Non-Thermal Microbial Inactivation Using Underwater Plasma: Synergistic Effects of Capillary Discharge on E. coli and M. testaceum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Bacterial Culture
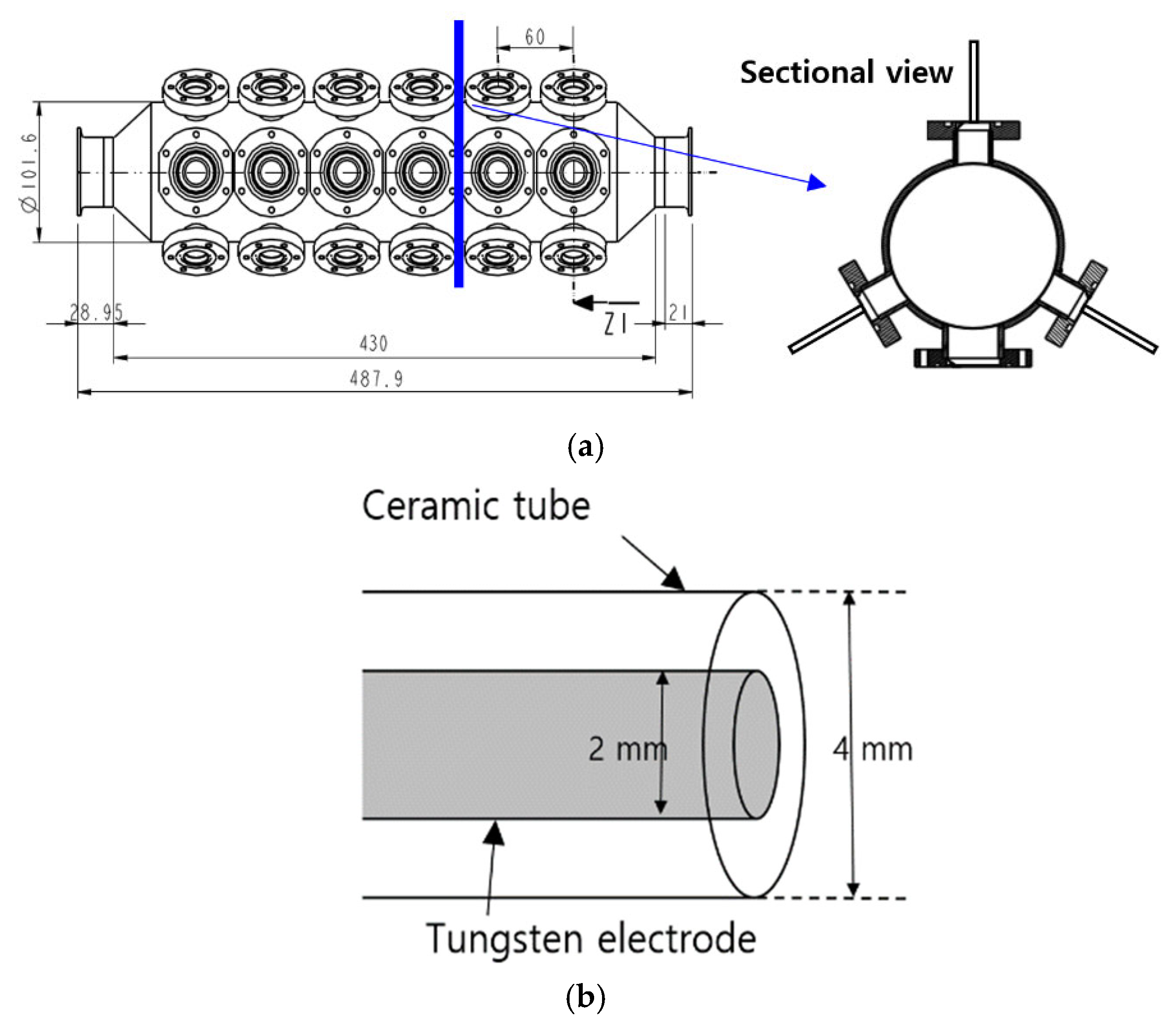
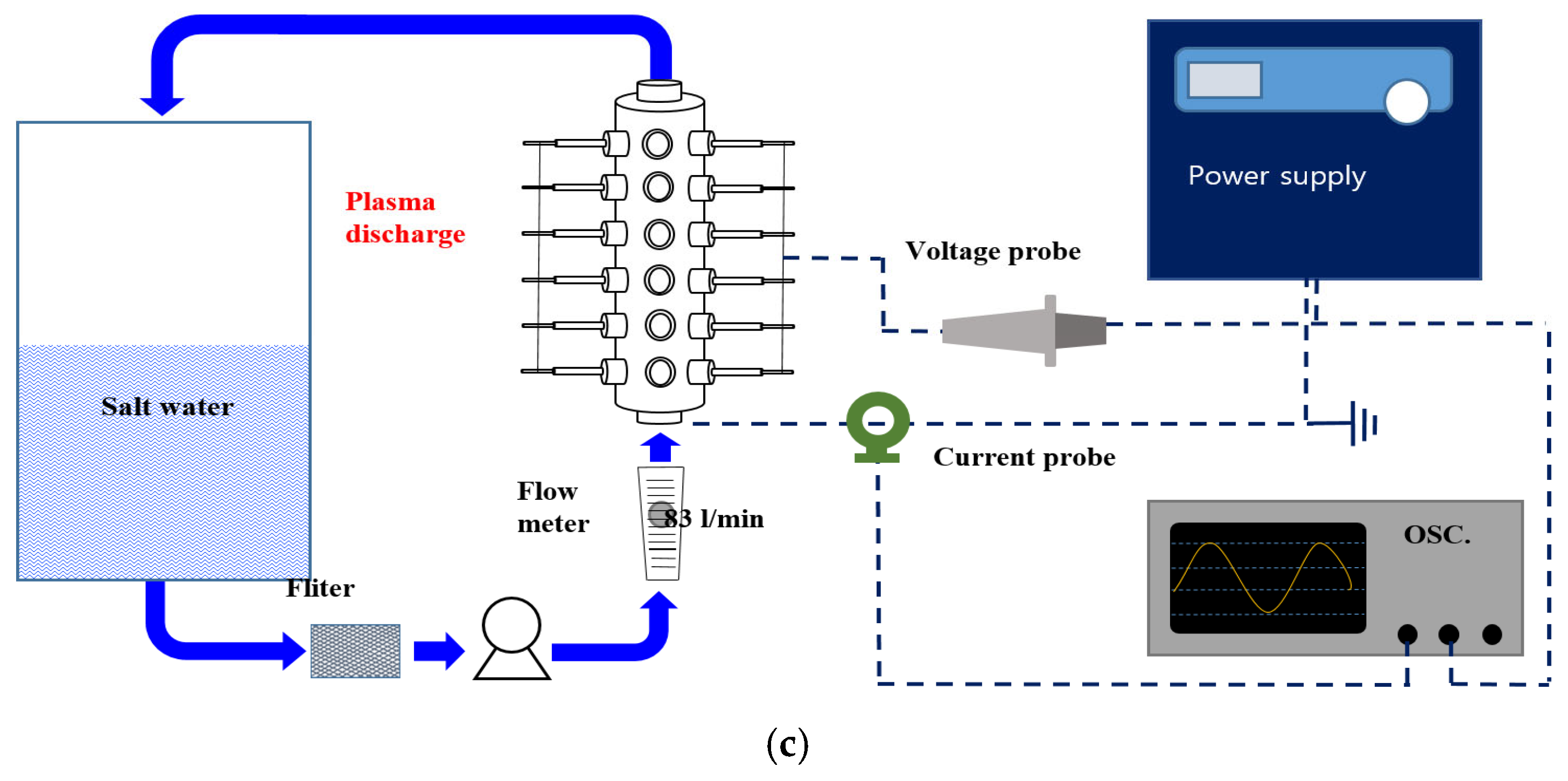
2.2. Plasma Reactor Design and Setup
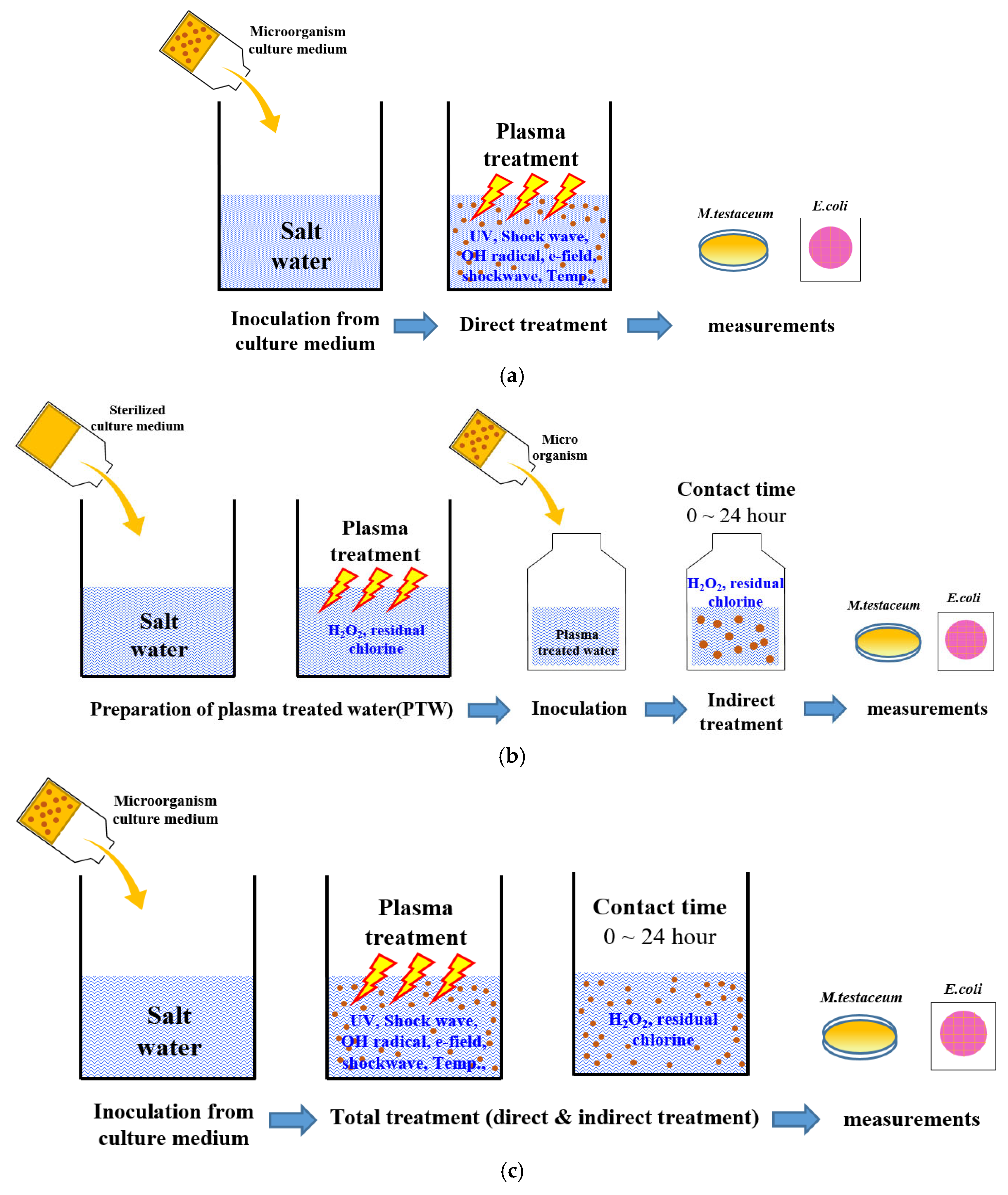
2.3. Plasma Treatment
2.4. Measurement of the Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Microbiological Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion: The Process of the Underwater Plasma Treatment
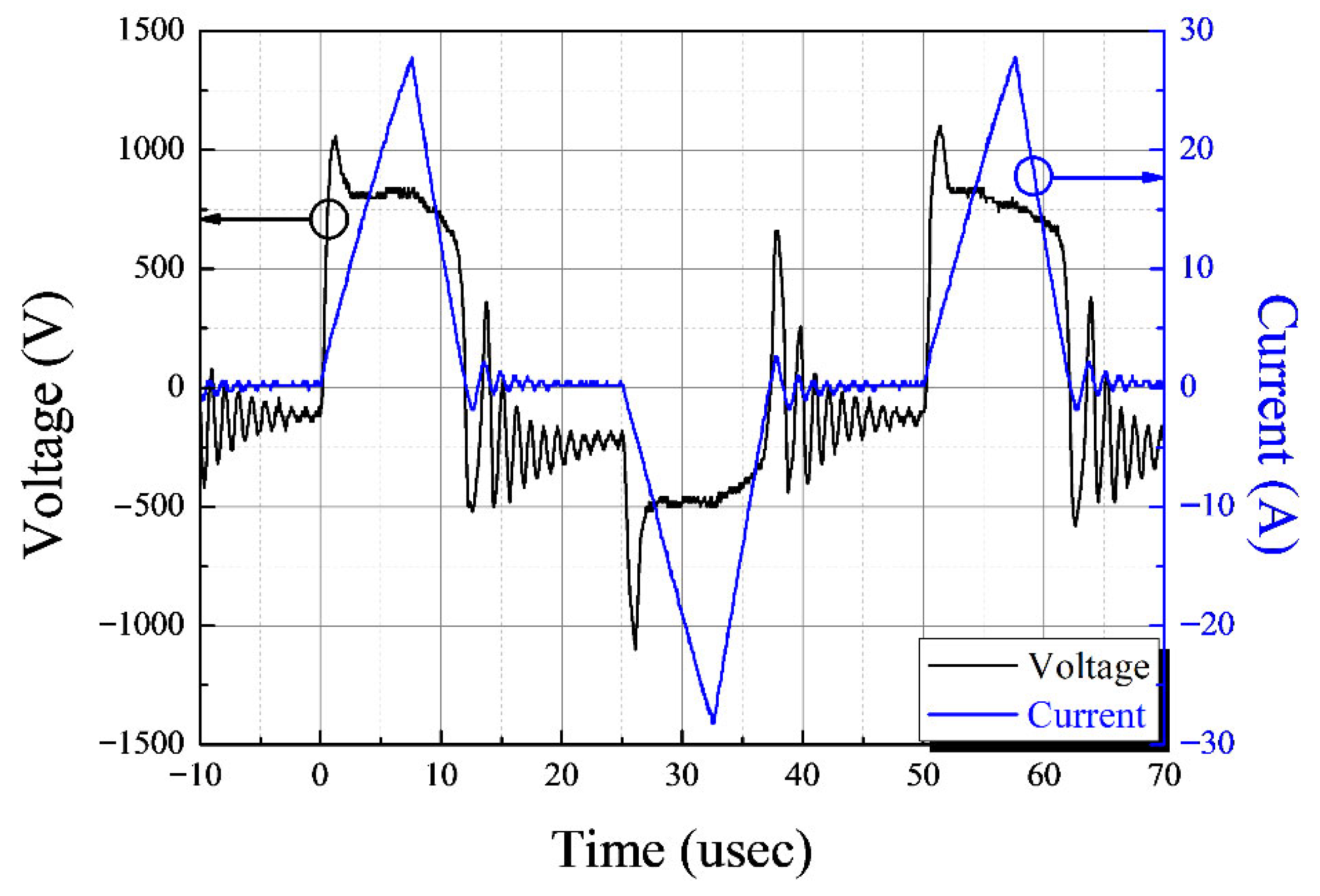
3.1. Characteristics of the Underwater Plasma Using a Capillary Electrode
3.2. Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of the Underwater Plasma
3.3. Effect of the Underwater Plasma Treatment on the Microorganisms
3.4. Effect Factors of the Underwater Plasma Inactivation in Saltwater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, R.; Liu, X.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, G.; Ai, L. Research Progress on Detection of Foodborne Pathogens: The More Rapid and Accurate Answer to Food Safety. Food Res. Int. 2024, 193, 114767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Kang, S. Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria: Prevalence and Control—Volume I. Foods 2024, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Z. Recent Advances in Sterilization and Disinfection Technology: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Calvo, T.; Prieto, M.; Múgica-Vidal, R.; Muro-Fraguas, I.; Alba-Elías, F.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. A Review on Non-Thermal Atmospheric Plasma for Food Preservation: Mode of Action, Determinants of Effectiveness, and Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, R.; Singh, A.; Pratap Singh, A. Recent Developments in Cold Plasma Decontamination Technology in the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahl, T.; Märkl, H. Killing of Microorganisms by Pulsed Electric Fields. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 45, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Zheng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Cheng, C.; Meng, X. Inactivation of Invasive Marine Species in the Process of Conveying Ballast Water Using OH Based on a Strong Ionization Discharge. Water Res. 2016, 96, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, M.A.; Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Khan, A.H.; Hussain, A.; Rahisuddin; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Vambol, V. Chlorination Disinfection By-Products in Municipal Drinking Water—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Portugal, S.; Mastanaiah, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Roy, S. Inactivation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in an Open Water System with Ozone Generated by a Compact, Atmospheric DBD Plasma Reactor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Q.; Ahn, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Ding, T. Inactivation Mechanisms of Non-Thermal Plasma on Microbes: A Review. Food Control 2017, 75, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Ishikawa, K.; Okumura, T.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M. Plasma Agriculture from Laboratory to Farm: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konchekov, E.M.; Gusein-zade, N.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Kolik, L.V.; Dorokhov, A.S.; Izmailov, A.Y.; Shokri, B.; Gudkov, S.V. Advancements in Plasma Agriculture: A Review of Recent Studies. IJMS 2023, 24, 15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butscher, D.; Zimmermann, D.; Schuppler, M.; Rudolf Von Rohr, P. Plasma Inactivation of Bacterial Endospores on Wheat Grains and Polymeric Model Substrates in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Food Control 2016, 60, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Puligundla, P.; Mok, C. Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens on the Surfaces of Different Packaging Materials Using Low-Pressure Air Plasma. Food Control 2015, 51, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranyi, P.; Wunderlich, J.; Heise, M. Influence of Relative Gas Humidity on the Inactivation Efficiency of a Low Temperature Gas Plasma. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-Y.; Song, W.-J.; Kang, J.H.; Min, S.C.; Eom, S.; Hong, E.J.; Ryu, S.; Kim, S.B.; Cho, S.; Kang, D.-H. Effect of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-Activated Water on the Microbial Safety of Korean Rice Cake. LWT 2020, 120, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Effect of Plasma Activated Water on the Postharvest Quality of Button Mushrooms, Agaricus Bisporus. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.-S.; Hong, E.J.; Yoo, S.; Lho, T.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kim, S.B.; Yoo, S.J.; Ryu, S. Ballast Water Treatment Test at Pilot-Scale Using an Underwater Capillary Discharge Device. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 2017, 37, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Jeong, J.; You, T.; Jung, J. Water Electrode Plasma Discharge to Enhance the Bacterial Inactivation in Water. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, B.; Sato, M.; Sunka, P.; Hoffmann, M.; Chang, J.-S. Electrohydraulic Discharge and Nonthermal Plasma for Water Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 882–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.M.; Hong, E.J.; Seok, D.C.; Yoo, S.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Lho, T.; Lee, B.J. Characteristics of Discharged Sea Water Generated by Underwater Plasma System. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, S87–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Ma, S.-H.; Hong, Y.C.; Choi, M.C. Effects of Pulsed and Continuous Wave Discharges of Underwater Plasma on Escherichia Coli. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, N.; Apostol, L.; Gherendi, F. Inactivation of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium on Egg Surface, by Direct and Indirect Treatments with Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Food Control 2017, 76, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.C.; Park, H.J.; Lee, B.J.; Kang, W.-S.; Uhm, H.S. Plasma Formation Using a Capillary Discharge in Water and Its Application to the Sterilization of E. Coli. Phys. Plasmas 2010, 17, 053502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Xue, Q. Review on Electrical Discharge Plasma Technology for Wastewater Remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Ghaffar, A.; Malik, S.A. Water Purification by Electrical Discharges. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2001, 10, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y. Degradation of Bisphenol A and Formation of Hydrogen Peroxide Induced by Glow Discharge Plasma in Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Q. Effect of Chloride on Bacterial Inactivation by Discharge Plasma at the Gas-solution Interface: Potentiation or Attenuation? Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, 1700153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kaletunç, G. Evaluation of the Heat Inactivation of Escherichia Coli and Lactobacillus Plantarum by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5379–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, S.C.; George, S.M.; Peck, M.W. Thermal Inactivation of Escherichia Coli O157:H7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 79S–89S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Q. New Insight into the Residual Inactivation of Microcystis Aeruginosa by Dielectric Barrier Discharge. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai-Prochnow, A.; Clauson, M.; Hong, J.; Murphy, A.B. Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria Differ in Their Sensitivity to Cold Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishime, T.M.C.; Borges, A.C.; Koga-Ito, C.Y.; Machida, M.; Hein, L.R.O.; Kostov, K.G. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Applied to Inactivation of Different Microorganisms. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 312, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Wei, J.; Lan, Y.; Ni, G.; Sun, Q.; Qian, S.; Zhang, H.; Xia, W.; et al. Bactericidal Effects of Plasma Induced Reactive Species in Dielectric Barrier Gas–Liquid Discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 2017, 37, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

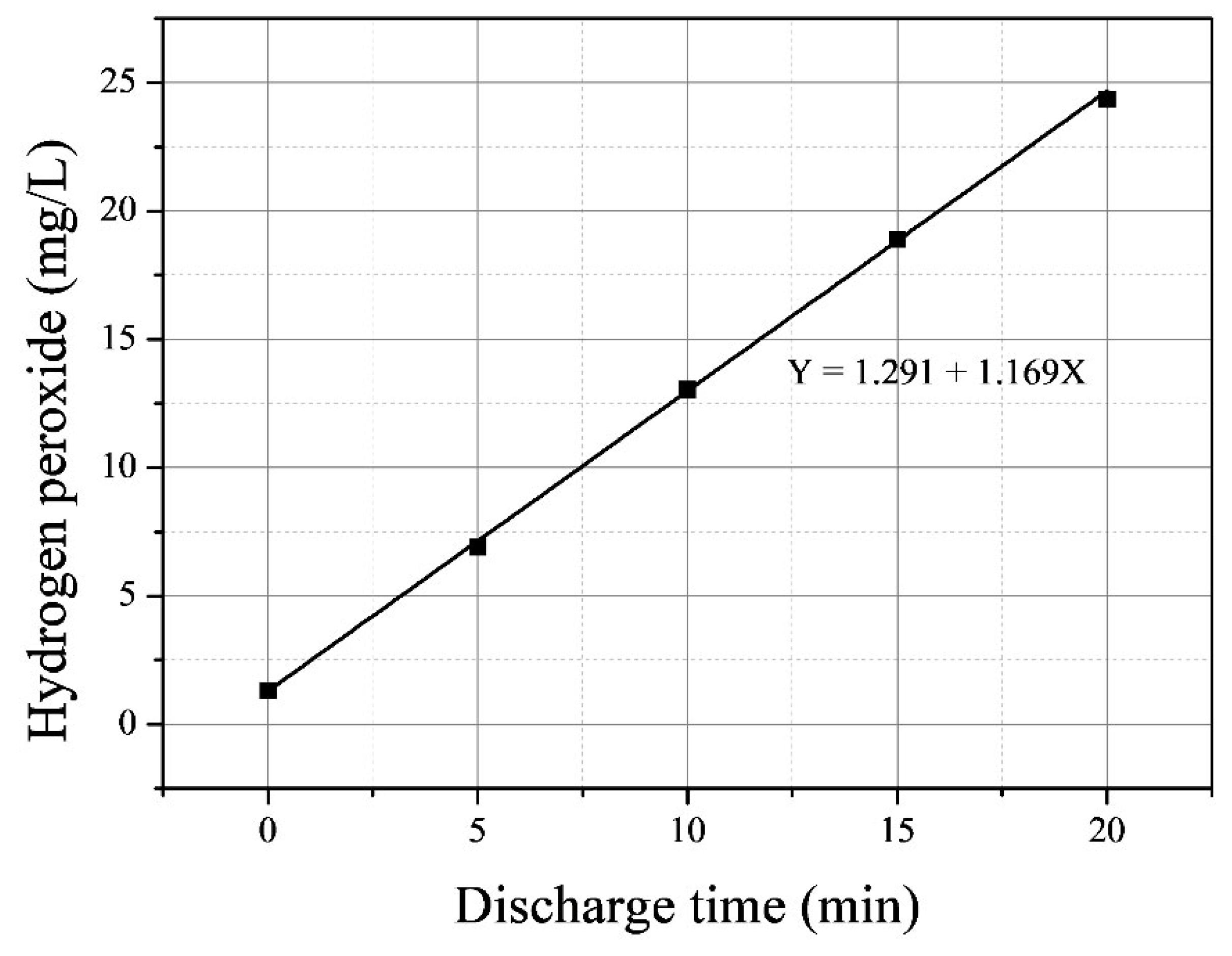
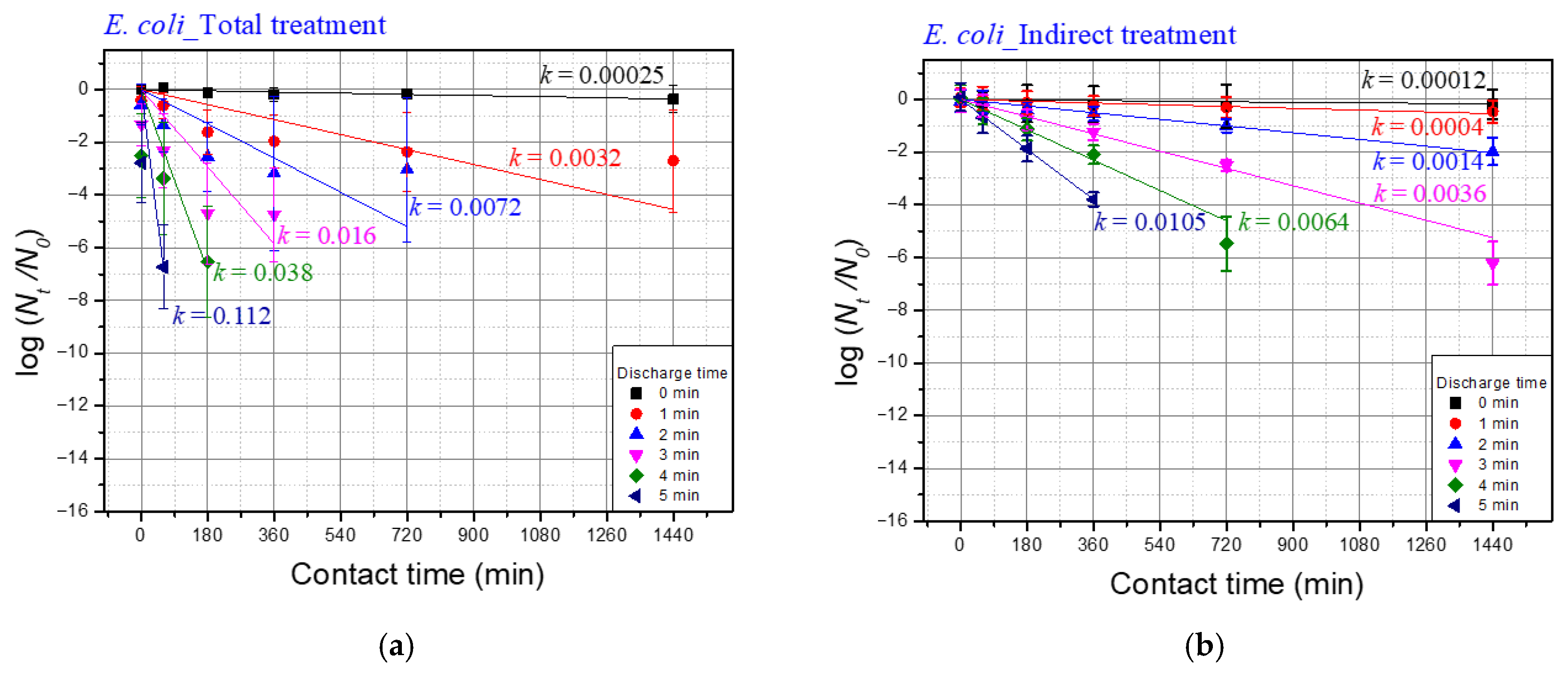
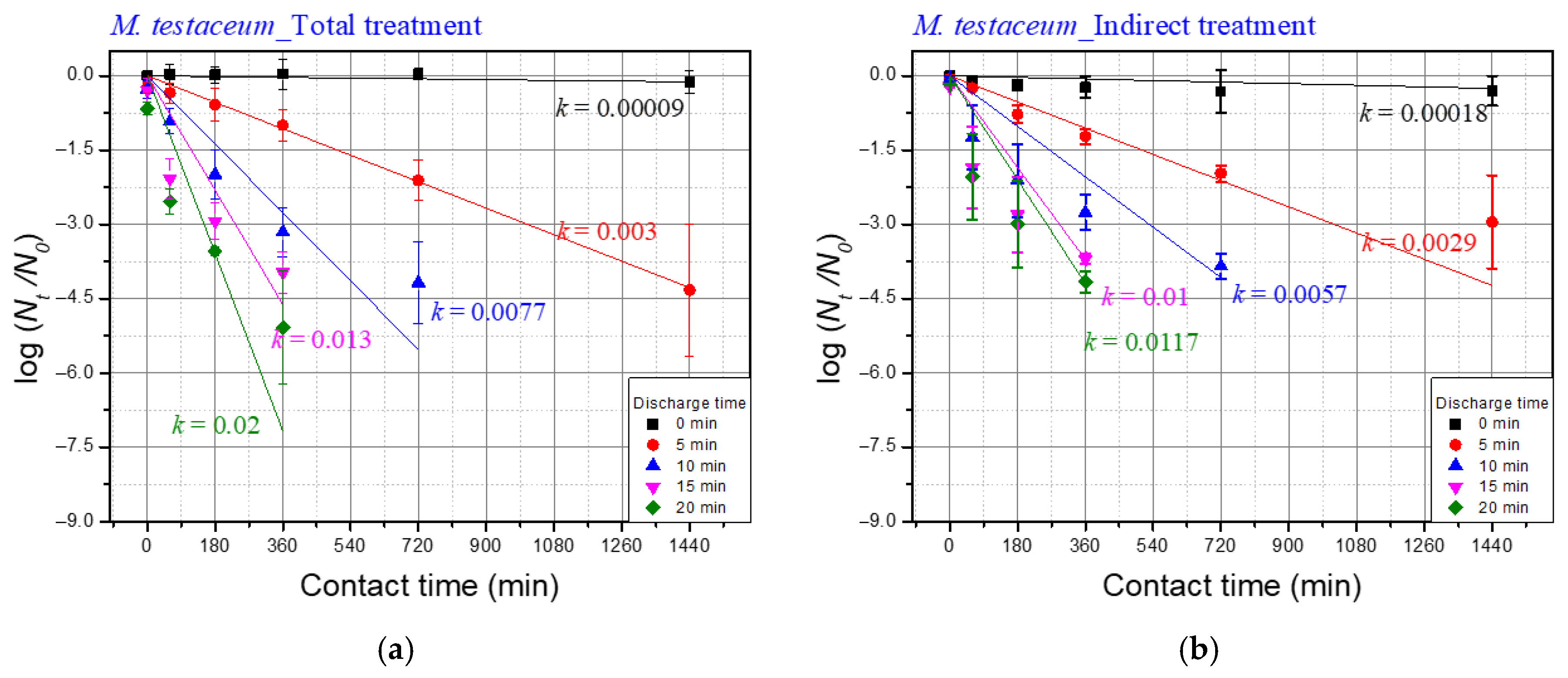
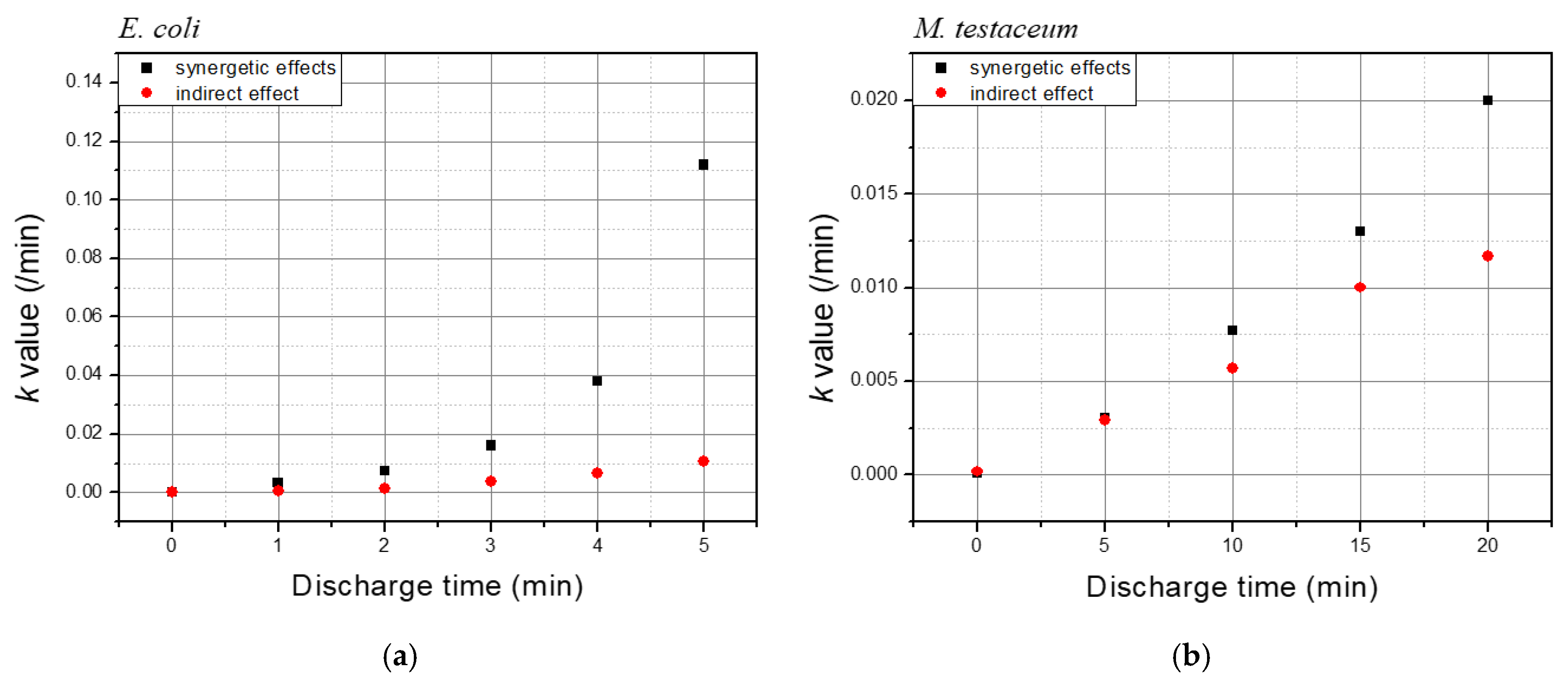

| Discharge Time | Temp. | pH | Conductivity (uS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 26.1 ± 2.1 | 7.2 ± 0.3 | 145.0 ± 5.4 |
| 5 min | 30.4 ± 2.2 | 7.2 ± 0.3 | 154.2 ± 5.5 |
| 10 min | 35.7 ± 2.2 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 166.0 ± 5.6 |
| 15 min | 40.7 ± 2.0 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 176.8 ± 6.7 |
| 20 min | 45.9 ± 2.0 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 187.3 ± 9.5 |
| Contact Time (h) | Discharge Time (min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 5.0 ± 1.8 | 4.7 ± 1.6 |
| 1 | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.1 ± 0.4 | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 4.1 ± 1.5 | 0.7 ± 1.3 |
| 3 | 7.4 ± 0.6 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 1.0 ± 1.6 | |
| 6 | 7.3 ± 0.4 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 2.3 | 0.8 ± 1.3 | ||
| 12 | 7.3 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 2.3 | |||
| 24 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 1.3 | 1.4 ± 2.4 | |||
| Contact Time (h) | Discharge Time (min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0 | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.1 |
| 1 | 6.9 ± 0.3 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.1 |
| 3 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.1 ± 0.2 | 5.8 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.2 |
| 6 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 5.7 ± 0.4 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.7 |
| 12 | 6.7 ± 0.4 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 1.4 | |
| 24 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 1.2 | ||
| Contact Time (h) | Discharge Time (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| 0 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 6.9 ± 0.02 |
| 1 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 5.0 ± 0.2 |
| 3 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.1 |
| 6 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 1.0 |
| 12 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.2 |
| 24 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 1.2 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | ||
| Contact Time (h) | Discharge Time (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| 0 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 7.4 ± 0.1 |
| 1 | 7.5 ± 0.03 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 5.6 ± 0.9 |
| 3 | 7.4 ± 0.02 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 0.8 |
| 6 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 3.9 ± 0.02 | 3.4 ± 0.3 |
| 12 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 0.1 |
| 24 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.5 |
| Discharge Time | k Values of E. coli | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Treatment (A) | Indirect Treatment (B) | Differences b/w Total and Indirect (A–B) | |
| 1 | 0.0032 | 0.0004 | 0.0028 |
| 2 | 0.0072 | 0.0014 | 0.0058 |
| 3 | 0.016 | 0.0036 | 0.0124 |
| 4 | 0.038 | 0.0064 | 0.0316 |
| 5 | 0.112 | 0.0105 | 0.1015 |
| Discharge Time | k Values of M. testaceum | ||
| Total Treatment (A) | Indirect Treatment (B) | Differences b/w Total and Indirect (A–B) | |
| 5 | 0.003 | 0.0029 | 0.0001 |
| 10 | 0.0077 | 0.0057 | 0.002 |
| 15 | 0.013 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| 20 | 0.02 | 0.0117 | 0.0083 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, E.J.; Park, S.; Kim, S.B.; Ryu, S. Non-Thermal Microbial Inactivation Using Underwater Plasma: Synergistic Effects of Capillary Discharge on E. coli and M. testaceum. Foods 2025, 14, 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173143
Hong EJ, Park S, Kim SB, Ryu S. Non-Thermal Microbial Inactivation Using Underwater Plasma: Synergistic Effects of Capillary Discharge on E. coli and M. testaceum. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173143
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Eun Jeong, Seungil Park, Seong Bong Kim, and Seungmin Ryu. 2025. "Non-Thermal Microbial Inactivation Using Underwater Plasma: Synergistic Effects of Capillary Discharge on E. coli and M. testaceum" Foods 14, no. 17: 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173143
APA StyleHong, E. J., Park, S., Kim, S. B., & Ryu, S. (2025). Non-Thermal Microbial Inactivation Using Underwater Plasma: Synergistic Effects of Capillary Discharge on E. coli and M. testaceum. Foods, 14(17), 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173143







