In Vivo Absorption of Iron Complexes of Chondroitin Sulfates with Different Molecular Weights and Their Anti-Inflammation and Metabolism Regulation Effects on LPS-Induced Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparations of CS-Fe and LCS-Fe
2.3. Fluorescent Labeling of CS and Its Iron Complexes
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Determination of Fluorescence Substitution Degree
2.6. High Performance Gel Permeation Chromatography (HPGPC)
2.7. In Vivo Absorption and Tissue Distribution Assays
2.8. Cell Culture and Viability Assays
2.9. Determination of Nitric Oxide (NO) Production
2.10. Determination of Inflammatory Factor Gene Expression by RT-PCR
2.11. Targeted Metabolite Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
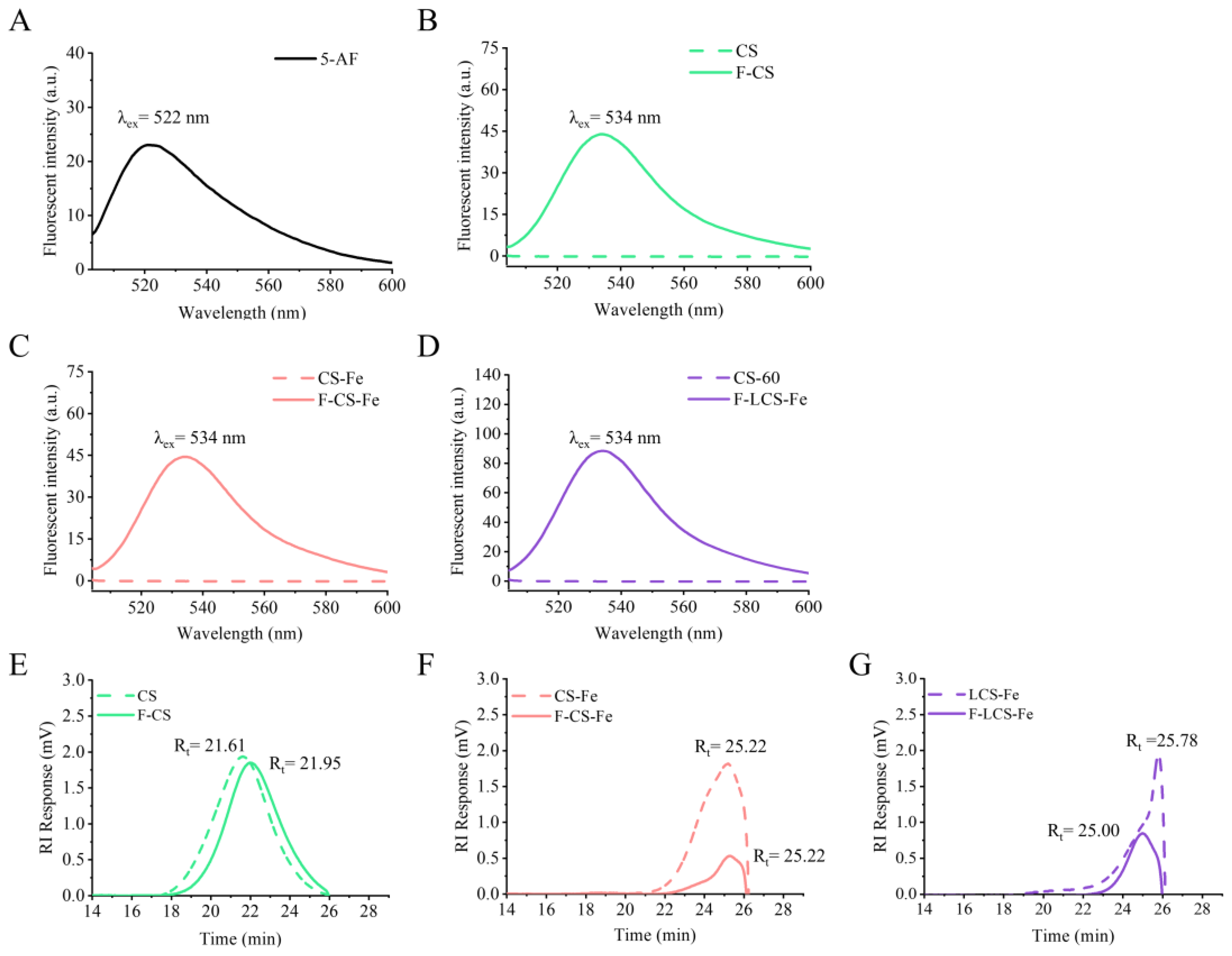
3.1. Characterization of CS, CS-Fe, LCS-Fe, and Their Fluorescently Labeled Derivatives
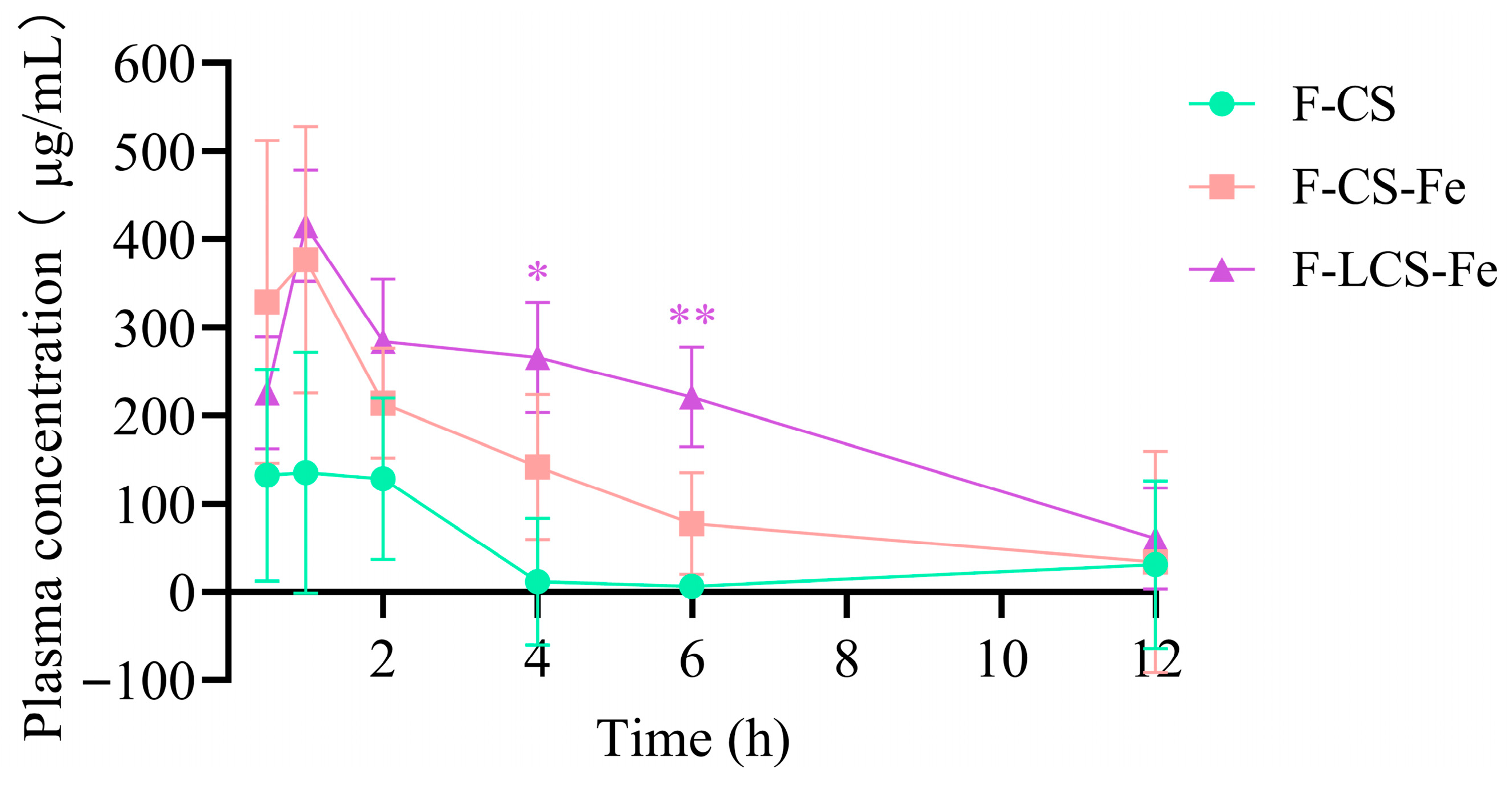
3.2. In Vivo Absorption of Fluorescently Labeled CS, CS-Fe, and LCS-Fe
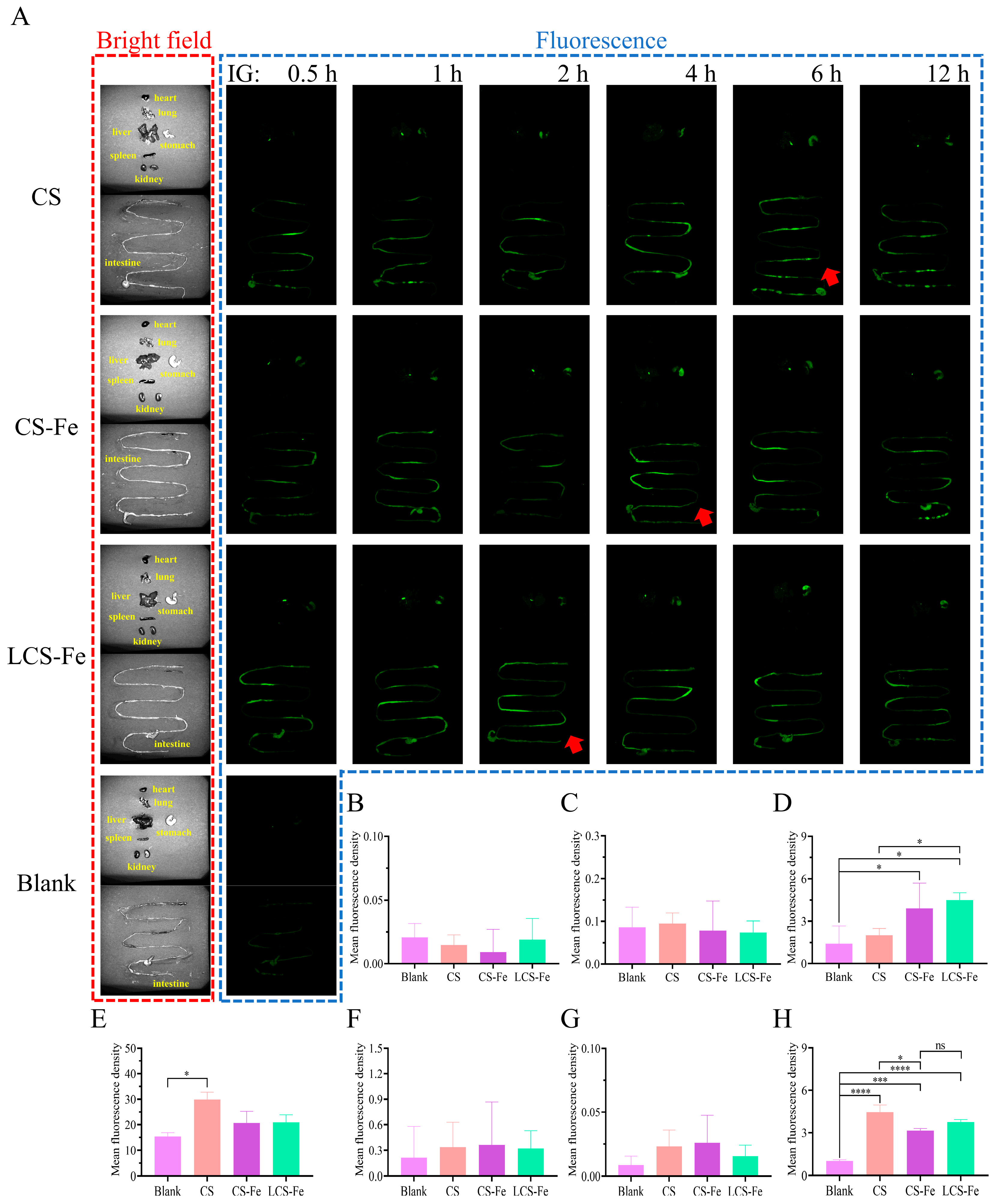
3.3. In Vivo Distribution of Fluorescently Labeled CS, CS-Fe, and LCS-Fe
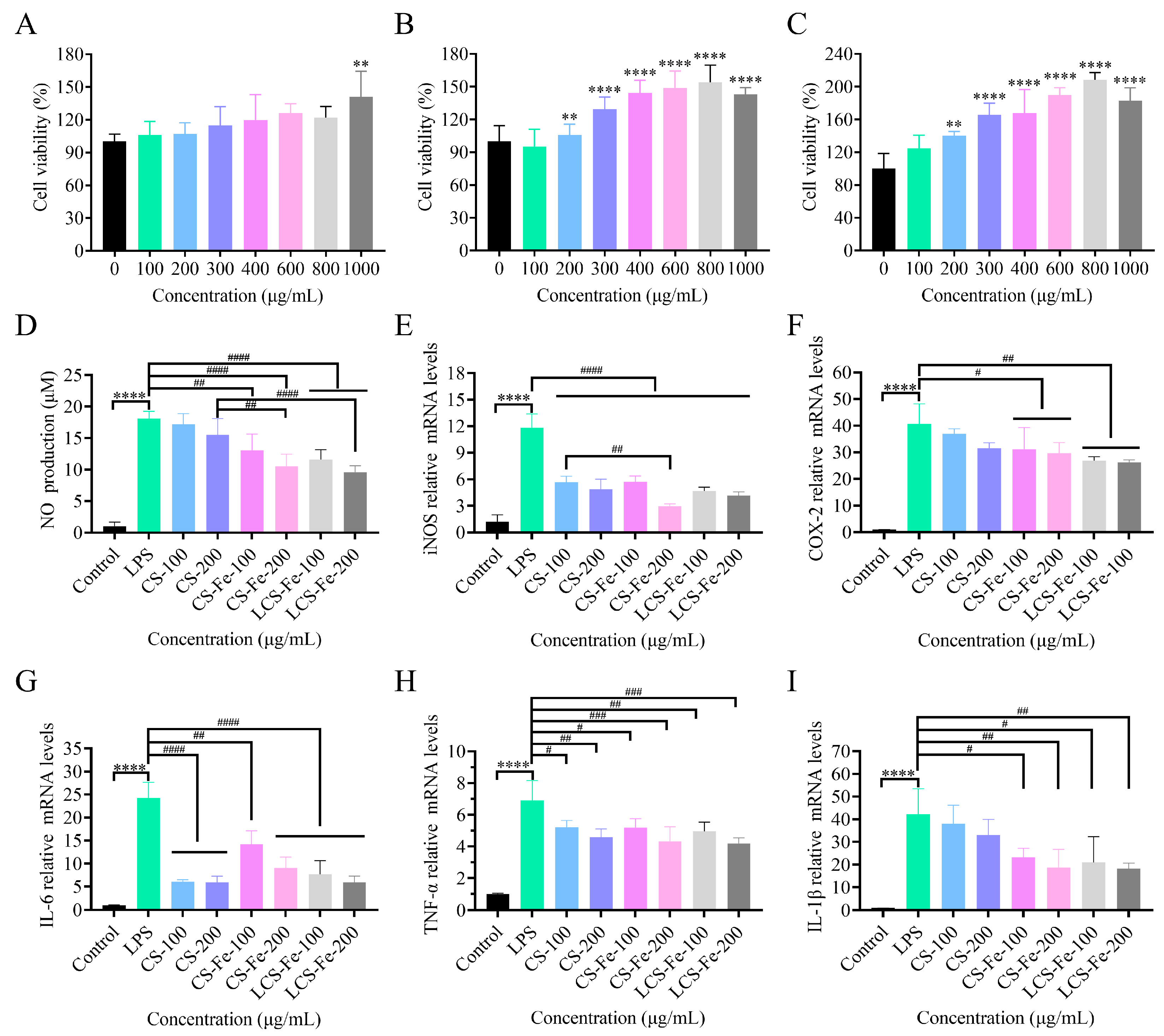
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of CS, CS-Fe, and LCS-Fe in RAW 264.7 Cells
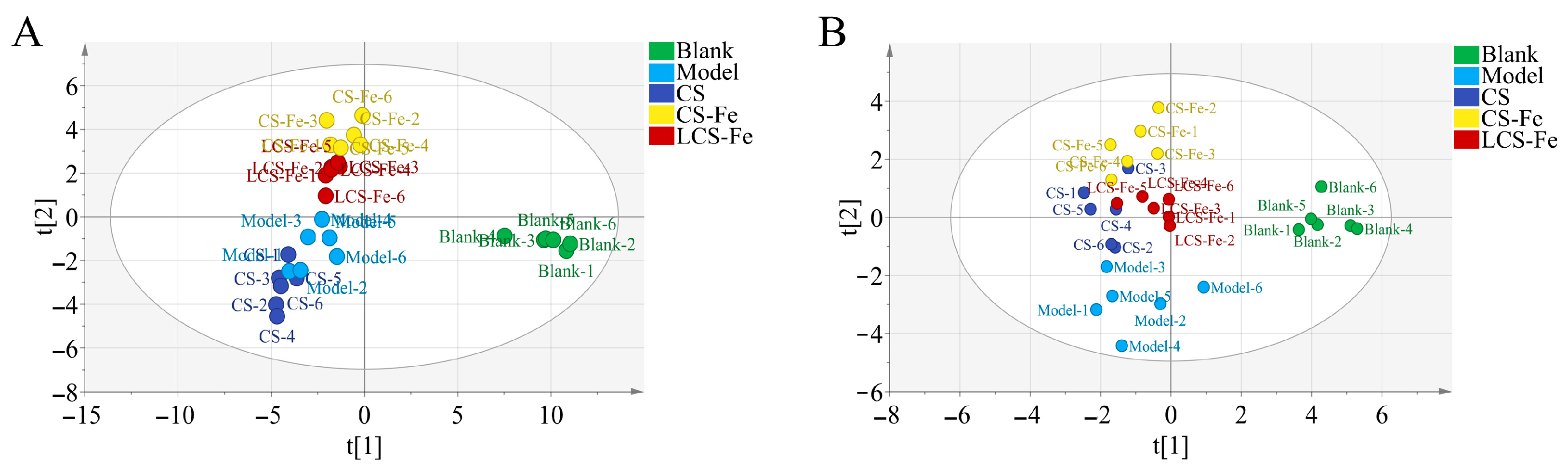
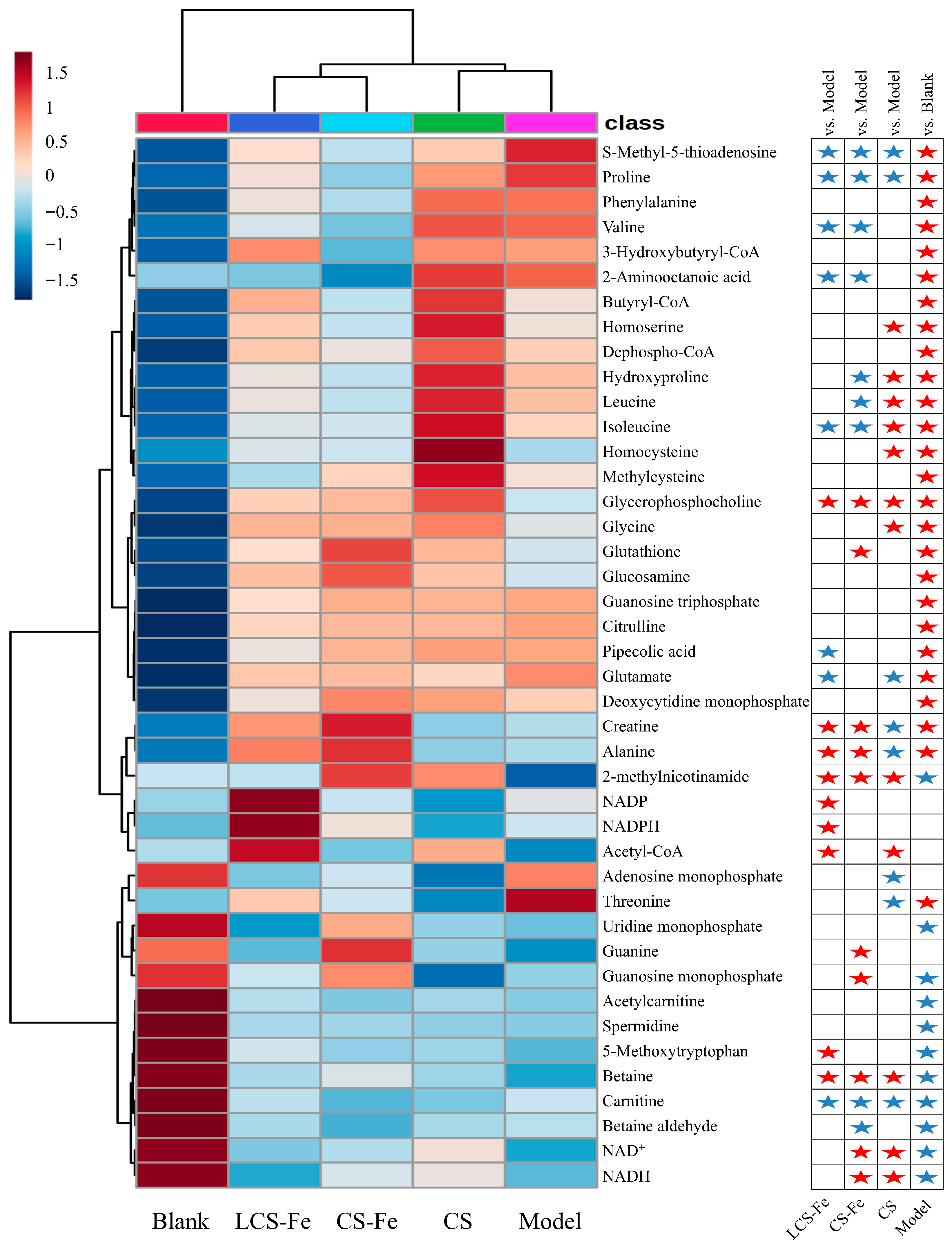
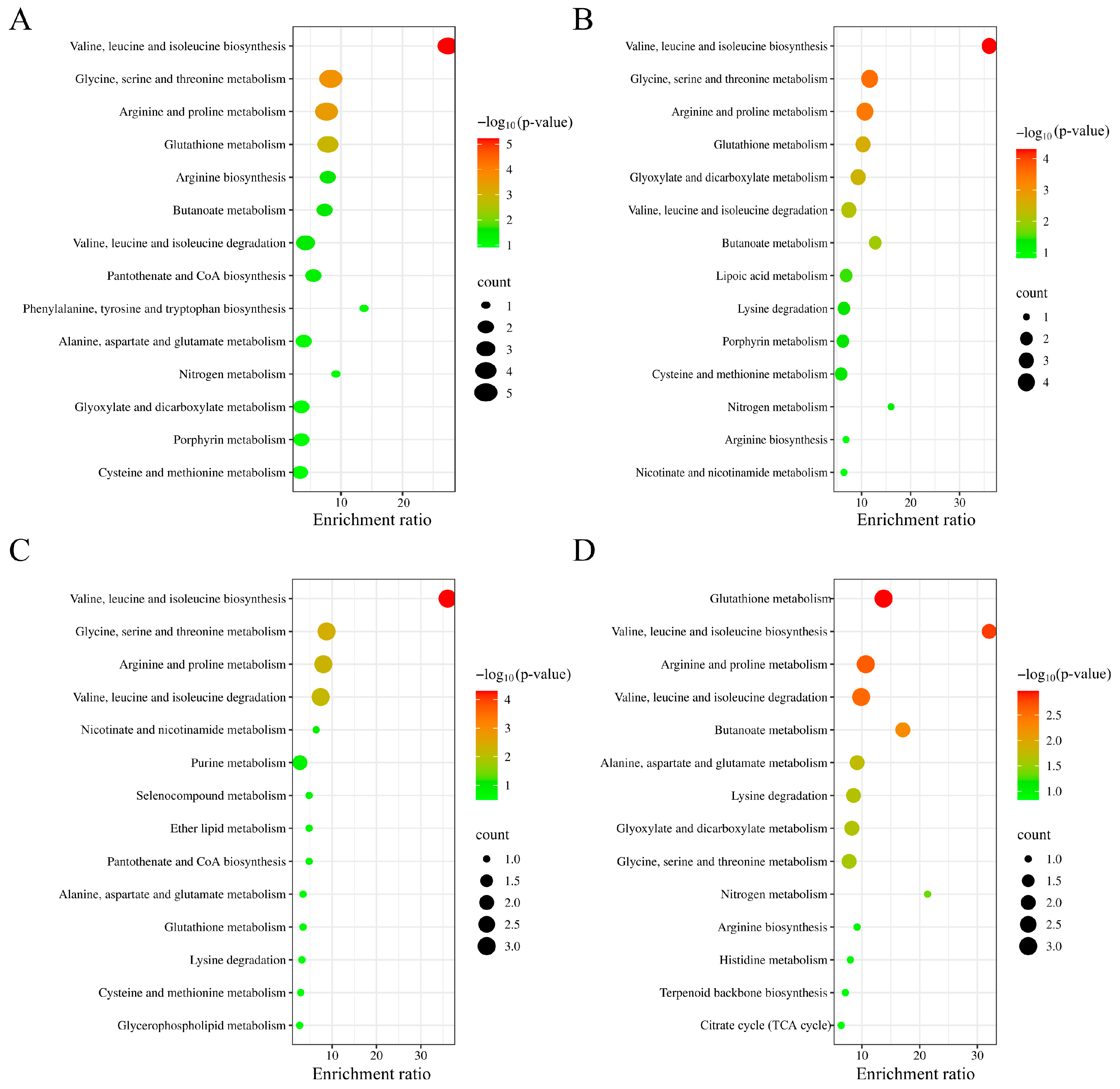
3.5. Metabolism Regulation Effects of CS, CS-Fe, and LCS-Fe on LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, H.; Lu, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, L.; Ren, Q. A chondroitin sulfate purified from shark cartilage and bovine serum albumin interaction activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qi, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C. Degradation of chondroitin sulfate: Mechanism of degradation, influence factors, structure-bioactivity relationship and application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, R.; Li, Y.; Shen, R.; Yu, R.; Jian, L.; Guo, S. Preparation of low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfates by complex enzyme hydrolysis and their antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, Q.; Lv, K.; Ma, H.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L. Low-molecular-weight fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and its oligosaccharides from sea cucumber as novel anticoagulants: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Wang, K.; Pi, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Ye, H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. Crucial role of low molecular weight chondroitin sulfate from hybrid sturgeon cartilage in osteoarthritis improvement: Focusing on apoptosis, systemic inflammation, and intestinal flora. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 139850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yin, H.; Qi, X.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Mou, J.; Yang, J. Immunomodulatory effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Stichopus chloronotus on RAW 264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Bai, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Gao, R.; Wu, H.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Y. Characterization of chondroitin sulfates isolated from large hybrid sturgeon cartilage and their gastroprotective activity against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Hoshino, J.; Yamazaki, C.; Sekiguchi, T.; Miyauchi, S.; Horie, K. Effects of chondroitin sulfate on colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium in rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 85, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Q.; Shi, J.; Song, G.; Zhang, M.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Structural modulation of gut microbiota by chondroitin sulfate and its oligosaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Pan, X.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Advances in oral absorption of polysaccharides: Mechanism, affecting factors, and improvement strategies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peana, M.; Medici, S.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Crisponi, G.; Garribba, E.; Sanna, D.; Zoroddu, M.A. Interaction of a chelating agent, 5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl) pyridin-4(1H)-one, with Al (III), Cu (II) and Zn (II) ions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 171, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, H. Effects of endogenous metal ions on the structure and antioxidant activity of lentinan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; He, C.; Chen, H. Effect of Fe (III), Zn (II), and Cr (III) complexation on the physicochemical properties and bioactivities of corn silk polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zheng, Z.; Qu, J.; Feng, T.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Su, F.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Q.; et al. Study on the synthesis of iron-based nanomedicine assisted by angelica sinensis polysaccharide with enhanced retention performance and its application in anemia treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, N.; Sheikh, Z.U.D.; Yadav, A.; Kothari, R.; Singh, A.; Pathania, D. An all-inclusive review on nanoscale zerovalent iron: Green synthesis routes and environmental applications. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Song, H.; Yan, C.; Ai, C.; Wu, S.; Song, S. Structural analysis and bioavailability study of low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfate-iron complexes prepared by photocatalysis-Fenton reaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 342, 122435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, N.; Tian, J.; Ai, C.; Song, S. Low-molecular-weight carrageenan prepared by photocatalysis-freeze-thaw circle and its in vivo distribution after oral administration. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 111027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q. In vivo pharmacokinetic study of a Cucurbita moschata polysaccharide after oral administration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wnag, L.; Tian, J.; Yan, C.; Song, C.; Xiao, S.; Song, S. Characterization of low-molecular-weight fucoidan prepared by photocatalysis degradation and its regulation effect on metabolomics of LPS-stimulated macrophages. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogamo, A.; Matsuzaki, K.; Uchiyama, H.; Nagasawa, K. Preparation and properties of fluorescent glycosamino-glycuronans labeled with 5-aminofluorescein. Carbohydr. Res. 1982, 105, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.; Bae, K.H.; Ng, S.; Yamashita, A.; Kurisawa, M. Hyaluronic acid-green tea catechin conjugates as a potential therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14285–14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Tang, W.; Teng, W.; Mu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Insights into oral lentinan immunomodulation: Dectin-1-mediated lymphatic transport from Peyer’s patch M cells to mononuclear phagocytes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 346, 122586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Cheng, F.; Wang, K. Degradation of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide: Structures and protective activities against ethanol-induced acute liver injury. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 328, 121745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lin, S.; Lin, Z.; Lu, H.; Ma, A.; Lin, D. Establishment of molecular weight specific chromatogram of Ganoderma glycopeptide and its application in extract. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruendken, M.; Blume, A. Network formation of low molecular weight ‘liquid’ polymers studied by gel permeation chromatography and stress-strain analysis according to Mooney-Rivlin. Polym. Test. 2023, 118, 107897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Pei, K.; Meng, X.; Zhang, S.; Hu, M.; Liu, Y. In vivo absorption, in vitro simulated digestion and fecal fermentation properties of polysaccharides from Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum Cum Alumine and their effects on human gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, G.; Xu, D.; Feng, Y.; Shen, L. Poly(ethylene glycol)-radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide conjugates: Preparation, characterization, pharmacokinetics and in vitro bioactivity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; You, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Ai, C.; Song, S. H2O2-TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of chondroitin sulfate and in vivo absorption and excertion of its product. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, M.; Turkova, K.; Schwarzer, M.; Nesporova, K.; Kubala, L.; Hermannova, M.; Foglov, T.; Safrankov, B.; Sindel, M.; Srůtkova, D.; et al. Molecular weight and gut microbiota determine the bioavailability of orally administered hyaluronic acid. Carbohyd Polym. 2023, 313, 120880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, C.; Cao, R.; et al. Enhancing the intestinal absorption of low molecular weight chondroitin sulfate by conjugation with α-linolenic acid and the transport mechanism of the conjugates. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Su, N.; Xiao, M.; Li, X.; Shang, N. Structural analysis and anti-cancer activity of low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfate from hybrid sturgeon cartilage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Cheng, C.; Lin, X.; Qian, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, G. Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide-iron (III) complex used to treat iron deficiency anemia after being absorbed via GLUT2 and SGLT1 transporters. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; He, C.; Shi, L.; Li, J. Fe (Ⅲ) concentrations controlled highly soluble carboxylated inulin–Fe toward efficient supplement of iron. Food Hydrocolloid 2023, 145, 109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, N.S.; Syama, S.; Sabareeswaran, A.; Mohanan, P.V. Toxicity, toxicokinetics and biodistribution of dextran stabilized Iron oxide Nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Song, J.H.; Go, M.R.; Yu, J.; Oh, J.; Choi, S.J. Cytotoxicity, intestinal transport, and bioavailability of dispersible iron and zinc supplements. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, D.; Wang, L.; Li, X. The gastrointestinal absorption characteristics and metabolic mechanisms of polysaccharides from Hohenbuehelia serotina. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.L.; Shi, L. Methods of study on conformation of polysaccharides from natural products: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Song, X.; Wang, R.; He, W.; Yin, J.; Nie, S. Mechanism exploration of intestinal mucus penetration of nano-Se: Regulated by polysaccharides with different functional groups and molecular weights. J. Control Release 2025, 379, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, D.A.; Vayenas, D.V.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Repanti, M. Concentration of iron and distribution of iron and transferrin after experimental iron overload in rat tissues in vivo: Study of the liver, the spleen, the central nervous system and other organs. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2000, 196, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; He, Y.; Ren, D.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Cong, H.; Zhou, H. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory effects of fucoidan compound agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Guo, D. Quyu Shengxin capsule (QSC) inhibits Ang-II-induced abnormal proliferation of VSMCs by down-regulating TGF-β, VEGF, mTOR and JAK-STAT pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 275, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Yan, C.; Ai, C.; Wen, C.; Guo, X.; Song, S. Two Ascophyllum nodosum Fucoidans with Different Molecular Weights Inhibit Inflammation via Blocking of TLR/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Discriminately. Foods 2022, 11, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Lian, X.; Zheng, T.; Xue, X.; Luo, Z.; Gao, H.; Zheng, X. Unraveling the link between structural properties of polysaccharides and anti-inflammatory activity: A review. Carbohydr. Res. 2025, 555, 109583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Wang, C.; Xia, X.; Kou, K.I.; Kraithong, S.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, R. Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Oligosaccharides in Psidium guajava Linn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 12474–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duan, R.; Wang, P.; Zhong, X.; Wu, X. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory effects of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharide-Fe/Zn complexes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, G.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, Y. Metabolomic profiles in allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Allerg. Asthma Im. 2025, 13, 594–602.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettore, L.A.; Westbrook, R.L.; Tennant, D.A. Proline metabolism and redox; maintaining a balance in health and disease. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Gao, Z.; Ru, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L. Metabolomics for in situ monitoring of attached Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus edulis: Effects of offshore wind farms on aquatic organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 187, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, X. Cyperus peptide SFRWQ inhibits oxidation and inflammation in RAW264.7 cell model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Jia, W.; Du, A.; Shi, L. Pseudo-targeted metabolomics analysis of the therapeutic effect of phenolics-rich extract from Se-enriched green tea (Camellia sinensis) on LPS-stimulated murine macrophage (RAW264.7). Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhung, T.T.M.; Ohat, N.K.; Anh, T.T.; Nghi, T.D.; Thu, N.Q.; Lee, A.; Tien, N.T.N.T.; Anh, N.K.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, K.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition preserves mitochondrial function and cell survival during the early onset of isoniazid-induced oxidative stress. Chem-Biol. Interact. 2025, 411, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, T.; Liang, S.; Niu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, J. Metabolic profiling of polysaccharides from Leccinum crocipodium (Letellier.) Watliag stem fermented by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and their immunomodulatory effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | ATGTCCGAAGCAAACATCAC | TAATGTCCAGGAAGTAGGTG |
| COX-2 | CAGCAAATCCTTGCTGTTCC | TGGGCAAAGAATGCAAACATC |
| TNF-α | GATCGGTCCCCAAAGGGATG | GGCTACAGGCTTGTCACTCG |
| IL-1β | TTCATCTTTGAAGAAGAGCCCAT | TCGGAGCCTGTAGTGCAGTT |
| IL-6 | TGGAAATGAGAAAAGAGTTGTGC | CCAGTTTGGTAGCATCCATCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Q.; Zheng, J.; Kong, F.; Wu, X.; Ai, C.; Song, S. In Vivo Absorption of Iron Complexes of Chondroitin Sulfates with Different Molecular Weights and Their Anti-Inflammation and Metabolism Regulation Effects on LPS-Induced Macrophages. Foods 2025, 14, 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193356
Du Q, Zheng J, Kong F, Wu X, Ai C, Song S. In Vivo Absorption of Iron Complexes of Chondroitin Sulfates with Different Molecular Weights and Their Anti-Inflammation and Metabolism Regulation Effects on LPS-Induced Macrophages. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193356
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Qianqian, Jiachen Zheng, Fanhua Kong, Xiuli Wu, Chunqing Ai, and Shuang Song. 2025. "In Vivo Absorption of Iron Complexes of Chondroitin Sulfates with Different Molecular Weights and Their Anti-Inflammation and Metabolism Regulation Effects on LPS-Induced Macrophages" Foods 14, no. 19: 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193356
APA StyleDu, Q., Zheng, J., Kong, F., Wu, X., Ai, C., & Song, S. (2025). In Vivo Absorption of Iron Complexes of Chondroitin Sulfates with Different Molecular Weights and Their Anti-Inflammation and Metabolism Regulation Effects on LPS-Induced Macrophages. Foods, 14(19), 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193356








