Development of Organic Sourdough Bread with Paste from Germinated Seeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
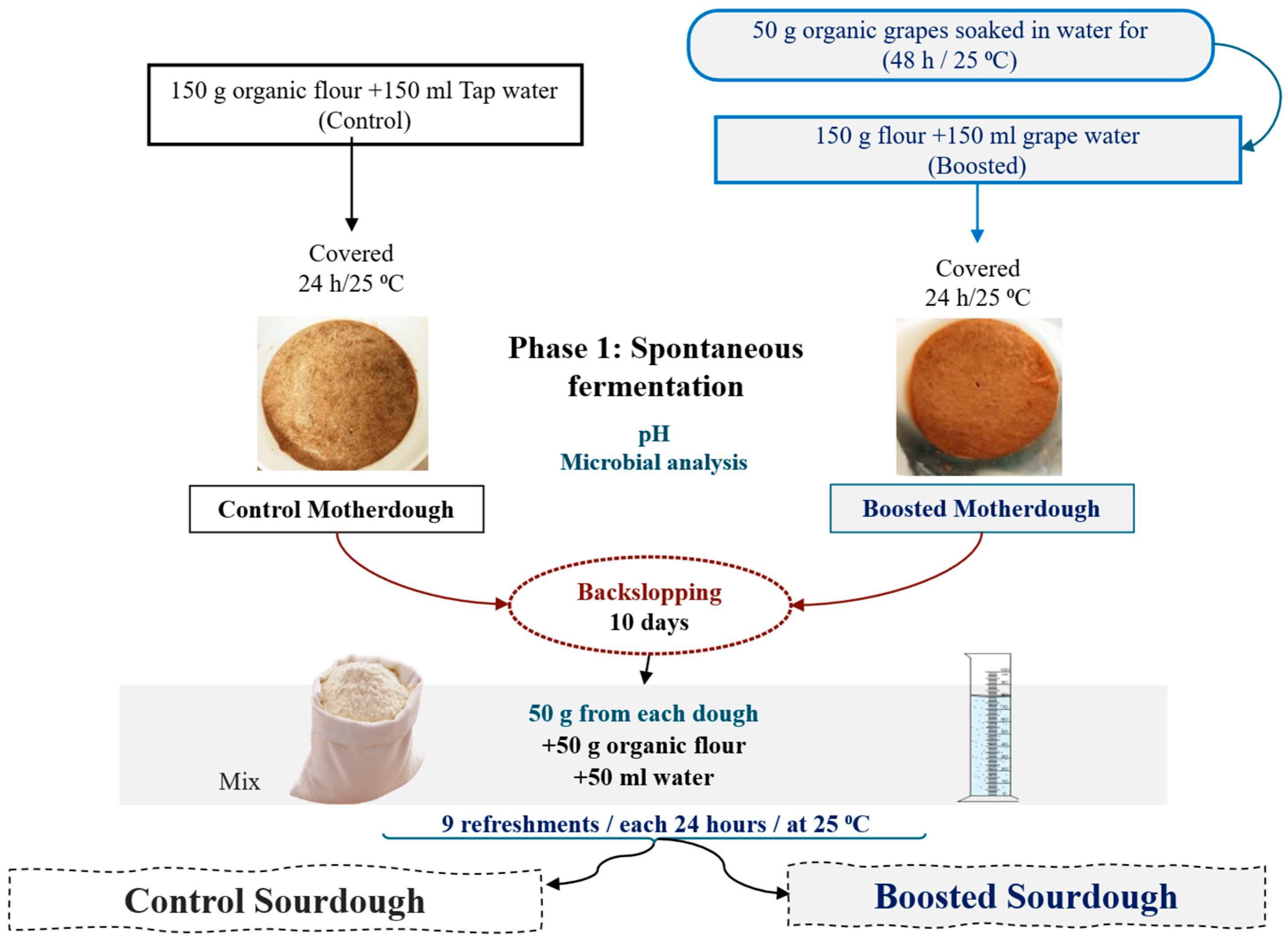
2.2. Sourdough Preparation
2.3. Seed Germination
2.4. Bread-Making
2.5. Microbiological Analyses
2.6. Descriptive Sensorial Analysis of Bread
2.7. Specific Volume, Image, and Color Analysis of Bread Samples
2.8. Nutritional Analysis of Bread
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
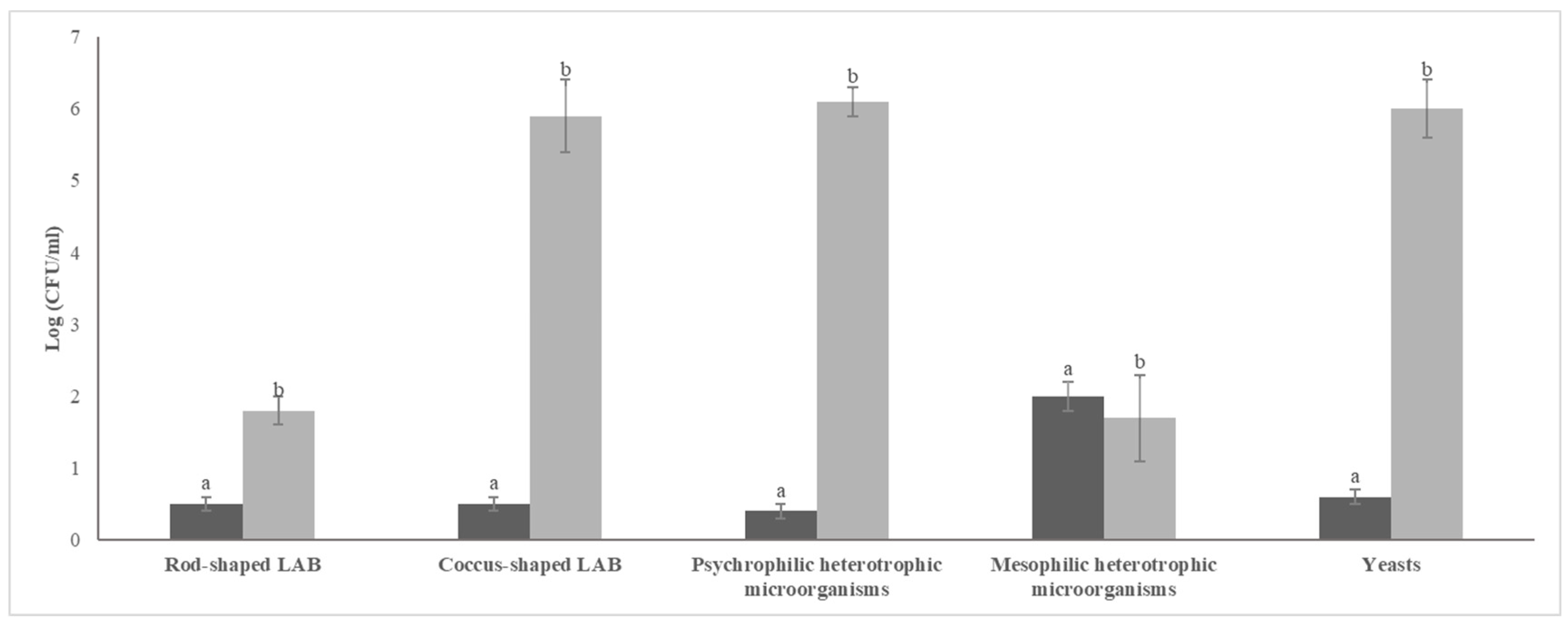
3.1. Microbial Cell Densities Differed Between Tap Water and Grape Water
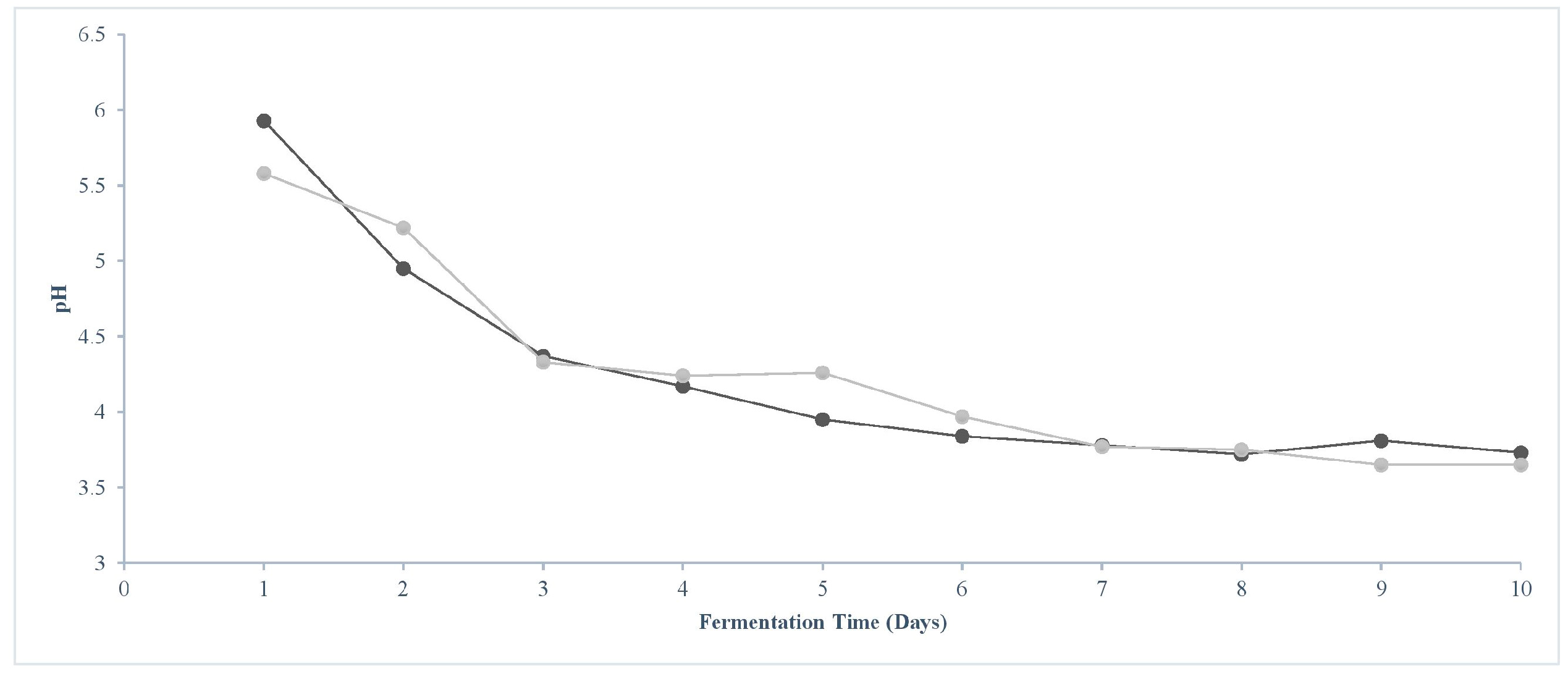
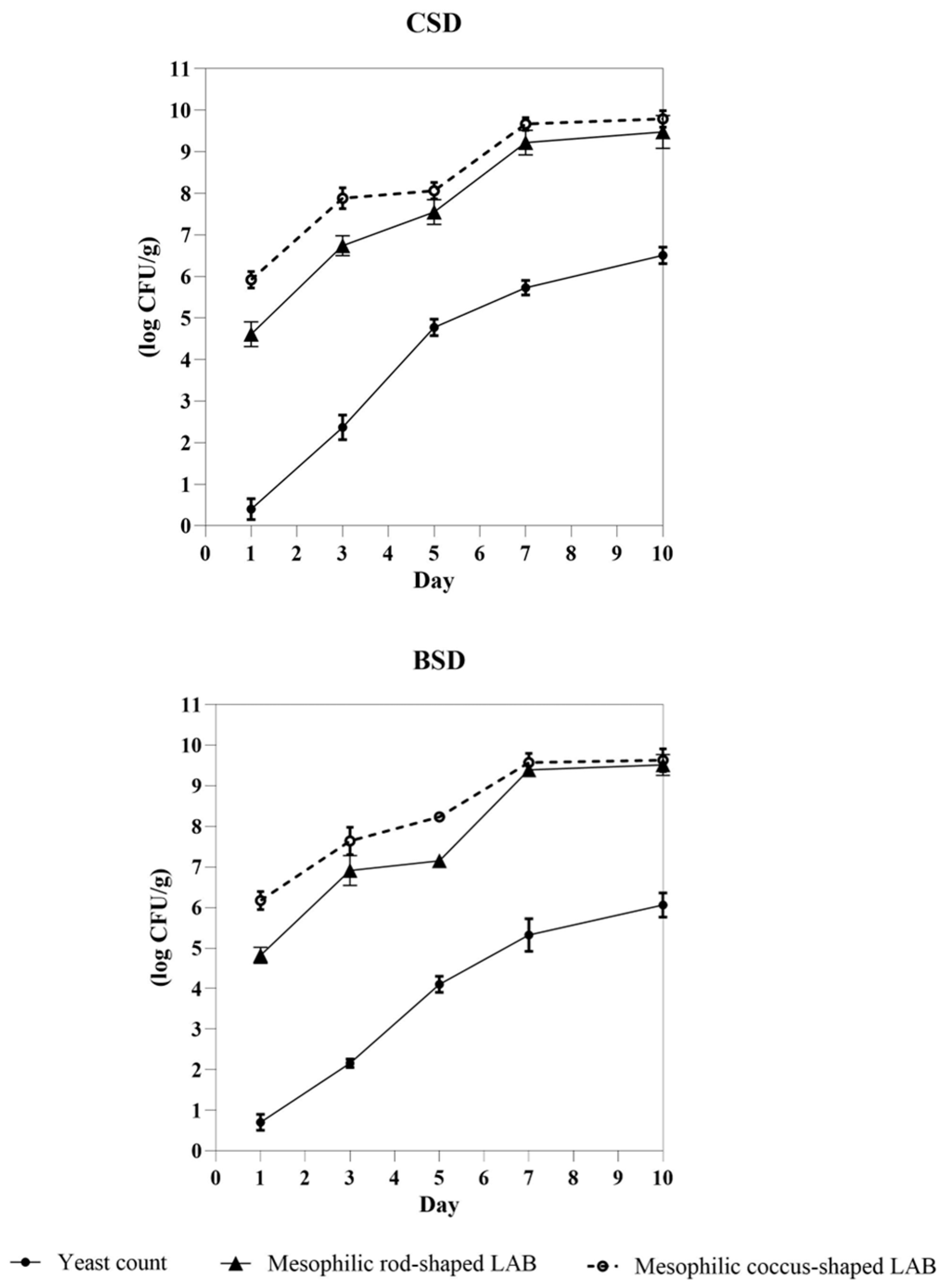
3.2. Boosted Sourdough Gave Similar Performances to Control Sourdough
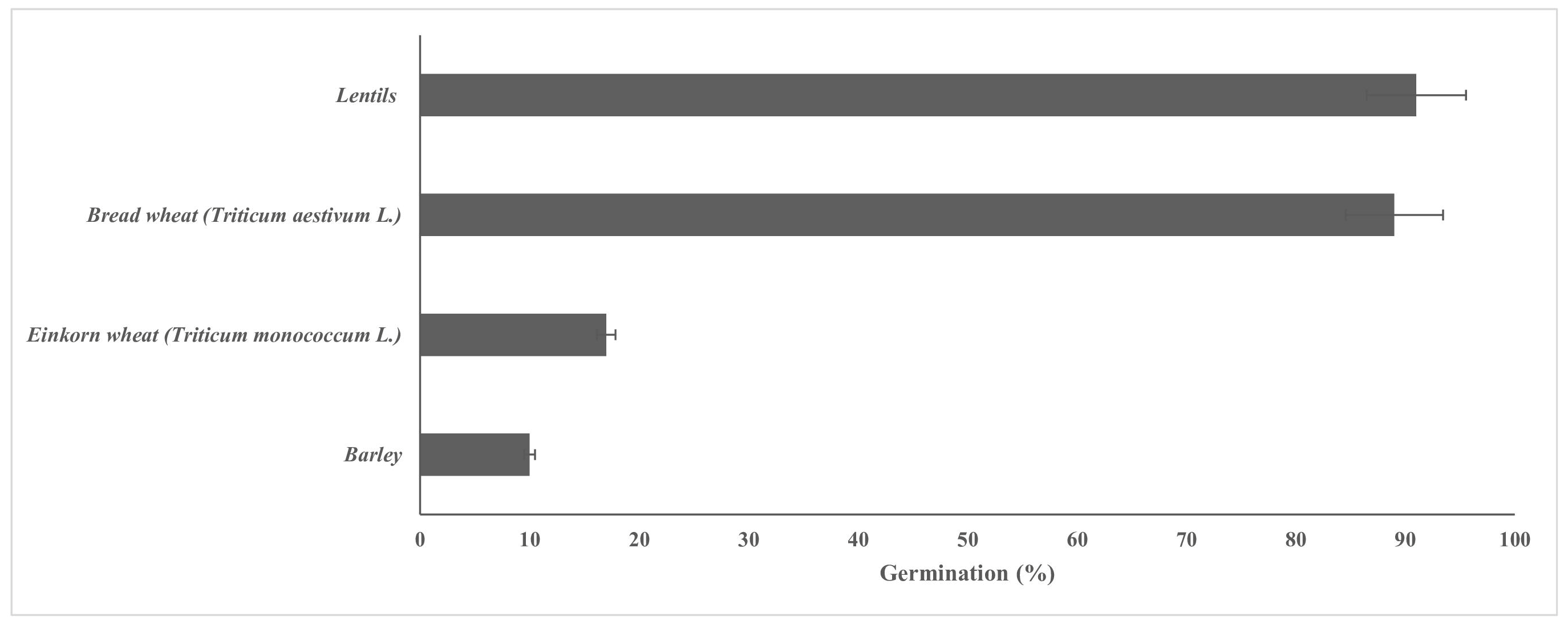
3.3. Germinated Lentil and Bread Wheat Seeds Were Selected as Additional Ingredients for Bread
3.4. Sourdough Bread Was Free from Total Coliforms
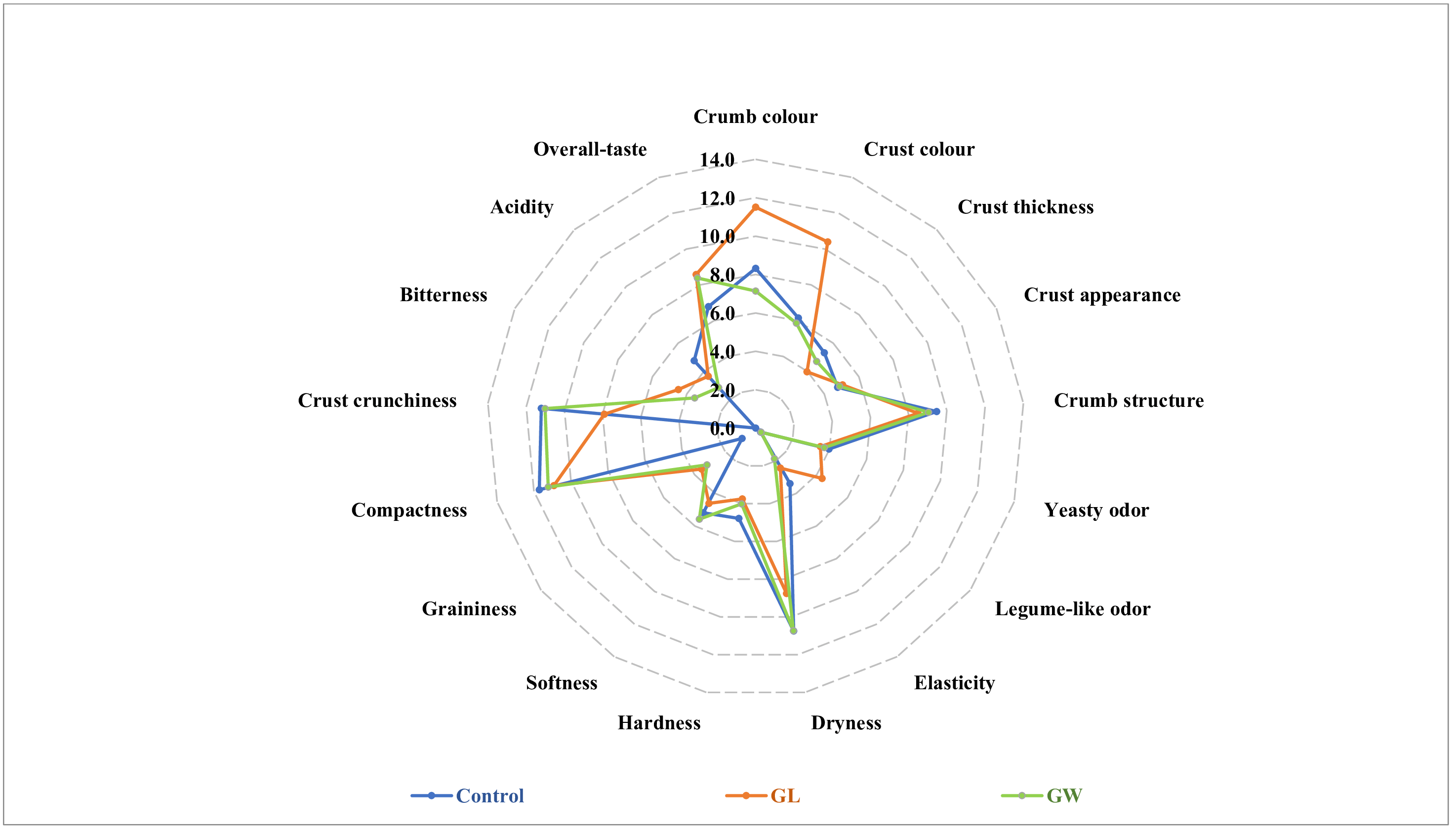
3.5. Bread Types Differed in Terms of Specific Sensory Attributes
3.6. Image Analysis and Color Indexes Differed Among the Bread Types
3.7. Nutritional Analysis of Bread
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GL | Bread made with addition of germinated lentils paste |
| GW | Bread made with addition of germinated wheat paste |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| CSD | Control sourdough |
| BSD | Boosted sourdough |
| G% | Germination percentage |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
References
- Fang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Consumer Preference and Willingness to Pay for Rice Attributes in China: Results of a Choice Experiment. Foods 2024, 13, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiki, A.; De Flaviis, R.; Sacchetti, G. A critical appraisal on emmer wheat composition and its potential health beneficial effect. Food Hum. 2025, 5, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintel. Taste Is the Top Reason US Consumers Eat Plant-Based Proteins. 2020. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/press-centre/taste-is-the-top-reason-us-consumers-eat-plant-based-proteins/ (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Ribet, L.; Kassis, A.; Jacquier, E.; Monnet, C.; Durand-Dubief, M.; Bosco, N. The nutritional contribution and relationship with health of bread consumption: A narrative review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boni, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Roma, R.; Acciani, C. Traditions, health and environment as bread purchase drivers: A choice experiment on high-quality artisanal Italian bread. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Morales, P.; Ciudad-Mulero, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Ferreira, E.; Heleno, S.; Rodrigues, P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Comparison of different bread types: Chemical and physical parameters. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, M.D.; Madden, A.A.; Nichols, L.M.; Haddad, N.M.; Lahne, J.; Dunn, R.R.; McKenney, E.A. A review of sourdough starters: Ecology, practices, and sensory quality with applications for baking and recommendations for future research. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, X. Sourdough Improves the Quality of Whole-Wheat Flour Products: Mechanisms and Challenges—A Review. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkay, Z.; Falah, F.; Cankurt, H.; Dertli, E. Exploring the Nutritional Impact of Sourdough Fermentation: Its Mechanisms and Functional Potential. Foods 2024, 13, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, C.; de Melo Nazareth, T.; Dopazo, V.; Meca, G.; Luz, C. Enhancing Bread Quality and Extending Shelf Life Using Dried Sourdough. LWT 2024, 203, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelle, S.; Guylaine, L.; Gänzle, M.; Gobbetti, M. Gobbetti, M., Gänzle, M., Eds.; History and Social Aspects of Sourdough. In Handbook on Sourdough Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Islam, S. Sourdough Bread Quality: Facts and Factors. Foods 2024, 13, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordún, E.; del Valle, L.J.; Ginovart, M.; Carbó, R. Comparison of the microbial dynamics and biochemistry of laboratory sourdoughs prepared with grape, apple and yogurt. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 21, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Ecological parameters influencing microbial diversity and stability of traditional sourdough. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 171, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, L.; Comasio, A.; Van Kerrebroeck, S. Sourdough production: Fermentation strategies, microbial ecology, and use of non-flour ingredients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2447–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.W.; Chong, A.Q.; Chin, N.L.; Talib, R.A.; Basha, R.K. Sourdough Microbiome Comparison and Benefits. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplevicz, K.S.; Mazo, J.Z.; dos Santos Neto, N.K.; Nalevaiko, F.S.; Sant, E.S. Evaluation of Sourdoughs for the Production of Bread Using Spontaneous Fermentation Technique. Acta Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, A.; Saeed, F.; Afzaal, M.; Imran, A.; Niaz, B.; Tufail, T.; Hussain, M.; Anjum, F.M. Nutritional and End-Use Perspectives of Sprouted Grains: A Comprehensive Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4617–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsakin, O.A.; Banwo, K.; Ogunremi, O.R.; Sanni, A.I. Microbiological and physicochemical properties of sourdough bread from sorghum flour. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 2610–2618. [Google Scholar]
- Montemurro, M.; Pontonio, E.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Investigation of the nutritional, functional and technological effects of the sourdough fermentation of sprouted flours. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 302, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, W.; Evert, K.; Van Nieuwenhove, C. Quinoa flour, the germinated grain flour, and sourdough as alternative sources for gluten-free bread formulation: Impact on chemical, textural and sensorial characteristics. Fermentation 2021, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.L.; Berstein, J.; Jones, S.S.; Blumberg, J.B.; Griffin, T.S. The impacts of germinating organic wheat: Effects on phytic acid, resistant starch, and functional properties of flour, and sensory attributes of sourdough bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, A.; Sergiacomo, A.; De Stefani, A.; Marti, A. Impact of Sprouted Chickpea Grits and Flour on Dough Rheology and Bread Features. Foods 2024, 13, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahira, R.F.; Antunes, A.E.C. Bacteriological Safety of Sprouts: A Brief Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 352, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, L.; Van Kerrebroeck, S.; Leroy, F. Microbial ecology and process technology of sourdough fermentation. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 100, 49–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.K.; Basu, B.; Ooraikul, F. Studies on Germination Conditions and Antioxidant Contents of Wheat Grain. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2001, 52, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific Opinion on the risk posed by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and other pathogenic bacteria in seeds and sprouted seeds. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Dinardo, F.R.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Tap water is one of the drivers that establish and assemble the lactic acid bacterium biota during sourdough preparation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejo, M.J. Present Situation on the Descriptive Sensory Analysis of Bread. J. Sens. Stud. 2011, 26, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczyńska, J.; Cavoski, I. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and sensory features of eugenol, carvacrol and trans-anethole in active packaging for organic ready-to-eat iceberg lettuce. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13299:2016; Sensory Analysis. Methodology. General Guidance for Establishing a Sensory Profile. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- AACC International. Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; Method 10-05.01. Guidelines for Measurement of Volume by Rapeseed Displacement; AACCI: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, P.; Grau, H.; Arendt, E.K. Influence of additives and mixing time on crumb grain characteristics of wheat bread. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrné, L.; Andersson, C.G.; Floberg, P.; Rosén, J.; Lingnert, H. Effect of crust temperature and water content on acrylamide formation during baking of white bread: Steam and falling temperature baking. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, L.K.; Raymond, J.L. (Eds.) Krause’s Food & the Nutrition Care Process, 14th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Wu, P.-S.; Teng, S.-H.; Wu, M.-J. Identification of Dominant Microbes and Functional Analysis of Sourdough Starters Made of Dried Longan and Raisin. Eng. Proc. 2023, 55, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, M.; Tanaka, M.; Momoda, R.; Zendo, T.; Nakayama, J. Mechanistic insight into yeast bloom in a lactic acid bacteria relaying-community in the start of sourdough microbiota evolution. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00662-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gastrow, L.; Michel, E.; Legrand, J.; Amelot, R.; Segond, D.; Guezenec, S.; Rué, O.; Chable, V.; Goldringer, I.; Dousset, X.; et al. Microbial Community Dispersal from Wheat Grains to Sourdoughs: A Contribution of Participatory Research. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 2413–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G. Seed Storage, Germination, Quality, and Enhancements. In The Physiology of Vegetable Crops; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaio, S.; Kappeler, E.; Zamprogna, M.; Jacobs, M. Partially Germinated Ingredients for Naturally Healthy and Tasty Products. Cereal Foods World 2013, 58, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Rehal, J.; Kaur, A.; Jyot, G. Enhancement of Attributes of Cereals by Germination and Fermentation: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1575–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. New perspectives on physiological, biochemical and bioactive components during germination of edible seeds: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Guan, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y. Influence of Sprouted Oat Flour Substitution on the Texture and In Vitro Starch Digestibility of Wheat Bread. Food Chem. 2022, 15, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza Moreno, E.J.; Palma-Rodríguez, H.M.; Hernández-Uribe, J.P.; Soto-Simental, S.; Berrios, J.D.; Vargas-Torres, A. Effect of Wheat Grain Germination Time on Physicochemical and Texture Properties, Starch Digestion, and Protein Hydrolysis Rate in Bread Making. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 121, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods. Microbiological Safety Evaluations and Recommendations on Sprouted Seeds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 52, 123–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Walcott, R.; Chen, J. Differential attachment of Salmonella enterica and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli to alfalfa, fenugreek, lettuce, and tomato seeds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e03170-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadias, M.; Usall, J.; Anguera, M.; Solsona, C.; Viñas, I. Microbiological quality of fresh, minimally-processed fruit and vegetables, and sprouts from retail establishments. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cui, Y.; Walcott, R.; Chen, J. Fate of Salmonella enterica and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli cells artificially internalized into vegetable seeds during germination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01888-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermelho, A.B.; Moreira, J.V.; Junior, A.N.; da Silva, C.R.; Cardoso, V.d.S.; Akamine, I.T. Microbial Preservation and Contamination Control in the Baking Industry. Fermentation 2024, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, É.; Laslo, É. Microbiological quality assessment of some commercially available breads. Foods 2024, 13, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atudorei, D.; Mironeasa, S.; Codină, G.G. Effects of germinated lentil flour on dough rheological behavior and bread quality. Foods 2022, 11, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, W.Z.; Al-Dalain, S.Y.; Abdelaziz, M.; Elgabaly, A.A.; Morsy, O.M.; Sami, R.; Alshehry, G.; Aljumayi, H.; Algarni, E.; Abushal, S.A.; et al. Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread. Open Chem. 2024, 22, 20240030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauduro, T.; D’Almeida, C.T.; Biduski, B.; dos Santos, A.; Santos, M.C.B.; Lima, L.R.D.S.; Cameron, L.C.; Bertolin, T.E.; Ferreira, M.S.; Gutkoski, L.C. Whole wheat flour replaced by sprouted wheat improves phenolic compounds profile, rheological and bread-making properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 114, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 304, 18–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Aguilar, C.; Dominguez-Pacheco, A.; Palma Tenango, M.; Valderrama-Bravo, C.; Soto Hernández, M.; Cruz-Orea, A.; Ordonez-Miranda, J. Lentil sprouts: A nutraceutical alternative for the elaboration of bread. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagianni, E.; Kotsiou, K.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Lazaridou, A. Flaxseed and sprouted lentil seeds as functional ingredients in the development of nutritionally fortified “clean-label” gluten-free breads. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2023, 4, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
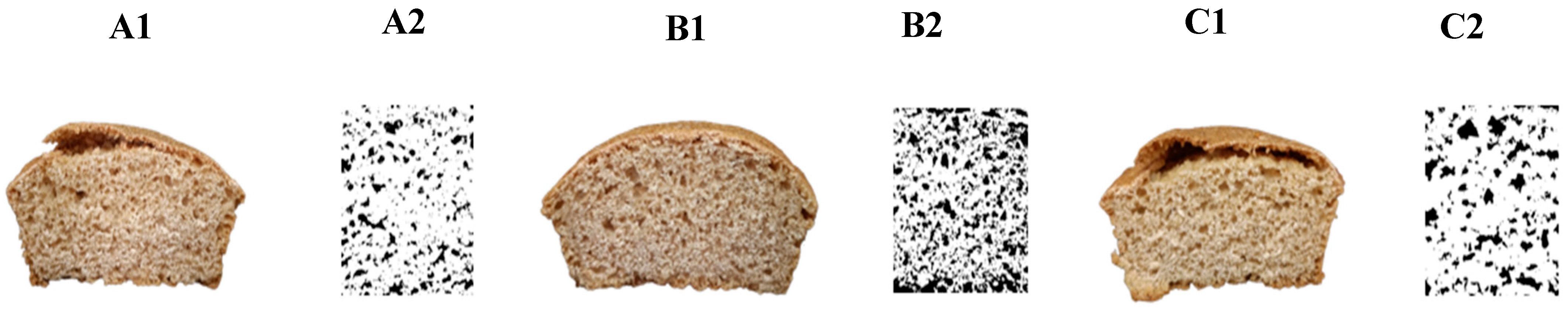

| Bread | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Gas Cells Area (%) | Crust Color | Crumb Color | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | a* | b* | L | a* | b* | |||
| Control | 2.2 ± 0.2 a | 14.1 ± 0.5 c | 59.6 ± 1.0 a | 9 ± 0.5 b | 23.7 ± 0.8 a | 62.3 ± 0.1 a | 4.4 ± 0.2 a | 16.9 ± 0.2 a |
| GL | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 28.6 ± 0.8 a | 52.1 ± 0.4 b | 11.0 ± 0.6 a | 24.2 ± 0.5 a | 56.4 ± 1.4 b | 4.5 ± 0.1 a | 17 ± 0.4 a |
| GW | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 18.1 ± 0.8 b | 58.4 ± 0.9 a | 8.5 ± 0.5 b | 22.5 ± 0.9 a | 58.9 ± 2.1 ab | 4.5 ± 0.4 a | 18 ± 1 a |
| Bread | Lipids (%) | Proteins (%) | Water (%) | Total Carbohydrates (%) | Dietary Fibers (%) | Energy Value (kcal/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.4 ± 0.1 a | 8.6 ± 0.1 b | 37.9 ± 0.1 a | 44.8 ± 0.1 a | 6.6 ± 1.2 a | 243 ± 1.0 a |
| GL | 0.3 ± 0.1 b | 9.9 ± 0.1 a | 37.4 ± 0.2 a | 43.3 ± 0.1 b | 5.7 ± 0.5 a | 245 ± 1.0 a |
| GW | 0.4 ± 0.1 a | 8.8 ± 0.1 b | 37.0 ± 0.1 b | 45.5 ± 0.1 a | 6.2 ± 0.6 a | 247 ± 1.0 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akiki, A.; Muhammed, Y.M.R.; Minervini, F.; Cavoski, I. Development of Organic Sourdough Bread with Paste from Germinated Seeds. Foods 2025, 14, 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183263
Akiki A, Muhammed YMR, Minervini F, Cavoski I. Development of Organic Sourdough Bread with Paste from Germinated Seeds. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183263
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkiki, Alberto, Yasmin Muhammed Refaie Muhammed, Fabio Minervini, and Ivana Cavoski. 2025. "Development of Organic Sourdough Bread with Paste from Germinated Seeds" Foods 14, no. 18: 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183263
APA StyleAkiki, A., Muhammed, Y. M. R., Minervini, F., & Cavoski, I. (2025). Development of Organic Sourdough Bread with Paste from Germinated Seeds. Foods, 14(18), 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183263







