Altay, F.; Akyıldız, A. Emulsion Electrospinning of Zein Nanofibers with Carotenoid Microemulsion: Optimization, Characterization and Fortification. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Almasi, H.; Amjadi, S.; Moradi, M.; Ghadiri Alamdari, N.; Salmasi, S.; Divsalar, E. Development and Characterization of Active Packaging System Based on Zein Nanofibers Mat Incorporated with Geraniol-Loaded Nanoliposomes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 5373–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.M.; Wang, C.N.; Guo, M.R. Interactions between Whey Protein or Polymerized Whey Protein and Soybean Lecithin in Model System. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9680–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, F.; Ling, J.; Ouyang, X.K.; Wang, Y.G. Delivery of Curcumin Using a Zein-Xanthan Gum Nanocomplex: Fabrication, Characterization, and In vitro Release Properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, L.; Bedjou, F.; Ferrari, G.; Donsì, F. Formulation and Characterization of Zein/Gum Arabic Nanoparticles for the Encapsulation of a Rutin-Rich Extract from Ruta chalepensis L. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 129982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xie, L.; Wu, A.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Dai, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, X. Delivery of Silybin Using a Zein-Pullulan Nanocomplex: Fabrication, Characterization, In vitro Release Properties and Antioxidant Capacity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Fan, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y. Fabrication of Stable Zein Nanoparticles Coated with Soluble Soybean Polysaccharide for Encapsulation of Quercetin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Echinacoside (g L−1) | Teupolioside (g L−1) * | Stachysoside A (g L−1) * | Poliumoside (g L−1) * | Verbascoside (g L−1) | TPC * (g L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.38 ± 0.08 | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 1.30 ± 0.64 | 0.92 ± 0.45 | 0.60 ± 0.29 | 8.92 ± 0.03 |
| Pullulan (PUL) (%) | Zein (ZE) (%) | Lecithin (lec) (%) | Sample Abbreviation | Electrospinnability Potential | Morphology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0 | - | 15PUL | - | nanofibers |
| 100 | 0 | 3 | 15PUL + lec | + | / |
| 80 | 20 | 3 | 80PUL:20ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 70 | 30 | 3 | 70PUL:30ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 60 | 40 | 3 | 60PUL:40ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 50 | 50 | 3 | 50PUL:50ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 40 | 60 | 3 | 40PUL:60ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 30 | 70 | 3 | 30PUL:70ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 20 | 80 | 3 | 20PUL:80ZE | + | nanofibers |
| 0 | 100 | - | 15ZE | - | / |
| 0 | 100 | 3 | 15ZE + lec | - | / |
| Sample | σ (mSI cm−1) | γ (mN m−1) |
|---|---|---|
| extract | 2.02 ± 0.01 | 36.19 ± 0.28 |
| acidified extract 1 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | 37.79 ± 0.06 |
| 15PUL | 1.51 ± 0.01 a | 35.11 ± 0.84 a |
| 15PUL + lec | 1.79 ± 0.00 b | 24.62 ± 0.23 b |
| 80PUL:20ZE | 1.67 ± 0.03 c | 30.38 ± 0.40 c |
| 70PUL:30ZE | 1.65 ± 0.01 cd | 31.39 ± 0.95 cd |
| 60PUL:40ZE | 1.57 ± 0.01 acd | 31.49 ± 1.08 cde |
| 50PUL:50ZE | 1.91 ± 0.01 be | 31.23 ± 0.40 cde |
| 40PUL:60ZE | 1.94 ± 0.00 e | 34.72 ± 1.20 a |
| 30PUL:70ZE | 1.82 ± 0.00 be | 42.03 ± 1.45 f |
| 20PUL:80ZE | 2.36 ± 0.06 | 40.84 ± 2.82 g |
| 15ZE | 2.53 ± 0.10 | 27.18 ± 0.48 b |
| 15ZE + lec | 2.78 ± 0.03 | 39.88 ± 0.24 fg |
| Sample | G′ LVE (Pa) | G″ LVE (Pa) | tan δ LVE | Viscosity at 25 s−1 (mPa s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15PUL | 4.63 ± 0.10 a | 36.90 ± 0.10 a | 7.97 ± 0.16 | 4129.55 ± 12.85 |
| 15PUL + lec | 9.70 ± 0.68 ab | 47.77 ± 1.65 ab | 4.94 ± 0.18 | 6169.65 ± 18.75 a |
| 80PUL:20ZE | 18.73 ± 4.02 ac | 44.00 ± 8.15 abc | 2.37 ± 0.07 | 3367.55 ± 8.05 b |
| 70PUL:30ZE | 47.03 ± 1.81 d | 81.68 ± 2.05 d | 1.74 ± 0.02 | 2645.9 ± 8.6 c |
| 60PUL:40ZE | 54.22 ± 0.35 de | 57.82 ± 0.78 abcde | 1.07 ± 0.01 a | 2405.15 ± 61.15 cd |
| 50PUL:50ZE | 52.29 ± 8.46 def | 41.12 ± 6.92 abef | 0.79 ± 0.01 ab | 2525.95 ± 49.55 cde |
| 40PUL:60ZE | 43.57 ± 1.62 defg | 30.68 ± 1.35 abcfg | 0.70 ± 0.01 abc | 2749.4 ± 39.7 bcde |
| 30PUL:70ZE | 43.57 ± 4.62 defgh | 30.68 ± 1.35 abcfgh | 0.70 ± 0.01 abcd | 7362.25 ± 10.05 f |
| 20PUL:80ZE | 138.43 ± 0.16 | 52.91 ± 0.44 abcefgh | 0.38 ± 0.00 bcdef | 7075.3 ± 71.2 f |
| 15ZE | 32.60 ± 1.66 bcdefgh | 12.15 ± 0.17 gh | 0.37 ± 0.01 bcdef | 665 ± 18.8 |
| 15ZE + lec | 696.91 ± 10.09 | 137.60 ± 9.19 | 0.20 ± 0.02 f | 5955.5 ± 31.25 a |
| Sample | Tevp (°C) | ∆H (J g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 15PUL | 68.77 | 123.52 |
| 15PUL_E | 65.90 | 99.66 |
| 80PUL:20ZE | 71.22 | 74.28 |
| 80PUL:20ZE_E | 72.37 | 62.94 |
| 70PUL:30ZE | 66.42 | 32.68 |
| 70PUL:30ZE_E | 75.22 | 44.91 |
| 60PUL:40ZE | 62.73 | 73.85 |
| 60PUL:40ZE_E | 65.44 | 56.46 |
| 50PUL:50ZE | 72.10 | 31.94 |
| 50PUL:50ZE_E | 72.28 | 27.99 |
| 40PUL:60ZE | 59.94 | 26.83 |
| 40PUL:60ZE_E | 72.91 | 19.24 |
| 30PUL:70ZE | 56.50 | 34.32 |
| 30PUL:70ZE_E | 68.18 | 5.95 |
| 20PUL:80ZE | 63.19 | 27.23 |
| 20PUL:80ZE_E | 66.24 | 12.56 |
| PUL* | 68.93 | 46.75 |
| ZE* | 63.08 | 25.30 |
| LEC | - | - |
| LE | 64.91 | 123.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandura Jarić, A.; Domazet Jurašin, D.; Petrović, P.; Kuzmić, S.; Nižić Nodilo, L.; Vojvodić Cebin, A.; Šeremet, D.; Komes, D. Development and Structural Characterization of Pullulan/Lecithin/Zein Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Mountain Germander (Teucrium montanum) Polyphenolic Extract. Foods 2025, 14, 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213619
Mandura Jarić A, Domazet Jurašin D, Petrović P, Kuzmić S, Nižić Nodilo L, Vojvodić Cebin A, Šeremet D, Komes D. Development and Structural Characterization of Pullulan/Lecithin/Zein Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Mountain Germander (Teucrium montanum) Polyphenolic Extract. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213619
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandura Jarić, Ana, Darija Domazet Jurašin, Predrag Petrović, Sunčica Kuzmić, Laura Nižić Nodilo, Aleksandra Vojvodić Cebin, Danijela Šeremet, and Draženka Komes. 2025. "Development and Structural Characterization of Pullulan/Lecithin/Zein Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Mountain Germander (Teucrium montanum) Polyphenolic Extract" Foods 14, no. 21: 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213619
APA StyleMandura Jarić, A., Domazet Jurašin, D., Petrović, P., Kuzmić, S., Nižić Nodilo, L., Vojvodić Cebin, A., Šeremet, D., & Komes, D. (2025). Development and Structural Characterization of Pullulan/Lecithin/Zein Composite Nanofibers Loaded with Mountain Germander (Teucrium montanum) Polyphenolic Extract. Foods, 14(21), 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213619









