Qualitative and Antioxidant Evaluation of High-Moisture Plant-Based Meat Analogs Obtained by Extrusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Manufacture of High Moisture Meat Analog
2.3.1. Technical Properties of Extruder
2.3.2. Production of High Moisture Meat Analogs
2.4. Meat Analogs Characteristics
2.4.1. Physicochemical Analysis of Meat Analogs
2.4.2. Determination of Meat Analogs pH
2.4.3. Water/Oil Holding Capacity (WHC/OHC)
2.4.4. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.4.5. CIELab Color Parameters
2.4.6. Digestibility of Proteins
2.4.7. Antioxidant Activity (AA)
2.4.8. AA In Vitro Digestion Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Physicochemical Quality Parameters and AA of Meat Analogs
3.2. Texture Profile Analysis of Meat Analogs
3.3. Color Measurement of Meat Analogs
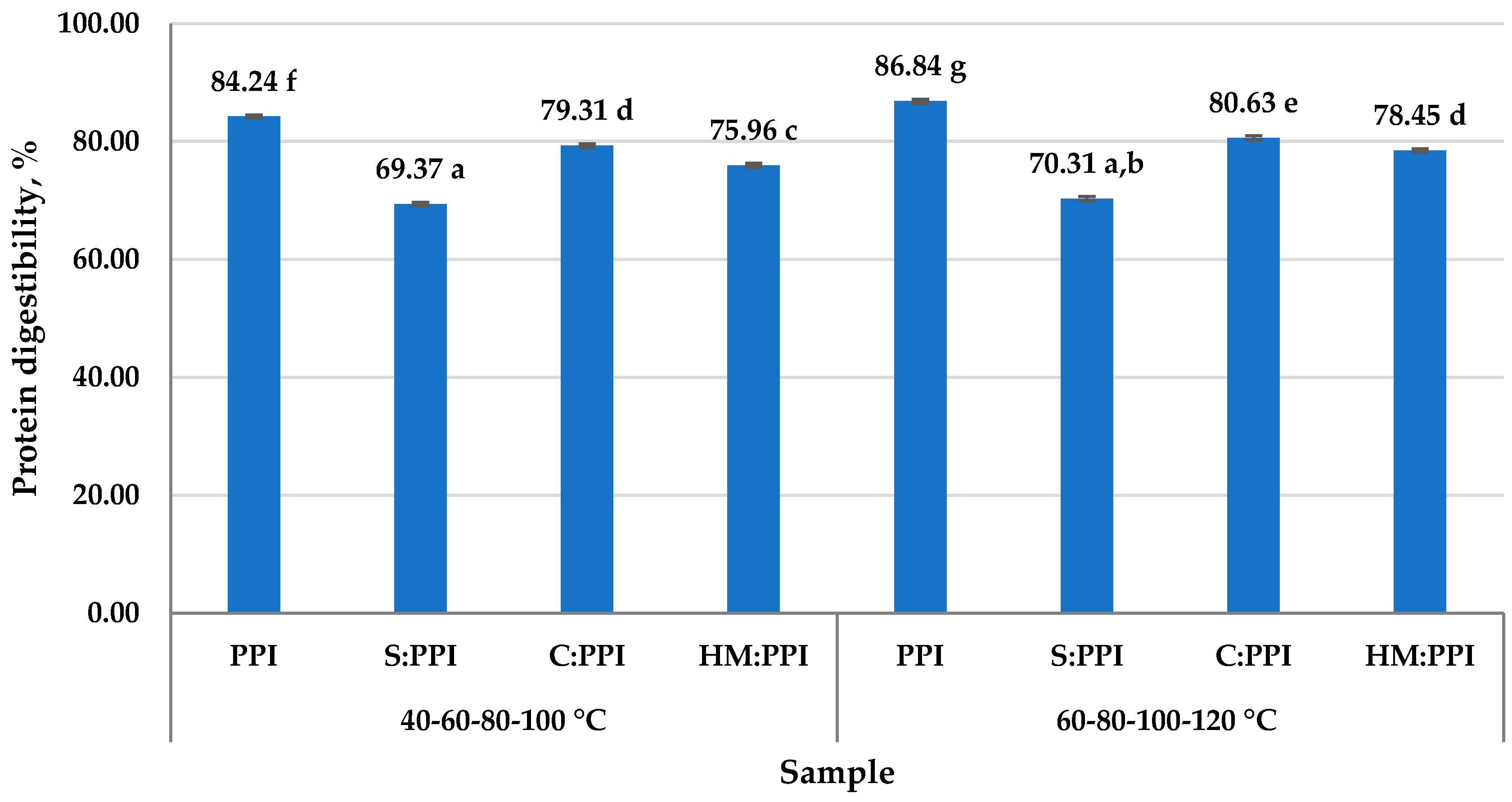
3.4. Protein Digestibility of Meat Analogs
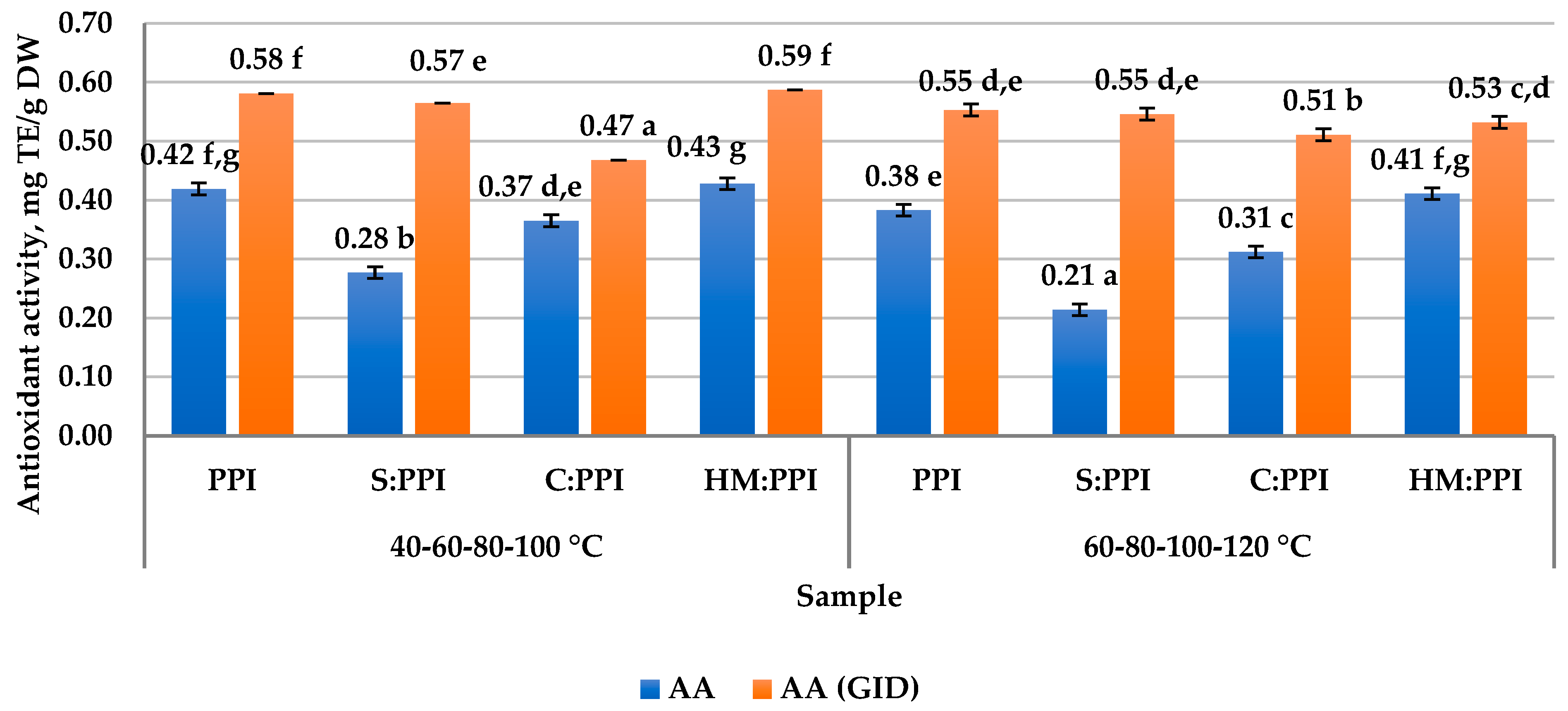
3.5. Antioxidant Activity Before and After In Vitro Digestion of Meat Analogs
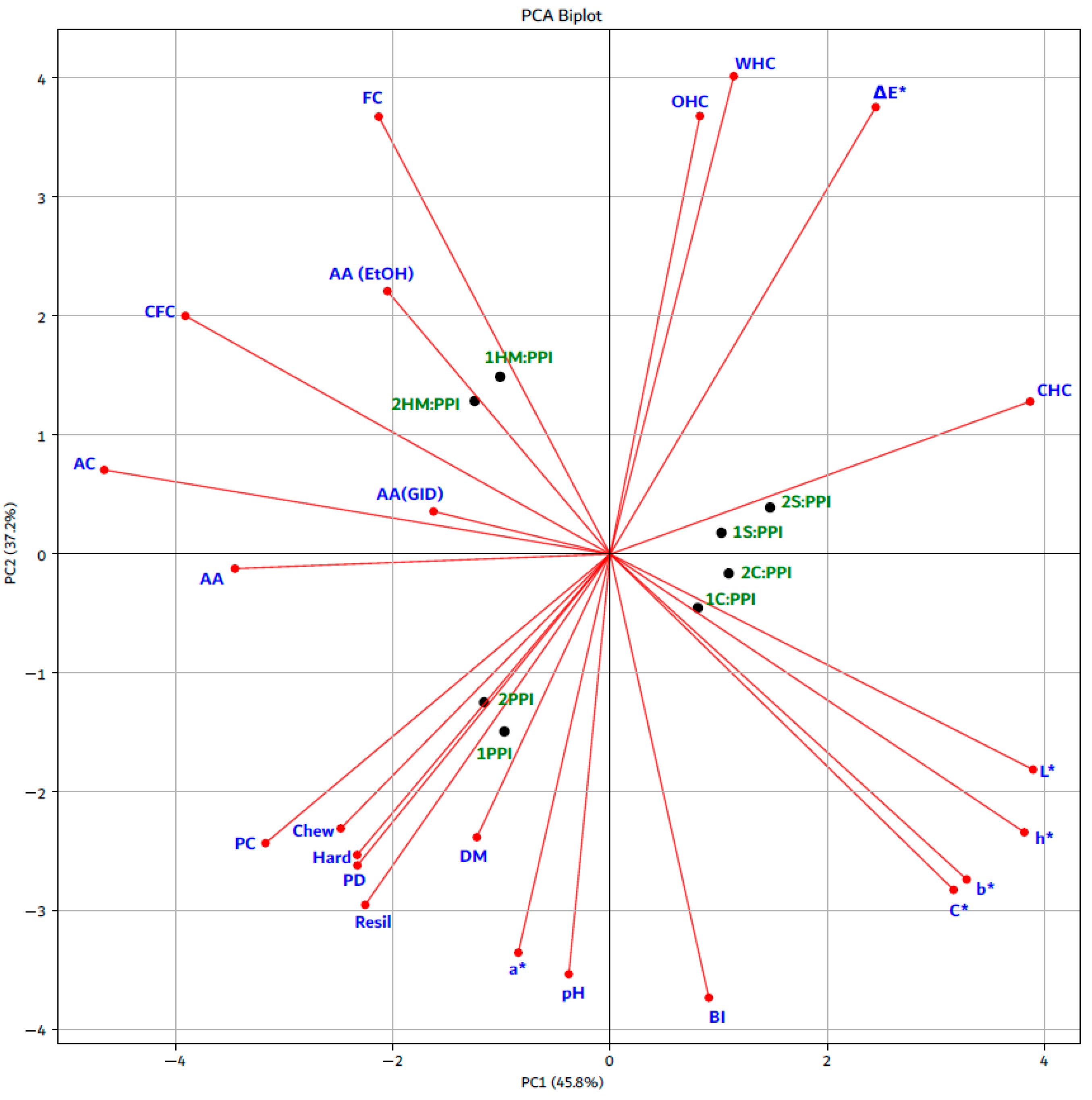
3.6. Relationship Between Physicochemical Characteristics, Protein Digestibility, Antioxidant Activity, Texture Profile Analysis, and CIELab Color Parameters in High Moisture Meat Analogs
4. Conclusions
5. Future Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachleitner, S.; Ata, Ö.; Mattanovich, D. The potential of CO2-based production cycles in biotechnology to fight the climate crisis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Poultry Quarterly Q3 2025: Geopolitics and Bird Flu to Shape the 2025/26 Poultry Outlook. Available online: https://www.rabobank.com/knowledge/q011332991-global-poultry-quarterly-q2-2025 (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Woolston, C. Healthy people, healthy planet: The search for a sustainable global diet. Nature 2020, 588, S54–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicka, M.; Havlík, P.; Valin, H.; Wollenberg, E.; Deppermann, A.; Leclère, D.; Lauri, P.; Moses, R.; Boere, E.; Frank, S.; et al. Feeding climate and biodiversity goals with novel plant-based meat and milk alternatives. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, S.; Painter, J.; Shea, M. Animal agriculture and climate change in the US and UK elite media: Volume, responsibilities, causes and solutions. Environ. Commun. 2021, 15, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.; Hamaker, B. Texturization of plant protein-based meat alternatives: Processing, base proteins, and other constructional ingredients. Future Foods 2023, 8, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, C.S.D.; Varela, P.; Poudroux, C.; Dessev, T.; Myhrer, K.; Rieder, A.; Zobel, H.; Sahlstrøm, S.; Knutsen, S. The impact of extrusion parameters on physicochemical, nutritional and sensorial properties of expanded snacks from pea and oat fractions. LWT 2019, 112, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Filho, P.F.; Andersson, D.; Ferreira, J.; Taherzadeh, M. Mycoprotein: Environmental impact and health aspects. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlborn, J.; Stephan, A.; Meckel, T.; Maheshwari, G.; Rühl, M.; Yorn, H. Upcycling of food industry side streams by basidiomycetes for production of a vegan protein source. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiao, X.; Du, W.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wakisaka, M.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; et al. Leveraging microalgae as a sustainable ingredient for meat analogues. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasitka, L.; Cohen, M.; Ehrlich, A.; Gildor, B.; Reuveni, E.; Ayyash, M.; Wissotsky, G.; Herscovici, A.; Kaminker, R.; Niv, A.; et al. Spontaneous immortalization of chicken fibroblasts generates stable, high-yield cell lines for serum-free production of cultured meat. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, M.; Costa, A.; Pozza, M.; Goi, A.; Manuelian, C.L. Detailed characterization of plant-based burgers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Evans, N.M.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. A review of research on plant-based meat alternatives: Driving forces, history, manufacturing, and consumer attitudes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2639–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, M.C.; Jeske, A.L.; Profeta, A.; Smetana, S.; Broucke, K.; Van Royen, G.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; Terjung, N. Effect of plant protein extrudates on hybrid meatballs—Changes in nutritional composition and sustainability. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, W.; Smetana, S.; Van Campenhout, L.; Lammers, V.; Heinz, V. Life cycle assessment of burger patties produced with extruded meat substitutes. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand View Research. Plant-Based Protein Market Size & Share Report, 2023–2028. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/plant-based-protein-supplements-market (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Bulgaru, V.; Mazur, M.; Netreba, N.; Paiu, S.; Dragancea, V.; Gurev, A.; Sturza, R.; Sensoy, I.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A. Characterization of Plant-Based Raw Materials Used in Meat Analog Manufacture. Foods 2025, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.; Zare, F.; Pletch, A. Pulse proteins: Processing, characterization, functional properties and applications in food and feed. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgaru, V.; Netreba, N.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A. Pre-Treatment of Vegetable Raw Materials (Sorghum Oryzoidum) for Use in Meat Analog Manufacture. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.P.; Senaratne-Lenagala, L.; Stube, A.; Brackenridge, A. Protein demand: Review of plant and animal proteins used in alternative protein product development and production. Anim. Front. 2020, 10, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. The development history and recent updates on soy protein-based meat alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 702–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. An investigation of the formulation and nutritional composition of modern meat analogue products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Food processing for the improvement of plant proteins digestibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3367–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Dekkers, B.; van der Goot, A.J. Plant-Based Meat Analogues. In Sustainable Meat Production and Processing; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- López-Calabozo, R.; Liberal, Â.; Fernandes, Â.; Revilla, I.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M. Determination of Carbohydrate Composition in Lentils Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors 2024, 24, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Sato, Y.; Okada, M.; Yamaguchi, S. Improved functional properties of meat analogs by laccase catalyzed protein and pectin crosslinks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Shen, S.; Ma, C.; Li, K.; Xue, C.; Jiang, X.; Xue, Y. High-moisture extrusion of yeast-pea protein: Effects of different formulations on the fibrous structure formation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, F.; Hojjatoleslamy, M. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of sponge cake made with olive leaf. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netreba, N.; Sergheeva, E.; Gurev, A.; Dragancea, V.; Codină, G.G.; Sturza, R.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A. The Influence of Pomace Powder of Musky Squash on the Characteristics of Foamy Confectionery Products during Storage. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Ogawa, Y. In vitro protein digestibility and biochemical characteristics of soaked, boiled and fermented soybeans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. Infogest static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khem, S. Development of Model Fermented Fish Sausage from New Zealand Marine Species: A Thesis Submitted to AUT University in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Applied Science (MAppSc); Auckland University of Technology: Auckland, New Zealand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Arnao, M.B.; Cano, A.; Alcolea, J.F.; Acosta, M. Estimation of free radical-quenching activity of leaf pigment extracts. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennells, J.; Trigona, L.; Patel, H.; Ying, D. Ingredient Functionality of Soy, Chickpea, and Pea Protein before and after Dry Heat Pretreatment and Low Moisture Extrusion. Foods 2024, 13, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snel, S.J.E.; Amroussi, Y.; van der Goot, A.J.; Beyrer, M. Rework Potential of Soy and Pea Protein Isolates in High-Moisture Extrusion. Foods 2023, 12, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camire, M. Chemical Changes during Extrusion Cooking. In Process-Induced Chemical Changes in Food; Shahidi, F., Ho, C.T., van Chuyen, N., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tas Ayten, A.; Brewood, K.; Onarinde, B. Comparison of the Resistant Starch Content and Physical Properties of Extruded Pea Flour-Based Snacks Enriched with Protein and Dietary Fibre. Act. Sci. Nutr. Health. 2023, 12, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, A.J.; Dunay, A.; Battay, M.; Illés, C.B.; Bittsánszky, A.; Süth, M. Microbial Spoilage of Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatansever, S.; Tulbek, M.C.; Riaz, M.N. Low- and High-Moisture Extrusion of Pulse Proteins as Plant-Based Meat Ingredients: A Review. Cereal Foods World 2020, 65, 0038. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Choi, I.; Han, J. Construction of rice protein-based meat analogues by extruding process: Effect of substitution of soy protein with rice protein on dynamic energy, appearance, physicochemical, and textural properties of meat analogues. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-H.; Gu, B.-J.; Ryu, G.-H. Investigating the Potential of Full-Fat Soy as an Alternative Ingredient in the Manufacture of Low- and High-Moisture Meat Analogs. Foods 2023, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, M.; Summo, C.; Centrone, M.; Rybicka, I.; D’Agostino, M.; Annicchiarico, P.; Caponio, F.; Pavan, S.; Tamma, G.; Pasqualone, A. Macro- and Micro-Nutrient Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Chickpea and Pea Accessions. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 71, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Gao, X.; Gong, H.; Lin, X.R.; Saint-Leger, D.; Senee, J. Chemical stability and degradation mechanisms of ferulic acid (F.A) within various cosmetic formulations. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 62, 483–503. [Google Scholar]
- Ceylan, F.D.; Adrar, N.; Bolling, B.W.; Capanoglu, E. Valorisation of Hazelnut By-Products: Current Applications and Future Potential. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2023, 39, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.B.; Kılıcarslan, E.; Demir, H.; Koca, E.; Salum, P.; Berkta, S.; Cam, M.; Erbay, Z.; Aydemir, L.Y. Upgrading the Bioactive Potential of Hazelnut Oil Cake by Aspergillus oryzae under Solid-State Fermentation. Molecules 2024, 29, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Wan, X.; Zhang, H.; Cai, M.; Hu, K.; Duan, Y. Effects of rapeseed protein addition on soybean protein-based textured protein produced by low-moisture extrusion: Changes in physicochemical attributes, structural properties and barrel flow behaviors. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, A.; Singh, G. Evaluating the potential of millets as blend components with soy protein isolate in a high moisture extrusion system for improved texture, structure, and colour properties of meat analogues. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, I.; Ferawati, F.; Helstad, A.; Ahlström, C.; Östbring, K.; Rayner, M.; Purhagen, J.K. Development of high-moisture meat analogues with hemp and soy protein using extrusion cooking. Foods 2020, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huff, H.E.; Hsieh, F. Texture and chemical characteristics of soy protein meat analog extruded at high moisture. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.; Plattner, B.J.; Donald, E.; Funk, D.; Plattner, B.S.; Alavi, S. Role of chickpea flour in texturization of extruded pea protein. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4180–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Diaz, J.M.; Kantanen, K.; Edelmann, J.M.; Suhonen, H.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Jouppila, K.; Piironen, V. Fibrous meat analogues containing oat fiber concentrate and pea protein isolate: Mechanical and physicochemical characterization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 77, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyony, V.; Fayolle, F.; Jury, V. High moisture extrusion of vegetable proteins for making fibrous meat analogs: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 39, 4262–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Wu, M. Study on the Residence Time and Texture Prediction of Pea Protein Extrusion Based on Image Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnés-Calle, C.; Matas, G.; Claret, A.; Guerrero, L.; Fulladosa, E.; Gou, P. High moisture extrusion of pea protein isolate to mimic chicken texture: Instrumental and sensory insights. Food Hydroc. 2024, 154, 110129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, J. The Maillard Reaction: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Implications by Harry Nursten. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzali, J.-G.; Suprabha-Raj, A.; Siliveru, K.; Aldrich, C.-G. Characterization of white and red sorghum flour and their potential use for production of extrudate crisps. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismag, R.Y.; Polo, M.P.; Hoyos, J.L.; Bravo, J.E.; Roa, D.F. Effect of extrusion cooking on the chemical and nutritional properties of instant flours: A review. F1000Research 2024, 12, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, D.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. Investigating the effect of roasting on functional properties of defatted hazelnut flour by response surface methodology (RSM). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hosry, L.; Elias, V.; Chamoun, V.; Halawi, M.; Cayot, P.; Nehme, A.; Bou-Maroun, E. Maillard Reaction: Mechanism, Influencing Parameters, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Food Industrial Applications: A Review. Foods 2025, 14, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoFaro, E.; Salerno, T.; Montevecchi, G.; Fava, P. Mitigation of Acrylamide Content in Biscuits through Combined Physical and Chemical Strategies. Foods 2022, 11, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalis, H.; See, X.Y.; Osen, R.; Chin, X.H.; Chow, Y. Significance of Fermentation in Plant-Based Meat Analogs: A Critical Review of Nutrition, and Safety-Related Aspects. Foods 2023, 12, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, L.; Huang, Z.; Shan, K.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Plant-Based Meat Analogues Weaken Gastrointestinal Digestive Function and Show Less Digestibility Than Real Meat in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12442–12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollone, M.A.; Tironi, V.A. Yellow pea flour and protein isolate as sources of antioxidant peptides after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Legum. Sci. 2020, 2, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, G.M.; Paul, S.R. Gastric digestion in vivo and in vitro: How the structural aspects of food influence the digestion process. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Teng, C.; Chen, D.; Campanella, O. Insights into protein digestion in plant-based meat analogs. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 52, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Advancing molecular understanding in high moisture extrusion for plant-based meat analogs: Challenges and perspectives. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Ying, D.; Sanguansri, L.; Augustin, M.A. Effect of extrusion conditions on the physico-chemical properties and in vitro protein digestibility of canola meal. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, M.; Arnal, M.; Barat, J.M.; Talens, P. Effect of Cooking on Protein Digestion and Antioxidant Activity of Different Legume Pastes. Foods 2021, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Delgado-Andrade, C. Effect of digestive process on Maillard reaction indexes and antioxidant properties of breakfast cereals. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.B.; He, T.P.; Li, H.B.; Tang, H.W.; Xia, E.Q. The structure-activity relationship of the antioxidant peptides from natural proteins. Molecules 2016, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kut, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Denaturation and Digestion Increase the Antioxidant Capacity of Proteins. Processes 2023, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzolf, M.; Szymusiak, H.; Swiglo, A.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Tyrakowska, B. pH-Dependent radical scavenging capacity of green tea catechins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Reginio, F.C., Jr.; Thuengtung, S.; Ogawa, Y. Changes in bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of plant-based foods by gastrointestinal digestion: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4684–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehnlein, E.A.; Koehnlein, É.M.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Nishida, V.S.; Correa, V.G.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Analysis of a whole diet in terms of phenolic content and antioxidant capacity: Effects of a simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyo, P.; Chamsai, T.; Toontom, N.; Nghiep, L.K.; Tudpor, K. Differential Effects of In Vitro Simulated Digestion on Antioxidant Activity and Bioaccessibility of Phenolic Compounds in Purple Rice Bran Extracts. Molecules 2024, 29, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Heating Temperature Profile, °C | Blends | DM, % | PC, % | FC, % | AC, % | CFC, % | CHC, % | pH | WHC, mL g−1 | OHC, mL g−1 | AA, mg TE/g DW (ABTS in 70% EtOH Extract) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40-60-80-100 | 1PPI | 49.66 ± 0.05 e | 37.83 ± 0.07 g | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 2.16 ± 0.02 c | 1.62 ± 0.02 c | 9.36 ± 0.15 b | 7.95 ± 0.01 d | 2.43 ± 0.04 b | 1.75 ± 0.0 a | 0.74 ± 0.03 c |
| 1S:PPI | 45.69 ± 0.09 d | 21.81 ± 0.10 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | 1.28 ± 0.01 b | 0.96 ± 0.0 a | 22.31 ± 0.11 g | 6.99 ± 0.01 c | 3.42 ± 0.06 d | 2.77 ± 0.05 d,e | 0.54 ± 0.02 a | |
| 1C:PPI | 43.48 ± 0.07 c | 24.22 ± 0.09 c | 0.58 ± 0.02 b | 1.30 ± 0.01 b | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 17.38 ± 0.08 d | 6.91 ± 0.01 c | 3.23 ± 0.05 c | 2.27 ± 0.06 c | 0.61 ± 0.04 a,b | |
| 1HM:PPI | 42.88 ± 0.05 b | 26.92 ± 0.06 d | 1.23 ± 0.02 c | 2.34 ± 0.02 d | 2.03 ± 0.02 d | 12.39 ± 0.01 c | 6.63 ± 0.01 b | 3.88 ± 0.03 f | 2.69 ± 0.04 d | 1.27 ± 0.03 f | |
| 60-80-100-120 | 2PPI | 45.13 ± 0.08 d | 34.49 ± 0.11 f | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 2.21 ± 0.01 c | 1.45 ± 0.01 b | 8.18 ± 0.09 a | 7.87 ± 0.01 d | 2.22 ± 0.02 a | 2.16 ± 0.03 b | 0.69 ± 0.02 b,c |
| 2S:PPI | 43.00 ± 0.06 b,c | 20.24 ± 0.08 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 1.19 ± 0.01 b | 0.91 ± 0.01 a | 21.27 ± 0.12 f | 6.93 ± 0.01 c | 3.69 ± 0.05 e | 2.75 ± 0.04 d | 0.54 ± 0.03 a | |
| 2C:PPI | 41.59 ± 0.04 a | 22.05 ± 0.09 b | 0.50 ± 0.02 b | 1.10 ± 0.01 a | 0.91 ± 0.02 a | 17.94 ± 0.09 e | 6.88 ± 0.01 c | 3.72 ± 0.04 e | 2.33 ± 0.02 c | 0.89 ± 0.03 d,e | |
| 2HM:PPI | 43.27 ± 0.07 c | 27.47 ± 0.12 e | 1.45 ± 0.01 d | 2.44 ± 0.0 d | 2.28 ± 0.03 e | 11.91 ± 0.13 c | 5.96 ± 0.01 a | 4.09 ± 0.06 g | 2.89 ± 0.05 e | 0.92 ± 0.04 d,e |
| Heating Temperature Profile, °C | Blends | Hardness, N | Resilience, % | Chewiness, N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40-60-80-100 | 1PPI | 224.12 ± 17.70 e | 41.70 ± 0.30 f | 152.68 ± 25.97 d,e |
| 1S:PPI | 146.73 ± 8.78 b | 35.34 ± 0.57 e | 78.13 ± 17.12 b | |
| 1C:PPI | 171.19 ± 9.59 c | 30.17 ± 0.66 c | 101.73 ± 18.04 b,c | |
| 1HM:PPI | 137.85 ± 6.43 a,b | 24.37 ± 0.73 a,b | 82.19 ± 5.21 b | |
| 60-80-100-120 | 2PPI | 320.85 ± 5.91 f | 45.17 ± 0.67 g | 244.63 ± 4.58 f |
| 2S:PPI | 121.98 ± 2.92 a | 23.16 ± 0.93 a | 56.89 ± 6.77 a,b | |
| 2C:PPI | 129.34 ± 4.94 a,b | 25.62 ± 0.80 b | 64.34 ± 9.54 a,b | |
| 2HM:PPI | 186.73 ± 12.23 c,d | 34.32 ± 0.76 d,e | 125.21 ± 7.15 c,d |
| Heating Temperature Profile, °C | Raw Materials/Blends | CIELab Color Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | C* | h*, ° | ΔE* | BI | ||
| - | PPI | 84.32 ± 0.93 f | 3.71 ± 0.07 b | 20.21 ± 0.46 e | 20.55 ± 0.25 d | 79.60 ± 0.18 d | - | 30.10 ± 0.37 b |
| S | 87.93 ± 1.27 f,g | 1.51 ± 0.30 a | 13.55 ± 0.53 b,c | 13.63 ± 0.29 b | 83.64 ± 0.11 e | - | 17.63 ± 0.18 a | |
| C | 91.76 ± 1.30 g | 1.41 ± 0.33 a | 17.27 ± 0.38 d | 17.33 ± 0.36 c | 85.33 ±0.13 f | - | 21.53 ± 0.27 a | |
| HM | 56.43 ± 2.20 c | 9.29 ± 0.08 f | 21.19 ± 0.53 e | 23.14 ± 0.26 e,f | 66.33 ± 0.09 b | - | 58.37 ± 0.31 e,f | |
| 40-60-80-100 | 1PPI | 54.15 ± 1.13 c | 8.19 ± 0.01 e | 20.77 ± 0.46 e | 22.33 ± 0.29 e | 68.48 ± 0.11 b | - | 58.63 ± 0.36 f |
| 1S:PPI | 71.86 ± 1.45 e | 4.90 ± 0.50 b,c | 20.34 ± 0.35 e | 20.92 ± 0.41 d,e | 76.46 ± 0.08 c | 18.06 ± 0.11 b | 37.68 ± 0.24 c | |
| 1C:PPI | 66.77 ± 0.91 d,e | 6.17 ± 0.17 d | 26.01 ± 0.42 g | 26.73 ± 0.26 g | 76.66 ± 0.14 c | 13.87 ± 0.19 a | 55.10 ± 0.31 e | |
| 1HM:PPI | 33.57 ± 0.97 a | 4.79 ± 0.30 b,c | 7.62 ± 0.25 a | 9.00 ± 0.27 a | 57.85 ± 0.09 a | 24.66 ± 0.26 d | 35.78 ± 0.17 b | |
| 60-80-100-120 | 2PPI | 44.68 ± 0.14 b | 6.08 ± 0.28 d | 16.15 ± 0.62 c,d | 17.26 ± 0.35 c | 69.37 ± 0.12 b | - | 54.09 ± 0.29 e |
| 2S:PPI | 67.93 ± 1.28 e | 4.63 ± 0.13 b,c | 23.05 ± 0.77 f | 23.51 ± 0.42 e,f | 78.64 ± 0.19 d | 24.36 ± 0.09 d | 45.63 ± 0.26 d | |
| 2C:PPI | 61.97 ± 1.61 d | 6.35 ± 0.01 d | 27.30 ± 0.93 g,h | 28.03 ± 0.64 h | 76.91 ± 0.08 d | 20.60 ± 0.10 c | 64.15 ± 0.51 f | |
| 2HM:PPI | 34.15 ± 0.53 a | 4.94 ± 0.15 c | 7.62 ± 0.18 a | 9.08 ± 0.16 a | 57.04 ± 0.06 a | 13.62 ± 0.14 a | 35.43 ± 0.21 b | |
| Heating Temperature Profile, °C | 40-60-80-100 | 60-80-100-120 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blends | 1PPI | 1S:PPI | 1C:PPI | 1HM:PPI | 2PPI | 2S:PPI | 2C:PPI | 2HM:PPI |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulgaru, V.; Sensoy, I.; Netreba, N.; Gurev, A.; Altanlar, U.; Paiu, S.; Dragancea, V.; Sturza, R.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A. Qualitative and Antioxidant Evaluation of High-Moisture Plant-Based Meat Analogs Obtained by Extrusion. Foods 2025, 14, 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172939
Bulgaru V, Sensoy I, Netreba N, Gurev A, Altanlar U, Paiu S, Dragancea V, Sturza R, Ghendov-Mosanu A. Qualitative and Antioxidant Evaluation of High-Moisture Plant-Based Meat Analogs Obtained by Extrusion. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172939
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulgaru, Viorica, Ilkay Sensoy, Natalia Netreba, Angela Gurev, Ulunay Altanlar, Sergiu Paiu, Veronica Dragancea, Rodica Sturza, and Aliona Ghendov-Mosanu. 2025. "Qualitative and Antioxidant Evaluation of High-Moisture Plant-Based Meat Analogs Obtained by Extrusion" Foods 14, no. 17: 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172939
APA StyleBulgaru, V., Sensoy, I., Netreba, N., Gurev, A., Altanlar, U., Paiu, S., Dragancea, V., Sturza, R., & Ghendov-Mosanu, A. (2025). Qualitative and Antioxidant Evaluation of High-Moisture Plant-Based Meat Analogs Obtained by Extrusion. Foods, 14(17), 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172939







