Construction and Comparison of UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-MS/MS Methods for the Detection of Diazepam Residues in Complex Aquatic Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Extraction Procedure
2.2.2. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
2.3. Standard Solution Preparation
2.3.1. Mixed Standard Stock Solution
2.3.2. Mixed Internal Standard Stock Solution
2.4. Instrumental Conditions
2.4.1. UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS Conditions
Chromatographic Conditions
Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.4.2. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
Chromatographic Conditions
Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.4.3. Qualitative Confirmation
2.4.4. Quantitative Analysis
2.5. Subsection
2.6. Matrix Model Construction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Sample Preparation Conditions
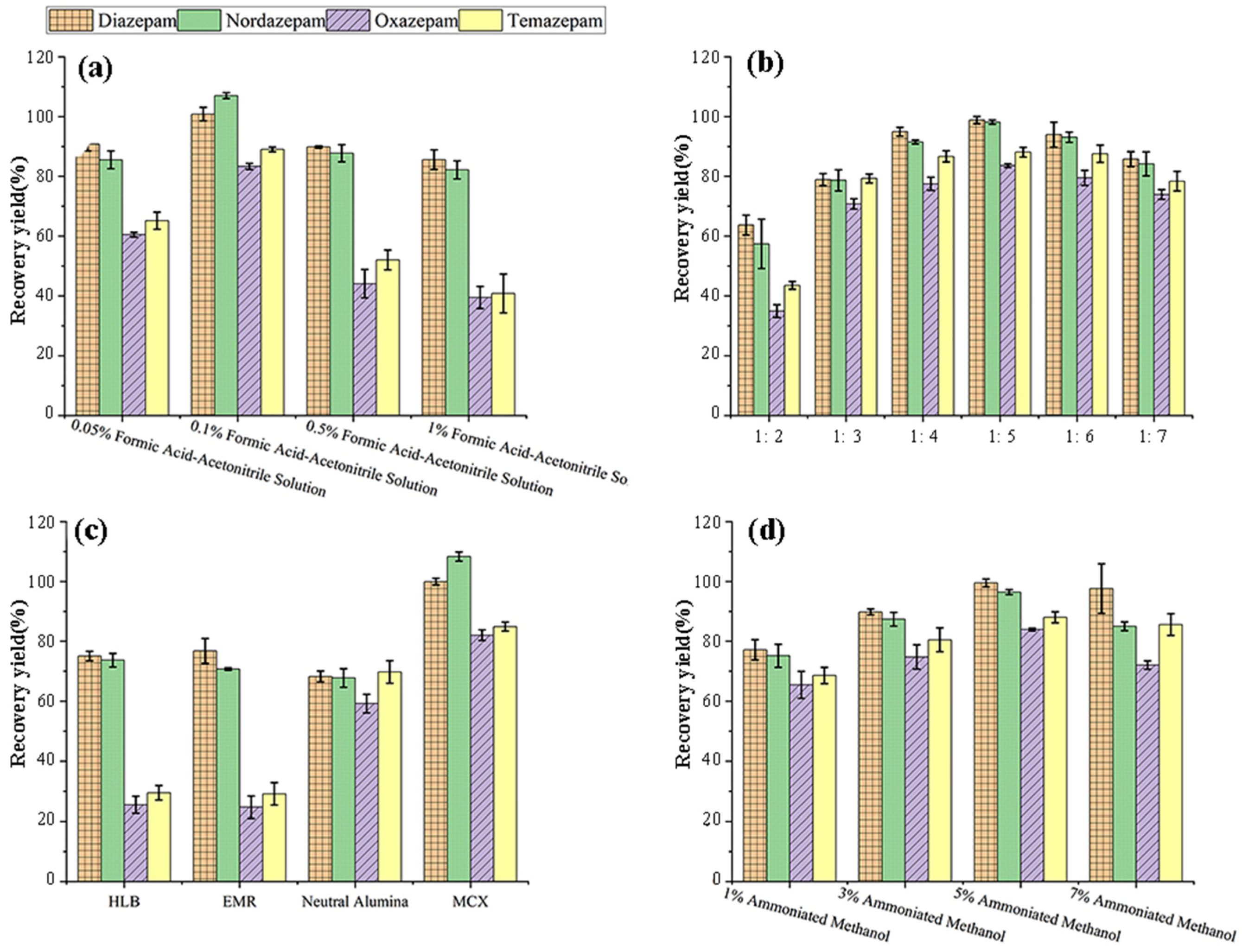
3.1.1. Selection of Extraction Solvents
3.1.2. Optimization of Purification Methods
Selection of Solid-Phase Extraction Columns
Optimization of Elution Conditions
3.2. Optimization of Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
3.2.1. Optimization of Liquid Chromatography Conditions
3.2.2. Optimization of Mass Spectrometry Conditions
3.2.3. Analysis of Mass Spectrometric Fragmentation Mechanisms
3.3. Methodological Investigation
3.3.1. Matrix Effects and Their Elimination
3.3.2. Linear Range
3.3.3. Limits of Detection and Quantification
3.3.4. Accuracy and Precision
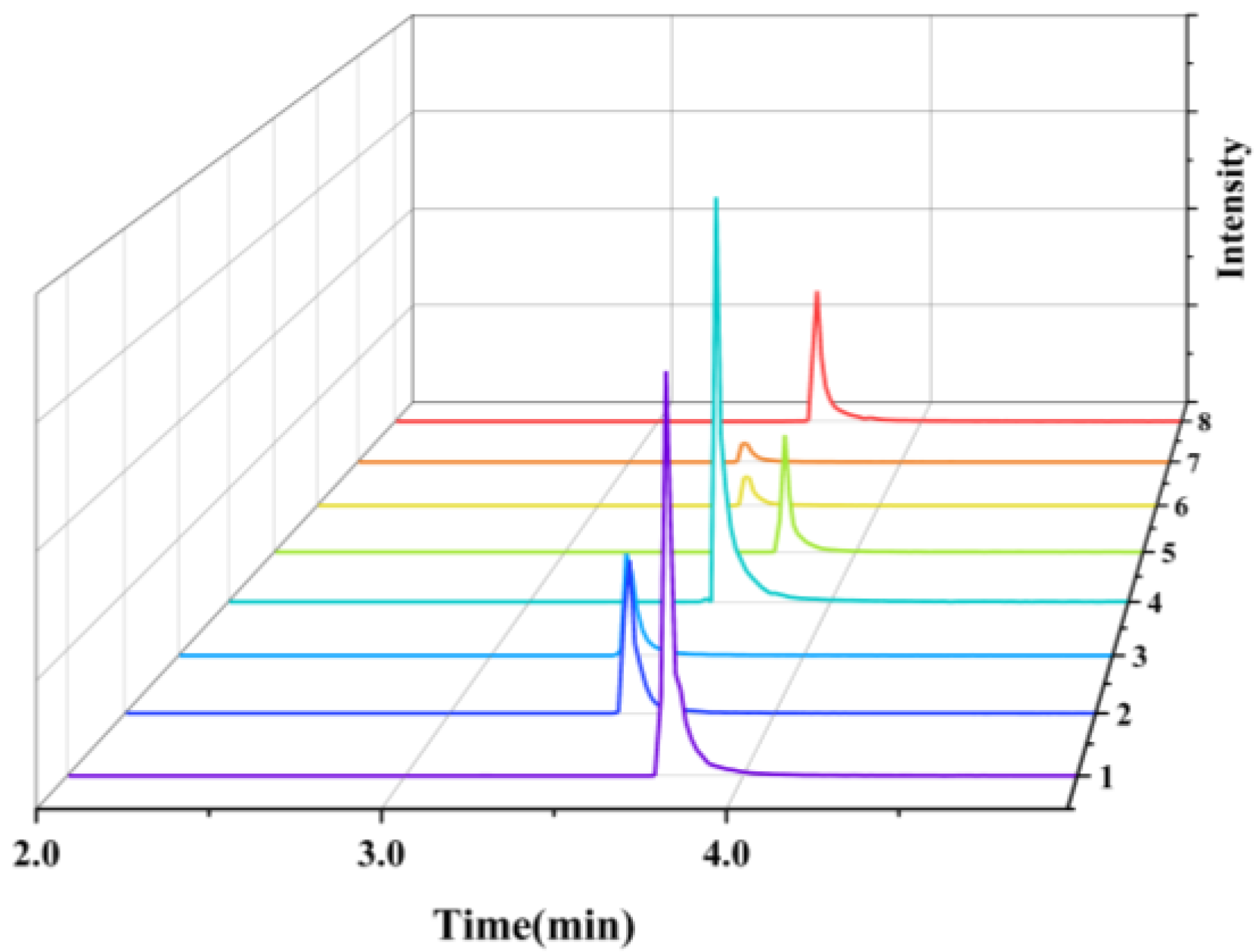
3.3.5. Comparison of the Testing Capabilities of the Two Mass Spectrometry Platforms
3.3.6. Practical Sample Testing and Ecological Safety Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, P.; Liu, X.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, Z.; Thomes, M.W.; Lee, C.W.; Bong, C.W.; Zhang, X.; Hao, F.; Li, X.; et al. Monitoring Consumption of Common Illicit Drugs in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, by Wastewater-Cased Epidemiology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariño, I.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodríguez, I.; González-Díez, M.; Cela, R. Screening and Selective Quantification of Illicit Drugs in Wastewater by Mixed-Mode Solid-Phase Extraction and Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centazzo, N.; Frederick, B.-M.; Jacox, A.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Concheiro-Guisan, M. Wastewater Analysis for Nicotine, Cocaine, Amphetamines, Opioids and Cannabis in New York City. Forensic Sci. Res. 2019, 4, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borova, V.L.; Maragou, N.C.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Pistos, C.; Thomaidis, Ν.S. Highly Sensitive Determination of 68 Psychoactive Pharmaceuticals, Illicit Drugs, and Related Human Metabolites in Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4273–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, B.; Bi, R.; Meng, J. Contamination, source and potential risks of pharmaceuticals and personal products (PPCPs) in Baiyangdian Basin, an intensive human intervention area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Martínez, S.A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; González-González, R.B.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Araújo, R.G.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.A.; Barceló, D.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Environmental Concerns and Bioaccumulation of Psychiatric Drugs in Water Bodies—Conventional versus Biocatalytic Systems of Mitigation. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobo, M.; Yamada, H.; Mihara, T.; Kondo, Y.; Irie, M.; Harada, K.; Ni, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Kayama, Y. Two Models for Weight Gain and Hyperphagia as Side Effects of Atypical Antipsychotics in Male Rats: Validation with Olanzapine and Ziprasidone. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, I.E.H.; Assem, H. Pharmacological Mechanisms of Diazepam in Fish: Effect on Growth. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Regalado, M.D.C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E.; Zafra-Gómez, A. Bioaccumulation/Bioconcentration of Pharmaceutical Active Compounds in Aquatic Organisms: Assessment and Factors Database. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y. Medicinal Chemistry, 1st ed.Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2009; ISBN 978-7-5641-1615-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, D.; Chen, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Geng, P.; Dai, D.; Zhou, Q.; Qiu, W. Inhibitory Effect of Imperatorin on the Pharmacokinetics of Diazepam In Vitro and In Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 01079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kong, C.; Yang, G. Investigation and Analysis of Residues of Diazepam and Desdiazepam in Aquatic Products Sold in Shanghai. Qual. Saf. Agro-Prod. 2020, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.F.; Sun, L.Z.; Xue, X.; Gong, P.X.; Wei, L.L.; Li, X.L.; Zhu, J.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, F. Determination of Diazepam in Aquatic Products by Solid Phase Extraction-Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2020, 38, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, G.X.; Kong, C.; Zhai, W.L.; Feng, H.F.; Sheng, X.S.; Yu, X.H. Determination of Sedatives and Their Metabolite Residues in Aquatic Products by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.A. Occurrence, Treatment, and Toxicological Relevance of EDCs and Pharmaceuticals in Water. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2008, 30, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. A GC/MS Method for the Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Chlorpromazine and Diazepam in Pork Samples. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercolini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Iannello, C.; Matrisciano, F.; Nicoletti, F.; Raggi, M.A. Simultaneous Analysis of Diazepam and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma and Brain Tissue by HPLC-UV and SPE. Talanta 2009, 80, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, S.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Tao, Y.; Yuan, Z. Establishment of Pressurized Liquid Extraction Followed by HPLC–MS/MS Method for the Screening of Adrenergic Drugs, Steroids, Sedatives, Colorants and Antioxidants in Swine Feed. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, S. Determination of 15 Sedative Residues in Mutton by Rapid Resolution Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, E.; In, S.; Choi, H.; Chung, H.; Chung, K.H. Determination of Illegally Abused Sedative-Hypnotics in Hair Samples from Drug Offenders. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madry, M.M.; Spycher, B.S.; Kupper, J.; Fuerst, A.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Kraemer, T.; Naegeli, H. Erratum to: Long-Term Monitoring of Opioid, Sedative and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Horse Hair Using a Selective and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Procedure. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, L. A Comparative Study of Primary Secondary Amino (PSA) and Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) as QuEChERS Absorbents for the Rapid Determination of Diazepam and Its Major Metabolites in Fish Samples by High-performance Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionisation–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.S.; Li, M.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, W.; Qi, S.G. Research on the Detection Method of Drug Residues in Aquatic Products. Food Saf. Guide 2024, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, K.; Lee, K. Veterinary Drug Residues in Animal-Derived Foods: Sample Preparation and Analytical Methods. Foods 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Ramalhosa, M.J.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Guimarães, L. Sertraline Accumulation and Effects in the Estuarine Decapod Carcinus Maenas: Importance of the History of Exposure to Chemical Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission Commission. Decision of 12 August 2002 Implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC Concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results; Official Journal of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2002; pp. 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Sheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.B.; Peng, X.T. Determination of 15 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Lotus Root by QuEChERS—High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2022, 41, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Ke, X.; Xu, Y. Study on the Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Patterns for Rapid Screening and Structure Identification of Ketamine Analogues in Illicit Powders. Molecules 2023, 28, 6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzimski, T.; Rejczak, T. A QuEChERS-Based Sample Preparation Method for the Analysis of 5-Nitroimidazoles in Bovine Milk by HPLC–DAD. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Jiang, K.; Wang, X. Determination of Migration Amounts of Endocrine Disruptors in PVC Children’s Products by Magnetic Graphene Oxide Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction/Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Instrum. Anal. 2022, 41, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar]
- CAC/GL 71-2009; Guidelines for the Design and Implementation of National Regulatory Food Safety Assurance Programme Associated with the Use of Veterinary Drugs in Food Producing Animals. Codex Alimentarius Commission: Rome, Italy, 2009.
- Huang, L.; Gao, L.; Wu, S.; Hao, Q.R. Variation and Accumulation Characteristics of Diazepam in Simulated Culture Environment. South China Fish. Sci. 2024, 20, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Study on Purification Ability of Six Aquatic Plants to Heavy Metals in Water. Master’s Thesis, AnHui University of Science and Technology, Chuzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]


| Name | Chromatographic Retention Time (t, min) | Exact Mass (m/z) | Collision Energy (eV) | Scanning Method (ESI±) | Ionization Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor Ion (m/z) | Quantifier Ions (m/z) | |||||
| Diazepam | 3.66 | 285.07892 | 193.08815 | 60 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Nordazepam | 3.48 | 271.06327 | 140.02582 | 60 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Oxazepam | 3.38 | 287.05818 | 241.05208 | 30 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Temazepam | 3.26 | 301.07383 | 255.06877 | 30 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Diazepam-D5 | 3.65 | 290.11030 | 198.11949 | 60 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Nordazepam-D5 | 3.48 | 276.09465 | 140.02583 | 60 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Oxazepam-D5 | 3.38 | 292.08957 | 274.07840 | 30 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Temazepam-D5 | 3.26 | 306.10522 | 260.09915 | 30 | ESI+ | [M + H]+ |
| Compound | Retention Time (min). | Precursor Ion (m/z). | Product Ions (m/z). | Declustering Voltage/eV | Collision Energy/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diazepam | 3.65 | 285.0 | 193.1 * | 50 | 34.7 |
| 153.9 | 50 | 34.2 | |||
| Nordazepam | 3.43 | 271.0 | 140.0 * | 40 | 38.0 |
| 165.0 | 40 | 37.0 | |||
| Oxazepam+ | 3.64 | 287.0 | 240.9 * | 50 | 30.0 |
| 269.1 | 50 | 21.0 | |||
| Temazepam | 3.49 | 301.0 | 255.2 * | 21 | 28.0 |
| 283.0 | 21 | 18.3 | |||
| Diazepam-D5 | 3.63 | 290.2 | 198.1 | 50 | 41.8 |
| 154.1 | 50 | 35.8 | |||
| Nordazepam-D5 | 3.41 | 276.1 | 213.0 | 60 | 37.2 |
| 140.0 | 60 | 38.9 | |||
| Oxazepam-D5 | 3.64 | 292.1 | 246.1 | 50 | 29.6 |
| 227.1 | 50 | 47.0 | |||
| Temazepam-D5 | 3.49 | 306.2 | 260.0 | 60 | 29.1 |
| 288.0 | 60 | 47.0 |
| Instrument | Compound of Interest | Regression Equations | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | Absolute Value of ME (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Standard Method | Internal Standard Method | |||||
| UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS | Diazepam | Y = 0.3077X − 2.256 × 10−2 | 0.2~200 | 0.9993 | 18.68~51.32 | 5.71~10.13 |
| Nordazepam | Y = 0.4086X − 2.685 × 10−2 | 0.2~200 | 0.9983 | 11.57~69.36 | 3.85~9.62 | |
| Oxazepam | Y = 0.3539X − 2.335 × 10−2 | 0.2~200 | 0.9971 | 15.48~59.67 | 1.75~8.64 | |
| Temazepam | Y = 0.2766X − 8.201 × 10−3 | 0.2~200 | 0.9981 | 22.38~48.61 | 2.56~6.97 | |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Diazepam | Y = 0.269X + 9.00 × 10−4 | 0.2~200 | 0.9998 | 33.95~71.82 | 4.11~11.17 |
| Nordazepam | Y = 0.342X + 2.10 × 10−4 | 0.2~200 | 0.9988 | 17.51~70.75 | 1.68~11.68 | |
| Oxazepam | Y = 0.171X − 3.16 × 10−3 | 0.2~200 | 0.9985 | 6.69~50.38 | 0.21~12.98 | |
| Temazepam | Y = 0.285X + 4.57 × 10−2 | 0.2~200 | 0.9996 | 19.90~65.08 | 1.00~4.48 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Su, W.; Wang, F.; Qu, S.; Wen, S.; Cao, W. Construction and Comparison of UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-MS/MS Methods for the Detection of Diazepam Residues in Complex Aquatic Matrices. Foods 2025, 14, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193296
Yang Y, Li Y, Tian Q, Yang J, Xu Y, Su W, Wang F, Qu S, Wen S, Cao W. Construction and Comparison of UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-MS/MS Methods for the Detection of Diazepam Residues in Complex Aquatic Matrices. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193296
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuanhao, Yi Li, Qiangbing Tian, Juanning Yang, Yiming Xu, Wen Su, Fei Wang, Siyao Qu, Sien Wen, and Wei Cao. 2025. "Construction and Comparison of UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-MS/MS Methods for the Detection of Diazepam Residues in Complex Aquatic Matrices" Foods 14, no. 19: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193296
APA StyleYang, Y., Li, Y., Tian, Q., Yang, J., Xu, Y., Su, W., Wang, F., Qu, S., Wen, S., & Cao, W. (2025). Construction and Comparison of UPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-MS/MS Methods for the Detection of Diazepam Residues in Complex Aquatic Matrices. Foods, 14(19), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193296





