Salt Equilibria and Protein Glycation in Young Child Formula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulae Collection, Reconstitution and Fractionation
2.2. Formula Composition and pH Analysis
2.3. Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Citrate, Potassium and Sodium Analysis
2.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. Furosine, Blocked Lysine, Reactive Lysine and HMF Analysis
3. Results
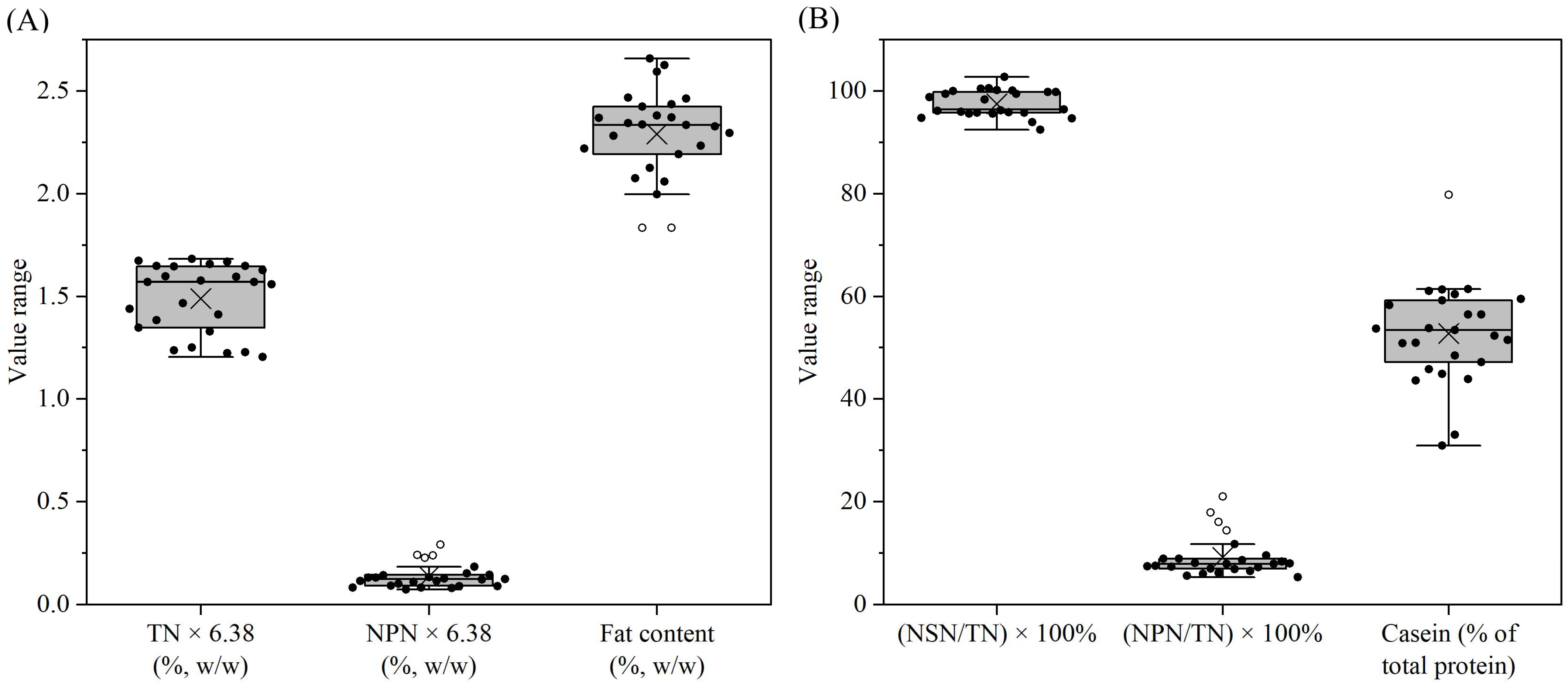
3.1. Formula Composition
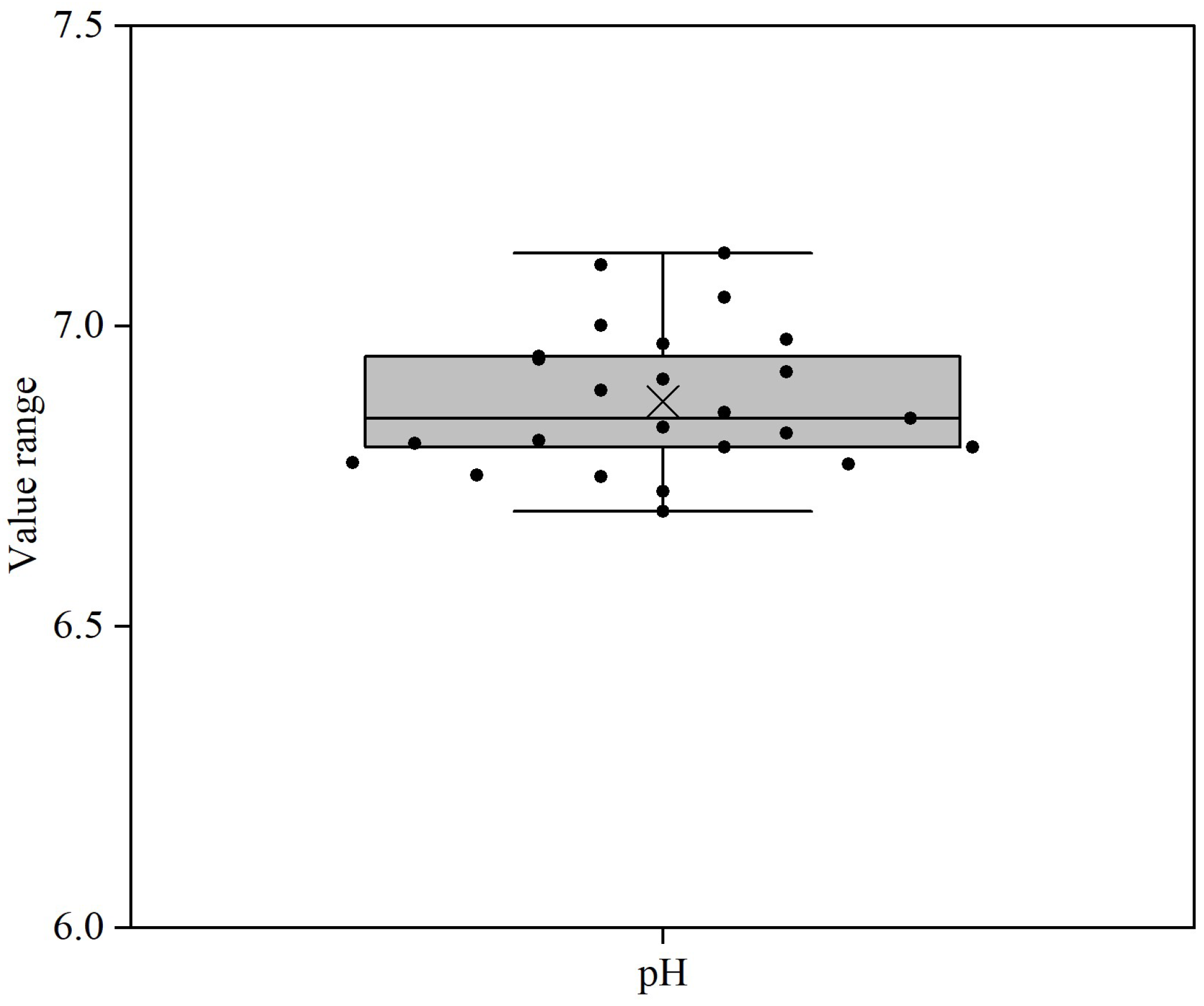
3.2. pH Value
3.3. Calcium Distribution
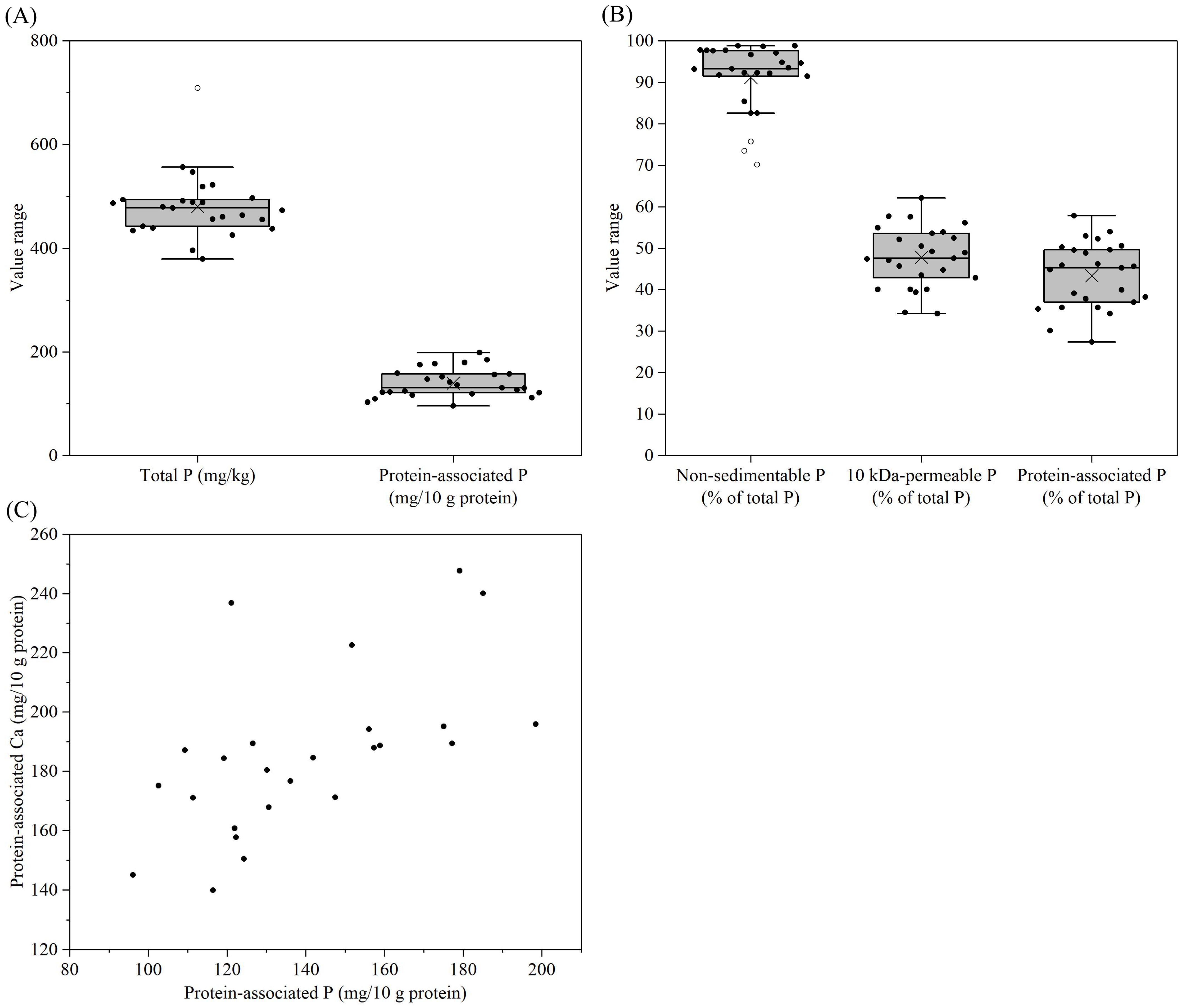
3.4. Phosphorus Distribution
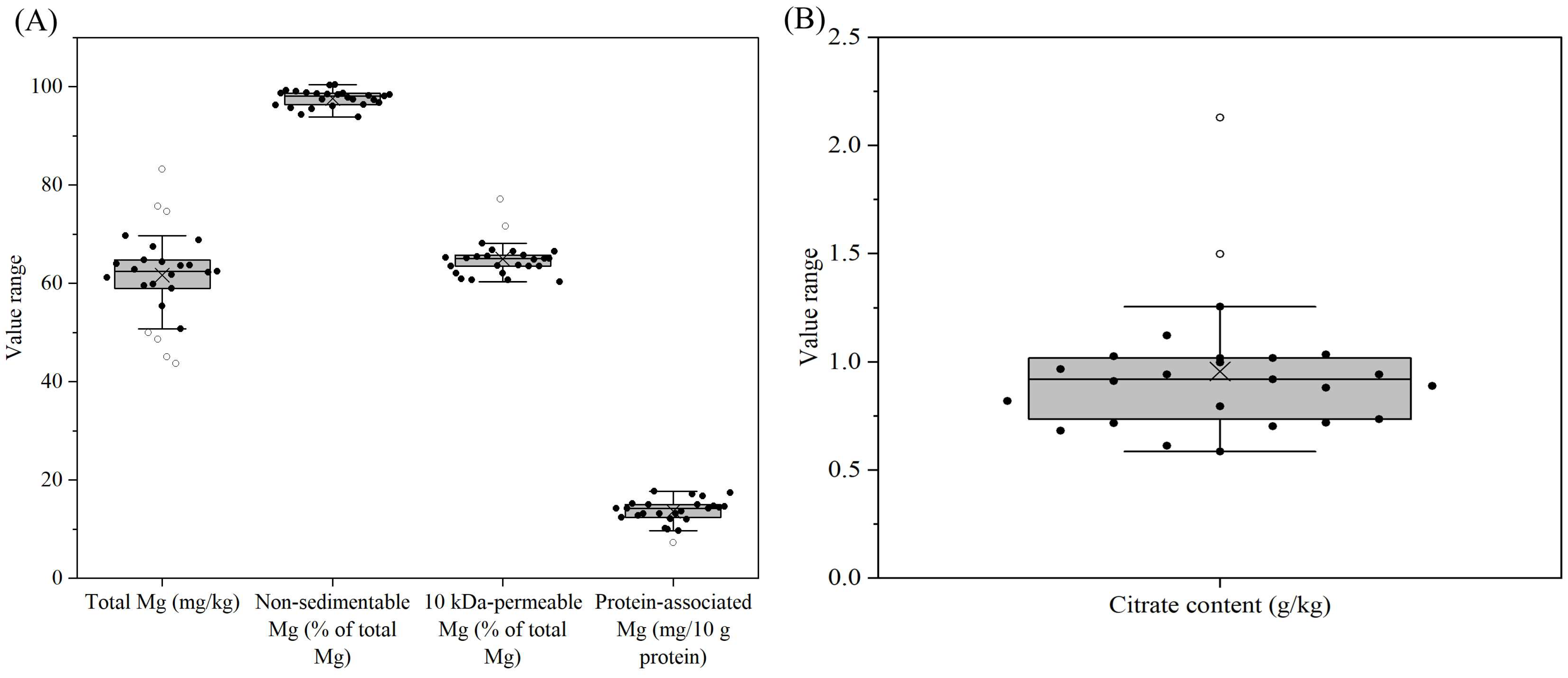
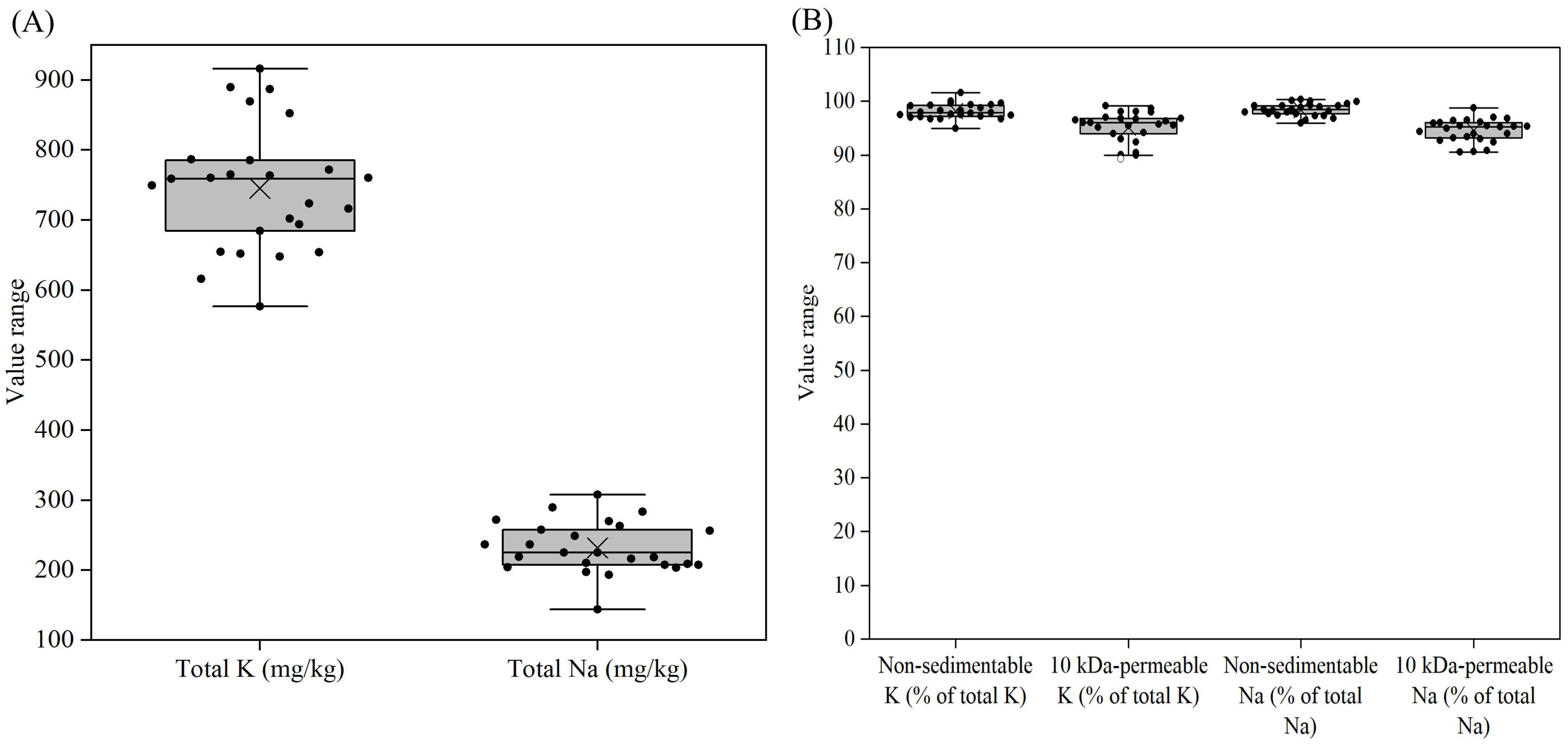
3.5. Distribution of Other Salts
3.6. SDS-PAGE Patterns
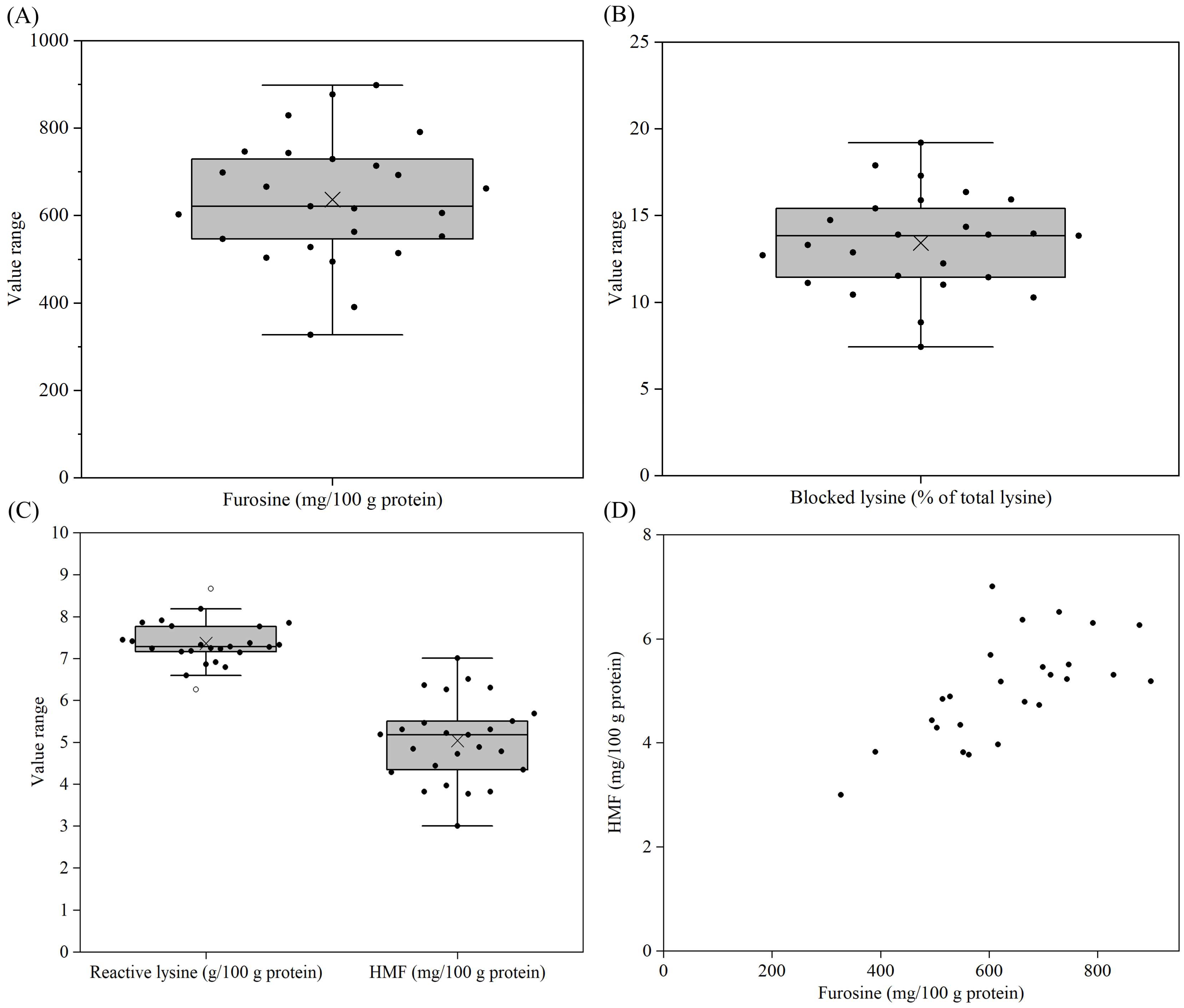
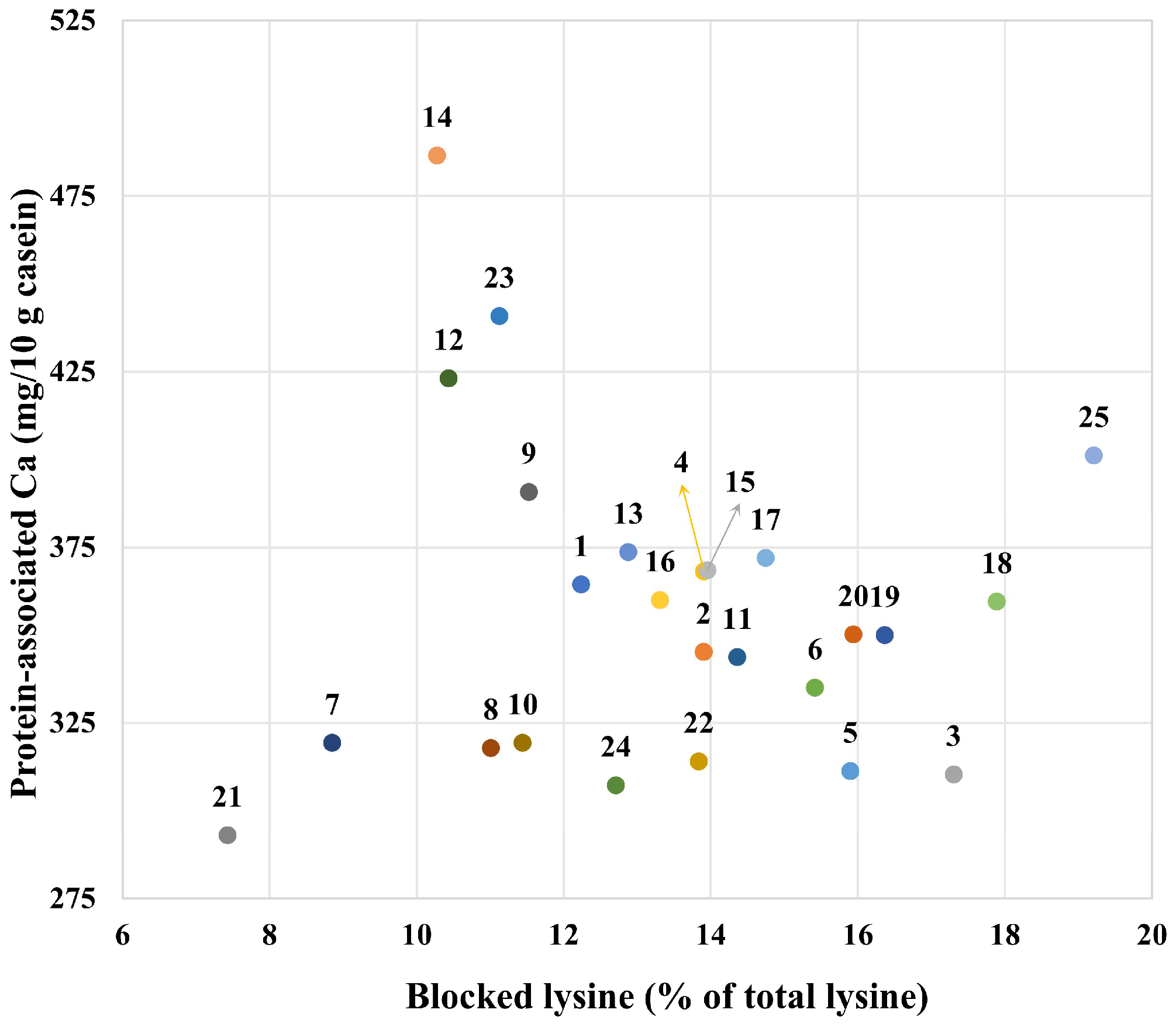
3.7. Furosine, Blocked Lysine, Reactive Lysine and HMF Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CCNFSDU. Standard for Follow-Up Formula for Older Infants and Product for Young Children CXS 156-1987; CCNFSDU: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, T.; Timmer, C. Salt Equilibria in Nutritional Formulae for Infants and Young Children. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y. Influence of Calcium Concentration on the Re-Assembly of Sodium Caseinate into Casein Micelles and on Their Renneting Behavior. Food Res. Int. 2024, 180, 113991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, E.; Markoska, T. Structural Properties of Casein Micelles with Adjusted Micellar Calcium Phosphate Content. Foods 2024, 13, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runthala, A.; Mbye, M.; Ayyash, M.; Xu, Y.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Caseins: Versatility of Their Micellar Organization in Relation to the Functional and Nutritional Properties of Milk. Molecules 2023, 28, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C. Calcium Secretion into Milk. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2005, 10, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, M.C.; Keller, R.P.; Casey, C.; Allen, J.C. Calcium Partitioning in Human and Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C. The Milk Salts and Their Interaction with Casein. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Fox, P.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 3, pp. 233–256. ISBN 978-1-4757-4409-5. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.E.; Deeth, H.C. Magnesium in Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.; Larsen, L.B.; Sørensen, J.; Poulsen, N.A. Natural Variations of Citrate and Calcium in Milk and Their Effects on Milk Processing Properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6830–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Huppertz, T.; Urban, V.S.; Petukhov, A.V. Casein Micelles and Their Internal Structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171–172, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bakry, M.; Mehta, B.M. Chapter 1—Casein: Types, Applications and Gastric Digestion. In Casein; El-Bakry, M., Mehta, B.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-0-443-15836-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Ye, A.; Yang, Z.; Everett, D.W.; Paul Gilbert, E.; Singh, H. Role of Ca2+ in the Pepsin-Induced Coagulation and in the Dynamic in Vitro Gastric Digestion Behavior of Casein Micelles. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6985–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Lambers, T.T. Influence of Micellar Calcium Phosphate on in Vitro Gastric Coagulation and Digestion of Milk Proteins in Infant Formula Model Systems. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 107, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Huppertz, T.; Regenstein, J.M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. Decalcification Strongly Affects in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Bovine Casein Micelles under Infant, Adult and Elderly Conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijnatten, E.J.M.V.; Roelofs, J.J.M.; Camps, G.; Huppertz, T.; Lambers, T.T.; Smeets, P.A.M. Gastric Coagulation and Postprandial Amino Acid Absorption of Milk Is Affected by Mineral Composition: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Servín, J.L.; De La Torre Carbot, K.; García-Gasca, T.; Castellote, A.I.; López-Sabater, M.C. Content and Evolution of Potential Furfural Compounds in Commercial Milk-Based Infant Formula Powder after Opening the Packet. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-14891-5. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Wakeling, L.; Gamlath, S. Retention of Essential Amino Acids during Extrusion of Protein and Reducing Sugars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8779–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, Q.; Ren, D.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y. Research of the Determination Method of Furfurals and Furosine in Milk and the Application in the Quality Evaluation of Milk. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2022, 14, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Fan, H.; Xie, J.; Xie, M. Maillard Reaction Harmful Products in Dairy Products: Formation, Occurrence, Analysis, and Mitigation Strategies. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhuang, P.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Y. Joint Control of Multiple Food Processing Contaminants in Maillard Reaction: A Comprehensive Review of Health Risks and Prevention. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tsao, R. Amadori Compounds: Analysis, Composition in Food and Potential Health Beneficial Functions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 406–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, P.; He, Z.; Qin, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Chen, J.; Zeng, M. Research Progress on Generation, Detection and Inhibition of Multiple Hazards—Acrylamide, 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, Advanced Glycation End Products, Methylimidazole—In Baked Goods. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, M.; Diel, P.; Eisenbrand, G.; Grune, T.; Guth, S.; Henle, T.; Humpf, H.-U.; Joost, H.-G.; Marko, D.; Raupbach, J.; et al. Dietary Glycation Compounds—Implications for Human Health. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2024, 54, 485–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, S.; Stuknytė, M.; Masotti, F.; De Noni, I. Protein Breakdown and Release of β-Casomorphins during in Vitro Gastro-Intestinal Digestion of Sterilised Model Systems of Liquid Infant Formula. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakayiru, J.; Lieshout, G.A.A.V.; Trommelen, J.; van Kranenburg, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Loon, L.J.C. van The Glycation Level of Milk Protein Strongly Modulates Post-Prandial Lysine Availability in Humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieshout, G.A.; Trommelen, J.; Hendriks, F.K.; Nyakayiru, J.; van Kranenburg, J.; Senden, J.M.; Goessens, J.P.; Verdijk, L.B.; Bragt, M.C.; van Loon, L.J. Milk Protein Glycation Compromises Postprandial Lysine Bioavailability but Does Not Modulate Postprandial Muscle Protein Synthesis Rates In Vivo in Males: A Double-Blind, Randomized Parallel Trial. J. Nutr. 2025, 155, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lieshout, G.A.; Trommelen, J.; Nyakayiru, J.; van Kranenburg, J.; Senden, J.M.; Gijsen, A.P.; Verdijk, L.B.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Bragt, M.C.; van Loon, L.J. Protein Glycation Compromises the Bioavailability of Milk Protein-Derived Lysine in Vivo in Healthy Adult Males: A Double-Blind, Randomized Cross-over Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 121, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucey, J.A.; Horne, D.S. Milk Salts: Technological Significance. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; McSweeney, P., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 351–389. ISBN 978-0-387-84864-8. [Google Scholar]
- ISO8968-1\IDF20-1; Milk and Milk Products—Determination of Nitrogen Content—Part 1: Kjeldahl Principle and Crude Protein Calculation. International Organisation for Standardisation: Brussels, Belgium; International Dairy Federation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO8968-4\IDF20-4; Milk and Milk Products—Determination of Nitrogen Content—Part 4: Determination of Protein and Nonprotein Nitrogen Content and True Protein Content Calculation (Reference Method). International Organisation for Standardisation: Brussels, Belgium; International Dairy Federation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- AOAC Official Method 994.12 Amino Acids in Feeds: Performic Acid Oxidation with Acid Hydrolysis-Sodium Metabisulfite Method. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL, 22nd ed.; Latimer, G.W., Jr., Ed.; AOAC Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, W.; Johns, P.; Haselberger, P.; Thompson, J.J.; Sullivan, D.; Baugh, S. Calculation of Whey Protein Fraction in Milk-Based Infant Formula: First Action 2012.07. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China; China Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Fat Content in Food GB 5009.6-2016; National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cruijsen, H.; Poitevin, E.; Brunelle, S.L. Collaborators: Determination of Minerals and Trace Elements in Milk, Milk Products, Infant Formula, and Adult Nutrition: Collaborative Study 2011.14 Method Modification. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1845–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnsworthy, P.C.; Masson, L.L.; Lock, A.L.; Mottram, T.T. Variation of Milk Citrate with Stage of Lactation and De Novo Fatty Acid Synthesis in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Hemar, Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Membrane-Based Fractionation, Enzymatic Dephosphorylation, and Gastrointestinal Digestibility of β-Casein Enriched Serum Protein Ingredients. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martysiak-Żurowska, D.; Stołyhwo, A. Content of Furosine in Infant Formulae and Follow-on Formulae. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2007, 57, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzoferrato, L.; Manzi, P.; Vivanti, V.; Nicoletti, I.; Corradini, C.; Cogliandro, E. Maillard Reaction in Milk-Based Foods: Nutritional Consequences. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Hernandez, E.; Leon Gomez, C.; Garcia-Villanova, B.; Corzo Sanchez, N.; Romera Gomez, J.M. Effect of Storage on Non-enzymatic Browning of Liquid Infant Milk Formulae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, M.; Chabanet, C.; Pélissier, J. Solubility of Peptides in Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Solutions Hypothesis on the Precipitation Mechanism. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1989, 34, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Salam, M.H.A.; El-Shibiny, S.; Buchheim, W. Characteristics and Potential Uses of the Casein Macropeptide. Int. Dairy J. 1996, 6, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; State Administration for Market Regulation. National Food Safety Standard: Infant Formula GB 10765-2021; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bijl, E.; van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Huppertz, T.; van Hooijdonk, A.C.M. Protein, Casein, and Micellar Salts in Milk: Current Content and Historical Perspectives. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Salts of Milk. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 241–270. ISBN 978-3-319-14892-2. [Google Scholar]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Fenelon, M.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Huppertz, T. Influence of Citrate- and Phosphate-Based Calcium Sequestering Salts on the Disruption of Casein Micelles. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 109970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Sandri, S.; Mariani, P.; Summer, A. Influence of Micellar Calcium and Phosphorus on Rennet Coagulation Properties of Cows Milk. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Heck, J.; Bijl, E.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B. Variation in Casein Distribution and Mineralisation in the Milk from Holstein-Friesian Cows. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurko, S.; Benninga, M.A.; Solari, T.; Chumpitazi, B.P. Pediatric Aspects of Nutrition Interventions for Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlieu, C.; Ménard, O.; Bouzerzour, K.; Mandalari, G.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A.R.; Dupont, D. Specificity of Infant Digestive Conditions: Some Clues for Developing Relevant In Vitro Models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1427–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieshout, G.A.A.; Lambers, T.T.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Hettinga, K.A. How Processing May Affect Milk Protein Digestion and Overall Physiological Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2422–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, M.H.; El-Shibiny, S. Glycation of Whey Proteins: Technological and Nutritional Implications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, H.E.; van Lieshout, G.A.A.; van Gool, M.P.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Hettinga, K.A. Lysine Blockage of Milk Proteins in Infant Formula Impairs Overall Protein Digestibility and Peptide Release. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Chen, K.-T.; Lin, J.-A.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-A.; Wu, J.-T.; Hsieh, C.-W. Recent Advances in Processing Technology to Reduce 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Yin, W.; Tao, X.; Liu, D.; Huppertz, T.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. Salt Equilibria and Protein Glycation in Young Child Formula. Foods 2025, 14, 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193445
Chen W, Yin W, Tao X, Liu D, Huppertz T, Liu X, Zhou P. Salt Equilibria and Protein Glycation in Young Child Formula. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193445
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wenfu, Wenzhu Yin, Xiumei Tao, Dasong Liu, Thom Huppertz, Xiaoming Liu, and Peng Zhou. 2025. "Salt Equilibria and Protein Glycation in Young Child Formula" Foods 14, no. 19: 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193445
APA StyleChen, W., Yin, W., Tao, X., Liu, D., Huppertz, T., Liu, X., & Zhou, P. (2025). Salt Equilibria and Protein Glycation in Young Child Formula. Foods, 14(19), 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193445





