Effect of Plastein Reaction on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Corn Glutelin Peptides and Quality of Chiffon Cake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Extraction of Corn Glutelin and Preparation of Its Hydrolysates
2.3. Preparation of Modifiers of Plastein Reaction
2.4. Determination of Free Amino Content and Hydrolysis Degree
2.5. Determination of Antioxidant Activity of Modifiers
2.6. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Modifiers
2.6.1. Solubility Determination
2.6.2. Determination of Emulsification and Emulsification Stability
2.6.3. Determination of Foaming and Foaming Stability
2.7. Determination of the Quality of Chiffon Cake After Adding Modifiers
2.7.1. The Preparation of Chiffon Cake
2.7.2. Determination of Density of Cake Batter
2.7.3. Determination of Baking Characteristics of Cakes
2.7.4. Analysis of Internal Structure of Cake Crumb
2.7.5. Determination of Texture Characteristics of Cakes
2.7.6. Determination of Cake Color
2.7.7. Sensory Measurement Evaluation of Cake Samples
2.8. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DH and Free Amino Group Content of All Samples
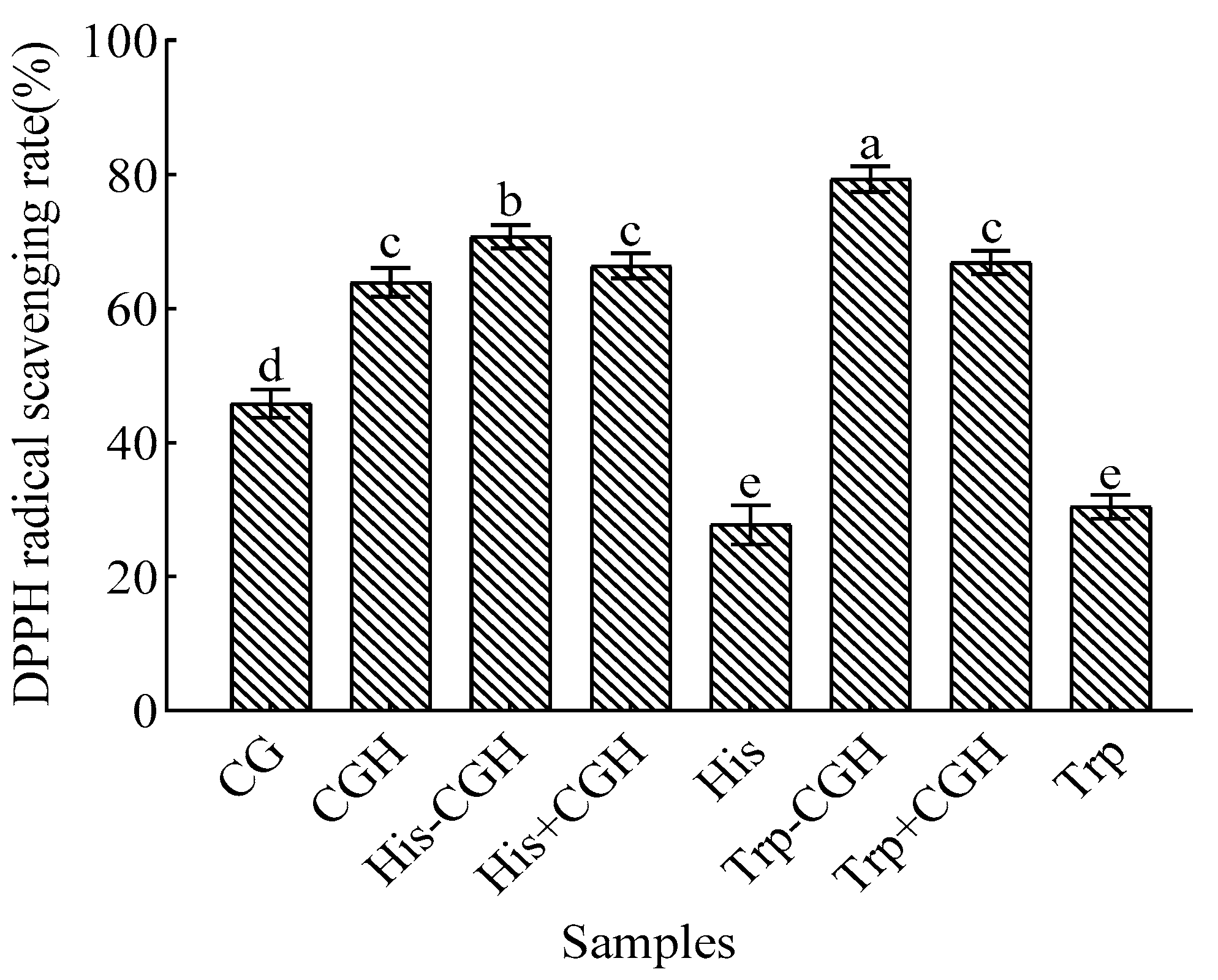
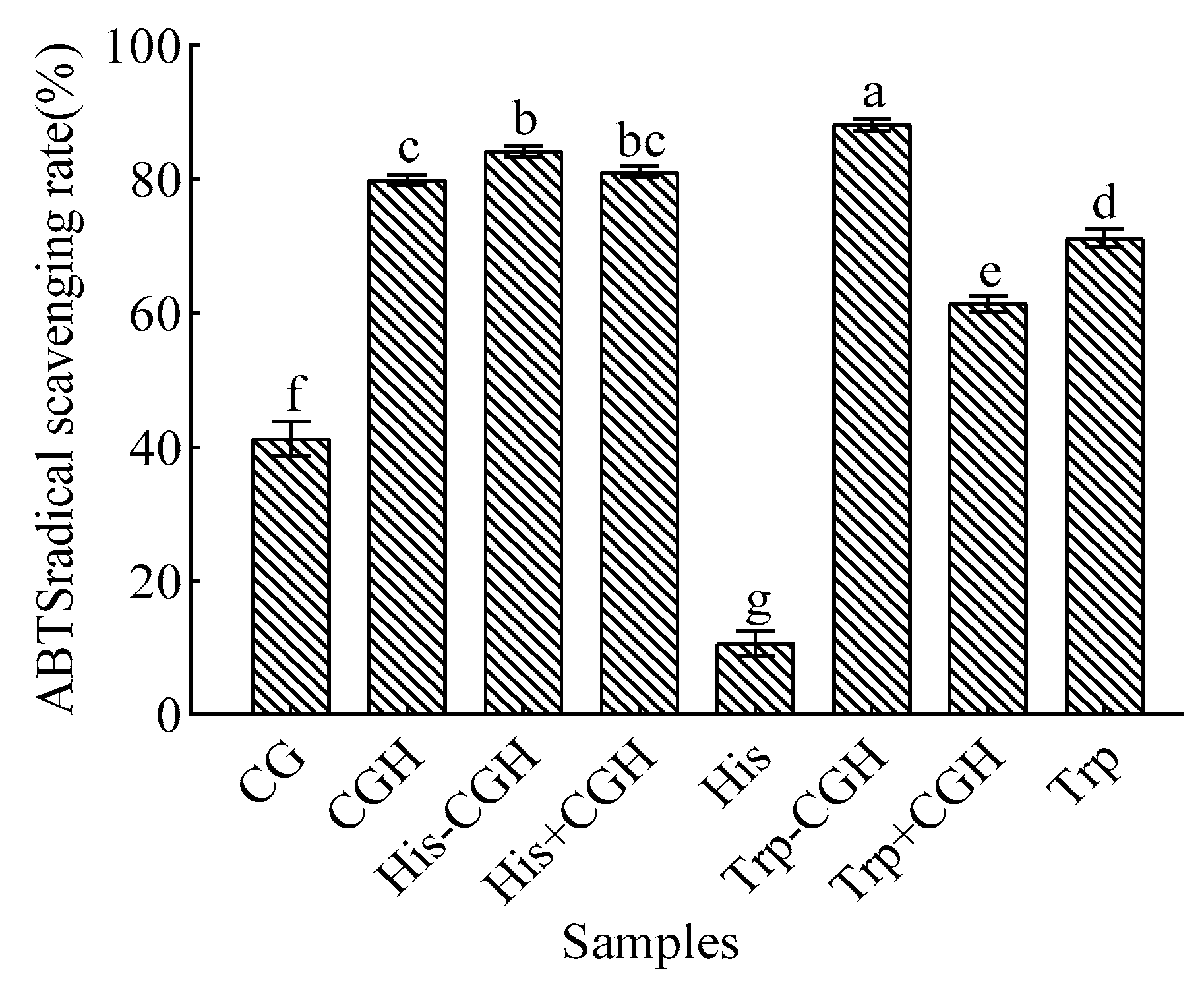
3.2. Effect of Plastein Reaction Modification on Antioxidant Activity of All Samples
3.3. Functional Characteristics Analysis of Modifiers
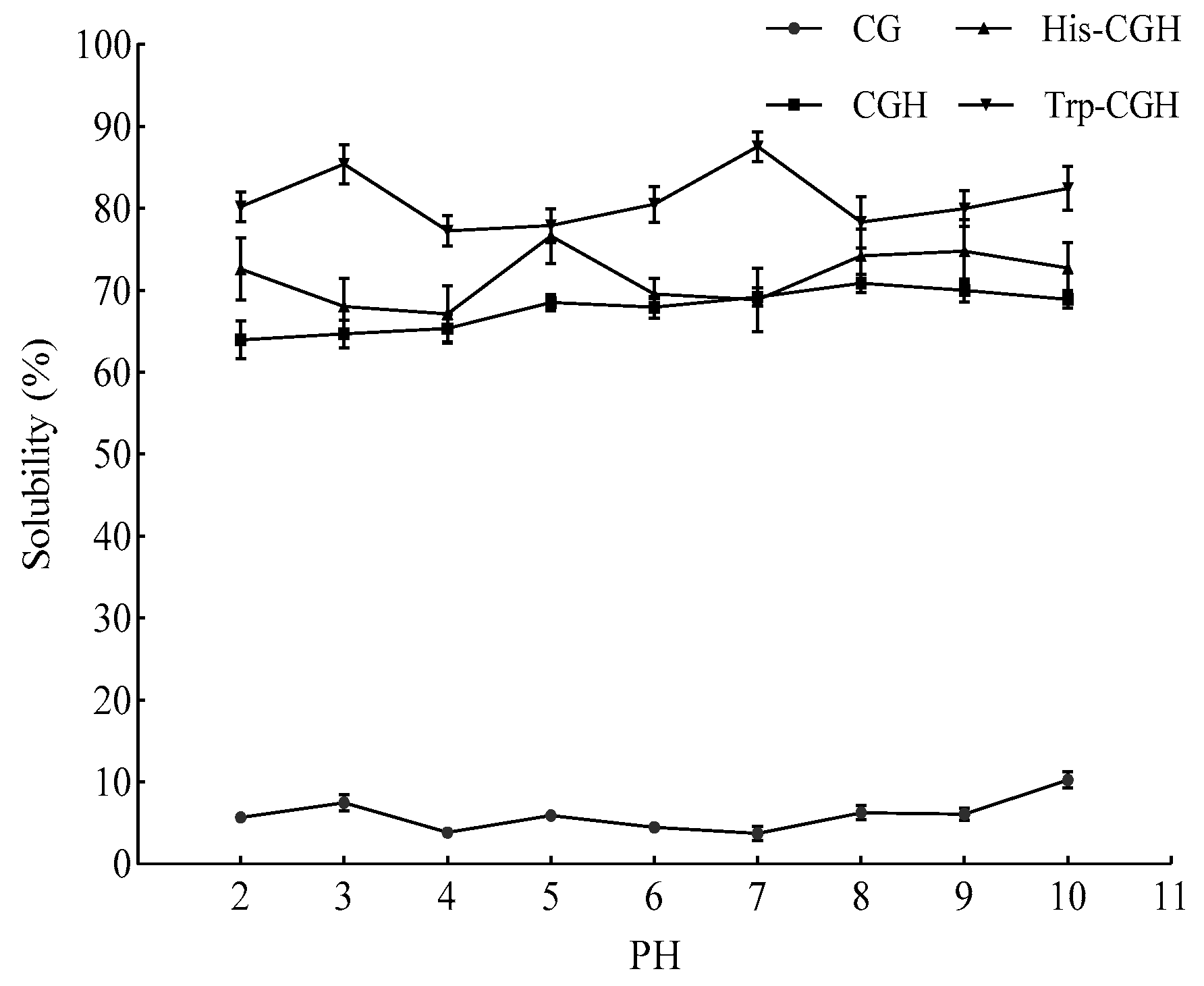
3.3.1. Changes in Solubility of Modified Products
3.3.2. Changes in Emulsification and Emulsification Stability of Modified Products
3.3.3. Effect of the Plastein Reaction on Foamability and Foam Stability of Modifiers
3.4. Effect of Modifier Addition on the Quality of Chiffon Cake
3.4.1. Effect of Modifier Addition on the Density of Cake Batter
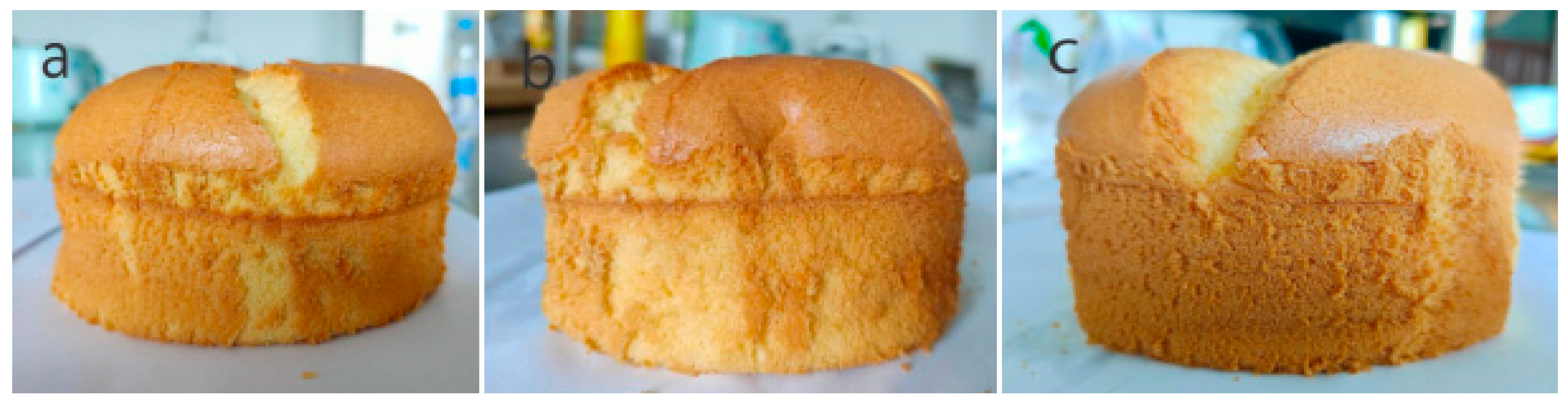
3.4.2. Effect of the Addition of Modifiers on Physical Characteristics of Chiffon Cake
3.4.3. Effect of the Addition of Modifiers on Cake Color
3.4.4. Effects of the Addition of Modifiers on the Texture Characteristics of Cake Samples
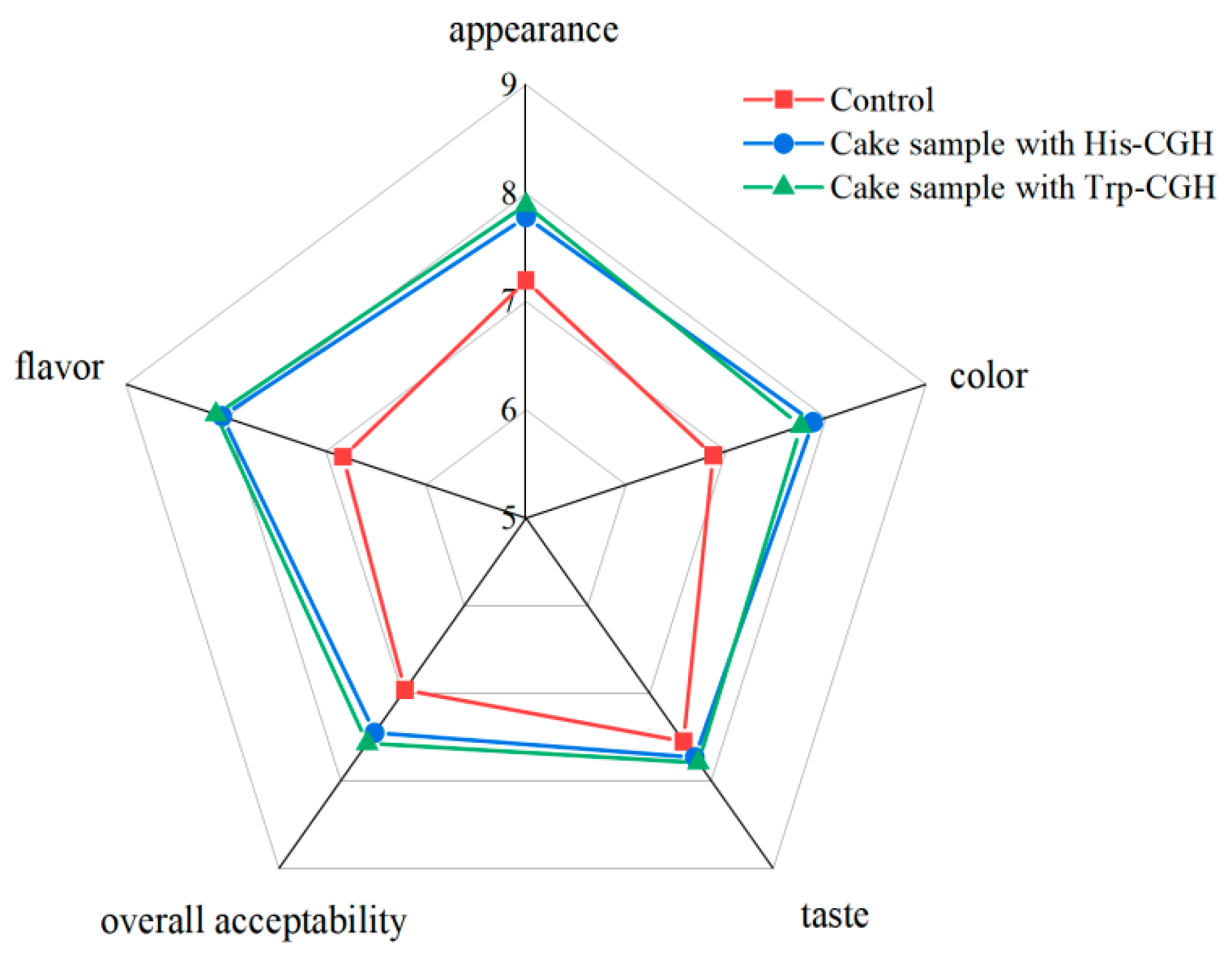
3.4.5. Effect of the Addition of Modifiers on Sensory Quality of Cake Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Andrade Júnior, F.P.; Sobreira de Cabral, A.L.; Dantas de Araújo, J.M.; Vilar Cordeiro, L.; de Barros Cândido, M.; Pontes da Silva, A.; De Medeiros Lima, B.T.; Braga Dantas, B. Food Nitrates and Nitrites as Possible Causes of Cancer: A Review. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Químico-Farm. 2021, 50, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Aovi, F.I.; Jahan, F.I.; Hossain, M.S.; Brishti, S.A.; Yamin, M.; Ahmed, M.; Rauf, A.; Sharma, R. Food Color Additives in Hazardous Consequences of Human Health: An Overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Varshney, A.; Rai, M.; Chikara, A.; Pohty, A.L.; Joshi, A.; Binjola, A.; Singh, C.P.; Rawat, K.; Rather, M.A.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceutical Potential of Underutilized Cereals and Cereal-Based Products. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, S.; Mollah, M.M.I. Analysis of black rice and some other cereal grains for protein, sugar, polyphenols, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory Properties. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Yan, D.; Barba, F.J.; Ferrer, E.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of Wheat Oligopeptide on the Baking and Retrogradation Properties of Bread Rolls: Evaluation of Crumb Hardness, Moisture Content, and Starch Crystallization. Foods 2024, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, E.; Jiang, L.; Cui, H.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, M. Only Plant-Based Food Additives: An Overview on Application, Safety, and Key Challenges in the Food Industry. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 39, 5132–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. Types and Characteristics of Food Additives and Their Impacts on Human Health. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 80, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Che, R.; Hong, J.; Liu, M.; Sun, B.; Shang, J.; Liu, Z.; Guan, E.; et al. Relation between quality characteristics of wheat flour and in vitro starch digestibility of dried noodles: Insights from noodle Structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 313, 144337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Cao, S.; Hu, Y.; Luan, G. Physicochemical properties and protein structure of extruded corn gluten meal: Implication of temperature. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Saran, S. Efficient production of bacterial cellulose based composites using zein protein extracted from corn gluten meal. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2022, 60, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Luo, M.; Liu, W.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Luo, L.; Yagoub, A.E.A. Effect of degree of hydrolysis on the bioavailability of corn gluten meal Hydrolysates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 95, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H.; Tang, N.; Dong, S.; Sun, B.; Liu, J. Optimisation of antioxidant peptide preparation from corn gluten Meal. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3264–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Towards the design of hypolipidaemic peptides: Deoxycholate binding affinity of hydrophobic peptide aggregates of casein plastein. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhu, X.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Zeng, M. Modification of ACE-inhibitory peptides from Acaudina molpadioidea using the plastein reaction and examination of its Mechanism. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-H.; Fu, Y.; Yue, N. In vitrocytoprotection of modified casein hydrolysates by plastein reaction on rat hepatocyte Cells. CyTA—J. Food 2013, 12, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Nilsuwan, K.; Zhang, B.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Protein hydrolysate from salmon frame debittered by plastein reaction: Amino acid composition, characteristics and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 58, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.; Batista, I. Functional properties of fish protein hydrolysates. In Utilization of Fish Waste; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, J.; Tomé, D.; Schmidely, P.; Demersay, T.-C.; Azzout-Marniche, D. Histidine: A Systematic Review on Metabolism and Physiological Effects in Human and Different Animal Species. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Histidine in Health and Disease: Metabolism, Physiological Importance, and Use as a Supplement. Nutrients 2020, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M Alazawi, S.; F Rodhan, W.; F Alkazazz, F.; Kh Huthefa, B. Histidine and Humans Disease. Diyala J. Med. 2022, 22, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałużna-Czaplińska, J.; Gątarek, P.; Chirumbolo, S.; Chartrand, M.S.; Bjørklund, G. How important is tryptophan in human Health? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 59, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.; Zadeh, K.; Vekariya, R.; Ge, Y.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut-Brain Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of hydrolysis time on the physicochemical and functional properties of corn glutelin by Protamex hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandy, S.L.; Doherty, J.M.; Wibisono, N.D.; Gonzales, R.A. High sensitivity HPLC method for analysis of in vivo extracellular GABA using optimized fluorescence parameters for o-phthalaldehyde (OPA)/sulfite derivatives. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1055, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, K.H.; Abdullah, A.; Kuswandi, B.; Hidayat, M.A. A novel high throughput method based on the DPPH dry reagent array for determination of antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4102–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, S.P.; Ferrarezi, A.C.; dos Santos, K.O.; Monteiro, M. Antioxidant activity of commercial ready-to-drink orange juice and nectar. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C392–C397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, H.; Yilmaz, Ö. Antioxidant defence of the actively feeding Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum 1792) larvae in relation to dietary PUFA and vitamin E contents. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokni Ghribi, A.; Maklouf Gafsi, I.; Sila, A.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on conformational and functional properties of chickpea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, M. Foam and conformational changes of egg white as affected by ultrasonic pretreatment and phenolic binding at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, B.; Donelson, T. Grain, flour, and batter properties estimating cake baking potential of wheat flour. Cereal Chem. 2022, 100, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim Monfared, M.; Nouri, L.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A. The effects of sesame protein isolate and transglutaminase enzyme on the quality characteristics of gluten-free batter and cake. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 4881–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.-H.; Abdul Aziz, N.A.; Azahari, B. Physico-chemical characteristics and sensory evaluation of wheat bread partially substituted with banana (Musa acuminata × balbisiana cv. Awak) pseudo-stem flour. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; de la Paz Salgado-Cruz, M.; Chanona-Pérez, J.; Gutiérrez-López, G.F.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Calderón-Domínguez, G. Evaluation of image analysis tools for characterization of sweet bread crumb structure. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 5, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, R.; Yunus, F.M.; Munaf, N.B.; Rahman, F.; Khanam, F.; Hawlader, M.D.H.; Vandenberg, A. Sensory acceptability of multiple-micronutrient-fortified lentils in Bangladesh. Foods 2024, 13, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, L. The influence of protease hydrolysis of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation induced soybean protein gel: Protein molecule, peptides and amino Acids. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Gao, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Physicochemical properties and action mechanism of chicken lung protein hydrolysate modified by plastein Reaction. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, R.; Dong, S.; Wu, H. Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure-Activity Relationship. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cai, C.; Liu, T.; Kang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, H. Enhancing the Antioxidant Activity of Fish Scale Collagen Hydrolysates Through Plastein Reaction. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-H.; Wang, J.-K.; Li, T.-J. In vitro ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities of the casein hydrolysates subjected to plastein reaction with addition of three extrinsic amino acids. Biotechnology 2011, 10, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-M.; Li, T.-J.; Zhao, X.-H. Pepsin-catalyzed plastein reaction with tryptophan increases the in vitro activity of lactoferrin hydrolysates with BGC-823 cells. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, F.; Manfredi, A.; Alongi, J.; Marinotto, D.; Ferruti, P.; Ranucci, E. D-, L- and D,L-Tryptophan-based Polyamidoamino acids: Ph-dependent structuring and fluorescent propertie. Polymers 2019, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Mohan, A.; Wu, S. Peptide Aggregation during Plastein Reaction Enhanced Bile Acid-Binding Capacity of Enzymatic Chicken Meat Hydrolysates. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Feng, C.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Chang, S.K.C.; Tan, Y. Plastein reaction enhances the emulsifying and rheological properties of silver carp hydrolysates in Oil-in-water Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Święch, D. Amino Acid Adsorption on Stainless Steel and Titanium Surfaces under Physiological Conditions: A Spectroscopic Analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1348, 143347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Tan, Y. Plastein reaction augments the metal chelating capabilities of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) hydrolysates: Unlocking the chemical modification Mechanism. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 138030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, I.S.; Yildiz, O.; Meral, R. Optimization of corn, rice and buckwheat formulations for gluten-free wafer production. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 22, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaszadeh, F.; Aalami, M.; Kadkhodaee, R.; Maghsoudlou, Y.; Sadeghi Mahoonak, A. Effect of Pickering emulsion stabilized by soy protein nanoparticles on physical and rheological properties of gluten-free cake batter. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2023, 2023, 3348944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotsna, R.; Sai Manohar, R.; Indrani, D.; Venkateswara Rao, G. Effect of Whey Protein Concentrate on the Rheological and Baking Properties of Eggless Cake. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ramírez, M.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; García-Garibay, M.; Jiménez-Guzmán, J.; Villanueva-Carvajal, A.; de la Paz Salgado-Cruz, M.; Arizmendi-Cotero, D.; Del Moral-Ramírez, E. Effect of whey protein isolate addition on physical, structural and sensory properties of sponge Cake. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemler, C.D.; Scherf, K.A. Improvement of cake baking properties by lipases compared to a traditional emulsifier. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.R.; Silva, L.M.; Komeroski, M.R.; Kist, T.B.L.; Rodrigues, C.E.; de O Rios, A.; Silva, M.M.; Doneda, D.; de O Schmidt, H.; Oliveira, V.R. Effect of whey protein addition on the nutritional, technological and sensory quality of banana Cake. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2617–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subagio, A.; Morita, N. Effects of Protein Isolate from Hyacinth Beans (Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet) Seeds on Cake Characteristics. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pycarelle, S.C.; Bosmans, G.M.; Nys, H.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Stabilization of the air-liquid interface in sponge cake batter by surface-active proteins and lipids: A foaming protocol based approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Hua, S.; Han, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Xia, N.; Yang, F.; Chuang, R.; Ghamry, M.; Rayan, A.M. Ultrasound-Assisted Covalent Cross-Linking of Egg White Protein with Ferulic Acid: Structure, Foaming, and Application in Chiffon Cake. Food Res. Int. 2025, 211, 116396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Barbosa Correia, B.; Drud-Heydary Nielsen, S.; Jorkowski, J.; Arildsen Jakobsen, L.M.; Zacherl, C.; Bertram, H.C. Maillard reaction products and metabolite profile of Plant-based meat burgers compared with traditional meat burgers and cooking-induced Alterations. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gularte, M.A.; Gómez, M.; Rosell, C.M. Impact of legume flours on quality and in vitro digestibility of starch and protein from gluten-free cake. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 5, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, J.; Torbica, A.; Belović, M. Effect of non-gluten proteins and transglutaminase on dough rheological properties and quality of bread based on millet (Panicum miliaceum) flour. LWT 2020, 118, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H. Study on Plant-based proteins and their complexes in improving food foam system: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2025, 212, 116514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucky, A.R.; Al-Mamun, A.; Hosen, A.; Toma, M.A.; Mazumder, M.A.R. Nutritional and sensory quality assessment of plain cake enriched with beetroot powder. Food Res. 2020, 4, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Hemalatha, M.S. Effect of High Protein Formulation on Rheological, Sensory and Microstructure of Cookies. J. Food Eng. Technol. 2025, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Gang, D.-O.; Song, J.-Y. Effects of protein and transglutaminase on the preparation of gluten-free rice bread. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | –NH2 Content (mmol/g Protein) | |
|---|---|---|
| CG | corn glutelin | 0.0231 ± 0.0013 f |
| CGH | corn glutelin hydrolysate | 1.7928 ± 0.0170 c |
| His-CGH | The Plastein modifier of CGH and His | 1.5724 ± 0.0150 d |
| His+CGH | The mixture of CGH and His | 1.9523 ± 0.0160 a |
| Trp-CGH | The Plastein modifier of CGH and Trp | 1.4382 ± 0.0120 e |
| Trp+CGH | The mixture of CGH and Trp | 1.8916 ± 0.0100 b |
| Samples | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Baking Loss (%) | Porosity (%) | Batter Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2.63 ± 0.12 b | 8.07 ± 0.17 a | 27.47 ± 0.63 b | 0.581 ± 0.012 a |
| C1 (His-CGH) | 2.86 ± 0.10 a | 7.25 ± 0.13 b | 30.95 ± 0.82 a | 0.560 ± 0.012 ab |
| C2 (Trp-CGH) | 2.92 ± 0.06 a | 7.08 ± 0.24 b | 31.88 ± 0.52 a | 0.553 ± 0.013 b |
| Type of Cake | C | C1 (His-CGH) | C2 (Trp-CGH) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crust color | L | 50.34 ± 1.60 a | 40.77 ± 1.46 b | 39.42 ± 1.55 b |
| a | 12.68 ± 1.51 a | 10.58 ± 0.88 a | 11.61 ± 1.12 a | |
| b | 25.21 ± 1.75 a | 20.07 ± 2.59 b | 23.14 ± 1.75 ab | |
| Crumb color | L | 30.40 ± 2.38 a | 19.63 ± 0.63 b | 14.79 ± 2.36 c |
| a | 2.15 ± 0.84 a | 1.45 ± 0.53 a | 1.28 ± 0.42 a | |
| b | 19.65 ± 1.66 a | 15.79 ± 0.51 b | 11.14 ± 1.51 c |
| Samples | Hardness (N) | Springiness (mm) | Chewiness (N) | Cohesion (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2.37 ± 0.14 a | 4.46 ± 0.32 b | 9.35 ± 0.45 b | 0.70 ± 0.02 a |
| C1 (His-CGH) | 2.10 ± 0.16 ab | 5.51 ± 0.13 a | 11.07 ± 0.90 a | 0.69 ± 0.01 a |
| C2 (Trp-CGH) | 2.01 ± 0.12 b | 5.43 ± 0.45 a | 11.49 ± 1.07 a | 0.69 ± 0.02 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Song, C.-L.; Pan, Z.-Q.; Du, G.-J.; Song, Z.-Q.; Ren, J.; Bo, L.-Y.; An, J.-J.; Wang, M. Effect of Plastein Reaction on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Corn Glutelin Peptides and Quality of Chiffon Cake. Foods 2025, 14, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193392
Sun Y, Zhang W-Y, Song C-L, Pan Z-Q, Du G-J, Song Z-Q, Ren J, Bo L-Y, An J-J, Wang M. Effect of Plastein Reaction on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Corn Glutelin Peptides and Quality of Chiffon Cake. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193392
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yang, Wan-Ying Zhang, Chun-Li Song, Zhi-Qin Pan, Guo-Jun Du, Zhi-Qiang Song, Jian Ren, Li-Ying Bo, Jing-Jing An, and Meng Wang. 2025. "Effect of Plastein Reaction on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Corn Glutelin Peptides and Quality of Chiffon Cake" Foods 14, no. 19: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193392
APA StyleSun, Y., Zhang, W.-Y., Song, C.-L., Pan, Z.-Q., Du, G.-J., Song, Z.-Q., Ren, J., Bo, L.-Y., An, J.-J., & Wang, M. (2025). Effect of Plastein Reaction on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Corn Glutelin Peptides and Quality of Chiffon Cake. Foods, 14(19), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193392






