Hydrogel-Shielded Ellagic Acid Nanoparticles Prolong Colonic Retention and Mitigate DSS-Induced Colitis via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of EA Nanoparticles
2.3. Assembly and Analysis of F-DP@EAs Nanoparticle Hydrogel
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Assessed In Vitro
2.6. Intracellular ROS Assay
2.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Assay
2.8. In Vivo Intestinal Retention
2.9. Biosafety of EAs
2.10. Preventive Effects of EAs in DSS-Induced Colitis
2.11. Histological Examination of Colon
2.12. Cytokine and Oxidative Stress Analysis in Colonic Tissue
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
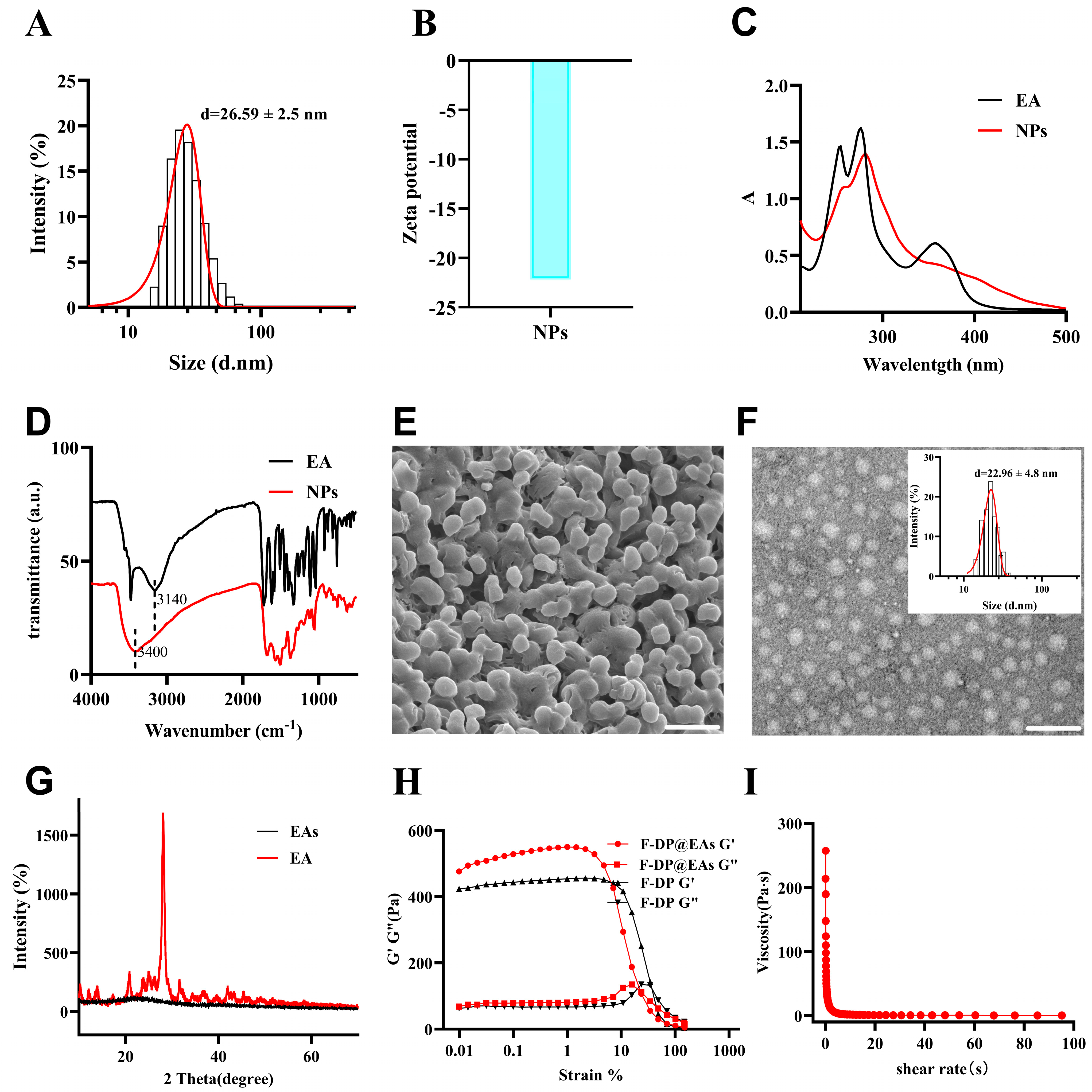
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of EAs and F-DP@EAs
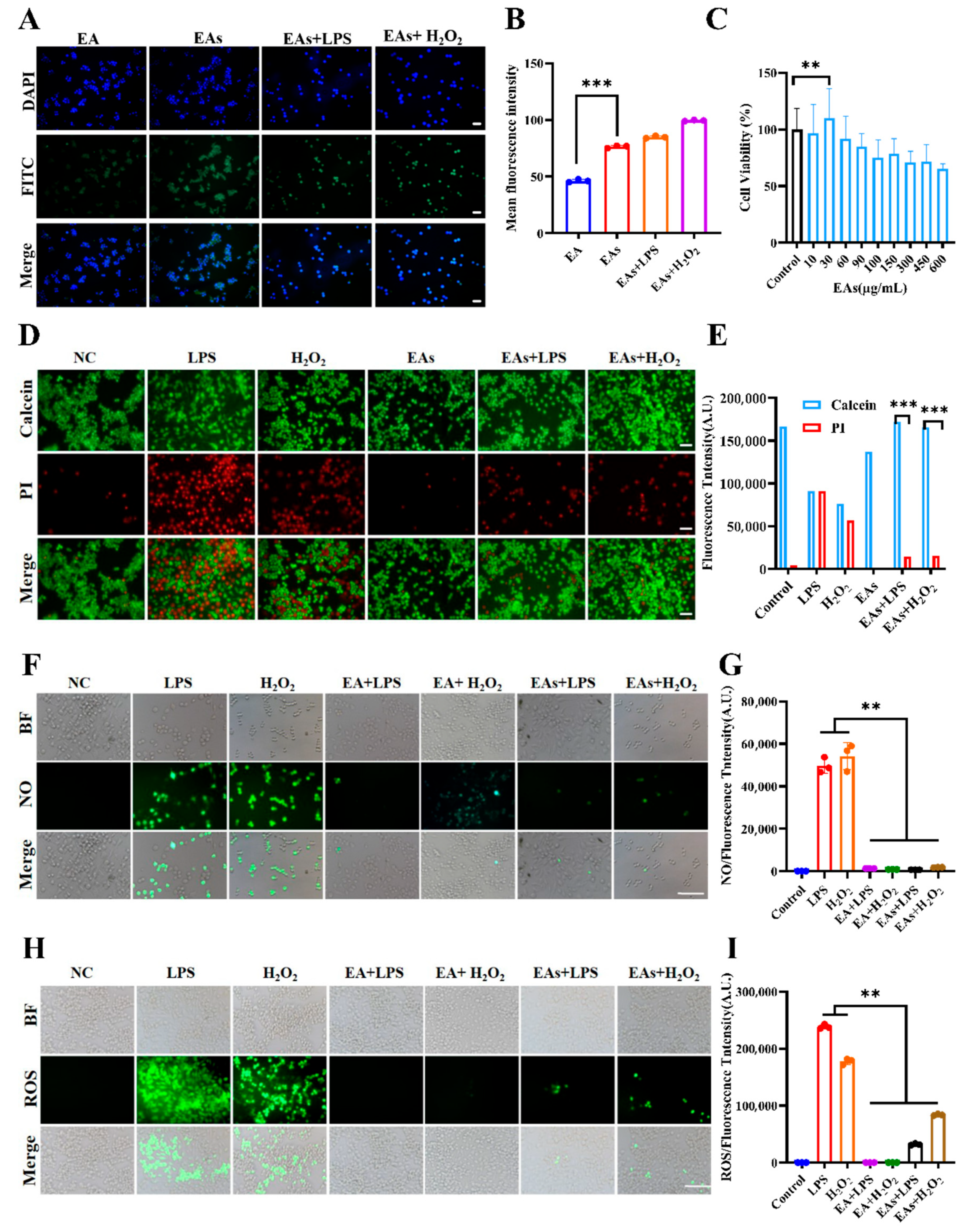
3.2. Cellular Uptake Behavior of EAs by Macrophages
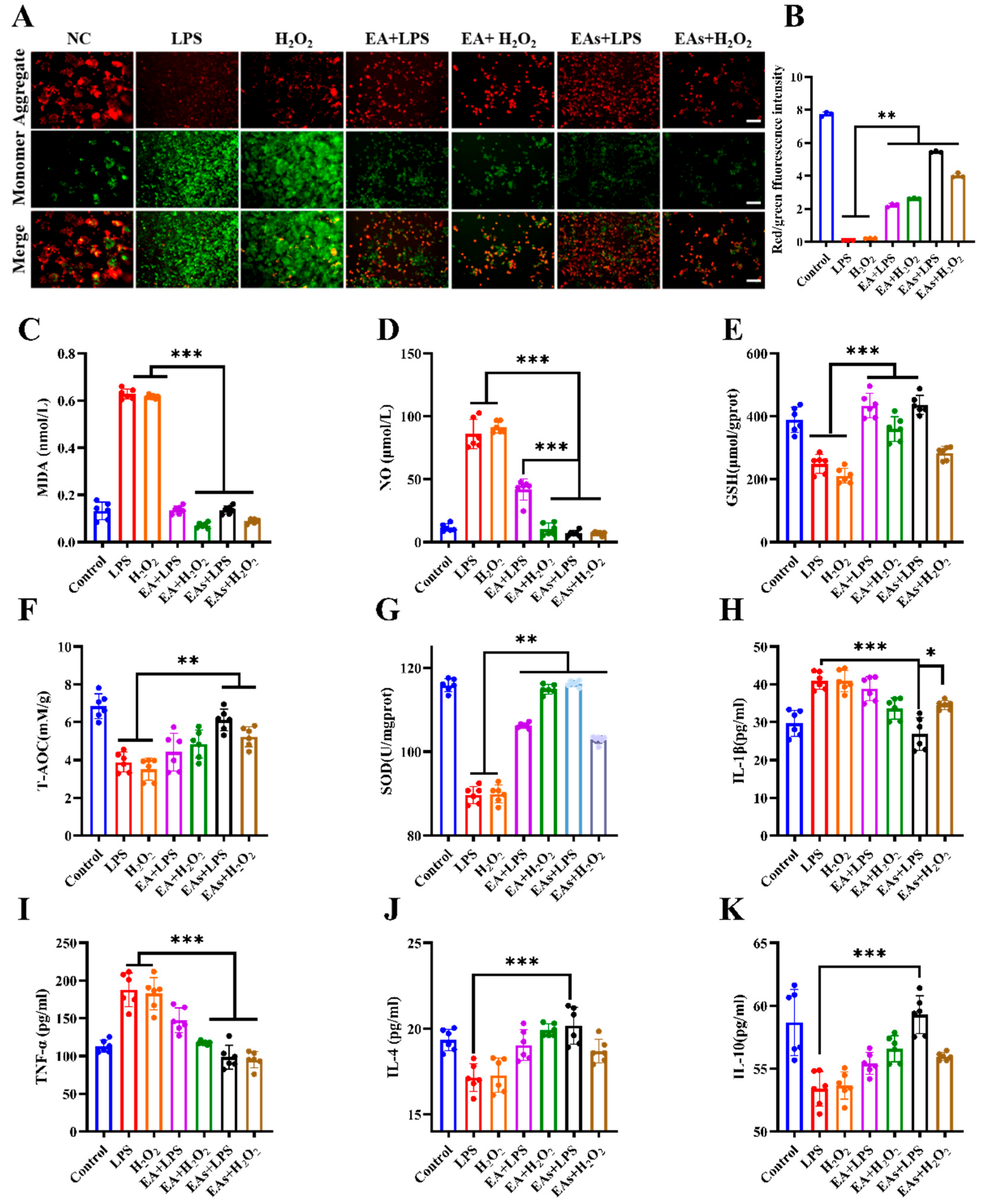
3.3. ROS-Scavenging Effects of EAs in Macrophages
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of EAs in Macrophages
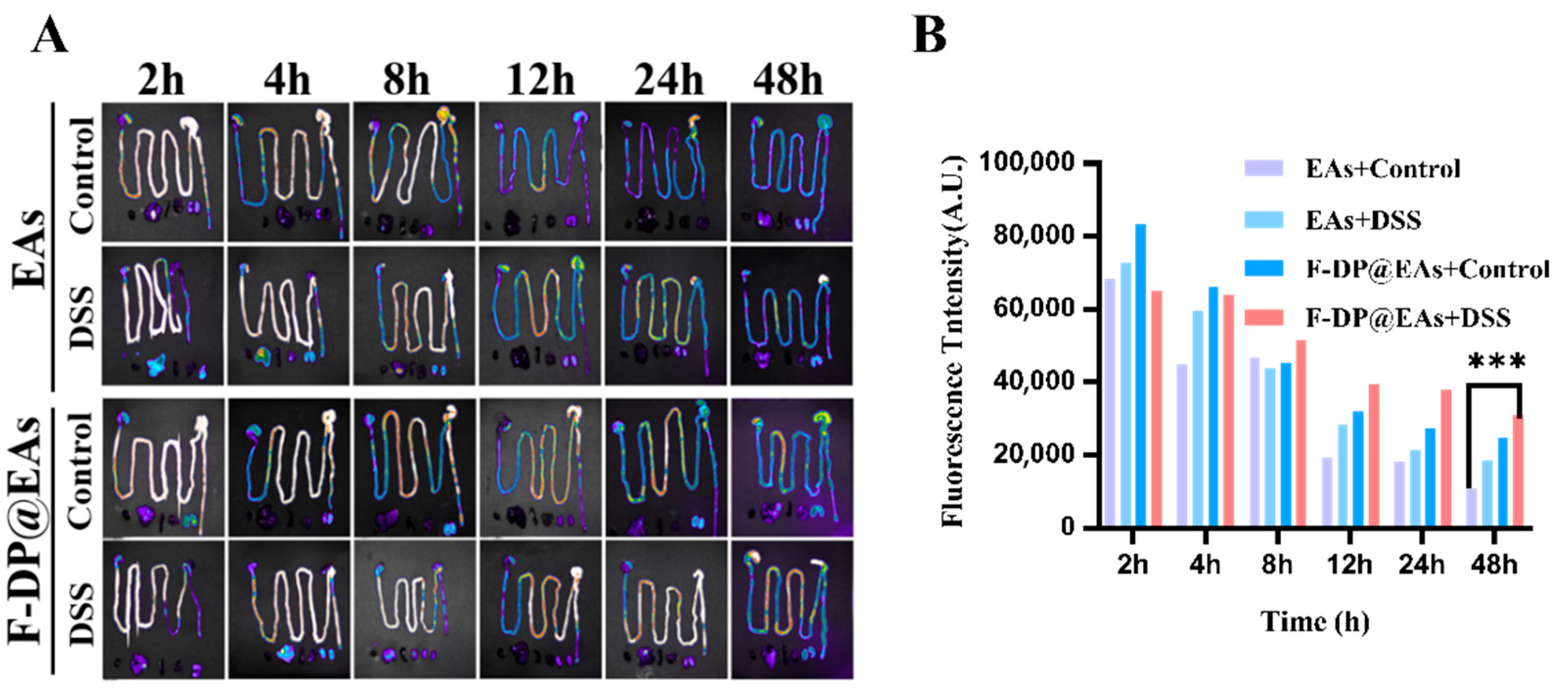
3.5. Biodistribution of EAs and F-DP@EAs In Vivo
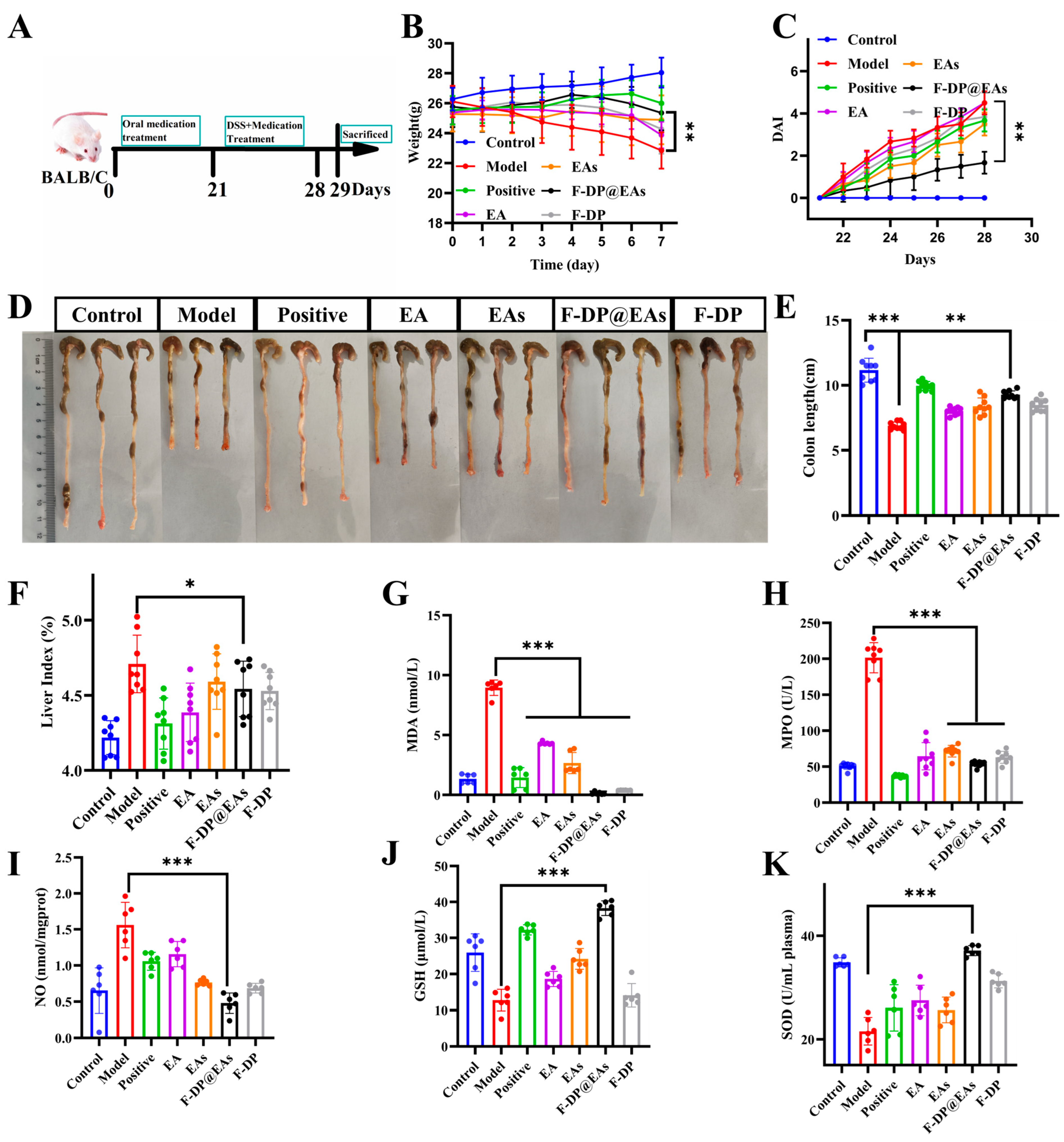
3.6. Preventive Effects of EAs in DSS-Induced IBD Mice
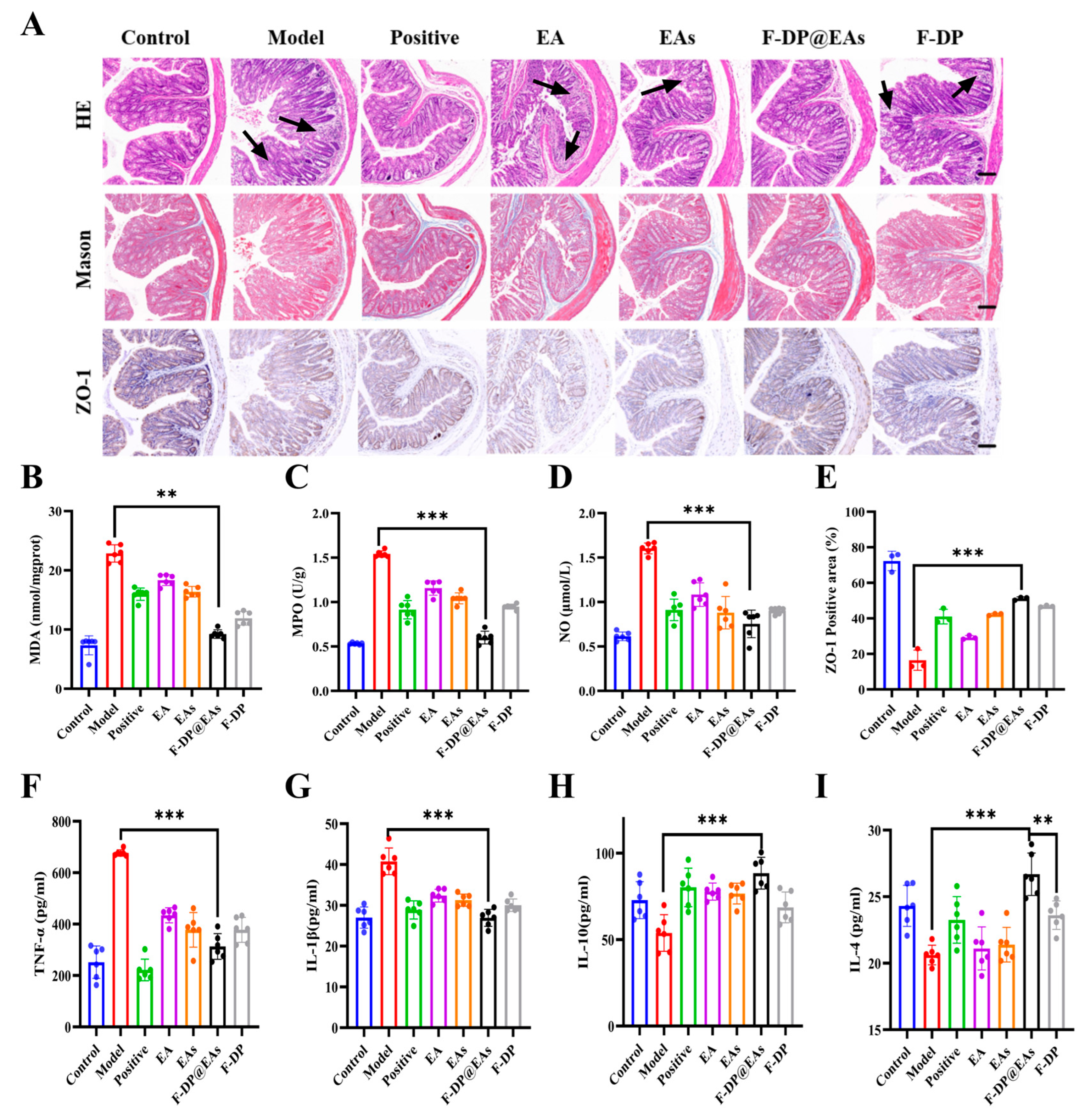
3.7. In Vivo Safety Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H. Gram-scale preparation of quercetin supramolecular nanoribbons for intestinal inflammatory diseases by oral administration. Biomaterials 2023, 295, 122039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Fan, H.; Ding, J.; Han, C.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, F.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hou, X.; et al. ROS-responsive nanoparticles for oral delivery of luteolin and targeted therapy of ulcerative colitis by regulating pathological microenvironment. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.-Q.; Liang, W.; Li, D.; Dai, W.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, B.-B.; Yang, Q. Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Polymer Drug Delivery System Targeted Oxidative Stressed Colon Cells to Ameliorate Colitis. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 17287–17308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.-W.; Sun, R.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Hu, J.-N. Colon-Targeting Angelica sinensis Polysaccharide Nanoparticles with Dual Responsiveness for Alleviation of Ulcerative Colitis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 26298–26315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Y.; Lin, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Miao, L.; Wei, C.-W.; et al. Integrated cascade nanozyme catalyzes in vivo ROS scavenging for anti-inflammatory therapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Jiang, S.; Li, Z. DNA Nanostructures Treat Inflammatory Bowel Disease through ROS Scavenging and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Han, Y.-J.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Song, L.-H.; Lv, L.-P.; Ma, P.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Two Birds with One Stone: Empowering Probiotic with Nanoenzyme for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Anemia through Oral Administration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 32878–32893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Gu, Z. Epicatechin-assembled nanoparticles against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6965–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fan, Q.; Hong, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Therapeutic Nanoparticles from Grape Seed for Modulating Oxidative Stress. Small 2021, 17, 2102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, Y. Polyphenolic Nanoparticle-Modified Probiotics for Microenvironment Remodeling and Targeted Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 12917–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Bai, W.; Dong, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Antioxidative myricetin-enriched nanoparticles towards acute liver injury. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7875–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, R.; Jin, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.X. Oral delivery of decanoic acid conjugated plant protein shell incorporating hybrid nanosystem leverage intestinal absorption of polyphenols. Biomaterials 2022, 281, 121373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Che, S.; Wu, K.; Wu, M. Ellagic acid prevents gut damage via ameliorating microbe-associated intestinal lymphocyte imbalance. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9822–9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Pan, J.; Sun, M.; Fang, Y. Comparative multiomics study of the effects of Ellagic acid on the gut environment in young and adult mice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Shi, L.; Bao, M.-Y.; Yu, F.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.-X.; Lin, J.-C.; Jia, W.; et al. Dietary ellagic acid therapy for CNS autoimmunity: Targeting on Alloprevotella rava and propionate metabolism. Microbiome 2024, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, W.; Ma, R.; Kang, J.-Y.; Iradukunda, Y.; Shi, Y.-P. Green and shape-tunable synthesis of ellagic acid crystalline particles by tannic acid for neuroprotection against oxidative stress. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 3610–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Lu, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y.; Cai, K.; et al. An Orally-Administered Nanotherapeutics with Carbon Monoxide Supplying for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapy by Scavenging Oxidative Stress and Restoring Gut Immune Homeostasis. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 21116–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Shionoya, M.; Gao, C.; Wang, R. Oral microsphere formulation of M2 macrophage-mimetic Janus nanomotor for targeted therapy of ulcerative colitis. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, A.; Andretto, V.; Chevalier, Y.; Kryza, D.; Sidi-Boumedine, J.; Grenha, A.; Guerreiro, F.; Gharsallaoui, A.; La Padula, V.; Montembault, A.; et al. Nanocomposite sponges for enhancing intestinal residence time following oral administration. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Chen, T.; Du, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Hu, J. Folic acid-based hydrogels co-assembled with protocatechuic acid for enhanced treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2025, 246, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Li, N.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Gut microbiota from green tea polyphenol-dosed mice improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis and ameliorates experimental colitis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Ma, X.; Cui, X.; Sun, Z.; Su, W.; Li, X. Preparation of Strong Antioxidative, Therapeutic Nanoparticles Based on Amino Acid-Induced Ultrafast Assembly of Tea Polyphenols. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33550–33563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Levin, A.; Chen, W.; Xing, R.; Zou, Q.; Herling, T.W.; Challa, P.K.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Yan, X. Nucleation and Growth of Amino Acid and Peptide Supramolecular Polymers through Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 18116–18123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, R.; Li, C. Rutin-Loaded Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel for Anti-Inflammation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 26327–26337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, M.; Pu, X.; Tang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L. Melittin-Loaded Multifunctional Nanozyme for Ulcerative Colitis Treatment via Enzyme-Immunotherapy and Ferroptosis Inhibition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, e03374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Han, G.; Jin, D.Y.; Gil, K.C.; Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Park, J.Y.; Jang, H.; Park, D.; Lee, S.; et al. Mucoadhesive Mesalamine Prodrug Nanoassemblies to Target Intestinal Macrophages for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 16297–16311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, B.-W.; Liu, D.; Tan, M. Hepatic-targeted delivery of astaxanthin for enhanced scavenging free radical scavenge and preventing mitochondrial depolarization. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lu, G.; Ren, M.; Lyu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; He, S. Yeast-Inspired Orally-Administered Nanocomposite Scavenges Oxidative Stress and Restores Gut Immune Homeostasis for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 7350–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Guo, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, Y. Somatostatin and Mannooligosaccharide Modified Selenium Nanoparticles with Dual-Targeting for Ulcerative Colitis Treatment. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 14914–14930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.-J.; Yu, F.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, W. Inflammatory Microenvironment-Responsive Microsphere Vehicles Modulating Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation for Intestinal Stem Cell Niche Remodeling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 12063–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, H.; Rao, Y.; Hong, D.; Lu, C.; Yu, M.; Lu, X.; Yu, C.; et al. Oral administration of inflammatory microenvironment-responsive carrier-free infliximab nanocomplex for the targeted treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.R.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, R.; Hu, Y.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Han, Q.; Kong, X.; Li, Y. Smart Silk-Based In Situ Sol-Gel Modulates Rectal Microenvironment for Effective Ulcerative Colitis Alleviation. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2025, 14, e2500984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Zhao, W.; Feng, R.; Zhang, L.; Ge, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, R. Melanin nanoparticles-loaded lactobacillus fermentum exosomes for targeted and visualized treatment of ulcerative colitis. J. Adv. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, X.; Chen, T.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Du, Y.; Hu, J. Hydrogel-Shielded Ellagic Acid Nanoparticles Prolong Colonic Retention and Mitigate DSS-Induced Colitis via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging. Foods 2025, 14, 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152559
Ye X, Chen T, Chen L, Wu D, Du Y, Hu J. Hydrogel-Shielded Ellagic Acid Nanoparticles Prolong Colonic Retention and Mitigate DSS-Induced Colitis via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152559
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Ximei, Tao Chen, Lihang Chen, Di Wu, Yinan Du, and Jiangning Hu. 2025. "Hydrogel-Shielded Ellagic Acid Nanoparticles Prolong Colonic Retention and Mitigate DSS-Induced Colitis via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging" Foods 14, no. 15: 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152559
APA StyleYe, X., Chen, T., Chen, L., Wu, D., Du, Y., & Hu, J. (2025). Hydrogel-Shielded Ellagic Acid Nanoparticles Prolong Colonic Retention and Mitigate DSS-Induced Colitis via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging. Foods, 14(15), 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152559





