Phyllanthus emblica Prevents Adipogenesis by Regulating Histone Acetylation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Histone Acetyltransferase (HAT) Activity Assay
2.3. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Oil-Red-O (ORO) Staining Assay
2.6. Triglyceride (TG) Content
2.7. Extraction of Histone from 3T3-L1 Cells
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Analysis of Main Compounds Using LC-MS/MS
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
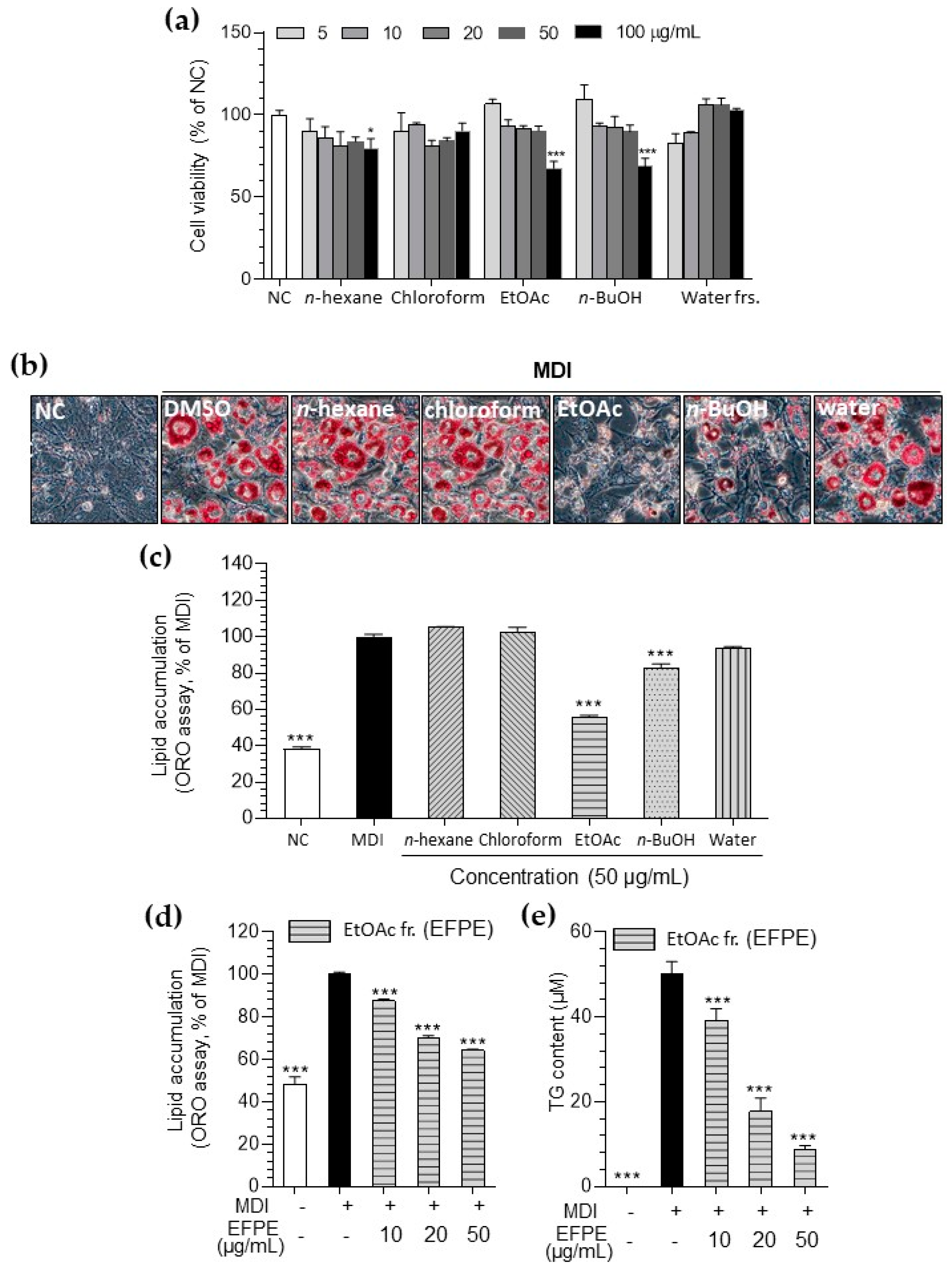
3.1. Inhibitory Effect of P. emblica on Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
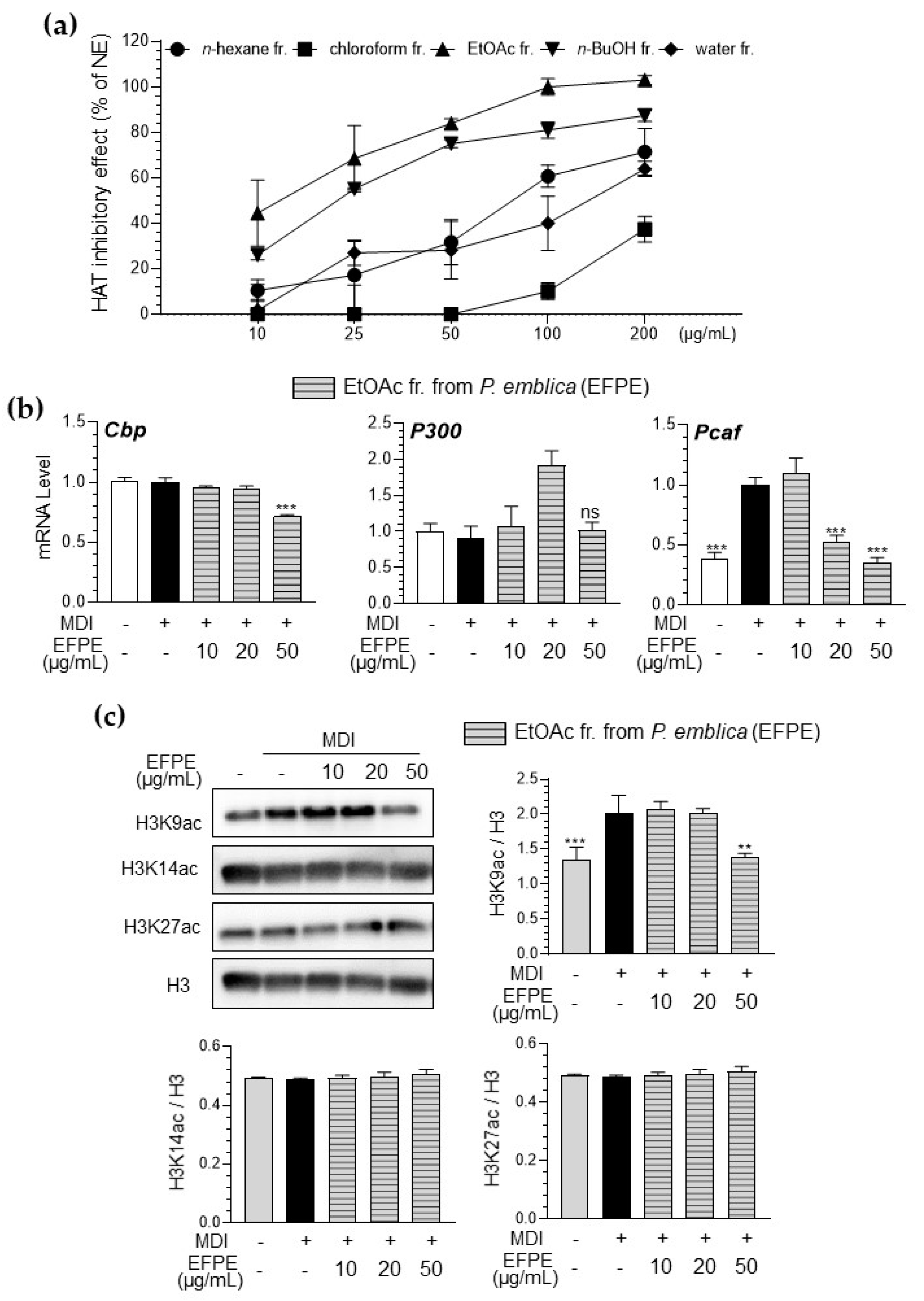
3.2. Inhibitory Effect of Various Fractions of P. emblica Against HAT Activity in a Cell-Free System
3.3. EFPE Regulates Adipogenesis-Related Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
3.4. Analysis of Bioactive Components in EFPE
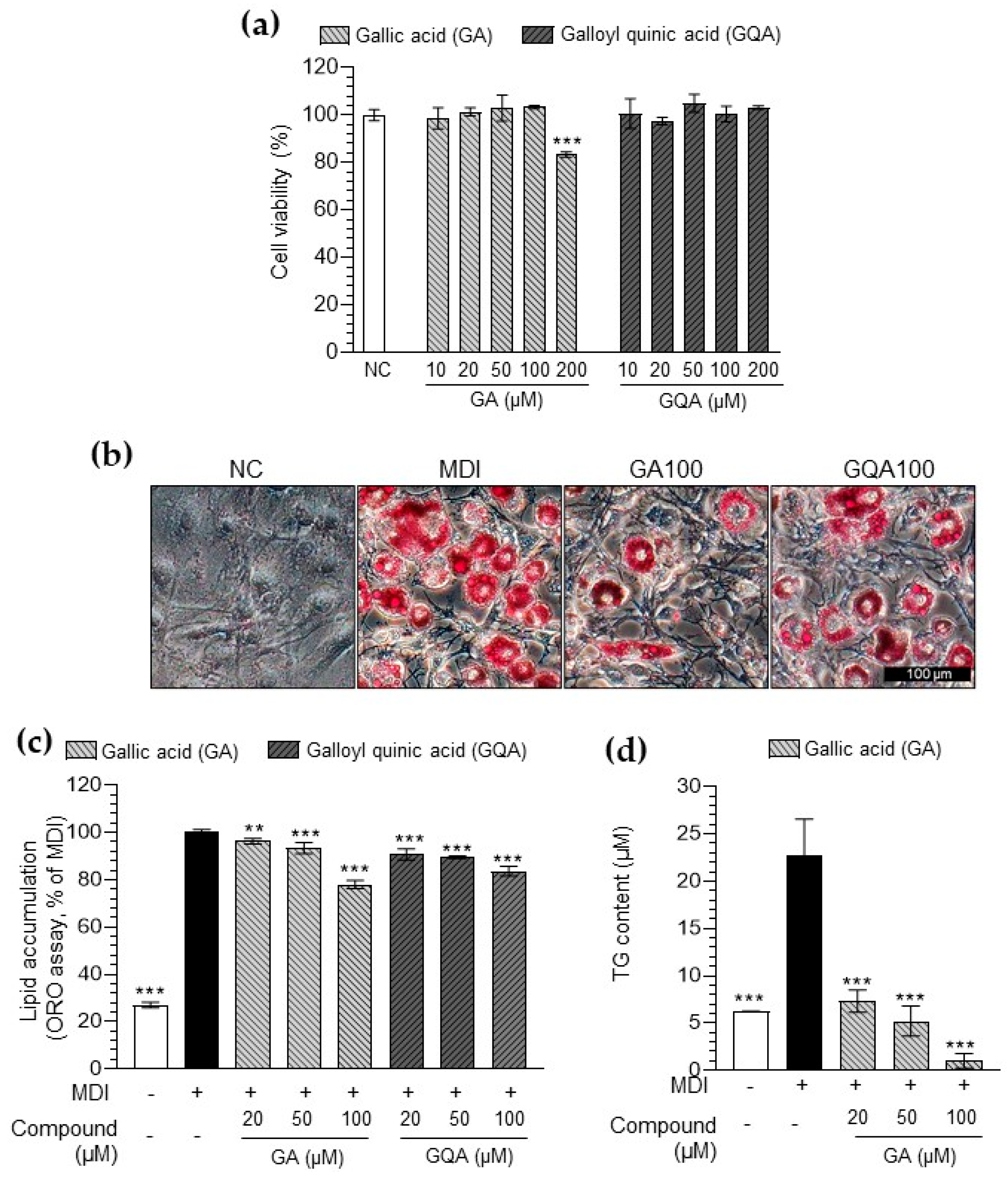
3.5. Inhibitory Effect of GA and GQA on Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
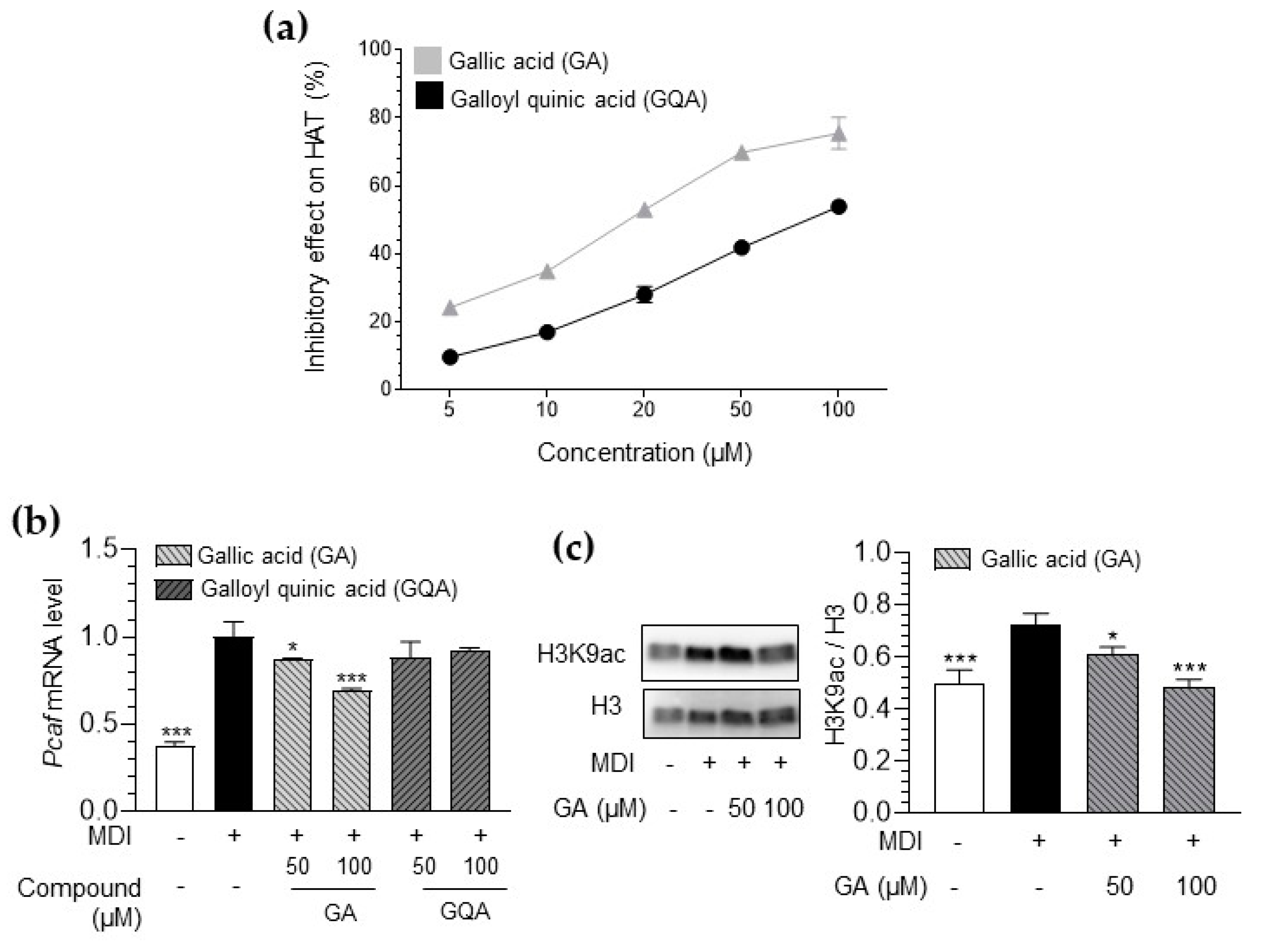
3.6. Inhibitory Effect of GA and GQA on HAT Activity and Histone Acetylation
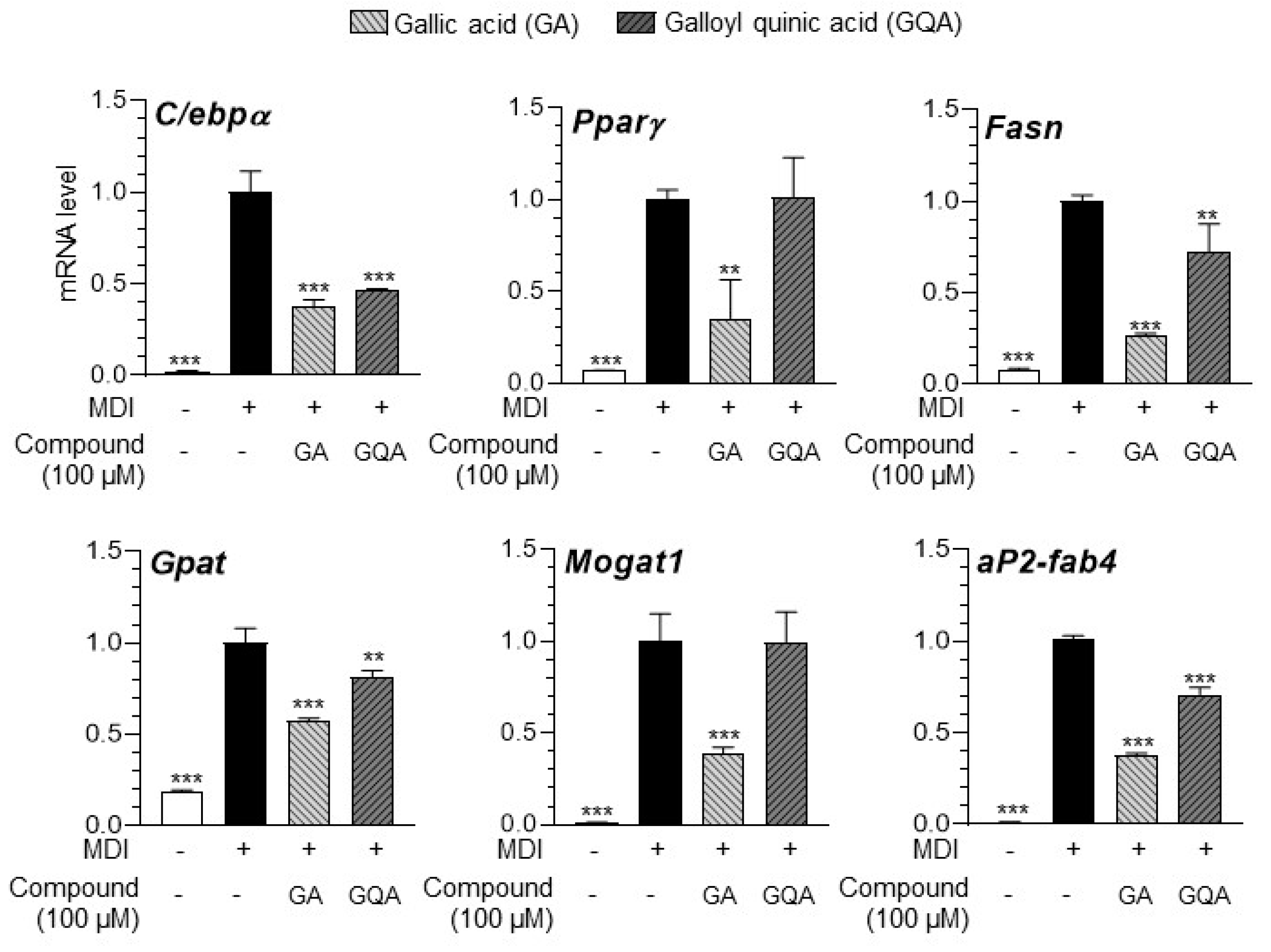
3.7. GA and GQA Regulates Adipogenesis-Related Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paniagua, J.A. Nutrition, insulin resistance and dysfunctional adipose tissue determine the different components of metabolic syndrome. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 483–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balusamy, S.R.; Veerappan, K.; Ranjan, A.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chellappan, D.K.; Dua, K.; Lee, J.; Perumalsamy, H. Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract attenuates lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via activating apoptosis mediated cell death. Phytomedicine 2020, 66, 153129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajas, L. Adipogenesis: A cross-talk between cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Ann. Med. 2003, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Walkey, C.J.; Puigserver, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, W.; Lee, S.-H.; Ko, H.M.; Jung, J.H.; Chung, W.-S.; Jang, H.-J. Anti-obesity effect of polygalin C isolated from Polygala japonica Houtt. via suppression of the adipogenic and lipogenic factors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillycrop, K.A.; Burdge, G.C. Maternal diet as a modifier of offspring epigenetics. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2015, 6, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.B.A.R.; Pinheiro-Castro, N.; Novaes, G.M.; Pascoal, G.D.F.L.; Ong, T.P. Bioactive food compounds, epigenetics and chronic disease prevention: Focus on early-life interventions with polyphenols. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Allahverdi, A.; Zahiri, J. Evaluation of post-translational modifications in histone proteins: A review on histone modification defects in developmental and neurological disorders. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Jiang, S. Role of histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases in adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milagro, F.I.; Mansego, M.L.; De Miguel, C.; Martínez, J.A. Dietary factors, epigenetic modifications and obesity outcomes: Progresses and perspectives. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 782–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Chillarón, J.C.; Díaz, R.; Martínez, D.; Pentinat, T.; Ramón-Krauel, M.; Ribó, S.; Plösch, T. The role of nutrition on epigenetic modifications and their implications on health. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2242–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y. Antioxidant activity of methanolic extract of Emblica fruit (Phyllanthus emblica L.) from six regions in China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Hafeez, N.; Rauf, A.; Bashir, S.; Linfang, H.; Rehman, M.; Mubarak, M.S.; Uddin, M.S.; Bawazeer, S.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Phyllanthus emblica: A comprehensive review of its therapeutic benefits. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 138, 278–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, B.P.; Subedi, L. Phytochemistry, pharmacology and medicinal properties of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goran, M.I. Energy metabolism and obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 84, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Xiao, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, J.L.; Zhai, Y.G. Review: Epigenetic regulation of adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.X.; Lee, J. Dietary regulation of histone acetylases and deacetylases for the prevention of metabolic diseases. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1868–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, J.A.; Yen, G.C. Preventive effect of Indian gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica L.) fruit extract on cognitive decline in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Z.; Tung, Y.-T.; Hsia, S.-M.; Wu, C.-H.; Yen, G.-C. The hepatoprotective effect of Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit on high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in SD rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Nian, C.; McIntosh, C.H.S. Adipocyte expression of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor involves gene regulation by PPARγ and histone acetylation. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barilla, S.; Treuter, E.; Venteclef, N. Transcriptional and epigenetic control of adipocyte remodeling during obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021, 29, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-E.; Schmidt, H.; Lai, B.; Ge, K. Transcriptional and epigenomic regulation of adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00601-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-T.; Choi, H.-K.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, S.; Hur, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Chung, M.-Y. Hypolipidemic activity of Quercus acutissima fruit ethanol extract is mediated by inhibition of acetylation. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-W.; Friso, S. Epigenetics: A new bridge between nutrition and health. Adv. Nutr. 2010, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yu, L.R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Kasper, L.H.; Lee, J.E.; Wang, C.; Brindle, P.K.; Dent, S.Y.R.; Ge, K. Distinct roles of GCN5/PCAF-mediated H3K9ac and CBP/p300-mediated H3K18/27ac in nuclear receptor transactivation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, B.X.; Brunmeir, R.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, X.; Idris, M.; Liu, C.; Xu, F. Regulation of thermogenic adipocyte differentiation and adaptive thermogenesis through histone acetylation. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Eldaim, M.A.; Matsuoka, S.; Okamatsu-Ogura, Y.; Kamikawa, A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Terao, A.; Nakajima, K.I.; Kimura, K. Retinoic acid modulates lipid accumulation glucose concentration dependently through inverse regulation of SREBP-1 expression in 3T3L1 adipocytes. Genes Cells 2017, 22, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Bahman, F.; Kochumon, S.P.; Jacob, T.K.; Alrashed, F.; Wilson, A.; Arefanian, H.; Thomas, R.S.; Akhter, N.; Al-Mansour, N.; et al. 162-OR: Sustained TNF-α transcription triggered in obesity through H3K9/K18 acetylation is associated with metabolic impairments. Diabetes 2024, 73, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketema, E.B.; Lopaschuk, G.D. The role of acetylation in obesity-induced cardiac metabolic alterations. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 27, 13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambele, M.A.; Dhanraj, P.; Giles, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipogenesis: A complex interplay of multiple molecular determinants and pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.; Chung, M.-Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.-K.; Hwang, J.-T. Tamarixetin abrogates adipogenesis through inhibiting p300/CBP-associated factor acetyltransferase activity in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totani, N.; Tateishi, S.; Takimoto, T.; Maeda, Y.; Sasaki, H. Gallic acid glycerol ester promotes weight-loss in rats. J. Oleo Sci. 2011, 60, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, P.K.; Devi, S.; Mittal, N. Therapeutic potential of gallic acid in obesity: Considerable shift! Obes. Med. 2023, 37, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.D.; Das, A.; Chai, Y.G. The anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory roles of gallic acid on transcriptional regulation. In Handbook on Gallic Acid; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Seong, A.R.; Yoo, J.Y.; Jin, C.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jun, W.J.; Yoon, H.G. Gallic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, suppresses β-amyloid neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora-Tatar, G.; Dayangaç-Erden, D.; Demir, A.S.; Dalkara, S.; Yelekçi, K.; Erdem-Yurter, H. Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

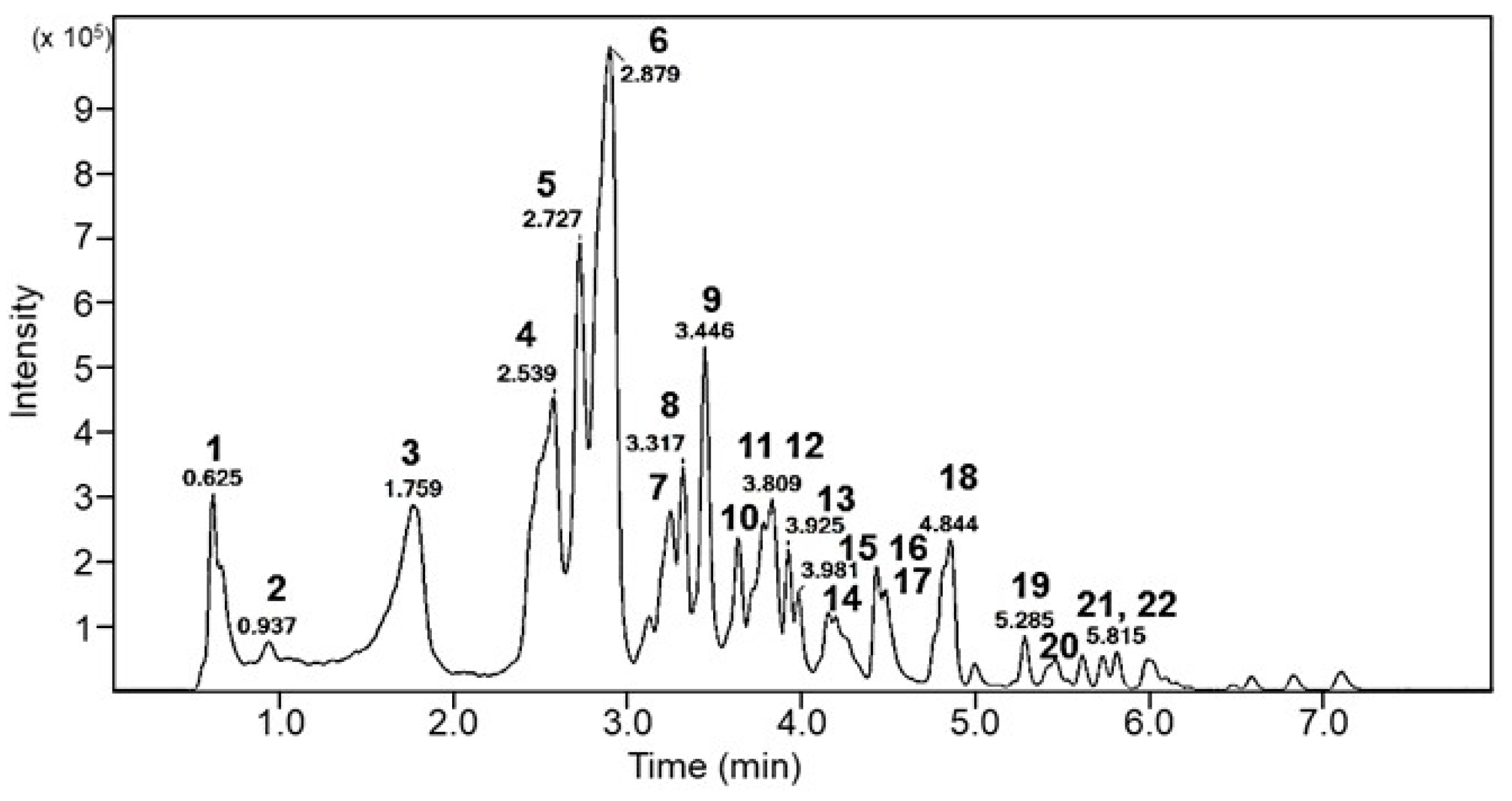
| Peak No. | Rt (min) | Proposed Compound | Precursor (m/z) [M−H]− | MS/MS Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.63 | Mucic acid gallate | 361 | 209, 191, 147, 133, 85, 71, 59 |
| 2 | 0.94 | Mucic acid gallate | 723.1 [2M−H]− | 361, 209, 191 |
| 3 | 1.76 | Galloylquinic acid isomer | 687.1 | 343, 191, 147, 85 |
| 4 | 2.54 | Gallic acid | 169 | 169, 125, 124, 123, 107, 97, 95, 81, 79, 69, 67, 53 |
| 5 | 2.73 | Galloylquinic acid isomer | 687.1 | 687, 343, 191, 169, 147, 85 |
| 6 | 2.88 | Galloylquinic acid isomer | 687.1 | 687, 343, 237, 191, 169, 147, 85 |
| 7 | 3.12 | Gallic acid derivative | 673.1 | 387, 285, 169, 133, 125, 115 |
| 8 | 3.24 | Gallic acid derivative | 387.1 | 169, 125, 129 |
| 9 | 3.32 | Gallic acid derivative | 455.0 (387) | 387, 325, 209, 191, 173, 169, 151, 129, 125 |
| 10 | 3.45 | Digalloyl glucose | 483.1 | 483, 331, 313, 271, 241, 211, 169, 168, 151, 125, 124 |
| 11 | 3.64 | Digallic acid | 321 | 169, 125 |
| 12 | 3.81 | Trigalloyl glucose isomer | 635.1 | 123, 113, 93, 68, 25 |
| 13 | 3.93 | Trigalloyl glucose isomer | 635.1 | 483, 465, 423, 313, 271, 211, 169 |
| 14 | 3.98 | Digalloyl-HHDP glucose | 785.1 | 633, 615, 300, 463, 275 |
| 15 | 4.16 | unidentified ellagitannin | 953.6 | 300 |
| 16 | 4.21 | Gallic acid derivative | 965.1 | 387, 285, 169, 133, 125 |
| 17 | 4.45 | Gallic acid derivative | 197 | 169, 125, 124, 78 |
| 17 | 4.84 | Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | 447.1 | 479, 314, 287, 223, 213, 163 |
| 19 | 5.29 | Kaempferol-3-O-deoxyhexoside | 431.1 | 285, 284, 255, 229, 227 |
| 20 | 5.62 | unidentified gallic acid | 461.1 | 313, 271, 241, 211, 169, 151, 125, 124 |
| 21 | 5.73 | unidentified gallic acid | 461.1 | 313, 211, 189, 169, 161, 151, 147, 125, 124, 123 |
| 22 | 5.82 | 613.1 | 465, 461, 313, 271, 211, 169 |
| Compound Name | Phenolic Acid (mg/g) |
|---|---|
| Gallic acid (GA) | 13.99 ± 0.07 |
| 3-Galloylquinic acid (GQA) | 10.71 ± 0.16 |
| Compound Name | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| Gallic acid (GA) | 18.32 |
| 3-Galloylquinic acid (GQA) | 83.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.K.; Lee, Y.G.; Lee, J.-I.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, J.-T.; Chung, M.-Y. Phyllanthus emblica Prevents Adipogenesis by Regulating Histone Acetylation. Foods 2025, 14, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020160
Park SK, Lee YG, Lee J-I, Kim M-S, Park J-H, Hwang J-T, Chung M-Y. Phyllanthus emblica Prevents Adipogenesis by Regulating Histone Acetylation. Foods. 2025; 14(2):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020160
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seon Kyeong, Yu Geon Lee, Jae-In Lee, Min-Sun Kim, Jae-Ho Park, Jin-Taek Hwang, and Min-Yu Chung. 2025. "Phyllanthus emblica Prevents Adipogenesis by Regulating Histone Acetylation" Foods 14, no. 2: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020160
APA StylePark, S. K., Lee, Y. G., Lee, J.-I., Kim, M.-S., Park, J.-H., Hwang, J.-T., & Chung, M.-Y. (2025). Phyllanthus emblica Prevents Adipogenesis by Regulating Histone Acetylation. Foods, 14(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020160








