Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soy Paste) Attenuates Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Gut Microbiota Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information on Doenjang
2.2. Analysis of Biogenic Amines and Sodium Content
2.3. Microbial Analysis
2.4. AOM/DSS-Induced CAC Study
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), Alcian Blue (AB), and Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
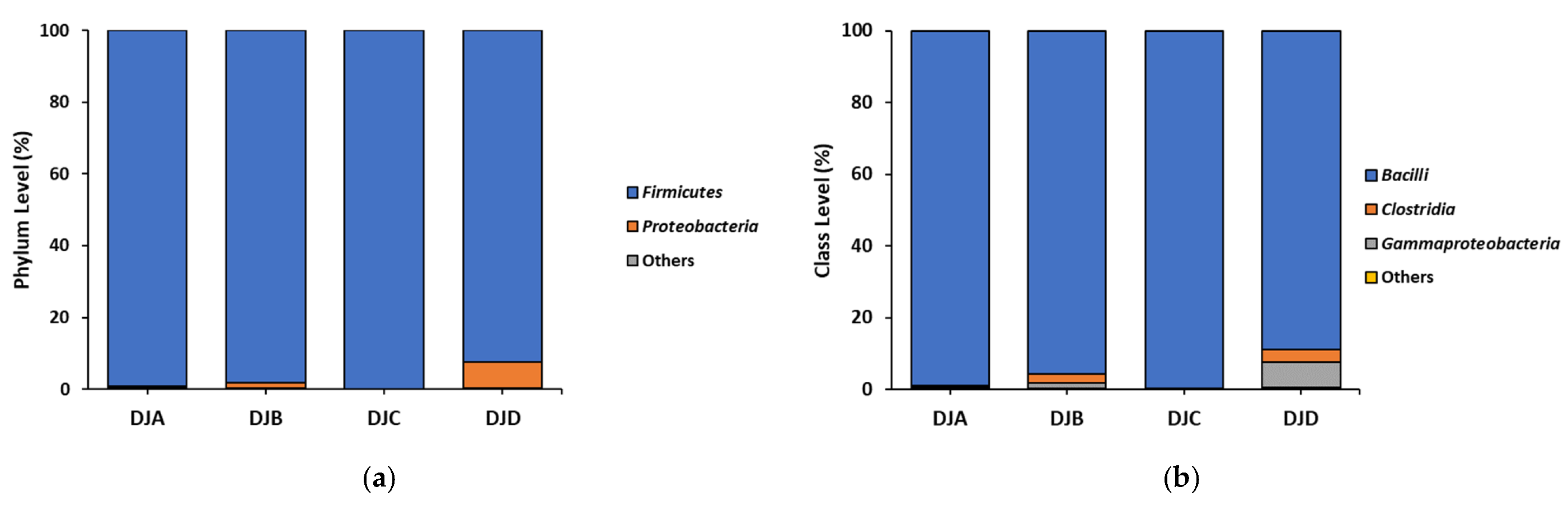
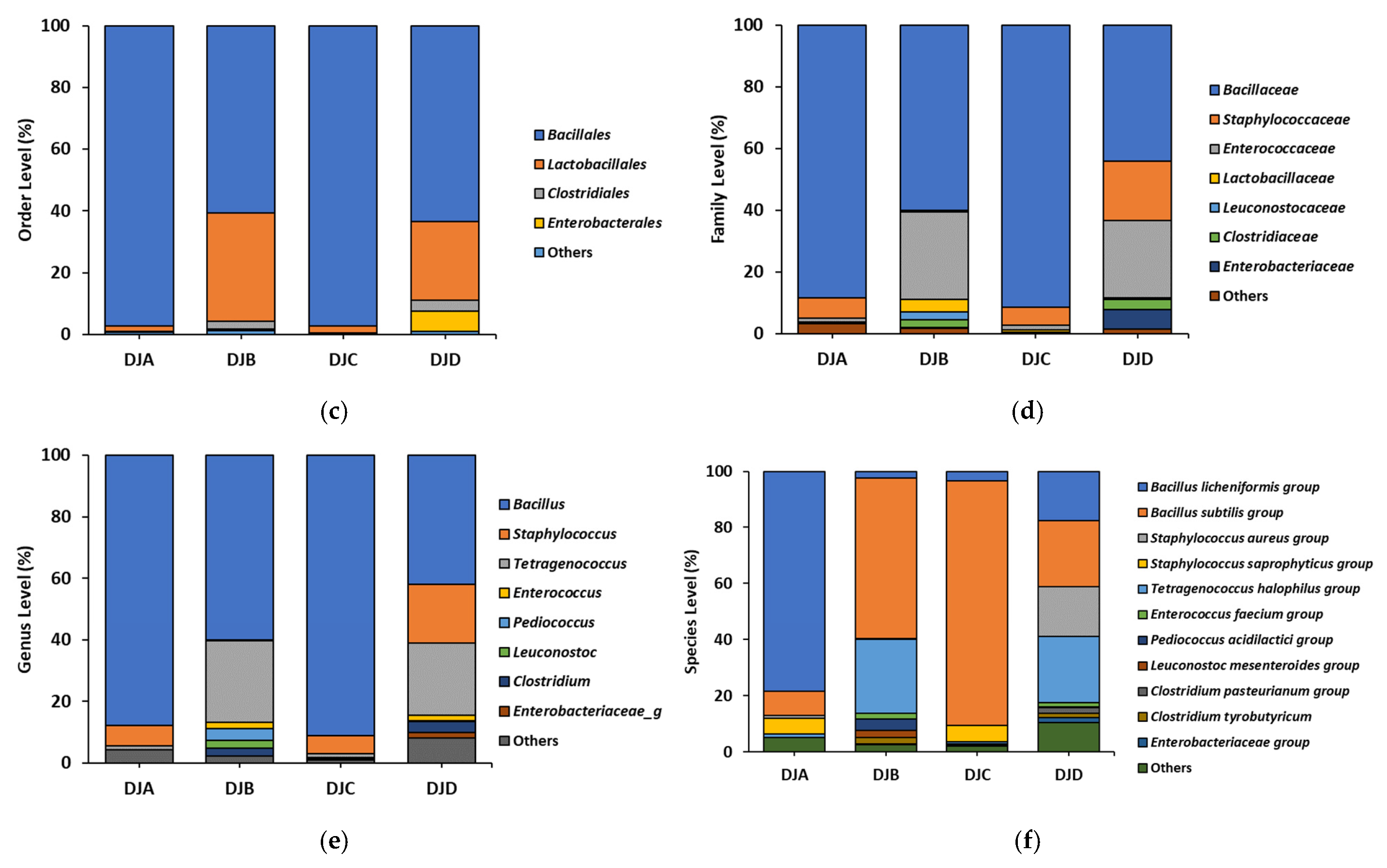
3.1. Bacterial Composition, BAs, and Salt Contents in Doenjang
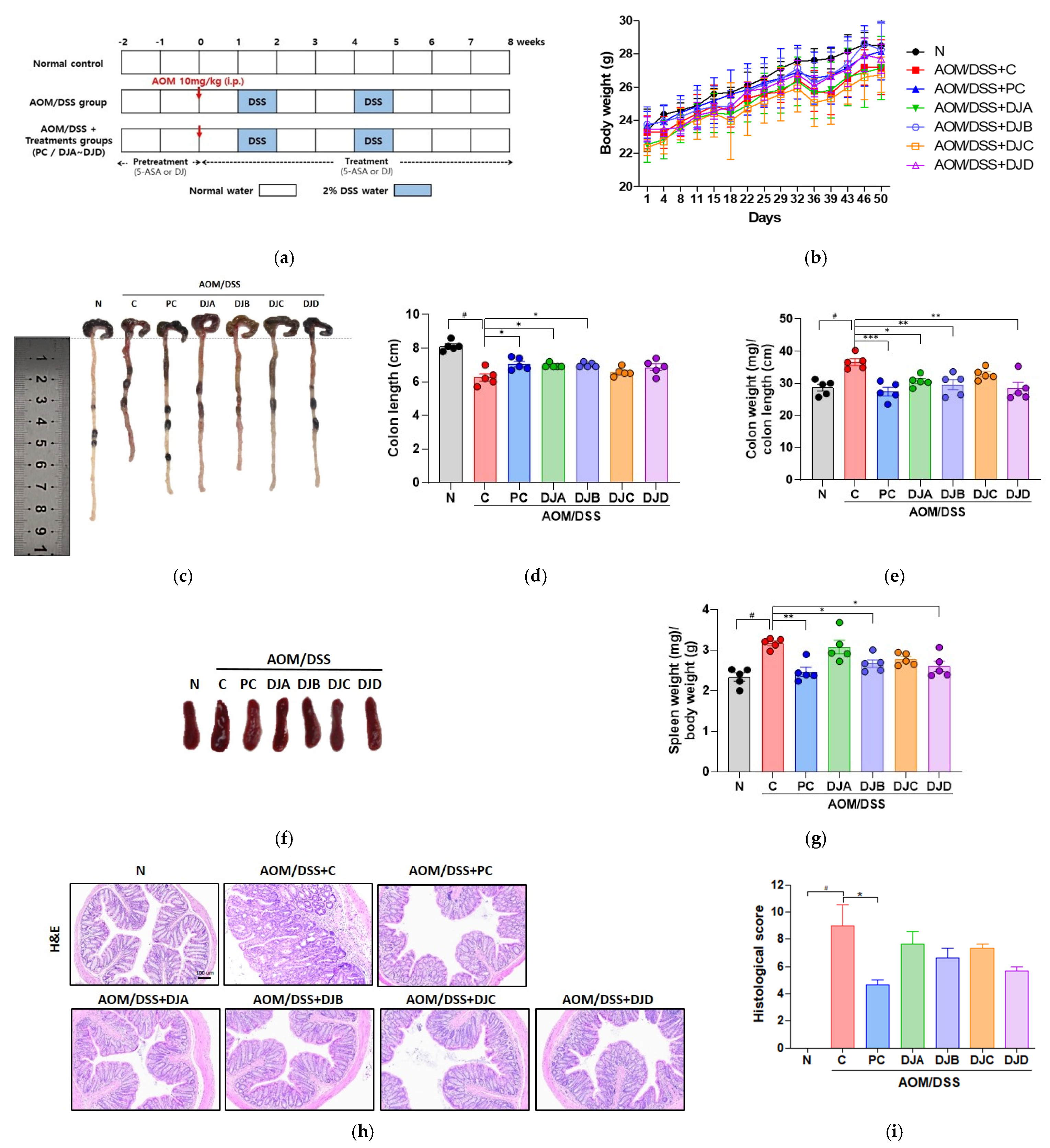
3.2. Doenjang Reduces CAC-Associated Features in Mice with AOM/DSS-Induced CAC
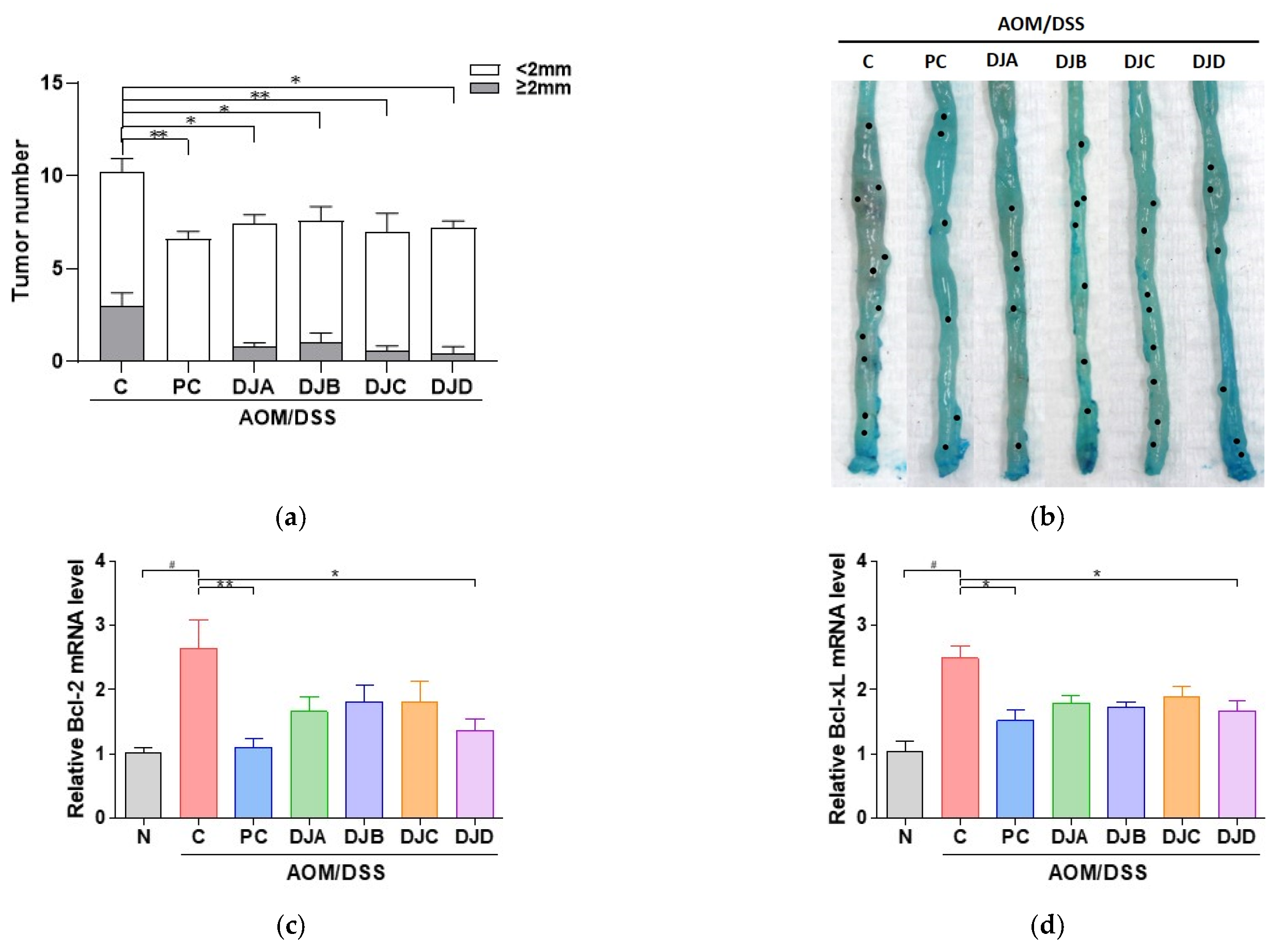
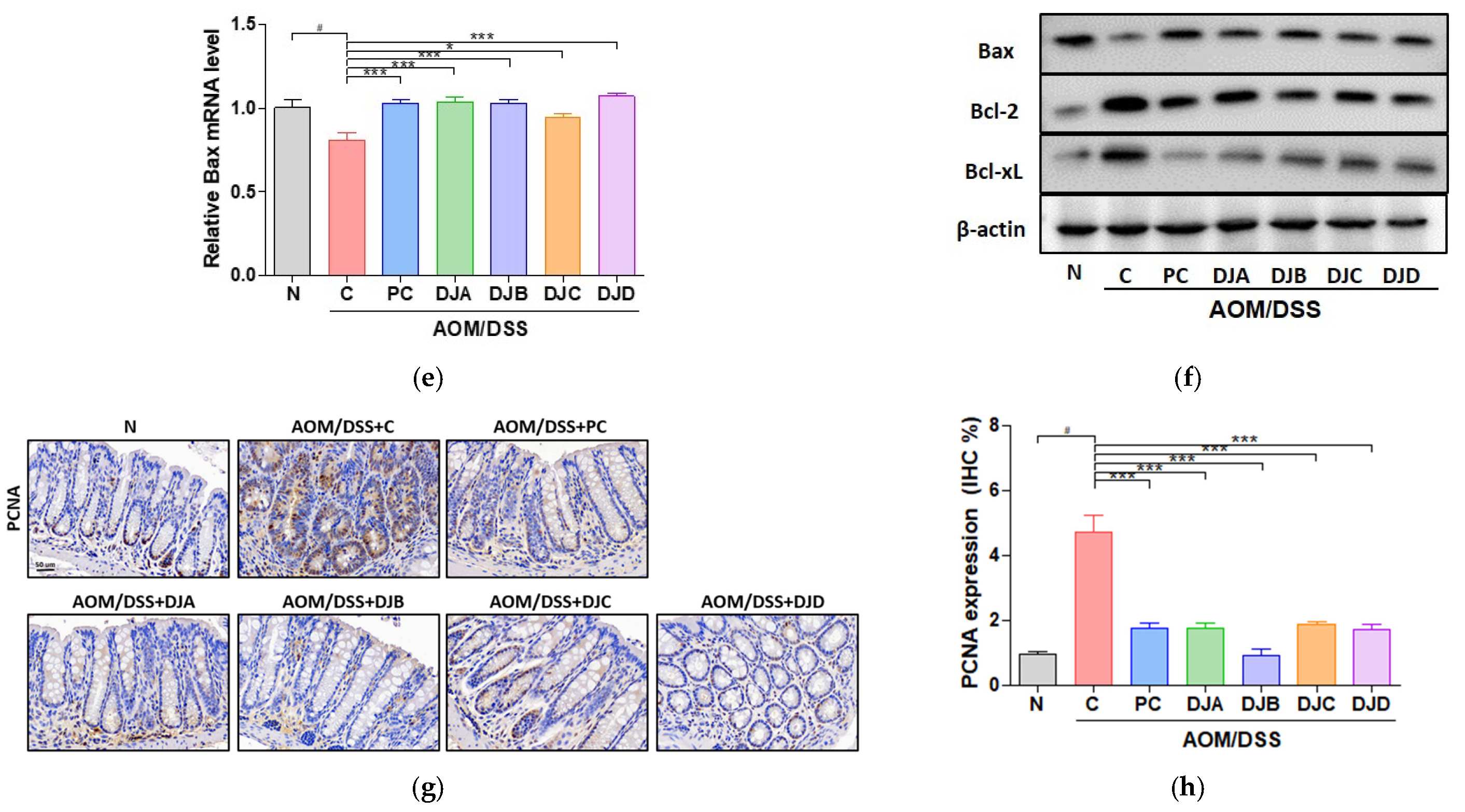
3.3. Doenjang Suppresses Tumor Growth by Regulating Apoptosis and Proliferation in CAC Mice
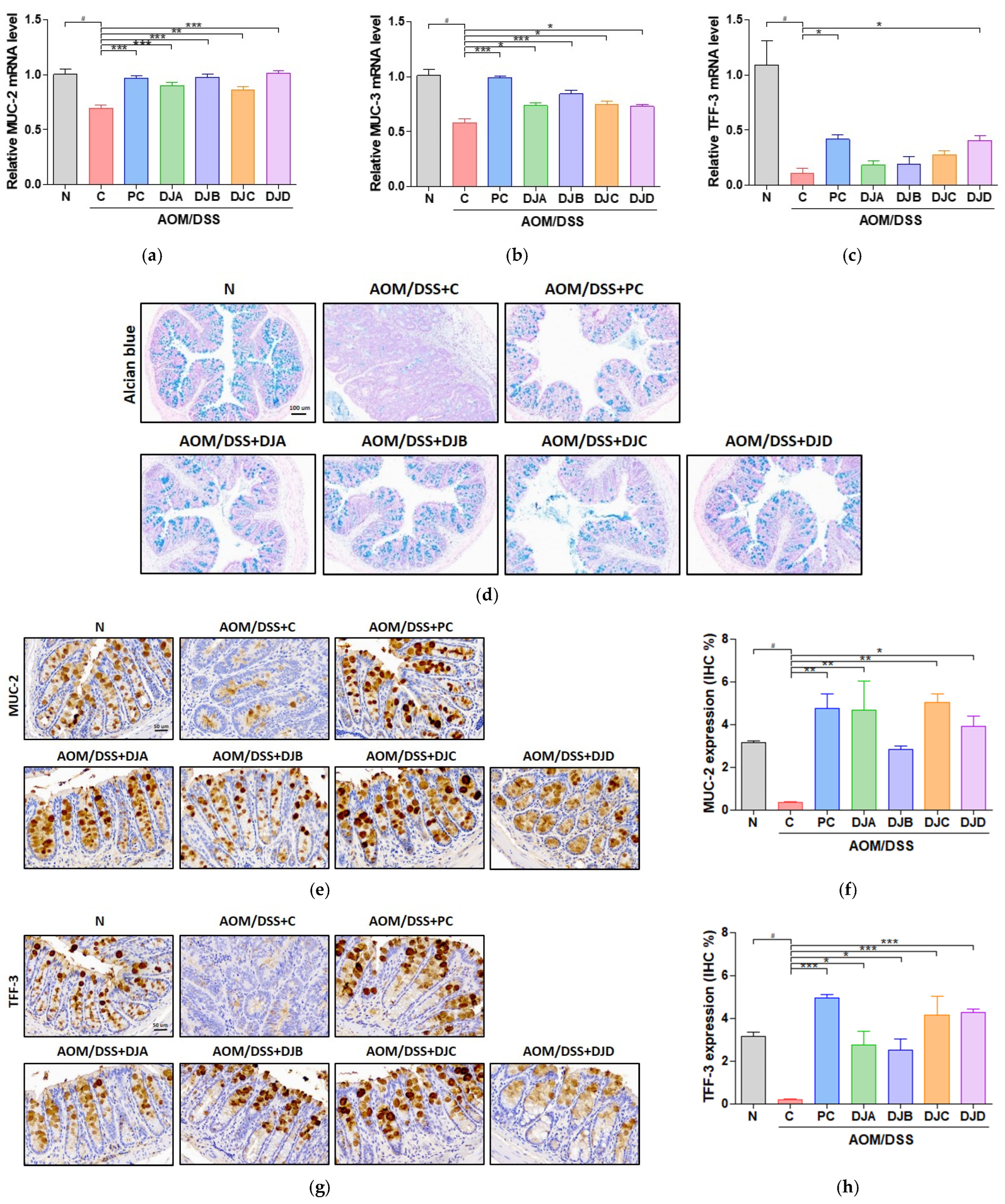
3.4. Doenjang Improves Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Integrity in Mice with AOM/DSS-Induced CAC
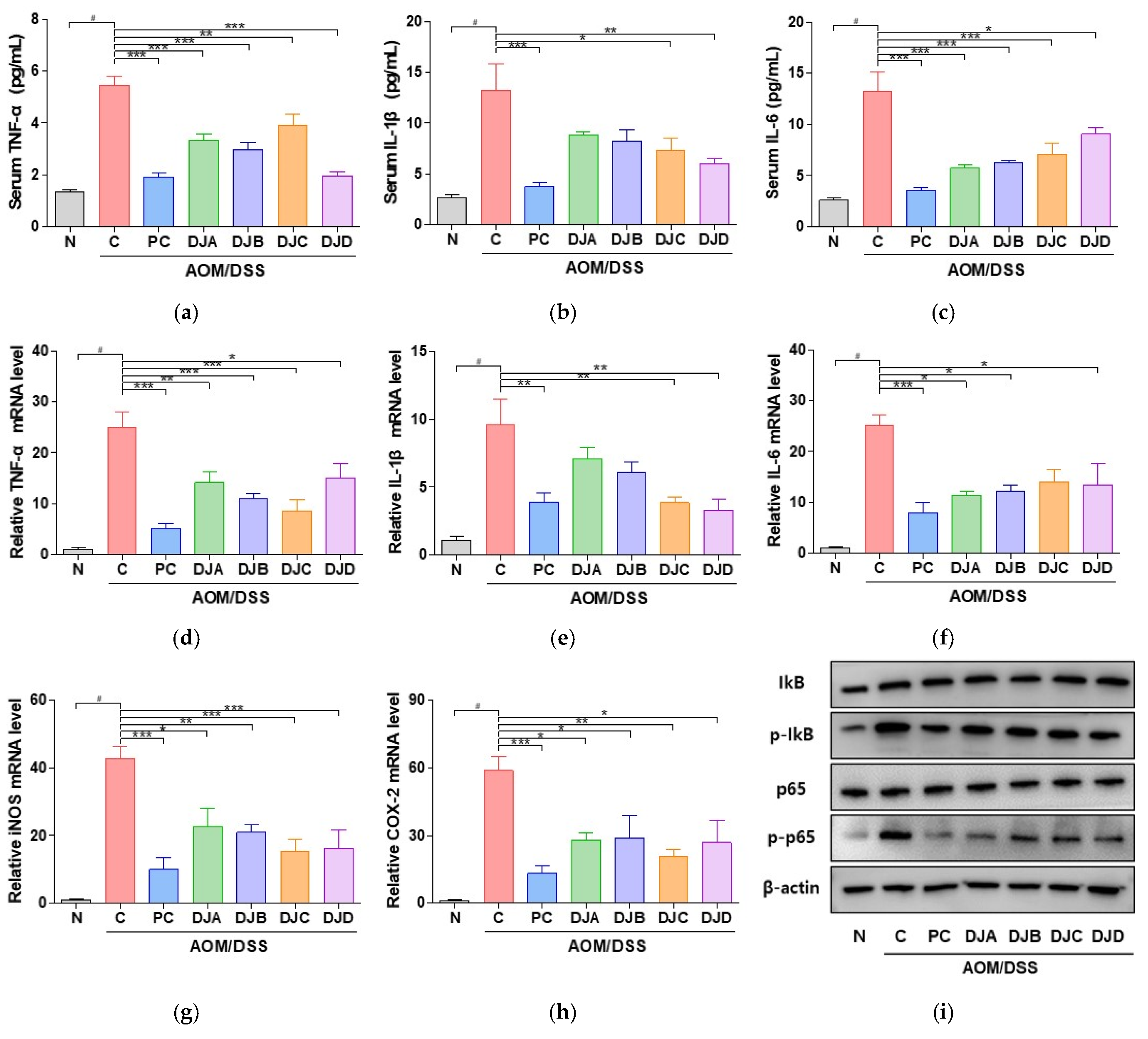
3.5. Doenjang Reduces Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Inflammatory Gene Expression via NF-κB Signaling Pathway in CAC Mice
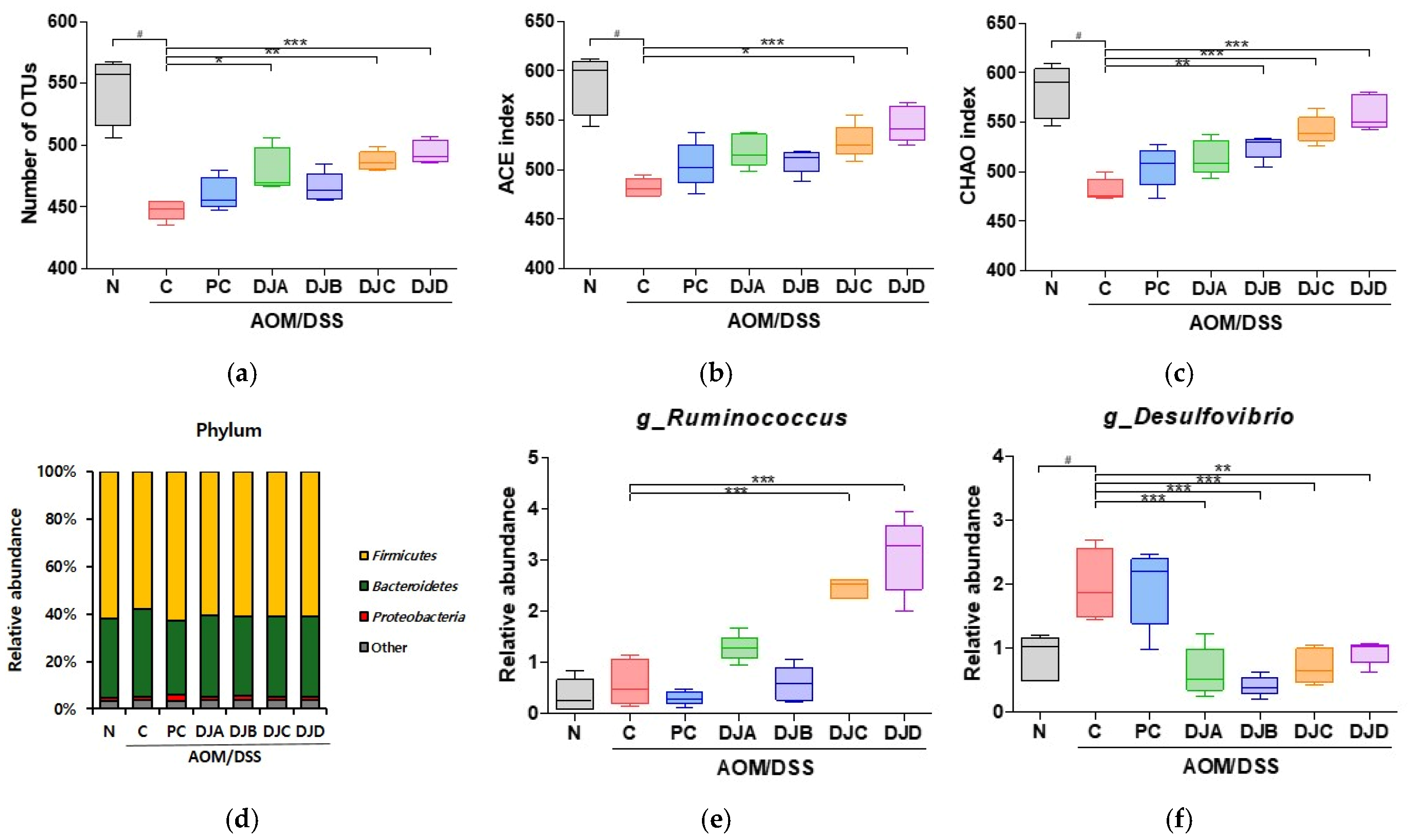
3.6. Doenjang Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity in CAC Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pardamean, C.I.; Sudigyo, D.; Budiarto, A.; Mahesworo, B.; Hidayat, A.A.; Baurley, J.W.; Pardamean, B. Changing colorectal cancer trends in Asians: Epidemiology and risk factors. Oncol. Rev. 2023, 17, 10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, H.; El Masri, J.; Fakhereddine, H.; Youssef, J.; Chemaly, C.; Doughan, S.; Abou-Kheir, W. Colorectal cancer: Recent advances in management and treatment. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1136–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J.; Ning, X.; Burd, C.E.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Tounkara, F.; Kalady, M.F.; Noonan, A.M.; McCabe, S.; Von Ah, D. Chemotoxicity and associated risk factors in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahgoli, V.K.; Noorolyai, S.; Ahmadpour Youshanlui, M.; Saeidi, H.; Nasiri, H.; Mansoori, B.; Holmskov, U.; Baradaran, B. Inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, and cancer: Unmasking the chronic inflammation link. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2024, 39, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grellier, N.; Severino, A.; Archilei, S.; Kim, J.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G.; Porcari, S.; Benech, N. Gut microbiota in inflammation and colorectal cancer: A potential toolbox for clinicians. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 72, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tito, R.Y.; Verbandt, S.; Aguirre Vazquez, M.; Lahti, L.; Verspecht, C.; Lloréns-Rico, V.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Arts, J.; Falony, G.; Dekker, E.; et al. Microbiome confounders and quantitative profiling challenge predicted microbial targets in colorectal cancer development. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB in inflammation and cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 811–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiescu, R.; Efferth, T.; Dawood, M. Dysregulation of different modes of programmed cell death by epigenetic modifications and their role in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 584, 216623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.C.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhou, G.Y.J.; Yin, T.F.; Zhao, D.Y.; Sun, X.Z.; Tan, C.; Zhou, L.; Yao, S.K. Matrine promotes colorectal cancer apoptosis by downregulating shank-associated RH domain interactor expression. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 16, 4700–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Reyna, D.E.; Gitego, N.; Kopp, F.; Zhou, H.; Miranda-Roman, M.A.; Nordstrøm, L.U.; Narayanagari, S.R.; Chi, P.; Vilar, E.; et al. Co-targeting of BAX and BCL-XL proteins broadly overcomes resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Takahashi, H.; Asai, H.; Uehara, S.; Harata, S.; Fujii, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yanagita, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ushigome, H.; et al. Bcl-xL-specific BH3 mimetic A-1331852 suppresses proliferation of fluorouracil-resistant colorectal cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 53, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Lee, H.; Song, Y.; Cha, J. Taxonomic variations of bacterial and fungal communities depending on fermentation temperature in traditional Korean fermented soybean food, Doenjang. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Park, I.S.; Jeong, S.J.; Ha, G.S.; Yang, H.J.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, C.H. Effects of cheonggukjang (fermented soybean) on the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. Foods 2023, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Kang, E.A.; Park, J.M.; Oh, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Hahm, K.B. Dietary intake of fermented kimchi prevented colitis-associated cancer. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020, 67, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Tian, W.; Han, Y.; Xu, X.; Ren, T.; Tian, C.; Chen, C. Natto: A medicinal and edible food with health function. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Khan, A.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y.; Salama, E.S.; Su, S.; Han, H.; Jin, W.; Li, X. A probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum GR-3 mitigates colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice via modulating gut microbiome. NPJ Sci. Food 2024, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Haque, M.A.; Cho, D.Y.; Jeong, J.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Jang, M.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, K.M. Comparison of microbial diversity and metabolites on household and commercial Doenjang. Food Chem. X 2023, 21, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Ni, D.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Wang, L. Effects of fermentation on bioactivity and the composition of polyphenols contained in polyphenol-rich foods: A review. Foods 2023, 12, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, K.; Kubo, S.; Tsuji, K.; Sugiyama, D.; Iizuk, Y.; Hamana, H. Bacillus coagulans (species of lactic acid-forming Bacillus bacteria) ameliorates azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate-induced colon cancer in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 100, 10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, A.; Hwang, H.J.; Mah, J.H. Validation of an HPLC analytical method for determination of biogenic amines in agricultural products and monitoring of biogenic amines in Korean fermented agricultural products. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.S.; Park, Y.; Lee, M.; Chae, S.W.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.S. Doenjang, a Korean fermented soy food, exerts antiobesity and antioxidative activities in overweight subjects with the PPAR-γ2 C1431T polymorphism: 12-week, double-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.O.; Park, S.Y.; Park, K.Y. Longer aging time increases the anticancer and antimetastatic properties of doenjang. Nutrition 2006, 22, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Han, A.; Park, J.E.; Cha, Y.S. Korean fermented soybean paste (Doenjang) has anti-obesity and anti-hypertensive effects via the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, M.K. Analysis of the region-specific characteristics of traditional Korean Doenjang produced in Gyeonggi-do. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Kang, G.S.; Lee, H.R.; Yu, S.J.; Jeong, S.U.; So, Y.S.; Park, C.S.; Shin, D.; Seo, D.H. Microbial communities in the fermentation of Meju, a Korean traditional soybean brick. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Park, H.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M. Determination of biogenic amines in Korean traditional fermented soybean paste (Doenjang). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Lee, J.S.; Bajpai, V.K.; Nile, S.H.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.K.; Kim, M. Detection of biogenic amines and microbial safety assessment of novel Meju fermented with addition of Nelumbo nucifera, Ginkgo biloba, and Allium sativum. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.Y.; Park, S.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Sul, W.J.; Chun, H.S. Mycotoxin and microbiome profiling for aflatoxin control in the Korean traditional fermented soybean paste Doenjang. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.S.; Ryu, H.M.; Sohn, S. Tetragenococcus halophilus alleviates intestinal inflammation in mice by altering gut microbiota and regulating dendritic cell activation via CD83. Cells 2022, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindo, C.O.; Morsli, M.; Bellali, S.; Drancourt, M.; Grine, G. A Tetragenococcus halophilus human gut isolate. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Park, I.S.; Seo, J.W.; Ha, G.; Yang, H.J.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, C.H. Anti-inflammatory effect of Korean soybean sauce (ganjang) on mice with induced colitis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Boltonm, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Girones, R.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lindqvist, R.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, V.; Muthukumar, S.P.; Halami, P.M. Safety assessment of Bacillus licheniformis Me1 isolated from milk for probiotic application. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.W.; Heo, S.; Lee, J.H. Safety assessment of Tetragenococcus halophilus isolates from doenjang, a Korean high-salt-fermented soybean paste. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak-Dados, A.; Michalski, M.; Osek, J. Histamine and Other Biogenic Amines in Food. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha Turna, N.; Chung, R.; McIntyre, L. A review of biogenic amines in fermented foods: Occurrence and health effects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Park, H.K.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, M. Reduction of biogenic amines and aflatoxins in Doenjang samples fermented with various Meju as starter cultures. Food Control 2014, 42, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Yu, T.; Lai, X.; He, Y. Study on the effect and mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus AFY06 on inflammation-associated colorectal cancer induced by AOM/DSS in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1382781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulat, A.; Mohsenpour, T.; Roshangar, L.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Soulat, F. Innovative therapeutic approach targeting colon cancer stem cells: Transitional cold atmospheric plasma. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 12109–12121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Kang, W.; Ye, X. Association between the gut microbiota, inflammatory factors, and colorectal cancer: Evidence from Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1309111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, X.; Huang, G.; Mo, G.; Cao, D.; Peng, X. Ruminococcus bromii-generated acetate alleviated Clonorchis sinensis-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1532599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, F.; Huang, J.; Gao, X. Gut microbiota and metabolic health risks from chronic low-dose microplastic exposure with focus on Desulfovibrio spp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zheng, Q. Gut microbiome-metabolites axis: A friend or foe to colorectal cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Okamura, T.; Bamba, R.; Yoshimura, Y.; Munekawa, C.; Kaji, A.; Miki, A.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; et al. Miso, fermented soybean paste, suppresses high-fat/high-sucrose diet-induced muscle atrophy in mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2024, 74, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Methods | Production Region | Sodium (mg/100 g) | Biogenic Amines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine (mg/kg) | Tyramine (mg/kg) | ||||
| DJA (Doenjang A) | Traditional | Sunchang, Jeonbuk | 4072.53 | 141.90 | 284.27 |
| DJB (Doenjang B) | Traditional | Sancheong, Gyeongnam | 3743.47 | 151.13 | 886.86 |
| DJC (Doenjang C) | Traditional | Seongju, Gyeongbuk | 4364.04 | 794.86 | 215.89 |
| DJD (Doenjang D) | Industrial | Sunchang, Jeonbuk | 4028.21 | 928.61 | 186.59 |
| Group | Treatment | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| N | Saline(i.p.)/Autoclaved water | Autoclaved water |
| AOM/DSS + C | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | Autoclaved water |
| AOM/DSS + PC | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | 5-ASA (75 mg/kg) |
| AOM/DSS + DJA | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | DJA (200 mg/kg) |
| AOM/DSS + DJB | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | DJB (200 mg/kg) |
| AOM/DSS + DJC | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | DJC (200 mg/kg) |
| AOM/DSS + DJD | AOM (i.p., 10 mg/kg)/2% DSS (drinking water) | DJD (200 mg/kg) |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Bax | AGACAGGGGCCTTTTTGCTAC | AATTCGCCGGAGACACTCG |
| Bcl-2 | GCTACCGTCGTGACTTCGC | CCCCACCGAACTCAAAGAAGG |
| Bcl-XL | GGCACTGTGCGTGGAAAGCGTA | CCGCCGTTCTCCTGGATCCA |
| TNF-α | CTGAACTTCGGGGTGATCGG | GGCTTGTCACTCGAATTTTGAGA |
| IL-1β | CAACCAACAAGTGATATTCTCCATG | GATCCACACTCTCCAGCTGCA |
| IL-6 | TGTCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAG | GCACAACTCTTTTCTCATTTCCAC |
| COX-2 | TTTGGTCTGGTGCCTGGTC | CTGCTGGTTTGGAATAGTTGCTC |
| iNOS | CGAAACGCTTCACTTCCAA | TGAGCCTATATTGCTGTGGCT |
| MUC-2 | ATGCCCACCTCCTCAAAGAC | GTAGTTTCCGTTGGAACAGTGAA |
| MUC-3 | CGTGGTCAACTGCGAGAATGG | CGGCTCTATCTACGCTCTC |
| TFF-3 | TAATGCTGTTGGTGGTCCTG | CAGCCACGGTTGTTACACTG |
| β-actin | CGGTTCCGATGCCCTGAGGCTCTT | CGTCACACTTCATGATGGAATTGA |
| Group | Number of OTUs | ACE Index | Chao 1 Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 544.0 ± 26.8 | 586.1 ± 29.6 | 581.2 ± 26.2 |
| AOM/DSS + C | 447.2 ± 7.9 # | 482.3 ± 9.0 # | 481.6 ± 11.1 # |
| AOM/DSS + PC | 460.8 ± 13.2 | 505.3 ± 22.5 | 505.0 ± 20.3 |
| AOM/DSS + DJA | 480.2 ± 17.2 * | 519.2 ± 16.4 | 514.0 ± 17.2 |
| AOM/DSS + DJB | 466.2 ±11.8 | 508.9 ± 12.4 | 524.7 ± 11.6 ** |
| AOM/DSS + DJC | 487.2 ± 7.7 ** | 528.2 ± 16.8 * | 542.3 ± 14.0 *** |
| AOM/DSS + DJD | 494.4 ± 8.8 *** | 545.8 ± 18.1 *** | 559.4 ± 17.7 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.-J.; Park, I.-S.; Kim, M.J.; Seo, J.W.; Ha, G.; Yang, H.-J.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jung, C.-H. Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soy Paste) Attenuates Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Gut Microbiota Pathways. Foods 2025, 14, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203565
Lim H-J, Park I-S, Kim MJ, Seo JW, Ha G, Yang H-J, Jeong D-Y, Kim S-Y, Jung C-H. Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soy Paste) Attenuates Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Gut Microbiota Pathways. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203565
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Hyeon-Ji, In-Sun Park, Min Ju Kim, Ji Won Seo, Gwangsu Ha, Hee-Jong Yang, Do-Youn Jeong, Seon-Young Kim, and Chan-Hun Jung. 2025. "Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soy Paste) Attenuates Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Gut Microbiota Pathways" Foods 14, no. 20: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203565
APA StyleLim, H.-J., Park, I.-S., Kim, M. J., Seo, J. W., Ha, G., Yang, H.-J., Jeong, D.-Y., Kim, S.-Y., & Jung, C.-H. (2025). Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soy Paste) Attenuates Development of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Gut Microbiota Pathways. Foods, 14(20), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203565






