Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Strains and Chemicals
2.2. Culture of Single and Mixed Bacteria
2.3. Preparation of AgNPs
2.4. Physico-Chemical Characterization of the SERS-Enhanced Substrate
2.4.1. Ultraviolet–Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy Characterization of AgNPs
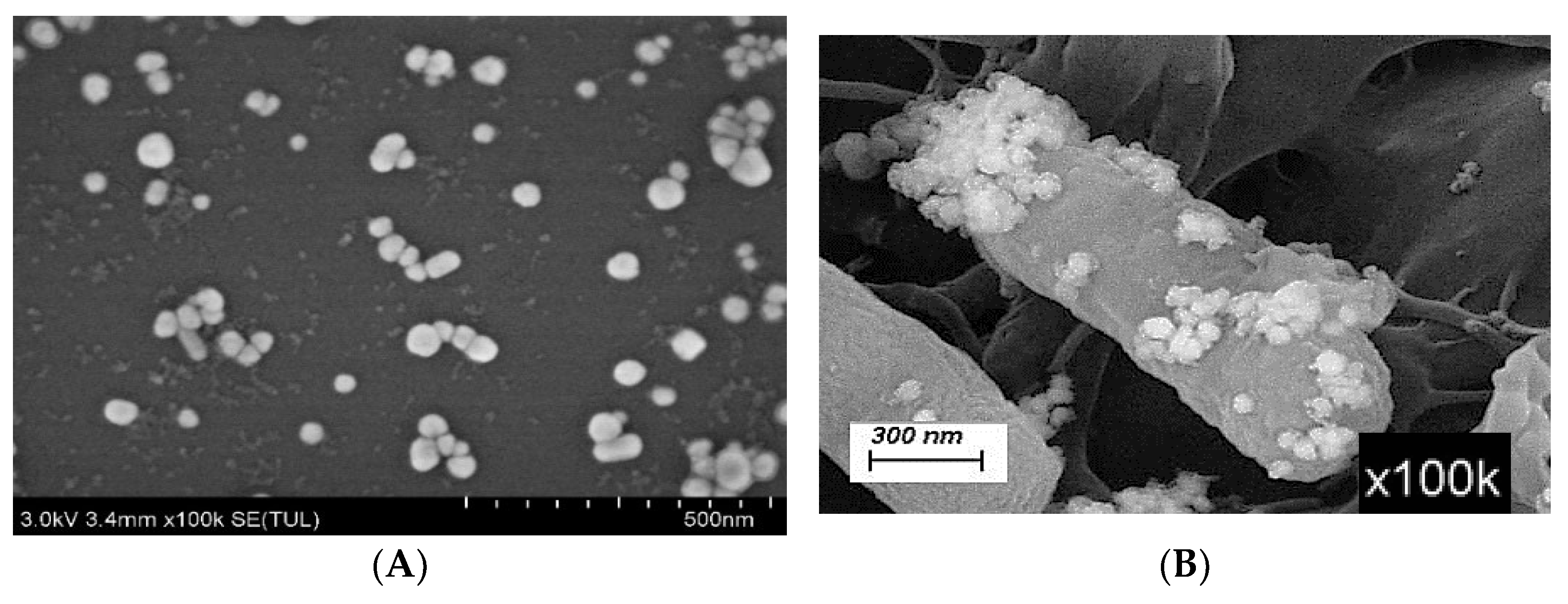
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Characterization of AgNPs
2.4.3. Setting of the Acquisition Parameters for Raman Spectroscopy
- (1)
- Settings for the acquisition parameters of the portable Raman spectrometer: The instrument used for scanning the Raman spectrum is a portable Raman spectrometer (Raman Pro, B&WTek, Newark, DE, USA), equipped with a 785 nm laser diode. The laser power is at the maximum of the instrument (i.e., 100%), the integration time is 20 s, the average scanning times are 2, and the range of Raman shift is 400–1800 cm−1.
- (2)
- Settings for the acquisition parameters of the laser confocal micro-Raman spectrometer: The excitation wavelength is 532 nm, the laser power is 14 mW, a 20× objective lens is used, the integration time is 1 s, the integration times are 10, and the range of Raman shift is 400–1800 cm−1.
2.4.4. SERS-Enhanced Effect Test of AgNPs
2.4.5. Stability Evaluation of the Stored Silver Nanosol over Time
2.5. Determination of SERS Limit of Detection (LOD) for Different Foodborne Pathogens
2.6. Preparation of Beef Samples
2.7. Determination of LODs of SERS for Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Samples
2.8. SERS Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of AgNPs as the SERS-Enhanced Substrate
3.1.1. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry of AgNPs
3.1.2. SEM Detection of AgNPs
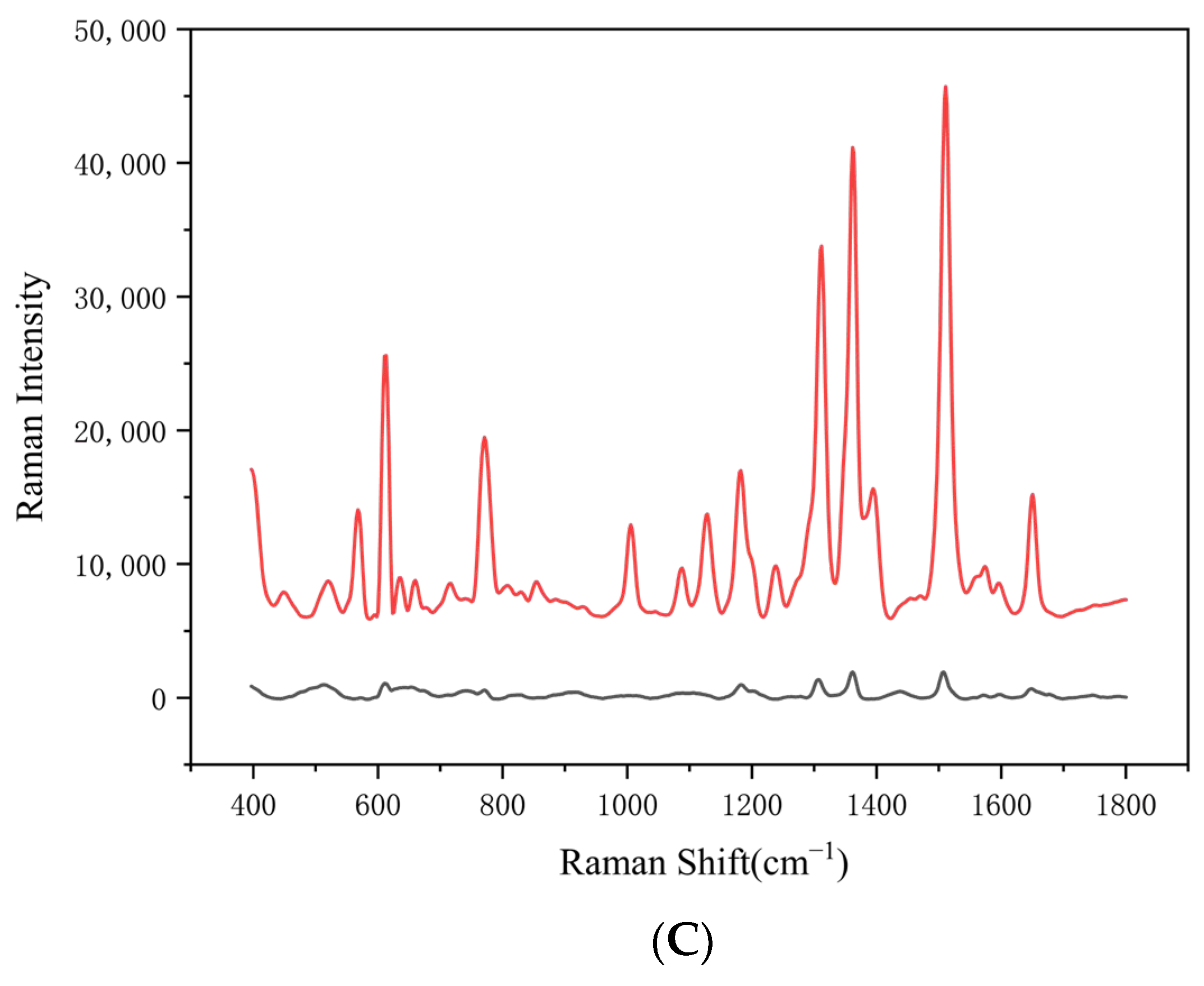
3.1.3. Evaluation of SERS-Enhanced Performance of AgNPs
3.1.4. Stability Evaluation of the Stored Silver Nanosol over Time
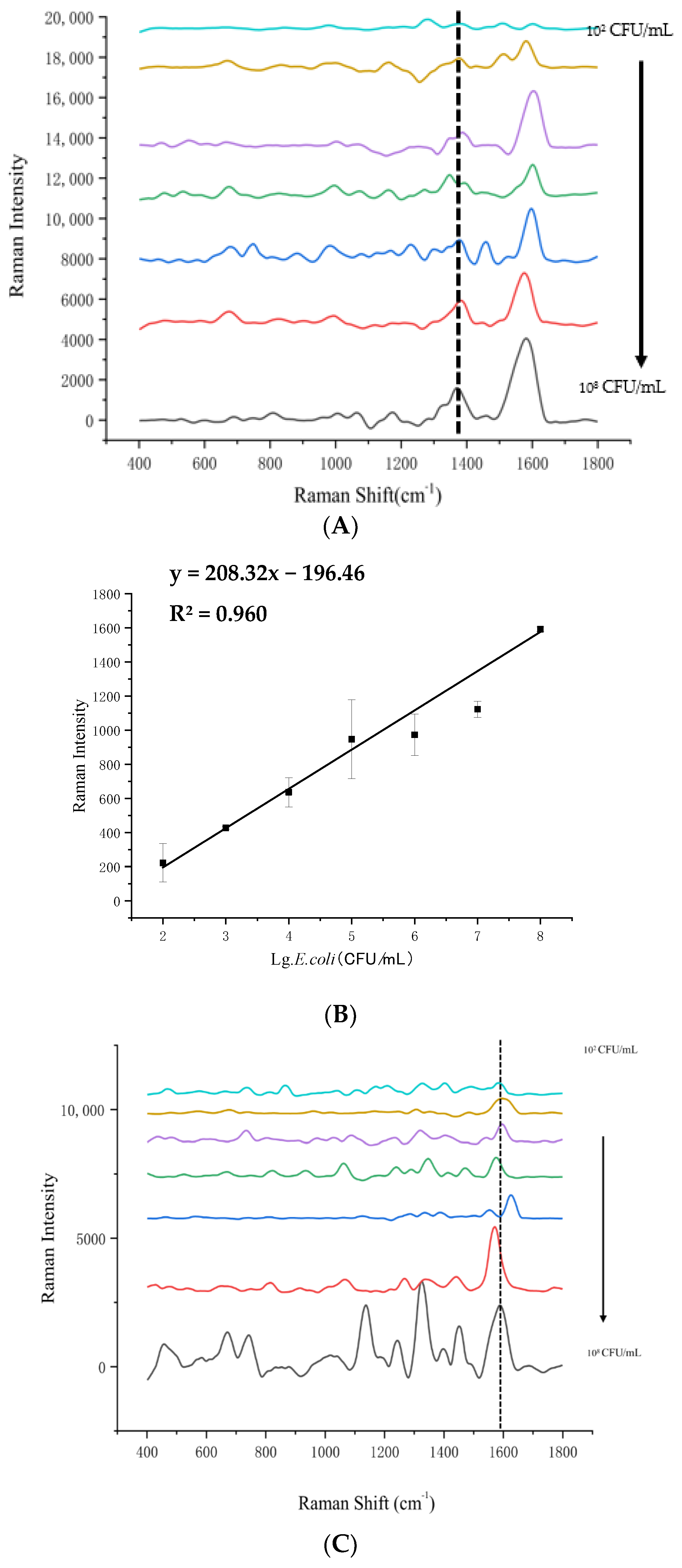
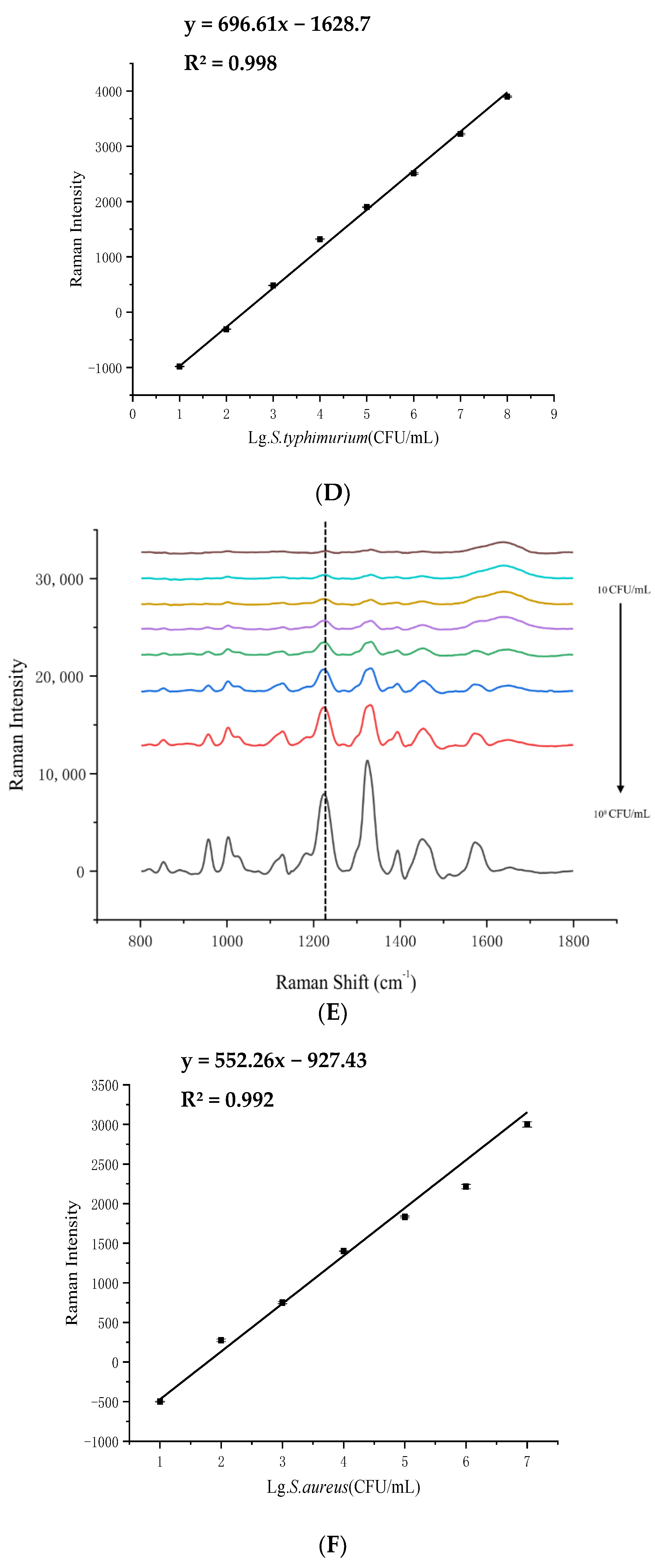
3.2. LOD Analysis of SERS Detection for 4 Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Pure Culture
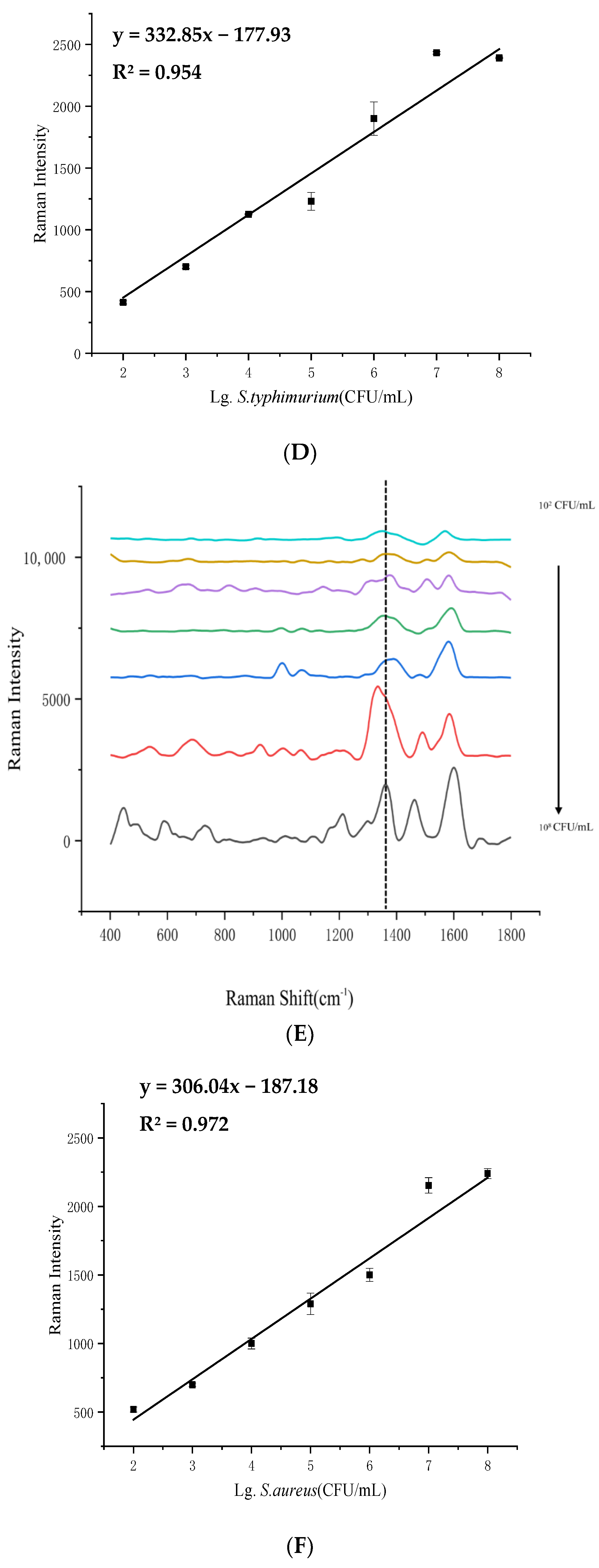
3.3. LOD Analysis of 4 Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Samples
3.4. LDA Results for the 4 Pathogenic Bacteria and Their Mixture in Beef Samples
3.5. The Practical Application Value and Potential Impact of the Research
3.5.1. The Impact on Farmers
3.5.2. The Impact on Meat Processing Plants
3.5.3. The Impact on Beef Sellers and Sales Points
3.5.4. The Impact on Family
3.5.5. The Impact on Catering Industry
3.6. Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordillo, R.; Córdoba, J.J.; Andrade, M.J.; Luque, M.I.; Rodríguez, M. Development of PCR assays for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in meat products. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, M.; Adriana, V.; Eva, K. Evaluation of DNA extraction methods for culture-independent real-time PCR-based detection of Listeria monocytogenes in cheese. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.J.; Zhong, J.L.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X.H. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella by multiplex PCR in milk. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Peng, Y.K.; Guo, Q.H.; Zhuang, Q.B.; Zuo, J.W.; Zhao, X.L. Rapid discrimination of pork contaminated with different pathogens by using Sers. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Poshtiban, S.; Evoy, S. Recent advances in bacteriophage based biosensors for food-borne pathogen detection. Sensors 2013, 13, 1763–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.M.; Elhanafi, D.; Drake, M.; Jaykus, L.A. Effect of food matrix and cell growth on PCR-based detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, S.; Stöckel, S.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Identification of meat-associated pathogens via Raman microspectroscopy. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M.; Marie Fowler, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y. Classification and identification of foodborne bacteria in beef by utilising surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with chemometric methods. Foods 2024, 13, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dina, N.E.; Gherman, A.M.R.; Colniță, A.; Marconi, D.; Sârbu, C. Fuzzy characterization and classification of bacteria species detected at single-cell level by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Spectrosc. Acta Part. A-Mol. Biomol. Srectrosc. 2021, 247, 119149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Zhu, Y.D.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Zhao, L.J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Xu, L.N.; Wang, N.; Zhao, G.M.; Liang, D.; et al. Rapid identification of different pathogenic spore-forming bacteria in spice powders using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, B.; Wichmann, C.; Stöckel, S.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Cultivation-free Raman spectroscopic investigations of bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmaire, D.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1997, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, S.; März, A.; Seise, B.; Hartmann, K.; Freitag, I.; Kämmer, E.; Böhme, R.; Deckert, V.; Weber, K.; Cialla, D.; et al. Bioanalytical application of surface-and tip-enhanced R aman spectroscopy. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Gu, B.; Liu, Q.Q.; Pang, Y.F.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S.Q. Combined use of vancomycin-modified Ag-coated magnetic nanoparticles and secondary enhanced nanoparticles for rapid surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçinar, H.Y.; Aslim, B.; Torul, H.; Güven, B.; Zengin, A.; Suludere, Z.; Boyaci, İ.H.; Tamer, U. Immunomagnetic separation and Listeria monocytogenes detection with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.C.; Meisel, D. Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 3391–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Hassan, M.M.; Chen, X.X.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Z.M.; Zhao, J.W. A magnetite/PMAA nanospheres-targeting SERS aptasensor for tetracycline sensing using mercapto molecules embedded core/shell nanoparticles for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.G.; Hopkins, D.L.; Schmidtke, L.; Morris, S.; Fowler, S.M. Preliminary investigation into the use of Raman spectroscopy for the verification of Australian grass and grain fed beef. Meat Sci. 2020, 160, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size and temperature dependence of the plasmon absorption of colloidal gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Tang, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Tian, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.; de la Chapelle, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.L. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering method for the identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using positively charged silver nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiri, L.; Bronk, B.V.; Shabtai, Y.; Czege, J.; Efrima, S. Silver metal induced surface enhanced Raman of bacteria. Colloids Surf. A 2002, 208, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.L.; Ying, Y.L.; Yu, R.J.; Long, Y.T. In situ food-borne pathogen sensors in a nanoconfined space by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, A.; Bihon, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence of Escherichia coli in foods of animal origin in Ethiopia. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoribi, M.F.; Doumith, M.; Alrodayyan, M.; Al Zayer, M.; Köster, W.L.; Muhanna, A.; Aljohani, S.M.; Balkhy, H.H.; Desin, T.S.S. Enteritidis and S. typhimurium harboring SPI-1 and SPI-2 are the predominant serotypes associated with human salmonellosis in Saudi Arabia. Front. Cell. Infect. Mi. 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Van Puyvelde, S.; Staes, A.; Timmerman, E.; Barbé, B.; Jacobs, J.; Gevaert, K.; Deborggraeve, S. Salmonella typhi, paratyphi A, Enteritidis and Typhimurium core proteomes reveal differentially expressed proteins linked to the cell surface and pathogenicity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögler, M.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Uusitalo, S.; Popov, A.; Popov, A.; Tselikov, G.; Välimaa, A.; Al-Kattan, A.; Hiltunen, J.; Laitinen, R.; et al. Bare laser-synthesized Au-based nanoparticles as nondisturbing surface-enhanced Raman scattering probes for bacteria identification. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, B.; Basaran-Akgul, N.; Temur, E.; Tamer, U.; Boyacı, İ.H. SERS-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for Escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst 2011, 136, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Ding, S.J.; Wang, G.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. In situ characterization and analysis of Salmonella biofilm formation under meat processing environments using a combined microscopic and spectroscopic approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cufaoglu, G.; Ambarcioglu, P.; Ayaz, N.D. Meta-analysis of the prevalence of Listeria spp. and antibiotic resistant L. monocytogenes isolates from foods in Turkey. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, Z.P.; Xu, B.C. Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Chang, B.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.P.; Wu, S.J. Salmonella typhimurium detection using a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based aptasensor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gopinathan, R.; Chandra, G.K.; Umapathy, S.; Saini, D.K. Rapid detection of bacterial infection and viability assessment with high specificity and sensitivity using Raman microspectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteki, M.; Shahsavari, Z.; Simal-Gandara, J. Use of spectroscopic methods in combination with linear discriminant analysis for authentication of food products (Spectroscopy-linear discriminant analysis for authenticating food products). Food Control 2018, 91, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.E.; Pitcher, A.J.; Ballard, S.A.; Grabsch, E.A.; Bell, J.M.; Barton, M.; Grayson, M.L. Superbugs in the supermarket? Assessing the rate of contamination with third-generation cephalosporin-resistant gram-negative bacteria in fresh Australian pork and chicken. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Bacteria | Concentration of Bacteria (lg(CFU/mL)) | Detected Concentration of SERS (lg(CFU/mL)) | Recovery Rate (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli O157:H7 | 1 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 90.51 | 1.21 |
| 2 | 2.21 ± 0.02 | 110.17 | 0.85 | |
| 3 | 3.03 ± 0.02 | 100.95 | 0.56 | |
| S. typhimurium | 1 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 92.98 | 2.37 |
| 2 | 1.92 ± 0.02 | 96.00 | 1.24 | |
| 3 | 3.03 ± 0.03 | 100.97 | 1.00 | |
| S. aureus | 1 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 91.44 | 2.88 |
| 2 | 2.18 ± 0.04 | 108.87 | 1.67 | |
| 3 | 3.04 ± 0.05 | 101.37 | 1.60 | |
| L. monocytogenes | 2 | 2.15 ± 0.13 | 107.61 | 1.71 |
| 3 | 2.90 ± 0.11 | 96.64 | 3.08 | |
| 4 | 3.84 ± 0.38 | 96.10 | 0.05 |
| Bacteria | Training Set (n = 240) | Test Set (n = 120) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | STM | S. aur | LM | Mixture of 4 Bacteria | Accuracy (%) | E. coli | STM | S. aur | LM | Mixture of 4 Bacteria | Accuracy (%) | |
| E. coli | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| STM | 4 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 1 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 95 |
| Saur | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| LM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 100 |
| mixture of 4 bacteria | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 100 |
| Overall accuracy | 91.67 | 94.17 | ||||||||||
| Average accuracy | 92.92 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y. Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Foods 2025, 14, 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193434
Zuo H, Sun Y, Huang M, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Mao Y. Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193434
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Huixin, Yingying Sun, Mingming Huang, Yuqi Liu, Yimin Zhang, and Yanwei Mao. 2025. "Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy" Foods 14, no. 19: 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193434
APA StyleZuo, H., Sun, Y., Huang, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Mao, Y. (2025). Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria in Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Foods, 14(19), 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193434




