Sea Cucumber Polysaccharides Promote Gut–Liver Axis Health by Modulating Microbiota, Metabolism, and Gene Expression in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of SCP
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical Analysis of Lipid-Related Compounds in Serum
2.4. Histological Examination
2.5. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Gut Metabolites Analysis
2.7. Transcriptome Sequencing of Liver Tissue
2.8. Data Analysis of RNA-Seq and Bioinformatics Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of Bioactive Compounds in SCP
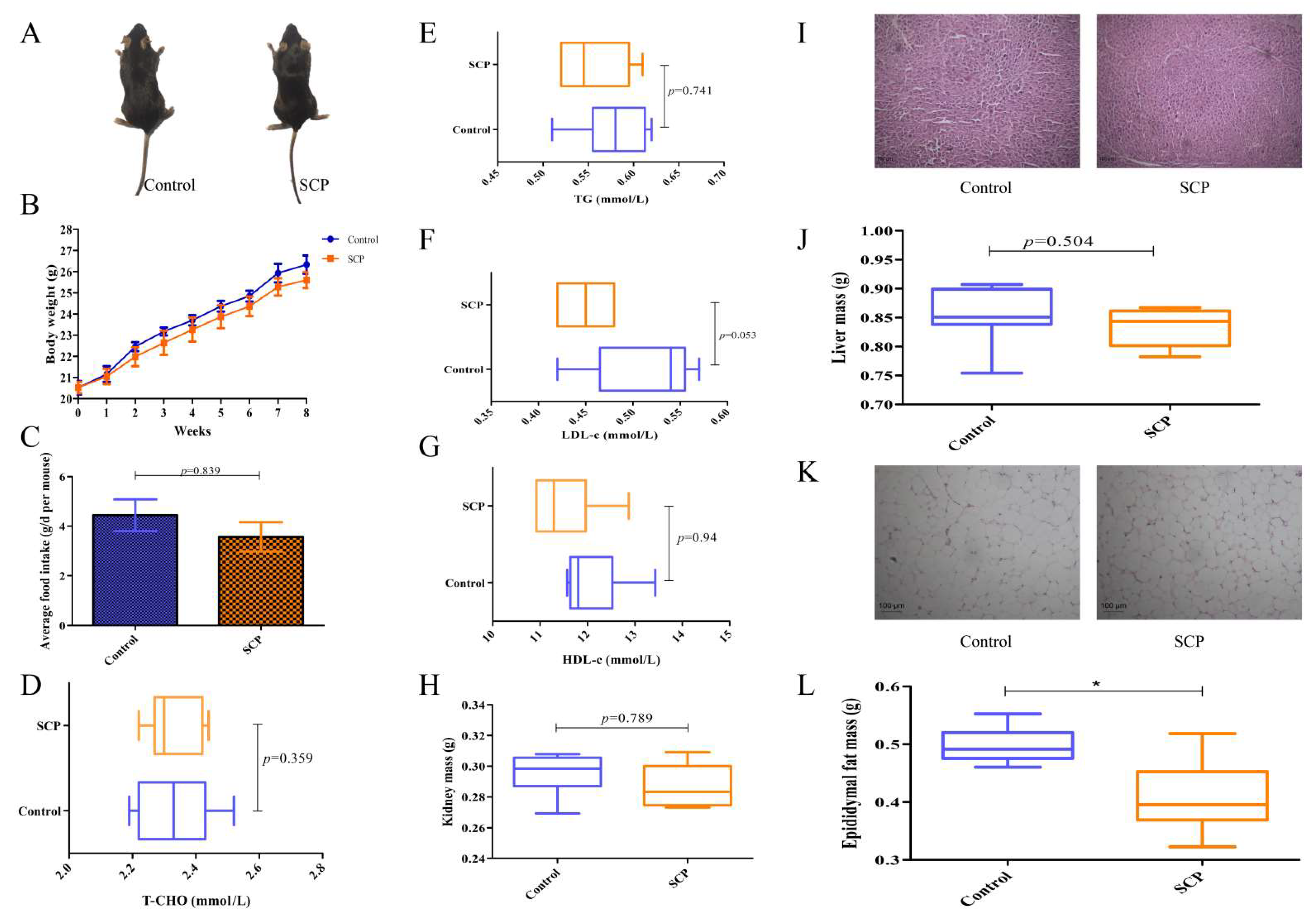
3.2. Impact of SCP on Body/Organ Mass, and Lipid Metabolism in Mice
3.3. Impact of SCP on Gut Microbiome
3.4. Impact of SCP on Metabolic Pathway Modifications
3.5. Impact of SCP on the Hepatic Transcriptome
3.6. Interrelationships Among Microbiome, Metabolome, and Transcriptome
3.6.1. Associations Between Body/Organ Weight Parameters, Lipid Metabolism-Related Indices, and Microbial Composition
3.6.2. Correlation Analysis Between Microbiome and Metabolome
3.6.3. Analysis of Correlations Between Gut Microbiota and Liver Transcriptomes
3.6.4. Combined Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Wang, D.; Gao, H.; Song, D.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Fu, J.; Feng, J.; Qiao, R.; et al. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2024; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, X.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yu, S.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q. Research progress on the interaction between sulfated polysaccharides from sea cucumber and gut microbiota with its regulation of glycolipid metabolism. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.E.; Hussein, N.A.; Rashad, M.M.; El-Sikaily, A.M.; Hassanin, A.E.-L.A.; El-Fakharany, E.M. Sea cucumber sulfated polysaccharides extract potentiates the anticancer effect of 5- fluorouracil on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 20255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Deng, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Jing, B.; Zhou, X. Structure-activity relationships and mechanisms of natural polysaccharides in modulating neurological disorders via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 367, 123960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rezaei, M.; Tabarsa, M.; Abdollahi, M. Expanding the pH-shift technique for sequential extraction of intact proteins and sulfated polysaccharide from fish heads: A novel biorefinery approach. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Guan, X.; Tong, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q. Sulfated polysaccharides from sea cucumber cooking liquid prevents obesity by modulating gut microbiome, transcriptome, and metabolite profiles in mice fed a high-fat diet. Foods 2024, 13, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gara-Ali, M.; Ben-Miled, H.; Mourali, D.; Zouaoui, E.; Ben Ouada, H.; Ben-Mahrez, K.; Hosni, K. Physicochemical characterization of sulfated polysaccharides from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. CIN61 and their antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, e03356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Dong, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, J. Beneficial effects of soluble dietary fiber from Dendrocalamus brandisii Munro shoots on high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice: Impact on liver, adipose tissue, and intestinal health. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2025, 7, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, S.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Z. ROS-mediated unfolded protein response activation drives hepatocyte apoptosis in mesaconitine-induced liver injury. Toxics 2025, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Sang, X.; Li, T.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, S. Structure, in vitro digestive characteristics and effect on gut microbiota of sea cucumber polysaccharide fermented by Bacillus subtilis Natto. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Nie, Q.; Chen, H.; Yin, J.; Chen, Y.; Nie, S. Polysaccharides from red kidney bean alleviating hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in type 2 diabetic rats via gut microbiota and lipid metabolic modulation. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Nie, S. Polysaccharides from small black soybean alleviating type 2 diabetes via modulation of gut microbiota and serum metabolism. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.-Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Suppl. 2), W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B.; Sang, X.; Zhao, Q. The nutritional function of active polysaccharides from marine animals: A review. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Jia, L.; Yang, F. Cordyceps militaris polysaccharide alleviates diabetic symptoms by regulating gut microbiota against TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Lan, Y. Rattan pepper polysaccharide regulates DSS-induced intestinal inflammation and depressive behavior through microbiota–gut–brain axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmaacol. Res. 2021, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Mei, C.; Han, L.; Lu, M.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, F.; Tang, X.; Huang, S. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations associated with lactose intolerance (LI): A case–control study and paired-sample study based on the American gut project (AGP). mSystems 2024, 9, e0083924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühlemann, M.C.; Hermes, B.M.; Bang, C.; Doms, S.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Thingholm, L.B.; Frost, F.; Degenhardt, F.; Wittig, M.; Kässens, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study in 8,956 German individuals identifies influence of ABO histo-blood groups on gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifuzzaman, M.; Won, T.H.; Li, T.-T.; Yano, H.; Digumarthi, S.; Heras, A.F.; Zhang, W.; Parkhurst, C.N.; Kashyap, S.; Jin, W.-B.; et al. Inulin fibre promotes microbiota-derived bile acids and type 2 inflammation. Nature 2022, 611, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Cole, C.G.; Coyne, M.J.; Lin, H.; Dylla, N.; Smith, R.C.; Pappas, T.E.; Townson, S.A.; Laliwala, N.; Waligurski, E.; et al. Comprehensive analyses of a large human gut Bacteroidales culture collection reveal species-and strain-level diversity and evolution. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppine, J.; Kaczmarczyk, A.; Petit, K.; Brochier, T.; Jenal, U.; Hallez, R.; Stock, A.M. Regulation of bacterial cell cycle progression by redundant phosphatases. J. Bactepiol. 2020, 202, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Seo, J.; Jung, Y.P.; Kim, H.; Kim, A.-J.; Kim, S.; Lim, K. Dietary arginine and citrulline supplements for cardiovascular health and athletic performance: A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Cai, J.; Pei, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, R.; Guo, X.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Gut microbial alterations in arginine metabolism determine bone mechanical adaptation. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1252–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N. Associations of caffeine and caffeine metabolites with sex hormones among 6–19-year-old children and adolescents. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; De Jesus, D.F.; Ju, C.-W.; Wei, J.B.; Hu, J.; DiStefano-Forti, A.; Tsuji, T.; Cero, C.; Männistö, V.; Manninen, S.M.; et al. m6A mRNA methylation in brown fat regulates systemic insulin sensitivity via an inter-organ prostaglandin signaling axis independent of UCP1. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 2207–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ran, Q.; Duan, Q.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Weng, L.; et al. 7-Dehydrocholesterol dictates ferroptosis sensitivity. Nature 2024, 626, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, H.-H.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.Y.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Ye, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, D.-T.; et al. Proto-oncogene Src links lipogenesis via lipin-1 to breast cancer malignancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-B.; Huang, Y.; Guo, X.-R.; Zhang, M.-Q.; Yuan, X.-S.; Zu, H.-B. DHCR24 reverses Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology and cognitive impairment via increasing hippocampal cholesterol levels in 5xFAD mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvinao-Quintero, D.L.; Sharp, G.C.; Sanderson, E.C.M.; Relton, C.L.; Elliott, H.R. Investigating causality in the association between DNA methylation and type 2 diabetes using bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomisation. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, O.A.; Ackerman, S.E.; Szwed, S.K.; Maganti, A.V.; Marchildon, F.; Huang, X.; Kramer, D.J.; Rosas-Villegas, A.; Gelfer, R.G.; Turner, L.E.; et al. Creatine-mediated crosstalk between adipocytes and cancer cells regulates obesity-driven breast cancer. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, N.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, W.; Ge, G. Pectolinarigenin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory response in Nrf2 and PPARa dependent manners. Phytomedicine 2023, 113, 154726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatua, B.; El-Kurdi, B.; Patel, K.; Rood, C.; Noel, P.; Crowell, M.; Yaron, J.R.; Kostenko, S.; Guerra, A.; Faigel, D.O.; et al. Adipose saturation reduces lipotoxic systemic inflammation and explains the obesity paradox. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Ericksen, R.E.; Escande-Beillard, N.; Lee, Q.Y.; Loh, A.; Denil, S.; Steckel, M.; Haegebarth, A.; Ho, T.S.W.; Chow, P.; et al. Metabolic pathway analyses identify proline biosynthesis pathway as a promoter of liver tumorigenesis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, A.; Patterson, L.F.S.; Öztürk, S.; Mohapatra, S.R.; Panitz, V.; Secker, P.F.; Pfänder, P.; Loth, S.; Salem, H.; Prentzell, M.T.; et al. IL4I1 is a metabolic immune checkpoint that activates the AHR and promotes tumor progression. Cell 2020, 182, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwelberger, H.G.; Feurle, J.; Houen, G. Mapping of the binding sites of human histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) monoclonal antibodies. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras-Cañellas, N.; Castells-Nobau, A.; de la Vega-Correa, L.; Latorre-Luque, J.; Motger-Albertí, A.; Arnoriaga-Rodriguez, M.; Garre-Olmo, J.; Zapata-Tona, C.; Coll-Martínez, C.; Ramió-Torrentà, L.; et al. Adipose tissue coregulates cognitive function. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Higgins, C.B.; Tica, S.; Adams, J.A.; Sun, J.; Kelly, S.C.; Zong, X.; Dietzen, D.J.; Pietka, T.; Ballentine, S.J.; et al. Hierarchical tricarboxylic acid cycle regulation by hepatocyte arginase 2 links the urea cycle to oxidative metabolism. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 2069–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.R.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, M.; Yiew, N.K.; Lutkewitte, A.J.; Singer, J.M.; McCommis, K.S.; Ferguson, D.; Liss, K.H.; Yoshino, J.; Renkemeyer, M.K.; et al. Silencing alanine transaminase 2 in diabetic liver attenuates hyperglycemia by reducing gluconeogenesis from amino acids. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase 1 as a potential target in human cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Zeng, S.; Ou, X.; Du, L.; Guo, Y. Gut microbiota changes in patients with hypertensive disorders and gestational diabetes in early pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.B.; Huang, H.; Ning, Y.; Xiao, J. Probiotics in the new era of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs): HMO utilization and beneficial effects of Bifidobacterium longumsubsp.infantisM-63 on infant health. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, H. Postbiotics from Lactobacillus Johnsonii activates gut innate immunity to mitigate alcohol-associated liver disease. Adv. Sci. 2024, 12, 2405781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, F.P.; Basso, C.; Antonini, G.; Perotti, M.; Li, N.; Sokolovska, A.; Neumann, J.; James, M.J.; Geiger, S.; Jin, W.; et al. Metabolic modulation of tumours with engineered bacteria for immunotherapy. Nature 2021, 598, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Xue, B.; Guo, W.; Huang, Z.; et al. Baicalin ameliorates multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced pulmonary inflammation in rat via arginine biosynthesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Azad, M.B.; Bäckhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Byndloss, M.; Chiu, C.Y.; Chu, H.; Dugas, L.R.; Elinav, E.; Gibbons, S.M.; et al. Clinical translation of microbiome research. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, X.; Xing, Z.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z. Sea Cucumber Polysaccharides Promote Gut–Liver Axis Health by Modulating Microbiota, Metabolism, and Gene Expression in Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172962
Sang X, Xing Z, Zhou B, Wang Y, Guan X, Wang F, Li Y, Zhao Q, Li Z. Sea Cucumber Polysaccharides Promote Gut–Liver Axis Health by Modulating Microbiota, Metabolism, and Gene Expression in Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172962
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Xue, Zhuobin Xing, Boqian Zhou, Yiting Wang, Xin Guan, Fuyi Wang, Ying Li, Qiancheng Zhao, and Zhibo Li. 2025. "Sea Cucumber Polysaccharides Promote Gut–Liver Axis Health by Modulating Microbiota, Metabolism, and Gene Expression in Mice" Foods 14, no. 17: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172962
APA StyleSang, X., Xing, Z., Zhou, B., Wang, Y., Guan, X., Wang, F., Li, Y., Zhao, Q., & Li, Z. (2025). Sea Cucumber Polysaccharides Promote Gut–Liver Axis Health by Modulating Microbiota, Metabolism, and Gene Expression in Mice. Foods, 14(17), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172962





