Modification of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Surimi Gels by Three Anionic Polysaccharides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of SMSGs
2.3. Gel Strength
2.4. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Water Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.7. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Relaxometry
2.8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.9. Dynamic Rheology Behavior
2.10. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy (Cryo-SEM)
2.11. Raman Spectroscopy
2.12. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.13. Chemical Forces
2.14. SDS-PAGE
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
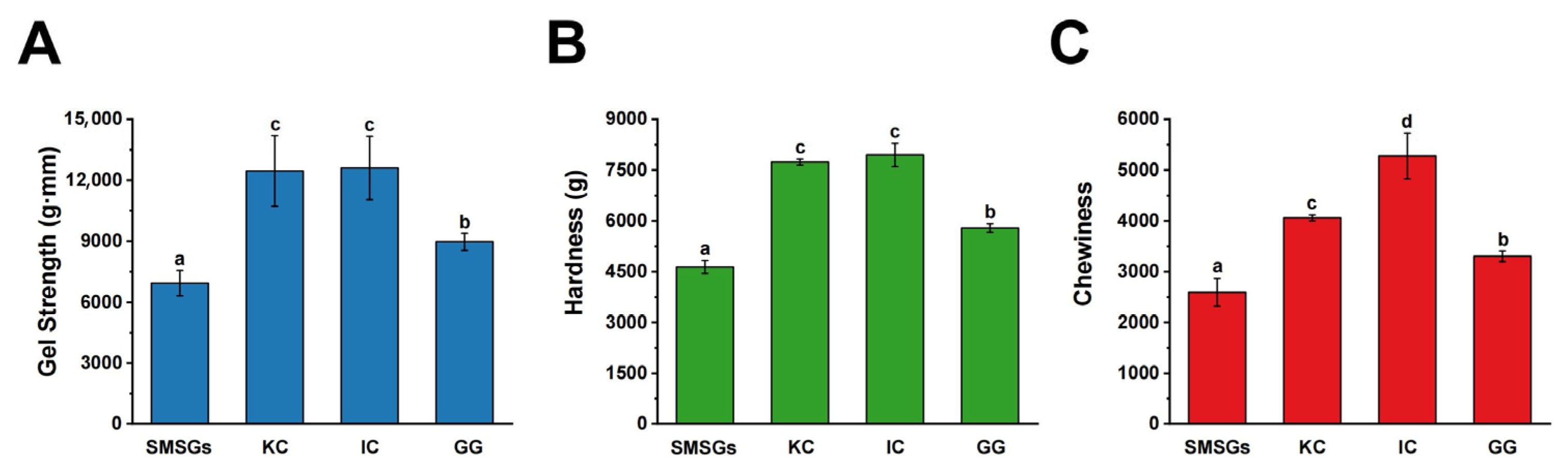
3.1. Effect of Polysaccharides on Gel Strength of SMSGs
3.2. Effect of Polysaccharides on TPA of SMSGs
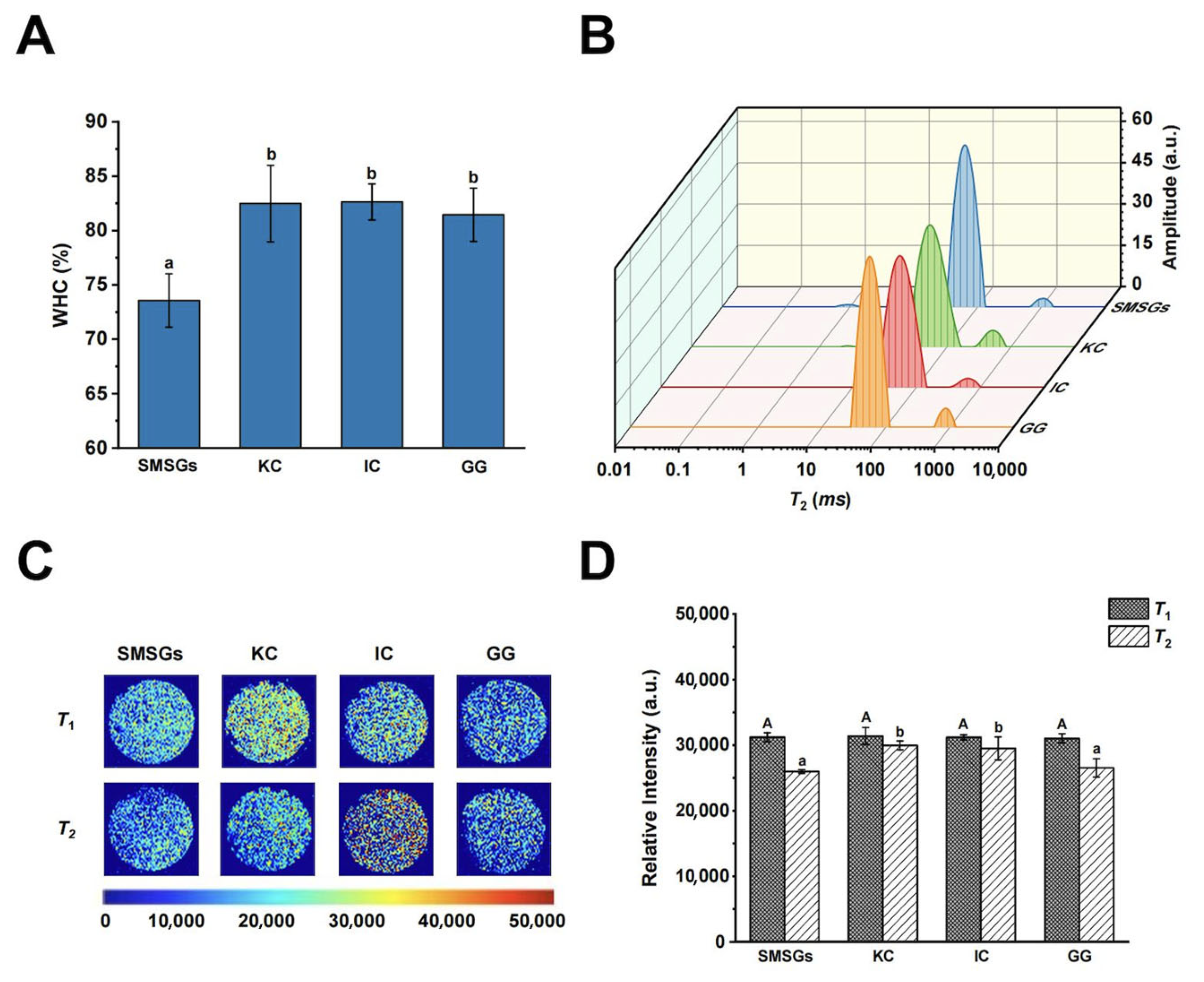
3.3. Effect of Polysaccharides on WHC of SMSGs
3.4. Effect of Polysaccharides on Water Migration and Distribution of SMSGs
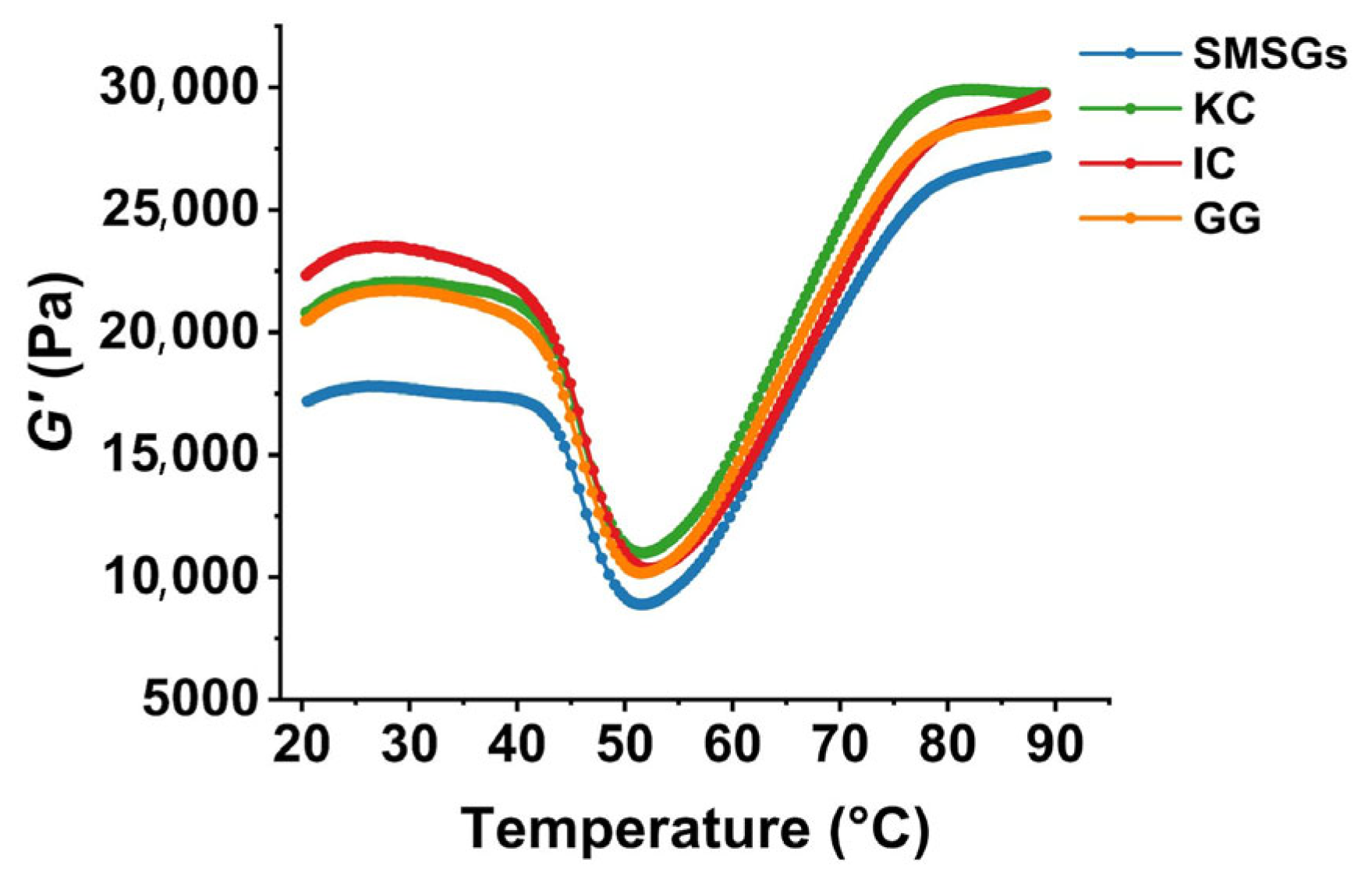
3.5. Effect of Polysaccharides on Dynamic Rheology of SMSGs
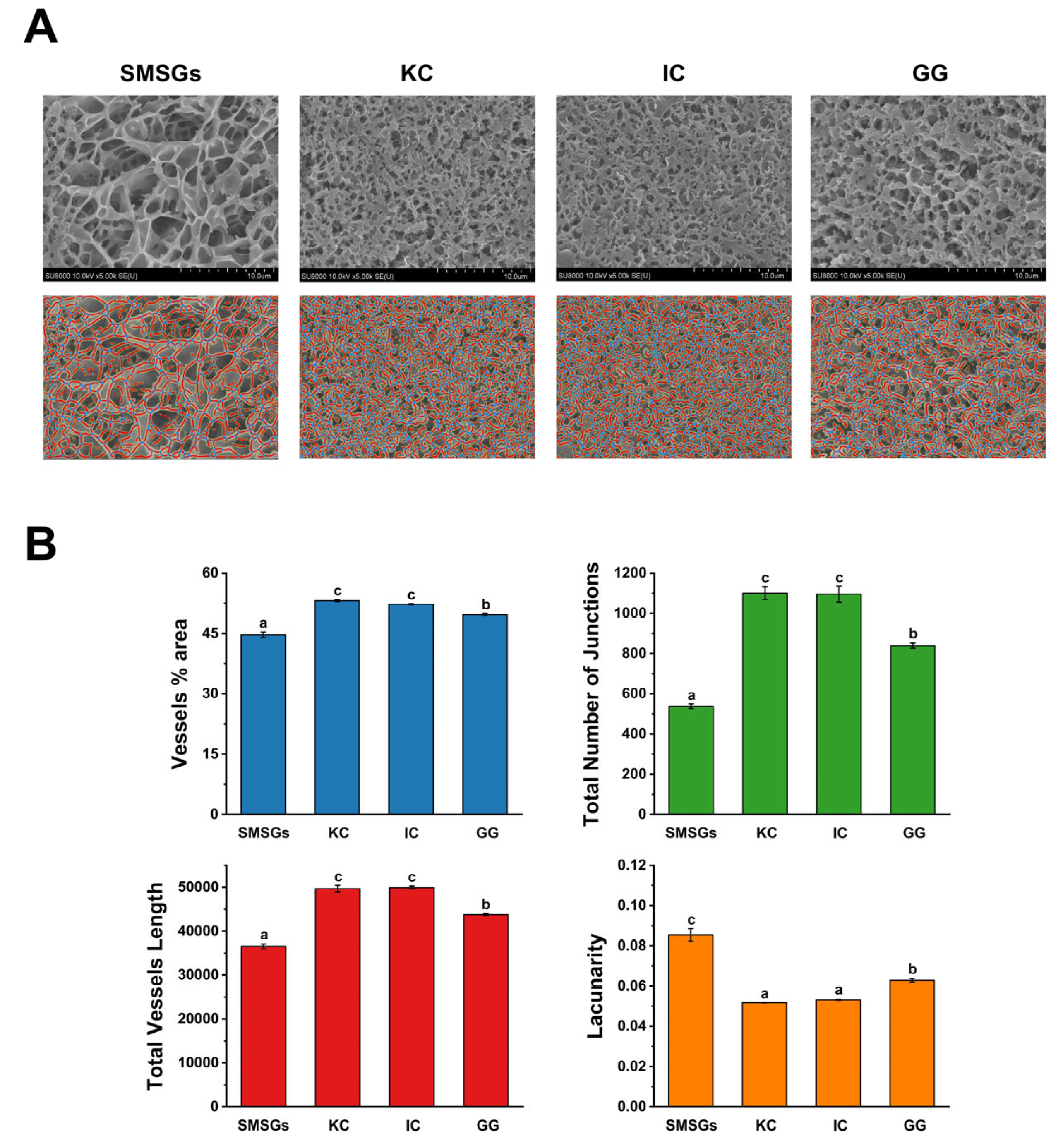
3.6. Effect of Polysaccharides on Cryo-SEM of SMSGs
3.7. Effect of Polysaccharides on Secondary Structure of SMSGs
3.8. Effect of Polysaccharides on FTIR Spectra of SMSGs
3.9. Effect of Polysaccharides on Chemical Forces of SMSGs
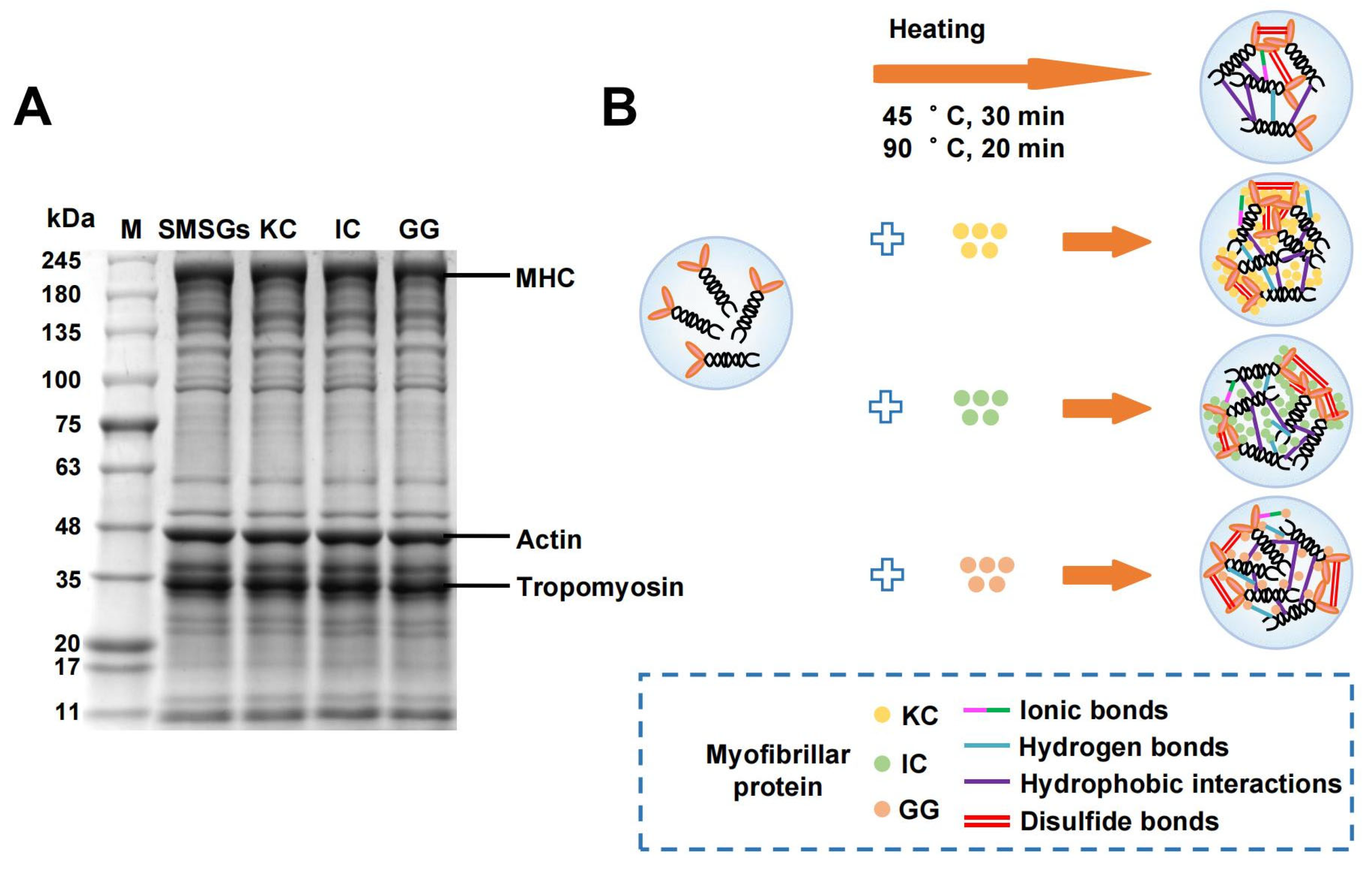
3.10. Effect of Polysaccharides on SDS-PAGE of SMSGs
3.11. The Formation Mechanism of SMSGs with the Addition of Various Polysaccharides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SMSGs | Spanish mackerel surimi gels |
| KC | κ-carrageenan |
| IC | ι-carrageenan |
| GG | gellan gum |
| TPA | texture profile analysis |
| WHC | water-holding capacity |
| LF-NMR | low-field nuclear magnetic resonance |
| T2 | Spin–spin relaxation time |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| Cryo-SEM | cryo-scanning electron microscopy |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| MHC | myosin heavy chain |
References
- Chen, J.; Deng, T.; Wang, C.; Mi, H.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effect of Hydrocolloids on Gel Properties and Protein Secondary Structure of Silver Carp Surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wei, C.; Jin, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wei, Z.; Liu, S.; Jia, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X. The Fabrication and Characterisation of surimi gel modified by konjac glucomannan with the different hydrolysis degree. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lámfalusy, T.; Ózsvári, L.; Szakos, D.; Kasza, G. Freshwater compared to marine Fish—A quantitative study on consumer perspectives. Aquaculture 2025, 603, 742382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Jia, H.; Shang, M.; Xu, C.; Lian, H.; Li, H.; Dong, X. Physiochemical properties and tastes of gels from Japanese Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) surimi by different washing processes. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.R.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wijaya, G.Y.A.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, L.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Gao, R. Recent developments in maintaining gel properties of surimi products under reduced salt conditions and use of additives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8518–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, Y. A Review of inhibition mechanisms of surimi protein hydrolysis by different exogenous additives and their application in improving surimi gel quality. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 140002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Jiang, X. Gelling properties of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) surimi as affected by washing process and high pressure. Int. J. Food Eng. 2010, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, H. Effects of anthocyanins and microbial transglutaminase on the physicochemical properties of silver carp surimi gel. J. Texture Stud. 2023, 54, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-L.; Yoshida, A.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yuan, J.; Maeda, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.-R.; Sun, X.-M.; Chen, C.-P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Quality improvement of threadfin bream (Nemipterus virgatus) surimi-gel using soy protein as a natural food additive. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Chu, P.; Zhu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhou, D. Achieving dual functions of texture modification and water retention of shrimp surimi products with the combination of epigallocatechin-3-Gallate and γ-Cyclodextrin. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 136034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Song, C.; Ma, H.; Hong, P.; Zhou, C. Tapioca starch improves the quality of Virgatus nemipterus surimi gel by enhancing molecular interaction in the gel system. Foods 2024, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. The interaction of starch-gums and their effect on gel properties and protein conformation of silver carp surimi. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Sang, Y.; Tian, G. Gel mechanism analysis of minced scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) meat modified by three kinds of food colloids. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, B.; Ai, C.; Teng, H. Effect of κ-Carrageenan on saltiness perception and texture characteristic related to salt release in low-salt surimi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.; Park, J.W. Alaska pollock fish protein gels as affected by refined carrageenan and various salts. J. Food Qual. 2013, 36, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S. Effect of gellan incorporation on gel properties of bigeye snapper surimi. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.S.; Dora, K.C. Suitability of chitosan as cryoprotectant on croaker fish (Johnius gangeticus) surimi during frozen storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Vardhanabhuti, B. Effect of charge density of polysaccharides on self-assembled intragastric gelation of whey protein/polysaccharide under simulated gastric conditions. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Teng, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X. Elucidate the molecular basis of ampholytic chitosan as a high-performance cryoprotectant to myosin denaturation: The importance of saccharide charges. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, S.; Jiang, P.; Feng, Q.; Bao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, N. Discovery of potential protein markers associated with quality characteristics of antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) surimi gel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11751–11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, J.; Fu, L.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Kang, Z. Effect of gellan gum on functional properties of low-fat chicken meat batters. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-N.; Nie, B.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Han, J.-R.; Du, Y.-N.; Wu, H.-T. Complex coacervation of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) male gonad hydrolysates and κ-Carrageenan: Effect of NaCl and KCl. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-N.; Xue, S.; Du, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Xu, S.-Q.; Wu, H.-T. Influence of pH and blend ratios on the complex coacervation and synergistic enhancement in composite hydrogels from scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) protein hydrolysates and κ-carrageenan/xanthan Gum. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.-N.; Lai, B.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.-T. Impact of plant and animal proteins with transglutaminase on the gelation properties of clam Meretrix meretrix surimi. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-N.; Du, Y.-N.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Xu, S.-Q.; Wu, H.-T. Curcumin-loaded composite hydrogel based on scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) male gonad hydrolysates and κ-carrageenan: Characterization and in vitro digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Xiao, X.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Yang, H. Effects of rice residue on physicochemical properties of silver carp surimi gels. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Tang, Y.; Dong, G. Various factors affecting the gel properties of surimi: A review. J. Texture Stud. 2024, 55, e12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, M. Effects of hydrocolloids as fat-replacers on the physicochemical and structural properties of salt-soluble protein isolated from water-boiled pork meatballs. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Dai, H.; Lin, L.; Lu, J. Employment of κ-carrageenan and high pressure processing for quality improvement of reduced NaCl surimi gels. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, N.; Xiang, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zeng, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; et al. Three-dimensional printing properties of polysaccharide hydrocolloids–unrinsed sturgeon surimi complex hydrogels. Foods 2022, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, S.; Khoobbakht, F.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Hosseini, S.M. Characterization of gellan gum-chitosan based hydrogel to evaluate as a potential gelatin substitute. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Enhancing gel performance of surimi gels via emulsion co-stabilized with soy protein isolate and κ-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, H.J.; Rezaei, M.; Shabanpour, B.; Tabarsa, M. Effects of sulfated polysaccharides from green alga ulva intestinalis on physicochemical properties and microstructure of silver carp surimi. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, S.; Jiang, P.; Qian, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, N. κ-Carrageenan improves the gelation capacity of antarctic krill myofibrillar proteins through covalent and noncovalent interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Blecker, C.; Wei, X.; Xie, X.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Effects of different plant polysaccharides as fat substitutes on the gel properties, microstructure and digestion characteristics of myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.D. Investigation on water status and distribution in broccoli and the effects of drying on water status using NMR and MRI methods. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.F.; Qian, C.Y.; Qin, S.; Cai, H.Z.; Wang, H.; Xiao, H.M. Gelation of crocodile myofibrillar protein- κ-carrageenan mixtures in two low-NaCl solution. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, P.; Pan, J.; Yu, C.; Dong, X. Effect of κ-carrageenan on quality improvement of 3D printed hypophthalmichthys molitrix-sea cucumber compound surimi product. LWT Food Sci. 2022, 154, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zheng, W.; Fu, T.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; Ai, L. Cryoprotective effect of tamarind seed polysaccharide on grass carp surimi: Characteristics, interactions, and mechanisms. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, M.; Ai, C.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Imran, M.; Chen, L.; Teng, H. Ultrasonic treatment combined with curdlan improves the gelation properties of low-salt Nemipterus virgatus surimi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Chang, T.; Yang, H.; Cui, M. Effects of starches on the textural, rheological, and color properties of surimi–beef gels with microbial tranglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Shi, L.; Ren, Z.; Hao, G.; Chen, J.; Weng, W. Effects of emulsified lard and TGase on gel properties of threadfin bream (Nemipterus virgatus) surimi. LWT Food Sci. 2021, 146, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Extreme pH treatments enhance the structure-reinforcement role of soy protein isolate and its emulsions in pork myofibrillar protein gels in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Xie, J. Gel properties and interactions of mesona blumes polysaccharide-soy protein isolates mixed gel: The effect of salt addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernklau, I.; Lucas, L.; Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Protein network analysis—A new approach for quantifying wheat dough microstructure. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, F.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wu, C. Gel properties and protein structures of minced pork prepared with κ-carrageenan and non-meat proteins. Gels 2024, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T.; Zhang, B. Effect of micro- and nano-starch on the gel properties, microstructure and water mobility of myofibrillar protein from grass carp. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wei, S.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Effects of camellia oil on the properties and molecular forces of myofibrillar protein gel induced by microwave heating. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 5708–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Qiu, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y. Tannic acid enhanced the physical and oxidative stability of chitin particles stabilized oil in water emulsion. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Nuthong, P. Effect of psyllium (Plantago ovata forks) husk on characteristics, rheological and textural properties of threadfin bream surimi gel. Foods 2021, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Piao, X.; Zheng, B.; Gao, P.; Miao, W.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mei, G.; Zhou, R.; Deng, S. Enhancement of surimi gel properties through the synergetic effect of fucoidan and oligochitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Zheng, B.; Rea, M.C.; Miao, S. Effect of plant protein mixtures on the microstructure and rheological properties of myofibrillar protein gel derived from red sea bream (Pagrosomus major). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Mei, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhang, M. Effects of exopolysaccharide by Pediococcus acidilactici S1 on the gelation properties and microstructure of porcine myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) | T23 (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMSGs | 1.74 ± 0.80 a | 61.34 ± 1.70 c | 1106.95 ± 15.32 c |
| KC | 3.02 ± 0.45 b | 52.43 ± 1.66 a | 503.19 ± 23.79 a |
| IC | - | 55.93 ± 1.80 b | 752.93 ± 171.35 b |
| GG | - | 55.92 ± 0.89 b | 970.60 ± 0.80 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.-J.; Kong, F.-Y.; Zhang, L.-D.; Luo, M.-M.; Lv, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Zhang, L.-C.; Yan, J.-N.; Wu, H.-T. Modification of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Surimi Gels by Three Anionic Polysaccharides. Foods 2025, 14, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152671
Zhang Z-J, Kong F-Y, Zhang L-D, Luo M-M, Lv Y-Y, Wang C, Lai B, Zhang L-C, Yan J-N, Wu H-T. Modification of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Surimi Gels by Three Anionic Polysaccharides. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152671
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhu-Jun, Fan-Yu Kong, Lin-Da Zhang, Miao-Miao Luo, Yin-Yin Lv, Ce Wang, Bin Lai, Li-Chao Zhang, Jia-Nan Yan, and Hai-Tao Wu. 2025. "Modification of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Surimi Gels by Three Anionic Polysaccharides" Foods 14, no. 15: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152671
APA StyleZhang, Z.-J., Kong, F.-Y., Zhang, L.-D., Luo, M.-M., Lv, Y.-Y., Wang, C., Lai, B., Zhang, L.-C., Yan, J.-N., & Wu, H.-T. (2025). Modification of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) Surimi Gels by Three Anionic Polysaccharides. Foods, 14(15), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152671







