Effect of Plant Protein Ingredients at a Range of Pre-Hydration Levels on Technological Properties of Hybrid Beef Patties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characteristics of Plant Protein Ingredients
2.3. Preparation and Forming of Beef and Hybrid Meat Patties
2.4. Measurement of pH in Beef and Hybrid Patties
2.5. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.6. Rheology
2.7. Cooking Loss
2.8. Proximate Analyses and Water Activity of Raw and Cooked Patties
2.9. Moisture Retention, Fat Retention, and Water-Holding Capacity (WHC) of Patties
2.10. Colour Measurements
2.11. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition and Techno-Functional Attributes of Plant Proteins
3.2. pH
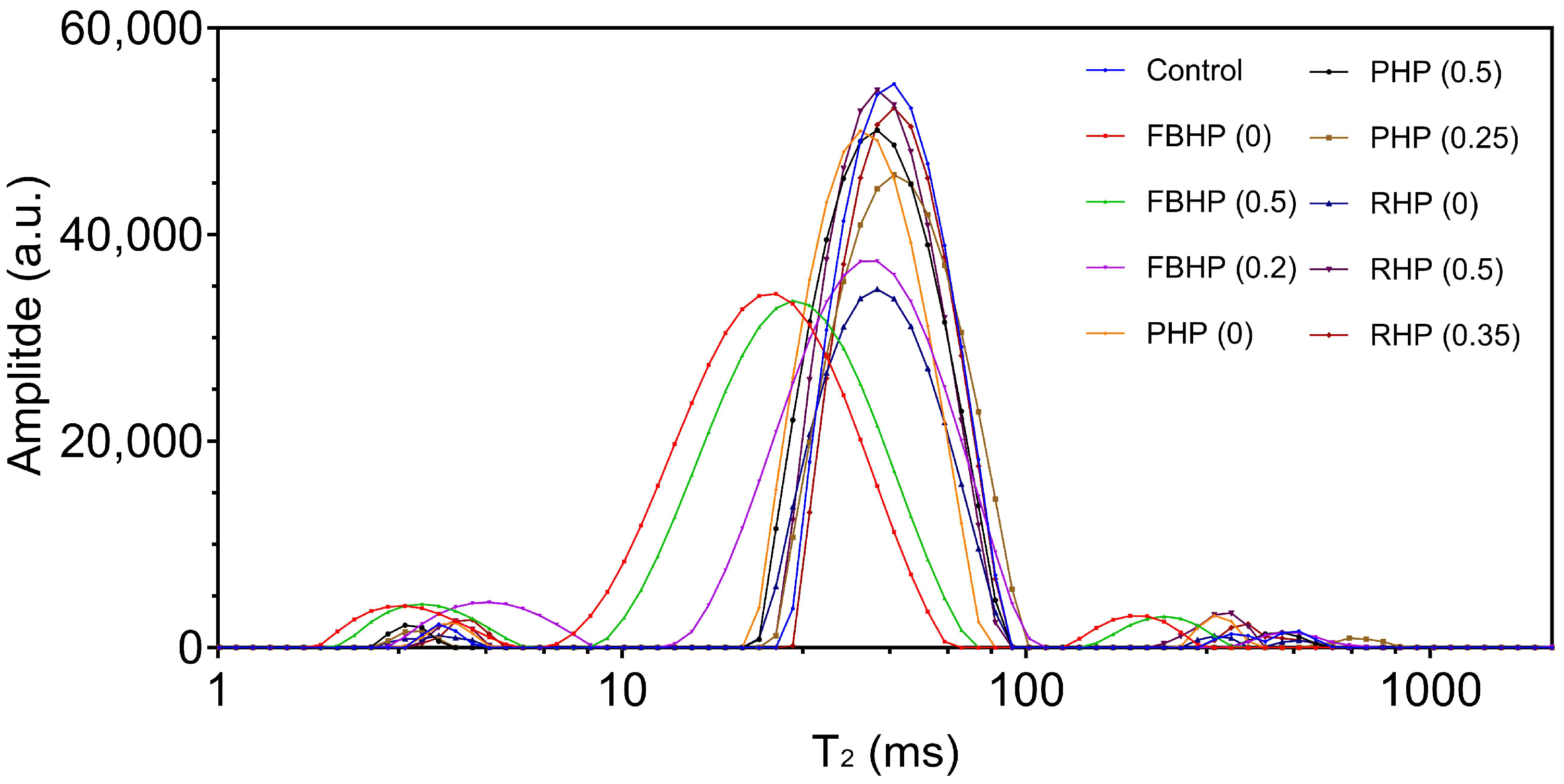
3.3. Water Mobility as Measured Using LF-NMR
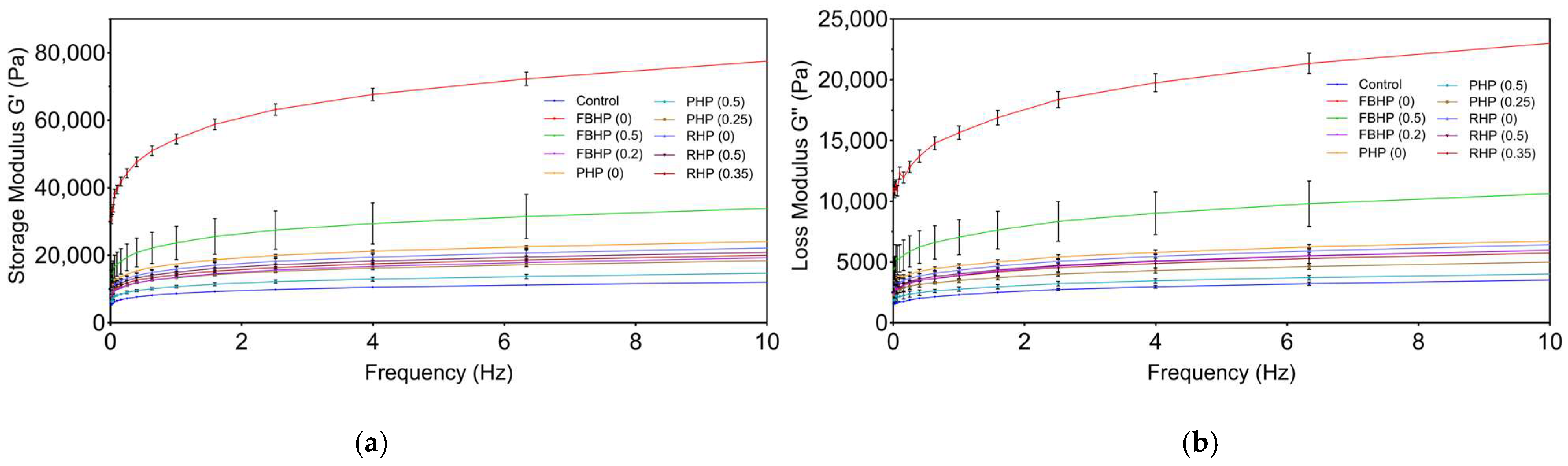
3.4. Rheological Properties
3.5. Cooking Loss
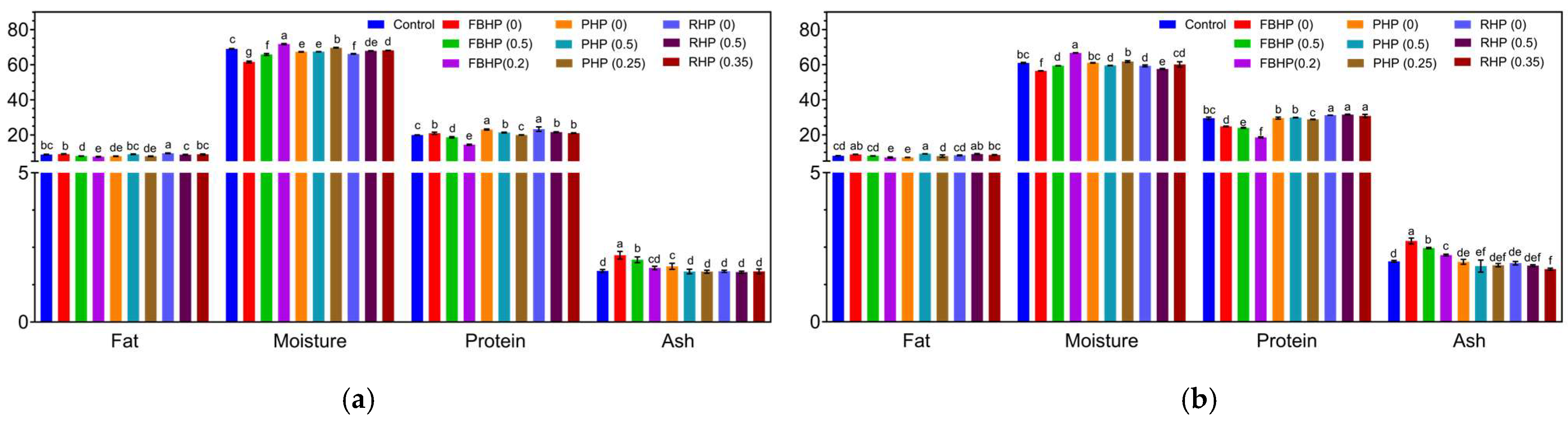
3.6. Proximate Analysis and aw of Raw and Cooked Patties
3.7. Water and Fat Retention and WHC
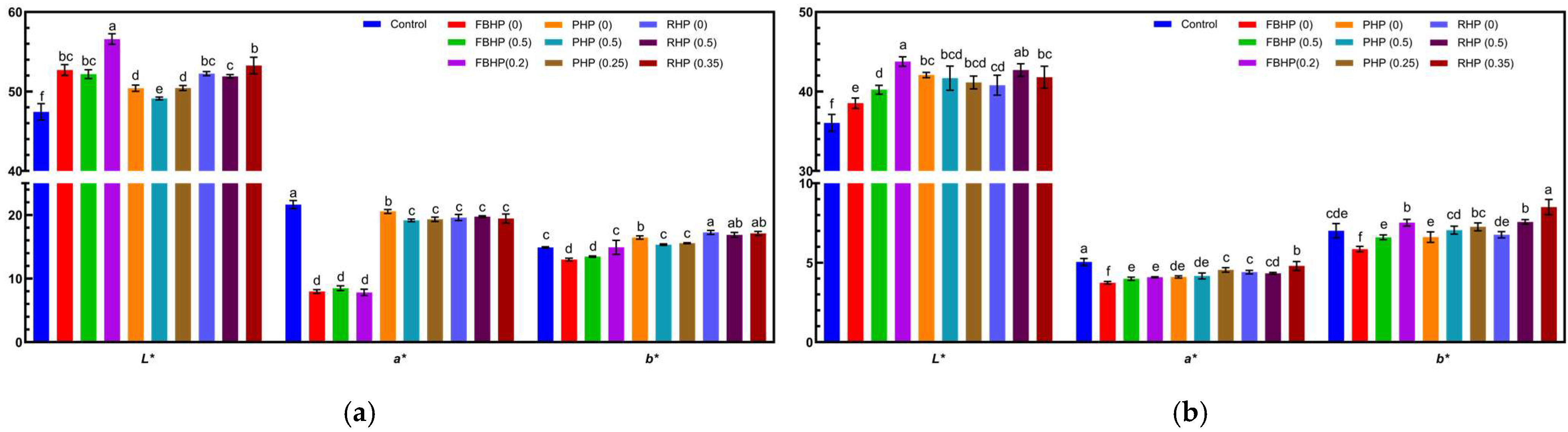
3.8. Colour Analysis
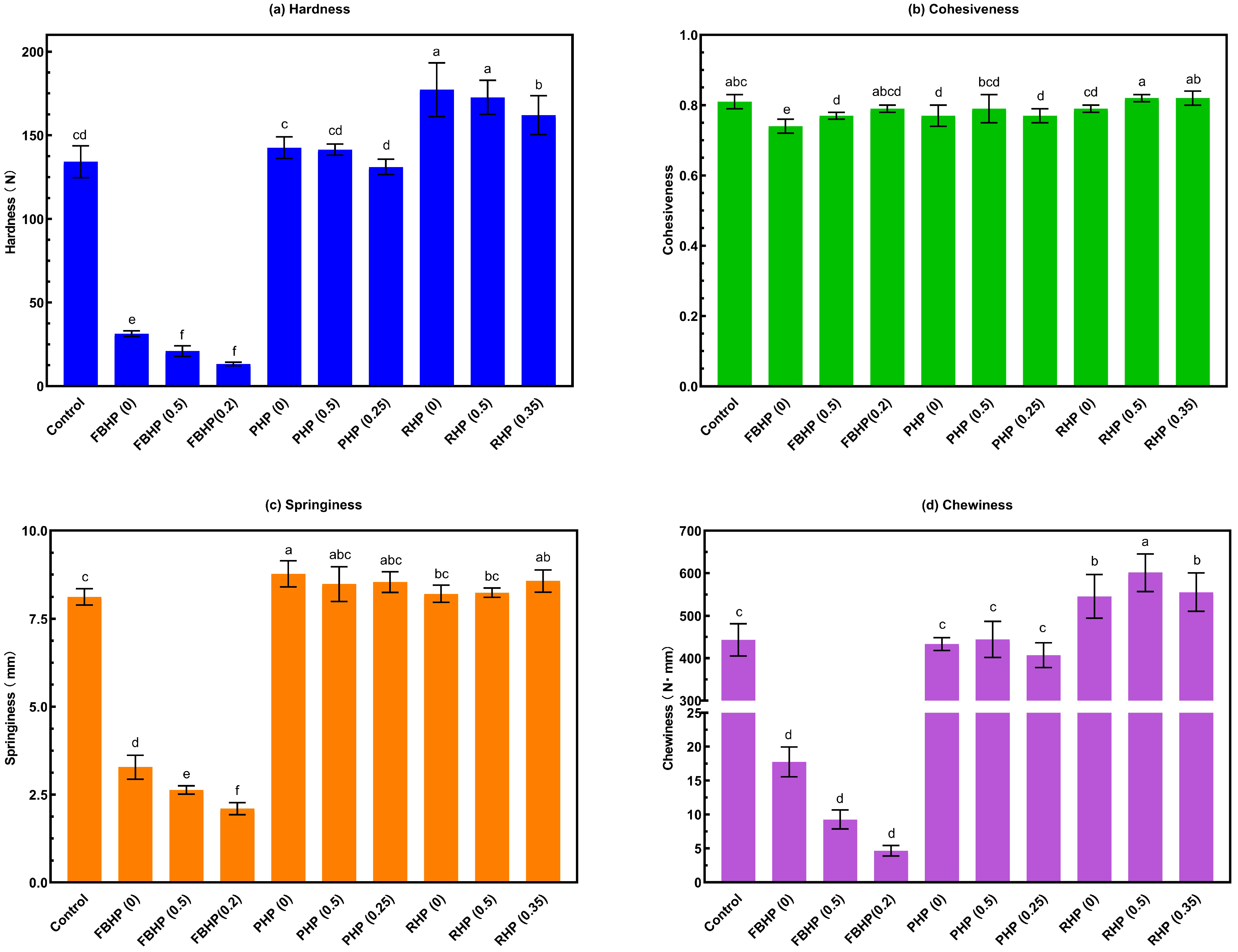
3.9. Texture Profile Analysis
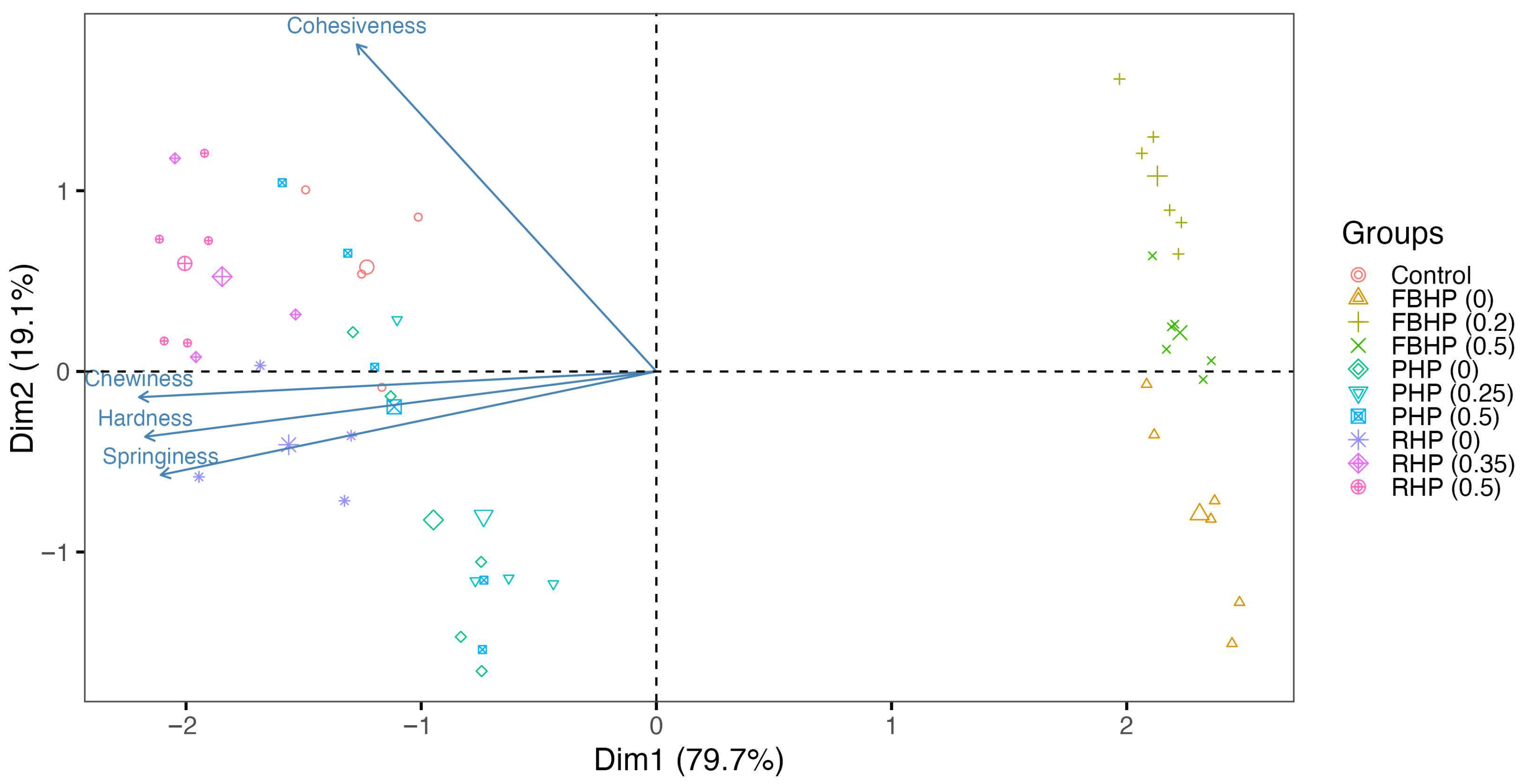
PCA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, M.d.; Rocha, D.A.V.F.d.; Bernardinelli, O.D.; Oliveira Júnior, F.D.; de Sousa, D.G.; Sabadini, E.; da Cunha, R.L.; Trindade, M.A.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Understanding the Performance of Plant Protein Concentrates as Partial Meat Substitutes in Hybrid Meat Emulsions. Foods 2022, 11, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, A.; Baune, M.-C.; Smetana, S.; Broucke, K.; Van Royen, G.; Weiss, J.; Hieke, S.; Heinz, V.; Terjung, N. Consumer preferences for meat blended with plant proteins—Empirical findings from Belgium. Futur. Foods 2021, 4, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Jaworska, S. Part Meat and Part Plant: Are Hybrid Meat Products Fad or Future? Foods 2020, 9, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, N.R.; Xiang, N.; Kaplan, D.L. Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, R.E.; Kim, B.F.; Goldman, S.E.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Biehl, E.M.B.; Bloem, M.W.; Neff, R.A.; Nachman, K.E. Considering Plant-Based Meat Substitutes and Cell-Based Meats: A Public Health and Food Systems Perspective. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richi, E.B.; Baumer, B.; Conrad, B.; Darioli, R.; Schmid, A.; Keller, U. Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2015, 85, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguglia, E.S.; Song, Z.; Kerry, J.P.; O’sullivan, M.G.; Hamill, R.M. Addressing Clean Label Trends in Commercial Meat Processing: Strategies, Challenges and Insights from Consumer Perspectives. Foods 2023, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asioli, D.; Banovic, M.; Barone, A.M.; Grasso, S.; Nayga, R.M., Jr. European consumers’ valuation for hybrid meat: Does information matter? Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2023, 45, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdiarmid, J.I.; Douglas, F.; Campbell, J. Eating like there’s no tomorrow: Public awareness of the environmental impact of food and reluctance to eat less meat as part of a sustainable diet. Appetite 2016, 96, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrat-Melin, B.; Dam, S. Textural and Consumer-Aided Characterisation and Acceptability of a Hybrid Meat and Plant-Based Burger Patty. Foods 2023, 12, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhanan, R.; Huerta-Leidenz, N.; Ibañez, F.C.; Beriain, M.J. High-pressure processing and sous-vide cooking effects on physicochemical properties of meat-based, plant-based and hybrid patties. LWT 2023, 173, 114273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming-Min, W.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R. Physicochemical, rheological and microstructural properties of chicken meat emulsion with the addition of Chinese yam (Dioscorea polystachya) and arrowroot (Maranta arundinacea) as meat substitutes. Futur. Foods 2023, 7, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Rosli, W.I.; Solihah, M.A.; Aishah, M.; Nik Fakurudin, N.A.; Mohsin, S.S.J. Colour, textural properties, cooking characteristics and fibre content of chicken patty added with oyster mushroom (Pleurotus sajor-caju). Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 612–618. [Google Scholar]
- Baune, M.-C.; Jeske, A.-L.; Profeta, A.; Smetana, S.; Broucke, K.; Van Royen, G.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; Terjung, N. Effect of plant protein extrudates on hybrid meatballs—Changes in nutritional composition and sustainability. Futur. Foods 2021, 4, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.; Hutchings, S.C.; Warner, R.D.; Fang, Z. Effects of incorporating roasted lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) flour on the physicochemical and sensory attributes of beef sausage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, X.; Fang, Z. Effects of incorporation of hempseed meal on the quality attributes of chicken sausage. Futur. Foods 2022, 6, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, M.H.; Meera, M.S.; Bhaskar, N.; Modi, V.K. Partial and total replacement of meat by plant-based proteins in chicken sausage: Evaluation of mechanical, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Smith, G.; Bowers, S.; Ajayi, O.M.; Swainson, M. Effect of texturised soy protein and yeast on the instrumental and sensory quality of hybrid beef meatballs. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugreet, S.; Kerry, J.P.; Botineştean, C.; Allen, P.; Hamill, R.M. Development of novel fortified beef patties with added functional protein ingredients for the elderly. Meat Sci. 2016, 122, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, S.L.; McSweeney, M.B. Characterizing the properties of hybrid meat burgers made with pulses and chicken. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argel, N.S.; Ranalli, N.; Califano, A.N.; Andrés, S.C. Influence of partial pork meat replacement by pulse flour on physicochemical and sensory characteristics of low-fat burgers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3932–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.; Orfila, C.; Ho, P.; Maycock, J. Vicia faba: A cheap and sustainable source of protein and its application in beef products. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, E137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Garza, A.E.; Zayas, J.F. EFFECT of WHEAT GERM PROTEIN FLOUR ON the QUALITY CHARACTERISTICS of BEEF PATTIES COOKED ON A GRIDDLE1. J. Food Process. Preserv. 1995, 19, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broucke, K.; Van Poucke, C.; Duquenne, B.; De Witte, B.; Baune, M.-C.; Lammers, V.; Terjung, N.; Ebert, S.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; et al. Ability of (extruded) pea protein products to partially replace pork meat in emulsified cooked sausages. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Jiang, J. Texture, microstructure, and in vitro digestion of hybrid meat gel-type sausages formulated with functionalized pea protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau-Côté, D.; Achouri, A.; Karboune, S.; L’hocine, L. Faba Bean: An Untapped Source of Quality Plant Proteins and Bioactives. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Lee, D.-W. Advancements in plant based meat analogs enhancing sensory and nutritional attributes. npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langton, M.; Ehsanzamir, S.; Karkehabadi, S.; Feng, X.; Johansson, M.; Johansson, D.P. Gelation of faba bean proteins—Effect of extraction method, pH and NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, physicochemical properties of pea protein and its application in functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthakumar, P.; Klepacka, J.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Dhull, S.B.; Najda, A. The Current Situation of Pea Protein and Its Application in the Food Industry. Molecules 2022, 27, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, G.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Fogarasi, M.; Fogarasi, S. A Narrative Review on Rice Proteins: Current Scenario and Food Industrial Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasundara, J.P.; Nickerson, M.T.; Stone, A.; Karaca, A.C. Chapter 5—Hydrodynamic properties I: Protein–water interactions, solubility, water adsorption, and wettability. In Functionality of Plant Proteins; Wanasundara, J.P.D., Schmitt, C., Lamsal, B.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, J.; Alavi, S. Use of hydration properties of proteins to understand their functionality and tailor texture of extruded plant-based meat analogues. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.P.; Vergeldt, F.J.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Water-binding capacity of protein-rich particles and their pellets. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, A.C.; Luning, P.A.; Weijzen, P.; Engels, W.; Kok, F.J.; De Graaf, C. Replacement of meat by meat substitutes. A survey on person-and product-related factors in consumer acceptance. Appetite 2011, 56, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Hartmann, C.; Siegrist, M. Consumers’ associations, perceptions and acceptance of meat and plant-based meat alternatives. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 87, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.S.; Zhu, X.; Hannon, S.; Mullins, E.; Alves, S.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Exploring Osborne fractionation and laboratory/pilot scale technologies (conventional extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, high-pressure processing and hydrodynamic cavitation) for protein extraction from faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 89, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. AOAC (2005) Solids (Total) and Moisture in Flour. 2005. Available online: http://www.aoacofficialmethod.org/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1&products_id=239 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Leffler, T.P.; Moser, C.R.; McManus, B.J.; Urh, J.J.; Keeton, J.T.; Claflin, A. Determination of Moisture and Fat in Meats by Microwave and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analysis: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Brink, M.; Sebranek, J.G. Combustion method for determination of crude protein in meat and meat products: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 1993, 76, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A., AOAC 920.153 Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) Official Method 920.153. Ash of Meat. Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC International, 1920. Available online: http://www.aoacofficialmethod.org/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1&products_id=1694 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- A. AOAC official Method 978.18, Water Activity of Canned Vegetables. Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC International, 1978. Available online: http://www.aoacofficialmethod.org/index.php?main_page=product_info&products_id=1970 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Malik, M.A.; Saini, C.S. Polyphenol removal from sunflower seed and kernel: Effect on functional and rheological properties of protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.; Álvarez, C.; Hamill, R.M.; O’Neill, E.; Mullen, A.M. Influence of meat sample geometry on dehydration dynamics during dry-aging of beef. Meat Sci. 2023, 202, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, C.K.; Allen, P.; Duggan, E.; Arimi, J.M.; Casey, E.; Duane, G.; Lyng, J.G. The effect of salt and fibre direction on water dynamics, distribution and mobility in pork muscle: A low field NMR study. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Meat Science Association. Research Guidelines for Cookery, Sensory Evaluation, and Instrumental Tenderness Measurements of Meat; American Meat Science Association: Savoy, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akwetey, W.; Knipe, C. Sensory attributes and texture profile of beef burgers with gari. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Kong, B.; Sun, F.; Cao, C.; Gong, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Feasibility of Tenebrio molitor larvae protein to partially replace lean meat in the processing of hybrid frankfurters: Perspectives on quality profiles and in vitro digestibility. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanizadeh, N.; Ghiasi-Esfahani, H. Qualitative improvement of low meat beef burger using Aloe vera. Meat Sci. 2015, 99, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.C.; Cho, H.; Hong, J.J.; Ryu, R.K.; Hwang, K.T.; Regenstein, J.M. Physicochemical and organoleptic characteristics of seasoned beef patties with added glutinous rice flour. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavelu, K.P.; Tiwari, B.; Kerry, J.P.; Álvarez, C. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Ultrasound-Treated Apple Pomace and Coffee Silverskin Powders as Phosphate Replacers in Irish Breakfast Sausage Formulations. Foods 2022, 11, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chiu, E.; Huang, J. Color and Gel-forming Properties of Horse Mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) as Related to Washing Conditions. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M.C. Texture profile analysis. Food Technol. 1978, 32, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kiosseoglou, V.; Paraskevopoulou, A. 3—Functional and physicochemical properties of pulse proteins. In Pulse Foods; Tiwari, B.K., Gowen, A., McKenna, B., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 57–90. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib, A.; Sahar, A.; Sameen, A.; Saleem, A.; Tahir, A.T. Use of pea and rice protein isolates as source of meat extenders in the development of chicken nuggets. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L. Reconstituted rice protein: The raw materials, techniques and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-K.; Jiang, H.; Yu, X.; Jane, J.-l. Physicochemical and functional properties of whole legume flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, M.H.; Liu, J.; Fitzsimons, S.M.; Fenelon, M.A.; Murphy, E.G. Determining the influence of fava bean pre-processing on extractability and functional quality of protein isolates. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.K.; Greis, M.; Lu, J.; Nolden, A.A.; McClements, D.J.; Kinchla, A.J. Functional Performance of Plant Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munialo, C.D.; Baeghbali, V.; Acharya, P. Plant-Based Alternatives to Meat Products. Foods 2025, 14, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, B.; Wea, A.; Andriati, N. Physicochemical, sensory attributes and protein profile by SDS-PAGE of beef sausage substituted with texturized vegetable protein. Food Res. 2017, 2, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Characteristics of Beef Patties Substituted by Different Levels of Textured Vegetable Protein and Taste Traits Assessed by Electronic Tongue System. Foods 2021, 10, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.J.; Dunay, A.; Battay, M.; Illés, C.B.; Bittsánszky, A.; Süth, M. Microbial Spoilage of Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Barbut, S. Hybrid meat batter system: Effects of plant proteins (pea, brown rice, faba bean) and concentrations (3–12%) on texture, microstructure, rheology, water binding, and color. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Cai, Q.; Huang, Q.; Lu, X. Application of LF-NMR to characterize the roles of different emulsifiers in 3D printed emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R. Texturization of Pea Protein Isolates Using High Moisture Extrusion Cooking. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Biduski, B.; Maçãs, M.; Vahedikia, N.; O’connor, P.M.; Hussey, K.; Simpson, J.C.; Mysior, M.M.; Gallagher, E. Dough rheology and internal structure of bread produced with wheat flour partially substituted by buckwheat flour: A step towards enhancing nutritional value. Food Struct. 2024, 39, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Shen, X.; Tang, X. Effect of low temperature extrusion-modified potato starch addition on properties of whole wheat dough and texture of whole wheat youtiao. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Rasco, B.A.; Tang, J.; Niu, L.; Lai, K.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Y. Effects of Freshness on the Cook Loss and Shrinkage of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) Fillets Following Pasteurization. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, G.; Zhou, H.; McClements, D.J. Impact of cooking method on properties of beef and plant-based burgers: Appearance, texture, thermal properties, and shrinkage. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 9, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hong, S.; Du, Z.; Chao, M.; O’Quinn, T.; Li, Y. Effect of adding modified pea protein as functional extender on the physical and sensory properties of beef patties. LWT 2022, 154, 112774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanyar, F.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S. Effects of replacing soy protein and bread crumb with quinoa and buckwheat flour in functional beef burger formulation. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasiewicz, K.; Szymanska, I.; Opat, D.; Hac-Szymanczuk, E. Development and Characterization of Hybrid Burgers Made from Pork and Multi-Ingredient Plant Mixtures and Protected with Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, J.; Joswig, G.; Böhnlein, C.; Fiedler, G.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Microbiological status of vegan ground meat products from German retail. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2024, 19, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Hernández, C.; Serna-Saldívar, S.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Vegetable and Cereal Proteins as Potential Sources of Novel Food Ingredients. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 53, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.O.; O’grady, M.N.; O’sullivan, M.G.; Hamill, R.M.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Kerry, J.P. Acceptable Inclusion Levels for Selected Brown and Red Irish Seaweed Species in Pork Sausages. Foods 2022, 11, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Rizawi, J.A.; Srivastava, P.K. Effect of soy protein isolate incorporation on quality characteristics and shelf-life of buffalo meat emulsion sausage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Hernán, A.; Salvador, A.; Belloch, C. Influence of soaking and solvent extraction for deodorization of texturized pea protein isolate on the formulation and properties of hybrid meat patties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Trindade, H. Rice antioxidants: Phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, tocopherols, tocotrienols, γ-oryzanol, and phytic acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.; Tarrega, A.; Hewson, L.; Foster, T. Consumer-orientated development of hybrid beef burger and sausage analogues. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baune, M.C.; Broucke, K.; Ebert, S.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; Enneking, U.; Profeta, A.; Terjung, N.; Heinz, V. Meat hybrids–An assessment of sensorial aspects, consumer acceptance, and nutritional properties. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serdaroglu, M. The characteristics of beef patties containing different levels of fat and oat flour. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.V.; Shamasundar, B.A. Texture Profile Analysis and Functional Properties of Gelatin from the Skin of Three Species of Fresh Water Fish. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Al-Mahrouqi, A.I. Instrumental texture profile analysis of gelatin gel extracted from grouper skin and commercial (bovine and porcine) gelatin gels. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60 (Suppl. S7), 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, R.A.; Darwin, E.C.; Medina, V.A.P.; Levenston, M.E.; Pierre, S.R.S.; Kuhl, E. Texture profile analysis and rheology of plant-based and animal meat. Food Res. Int. 2025, 205, 115876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, W.; Aalhus, J.; Best, D.; Dugan, M.; Jeremiah, L. Relationship of texture profile analysis and Warner-Bratzler shear force with sensory characteristics of beef rib steaks. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Overview of Texture Profile Analysis. 2015 October 2023. Available online: https://www.texturetechnologies.com/resources/texture-profile-analysis (accessed on 3 July 2025).
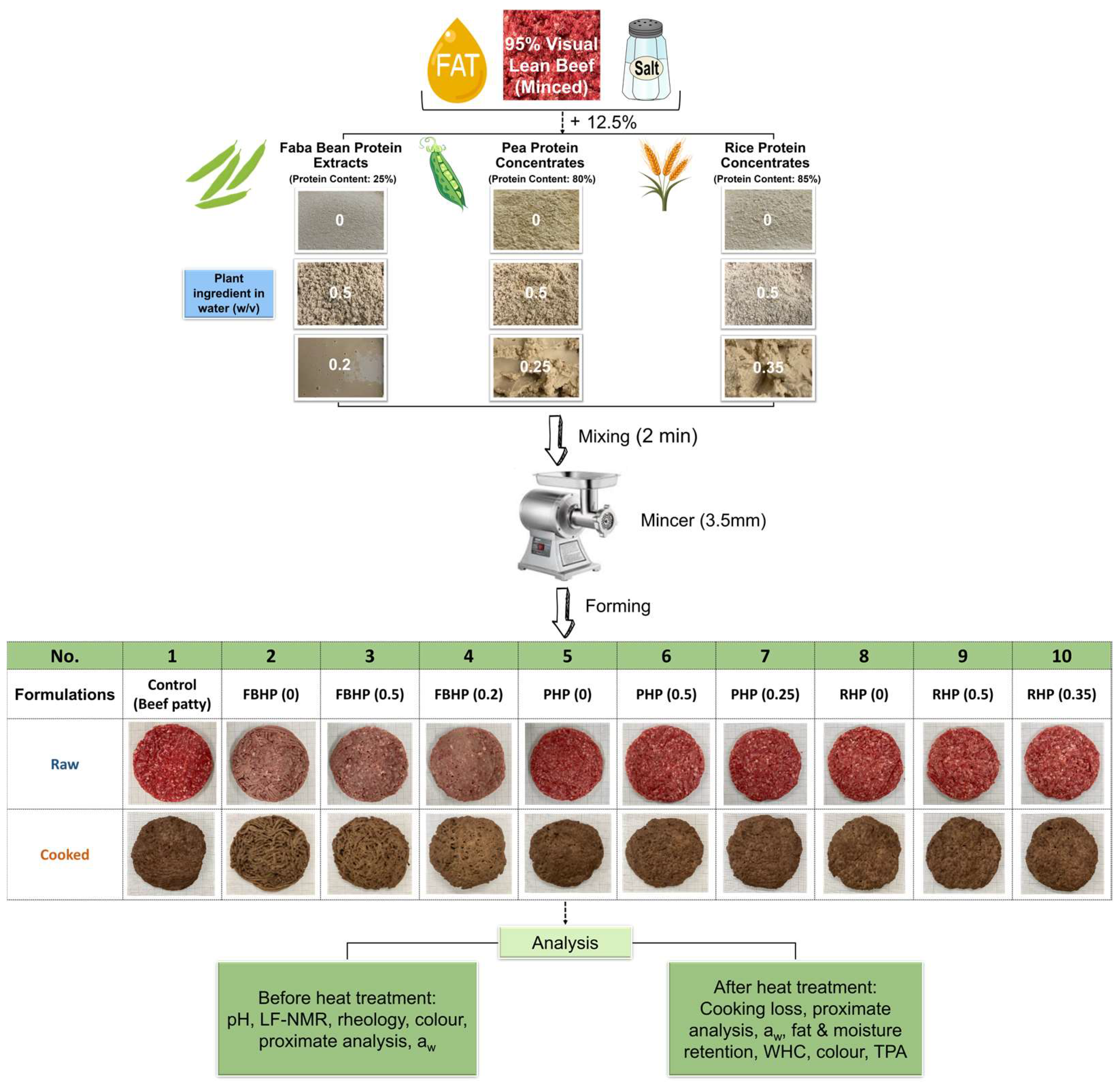
| Formulation No. | Formulation Code | Formulation | Plant Ingredient | Pre-Hydration Rate of Plant Protein Ingredient in Water (w/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Control | Beef patty | NA | NA |
| 2 | FBHP (0) | Faba bean hybrid patty with dry FBP (no pre-hydration) | FBP | 0 |
| 3 | FBHP (0.5) | Faba bean hybrid patty with hydrated FBP | FBP | 0.5 |
| 4 | FBHP (0.2) | Faba bean hybrid patty with hydrated FBP | FBP | 0.2 |
| 5 | PHP (0) | Pea hybrid patty with dry PP (no pre-hydration) | PP | 0 |
| 6 | PHP (0.5) | Pea hybrid patty with hydrated PP | PP | 0.5 |
| 7 | PHP (0.25) | Pea hybrid patty with hydrated PP | PP | 0.25 |
| 8 | RHP (0) | Rice hybrid patty with dry RP (no pre-hydration) | RP | 0 |
| 9 | RHP (0.5) | Rice hybrid patty with hydrated RP | RP | 0.5 |
| 10 | RHP (0.35) | Rice hybrid patty with hydrated RP | RP | 0.35 |
| Properties | Faba Bean | Pea | Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 0.94 ± 0.30 c | 4.61 ± 0.17 a | 1.81 ± 0.09 b |
| Moisture | 8.29 ± 0.08 a | 8.02 ± 0.04 b | 3.46 ± 0.07 c |
| Protein | 24.70 ± 0.14 c | 80.94 ± 0.13 a | 81.14 ± 0.03 a |
| Ash | 5.54 ± 0.30 a | 3.64 ± 0.05 b | 1.09 ± 0.03 c |
| Carbohydrate | 60.53 ± 0.21 a | 2.79 ± 0.34 c | 12.51 ± 0.17 b |
| aw | 0.46 ± 0.00 b | 0.48 ± 0.00 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 c |
| pH | 4.90 ± 0.04 c | 7.52 ± 0.01 a | 6.74 ± 0.11 b |
| WBC | 3.69 ± 0.06 b | 4.70 ± 0.04 a | 1.73 ± 0.08 c |
| OBC | 2.34 ± 0.09 a | 0.99 ± 0.06 c | 1.24 ± 0.04 b |
| Beef/Hybrid Patties | Cooking Loss (%) | Moisture Retention (%) | Fat Retention (%) | WHC (%) | pH | aw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 30.20 ± 3.39 a | 42.56 ± 0.24 fg | 61.46 ± 2.19 e | 55.62 ± 4.33 de | 6.04 ± 0.16 abc | 0.975 ± 0.001 c |
| FBHP (0) | 13.28 ± 3.14 e | 48.95 ± 0.11 b | 81.94 ± 2.23 a | 78.02 ± 0.63 a | 5.55 ± 0.08 d | 0.975 ± 0.001 c |
| FBHP (0.5) | 18.95 ± 3.37 d | 48.13 ± 0.06 c | 83.61 ± 1.12 a | 74.61 ± 2.58 a | 5.38 ± 0.04 e | 0.980 ± 0.001 ab |
| FBHP (0.2) | 19.29 ± 0.01 d | 53.82 ± 0.14 a | 75.85 ± 5.31 b | 57.62 ± 1.56 de | 5.36 ± 0.04 e | 0.979 ± 0.001 ab |
| PHP (0) | 23.34 ± 1.68 cd | 46.80 ± 0.11 d | 68.36 ± 1.43 cd | 64.39 ± 3.77 b | 6.12 ± 0.04 ab | 0.979 ± 0.002 b |
| PHP (0.5) | 24.32 ± 0.32 bc | 43.47 ± 0.08 e | 76.58 ± 0.25 b | 58.75 ± 1.54 cd | 6.15 ± 0.06 a | 0.979 ± 0.002 b |
| PHP (0.25) | 27.51 ± 0.61 abc | 46.78 ± 0.38 d | 72.26 ± 5.78 bc | 59.57 ± 1.57 cd | 6.12 ± 0.05 abc | 0.982 ± 0.001 a |
| RHP (0) | 26.74 ± 0.59 abc | 42.99 ± 0.39 ef | 63.24 ± 2.52 de | 62.45 ± 1.76 bc | 6.02 ± 0.06 abc | 0.978 ± 0.000 b |
| RHP (0.5) | 28.54 ± 0.65 ab | 42.18 ± 0.19 g | 73.47 ± 2.53 bc | 53.89 ± 0.57 f | 5.94 ± 0.06 c | 0.979 ± 0.002 ab |
| RHP (0.35) | 26.99 ± 1.82 abc | 42.98 ± 1.09 ef | 68.66 ± 1.21 cd | 51.48 ± 0.73 f | 5.97 ± 0.04 bc | 0.979 ± 0.002 ab |
| Beef/Hybrid Patties | T2b (ms) | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) | P2b (%) | P21 (%) | P22 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.64 ± 0.20 c | 47.12 ± 0.00 a | 422.74 ± 87.17 b | 1.22 ± 0.24 ef | 97.08 ± 0.84 abc | 1.70 ± 0.71 bc |
| FBHP (0) | 2.90 ± 0.00 d | 24.04 ± 0.00 e | 187.02 ± 10.54 e | 6.19 ± 0.25 b | 90.41 ± 0.43 ef | 3.41 ± 0.21 a |
| FBHP (0.5) | 3.10 ± 0.17 d | 26.47 ± 0.00 d | 226.65 ± 12.77 de | 6.44 ± 0.26 b | 89.99 ± 0.57 f | 3.56 ± 0.76 a |
| FBHP (0.2) | 4.55 ± 0.25 a | 41.49 ± 2.26 b | 458.62 ± 25.03 b | 7.18 ± 0.24 a | 91.41 ± 0.32 e | 1.41 ± 0.31 c |
| PHP (0) | 3.75 ± 0.20 bc | 38.88 ± 0.00 c | 292.57 ± 0.00 cd | 1.68 ± 0.08 cd | 96.41 ± 0.32 cd | 1.90 ± 0.37 bc |
| PHP (0.5) | 3.00 ± 0.17 d | 42.80 ± 0.00 b | 431.04 ± 41.38 b | 1.33 ± 0.10 def | 97.60 ± 0.28 ab | 1.08 ± 0.19 c |
| PHP (0.25) | 3.10 ± 0.17 d | 47.12 ± 0.00 a | 654.34 ± 70.15 a | 1.08 ± 0.07 f | 98.17 ± 0.07 a | 0.74 ± 0.05 c |
| RHP (0) | 3.32 ± 0.50 cd | 42.80 ± 0.00 b | 428.81 ± 120.38 b | 1.56 ± 0.17 cde | 97.03 ± 0.72 bc | 1.42 ± 0.55 c |
| RHP (0.5) | 3.75 ± 0.20 bc | 42.80 ± 0.00 b | 312.24 ± 17.04 cd | 1.55 ± 0.25 cde | 95.75 ± 1.18 d | 2.70 ± 1.43 ab |
| RHP (0.35) | 4.13 ± 0.23 b | 47.12 ± 0.00 a | 368.79 ± 55.21 bc | 1.87 ± 0.25 c | 96.25 ± 0.61 cd | 1.88 ± 0.36 bc |
| Beef/Hybrid Patties | Redness Index (RI) | Browning Index (BI) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.45 ± 0.05 a | 31.55 ± 2.62 a |
| FBHP (0) | 0.61 ± 0.03 d | 23.28 ± 0.89 c |
| FBHP (0.5) | 0.63 ± 0.03 d | 24.85 ± 0.58 bc |
| FBHP (0.2) | 0.53 ± 0.01 e | 25.36 ± 0.95 bc |
| PHP (0) | 1.25 ± 0.01 b | 23.90 ± 1.01 c |
| PHP (0.5) | 1.25 ± 0.01 b | 25.55 ± 1.81 bc |
| PHP (0.25) | 1.24 ± 0.02 b | 27.20 ± 1.58 b |
| RHP (0) | 1.14 ± 0.01 c | 25.73 ± 1.44 bc |
| RHP (0.5) | 1.17 ± 0.03 c | 26.59 ± 0.56 b |
| RHP (0.35) | 1.14 ± 0.05 c | 30.85 ± 2.92 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Kerry, J.P.; Das, R.S.; Tiwari, B.K.; Santos, A.; Hamill, R.M. Effect of Plant Protein Ingredients at a Range of Pre-Hydration Levels on Technological Properties of Hybrid Beef Patties. Foods 2025, 14, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172957
Song Z, Kerry JP, Das RS, Tiwari BK, Santos A, Hamill RM. Effect of Plant Protein Ingredients at a Range of Pre-Hydration Levels on Technological Properties of Hybrid Beef Patties. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172957
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zuo, Joseph P. Kerry, Rahel Suchintita Das, Brijesh K. Tiwari, Antonia Santos, and Ruth M. Hamill. 2025. "Effect of Plant Protein Ingredients at a Range of Pre-Hydration Levels on Technological Properties of Hybrid Beef Patties" Foods 14, no. 17: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172957
APA StyleSong, Z., Kerry, J. P., Das, R. S., Tiwari, B. K., Santos, A., & Hamill, R. M. (2025). Effect of Plant Protein Ingredients at a Range of Pre-Hydration Levels on Technological Properties of Hybrid Beef Patties. Foods, 14(17), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172957







