Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of SBQE
2.2. HS Protocol in Rats
2.3. Animal Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Assessment of Liver Function and Injury
2.6. Detection of Oxidative Stress Indicators
2.7. Quantification of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.8. Histopathological Examination
2.9. Detection of Apoptosis
2.10. Western Blotting Analysis
2.11. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Yield of SBQE
3.2. SBQE Attenuated HS-Induced Liver Dysfunction and Histopathological Alterations in Rats
3.3. SBQE Mitigated Hepatic Oxidative Stress Caused by HS in Rats
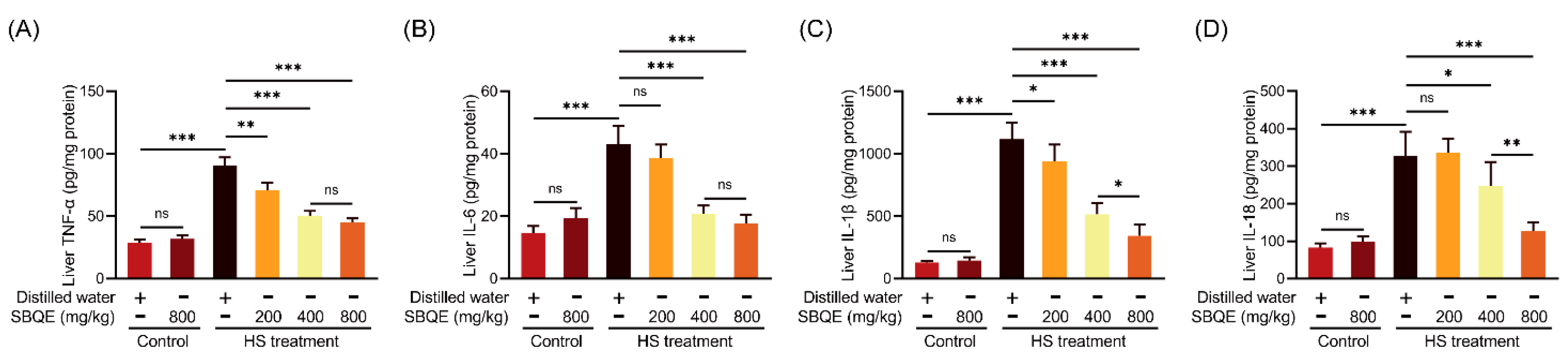
3.4. SBQE Inhibited the Hepatic Inflammatory Response Elicited by HS in Rats
3.5. SBQE Activated the Nrf2 Antioxidant Signaling Pathway in the Liver of HS Rats
3.6. SBQE Effectively Suppressed the Activation of NF-κB and the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway Induced by HS
3.7. SBQE Suppressed HS-Induced Hepatocellular Apoptosis in Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 |
| HS | Heat stress |
| SBQ | Sprouted black quinoa |
| SBQE | Sprouted black quinoa extract |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IL | Interleukin |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| ARE | Antioxidant response element |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
References
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Ji, P.; Yao, W.; Hua, Y.; Wei, Y. Sheng Mai San ameliorated heat stress-induced liver injury via regulating energy metabolism and AMPK/Drp1-dependent autophagy process. Phytomedicine 2022, 97, 153920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-X.; Yuan, Y.-M.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Yao, Q.-H.; Ye, X.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.-M.; Jha, R.; Balasubramanian, B.; Liu, W.-C. Phlorotannin Alleviates Liver Injury by Regulating Redox Balance, Apoptosis, and Ferroptosis of Broilers under Heat Stress. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaz, S.A.; Wasti, S.; Adnan, M.R.; Chaudhary, A.; Jha, R.; Mishra, B. Dried plum supplementation enhanced the expression of liver antioxidant capacity, metabolism, and epigenetic-related gene markers in broiler chickens under heat stress conditions: Dried plum increased liver metabolism in broiler. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, A.; Michiels, J.; Degroote, J.; Majdeddin, M.; Golian, A.; De Smet, S. Association between heat stress and oxidative stress in poultry; mitochondrial dysfunction and dietary interventions with phytochemicals. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Luo, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Chitosan Oligosaccharides Alleviate Heat-Stress-Induced Lipid Metabolism Disorders by Suppressing the Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in the Liver of Broilers. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimen, I.B.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Dabbebi, H.; Ben Mrad, M.; Abdrabbah, M. Reactive oxygen species, heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Xi, Y.; Liu, X. A Comprehensive Comparison of Different Selenium Supplements: Mitigation of Heat Stress and Exercise Fatigue-Induced Liver Injury. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 917349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.-N.; Peng, N.; Yuan, F.-F.; Li, X.-G.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.-S.; Li, B.-l.; Song, W.-b.; et al. Heatstroke induces liver injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, K.-J.; Chei, S.; Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, K.; Lee, B.-Y. Korean Red Ginseng and Korean black ginseng extracts, JP5 and BG1, prevent hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation induced by environmental heat stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shan, Q.; Ma, F.; Li, S.; Sun, P. Chlorogenic acid mitigates heat stress-induced oxidative damage in bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via upregulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Khan, I.; Manzoor, A.; Abdullah; Khan, F.; Al-Habsi, N.; Rahman, M.S. Quinoa: An Underutilized Pseudocereal with Promising Health and Industrial Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 14722–14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, G. Phenolic Constituents from Black Quinoa Alleviate Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating IRS1/PI3K/Akt/GLUTs Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 18780–18791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, R. Effects of quinoa on cardiovascular disease and diabetes: A review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1470834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, M.; Della Croce, C.M.; Bellani, L.; Tassi, E.L.; Echeverria, M.C.; Giorgetti, L. Effect of Sprouting, Fermentation and Cooking on Antioxidant Content and Total Antioxidant Activity in Quinoa and Amaranth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Bao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Wei, J.; Shen, Z.; Su, N. Comparative Evaluation of Chemical Composition and Nutritional Characteristics in Various Quinoa Sprout Varieties: The Superiority of 24-Hour Germination. Foods 2024, 13, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-A.; Ke, B.-J.; Cheng, C.-S.; Wang, J.-J.; Wei, B.-L.; Lee, C.-L. Red Quinoa Bran Extracts Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury and Fibrosis in Mice via Activation of Antioxidative Enzyme Systems and Blocking TGF-β1 Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Kousar, S.; Din, A.; Afzaal, M.; Faisal, M.N.; Sharif, M.K.; Rasheed, H.; Saeed, F.; Akram, N.; Ahmed, F.; et al. Hepatoprotective efficacy of quinoa seed extract against CCl4-induced acute liver toxicity in rat model. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 5007–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziminezhad, H.; Esmaeilzadeh Kenari, R.; Raftani Amiri, Z. Nanoemulsions of red quinoa and ginseng extracts with chitosan wall: Investigating the antioxidant properties and its effect on the shelf life of dairy cream. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 5734–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlene, A.A.; Prima, K.A.; Utama, L.; Anggraini, S.A. The Preliminary Study of the Dye Extraction from the Avocado Seed Using Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction. Procedia Chem. 2015, 16, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Lv, W.; Jing, X.; Yu, C.; Wuen, J.; Hasi, S. Camel whey protein alleviates heat stress-induced liver injury by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and inhibiting HMGB1 release. Cell Stress Chaperones 2022, 27, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; MacSween, R.N. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Fang, W.; Chen, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Ling, W. Adropin protects against liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via the Nrf2 mediated antioxidant capacity. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lan, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, X.; Dong, L.; Luo, G.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Screening of the Hepatotoxic Components in Fructus Gardeniae and Their Effects on Rat Liver BRL-3A Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.-N.; Lu, M.-H.; Guo, Y.-N.; Liang, S.-S.; Mou, R.-W.; He, Y.-M.; Tang, L.-P. Resveratrol relieves chronic heat stress-induced liver oxidative damage in broilers by activating the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, P.X.; Liu, R.; Tsao, R. Characterisation of phenolics, betanins and antioxidant activities in seeds of three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. genotypes. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, X.; Fan, G.; Xue, H.; Peng, S.; Huang, W.; Zhan, J. Harnessing the Potential of Quinoa: Nutritional Profiling, Bioactive Components, and Implications for Health Promotion. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, E.S.; Pek, C.J.N.; Tan, J.C.W.; Leo, C.H. Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Effect of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) with Pressurized Hot Water Extraction (PHWE). Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrali, D.; Giupponi, L.; De la Peña-Armada, R.; Villanueva-Suárez, M.J.; Mateos-Aparicio, I. The quinoa variety influences the nutritional and antioxidant profile rather than the geographic factors. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 133531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıkardeş, E.; Güzel, N. Impact of germination pre-treatments on buckwheat and Quinoa: Mitigation of anti-nutrient content and enhancement of antioxidant properties. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinder, S.; Kumari, S.; Singh, B.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Impact of germination on phenolic composition, antioxidant properties, antinutritional factors, mineral content and Maillard reaction products of malted quinoa flour. Food Chem 2021, 346, 128915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, R.A.; Galván-D’Alessandro, L.; Vandendriessche, P.; Chollet, S. Effect of Germination and Fermentation Process on the Antioxidant Compounds of Quinoa Seeds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso-Roca, E.C.; Aguilar-Felices, E.J.; Tinco-Jayo, J.A.; Arroyo-Acevedo, J.L.; Herrera-Calderon, O. Biomolecules with Antioxidant Capacity from the Seeds and Sprouts of 20 Varieties of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. (Quinoa). Plants 2021, 10, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qabba, M.M.; El-Mowafy, M.A.; Althwab, S.A.; Alfheeaid, H.A.; Aljutaily, T.; Barakat, H. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant Activity, and Ameliorating Efficacy of Chenopodium quinoa Sprouts against CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, D. The protective effect of quinoa on the gastric mucosal injury induced by absolute ethanol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tsao, R. Phytochemicals in quinoa and amaranth grains and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential health beneficial effects: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.; Ren, G. Anti-inflammatory activity of saponins from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages cells. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, H1018–H1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.; Cheng, X.; Wu, M.; Lv, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) Bran Saponins Alleviate Hyperuricemia and Inhibit Renal Injury by Regulating the PI3K/AKT/NFκB Signaling Pathway and Uric Acid Transport. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6635–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, J. Detection of lunasin in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and the in vitro evaluation of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Lv, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Du, D. Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Foods 2025, 14, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162758
Zhou J, Lv W, Li Z, Wang L, Guo B, Du D. Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162758
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Wenting Lv, Zhonghao Li, Li Wang, Bing Guo, and Donghua Du. 2025. "Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway" Foods 14, no. 16: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162758
APA StyleZhou, J., Lv, W., Li, Z., Wang, L., Guo, B., & Du, D. (2025). Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Foods, 14(16), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162758





