Integrating RPA-LFD and TaqMan qPCR for Rapid On-Site Screening and Accurate Laboratory Identification of Coilia brachygnathus and Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
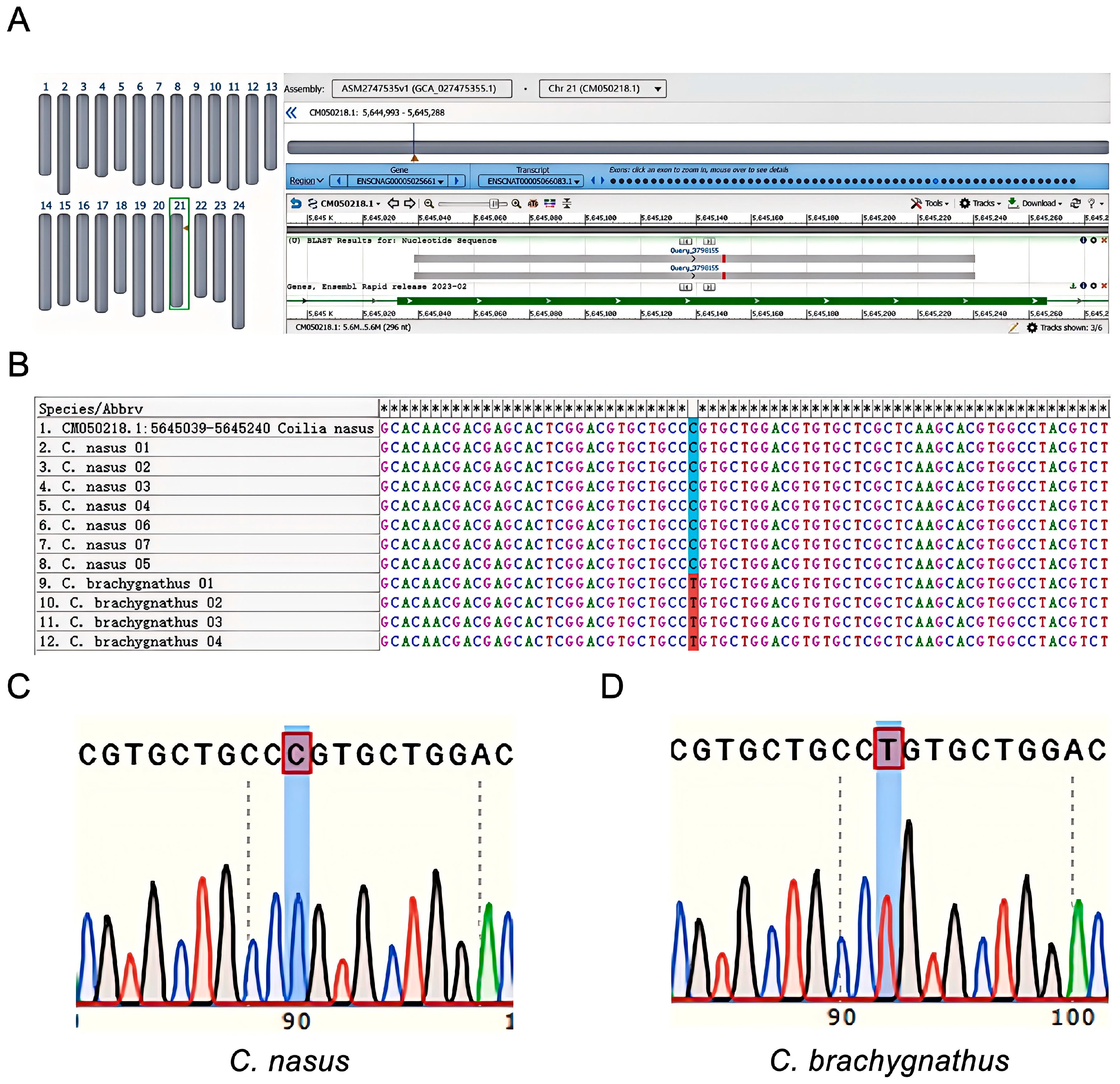
2.3. Primer and Probe Synthesis and SNP Verification
2.4. Development and Optimization of the RPA-LFD Assay
2.5. Establishment of Duplex TaqMan-MGB qPCR Assay and Standard Curves
2.6. Preparation of Plasmid DNA Standards
2.7. Specificity Testing
2.8. Limit of Detection (LOD) Determination
2.9. Validation with Samples of Known Origin
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Primers and SNP Genotyping
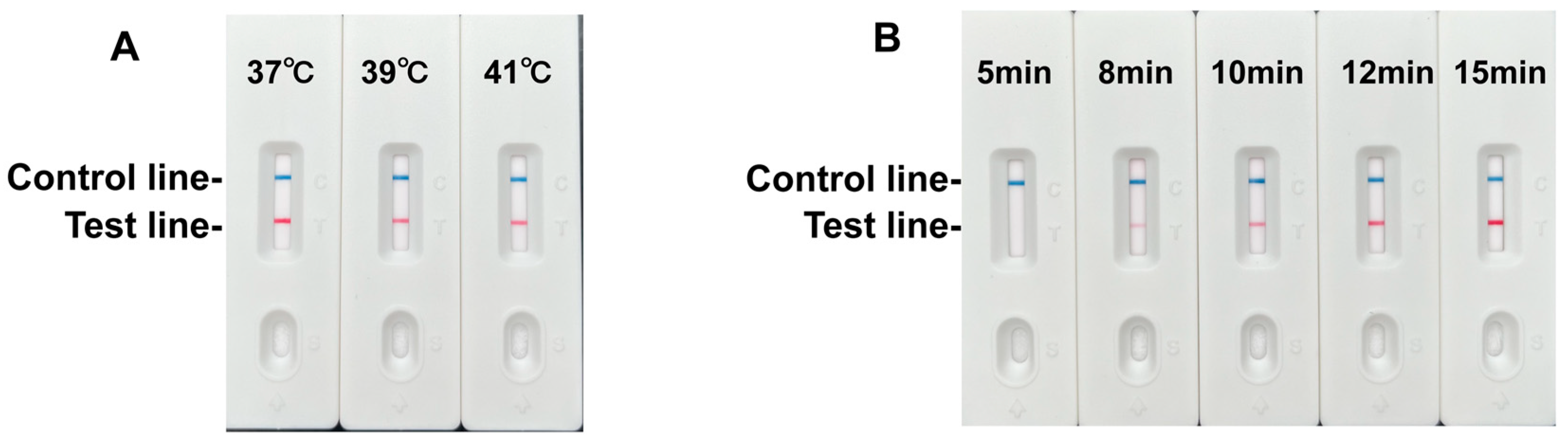
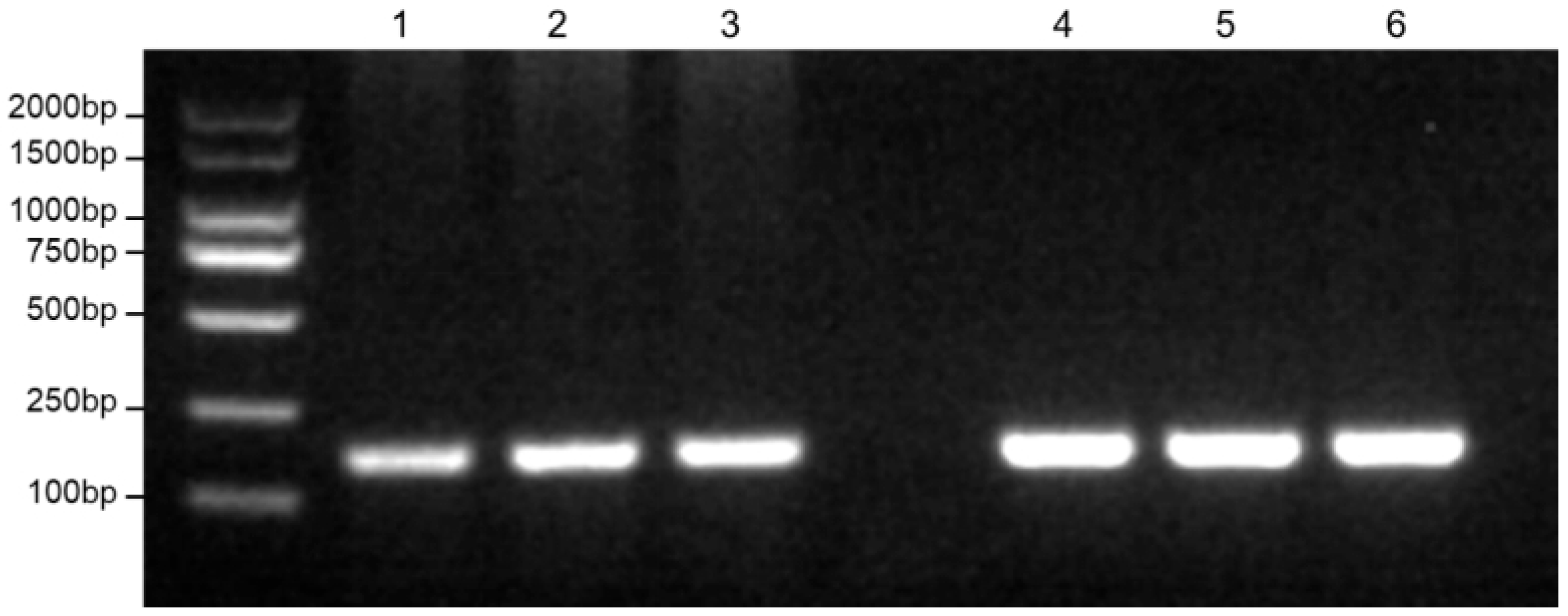
3.2. Development and Optimization of the RPA-LFD Assay
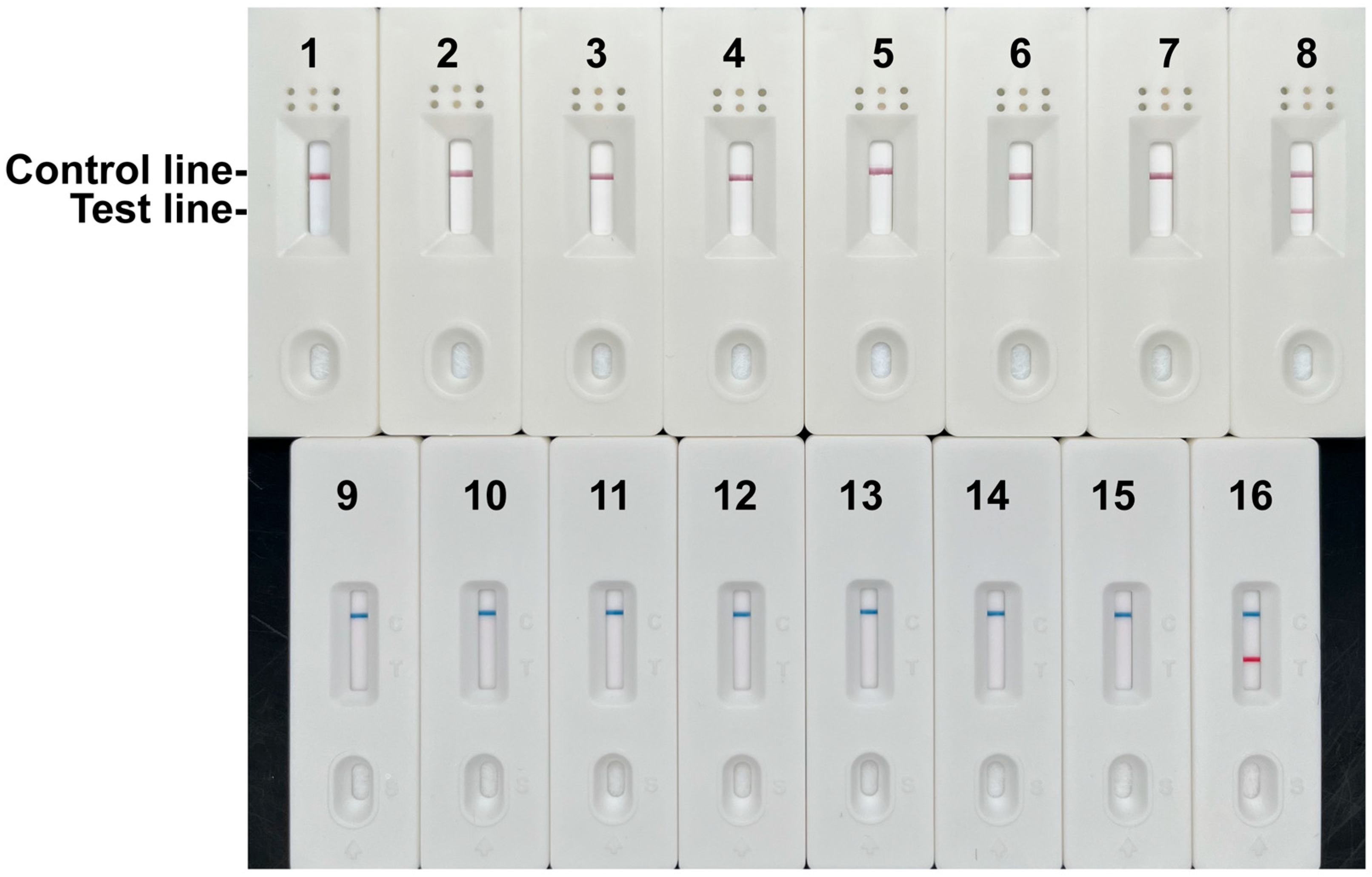
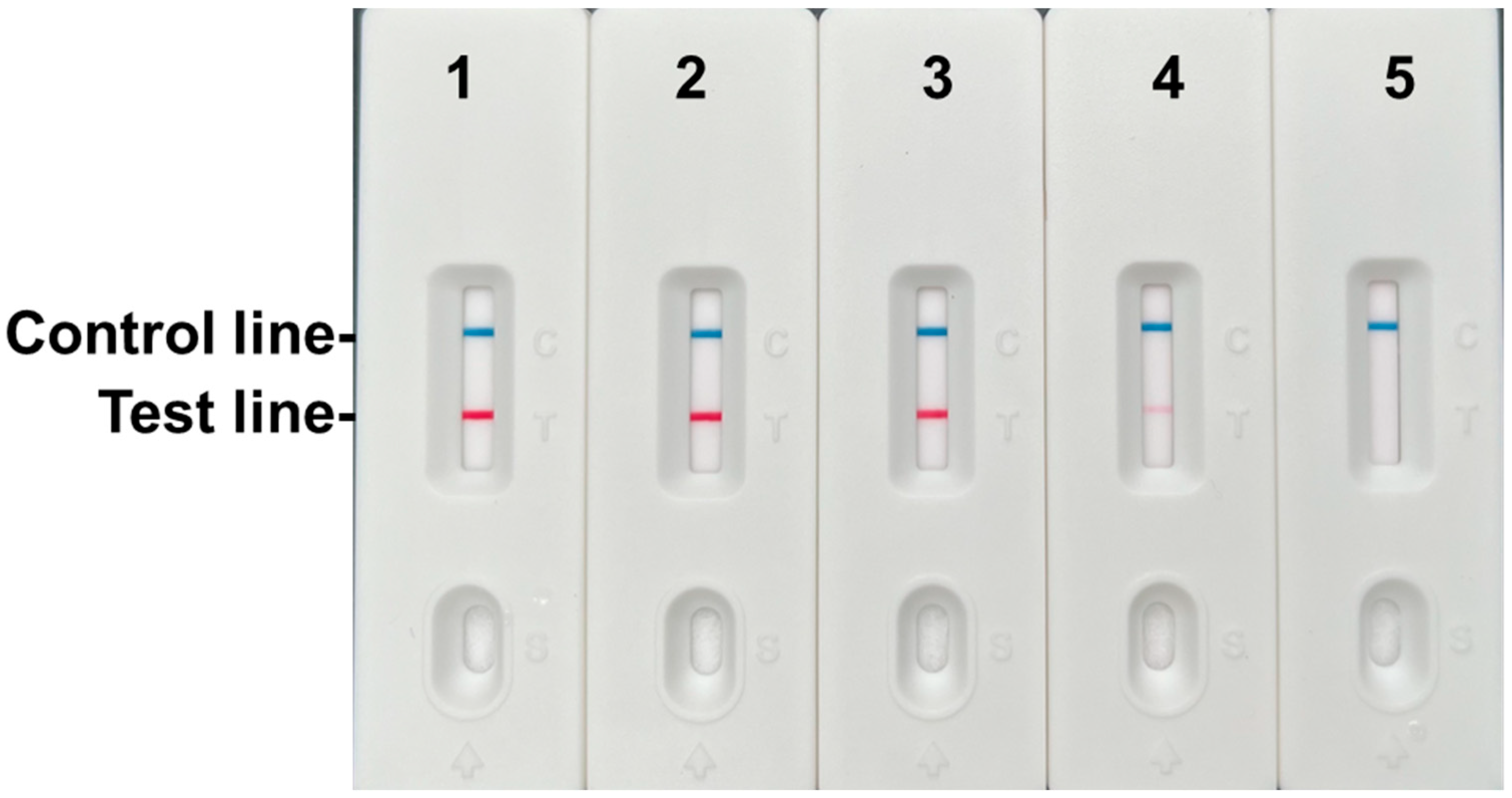
3.3. Specificity and Sensitivity Analysis of the RPA-LFD Assay
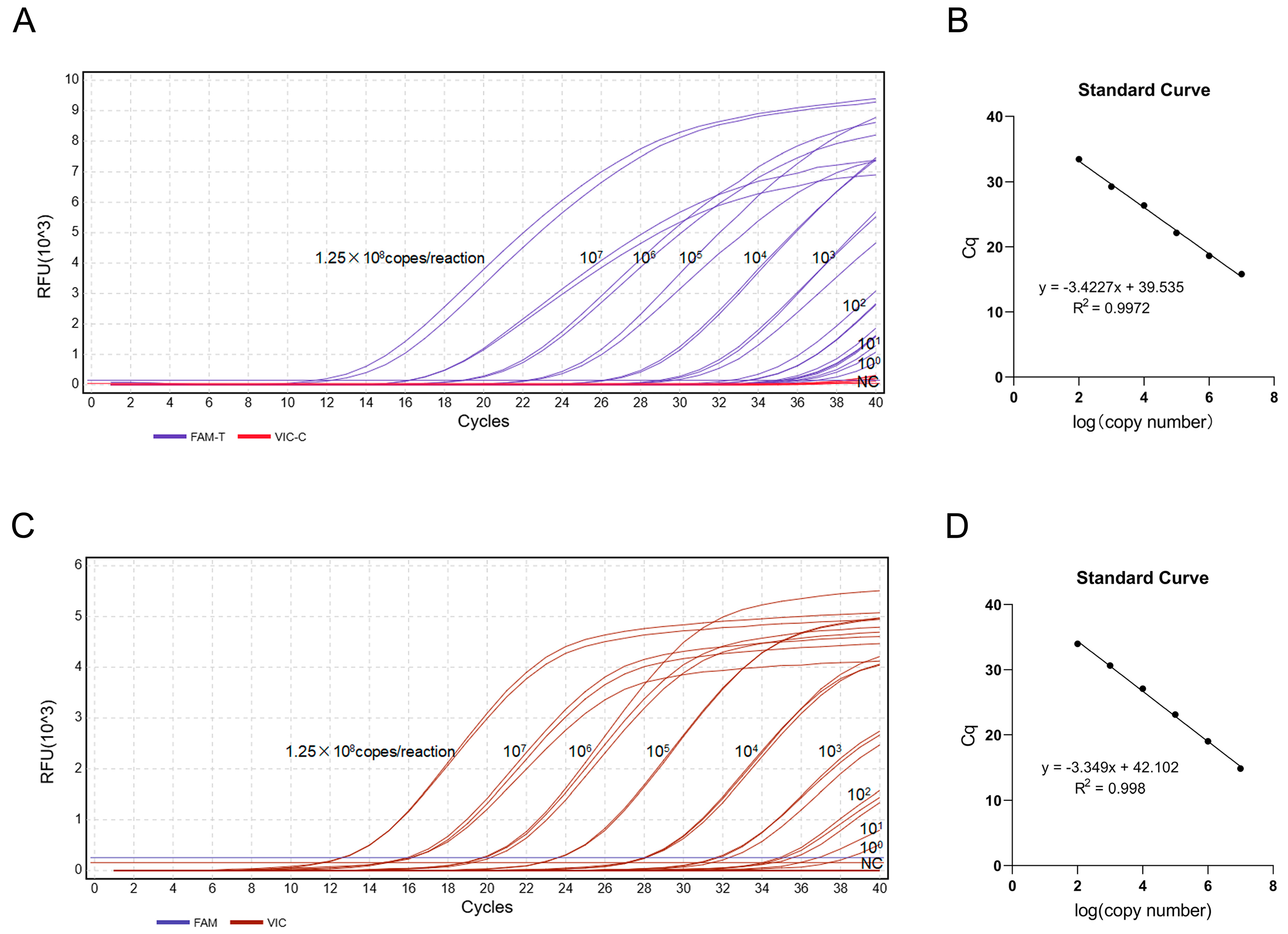
3.4. Establishment of the Duplex TaqMan-MGB qPCR Standard Curve
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis of the Duplex TaqMan-MGB qPCR Assay
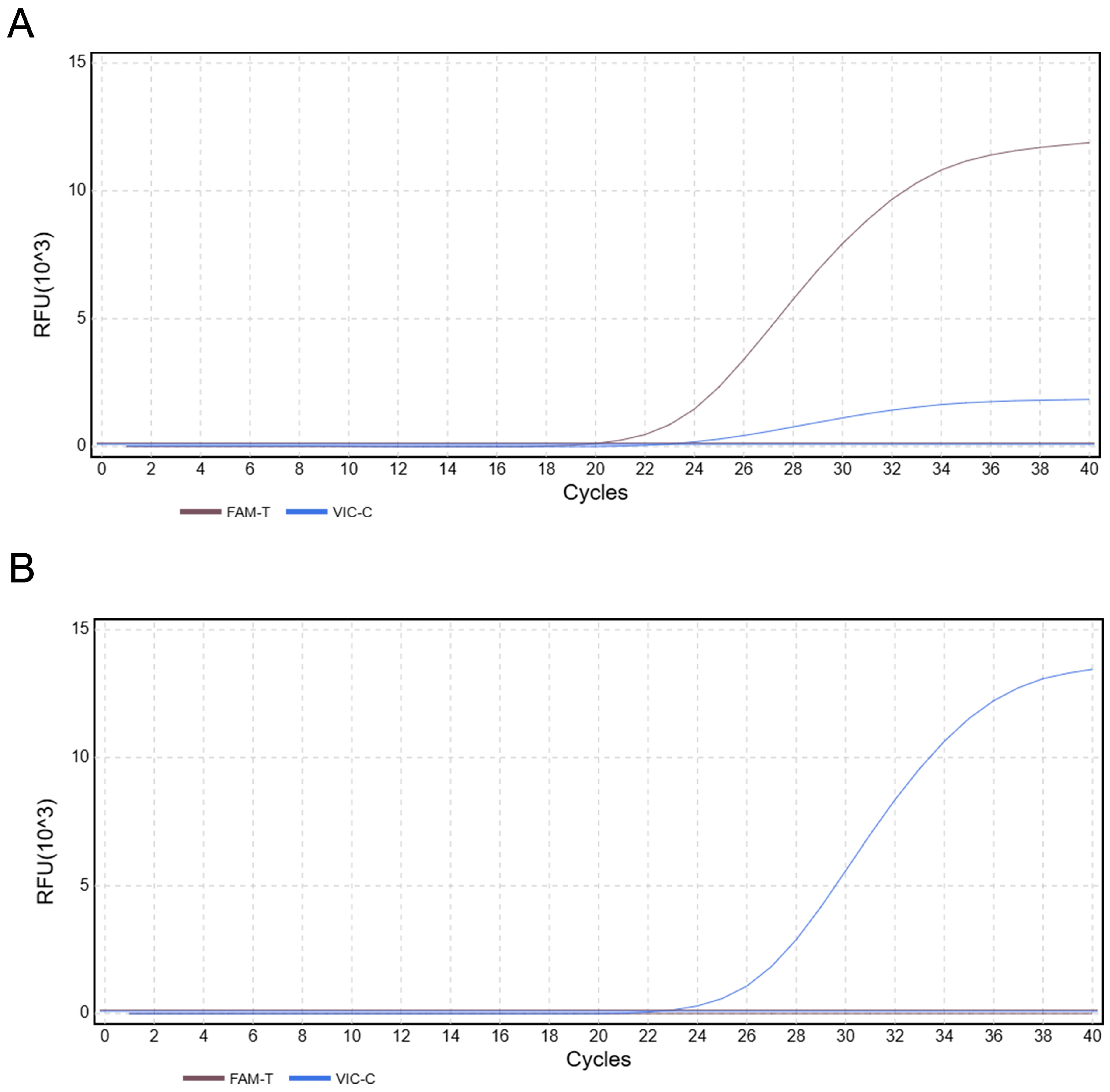
3.6. Specificity Analysis of the Duplex TaqMan-MGB qPCR Assay
3.7. Validation Using Samples of Known Origin
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: http://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Kan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Jawad, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Ren, M.; Xu, G.; Gui, L.; Li, M. Establishment of a Coilia nasus Gonadal Somatic Cell Line Capable of Sperm Induction In Vitro. Biology 2022, 11, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, P. Whole-genome resequencing of three Coilia nasus population reveals genetic variations in genes related to immune, vision, migration, and osmoregulation. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.M.; Qin, A.L. Ecological Habits and Distribution of Coilia Along the Chinese Coast and Its Changes of Output. Mar. Sci. 1984, 5, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Ye, S.; Qin, S.; Fan, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, W. Habitat for Coilia nasus in southern Zhejiang Province, China, based on a maximum entropy model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Bian, C.; Nie, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; You, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Li, H.; et al. Genome and population sequencing of a chromosome-level genome assembly of the Chinese tapertail anchovy (Coilia nasus) provides novel insights into migratory adaptation. GigaScience 2020, 9, giz157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Nie, Z.; Xu, G.; Xu, P. Genome-wide identification of the NHE gene family in Coilia nasus and its response to salinity challenge and ammonia stress. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, Q.; Maisano Delser, P.; Li, C. Multiple freshwater invasions of the tapertail anchovy (Clupeiformes: Engraulidae) of the Yangtze River. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 12202–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Luo, L.; Gu, S.; Hu, Z.; Wan, S.; Gao, Z. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Coilia nasus Revealed by 2b-RAD Sequencing. Biology 2023, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Tian, J.; Ma, F.; Liu, K. Status of Coilia nasus resources in the National Aquatic Germplasm Resources Conservation Area in the Anqing Section of the Yangtze River. J. Fish. Sci. China 2020, 27, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.L.; Dinesh, K.R.; Lim, T.M.; Chan, W.K.; Phang, V.P. Inheritance of RAPD markers in the guppy fish, Poecilia reticulata. Zool. Sci. 1995, 12, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; He, S. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers in a highland fish, Pareuchiloglanis sinensis (Siluriformes: Sisoridae) by next-generation sequencing. J. Genet. 2018, 97, e111–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, L.; Bai, W.; Ye, L. Species identification and quantification of silver pomfret using the droplet digital PCR assay. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ito, S.I.; Wong, M.K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Inoue, J.; Itoh, S.; Yukami, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Guo, C.; Ijichi, M.; et al. Comparison of species-specific qPCR and metabarcoding methods to detect small pelagic fish distribution from open ocean environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Guan, L.; Wang, D.; Gan, X. DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenburg, O.; Haber, J.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.Z.; Deng, J.H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, D.J.; Yuan, X.F.; Wei, F.; Wang, C.X.; Xu, X.L.; Wu, S.Q. Development of Real-Time and Lateral Flow Dipstick Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assays for the Rapid Field Diagnosis of MGF-505R Gene-Deleted Mutants of African Swine Fever Virus. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.L.; Tian, Q.; Meng, Q.Q.; Bao, X.Y.; Xu, P.D.; Liu, J.; Zhao, W.J.; Wang, H. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid Field Diagnosis of Stewart’s Wilt of Corn Pathogen Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, C.; Benkaroun, J.; Kurucay, H.N.; Albayrak, H.; Weidmann, M. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Tao, Z.Y.; Li, C.H. Speices identification of Coilia brachgnathus, C. nasus and C. nasus taihuensis with SNP markers. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2019, 28, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.; Wong, P.Y.; Parikh, C.; Wong, S. Moving toward rapid and low-cost point-of-care molecular diagnostics with a repurposed 3D printer and RPA. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 545, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Diagnostic Applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Lin, L.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, M. Development of a POCT detection platform based on a locked nucleic acid-enhanced ARMS-RPA-GoldMag lateral flow assay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 235, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-Q.; Han, G.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Gao, T.-X. The Possible Physical Barrier and Coastal Dispersal Strategy for Japanese Grenadier Anchovy, Coilia nasus in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea: Evidence from AFLP Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3283–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, H.-Y.; Tang, W.-Q.; Yang, J.-Q. Comparative Evolution of S7 Intron 1 and Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer in Coilia nasus (Clupeiformes: Engraulidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3085–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Cordes, J.F. DNA marker technologies and their applications in aquaculture genetics. Aquaculture 2004, 238, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q. Role of body size and temporal hydrology in the dietary shifts of short jaw tapertail anchovy Coilia nasus brachygnathus (Actinopterygii, Engraulidae) in a large floodplain lake. Hydrobiologia 2013, 703, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.Y. Genetic and morphological variation of three freshwater lake populations of Coilia ectenes (Engraulidae). Genetika 2012, 48, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-Q.; Hsu, K.-C.; Zhou, X.-D.; Kuo, P.-H.; Lin, H.-D.; Liu, D.; Bao, B.-L.; Tang, W.-Q. New insights on geographical/ecological populations within Coilia nasus (Clupeiformes: Engraulidae) based on mitochondrial DNA and microsatellites. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 29, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.X.; Tang, W.Q.; Li, S.F. Morphological changes of silver and bighead carp in the Yangtze River over the past 50 years. Dongwuxue Yanjiu 2010, 31, 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Xing, R.-R.; Zhou, M.-Y.; Sun, R.-X.; Han, J.-X.; Zhang, J.-K.; Zheng, W.-J.; Chen, Y. Application of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding for species identification in salmon products. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcoding of Commercially Important Salmon and Trout Species (Oncorhynchus and Salmo) from North America. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8379–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partis, L.; Wells, R.J. Identification of fish species using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Mol. Cell. Probes 1996, 10, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bergmann, S.M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Lv, Y.; Yin, J.; Yang, G.; Qv, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Development and comparative evaluation of real-time PCR and real-time RPA assays for detection of tilapia lake virus. Mol. Cell Probes 2021, 60, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Detection of fish pathogens by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technique. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1247, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Maji, U.J.; Shim, K.Y.; Yeo, I.C.; Jeong, C.B. Detection of the jellyfish Chrysaora pacifica by RPA-CRISPR-Cas12a environmental DNA (eDNA) assay and its evaluation through field validation and comparative eDNA analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Yi, J.; Su, L.; Guo, B.; Xiu, Y. Development of Two Recombinase Polymerase Amplification EXO (RPA-EXO) and Lateral Flow Dipstick (RPA-LFD) Techniques for the Rapid Visual Detection of Aeromonas salmonicida. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, S.; Lu, L.; Jiang, Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of large yellow croaker iridovirus by real-time RPA and RPA-LFD. J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Chang, J.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Yuan, G.; Su, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic Elizabethkingia miricola in black spotted frog by RPA-LFD and fluorescent probe-based RPA. Fish Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2022, 3, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davi, S.D.; Kissenkötter, J.; Faye, M.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Stahl-Hennig, C.; Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Sall, A.A.; Weidmann, M.; Ademowo, O.G.; et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Monkeypox virus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.; Ochoa-Corona, F.M.; Paret, M.L. Recombinase polymerase amplification applied to plant virus detection and potential implications. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 546, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, C.; Ye, S.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Huang, W. One-tube SARS-CoV-2 detection platform based on RT-RPA and CRISPR/Cas12a. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, H.; Jia, H.J.; Bu, L.K.; Pei, D.S. Ultra-sensitive detection of ecologically rare fish from eDNA samples based on the RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a technology. iScience 2023, 26, 107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Fujii, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Omura, M.; Shimada, T. TaqMan-MGB SNP genotyping assay to identify 48 citrus cultivars distributed in the Japanese market. Breed. Sci. 2020, 70, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleinitz, D.; Distefano, J.K.; Kovacs, P. Targeted SNP genotyping using the TaqMan® assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 700, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Species | Sample Sizes | Habitat Vegetation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Coilia nasus | 29 | Migratory (freshwater—brackish water) upstream during the breeding season, endangered species |
| Coilia brachygnathus | 6 | Small freshwater/brackish water (some migratory) fish, commonly found in estuaries |
| Tachysurus fulvidraco | 14 | Fresh water at the bottom, still water/slow flow |
| Pelteobagrus eupogon | 6 | Freshwater bottom layer, rivers/lakes |
| Pelteobagrus vachellii | 6 | Freshwater bottom, slow-flowing/reservoir |
| Pelteobaggrus nitidus | 6 | Freshwater bottom, stream/estuary |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 20 | The upper and middle layers of freshwater, open water areas |
| Hypophthalmichthys Nobilis | 14 | Upper and middle layers of freshwater, lakes/reservoirs |
| Mylopharyngodon piceus | 6 | Freshwater bottom, deep water area/river |
| Ctenopharyngodon Idella | 12 | The middle and lower layers of freshwater, an area rich in aquatic plants |
| Siniperca chuatsi | 14 | Freshwater bottom layer, crevices in rocks/water grass; Ambush carnivorous, high economic value |
| Siniperca knerii | 6 | Freshwater bottom layer, clear stream; Large eyes can adapt to weak light and are widely distributed |
| Culter alburnus | 14 | Upper and middle layers of freshwater, open water area; Fierce and predatory, good at jumping |
| Chanodichthys dabryi | 6 | Upper and middle layers of freshwater, slow-flowing/lake; Small fish, moving in groups |
| Chanodichthys mongolicus | 6 | The upper and middle layers of freshwater, rivers/lakes |
| Culter erythropterus | 6 | The upper and middle layers of freshwater, the edges of aquatic plants |
| Name | Sequence 5′–3′ | Product Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. nasus-Fe | CTCGCCACTTTACACGGCGGCGTCATTAAATG | 103 | Designed in this study |
| C. nasus-Rn | 5′Biotin-AGAACGATGTCAAGTGATGAGTTGGCTAGAACA | ||
| C. nasus-Pn | 5′FAM-ACCCATACTGTGAGCATTAGGATTCATTTTCC[THF]ATTTACAGTAGGAGG-3′C3 Spacer | ||
| Cn-Cb-F | CGCTACGCTGCTGACTGCAC | 202 | [20] |
| Cn-Cb-R | CAGCGTGGTCTGCTGGTTCAT | ||
| Cb-p-FAM | 5′FAM-AGCACAGGCAGCA-3′MGB | Designed in this study | |
| Cn-p-VIC | 5′VIC-AGCACGGGCAGCA-3′MGB |
| Number of Samples | Known Sample Name | Detection Method | Identify | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA-LFD | Duplex Taqman-MGB qPCR | ||||
| Coilia (+) non-Coilia (−) | FAM-T | VIC-C | |||
| 1 | C. brachygnathus | + | 29.98 | 32.12 | C. brachygnathus |
| 2 | C. brachygnathus | + | 22.08 | 23.72 | C. brachygnathus |
| 3 | C. brachygnathus | + | 22.03 | 23.87 | C. brachygnathus |
| 4 | C. brachygnathus | + | 21.28 | 22.90 | C. brachygnathus |
| 5 | C. brachygnathus | + | 23.50 | NA | C. brachygnathus |
| 6 | C. brachygnathus | + | 23.37 | 24.45 | C. brachygnathus |
| 7 | C. nasus | + | NA | 29.15 | C. nasus |
| 8 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.37 | C. nasus |
| 9 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.81 | C. nasus |
| 10 | C. nasus | + | NA | 27.41 | C. nasus |
| 11 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.48 | C. nasus |
| 12 | C. nasus | + | NA | 32.46 | C. nasus |
| 13 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.19 | C. nasus |
| 14 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.57 | C. nasus |
| 15 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.86 | C. nasus |
| 16 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.83 | C. nasus |
| 17 | C. nasus | + | NA | 25.27 | C. nasus |
| 18 | C. nasus | + | NA | 25.43 | C. nasus |
| 19 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.08 | C. nasus |
| 20 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.20 | C. nasus |
| 21 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.46 | C. nasus |
| 22 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.19 | C. nasus |
| 23 | C. nasus | + | NA | 25.10 | C. nasus |
| 24 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.53 | C. nasus |
| 25 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.56 | C. nasus |
| 26 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.94 | C. nasus |
| 27 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.11 | C. nasus |
| 28 | C. nasus | + | NA | 21.12 | C. nasus |
| 29 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.99 | C. nasus |
| 30 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.91 | C. nasus |
| 31 | C. nasus | + | NA | 24.06 | C. nasus |
| 32 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.79 | C. nasus |
| 33 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.63 | C. nasus |
| 34 | C. nasus | + | NA | 22.53 | C. nasus |
| 35 | C. nasus | + | NA | 23.74 | C. nasus |
| 36 | Tachysurus fulvidraco | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 37 | Pelteobagrus eupogon | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 38 | Pelteobagrus vachellii | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 39 | Pelteobaggrus nitidus | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 40 | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 41 | Hypophthalmichthys Nobilis | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 42 | Mylopharyngodon piceus | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 43 | Ctenopharyngodon idella | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 44 | Siniperca chuatsi | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 45 | Siniperca knerii | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 46 | Culter alburnus | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 47 | Chanodichthys dabryi | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 48 | Chanodichthys mongolicus | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 49 | Culter erythropterus | − | / | / | non-Coilia |
| 50 | H2O | − | - | - | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Jing, H.; Lv, J.; Wu, S. Integrating RPA-LFD and TaqMan qPCR for Rapid On-Site Screening and Accurate Laboratory Identification of Coilia brachygnathus and Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River. Foods 2025, 14, 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203484
Lin Y, Wang S, Zhang M, Wang N, Jing H, Lv J, Wu S. Integrating RPA-LFD and TaqMan qPCR for Rapid On-Site Screening and Accurate Laboratory Identification of Coilia brachygnathus and Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203484
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu, Suyan Wang, Min Zhang, Na Wang, Hongli Jing, Jizhou Lv, and Shaoqiang Wu. 2025. "Integrating RPA-LFD and TaqMan qPCR for Rapid On-Site Screening and Accurate Laboratory Identification of Coilia brachygnathus and Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River" Foods 14, no. 20: 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203484
APA StyleLin, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, M., Wang, N., Jing, H., Lv, J., & Wu, S. (2025). Integrating RPA-LFD and TaqMan qPCR for Rapid On-Site Screening and Accurate Laboratory Identification of Coilia brachygnathus and Coilia nasus in the Yangtze River. Foods, 14(20), 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203484





