Interactions Between HEP Peptide and EGFR Involved in the Osteoblast Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Preparation and Identification of Soybean Yogurt Peptides
2.3.1. Preparation of Soy Yogurt
2.3.2. Identification of Peptides by UPLC-Q-TOF
2.4. Screening of High EGFR Affinity Peptides
2.5. High EGFR Affinity Peptide Synthesis and Verification
2.6. Osteogenic Activity Analysis
2.6.1. Cell Culture
2.6.2. Analysis of ALP Activity
2.6.3. Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration ([Ca2+]I) Measurement
2.7. Analysis of HEP and EGFR Docking Mode
2.7.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis
2.7.2. Receptor Domain Site-Directed Mutagenesis
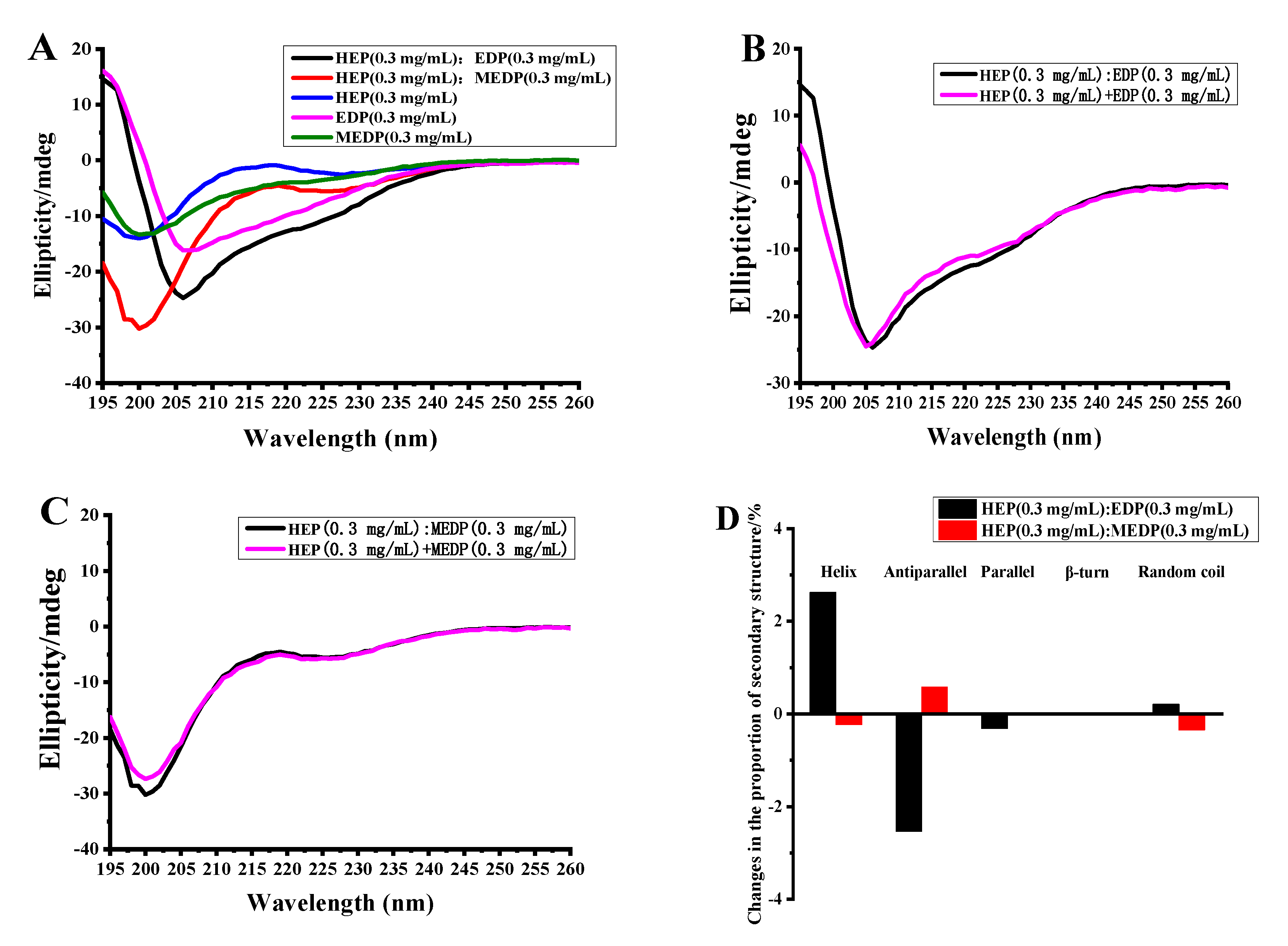
2.7.3. Binding Analysis of Peptides with EGFR Domain by Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra
2.8. Western Blot Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Purification of Osteoblast-Activating Soybean Peptide from Soy Yogurt
3.2. Isolation of Peptides and Identification by UPLC-Q-TOF
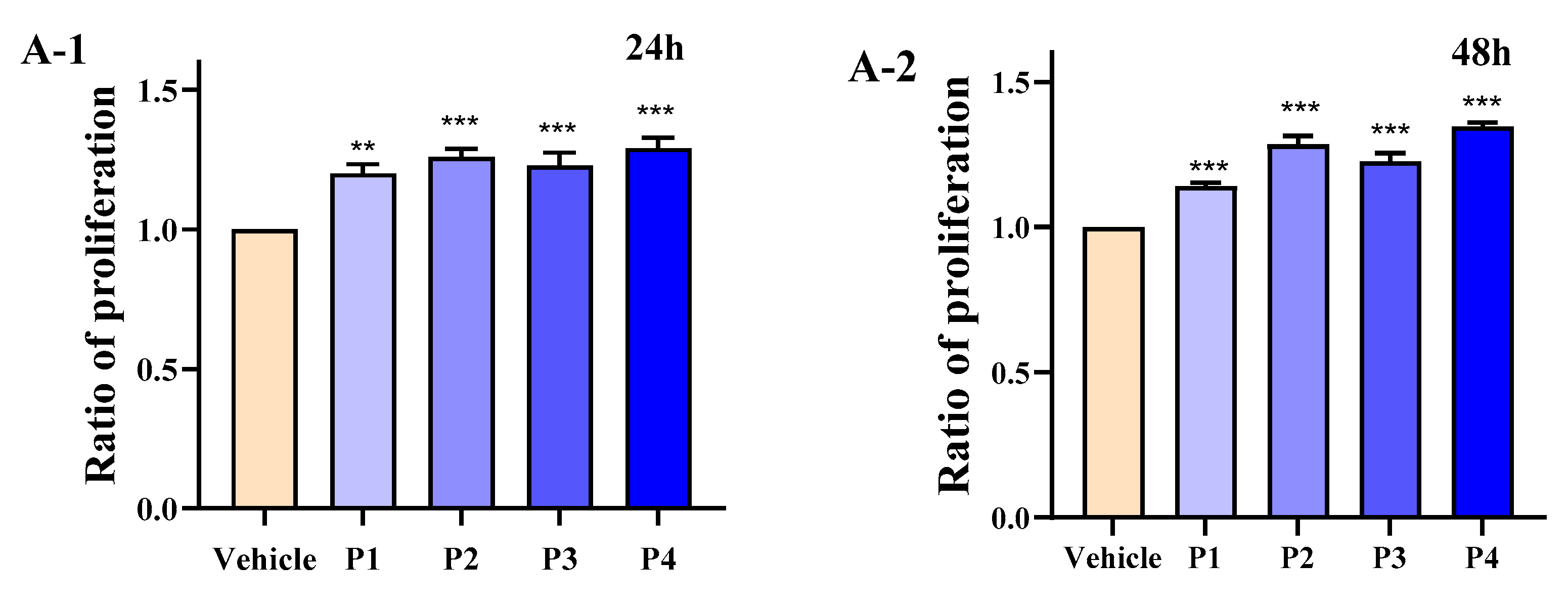
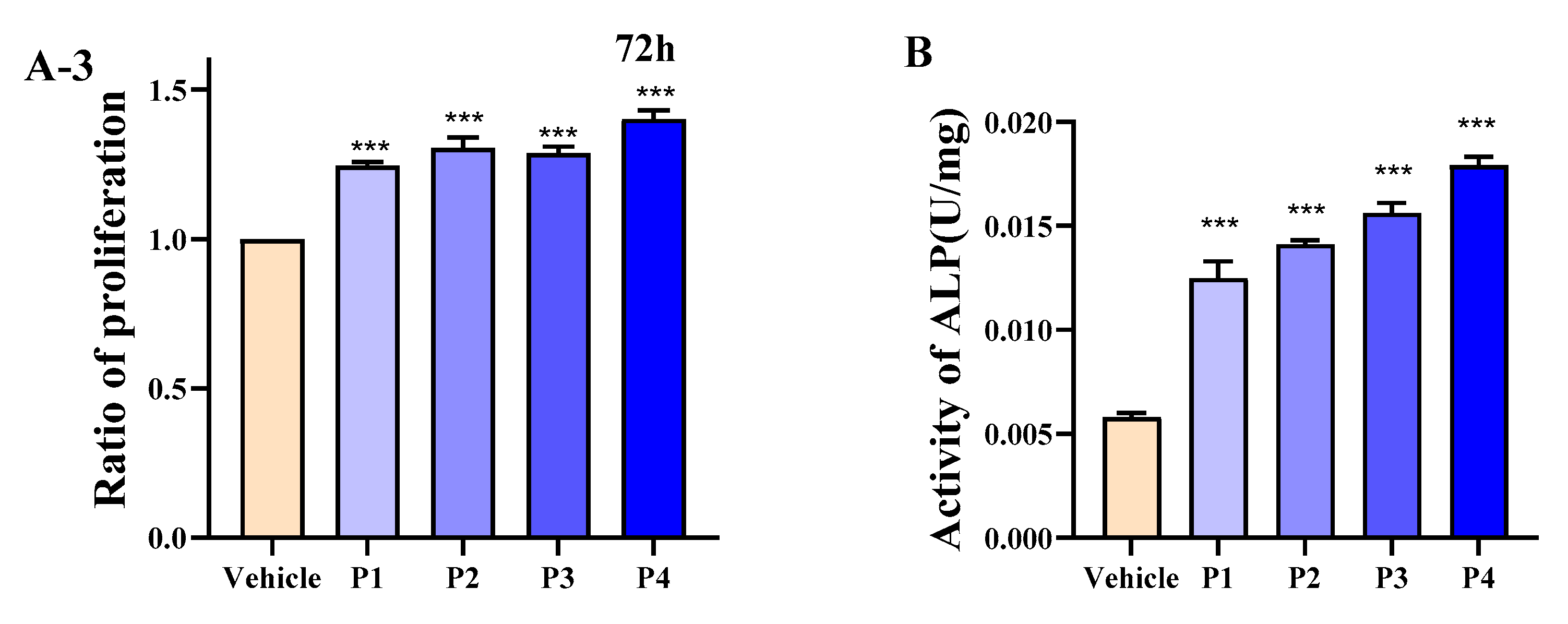
3.3. Screening of Peptides with High EGFR Binding Ability
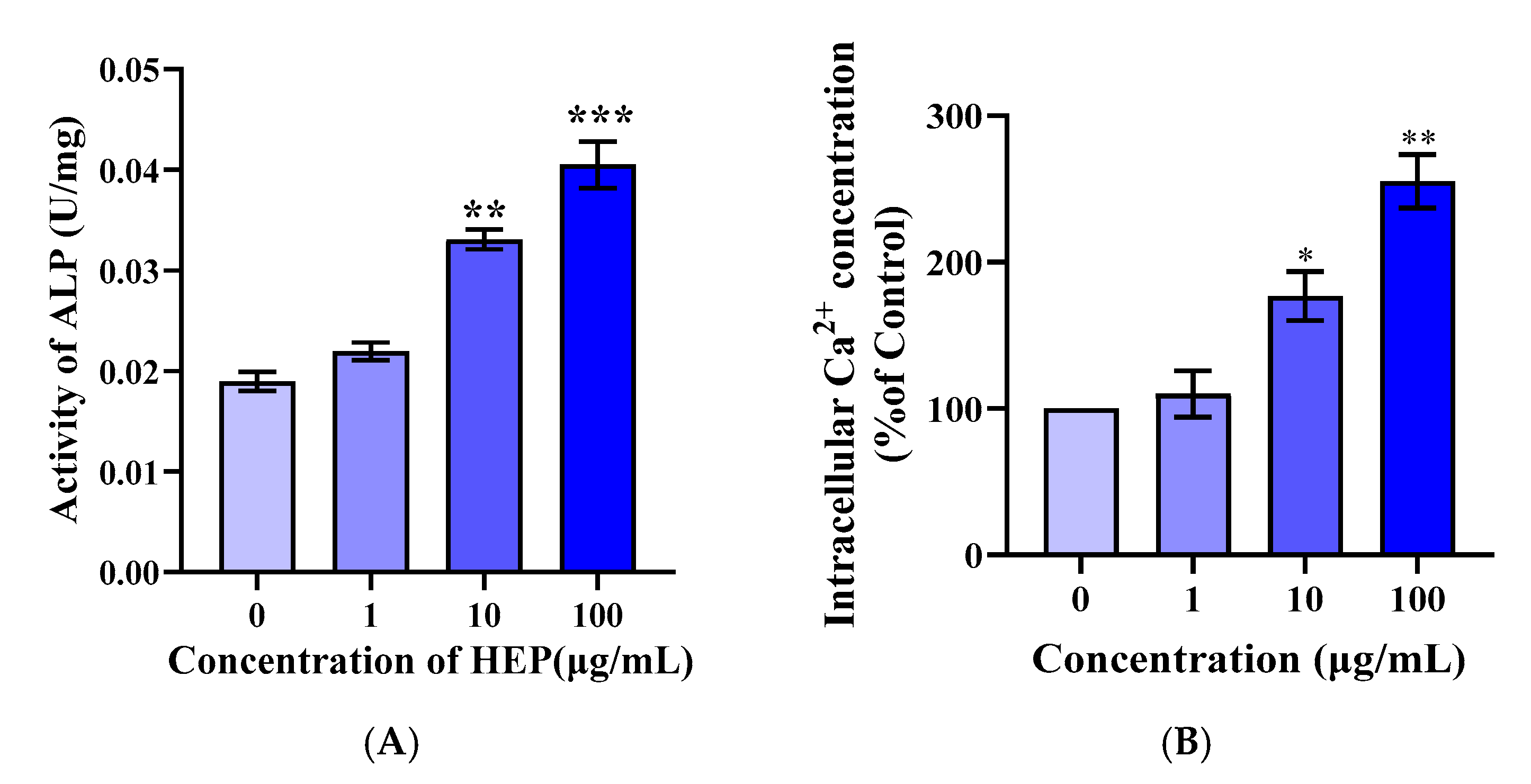
3.4. HEP Stimulates Differentiation and Intracellular Calcium of MC3T3-E1 Cells
3.5. Interactions Between the Peptides and EGFR
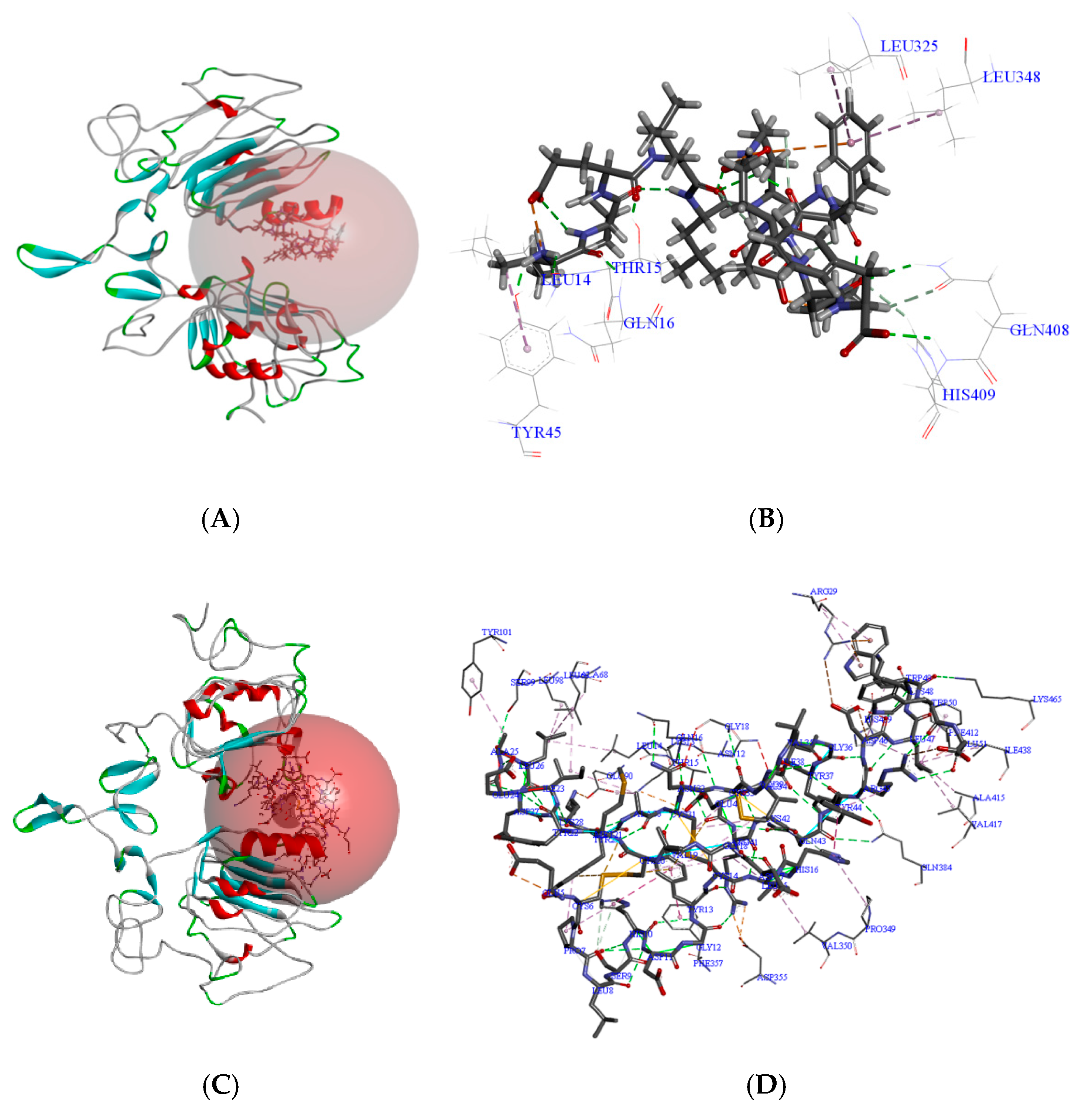
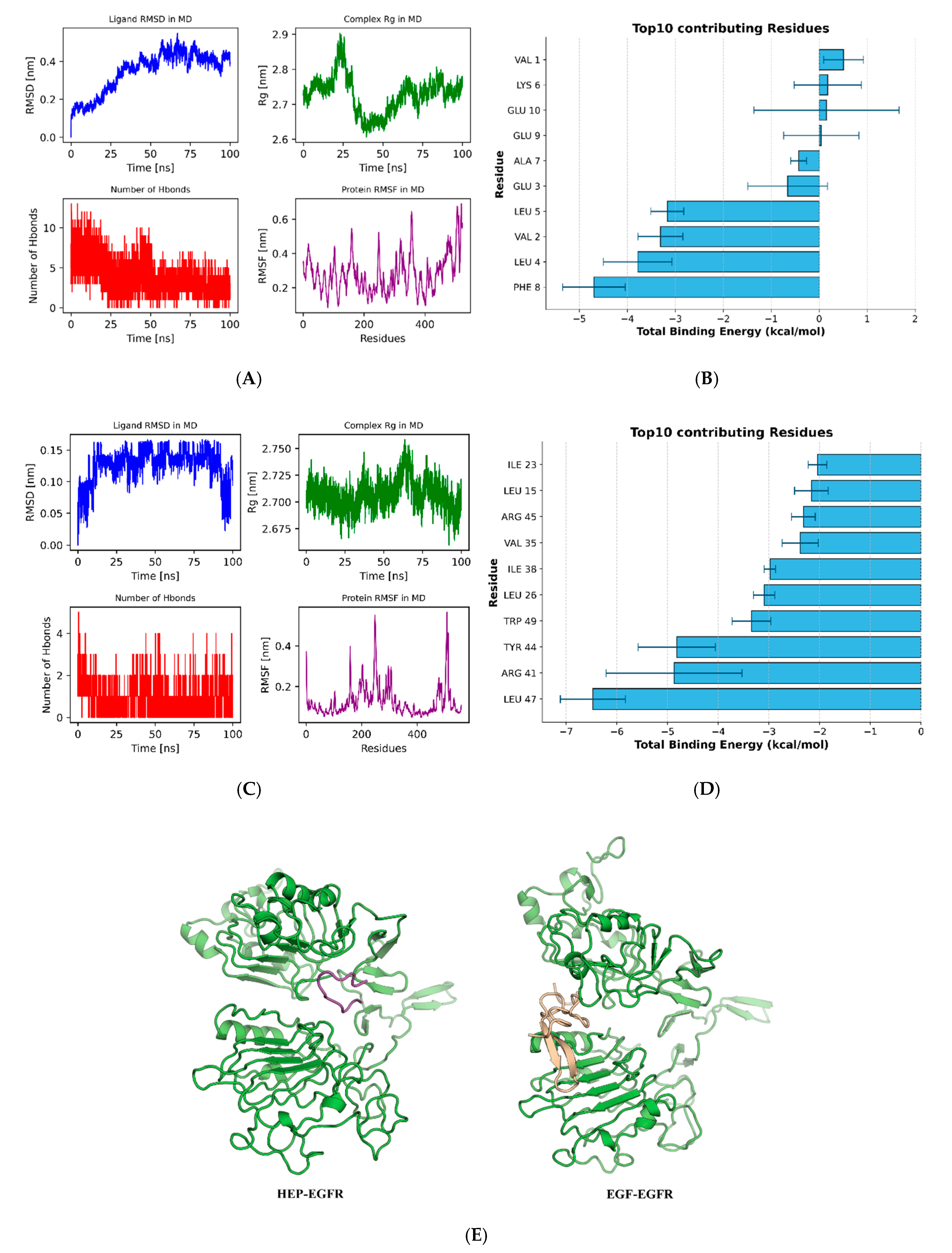
3.5.1. Molecular Docking Binding Site Analysis
3.5.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
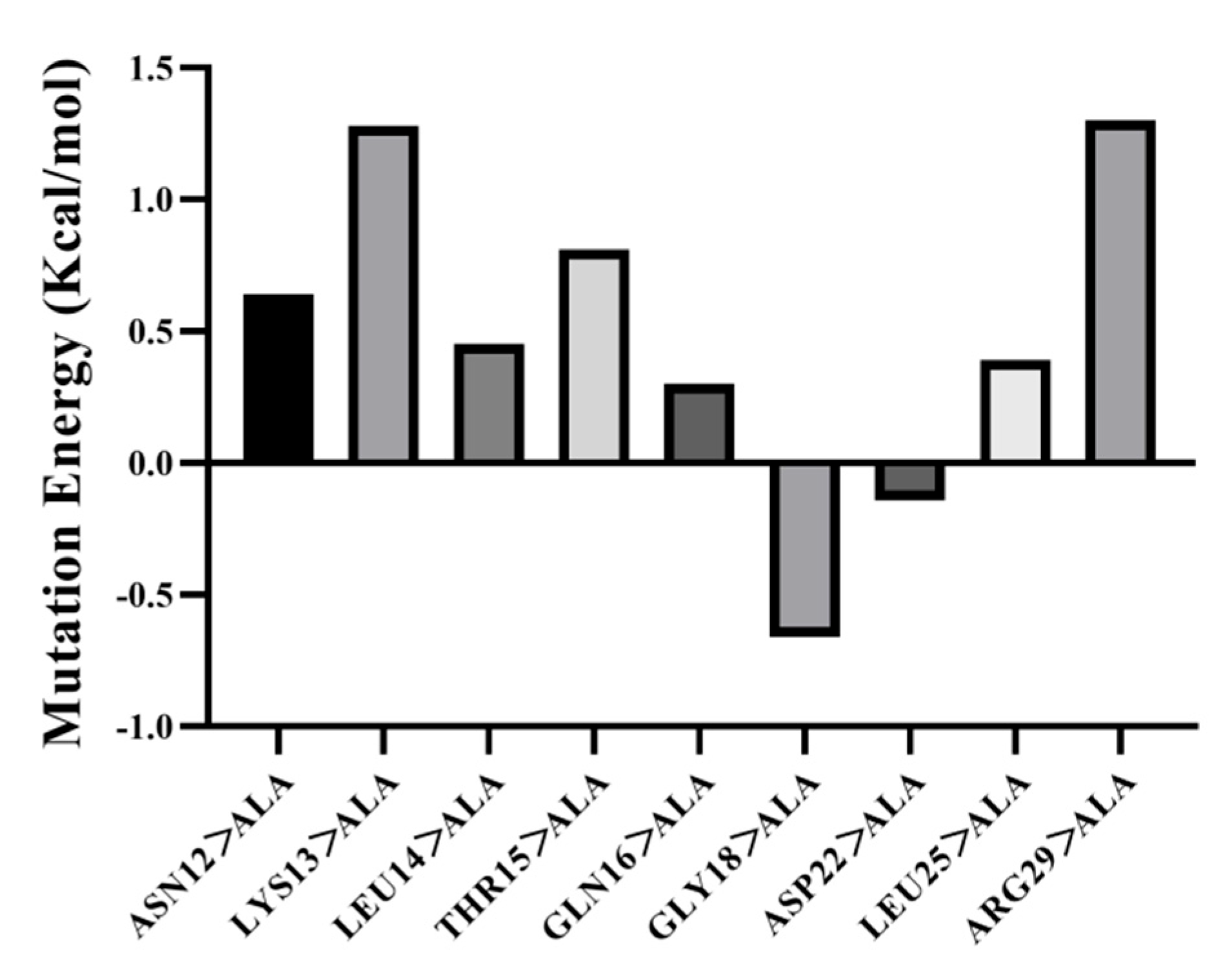
3.5.3. Amino Acid Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.6. Analysis of the Peptide-Binding Activity of the EGFR
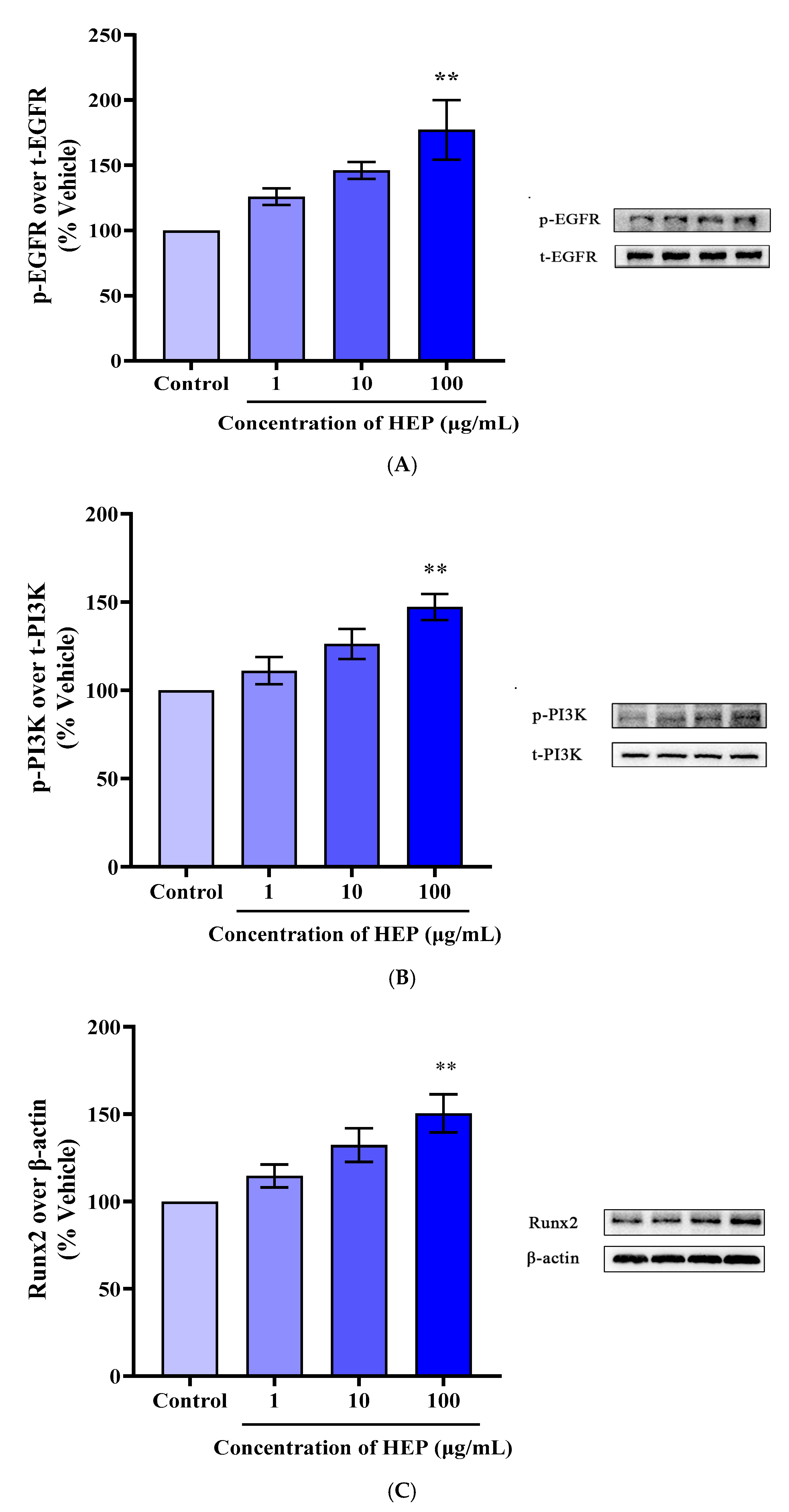
3.7. HEP Induced the Activation of EGFR/PI3K/RUNX2 Pathways in MC3T3-E1 Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HEP | soy peptide |
| VVELLKAFEEKF | Val-Val-Glu-Leu-Leu-Lys-Ala-Phe-Glu-Glu-Lys-Phe |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| ALP | cellular alkaline-phosphatase |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| Rg | radius of gyration |
| Hbond | number of hydrogen bond |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuation |
References
- Yamada, T.; Fukasawa, K.; Horie, T.; Kadota, T.; Lyu, J.; Tokumura, K.; Ochiai, S.; Iwahashi, S.; Suzuki, A.; Park, G.; et al. The role of CDK8 in mesenchymal stem cells in controlling osteoclastogenesis and bone homeostasis. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Patil, S.; Jia, J. The Development of Molecular Biology of Osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhui, Y.; Wenjun, C.; Hui, W.; Liquan, S.; Changwei, Z.; Tianzhu, Z.; Wenhai, Z. Pilose antler peptide protects osteoblasts from inflammatory and oxidative injury through EGF/EGFR signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Su, J.; Qin, H.; Wu, H.; Li, K.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X. The role of EGFR signaling in age-related osteoporosis in mouse cortical bone. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11137–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ozawa, T.; Okizono, R.; Banba, A.; Yamamura, T.; Oga, E.; Muraguchi, A.; Sakurai, H. Ligand-activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling governs endocytic trafficking of unliganded receptor monomers by non-canonical phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Lee, W.G.; Seok, J.; Park, K.Y. The use of epidermal growth factor in dermatological practice. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhipov, A.; Shan, Y.; Das, R.; Endres, N.F.; Eastwood, M.P.; Wemmer, D.E.; Kuriyan, J.; Shaw, D.E. Architecture and Membrane Interactions of the EGF Receptor. Cell 2013, 152, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.A.; Sahoo, A.R.; Kim, S.; Pyron, R.J.; Pitts, S.B.; Guleryuz, S.; Smith, A.W.; Buck, M.; Barrera, F.N. Allosteric inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor through disruption of transmembrane interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirukkumaran, O.M.; Kluba, M.; Hofkens, J.; Mizuno, H. Autophosphorylation of EGFR at Y954 Facilitated Homodimerization and Enhanced Downstream Signals. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Ito, S.; Itoh, K. EGF-stimulated AKT activation is mediated by EGFR recycling via an early endocytic pathway in a gefitinib-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Ran, D.; Xie, C.; Shen, Q.; Wang, S.; Lu, W. EGFR/EGFRvIII Dual-Targeting Peptide-Mediated Drug Delivery for Enhanced Glioma Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24462–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Tu, M.; Liu, M.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Du, M. Isolation and Characterization of Lactoferrin Peptides with Stimulatory Effect on Osteoblast Proliferation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7179–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, B.; Hou, T.; He, H. Duck Egg White-Derived Peptide VSEE (Val-Ser-Glu-Glu) Regulates Bone and Lipid Metabolisms by Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Intestinal Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Characterizations and the Mechanism Underlying Osteogenic Activity of Peptides from Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Stichopus japonicus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15611–15623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y. Cell Proliferation Stimulation Ability and Osteogenic Activity of Low Molecular Weight Peptides Derived from Bovine Gelatin Hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7630–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Kong, X.; Du, M.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Novel Soy Peptide CBP: Stimulation of Osteoblast Differentiation via TβRI-p38-MAPK-Depending RUNX2 Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jian, M.; Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Tang, N.; Cheng, Y.; Gan, J. Soy Peptide Ameliorate TGF-β1-Mediated Osteoblast Differentiation through Smad and MAPK Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 23246–23257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, K.; Kong, X.; Du, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y. Isolation, characterization, and molecular docking analyses of novel calcium-chelating peptide from soy yogurt and the study of its calcium chelation mechanism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liao, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hua, Z.; Masuda, T.; Goto, F.; Yoshihara, T.; Zhao, G. Role of H-1 and H-2 subunits of soybean seed ferritin in oxidative deposition of iron in protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32075–32086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Deh, K.P.U.; Yoo, H.S.; Chung, K.H.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, J.A.; An, J.H. Collagen Extract Derived from Yeonsan Ogye Chicken Increases Bone Microarchitecture by Suppressing the RANKL/OPG Ratio via the JNK Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, T.; Gan, J. Calcium-binding properties, stability, and osteogenic ability of phosphorylated soy peptide-calcium chelate. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1129548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Masson, A.; Li, Y.P. Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Han, L.; Dong, X.; Du, M.; Li, T. Characterization of Chelation and Absorption of Calcium by a Mytilus edulis Derived Osteogenic Peptide. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 840638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Kan, R.; Wu, S.; Guo, H.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Zheng, F.; Liu, J. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptides derived from tuna protein: Virtual screening, inhibitory activity, and molecular mechanisms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghiabbasabadi, M.; Taghavian, H.; Gholami, P.; Khodabakhshi, S.; Gheibi, M.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Silvestri, D.; Raczak, K.B.; Moezzi, R. A Novel Organic-Inorganic-Nanocomposite-Based Reduced Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Nanosensor for NO(2) Detection. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, B.; Fu, Y. Unraveling the Osteogenic Activity and Molecular Mechanism of an Antioxidant Collagen Peptide in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Nutrients 2025, 17, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; He, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, G.; Hou, T. Desalted duck egg white peptides promoted osteogenesis via wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-W.; Han, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Cai, X.-S.; Liu, H.-M.; Ma, Y.-X.; Wang, X.-D. Impact of high temperature on microstructural changes and oil absorption of tigernut (Cyperus esculentus L.) starch: Investigations in the starch-oil model system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 328, 121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaneh, G.; Safar, F.; Atefeh, N.; Nasrin, B.; Mina, M. Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Analysis of EGFR-derived Peptides against the EGF. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2024, 21, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Yu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Zeng, X.; Liang, Y. ACE-inhibitory peptides from Morchella esculenta: Screening, kinetics, and molecular dynamics simulation. Food Chem. 2025, 490, 145011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.H.; Yuan, K.; Xu, D.W.; Chen, J.J.; Cui, Z.M. EGFR-AKT-mTOR activation mediates epiregulin-induced pleiotropic functions in cultured osteoblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 398, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, P.; Nanding, K.; Wu, M.; Bai, X.; Morigen, M.; Fan, L. Lysophosphatidic acid suppresses apoptosis of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells by inducing autophagy activity and promotes cell-cycle progression via EGFR-PI3K/Aurora-A(Thr288)-geminin dual signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1046269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.C.; Zang, H.Y.; Guo, L.X.; Xue, H.B.; Liu, X.D.; Bai, Y.B.; Ma, Y.Z. The PI3K/AKT cell signaling pathway is involved in regulation of osteoporosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Lin, L.; Chen, P.; Ma, K.T.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ao, Y.F. Runx2 overexpression enhances osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in adipose--derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2006, 79, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, M.D.; Rashid, H.; Chen, H.; Clarke, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Javed, A. Loss of Runx2 in committed osteoblasts impairs postnatal skeletogenesis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
| Amino Acid Distribution (%) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | m/z | Scan | z | AA Sequence | pI | Net Charge | -CDOCKER ENERGY | Hydrophobic Uncharged | Acidic | Basic | Others | Aromatic | Aliphatic Amino Acid Index | GRAVY | Permeability | Peptide Ranker Score |
| 1 | 484.61 | 16,182 | 3 | VVELLKAFEEKF | 4.48 | −1 | 184.077 | 58.3 | 25 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 121.67 | 0.425 | 0.210606 | 0.253008 | |
| 2 | 504.7534 | 7322 | 2 | ATAGDEGKLF | 4.18 | −1 | 143.983 | 40 | 20 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 59 | −0.22 | 0.147783 | 0.407089 |
| 3 | 540.3026 | 11,560 | 2 | LFEESLKTL | 4.26 | −1 | 138.631 | 44.4 | 22.2 | 11.11 | 22.2 | 11.11 | 130 | 0.2 | 0.185338 | 0.206268 |
| 4 | 338.8695 | 4925 | 3 | AVGGLGKLGK | 9.54 | 1 | 149.434 | 36.36 | 9.09 | 18.18 | 36.36 | - | 106.36 | 0.064 | 0.386555 | 0.341914 |
| 5 | 532.2457 | 13,585 | 2 | NGDDLFVHF | 4.11 | -2 | 114.448 | 44.44 | 22.22 | 11.11 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 75.56 | −0.056 | 0.059725 | 0.800047 |
| 6 | 473.8885 | 4251 | 3 | EDDEQLPSHPP | 4.10 | -3 | 130.008 | 8.33 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 41.67 | - | 32.5 | −2.25 | 0.0890831 | 0.37201 |
| 7 | 518.7401 | 13,601 | 2 | SGDDLFVFH | 4.11 | -2 | 131.248 | 44.44 | 22.22 | 11.11 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 75.56 | 0.244 | 0.0539904 | 0.815582 |
| 8 | 521.7354 | 10,322 | 2 | WFNDEKGF | 4.18 | −1 | 140.384 | 37.5 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 | 37.5 | 0 | −1.263 | 0.0730926 | 0.8241 |
| 9 | 391.5593 | 3681 | 3 | VSETGKLVPSR | 9.70 | 1 | 131.957 | 27.27 | 9.09 | 18.18 | 45.45 | - | 88.18 | −0.364 | 0.289799 | 0.122207 |
| 10 | 315.19 | 4360 | 3 | VGGLGKLGKD | 9.54 | 1 | 135.765 | 30 | 10 | 20 | 40 | - | 107 | −0.11 | 0.361272 | 0.279506 |
| 11 | 425.2395 | 7354 | 2 | LLKAFEE | 4.26 | −1 | 114.8 | 57.14 | 28.57 | 14.29 | - | 14.29 | 125.71 | 0.186 | 0.210617 | 0.126237 |
| 12 | 365.2287 | 5542 | 2 | LLNLEK | 6.41 | 0 | 98.5768 | 50 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 | - | 195 | 0.083 | 0.550142 | 0.0947654 |
| 13 | 426.2471 | 6197 | 2 | LVELYSK | 6.40 | 0 | 108.511 | 57.14 | 14.29 | 14.29 | 14.29 | 14.29 | 152.86 | 0.329 | 0.220626 | 0.073327 |
| 14 | 365.2286 | 6662 | 2 | VELKLQ | 6.41 | 0 | 102.062 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 | - | 178.33 | 0.15 | 0.535372 | 0.0609186 |
| 15 | 350.7338 | 6859 | 2 | VVELLK | 6.41 | 0 | 100.583 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 16.67 | - | - | 226.67 | 1.433 | 0.610505 | 0.0667024 |
| 16 | 336.7177 | 6312 | 2 | LLADLK | 6.34 | 0 | 95.7294 | 66.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 | - | - | 211.67 | 0.967 | 0.548048 | 0.228773 |
| 17 | 460.2653 | 6597 | 2 | LAGALPSYK | 9.30 | 1 | 93.3458 | 55.56 | - | 11.11 | 33.33 | 11.11 | 108.89 | 0.356 | 0.236381 | 0.435549 |
| 18 | 340.2099 | 2603 | 2 | GFKSLK | 10.81 | 2 | 87.2354 | 33.33 | - | 33.33 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 65 | −0.4 | 0.262743 | 0.48218 |
| 19 | 332.1945 | 8994 | 2 | FDLLR | 6.34 | 0 | 78.0346 | 60 | 20 | 20 | - | 20 | 156 | 0.48 | 0.366771 | 0.750974 |
| 20 | 343.7315 | 6976 | 2 | SVVLLR | 10.55 | 1 | 78.4668 | 66.67 | - | 16.67 | 16.67 | - | 226.67 | 1.783 | 0.626641 | 0.247147 |
| 21 | 381.2316 | 6090 | 2 | LLPYGKA | 9.30 | 1 | 79.483 | 57.14 | - | 14.29 | 28.57 | 14.29 | 125.71 | 0.314 | 0.332674 | 0.349653 |
| 22 | 339.7 | 5373 | 2 | AFSRVV | 10.55 | 1 | 75.3562 | 66.67 | - | 16.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 113.33 | 1.283 | 0.267797 | 0.293781 |
| 23 | 311.1894 | 5862 | 2 | AVRLY | 9.35 | 1 | 67.5503 | 60 | - | 20 | - | 20 | 156 | 0.8 | 0.578736 | 0.293136 |
| 24 | 335.2177 | 4103 | 2 | LPALQK | 9.70 | 1 | 68.0429 | 50 | - | 16.67 | 33.33 | - | 146.67 | 0.067 | 0.589914 | 0.235953 |
| 25 | 331.6788 | 7513 | 2 | TLFGPQ | 6.10 | 0 | 63.0582 | 33.33 | - | - | 66.67 | 16.67 | 65 | 0.067 | 0.126841 | 0.42418 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, J.; Huang, Y.; Jian, M.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Y. Interactions Between HEP Peptide and EGFR Involved in the Osteoblast Differentiation. Foods 2025, 14, 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173032
Gan J, Huang Y, Jian M, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Qiao Y, Li Y. Interactions Between HEP Peptide and EGFR Involved in the Osteoblast Differentiation. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173032
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Jing, Yanling Huang, Mengqi Jian, Yuhang Chen, Yuxuan Jiang, Yang Qiao, and Yang Li. 2025. "Interactions Between HEP Peptide and EGFR Involved in the Osteoblast Differentiation" Foods 14, no. 17: 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173032
APA StyleGan, J., Huang, Y., Jian, M., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Qiao, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Interactions Between HEP Peptide and EGFR Involved in the Osteoblast Differentiation. Foods, 14(17), 3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173032








