Spatiotemporal Profiling of Starch-Degrading Enzymes in Nong-Flavor Daqu: Molecular Markers for Quantitative Quality Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Daqu Samples
2.2. Design of Specific and Degenerate Primers for Starch Hydrolase Genes in NF Daqu
2.3. Total DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing of Starch Hydrolase Genes
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-qPCR Analysis
2.5. Diversity Analysis of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes
2.6. Determination of Saccharification and α-Glucosidase Activities in NF Daqu
2.7. Correlation Analysis of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Analysis of DNA-Based Amplification of Target Starch Hydrolase Genes and Their Distribution in Different NF Daqu Samples
3.2. Distribution of Key Starch Hydrolase Genes During the Daqu-Making Process in Two Representative NF Daqus by DNA-Based Amplification
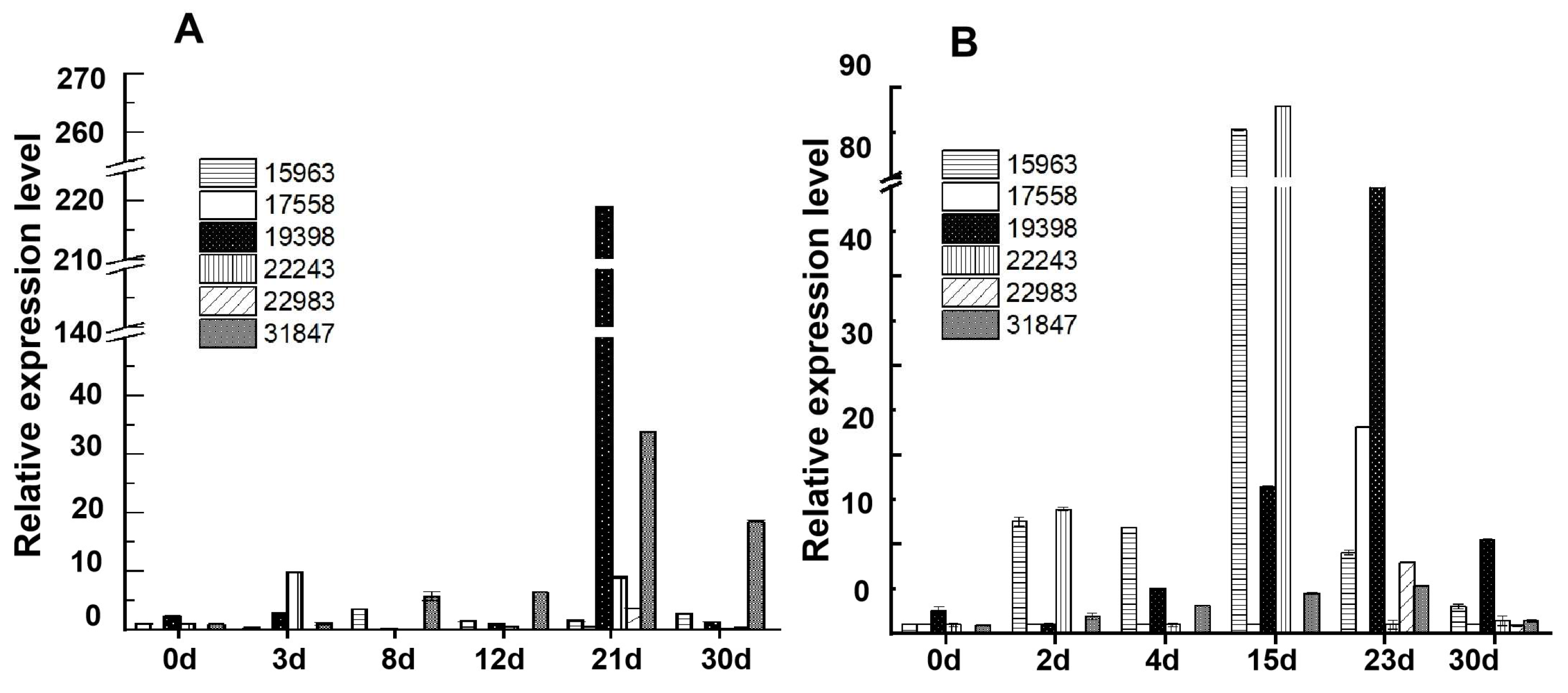
3.3. Fluorescence Quantitative Analysis of the Relative Expression Levels of Starch Hydrolase Genes During the NF Daqu-Making Process
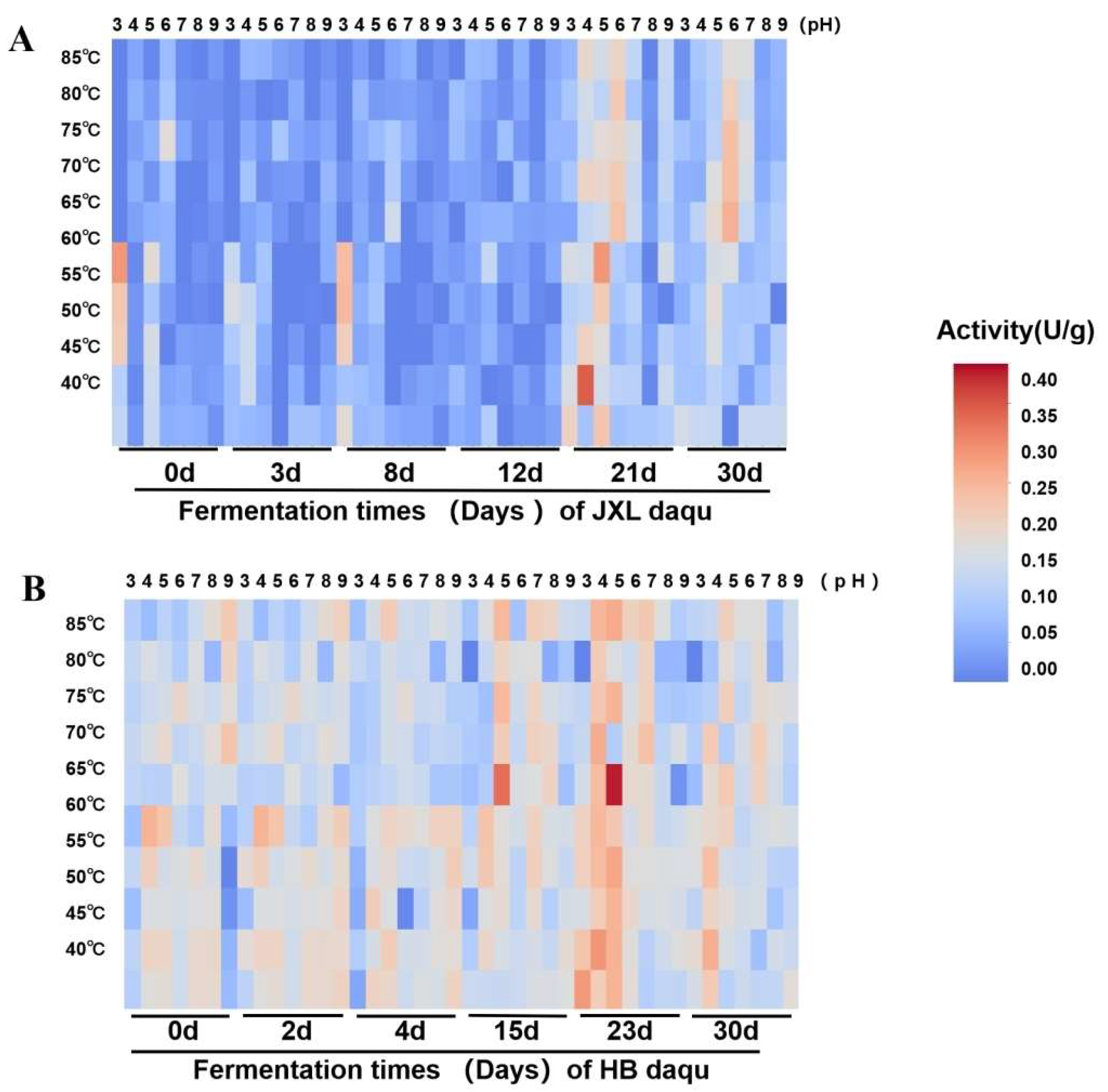
3.4. Effects of Temperature and pH on the Activities of Saccharification and α-Glucosidases During the Daqu-Making Process in JXL and HB Distilleries
3.5. Metagenomic Analysis of Starch-Hydrolyzing Enzymes in NF Daqu
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Starch Hydrolyzing Activity and Gene Expression in JXL and HB Daqu
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NF | Nong-flavor |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription quantitative PCR |
| GH | glycoside hydrolase |
References
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhao, C.; Luo, H. Diversity and Function of Microbial Community in Chinese Strong-Flavor Baijiu Ecosystem: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Dai, M.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B. Simulated Fermentation of Strong-Flavor Baijiu through Functional Microbial Combination to Realize the Stable Synthesis of Important Flavor Chemicals. Foods 2023, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Microbial Diversity in Jiuqu and Its Fermentation Features: Saccharification, Alcohol Fermentation and Flavors Generation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery behind Chinese Liquor Fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Hui, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Xiao, R.; Wang, J.; Pan, C.; Li, R. Comparative Analysis of the Microbiotas and Physicochemical Properties inside and Outside Medium-Temperature Daqu during the Fermentation and Storage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Synergistic Effect of Multiple Saccharifying Enzymes on Alcoholic Fermentation for Chinese Baijiu Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00013-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; Yu, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, N.; Li, Z. Metagenomics-Based Gene Exploration and Biochemical Characterization of Novel Glucoamylases and α-Amylases in Daqu and Pu-Erh Tea Microorganisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhang, K.; Su, L.; Wu, J. Microbial Starch Debranching Enzymes: Developments and Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 50, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, G.; Wieser, S.; Bogdos, M.K.; Gattinger, P.; Nakamura, R.; Ebisawa, M.; Mäkelä, M.; Papadopoulos, N.; Valenta, R.; Keller, W. Three-dimensional Structure of the Wheat Β-amylase Tri a 17, a Clinically Relevant Food Allergen. Allergy 2019, 74, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urnukhsaikhan, E.; Bold, B.-E.; Khurelbaatar, L.; Bazarvaani, A.; Mishig-Ochir, T. Effects of Electromagnetic Field on Seed Germination, β-Amylase Activity, Total Protein Content, Water Uptake, and Growth of Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum). Bioelectromagnetics 2025, 46, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dou, W.; Jiang, C.-X.; Wei, Z.-J.; Liu, J.; Jones, R.L. Hydrogen Sulfide Stimulates β-Amylase Activity during Early Stages of Wheat Grain Germination. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faltermaier, A.; Waters, D.; Becker, T.; Arendt, E.; Gastl, M. Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Its Use as a Brewing Cereal—A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Yang, F.; Du, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. The Differences in Carbohydrate Utilization Ability between Six Rounds of Sauce-Flavor Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ji, W.; Xia, X. Multidimensional Analysis of Wheat Original Crucial Endogenous Enzymes Driving Microbial Communities Metabolism during High-Temperature Daqu Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 413, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Mu, Y.; Su, W. Exploring the Heterogeneity of Community and Function and Correspondence of “Species-Enzymes” among Three Types of Daqu with Different Fermentation Peak-Temperature via High-Throughput Sequencing and Metagenomics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Jin, Y.; Huang, M.; He, K.; Liu, D.; Luo, H.; Zhao, D.; He, H.; Fang, Y.; et al. Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Functions and Enzyme Profiles of the Microbial Community in Chinese Nong-Flavor Liquor Starter. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Han, B.; Pu, J.; Rao, J.; Huang, D.; Luo, H. Linking Microbial Functional Gene Abundance and Daqu Extracellular Enzyme Activity: Implications for Carbon Metabolism during Fermentation. Foods 2022, 11, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shu, N.; Zhao, H.; Tang, F.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z.; Shan, C. The Fungal Communities and Flavor Profiles in Different Types of High-Temperature Daqu as Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing and Electronic Senses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 784651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; Ning, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, B.; Nie, H.; Huang, D.; Luo, H. Comparative Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Composition in High-Temperature Daqu with Different Colors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 588117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Balcerek, M.; Nowak, A.; Wojtczak, M.; Czyżowska, A.; Dziekońska-Kubczak, U.; Patelski, P. The Effect of Different Starch Liberation and Saccharification Methods on the Microbial Contaminations of Distillery Mashes, Fermentation Efficiency, and Spirits Quality. Molecules 2017, 22, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hui, M.; Pan, C. Functional Microorganisms in Baijiu Daqu: Research Progress and Fortification Strategy for Application. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1119675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Yang, F.; Sahu, S.K.; Luo, R.; Liao, S.; Wang, H.; Jin, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; et al. Deciphering the Composition and Functional Profile of the Microbial Communities in Chinese Moutai Liquor Starters. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 456693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Luo, H.; Zhao, D.; Qiao, Z.; Zheng, J.; An, M.; Huang, D. Environmental Factors and Interactions among Microorganisms Drive Microbial Community Succession during Fermentation of Nongxiangxing Daqu. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Revealing Novel Insights into the Enhancement of Quality in Black Tea Processing through Microbial Intervention. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, H.; Yu, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Employment of Near Full-Length Ribosome Gene TA-Cloning and Primer-Blast to Detect Multiple Species in a Natural Complex Microbial Community Using Species-Specific Primers Designed with Their Genome Sequences. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fan, A. Development of a Real-Time PCR for Quantification of the Family Syntrophomonadaceae in Pit Mud from Chinese Luzhou-Flavour Liquor Distilleries. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Li, W.; Luo, Q.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Analysis of the Bacterial Community in Aged and Aging Pit Mud of Chinese Luzhou-Flavour Liquor by Combined PCR-DGGE and Quantitative PCR Assay. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2729–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tan, G.; Chen, Q.; Dong, W.; Chen, P.; Cai, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y.; et al. Detection of Viable and Total Fungal Community in Zaopei of Chinese Strong-Flavor Baijiu Using PMA Combined with qPCR and HTS Based on ITS2 Region. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, L. Biodegradation of Commercial Polyester Polyurethane by a Soil-Borne Bacterium Bacillus velezensis MB01B: Efficiency, Degradation Pathway, and In-Situ Remediation in Landfill Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chai, L.; Shen, C.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Metagenomics Unveils Microbial Roles Involved in Metabolic Network of Flavor Development in Medium-Temperature Daqu Starter. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, S.-T.; Ao, L.; Shen, C.-H.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Bio-Heat Is a Key Environmental Driver Shaping the Microbial Community of Medium-Temperature Daqu. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01550-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ge, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y. Metagenomic Analyses Reveal Microbial Communities and Functional Differences between Daqu from Seven Provinces. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ran, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. The Active Synergetic Microbiota with Aspergillus as the Core Dominates the Metabolic Network of Ester Synthesis in Medium-High Temperature Daqu. Food Microbiol. 2023, 115, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Ji, Z.; Mao, J. Combined Use of Single Molecule Real-Time DNA Sequencing Technology and Culture-Dependent Methods to Analyze the Functional Microorganisms in Inoculated Raw Wheat Qu. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Zou, S.; Ji, C.; Dong, L.; Zhang, S.; Liang, H.; Lin, X. Analysis of Fungal Diversity, Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Organic Compounds of Strong-Flavor Daqu from Seven Different Areas. Foods 2024, 13, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Fang, Y.; He, K.; Liu, D.; Luo, H.; Zhao, D.; He, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, H. Directly Mining a Fungal Thermostable α-Amylase from Chinese Nong-Flavor Liquor Starter. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Z. High-Level Expression of a Novel α-Amylase from Thermomyces dupontii in Pichia pastoris and Its Application in Maltose Syrup Production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yi, Z.; Fang, Y.; Jin, Y.; He, K.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Luo, H.; He, H.; Sun, Q.; et al. Biochemical and Synergistic Properties of a Novel Alpha-amylase from Chinese Nong-flavor Daqu. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Kim, R.-C.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Y. Purification and Characterization of Novel Thermostable and Ca-Independent α-Amylase Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BH072. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Huang, Z.; Tu, R.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, P.; Zeng, Y.; Shi, B. Revealing the Differences in Microbial Community and Quality of High-Temperature Daqu in the Southern Sichuan–Northern Guizhou Region. Foods 2025, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ni, D.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, F.; Ye, X. Characterizing the Microbial Community Constructure and the Metabolites among Different Colour Moutai Daqu. Food Chem. X 2025, 26, 102223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, M. A New Reaction for Colorimetric Determination of Carbohydrates. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, L.; Jin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, N.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, K.; He, K.; et al. Insight into Broad Substrate Specificity and Synergistic Contribution of a Fungal α-Glucosidase in Chinese Nong-Flavor Daqu. Microb. Cell Factories 2023, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-H.; Seo, D.-H.; Holden, J.F.; Kim, H.-S.; Baik, M.-Y.; Park, C.-S. Broad Substrate Specificity of a Hyperthermophilic α-Glucosidase from Pyrobaculum arsenaticum. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Park, C.-S.; Rho, J.-R.; Cha, J. Characterization of the Catalytic and Kinetic Properties of a Thermostable Thermoplasma acidophilum α-Glucosidase and Its Transglucosylation Reaction with Arbutin. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, A.; Putyrski, M.; Liebl, W. Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of α-Glucosidase and α-Mannosidase and Their Clustered Genes from the Thermoacidophilic Archaeon Picrophilus torridus. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7123–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhou, S.; Duan, C.; Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Liu, G. Exploring the Role of Active Functional Microbiota in Flavor Generation by Integrated Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics during Niulanshan Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Luo, L.; Han, Y.; Song, L.; Zhen, P.; Han, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Z.; Qiu, J.; et al. Microbial Community Affects Daqu Quality and the Production of Ethanol and Flavor Compounds in Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadkar, V.J.; Filion, M. New Developments in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Technology. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2014, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghetto De Almeida, P.; Alnoch, R.C.; Pinheiro, V.E.; Pereira Gimenez, M.; De Lourdes Teixeira De Moraes Poliz, M. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Thermostable 1,4-α-Glucoamylase from Aspergillus brasiliensis Strain Isolated in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 7273–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Huang, H.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tu, T.; Yao, B.; Qin, X.; et al. Engineering a Carbohydrate-Binding Module to Increase the Expression Level of Glucoamylase in Pichia pastoris. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelin, M.; Silva, T.M.; Benassi, V.M.; Peixoto-Nogueira, S.C.; Moraes, L.A.B.; Leão, J.M.; Jorge, J.A.; Terenzi, H.F.; Polizeli, M.D.L.T.M. Purification and Characterization of a Thermostable α-Amylase Produced by the Fungus Paecilomyces variotii. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2348–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, S.; Ning, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; You, R.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Luo, X.; et al. Identification of an Essential Regulator Controlling the Production of Raw-Starch-Digesting Glucoamylase in Penicillium oalicum. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhou, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Difference of Microbial Community and Gene Composition with Saccharification Function between Chinese Nongxiangxing Daqu and Jiangxiangxing Dqu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Rao, J.; Zou, Y.; Liao, L.; Huang, D.; Luo, H. The Community Assembly Patterns Determined Differences between the Surface and the Core Microbial Communities of Nongxiangxing Daqu. LWT 2023, 183, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, K.; Liu, D.; Zhao, D.; He, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. New Microbial Resource: Microbial Diversity, Function and Dynamics in Chinese Liquor Starter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichart, N.J.; Bowers, R.M.; Woyke, T.; Hatzenpichler, R. High Potential for Biomass-Degrading Enzymes Revealed by Hot Spring Metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 668238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Cai, W.; Guo, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Shan, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative Analysis of Bacterial Community Structure and Physicochemical Quality in High-Temperature Daqu of Different Colors in Qingzhou Production Area. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chai, L.; Fang, G.; Mei, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Shi, J.; et al. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Microbiome and Metabolome Profiles of High-Temperature Daqu in the Same Workshop. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y. Effect of Fortified Daqu on the Microbial Community and Flavor in Chinese Strong-Flavor Liquor Brewing Process. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Osborn, A.M. Advantages and Limitations of Quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)-Based Approaches in Microbial Ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Spandidos, A.; Wang, H.; Seed, B. PrimerBank: A PCR Primer Database for Quantitative Gene Expression Analysis, 2012 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1144–D1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Qu-Omics Elucidates the Formation and Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Mechanism Underlying the Microecology of High Temperature Daqu. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Exploration of Seasonal Fermentation Differences and the Possibility of Flavor Substances as Regulatory Factors in Daqu. Food Res. Int. Ott. Ont 2023, 168, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Hu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Q.; Guo, Z. Understanding the Factors Influencing High-Temperature Daqu from Different Geographical Regions. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Analysis of Microbial Community Structure and Gene Expression of Activated Sludge. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Dai, H.; Shao, Y.; Luo, H.; Huang, D. Rare Taxa as the Microbial Taxa More Sensitive to Environmental Changes Drive Alterations of Daqu Microbial Community Structure and Function. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Mao, J.; Qian, B.; Wang, L.; Mao, J. Metagenomics-Based Insights into the Microbial Community Profiling and Flavor Development Potentiality of Baijiu Daqu and Huangjiu Wheat Qu. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, B. Understanding the Shifts of Microbial Community and Metabolite Profile From Wheat to Mature Daqu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 714726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeček, Š.; Svensson, B.; MacGregor, E.A. α-Amylase: An Enzyme Specificity Found in Various Families of Glycoside Hydrolases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1149–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, M.; Saburi, W.; Mori, H.; Kimura, A. α-Glucosidases and α-1,4-Glucan Lyases: Structures, Functions, and Physiological Actions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2727–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shang, J.; Bai, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Ou, H.; Shao, L. Metabolites Extracted from Microorganisms as Potential Inhibitors of Glycosidases (α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase): A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1050869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayllace, N.M.; Martín, M.; Busi, M.V.; Gomez-Casati, D.F. Microbial Glucoamylases: Structural and Functional Properties and Biotechnological Uses. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekiunaite, L.; Arntzen, M.Ø.; Svensson, B.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G.; Abou Hachem, M. Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenases and Other Oxidative Enzymes Are Abundantly Secreted by Aspergillus nidulans Grown on Different Starches. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasse, L.; Bercovici, J.; Pizzut-Serin, S.; Robe, P.; Tap, J.; Klopp, C.; Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B.; Leclerc, M.; et al. Functional Metagenomics to Mine the Human Gut Microbiome for Dietary Fiber Catabolic Enzymes. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, F.; Takeda, M.; Yoshitake, H. Effective Adsorption of Perrhenate Ions on the Filamentous Sheath-Forming Bacteria, Sphaerotilus montanus, Sphaerotilus natans and Thiothrix fructosivorans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, P.; Ge, X.; Xia, Y.; Hao, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, M. Recent Advances in Microbial Raw Starch Degrading Enzymes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.; Rejzek, M.; Naested, H.; Smedley, M.; Otero, S.; Fahy, B.; Thorpe, F.; Nash, R.J.; Harwood, W.; Svensson, B.; et al. The Role of α-Glucosidase in Germinating Barley Grains. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Filamentous Fungal Diversity and Community Structure Associated with the Solid State Fermentation of Chinese Maotai-Flavor Liquor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.C.; Freund, H.L.; Kasanjian, J.; Berlemont, R. Function, Distribution, and Annotation of Characterized Cellulases, Xylanases, and Chitinases from CAZy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Primer | Forward and Reverse Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Type of Primer | The Glycoside Hydrolase Family |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH15-1 | F-CCTACTGGACGGGCTCGTAC | 502 | 60 | Specificity | GH15 |
| R-GGGGTGTATTTTTGCGCCAC | |||||
| GH15-4 | F-AGCAATTCTCCCGCAACGAC | 578 | 55 | ||
| R-TCATCTCCAGCTATCGTTC | |||||
| GH13-1 | F-CGGGTGGTGGTACAATGTCG | 155 | 55 | GH13 | |
| R-ATGCGAATAGCAGTACTTTG | |||||
| GH13-3 | F-CAATCGCTCGTGGCCAATTC | 984 | 60 | ||
| R-CATAATCGCTGCTACCCGCC | |||||
| GH31-1 | F-CCATTGCCTGGATTCCC | 310 | 56 | GH31 | |
| R-CGGCAAAAGTGCTTCGAG | |||||
| GH31-3 | F-GATGTTGCCAAGCAGTACGC | 651 | 57 | ||
| R-CTGGAACACATCCGGGAATC | |||||
| 22243 | F-GASATCATCTGGCCGATTG | 867 | 55 | Degeneracy | GH15 |
| R-CYGRSGGAGTRTATTTCT | |||||
| 19398 | F-CVACGGCSMTGATTGCMT | 1344 | 55 | ||
| R-CRTCBGTCTCYTTYTTGA | |||||
| 17723 | F-GAYTTYATGTGCTGGCC | 890 | 49 | ||
| R-ACCCAKGARTARCGRTA | |||||
| 22983 | F-TGGATGCYGYBAARCAYT | 560 | 55 | GH13 | |
| R-GTTGCCRTAKCGRACGAAG | |||||
| 17558 | F-GTATCACGGTTATTGGCAGAA | 220 | 54 | ||
| R-GAGACAGAACGGGTGGAAG | |||||
| 31847 | F-ATCTATGACSSBGATGAGG | 697 | 56 | GH31 | |
| R-TRTCSGTCCACATKGTCTC | |||||
| 15963 | F-ATCCTCTGCCAACCCACT | 823 | 56 | ||
| R-GGCTCCAGCATAATACGAC |
| Primer | Forward and Reverse Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| q15963 | F-GGAACGCCAATCGTGAGA | 197 | 56 |
| R-CCCTGGTAGACGGTGTAGTC | |||
| q31847 | F-CTTGAAAGATGCGGATGG | 187 | 56 |
| R-AGAAGTTGGACGGCTCGT | |||
| q22983 | F-TAGCAAACCACGATACTCAA | 228 | 54 |
| R-GCACTCCGTAGGCATAAA | |||
| q17558 | F-TACACCTGCCCATACCAGGA | 198 | 60 |
| R-CGAAGCAAAGCGAGCAATGT | |||
| q22243 | F-CCTATGCGGACGGGTTTC | 280 | 56 |
| R-GGTGGCTGCGTAGTGGTT | |||
| q19398 | F-AAGCGACCACAACCGCAACC | 129 | 60 |
| R-TCGAGCCGACGAGGAAGACG | |||
| q17723 | F-CCTACAGGTGCCGTCGTT | 193 | 56 |
| R-GTTGAGGCGGGAAGATGC | |||
| gapdh | F-CGGCATCGTTGAGGGTCT | 279 | 57 |
| R-GCCTTCTTGATCTCGTCGTA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, N.; Bao, S.; Peng, K.; Gan, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Spatiotemporal Profiling of Starch-Degrading Enzymes in Nong-Flavor Daqu: Molecular Markers for Quantitative Quality Evaluation. Foods 2025, 14, 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183239
Jiang Y, Lu Y, Jin Y, Shen Y, Liu N, Bao S, Peng K, Gan L, Wang C, Zhang Y, et al. Spatiotemporal Profiling of Starch-Degrading Enzymes in Nong-Flavor Daqu: Molecular Markers for Quantitative Quality Evaluation. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183239
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yijia, Yue Lu, Yanling Jin, Yi Shen, Nian Liu, Shu Bao, Kui Peng, Langfei Gan, Chaokai Wang, Yuling Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Profiling of Starch-Degrading Enzymes in Nong-Flavor Daqu: Molecular Markers for Quantitative Quality Evaluation" Foods 14, no. 18: 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183239
APA StyleJiang, Y., Lu, Y., Jin, Y., Shen, Y., Liu, N., Bao, S., Peng, K., Gan, L., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Chen, B., Xiao, Y., He, K., Yi, Z., & Zhao, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal Profiling of Starch-Degrading Enzymes in Nong-Flavor Daqu: Molecular Markers for Quantitative Quality Evaluation. Foods, 14(18), 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183239






