Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Rinsing on Tilapia Storage: An Investigation Based on Muscle Quality and Tissue Protease Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Extraction of Myofibrillar Protein (MP)
2.4. Extraction and Activity Determination of Tissue Proteases B and L
2.5. Extraction and Activity Assay of Tissue Protease D
2.6. Determination of Texture
2.7. Determination of Colour and Lustre
2.8. Determination of pH
2.9. Determination of Myofibrillar Fibril Fragmentation Index (MFI)
2.10. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.11. Observations on the Ultrastructure of Fish Muscle Fibres
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
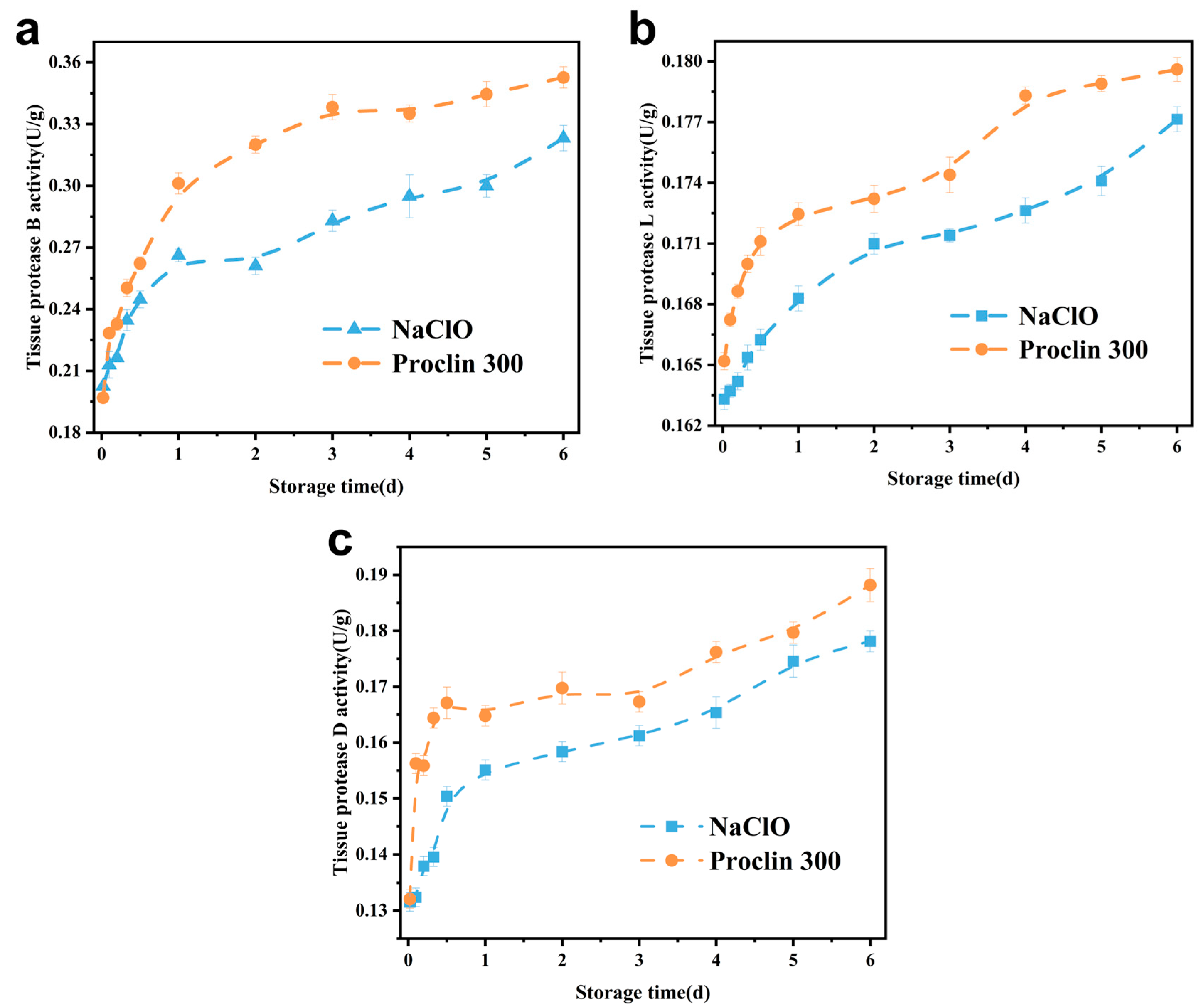
3.1. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite Oxidation on Tissue Protease Activity of Tilapia Fillets
3.1.1. Tissue Protease B
3.1.2. Tissue Protease L
3.1.3. Tissue Protease D
3.2. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite Oxidation on the Textural Properties of Tilapia Fillets
3.3. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite Oxidation on Quality Characteristics of Tilapia Fillets
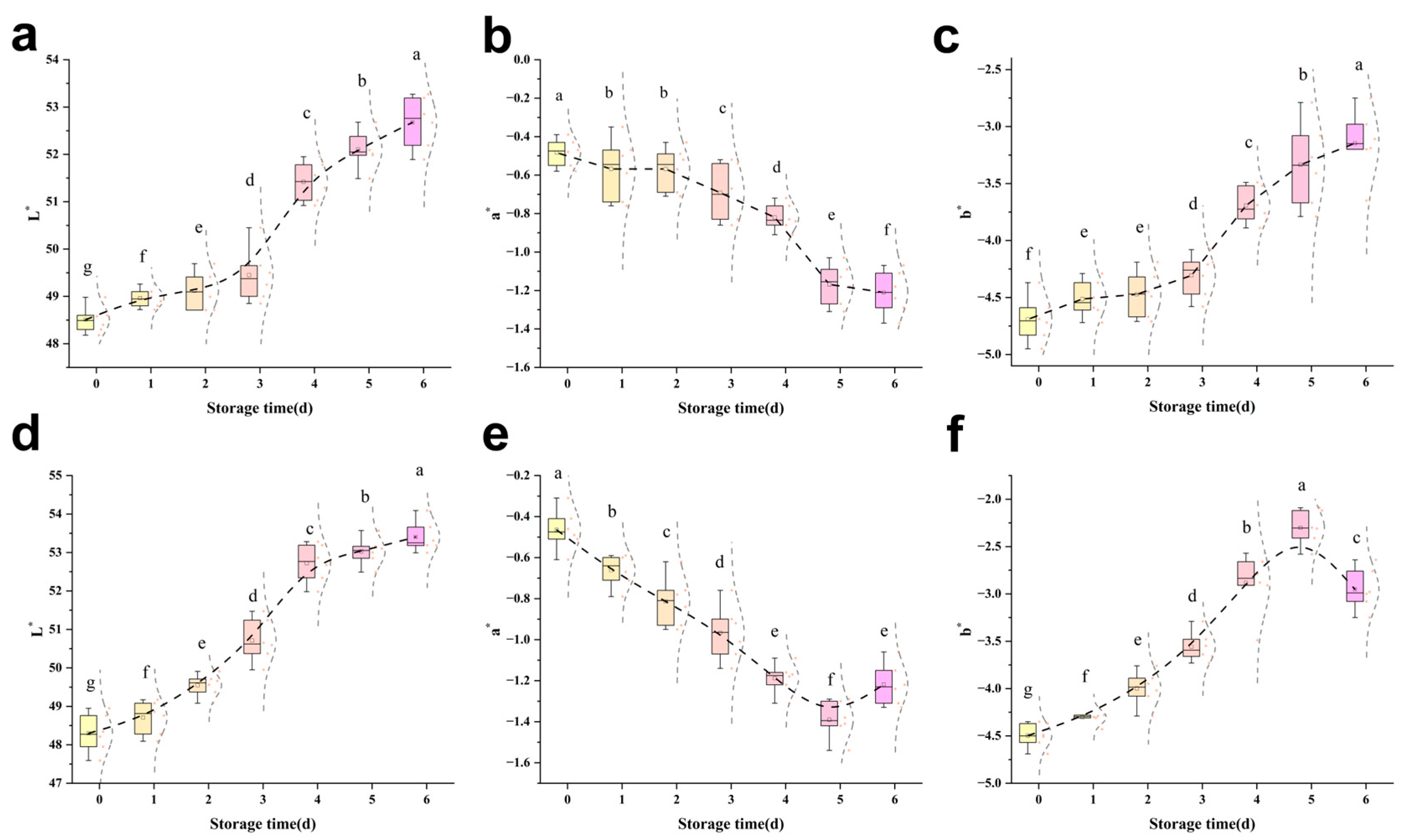
3.3.1. Colour and Lustre
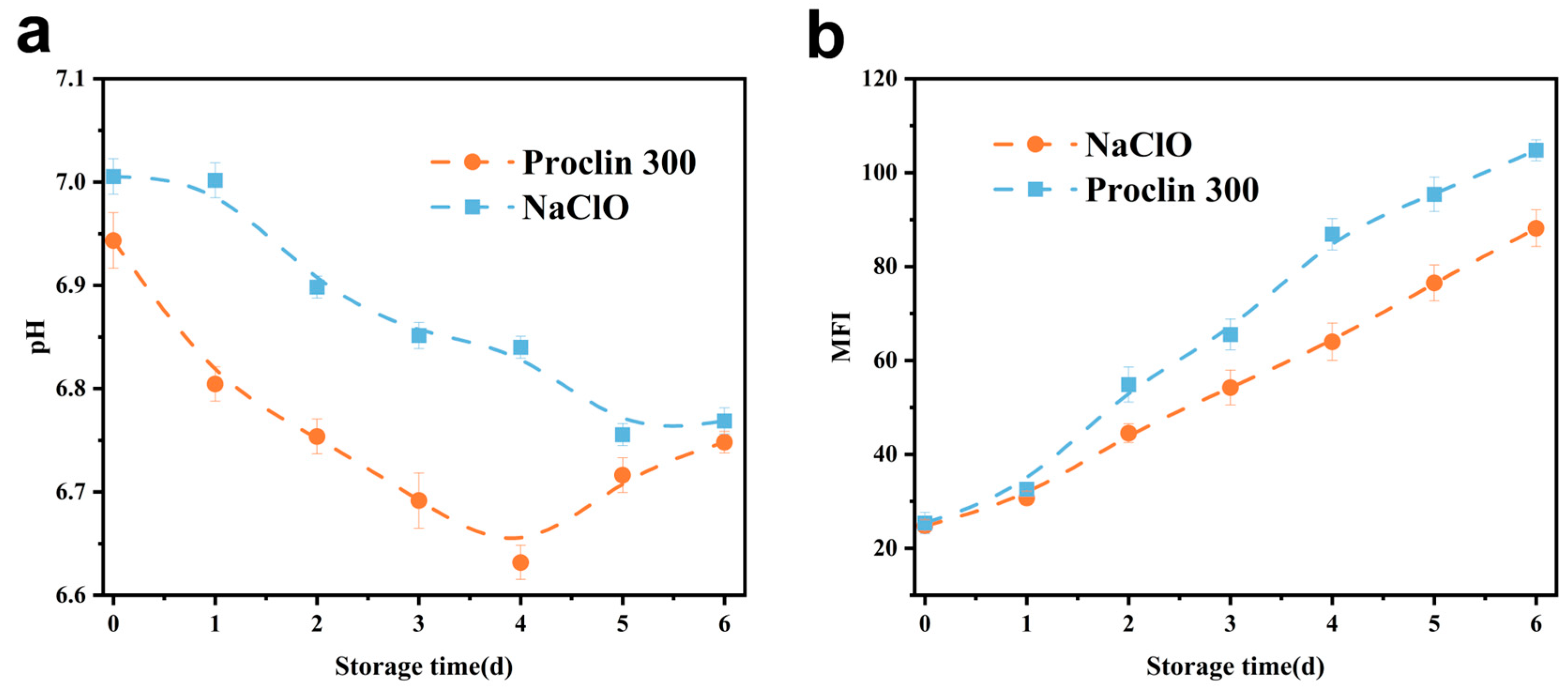
3.3.2. pH
3.3.3. MFI
3.4. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite Oxidation on the Protein Structure of Tilapia Fillets
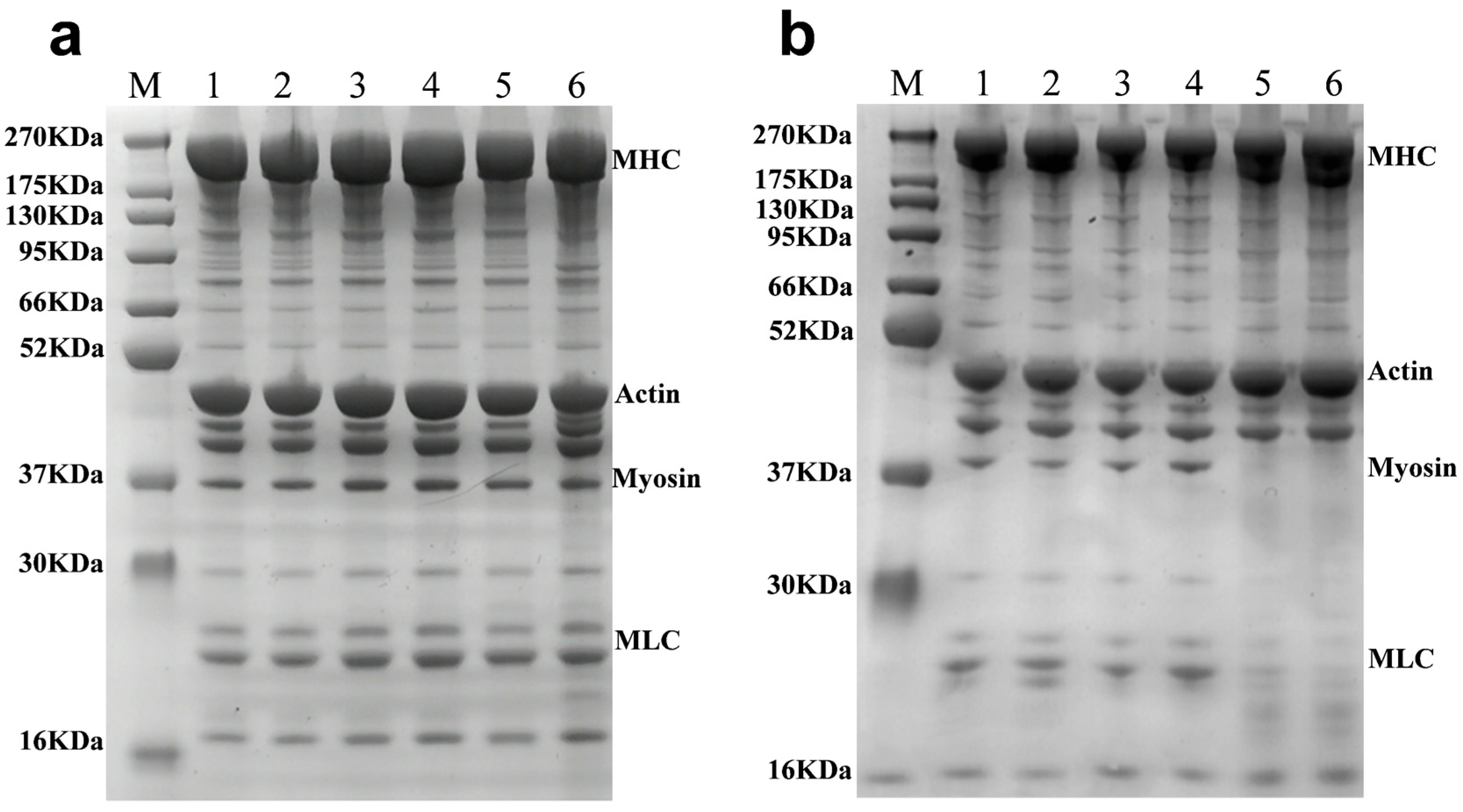
3.4.1. SDS-PAGE
3.4.2. SEM
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Tissue Protease Activity and Various Physicochemical Indices of Fish Flesh
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tian, X.; Zheng, M.; Su, Z.; Zhong, N. Rapid non-destructive evaluation of texture properties changes in crispy tilapia during crispiness using hyperspectral imaging and data fusion. Food Control 2024, 162, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tian, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, N. Synergizing meat science and interpretable AI: Quantifying crispness gradients for quality authentication of Tilapia fillet processing. Food Chem. 2025, 484, 144252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, L.; Zhu, X.; Guo, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. The effect of caspase-3 in mitochondrial apoptosis activation on degradation of structure proteins of Esox lucius during postmortem storage. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Qin, L.; Ma, L.-X.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Du, M.; Kunihiko, K.; Zhu, B.-W. Postmortem nucleotide degradation in turbot mince during chill and partial freezing storage. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Xia, X.; Kong, B. Changes in functional properties of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) myofibrillar protein as affected by ultrasound-assisted freezing. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Lemos Junior, W.J.; dos Santos Alves, J.; Mattos Dias Martins, A.; Silva Minafra e Rezende, C.; Pereira Cappato, L. Fogging vs immersion techniques for sustainable pathogen inactivation on stainless steel surfaces using commercial sanitizers. J. Food Eng. 2025, 384, 112249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Dong, Y.; Ma, X.; Xie, J.; Mei, J. Effects of multi-frequency ultrasound-assisted immersion freezing processing on myofibrillar protein structure and lipid oxidation of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) during long-time frozen storage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 107, 106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Uncovering quality changes of salted bighead carp fillets during frozen storage: The potential role of time-dependent protein denaturation and oxidation. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhu, X.; Mao, X.; Guo, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. μ-Calpain oxidation and proteolytic changes on myofibrillar proteins from Coregonus peled in vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ojangba, T.; Nan, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q. Effects of iron-catalyzed oxidation and methemoglobin oxidation systems on endogenous enzyme activity and myofibrillar protein degradation in yak meat. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, L.; Hao, S.; Chen, S.; Cen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xiang, H. Effects of five oxidizing bacteria-reducing agents on the quality and protein of tilapia fillets. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pazos, M.; Maestre, R.; Gallardo, J.M.; Medina, I. Proteomic evaluation of myofibrillar carbonylation in chilled fish mince and its inhibition by catechin. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizi, C.; Liburdi, K.; Esti, M. Extraction, catalytic study and milk-clotting properties of proteases from Brassica oleracea. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liao, J.; Qi, J. Citrus endogenous components as prebiotics: Advances in extraction, digestion, mechanisms, and delivery. Food Res. Int. 2025, 208, 116141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Jiao, D.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Guo, A.; Zhu, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Effect of ultra-high pressure on the relationship between endogenous proteases and protein degradation of Yesso scallop (Mizuhopecten yessoensis) adductor muscle during iced storage. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liburdi, K.; Emiliani Spinelli, S.; Benucci, I.; Lombardelli, C.; Esti, M. A preliminary study of continuous milk coagulation using Cynara cardunculus flower extract and calf rennet immobilized on magnetic particles. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of fish protein degradation caused by grass carp spoilage bacteria: A bottom-up exploration from the molecular level, muscle microstructure level, to related quality changes. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q. Effects of starters on the quality of fermented fish (Zaoyu): Key microorganisms for coloring, softening, and improving flavor. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009. 237-2016; National Standard for Food Safety Determination of Food pH. National Health and Family Planning Commission. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Prill, L.L.; Phelps, K.J.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Houser, T.A.; Boyle, E.A.; O’Quinn, T.G. Relationship of Myofibrillar Fragmentation Index to Warner-Bratzler Shear Force and Palatability Tenderness of Longissimus Lumborum and Semitendinosus Steaks. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2018, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Liang, X.; Chen, S.; Tao, F.; Yang, X.; Cen, J. Red color-related proteins from the shell of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Isolation, identification and bioinformatic analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Babol, J.; Wallby, A.; Lundström, K. Meat quality, microbiological status and consumer preference of beef gluteus medius aged in a dry ageing bag or vacuum. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, L. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan nanoemulsions loading thymol or thyme essential oil for the preservation of refrigerated pork. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xie, J. Stable chlorine dioxide combined with slightly acidic electrolyzed water: An effective way to delay protein deterioration of refrigerated large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, P.; Deng, X.; Guo, X.; Mao, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of hydroxyl radical oxidation on myofibrillar protein and its susceptibility to μ-calpain proteolysis. LWT 2021, 137, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Ji, M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q. Preservative effects of fish gelatin coating enriched with CUR/βCD emulsion on grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets during storage at 4 C. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yao, Y.; He, J.; Tang, J.; Jiao, Y. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) subjected to radio frequency tempering on melanosis and quality. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, Q.; Dong, X.; Ji, H. Insight into muscle quality of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) frozen with static magnetic-assisted freezing at different intensities. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Qi, X.; Shui, S.; Benjakul, S.; Aubourg, S.P.; Zhang, B. Label-free proteomic analysis revealed the mechanisms of protein oxidation induced by hydroxyl radicals in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) muscle. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4337–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.; Coombs, C.E.; Morris, S.; Kerr, M.J.; Hopkins, D.L. Effect of long term chilled (up to 5 weeks) then frozen (up to 12 months) storage at two different sub-zero holding temperatures on beef: 1. Meat quality and microbial loads. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheerzad, S.; Khorrami, R.; Khanjari, A.; Gandomi, H.; Basti, A.A.; Khansavar, F. Improving chicken meat shelf-life: Coating with whey protein isolate, nanochitosan, bacterial nanocellulose, and cinnamon essential oil. LWT 2024, 197, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Cui, G.; Lin, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhao, G. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial properties of double lysine-modified chitosan and its preservation ability in chicken meat refrigeration. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Castillo, C.J.; Lomiwes, D.; Wu, G.; Frost, D.; Farouk, M.M. The effect of electrical stimulation on post mortem myofibrillar protein degradation and small heat shock protein kinetics in bull beef. Meat Sci. 2016, 113, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Refrigerated storage-induced quality deterioration of Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi): Analyzing the role of endogenous enzymes through TMT-based quantitative proteomics. LWT 2024, 209, 116721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Effects of chitosan-gentianic acid derivatives on myofibrillar proteins in sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xie, J.; Chu, Y.M. Degradation and evaluation of myofibril proteins induced by endogenous protease in aquatic products during storage: A review. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ma, Q.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, W. Changes in quality characteristics of shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) during refrigerated storage and their correlation with protein degradation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Effect of Cold Storage on Composition and Properties of Grass Carp Muscle Proteins. Pak. J. Zool. 2019, 51, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Tong, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, P. Mechanism study on the effect of heat shock on the functional characteristics of soybean protein isolate by regulating the change of endogenous enzyme activity in soybeans. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Dong, R.; Yu, M.; Benjakul, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B. Physicochemical, volatile flavor, and microflora changes in the cephalothorax and pincer muscles of swimming crab (Ovalipes punctatus) during frozen storage: Molecular mechanisms of quality deterioration. Food Res. Int. 2025, 218, 116922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D.; Yang, F.; Xia, W. Effects of deheading and rinsing pretreatment on the quality of white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) surimi based on endogenous proteases. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yang, F.; Jia, S.; Yu, D.; Gao, P.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. The role of endogenous proteases in degrading grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) myofibrillar structural proteins during ice storage. LWT 2022, 154, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
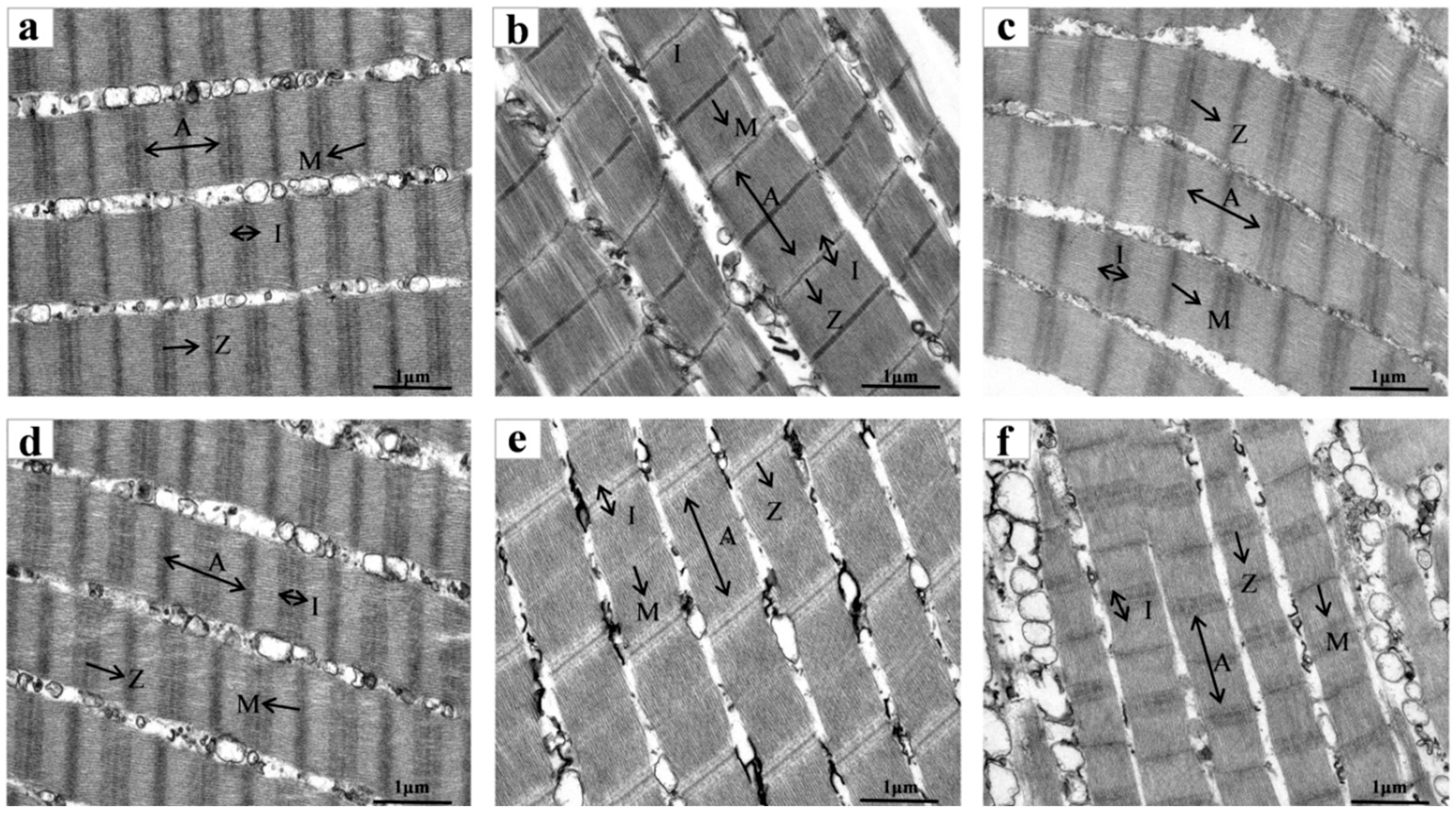
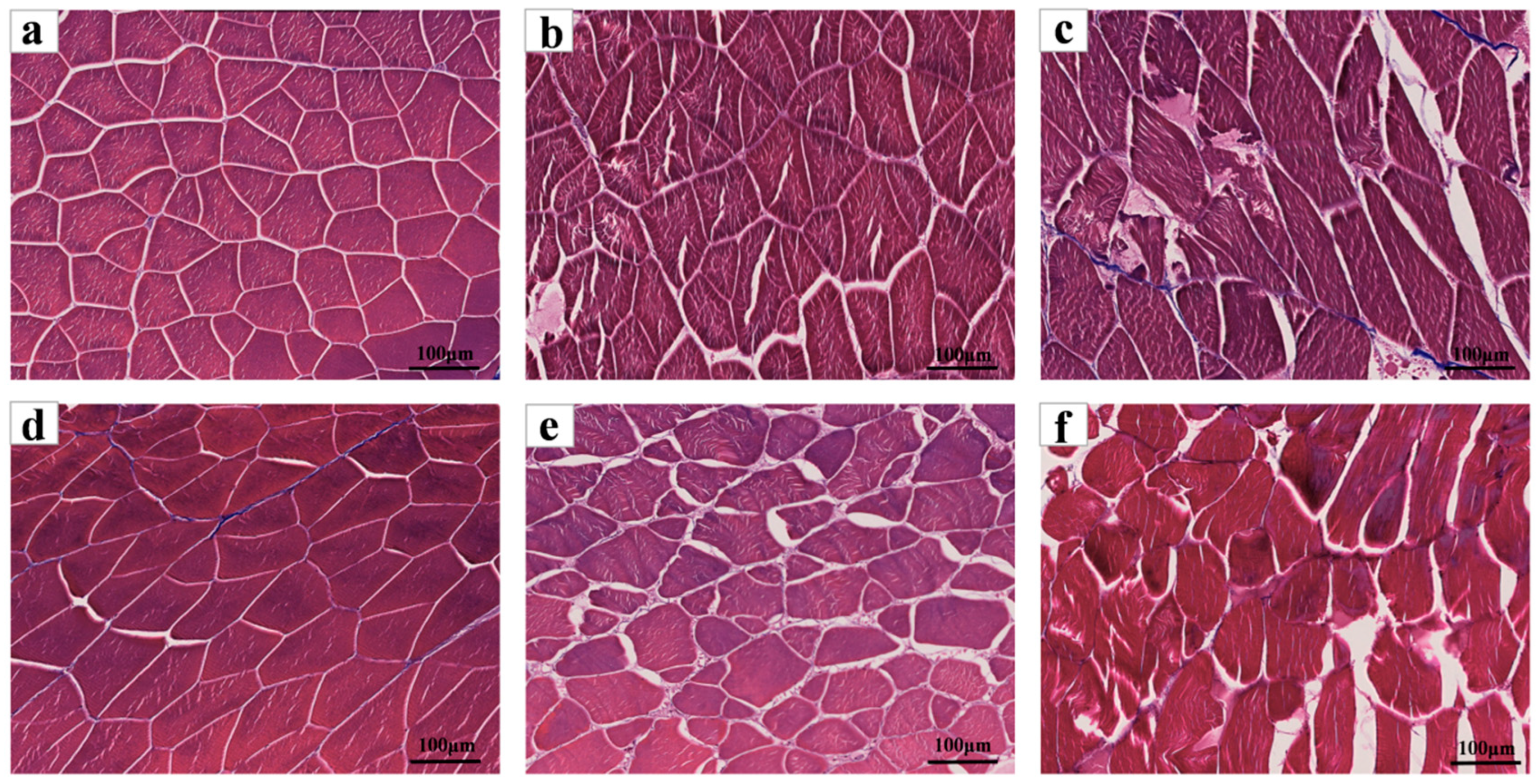

| Storage Time (d) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness/Pa | A | 342.83 ± 23.01 a | 316.96 ± 16.88 b | 288.78 ± 12.20 c | 265.25 ± 11.23 d | 237.56 ± 13.41 e | 208.24 ± 20.23 f | 189.83 ± 16.11 g |
| B | 338.83 ± 17.05 a | 298.85 ± 14.25 b | 269.23 ± 25.36 c | 229.36 ± 16.85 d | 207.9 ± 17.45 e | 182.52 ± 15.25 f | 171.56 ± 18.10 g | |
| Cohesion | A | 0.50 ± 0.01 a | 0.46 ± 0.05 b | 0.42 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.04 c | 0.37 ± 0.07 d | 0.35 ± 0.05 e | 0.35 ± 0.04 e |
| B | 0.49 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.03 b | 0.40 ± 0.01 c | 0.39 ± 0.03 d | 0.36 ± 0.07 e | 0.35 ± 0.02 f | 0.36 ± 0.08 e | |
| Elasticity/mm | A | 3.54 ± 0.08 a | 3.53 ± 0.02 b | 3.53 ± 0.09 b | 3.51 ± 0.09 d | 3.52 ± 0.07 c | 3.51 ± 0.02 d | 3.48 ± 0.37 e |
| B | 3.53 ± 0.02 a | 3.52 ± 0.07 b | 3.52 ± 0.05 b | 3.51 ± 0.01 c | 3.50 ± 0.06 d | 3.51 ± 0.09 c | 3.42 ± 0.56 e | |
| Adhesion | A | 132.56 ± 2.47 a | 120.10 ± 1.89 b | 110.29 ± 12.49 c | 105.75 ± 2.90 d | 88.9 ± 11.85 e | 60.45 ± 12.25 g | 63.4 ± 9.6 f |
| B | 132.23 ± 2.28 a | 119.23 ± 2.64 b | 101.26 ± 2.56 c | 96.55 ± 1.87 d | 62.85 ± 13.1 e | 46.25 ± 8.9 f | 44.3 ± 7.7 g | |
| Chewability/mJ | A | 4.59 ± 0.13 a | 3.96 ± 0.43 b | 3.58 ± 0.25 c | 3.02 ± 0.28 d | 2.87 ± 0.51 e | 2.56 ± 0.43 f | 2.23 ± 0.56 g |
| B | 4.58 ± 0.37 a | 3.25 ± 0.29 b | 2.75 ± 0.14 c | 2.57 ± 0.11 d | 2.22 ± 0.88 e | 2.15 ± 0.12 f | 1.68 ± 0.72 g | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Z.; Hao, S.; Xiang, H.; Li, C.; Cen, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Yan, Y.; et al. Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Rinsing on Tilapia Storage: An Investigation Based on Muscle Quality and Tissue Protease Activity. Foods 2025, 14, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162868
Fu Z, Hao S, Xiang H, Li C, Cen J, Wei Y, Chen S, Zhao Y, Hu X, Yan Y, et al. Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Rinsing on Tilapia Storage: An Investigation Based on Muscle Quality and Tissue Protease Activity. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162868
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Zirui, Shuxian Hao, Huan Xiang, Chunsheng Li, Jianwei Cen, Ya Wei, Shengjun Chen, Yongqiang Zhao, Xiao Hu, Yuhong Yan, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Rinsing on Tilapia Storage: An Investigation Based on Muscle Quality and Tissue Protease Activity" Foods 14, no. 16: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162868
APA StyleFu, Z., Hao, S., Xiang, H., Li, C., Cen, J., Wei, Y., Chen, S., Zhao, Y., Hu, X., Yan, Y., Huang, H., & Li, J. (2025). Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Rinsing on Tilapia Storage: An Investigation Based on Muscle Quality and Tissue Protease Activity. Foods, 14(16), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162868










