Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics for Liquor Product Quality Assessment: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
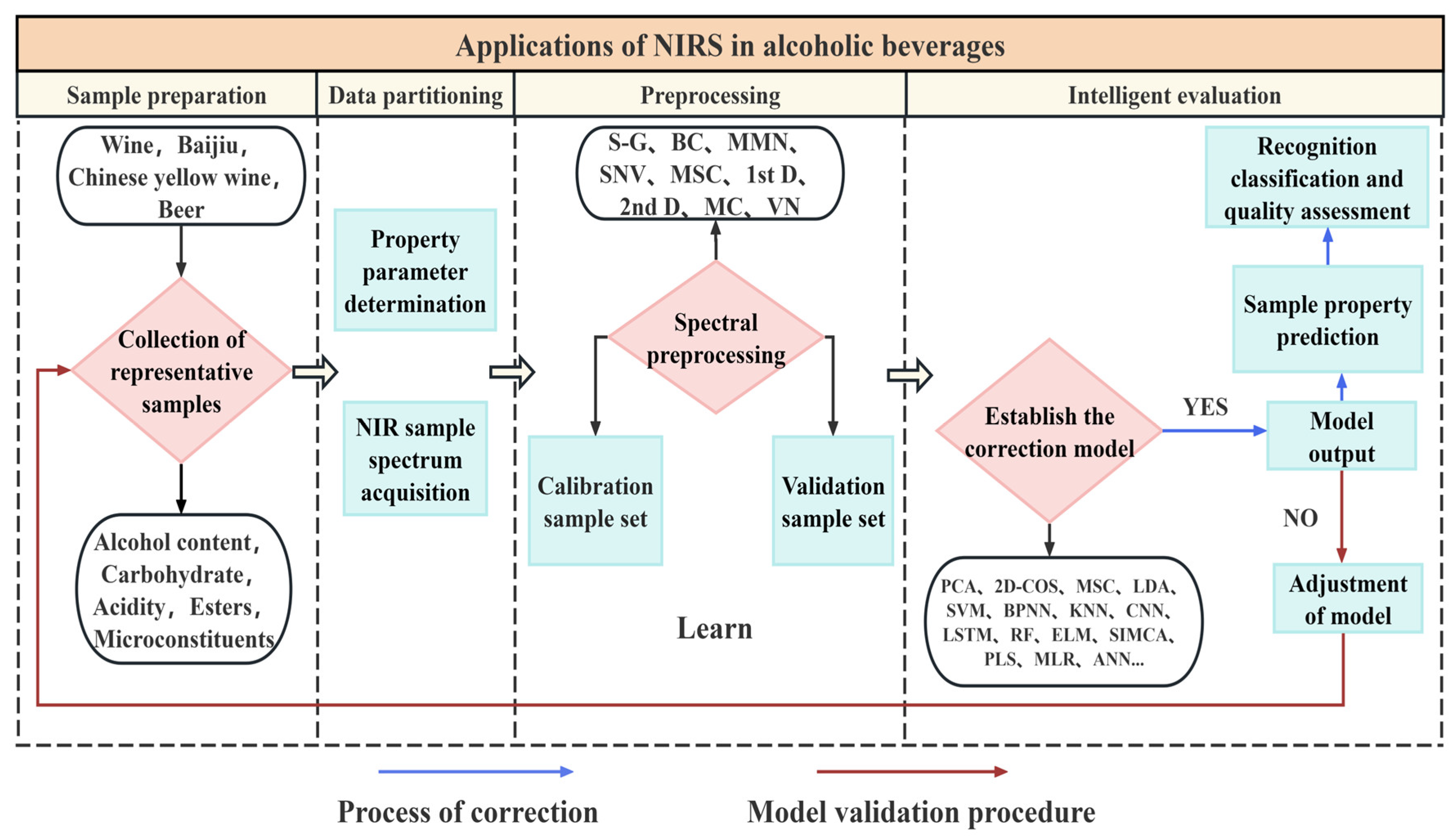
2. The Role of Chemometric Methods in the Processing of Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Data
2.1. Data Preprocessing Techniques and Their Impact on Model Performance
2.2. Qualitative Discriminant Model Construction and Validation Methods
2.3. Quantitative Analysis Model Construction and Optimization Strategy
2.4. Application of Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in Liquor Analysis
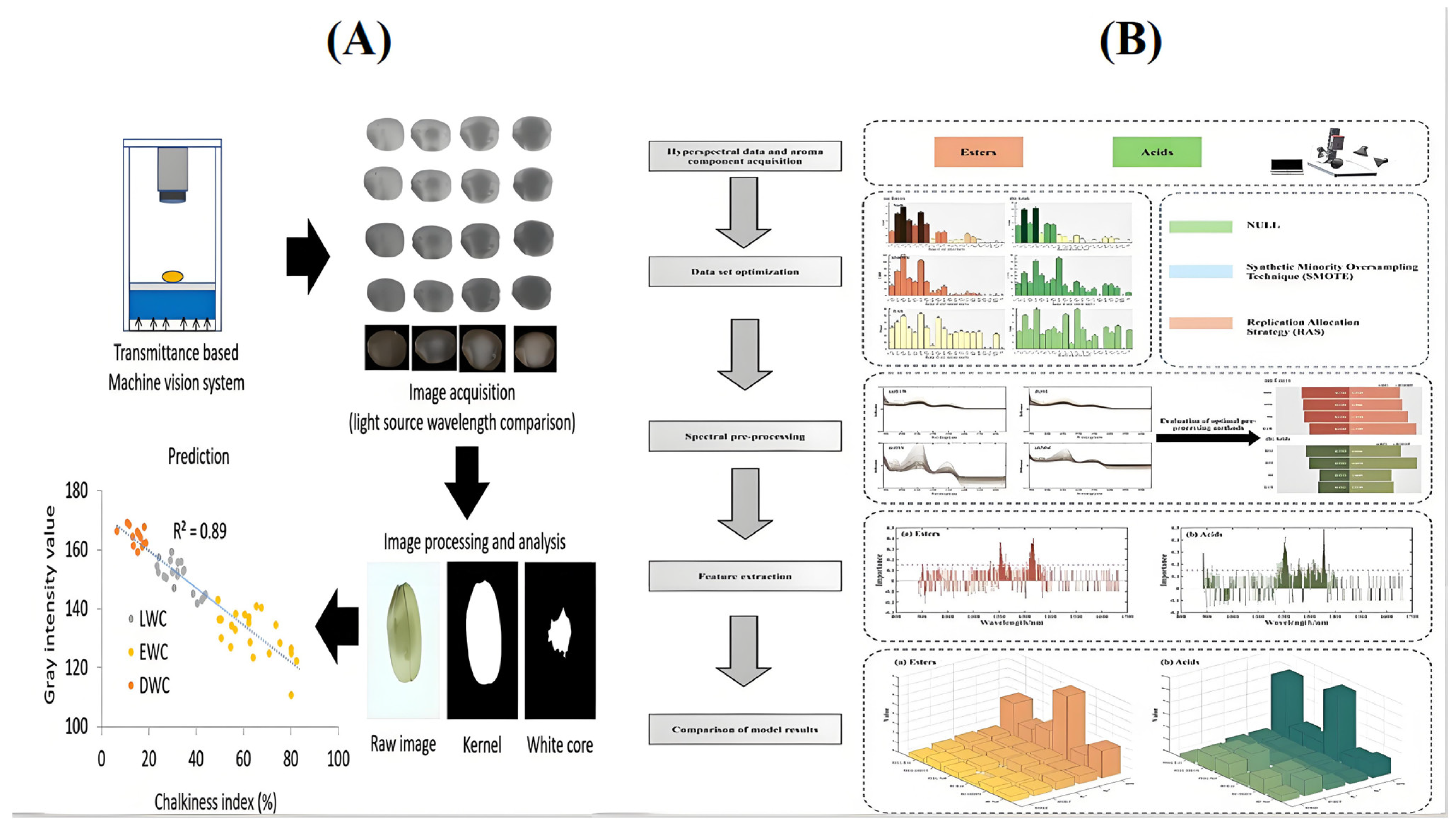
3. Specific Applications of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics in Wine Quality Assessment
3.1. Rapid Determination of Alcohol and Accuracy Assessment
3.2. Research on Quantitative Analysis Methods for the Contents of Major Components
3.3. Qualitative Identification Techniques for Trace Ingredients and Flavor Substances

| Detection Object | Instrument Type | Preprocessing Method | Band Range | Modeling Approach | Accuracy (%) Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wine | FT-NIR | S-G + SNV + MC | 4000–12,500 cm−1 | PCA + PLS | RP2 = 0.990 | [38] |
| Baijiu | NIR | SNV + MSC + S-G | 886–1735 nm | PLSR + SVM + LLF + ILF | RP2 = 0.9925 | [39] |
| Liquor | NIR | S-G + SNV + MC | 908–1676 nm | PLS | RPD = 4.1 | [40] |
| Baijiu | UV-Vis-NIR | SNV + MSC | 1000–1800 nm | PLS | R2 = 0.9993 | [41] |
| Baijiu | NIR | UVE + SPA + PCA | 770–2500 nm | PLS | R2 = 0.9928 | [42] |
| Baijiu | FT-NIR | SPA + iPLS | 770–2500 nm | PLSR | R2 = 0.952 | [43] |
| Chinese yellow wine | NIR | - | 770–2500 nm | PLSR + SVR | R = 0.9848 RPD = 3.6875 | [44] |
| Beer | NIR | - | 800–2500 nm | - | RMSE = ±0.33% v/v | [45] |
| Cachaca | NIR | OFF + SGD | 1350–1850 nm | PLS | RPD = 59.04 RP = 0.99 | [46] |
| Shochu | NIR | - | 780–2500 nm | LR | R = 0.99 | [47] |
| Wine | NIR | S-G + SNV | 1100–2498 nm | PLS | RP2 = 0.98 | [48] |
| Sake | Vis-NIR | GLM | 350–1800 nm | LSM | R2 = 0.89 | [49] |
| Chinese yellow wine | FT-NIR | MSC + S-G + SNV | 3999–10,001 cm−1 | PLS-DA | R = 0.9852 | [50] |
| Chinese rice wine | FT-NIR | MSC + S-G | 4000–12,000 cm−1 | PLSR + SMLR + ANN | RV2 = 0.941 RPD = 4.1 | [51] |
| Baijiu | NIR | MC + SNV + MSC | 900–2500 nm | PLS + SPXY | R2 = 0.92 | [53] |
| Baijiu | NIR | MSC + SNV + S-G | 900–1700 nm | PSO-SVR + RBFNN + PLSR + SEL | RP2 = 0.9914 RPD = 10.8007 | [54] |
| Base Liquor | FT-NIR | MSC | 11,998–4597 cm−1 | PLS | R2 = 97.96 | [55] |
| Base Liquor | FT-NIR | MSC + SNV + PLS | 780–2526 nm | PLS | R2 = 0.9694 | [56] |
| Original liquor | FT-NIR | MSC + SNV + CARS | 4000–12,500 cm−1 | SVR + RF + PCA | 100% | [57] |
| Red wine | FT-NIR | - | 12,500–4000 cm−1 | PLS + PCA | R2 = 0.9211 | [58] |
| Wine | NIR | - | 1100–2600 nm | PLS-DA | 100% | [60] |
| Wine | FT-NIR | MMN + VN + FD + SD + PCA | 870–2500 nm | PLSR + Si-PLS | RPD = 2.39 | [61] |
| Base wine | FT-NIR | BC + S-G + MSC + SNV | 1100–2300 nm | PLSR | R2 = 0.935 RPD = 4.39 | [9] |
| Wine | NIR | MC + S-G | 350–2500 nm | PLS | R = 0.92 RPD = 2.54 | [62] |
| Wine | NIR | MSC + SNV + S-G | 450–1800 nm | PCR + PLSR + MLR + PLS + PLS-DA | RPD = 4.44 | [63] |
| Beer | NIR | MSC | 1400–2400 nm | MLR | R2 = 0.592 | [64] |
| Vodka | NIR | - | 700–1070 nm | SNV | 98% | [65] |
3.4. Identification and Traceability Techniques for Counterfeit Liquor
3.5. Methods for the Dynamic Monitoring of Quality Changes in the Aging Process

| Detection Object | Instrument Type | Preprocessing Method | Band Range | Modeling Approach | Accuracies (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wine | NIR | PCA | 1100–2300 nm | PCR | RCV2 = 0.68 | [77] |
| Wine | NIR | S-G | 1350–2150 nm | PLS | RPD = 3.03 R2 = 0.91 | [78] |
| Fruit wine (kiwi wine) | FT-NIR | VN | 6101–5446 cm−1 | PLS | RP2 = 0.978 | [81] |
| Fruit wine (Pineapple wine) | FT-NIR | SD + SNV | 11,536–3952 cm−1 | PLS-DA | 100% | [82] |
| Rosé sparkling wine | FT-NIR | PCA | 9091–4000 cm−1 | PCA | 100% | [83] |
| Wine | FT-NIR | MSC + MMN | 10,500–4300 cm−1 | PLS | RMSEP = 71.1 mg/L R2 = 0.97 | [84] |
| Wine | FT-NIR | SNV | 4555–4353 cm−1 | PCA + SIMCA + DA | 97% | [85] |
4. Technical Challenges and Trends in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics
4.1. Research on Effective Elimination Methods for Complex Matrix Interference
4.2. Current Status of Development and Application of Online Inspection Systems
4.3. Synergistic Analysis Strategy with Multi-Technology Linkage
4.4. Prospects for the Application of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Technologies in Model Optimization
5. Summary and Outlook
- (1)
- Augmenting investigations into the mechanisms underlying complex matrix interferences and delving into more sophisticated data preprocessing methodologies and feature extraction techniques to bolster the model’s resilience against such interferences.
- (2)
- Enhancing the architecture and algorithms of online detection systems to elevate the system’s stability and detection precision, thereby fulfilling the requisite for swift detection in real-world production scenarios.
- (3)
- Intensifying research on synergistic technology use for precise wine quality evaluation.
- (4)
- Incorporating AI and Big Data analytics via machine learning to enhance model accuracy.
- (5)
- Uncovering deeper spectral data–quality metric correlations to expand the informational scope.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.Y.; Yan, T.Y.; Fu, T.T.; Wang, K.; Rong, X.D.; Liu, X.T.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.Y.; Sheng, W.L.; Zhu, B.C. A NIR fluorescent probe based on carbamoyl oxime with high specificity for detecting ferrous ions in food and in vivo. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Zeng, Y.L.; Ding, H.C.; Liu, Q.L.; Mao, L.T.; Liu, G.; Pu, S.Z. Rapidly responsive and highly selective NIR fluorescent probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide in food samples and living cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 320, 124640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Munnaf, M.A.; Mouazen, A.M. Micro-near-infrared (micro-NIR) sensor for predicting organic carbon and clay contents in agricultural soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 242, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.Y.; Fu, X.P.; Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.Y. Calibration transfer of sugar content prediction models for agricultural products via NIR spectral augmentation and reconstruction architecture. Biosyst. Eng. 2025, 253, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Wan, X.H.; Luo, X.R.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.C.; Zhong, Z.J.; Tao, Q.; Wu, Z.F. Development of a Data Fusion Strategy Combining FT-NIR and Vis/NIR-HSI for Non-Destructive Prediction of Critical Quality Attributes in Traditional Chinese Medicine Particles. Vib. Spectrosc. 2025, 137, 103780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.T.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.T.; Tian, M.Y.; Liang, T.Y.; Zhong, K.L.; Yan, X.M.; Tang, L.J. A quinolinium-based colorimetric and NIR fluorescent dual-channel sensing platform for specific detection of bisulfite in food, traditional Chinese medicine and living cells. Dye. Pigment. 2025, 239, 112767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakabová, S.; Fikselová, M.; Mendelová, A.; Ševčík, M.; Jakab, I.; Aláčová, Z.; Kolačkovská, J.; Ivanova-Petropulos, V. Chemical Composition of White Wines Produced from Different Grape Varieties and Wine Regions in Slovakia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Melle, A.; Marcotuli, V.; Botturi, D.; Fawole, O.A.; Mazzeo, A. The prediction of ripening parameters in Primitivo wine grape cultivar using a portable NIR device. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véstia, J.; Barroso, J.M.; Ferreira, H.; Gaspar, L.; Rato, A. Predicting calcium in grape must and base wine by FT-NIR spectroscopy. Food. Chem. 2019, 276, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, S.H. Wine composition detection utilizing 1D-CNN and the self-attention mechanism. Vib. Spectrosc. 2025, 137, 103768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, C.; Lin, Z. Application of subspace ensemble radical basis function networks to quantitative analysis of near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2025, 212, 113354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Huan, K.W.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.W. Quantitative model of near infrared spectroscopy based on pretreatment combined with parallel convolution neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 132, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Tian, J.P.; Yang, H.L.; Hu, X.J.; Xie, L.L.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xia, Y.Y.; Huang, D. Utilization of hyperspectral imaging for the analysis of aroma components of Soy Sauce-Aroma Type Baijiu. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Segura-Borrego, M.P.; Camiña, J.M.; Callejón, R.M.; Azcarate, S.M. Multiplatform spectralprint strategies for the authentication of Spanish PDO fortified wines using AHIMBU, an automatic hierarchical classification tool. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2025, 257, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J.H.; Wen, L.; Huang, M.; Ao, F.; Luo, W.L.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantitative analysis of key components in Qingke beer brewing process by multispectral analysis combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, N.; Cavallini, E.; Savorani, F. Monitoring the homemade fermentation of readymade malt extract using the SCiO NIR sensor, A convergence of technology and tradition. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 325, 125126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.Q. Insights into ethanol–water clusters in alcoholic beverages by vibration spectroscopy connecting with quality and taste. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wu, S.; Yu, W.; Xu, X.; Huang, M.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Z. Wine Authentication Using Integration Assay of MIR, NIR, E-tongue, HS-SPME-GC-MS, and Multivariate Analyses: A Case Study for a Typical Cabernet Sauvignon Wine. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Xiao, L.C.; Jing, Z.; Li, J.W.; Zhao, D.; Huang, Y.; Huo, D.Q.; Luo, X.G.; Hou, C.J. Identification of liquors from the same brand based on ultraviolet, near-infrared and fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134064. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, J. Intelligent sensing sensory quality of Chinese rice wine using near infrared spectroscopy and nonlinear tools. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 154, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, A.; Pacifico, S.; Santini, G.; Pettinelli, S.; Alfieri, G.; Modesti, M.; Bellincontro, A.; Sanmartin, C.; Pittari, E.; Piccolella, S.; et al. Carbonic or nitrogen maceration of wine grape: Biochemical differences of grape and wine using destructive and non-destructive approach. Food Chem. 2025, 487, 144782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, J.E.; Hernandes, K.C.; Lago, L.O.; Silveira, R.D.; Marques, A.T.B.; Zini, C.A. Flavoromic analysis of wines using gas chromatography, mass spectrometry and sensory techniques. J. Chromatogr. 2024, 1734, 465264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Liang, Y.Y.; Du, W.H.; Kuang, M.M.; Meng, Z.Y.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, S.F. A novel BODIPY-based colorimetric turn-on NIR fluorescent probe for sensitive and visual detection of H2S in food samples with smartphone platform. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.; Truong, V.K.; Chapman, J.; Cozzolino, D. The use of two-dimensional spectroscopy to interpret the effect of temperature on the near infrared spectra of whisky. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2020, 28, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; He, M.; Zheng, J.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.B.; Hou, C.J.; Huo, D.Q. Methodology and optimization research for discrimination of different brands of Baijiu based on multispectral techniques. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7855–7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Tuo, X.G.; Peng, Y.J.; Li, X.P.; Pang, T.T. A Rapid Nondestructive Detection Method for Liquor Quality Analysis Using NIR Spectroscopy and Pattern Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Ta, N.; Wei, H.C.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, J.; Li, M. Research of 2D-COS with metabolomics modifications through deep learning for traceability of wine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.S.; Zheng, E.R.; Chen, B. Research on a classification algorithm of near-infrared spectroscopy based on 1D-CNN. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Li, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, P.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, Y.L.; Guan, H.H.; Liang, Y.X.; Yuan, D.P.; Lu, T.L.; et al. Machine learning combined with multi-source data fusion for rapid quality assessment of yellow rice wine with different aging years. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Tosi, D. An Artificial Intelligence-based tool to predict “unhealthy” wine and olive oil. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljančić, N.; Furdíková, K.; Araújo Gomes, A.; Špánik, I. Wine authentication: Current progress and state of the art. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.; Viejo, C.G.; Barnes, C.; Pang, A.; Fuentes, S. Wine quality assessment for Shiraz vertical vintages based on digital technologies and machine learning modeling. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Freitas, O.; Melo Pinto, P. Evaluating the generalization ability of deep learning models: An application on sugar content estimation from hyperspectral images of wine grape berries. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 250, 123891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobaric, A.; Orrell-Trigg, R.; Orloff, S.; Fraser, V.; Chapman, J.; Cozzolino, D. The Use of a Droplet Collar Accessory Attached to a Portable near Infrared Instrument to Identify Methanol Contamination in Whisky. Sensors 2023, 23, 8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.B.; He, Y.K.; Luo, Y.S.; Wang, S.J.; Xie, B.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Tuo, X.G. Study on Analysis Method of Distiller’s Grains Acidity Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 3726–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pang, A.; Hernandez-Brenes, C.; Fuentes, S. Enhancing beer authentication, quality, and control assessment using non-invasive spectroscopy through bottle and machine learning modeling. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, K.; Lu, D.Q.; Su, Y.; Ju, Y.L.; Fang, Y.L.; Yang, J.H. Discrimination of maturity stages of cabernet sauvignon wine grapes using visible–near-infrared spectroscopy. Foods 2023, 12, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menozzi, C.; Foca, G.; Calvini, R.; Catellani, L.; Bezzecchi, L.; Ulrici, A. Comparison of Different Spectral Ranges to Monitor Alcoholic and Acetic Fermentation of Red Grape Must Using FT-NIR Spectroscopy and PLS Regression. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tian, J.P.; Hu, X.J.; Huang, Y.X.; He, K.L.; Xie, L.L.; Yang, H.L.; Huang, D.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xia, Y.Y. Rapid determination of starch and alcohol contents in fermented grains by hyperspectral imaging combined with data fusion techniques. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Fulgêncio, A.C.; Resende, G.A.P.; Teixeira, M.C.F.; Botelho, B.G.; Sena, M.M. Combining Portable NIR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Calibration for the Determination of Ethanol in Fermented Alcoholic Beverages by a Multi-Product Model. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Q.; Guo, M.; Ye, X.S.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.N.; Wu, Z.J. Indirect Determination of Liquor Alcohol Content Based on Near-Infrared Spectrophotometry. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 42, 410–414. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Sun, A.; He, S.Y. Rapid Detection of Baijiu Alcohol Content Based on NIR and SNV-UVE-PLS. In Proceedings of the 2023 CAA Symposium on Fault Detection, Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes (SAFEPROCESS), Yibin, China, 22–24 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Tuo, X.G.; Zhang, G.Y.; Luo, L.; Zhai, S.; Zeng, X.L. Application of Near-infrared Spectroscopy Combined with iPLS_SPA Band Screening in the Prediction Model of Yellow Water Alcohol Content. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 366. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Y.; Zhao, Z.G.; Liu, F. mRMR-based wavelength selection for quantitative detection of Chinese yellow wine using NIRS. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskell, P.D.; Holmes, C.; Huismann, M.; Reidb, S.; Carrc, M.; Jonesa, B.J.; Maskell, D.L. The influence of alcohol content variation in UK packaged beers on the uncertainty of calculations using the Widmark equation. Sci. Justice 2018, 58, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.E.; Neto, J.F.B.; Bezerra, T.K.A.; Silva, V.P.; Veras, G.; Oliveira Ramos, R.; Sousa Fernandes, D.D. Quantification of alcohol content and identification of fraud in traditional cachaças using NIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimba, C.I.; Yumiko, Y.; Kayu, O.; Kazunori, T. Measuring the Alcohol Content in Shochu Moromi by Near-infrared Spectroscopy. Bunseki Kagaku 2022, 71, 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, C.A.T.; Páscoa, R.N.M.J.; Porto, P.A.L.S.; Cerdeira, A.L.; González-Sáiz, J.M.; Pizarro, C.; Lopes, J.A. Raman spectroscopy for wine analyses: A comparison with near and mid infrared spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 186, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.K.; Al Riza, D.F.; Ogawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Kondo, N. Assessment of chalkiness index of Sake rice using transmission imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 275, 121149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Wu, H.S.; Tang, R.; Zhao, M.F.; Li, Y.F.; Wei, F.Y.; Ge, W.H.; Li, C.Y.; Du, W.F. Rapid quality identification of the whole wine-steamed process of Polygonati Rhizome by chromaticity and near-infrared spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.Q.; Liu, X.; Tang, P.A. Evaluation of near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopy for the determination of routine parameters in Chinese rice wine. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljusurić, J.G.; Boban, A.; Mucalo, A.; Budić-Leto, I. Novel Application of NIR Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Determination of ‘Maraština’ Wine Parameters. Foods 2022, 11, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.N.; Wang, Q. Rapid Analysis by NIR about Physicochemical Indexes of Fermented Grains of Nongxiang Baijiu in Northern China. Liquor. Mak. 2023, 50, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.X.; Tian, J.P.; Hu, X.J.; Yang, H.L.; Xie, L.L.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xia, Y.Y.; Huang, D.; He, K.P. Predicting the composition of aroma components in Baijiu using hyperspectral imaging combined with a replication allocation strategy-enhanced stacked ensemble learning model. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 341, 126398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.H.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, X.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.X. Determination of three alcohols in Chinese Dukang Base liquor by FT-NIR spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.F.; Liu, L.L.; Yan, Z.K.; Zhang, P.F.; Zhang, W.G. Establishment of NIR Rapid Analysis Model of Ethyl Acetate Index in Feng Flavour Base Liquor. Liquor. Mak. 2022, 49, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zou, Y.F.; Zhu, X.M.; Peng, H.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Preliminary Exploration and Application Research on the Model of Gathering Distillate According to the Quality Based on Fourier Transform Near Infrared Spectroscopy. China Brew. 2025, 44, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht, K.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Toit, W.; Aleixandre-Tudo, J.L. Moving towards in-line monitoring of phenolic extraction during red wine fermentations using infra-red spectroscopy technology. Influence of sample preparation and instrumentation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, J.I.; Cozzolino, D.; Vilanova, M. Optimisation of the optical path-length for the measurement of volatile compounds in wine using ultraviolet/visible/and near-infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, vvaf090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinelli, S.; Alfieri, G.; Bianchi, A.; Baris, F.; Chinnici, F.; Mencarelli, F.; Mencarelli, A.; Modesti, M. Fortified or passito sweet wines from Aleatico grapes subjected to different dehydration conditions: Chemical and aromatic profile using destructive and non-destructive analyses. OENO One 2025, 59, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.B.; Xu, Y.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Dai, B.X.; Tao, Y.S.; Xiong, X.L. Analysis of Near-Infrared Spectral Properties and Quantitative Detection of Rose Oxide in Wine. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, J.A.; Puertas, B.; Cantos-Villar, E. Assessing wine sensory attributes using Vis/NIR. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.D.; Mesa, N.F.O.; Freire, M.S.; Ramosc, R.P.; Mederos, B.J.T. Development of predictive models for quality and maturation stage attributes of wine grapes using vis-nir reflectance spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 150, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, G.M.P.; Simon, E.; Gibert, A.; Miranda, J.; Alcoba, E.R.; Martínez, O.; Cerezo, E.V.; Bustamante, M.A. Gluten assessment in beers: Comparison by different commercial elisa kits and evaluation of nir analysis as a complementary technique. Foods 2021, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, Q.T.; Nguyen, U.D.; Nguyen, H.N. Detect Level of Methanol in Alcohol Using Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometer Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC), Da Nang, Vietnam, 19–21 October 2023; pp. 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Araujo, L.D. Inter-regional characterization of New Zealand pinot noir wines: Assessing geographical origin through mid-FTIR and phenolic profile analysis. Food Res. Int. 2025, 212, 116485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machyňáková, A.; Schneider, M.P.; Khvalbota, L.; Vyviurska, O.; Špánik, I.; Gomes, A.A. A fast and inexpensive approach to characterize Slovak Tokaj selection wines using infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.; Gonzalez, V.C.; Barnes, C.; Fuentes, S. Non-invasive digital technologies to assess wine quality traits and provenance through the bottle. Fermentation 2022, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhan, J.C.; Huang, W.D. Identification of wine according to grape variety using near-infrared spectroscopy based on radial basis function neural networks and least-squares support vector machines. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3306–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, X.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Luo, D.L.; Xu, B.C. Rapid determination of ethyl pentanoate in liquor using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 49, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.Y.; Peng, H.B.; Wu, J.H.; Sheng, X.F.; Li, L. Study on the year and grade of Luzhou-flavor liquor by chemometrics and NIR. Packag. Food Mach. 2022, 40, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, V.C.; Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F.R. Assessment of beer quality based on foamability and chemical composition using computer vision algorithms, near infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.C.; Fuentes, S. A digital approach to model quality and sensory traits of beers fermented under sonication based on chemical fingerprinting. Fermentation 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, X.X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xie, G.F.; Peng, Q. Rapid discrimination of Chinese rice Wine (Huangjiu) from various regions using Benchtop-NIR and Micro-NIR spectrometers in conjunction with chemometrics. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 149, 105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Chen, J.L.; Meng, K.; Zheng, H.J.; Chen, G.Q.; Xu, X.; Lin, Z.C.; Xie, G.F. Rapid detection of adulteration of glutinous rice as raw material of Shaoxing Huangjiu (Chinese Rice Wine) by near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 111, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubíková, M.; Sádecká, J.; Kleinová, A. On the use of the fluorescence, ultraviolet–visible and near infrared spectroscopy with chemometrics for the discrimination between plum brandies of different varietal origins. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littarru, E.; Modesti, M.; Alfieri, G.; Pettinelli, S.; Floridia, G.; Bellincontro, A.; Sanmartinc, C.; Brizzolara, S. Optimizing the winemaking process: NIR spectroscopy and e-nose analysis for the online monitoring of fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, G.; Riggi, R.; Modesti, M.; Bellincontro, A.; Renzi, F.; leixandre-Tudo, J.L. Feasibility assessment of a low-cost near-infrared spectroscopy-based prototype for monitoring polyphenol extraction in fermenting musts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 6115–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann, L.; Layfield, J.B.; Sheppard, J.D. The application of near-infrared spectroscopy in beer fermentation for online monitoring of critical process parameters and their integration into a novel feedforward control strategy. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Yuan, L.M.; Zhang, H.N.; Li, L.M. Rapid Measurement of the Polyphenol Content in Fruit-Wine by Near Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Consensus Modeling Approach. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 777–781. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Q.; Peng, B.Z. A feasibility study on monitoring residual sugar and alcohol strength in kiwi wine fermentation using a fiber-optic FT-NIR spectrometry and PLS regression. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemsumran, S.; Boondaeng, A.; Ngowsuwan, K.; Jungtheerapanich, S.; Apiwatanapiwat, W.; Janchai, P.; Vaithanomsat, P. Mid-infrared and near-infrared spectroscopies to classify improper fermentation of pineapple wine. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, S.; Toaldo, I.M.; Panceri, C.P.; Caliaric, V.; Lunae, A.S.; Goise, J.S.; Bordignon-Luiz, M.T. Changes in organic acids, polyphenolic and elemental composition of rosé sparkling wines treated with mannoproteins during over-lees aging. Food Res. Int. 2019, 124, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre, T.J.L.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Aleixandre, J.L.; du Toit, W. Chemometric compositional analysis of phenolic compounds in fermenting samples and wines using different infrared spectroscopy techniques. Talanta 2018, 176, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Z.; Liu, S.Q.; Li, X.H.; Wang, C.X.; Ni, X.L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.H. Geographical origin traceability of Cabernet Sauvignon wines based on Infrared fingerprint technology combined with chemometrics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, G.A.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Hermes, E.; Fagundes, B.J.; Santos, R.O.; Costa, A.B. The application of parallel processing in the selection of spectral variables in beer quality control. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, N.; Bakardzhiyski, I.; Manolova, Y.; Bambalov, V.; Cozzolino, D.; Antonov, L. The effect of path length on the measurement accuracies of wine chemical parameters by UV, visible, and near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Zhao, Z.G.; Liu, F. An updating method of NIR model based on characteristic wavelength for yellow rice wine detection. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2017, 37, 3414–3418. [Google Scholar]
- Debebe, A.; Temesgen, S.; Abshiro, M.R.; Chandravanshi, B.S. Partial least squares− near infrared spectrometric determination of ethanol in distilled alcoholic beverages. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2017, 31, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fulgêncio, A.C.C.; Resende, G.A.P.; Teixeira, M.C.F.; Botelho, B.G.; Sena, M.M. Screening method for the rapid detection of diethylene glycol in beer based on chemometrics and portable near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, L.; Grassi, S.; Pimentel, M.F.; Amigo, J.M. A single model to monitor multistep craft beer manufacturing using near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre-Tudo, J.L.; Nieuwoudt, H.; du Toit, W. Towards on-line monitoring of phenolic content in red wine grapes: A feasibility study. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxinol, M.I.; Martins, M.R.; Murta, G.C.; Mota Barroso, J.; Rato, A.E. Quality Assessment of Red Wine Grapes through NIR Spectroscopy. Agronomy 2022, 12, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, X.; Han, S.; Xie, A.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Xu, B.; Luo, D. Determination of ethyl octanoate in Chinese liquor using FT-NIR spectroscopy. Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, O.; Caldeira, I.; Roque, R.; Pedro, S.I.; Lourenço, S.; Canas, S. Screening of Different ageing technologies of wine spirit by application of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and volatile quantification. Processes 2020, 8, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanova, M.; Atanassova, S.; Atanasov, V.; Grozeva, N. Content of polyphenolic compounds and antioxidant potential of some Bulgarian red grape varieties and red wines, determined by HPLC, UV, and NIR spectroscopy. Agriculture 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, G.; Vazquez, M.; Vilanova, M. Ultraviolet–visible-near infrared spectroscopy for rapid determination of volatile compounds in white grapes during ripening. Ciênc. Téc. Vitiviníc. 2017, 32, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hanousek-Čiča, K.; Pezer, M.; Mrvčić, J.; Stanzer, D.; Cacic, J.; Jurak, V.; Krajnovic, M.; Kljusuric, J.G. Identification of phenolic and alcoholic compounds in wine spirits and their classification by use of multivariate analysis. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2019, 84, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.C.; Fuentes, S. Beer aroma and quality traits assessment using artificial intelligence. Fermentation 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Ren, J.C.; Tschannerl, J.; Zhao, H.M.; Harrison, B.; Jack, F. Nondestructive phenolic compounds measurement and origin discrimination of peated barley malt using near-infrared hyperspectral imagery and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5010715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Q.; Yin, C.L.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z.M. Rapid detection of three quality parameters and classification of wine based on Vis-NIR spectroscopy with wavelength selection by ACO and CARS algorithms. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 205, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.D.; Tongson, E.; Viejo, C.J. Machine learning modeling of wine sensory profiles and color of vertical vintages of pinot noir based on chemical fingerprinting, weather and management data. Sensors 2020, 20, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowska, K.; Tobiszewski, M. Green, simple analytical method for total biogenic amines content determination in wine using spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Detection Object | Instrument Type | Preprocessing Method | Band Range | Modeling Approach | Accuracies (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wine | NIR | - | 1596–2396 nm | ANN | R = 0.92 | [66] |
| Wine | NIR | PLS + S-G | 4000–650 cm−1 | DD-SIMCA | 100% | [67] |
| Wine | NIR | SGD + OFF | 1596–2396 nm | ANN | R = 0.95 | [68] |
| Wine | FT-NIR | SNV + MSC + PCA | 1000–2500 nm | RBFNN | 100% | [69] |
| Baijiu | FT-NIR | MSC | 6105–5446 cm−1 | PLS | R2 = 0.964 RMSEP = 0.023 g/L | [70] |
| Baijiu | NIR | SNV + MSC | 4833–6846 cm−1 | LSSVM | RP2 = 58.17% RMSEP = 0.2134 RPD = 44.72 | [71] |
| Beer | NIR | - | 1600–2396 nm | PLS + ANN | R2 = 0.99 | [72] |
| Beer | NIR | S-G | 1596–2396 nm | ANN | R = 0.99 | [73] |
| Chinese rice Wine | NIR | VN + S-G + SNV | 833–2500 nm | FA + PCA | R2 = 0.988 | [74] |
| Chinese rice Wine | FT-NIR | SNV | 10,828–3949 cm−1 | FA + PLS | RP2 = 98.3% RMSEP = 4.2% | [75] |
| Brandies | FT-NIR | PCA | 4000–7500 cm−1 | PCA + LDA | 100% | [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, W.; Jiang, Q.; Ma, T.; Tan, Y.; Yan, R.; Erihemu, E. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics for Liquor Product Quality Assessment: A Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172992
Qi W, Jiang Q, Ma T, Tan Y, Yan R, Erihemu E. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics for Liquor Product Quality Assessment: A Review. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172992
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Wenliang, Qingqing Jiang, Tianyu Ma, Yazhi Tan, Ruili Yan, and Erihemu Erihemu. 2025. "Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics for Liquor Product Quality Assessment: A Review" Foods 14, no. 17: 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172992
APA StyleQi, W., Jiang, Q., Ma, T., Tan, Y., Yan, R., & Erihemu, E. (2025). Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics for Liquor Product Quality Assessment: A Review. Foods, 14(17), 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172992