Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumers’ Perception of Food Safety Risks in the Prepared Food Market
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Foundation and Research Hypotheses
3.1. Perceived Risk Theory on Food Safety
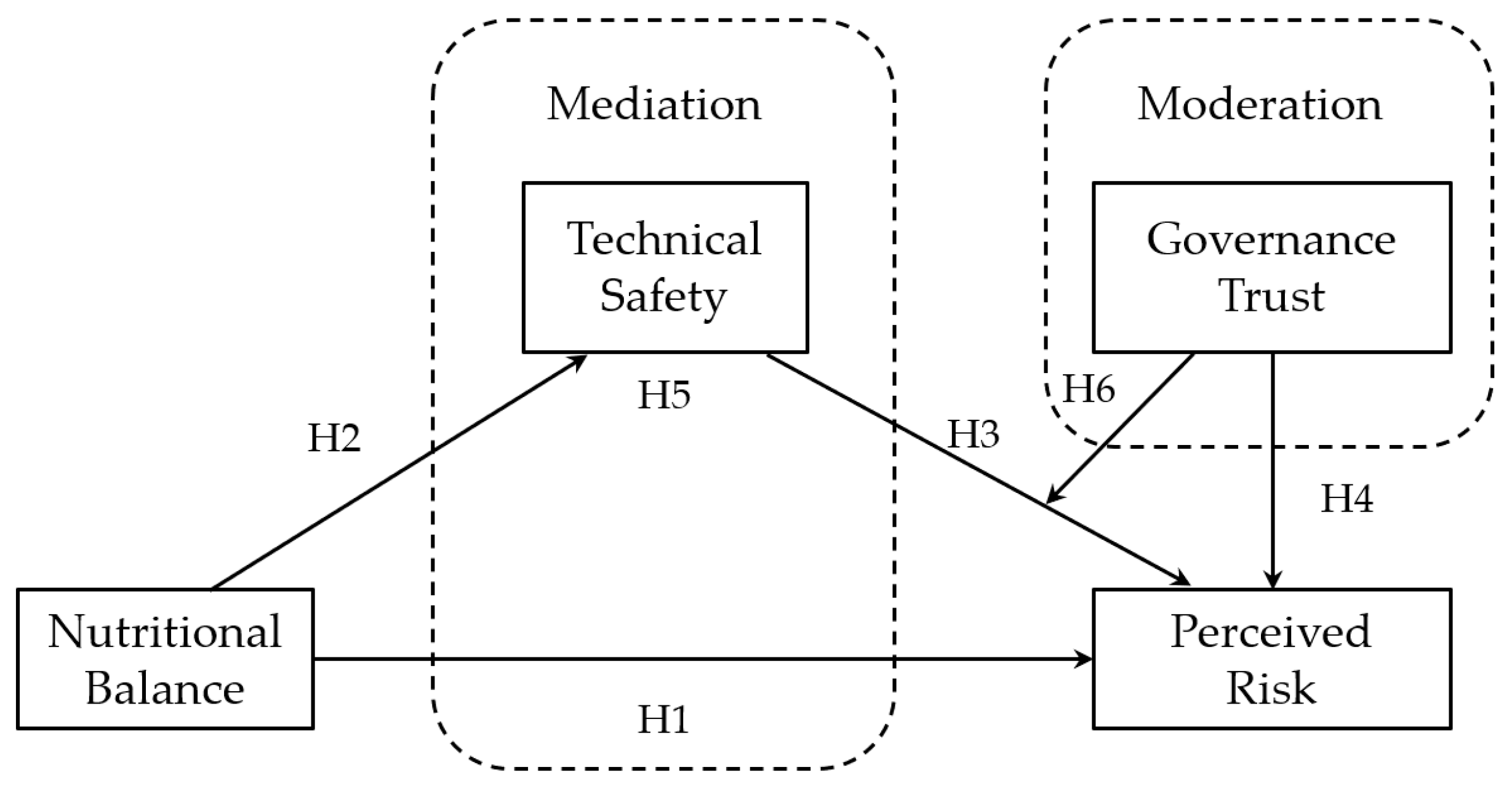
3.2. Research Hypotheses
3.2.1. Nutritional Balance
3.2.2. Technical Safety
3.2.3. Governance Trust
4. Research Design
5. Model Analysis and Hypothesis Testing
5.1. Reliability Analysis and Validity Analysis
5.2. Regression Analysis
5.3. Mediation Effect Test
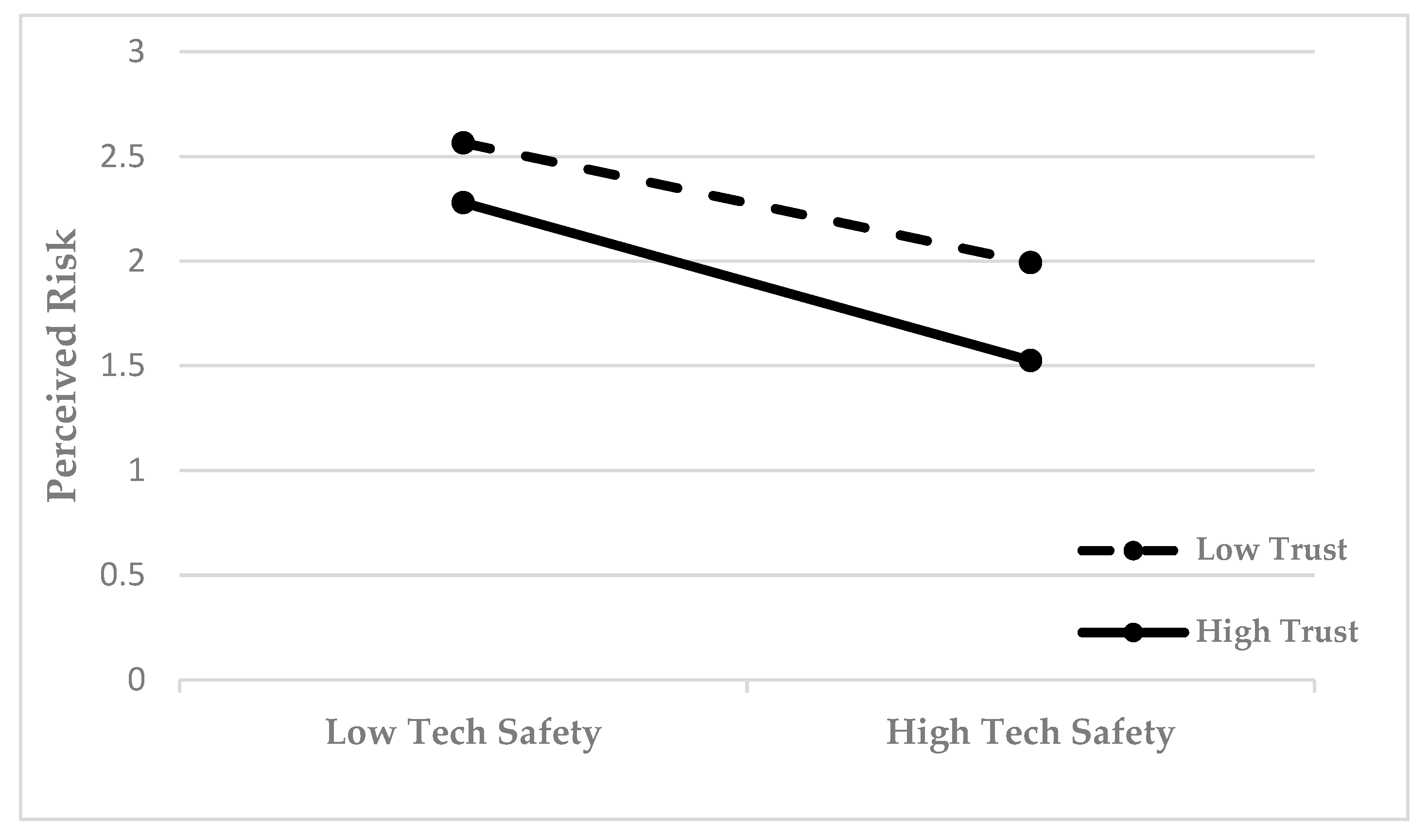
5.4. Moderation Effect Test
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Astbury, C.C.; Penney, T.L.; Adams, J. Home-prepared food, dietary quality and socio-demographic factors: A cross-sectional analysis of the UK National Diet and nutrition survey 2008–16. Int. J. Behav. Nutri. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, S.; Vandevijvere, S.; Xie, P.; Lee, A.; Swinburn, B. Paying for convenience: Comparing the cost of takeaway meals with their healthier home-cooked counterparts in New Zealand. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hong, Y.K.; Inanoglu, S.; Liu, F. Microwave pasteurization for ready-to-eat meals. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 23, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bachir, M.; Othman, I. Radiation technology to enhance food quality and ensure food safety in Syria. Arab Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2016, 34, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Hao, C. Will food safety incidents stimulate the public’s desire for food safety governance? Foods 2024, 13, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbot, J.M.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C.; Schaffner, D.; Bruhn, C.M.; Blalock, L. Comparison of food safety cognitions and self-reported food-handling behaviors with observed food safety behaviors of young adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, E.; Thomas, M.; Feng, Y. Young adult food safety knowledge gaps and perceptions of roommates’ food handling practices: A survey of university students in Indiana. Food Control 2021, 126, 108055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J.; Akkerman, R.; Ornholt-Johansson, G. Improving the supply chain and food quality of professionally prepared meals. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2013, 29, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, G.S. The formation mechanism and control strategies of warmed-over flavor in prepared dishes: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 153, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Muniz, F.J.; Bastida, S. Impact of cooking methods on the safety and quality of prepared meals: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, R.A. Consumer behavior as risk taking. In Dynamic Marketing for a Changing World; Hancock, R.S., Ed.; American Marketing Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1960; pp. 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, J.P.; Tarpey, L.X. A comparative analysis of three consumer decision strategies. J. Consum. Res. 1975, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, M.L.; Alhakami, A.; Slovic, P.; Johnson, S.M. The affect heuristic in judg-ments of risks and benefits. J. Behav. Decis. Making 2000, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antle, J.M. Benefits and costs of food safety regulation. Food Policy 1999, 24, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, J.; Kaplan, L.B. The components of perceived risk. In Proceedings of the Third Annual Convention of the Association for Consumer Research, Chicago, IL, USA, 2–5 November 1972; pp. 382–393. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, V.W. Consumer perceived risk: Conceptualizations and models. Eur. J. Mark. 1999, 33, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P. Information and consumer behavior. J. Political Econ. 1970, 78, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.S.T.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, M.C. Effect of institutional trust on consumers’ health and safety perceptions and repurchase intention for traceable fresh food. Foods 2021, 10, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, F.; Vaidean, G.; Parekh, N. Ultra-processed foods and cardiovascular diseases: Potential mechanisms of action. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummon, A.H.; Barrett, J.L.; Block, J.P.; Mcculloch, S.; Bolton, A.; Dupuis, R.; Petimar, J.; Gortmaker, S.L. Cost-effectiveness of mandating calorie labels on prepared foods in supermarkets. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2025, 68, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellard-Cole, L.; Davies, A.; Chen, J.L.N.; Jung, J.S.; Bente, K.B.; Kay, J.; Watson, W.L.; Hughes, C.; Rangan, A.; Yacef, K.; et al. The contribution of foods prepared outside the home to the diets of 18-to 30-year-old Australians: The MYMeals study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, L.; Gómez, B.; Garrido, M.D.; Fiszman, S.; Tarrega, A.; Linares, M.B. Do consumers change their perception of liking, expected satiety, and healthiness of a product if they know it is a ready-to eat meal? Foods 2020, 9, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, R.; Yang, W.; Khalifa, I.; Bi, J.; Li, Y.B.; Zhen, J.L.; Wang, B.P.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Innovations and challenges in the production of prepared dishes based on central kitchen engineering: A review and future perspectives. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 91, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, C.H.; Boyd, G. Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes from ready-to-eat turkey and cheese tortilla wraps using ionizing radiation. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Xiao, G. Spatial analysis of heavy metals in meat products in China during 2015–2017. Food Control 2019, 104, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, S.L.; Patel, A.S.; Nayak, B. Surface modification of cellulose nanofiber film with fatty acids for developing renewable hydrophobic food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Silva, L.J.; Simões, B.D.; Lino, C.; Pena, A. Exposure to nickel through commercial premade baby foods: Is there any risk? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 92, 103541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jing, P.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Jiao, S. Research progress on microbial control techniques of prepared dishes. Food Phys. 2024, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, M.; Ablan, M.; Crawford, T.N.; Conrad, A.; Busbee, A.; Robyn, M.; Marshall, K.E. Preparation methods and perceived risk of foodborne illness among consumers of prepackaged frozen vegetables–United States, September 2022. J. Food Protect. 2025, 88, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Xu, H. Research and development status of prepared foods in China: A review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Sun, Y.; Du, H.; Jiang, X. Research on safety risk control of prepared foods from the perspective of supply chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.R.S.; Shen, P.; Yu, W.Z.; Cai, M.; Tay, A.J.; Lim, I.; Chin, Y.S.; Ang, W.M.; Er, J.C.; Lim, G.S.; et al. Occurrence and dietary exposure of 3-MCPD esters and glycidyl esters in domestically and commercially prepared food in Singapore. Foods 2023, 12, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Tatham, R.L.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate data analysis. Technometrics 1998, 30, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, C.; Garg, V.; Kapoor, D.; Wasser, H.; Prabhakaran, D.; Jaacks, L.M. Food choice drivers in the context of the nutrition transition in Delhi, India. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2018, 50, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Zang, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, L. A literature review of public perception of food additive safety. Agro Food Ind. Hi Tech 2015, 26, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; William, S. Trust in government, perceived integrity and food safety protective behavior: The mediating role of risk perception. Int. J. Public Health 2023, 68, 1605432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
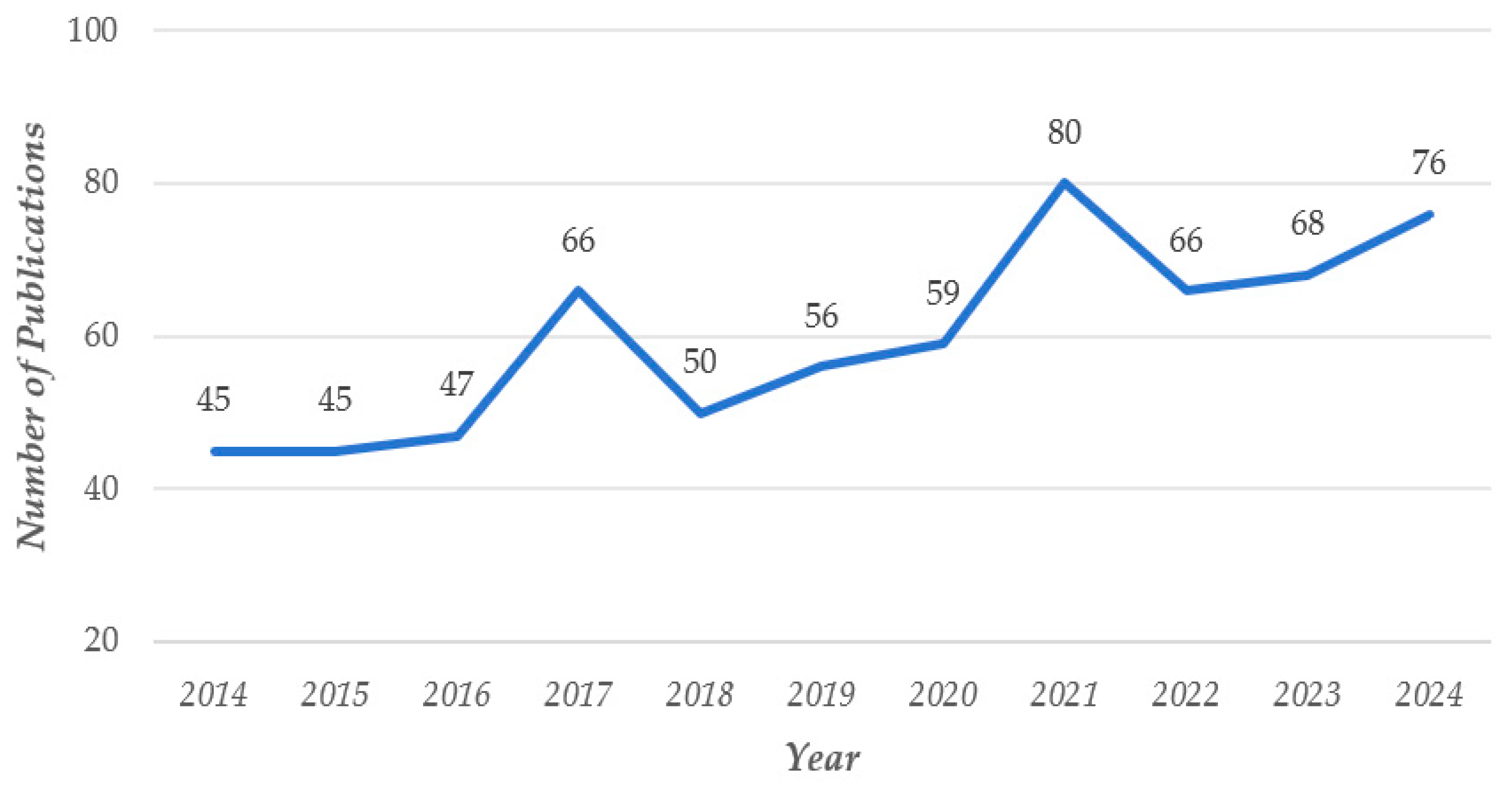
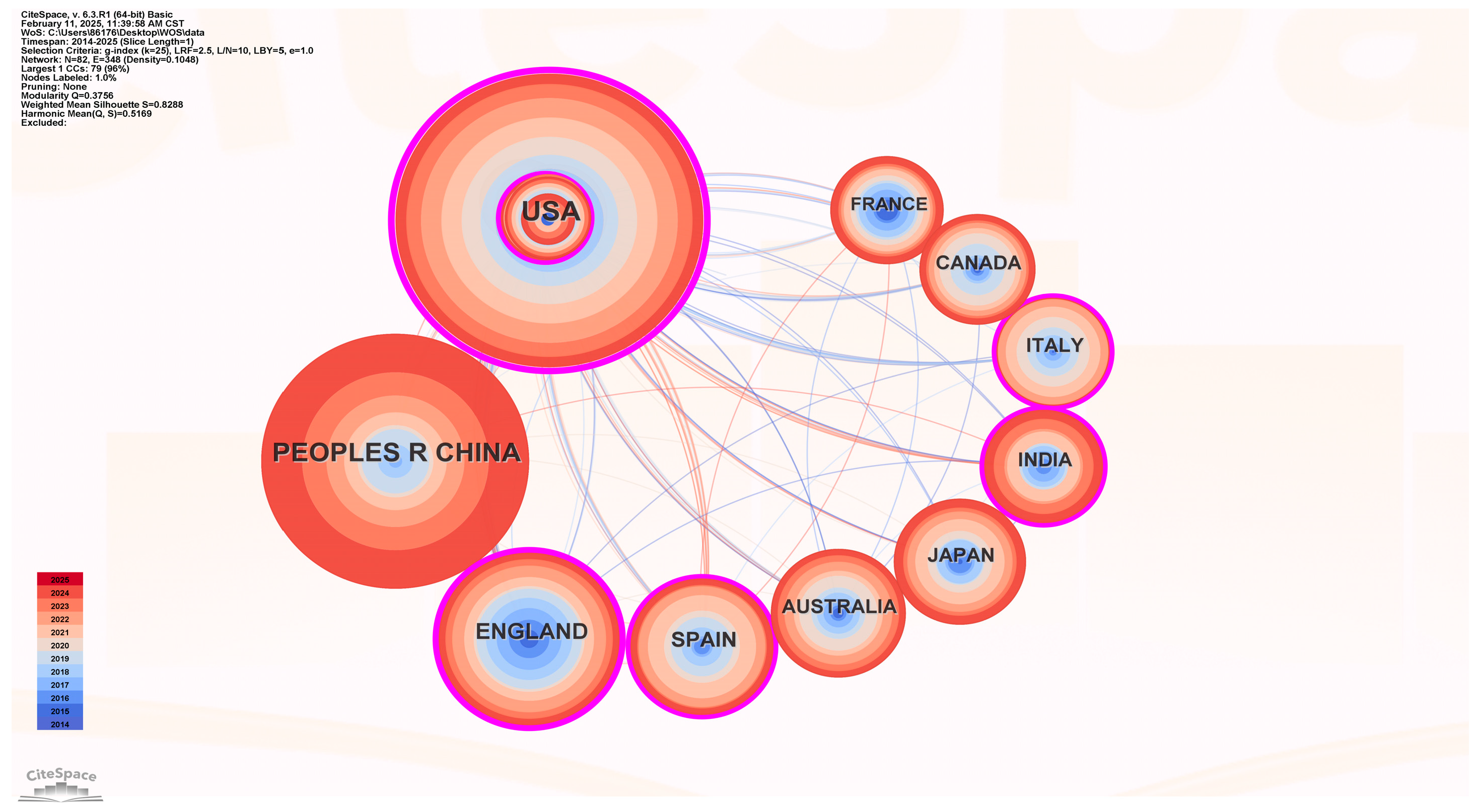
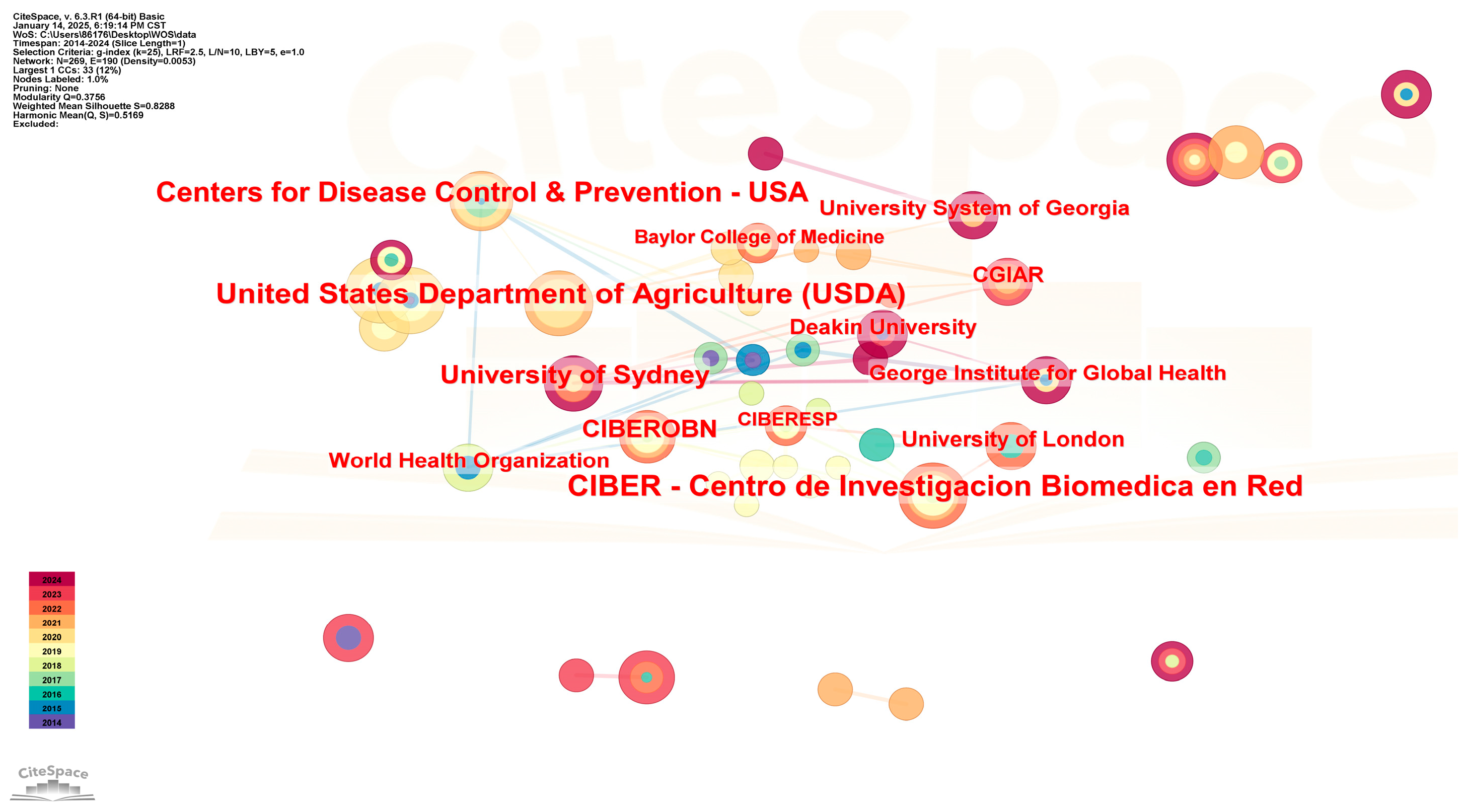
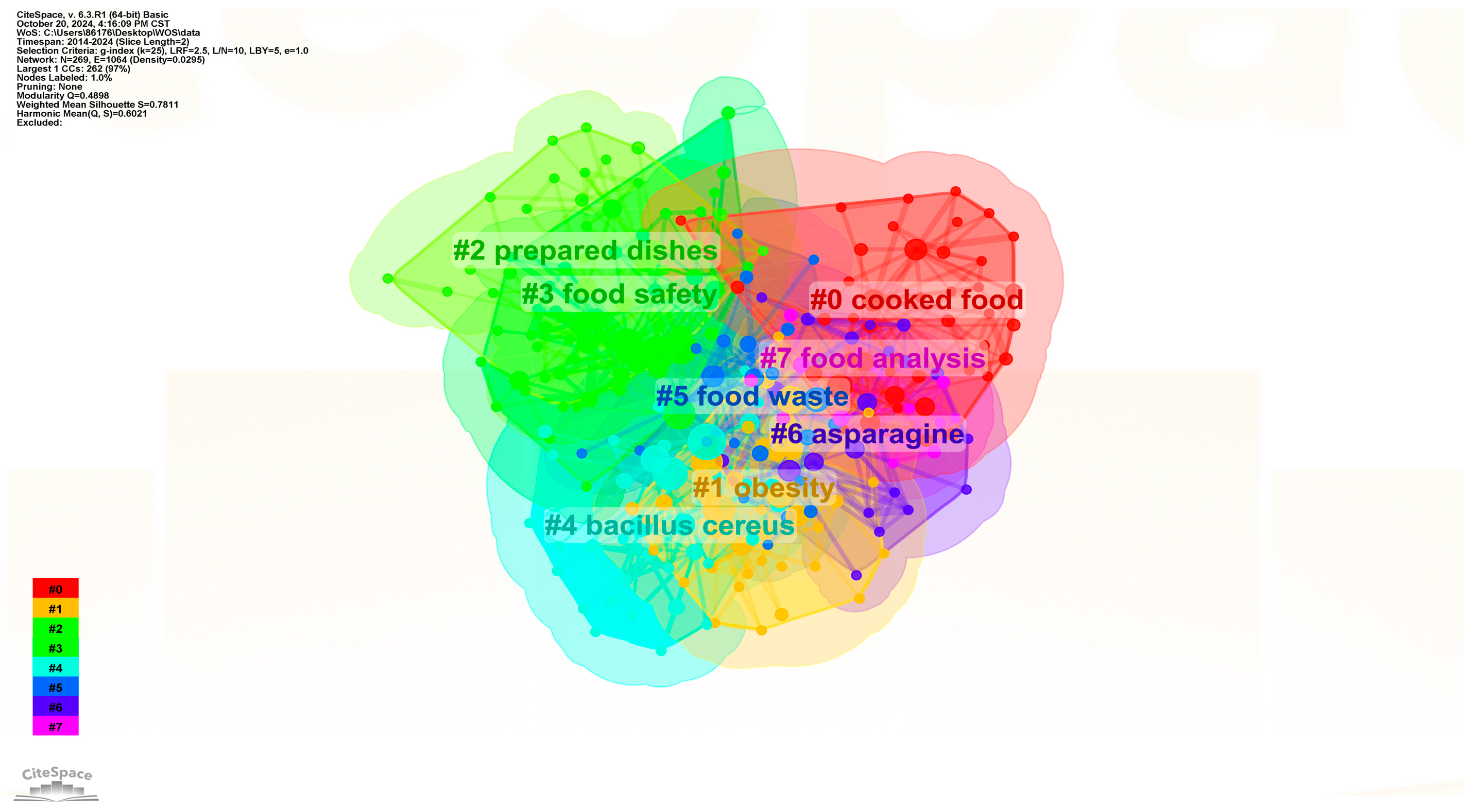
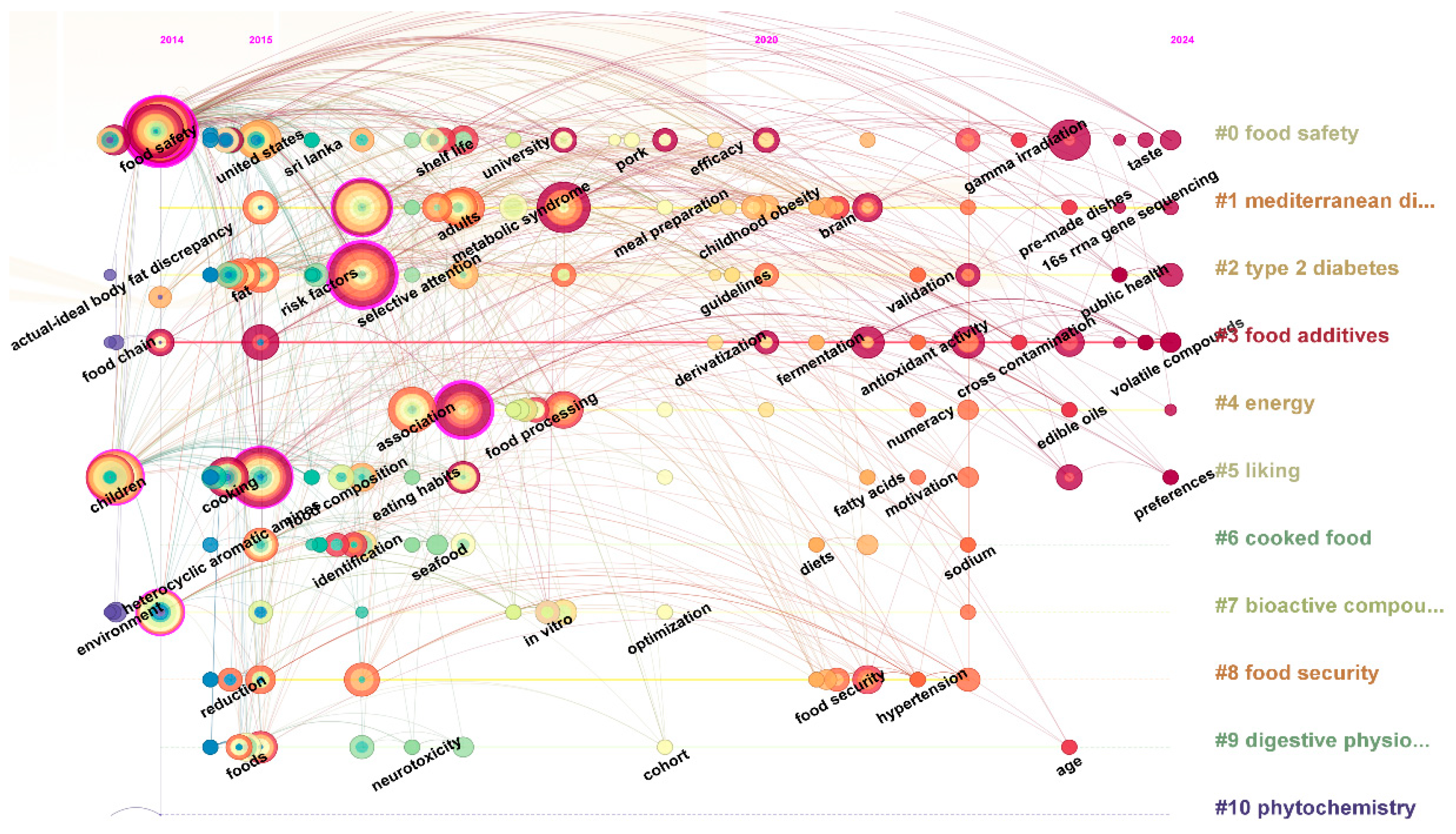
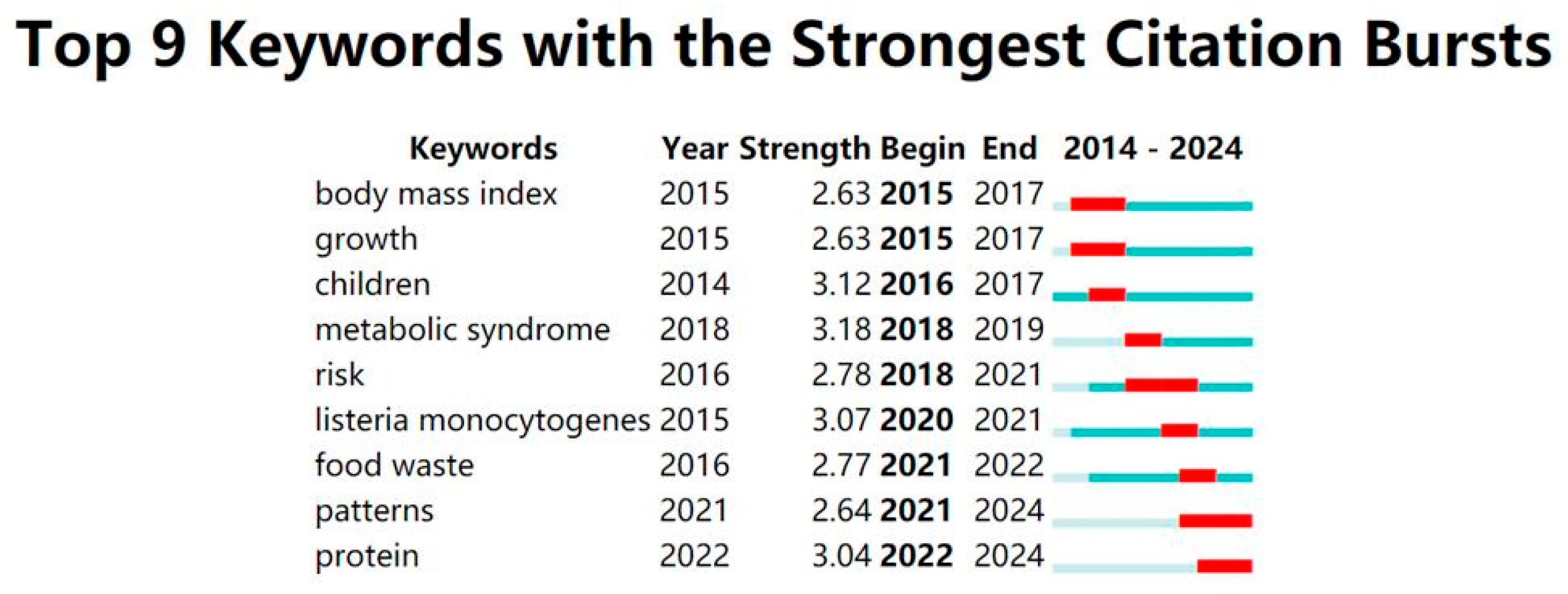
| Ranking | Cited Journal | Counts | Ranking | Cited Authors | Counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plos One | 176 | 1 | Silvennoinen K | 413 |
| 2 | Food Chem | 160 | 2 | Adams J | 275 |
| 3 | Am J Clin Nutr | 150 | 3 | Zhang M | 169 |
| 4 | Food Control | 134 | 4 | Gogswell M E | 51 |
| 5 | J Agr Food Chem | 131 | 5 | Gooderham N J | 40 |
| Demographic Variable | Item | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 291 | 49.7% |
| Female | 294 | 50.3% | |
| Age | ≤30 | 153 | 26.2% |
| 31 to 40 | 209 | 35.7% | |
| 41 to 50 | 122 | 20.9% | |
| >50 | 101 | 17.3% | |
| Educational Background | High school and below | 175 | 30.0% |
| Undergraduate | 304 | 52.0% | |
| Master and above | 106 | 18.1% | |
| Monthly household income | 5000 yuan and below | 231 | 39.5% |
| 5001–10,000 yuan | 208 | 35.6% | |
| 10,001 yuan and above | 146 | 25.0% |
| Dimension | Item | Factor Loading | CR | AVE | Cronbach’s Alpha | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional balance | Prepared food can provide all the necessary nutrients for daily consumption. | 0.801 | 0.8267 | 0.614 | 0.826 | [34] |
| Prepared food can be created with minimal use of preservative additives. | 0.795 | |||||
| Prepared food serve as a means to minimize the use of salt and oil. | 0.754 | |||||
| Technical safety | The production process of prepared food may incorporate additives in accordance with regulatory standards. | 0.780 | 0.8103 | 0.5874 | 0.810 | [26] |
| The production technology employed in the processing of prepared food is considered safe. | 0.750 | |||||
| Prepared foods are considered safe during transportation and storage. | 0.769 | |||||
| Governance trust | The government can implement policies to promote the high-quality development of the prepared food market. | 0.797 | 0.8225 | 0.6071 | 0.822 | [30] |
| The government departments possess the capacity to effectively oversee food safety within the prepared food market. | 0.758 | |||||
| The government departments demonstrate a proactive commitment to overseeing food safety within the prepared food market. | 0.782 | |||||
| Perceived risk | I am highly concerned about the overall qualifications of food enterprises in the current prepared food market. | 0.783 | 0.7991 | 0.5705 | 0.799 | [29] |
| I am apprehensive about the safety of the basic materials employed in the production of prepared food. | 0.710 | |||||
| The news media’s exposure has prompted apprehension regarding the potential hazards associated with my consumption of prepared food. | 0.771 |
| Discriminant Validity (Pearson Correlation) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Balance | Technical Safety | Governance Trust | Perceived Risk | |
| Nutritional balance | 0.784 | |||
| Technical safety | 0.537 | 0.766 | ||
| Governance trust | 0.449 | 0.455 | 0.779 | |
| Perceived risk | −0.289 | −0.390 | −0.274 | 0.755 |
| KMO Sample Appropriateness Measure. | 0.828 | |
|---|---|---|
| Bartlett sphericity test | Approximate chi-square | 2749.507 |
| Degree of freedom | 66 | |
| significance | 0.001 | |
| Initial Eigenvalue | Extract the Sum of Squared Loads | Rotating Load Sum of Squares | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Percent Variance | Cumulative % | Total | Percent Variance | Cumulative % | Total | Percent Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 4.369 | 36.408 | 36.408 | 4.369 | 36.408 | 36.408 | 2.223 | 18.523 | 18.523 |
| 2 | 1.766 | 14.717 | 51.125 | 1.766 | 14.717 | 51.125 | 2.222 | 18.517 | 37.040 |
| 3 | 1.432 | 11.930 | 63.055 | 1.432 | 11.930 | 63.055 | 2.166 | 18.050 | 55.090 |
| 4 | 1.208 | 10.067 | 73.122 | 1.208 | 10.067 | 73.122 | 2.164 | 18.032 | 73.122 |
| 5 | 0.477 | 3.975 | 77.097 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.468 | 3.898 | 80.995 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.440 | 3.664 | 84.659 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.418 | 3.480 | 88.139 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.386 | 3.214 | 91.353 | ||||||
| 10 | 0.375 | 3.128 | 94.481 | ||||||
| 11 | 0.337 | 2.810 | 97.292 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.325 | 2.708 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Item | Ingredient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Nutritional balance 1 | 0.812 | |||
| Nutritional balance 2 | 0.836 | |||
| Nutritional balance 3 | 0.827 | |||
| Technical safety 1 | 0.827 | |||
| Technical safety 2 | 0.794 | |||
| Technical safety 3 | 0.807 | |||
| Governance trust 1 | 0.858 | |||
| Governance trust 2 | 0.804 | |||
| Governance trust 3 | 0.827 | |||
| Perceived risk 1 | 0.823 | |||
| Perceived risk 2 | 0.825 | |||
| Perceived risk 3 | 0.837 | |||
| Nutritional Balance | Technical Safety | Governance Trust | Perceived Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional balance | 1 | |||
| Technical safety | 0.439 ** | 1 | ||
| Governance trust | 0.370 ** | 0.374 ** | 1 | |
| Perceived risk | −0.234 ** | −0.313 ** | −0.223 ** | 1 |
| Unnormalized Coefficient | Standardization Coefficient | t | Sig. | VIF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | Beta | ||||
| (Constant) | 4.282 | 0.152 | 28.103 | 0.000 | ||
| Nutritional balance | −0.090 | 0.043 | −0.094 | −2.109 | 0.035 | 1.319 |
| Technical safety | −0.230 | 0.044 | −0.234 | −5.209 | 0.000 | 1.324 |
| Governance trust | −0.099 | 0.042 | −0.101 | −2.328 | 0.020 | 1.238 |
| R2 | 0.118 | |||||
| The adjusted R2 | 0.113 | |||||
| F | 25.831 | |||||
| P | 0.000 | |||||
| Path | Effect Type | Effect Size | Standard Error | Bootstrap 95% CI | Relative Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||
| Nutrition balance → Technical safety → Perceived risk | Total effect | −0.224 | 0.039 | 0.210 | −0.234 | |
| Direct effect | −0.115 | 0.042 | −0.108 | −0.120 | 51.34% | |
| Indirect effect | −0.109 | 0.020 | −0.151 | −0.077 | 48.66% | |
| Regulating Variable | Effect | SE | t | P | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean − SD | −0.171 | 0.058 | −2.935 | 0.003 | −0.286 | −0.057 |
| Mean | −0.263 | 0.041 | −6.354 | 0.000 | −0.344 | −0.181 |
| Mean + SD | −0.354 | 0.059 | −6.052 | 0.000 | −0.469 | −0.239 |
| Level | Effect | SE | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean − SD | −0.054 | 0.025 | −0.103 | −0.004 |
| Mean | −0.097 | 0.021 | −0.137 | −0.057 |
| Mean + SD | −0.139 | 0.028 | −0.196 | −0.087 |
| Moderated mediation tests | −0.039 | 0.015 | −0.070 | −0.010 |
| Research Hypothesis | Result |
|---|---|
| The nutritional balance has a significant negative impact on perceived risk. | H1 established |
| The nutritional balance has a significant positive impact on technical safety. | H2 established |
| The technical safety has a significant negative impact on perceived risk. | H3 established |
| Governance trust has a significant negative impact on perceived risk. | H4 established |
| Technical safety has a mediating effect on nutritional balance and perceived risk. | H5 established |
| Governance trust has a significant moderating effect on technical safety and perceived risk. | H6 established |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, C.; Meng, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Wu, X.; Yu, Q. Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumers’ Perception of Food Safety Risks in the Prepared Food Market. Foods 2025, 14, 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203463
Shen C, Meng W, Chen X, Liu K, Wu X, Yu Q. Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumers’ Perception of Food Safety Risks in the Prepared Food Market. Foods. 2025; 14(20):3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203463
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Cong, Wenyuan Meng, Xue Chen, Kexin Liu, Xinyao Wu, and Qinhe Yu. 2025. "Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumers’ Perception of Food Safety Risks in the Prepared Food Market" Foods 14, no. 20: 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203463
APA StyleShen, C., Meng, W., Chen, X., Liu, K., Wu, X., & Yu, Q. (2025). Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumers’ Perception of Food Safety Risks in the Prepared Food Market. Foods, 14(20), 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14203463





