Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
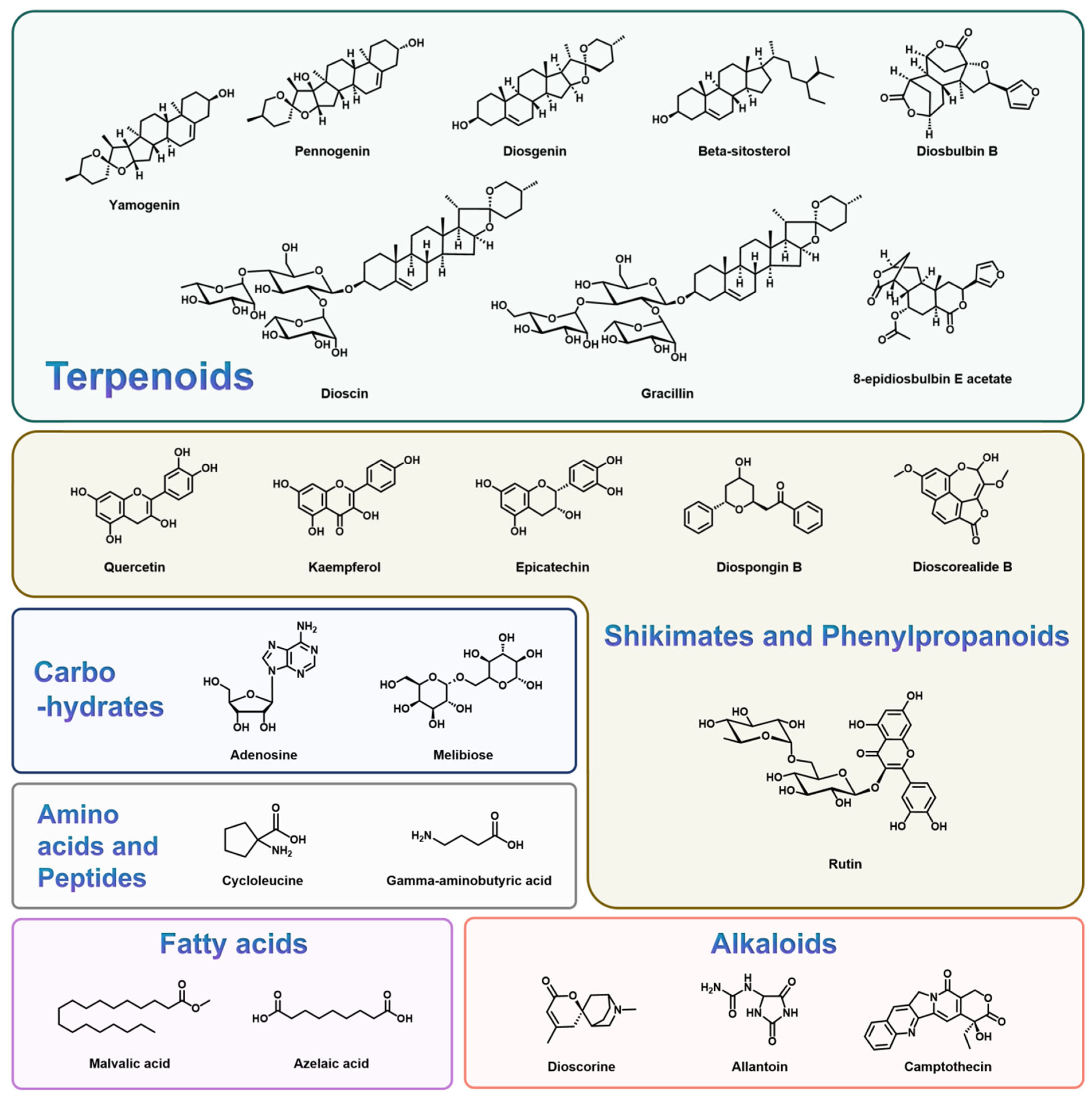
3. Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea spp.
3.1. Terpenoid Compounds
3.2. Shikimate and Phenylpropanoid Compounds
3.3. Carbohydrate Compounds
3.4. Fatty Acid Compounds
3.5. Alkaloids Compounds
3.6. Amino Acids and Peptide Compounds
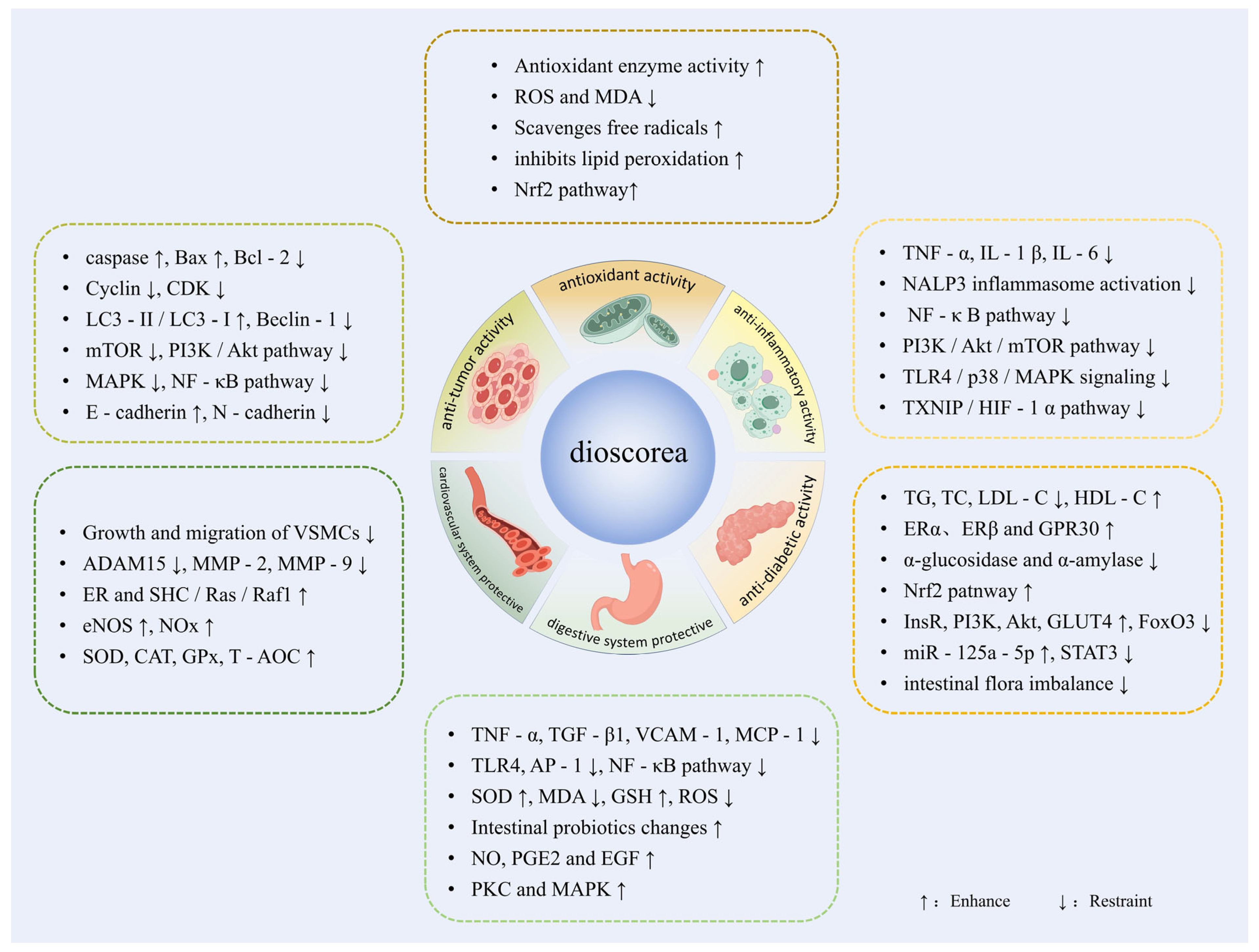
4. Functional Properties of Dioscorea spp.
4.1. Antioxidant Activity
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Activity
4.3. Anti-Diabetic and Endocrine Modulating Activity
4.4. Digestive System Protective Activity
4.5. Cardiovascular System Protective Activity
4.6. Anti-Tumor Activity
4.7. Other Functional Activities
5. Functional Food Regulation
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional Foods: Product Development, Technological Trends, Efficacy Testing, and Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agregán, R.; Pateiro, M.; Bohrer, B.M.; Shariati, M.A.; Nawaz, A.; Gohari, G.; Lorenzo, J.M. Biological Activity and Development of Functional Foods Fortified with Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6018–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrijević, D.; Pastor, K.; Nastić, N.; Özogul, F.; Krulj, J.; Kokić, B.; Bartkiene, E.; Rocha, J.M.; Kojić, J. Betaine as a Functional Ingredient: Metabolism, Health-Promoting Attributes, Food Sources, Applications and Analysis Methods. Molecules 2023, 28, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-L.; Ma, R.-H.; Zhang, F.; Ni, Z.-J.; Thakur, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Evolutionary Research Trend of Polygonatum Species: A Comprehensive Account of Their Transformation from Traditional Medicines to Functional Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 3803–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Joshi, P.B.; Ahmad, Z.; Hemeg, H.A.; Olatunde, A.; Naz, S.; Hafeez, N.; Simal-Gandara, J. Edible Mushrooms as Potential Functional Foods in Amelioration of Hypertension. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 2644–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łysakowska, P.; Sobota, A.; Wirkijowska, A. Medicinal Mushrooms: Their Bioactive Components, Nutritional Value and Application in Functional Food Production—A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasdaran, A.; Hamedi, A.; Shiehzadeh, S.; Hamedi, A. A Review of Citrus Plants as Functional Foods and Dietary Supplements for Human Health, with an Emphasis on Meta-Analyses, Clinical Trials, and Their Chemical Composition. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 54, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Exploring Novel Frontiers of Advancements in Purple Yam (Dioscorea Alata L.) Starch Extraction, Modification, Characterization, Applications in Food and Other Industries. Meas. Food 2024, 15, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; et al. Chinese Yam (Dioscorea): Nutritional Value, Beneficial Effects, and Food and Pharmaceutical Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, C.; AdeOluwa, O.O.; Bhullar, G.S. Yam (Dioscorea spp.). In Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 435–441. ISBN 978-0-12-394808-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, C.; Ge, M.; Qian, Y.; Ma, B. Physicochemical Properties and Biological Activities of Polysaccharides from the Peel of Dioscorea Opposita Thunb. Extracted by Four Different Methods. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Kumar, V.; Dey, A.; Pandey, D.K. HPTLC Quantification of Diosgenin in Dioscorea deltoidea: Evaluation of Extraction Efficacy, Organ Selection, Drying Method and Seasonal Variation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 138, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebot, V.; Faloye, B.; Okon, E.; Gueye, B. Simultaneous Quantification of Allantoin and Steroidal Saponins in Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Powders. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 13, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, B.; Biswas, M.; Panda, D. Nutritional, Anti-Nutritional and Physico-Functional Properties of Wild Edible Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Tubers from Koraput, India. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Hossain, M.; Das, N.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, N.; Hasan, R.; Alam, J.; Islam, N.; Wahed, T.B.; Kundu, S.K. Investigation of Bioactivities of Methanolic and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Dioscorea pentaphylla Leaf along with Its Phenolic Composition. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Naz, R.; Yousaf, Z.; Mudau, F.N.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Ezzat, S.M.; El Bishbishy, M.H.; et al. Dioscorea Plants: A Genus Rich in Vital Nutrapharmaceuticals—A Review. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hou, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Reveals the Effects of Soil on the Metabolites in Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Molecules 2023, 28, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Wang, M.; Leber, C.A.; Nothias, L.-F.; Reher, R.; Kang, K.B.; Van Der Hooft, J.J.J.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gerwick, W.H.; Cottrell, G.W. NPClassifier: A Deep Neural Network-Based Structural Classification Tool for Natural Products. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.A.; Hasan, S.; Gnanaselvan, S.; Baskaran, S.; Danaraj, J. Biological Activities and Nanoparticle Synthesis of Dioscorea bulbifera Andits Mechanistic Action—An Extensive Review. PNT 2024, 12, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.X.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Ye, S.; Luan, Y. Identification of Genetic Variants Controlling Diosgenin Content in Dioscorea zingiberensis Tuber by Genome-Wide Association Study. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Seto, K. The Effect of Dioscorea esculenta Powder on Prostaglandin E2 and Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 2 Levels, Menstrual Pain, and Premenstrual Syndrome in Young Women: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutr. Health 2024, 30, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y.; Mo, L.J. Diosgenin biosynthesis pathway and its regulation in Dioscorea cirrhosa L. PeerJ 2024, 12, e16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Graczyk, P.; Hering, A.; Gucwa, M.; Nowak, A.; Hałasa, R. An In Vitro Study on the Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Properties of Yamogenin—A Plant Steroidal Saponin and Evaluation of Its Mechanism of Action in Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoda, K.; Kato, M.; Tsunematsu, Y.; Eto, F.; Sato, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Tamura, K.; Yao, I.; Dohra, H.; et al. Biosynthetic Gene Expression and Tissue Distribution of Diosgenin in Dioscorea japonica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-F.; Tang, Y.-N.; Ji, H.; Xiao, Z.-G.; Zhu, L.; Yi, T. Biotransformation of Dioscorea nipponica by Rat Intestinal Microflora and Cardioprotective Effects of Diosgenin. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4176518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, N.; Fatima, K.; Singh, S.; Mishra, D.; Gupta, A.C.; Kumar, Y.; Chanda, D.; Bawankule, D.U.; Shanker, K.; Khan, F.; et al. Bivalent Furostene Carbamates as Antiproliferative and Antiinflammatory Agents. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 194, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Chen, F. Chinese Yam and Its Active Components Regulate the Structure of Gut Microbiota and Indole-like Metabolites in Anaerobic Fermentation In Vitro. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharazi, W.Z.; McGowen, A.; Rose, P.; Jethwa, P.H. Could Consumption of Yam (Dioscorea) or Its Extract Be Beneficial in Controlling Glycaemia: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jakaria, M.; Yu, Y.-J.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, D.-K. Dioscorea nipponica Makino Rhizome Extract and Its Active Compound Dioscin Protect against Neuroinflammation and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.-J.; Luo, Y.-Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Njolibimi, M.; Li, W.; Hong, B.; Zhao, C. A New Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Separation and Purification of Dioscin, Protodioscin, and Diosgenin from Purple Yam. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L.; Niu, T.; Wang, X. Efficient Discovery of Active Isolates from Dioscorea spongiosa by the Combination of Bioassay-guided Macroporous Resin Column Chromatography and High-speed Counter-Current Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, 2300741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-N.; Zhang, D.-L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Song, W.-T.; Chen, W.-B.; Hu, G.-L.; Han, L.-Y.; Zhou, J.-C. Anti-Obesity Effects Exerted by Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Polysaccharides in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 6459–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.-N.; Yin, L.-H.; Jin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.-W.; Liu, K.-X.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Peng, J.-Y. Effect and Possible Mechanisms of Dioscin on Ameliorating Metabolic Glycolipid Metabolic Disorder in Type-2-Diabetes. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhan, Y.; Ke, J.; Wang, K.; Liang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ao, W.; Wei, X.; et al. Dioscin Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells by Reversing TGF-Β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Molecules 2019, 24, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.-S.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Y.-M.; Wen, W.-B.; et al. Dioscin, a Steroidal Saponin Isolated from Dioscorea nipponica, Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Inhibiting Th17 Cell Response. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Ali, Z.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Khan, I.A. Hepatoprotective Effect of Steroidal Glycosides from Dioscorea villosa on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in HepG2 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Bai, W.; Guan, P.; Song, Z.; Chen, H. Effect of Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Drying on Active Ingredients, Textural Properties and Moisture Distribution of Yam (Dioscorea opposita). Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitani, M.; Cheng, K.-C.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; Kairupan, T.S.; Sameshima, N.; Shimizu, T.; Hashiguchi, T.; Inui, A. Allantoin Ameliorates Chemically-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Damage Through Activation of the Imidazoline I3 Receptors. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, H.-K.; Rahman, M.M.; Kim, G.-B.; Na, C.-S.; Song, C.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Kang, H.-S. Antidiabetic Effects of Yam (Dioscorea batatas) and Its Active Constituent, Allantoin, in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8532–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Man, S.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Wang, T. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of the Extracts from Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposite Thunb.) Flesh and Peel and the Effective Compounds. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H1553–H1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liang, T.; Jin, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, P. Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Alleviates Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Modifies Intestinal Microbiota, and Increases the Level of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mice. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Zou, Z.; Han, J.; Gao, X.; Tang, R.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.; et al. Analysis of the N-glycoforms and immunoactivity of Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita thunb.) glycoprotein 30CYGP. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Zang, L.; Li, W.; Xiao, X.; Yu, J.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ye, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, W. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Yam Glycoprotein on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the NLRP3 and NF-κB/TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Su, T. Antifatigue Effects and Antioxidant Activity in Polysaccharide Fractions from Chinese Yam Bulbils. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Xian, C.J. Dioscorea bulbifera Polysaccharide and Cyclophosphamide Combination Enhances Anti-Cervical Cancer Effect and Attenuates Immunosuppression and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 19185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, B.; Kan, Y.; Yang, H.; Feng, W.; Zheng, X. Chinese Yam Extract and Adenosine Attenuated LPS-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting RAS and Apoptosis via the ER-Mediated Activation of SHC/Ras/Raf1 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Yu, H.; Meng, M.; Wang, C. Research on the Structural Characteristics of a Novel Chinese Iron Yam Polysaccharide and Its Gastroprotection Mechanism Against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Lesion in a BALB/c Mouse Model. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6054–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegal, J.; Park, N.-J.; Jo, B.-G.; Bong, S.-K.; Jegal, H.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, S.-N. Anti-Atopic Properties of Gracillin Isolated from Dioscorea quinqueloba on 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Skin Lesions in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuia, M.S.; Chowdhury, R.; Sonia, F.A.; Kamli, H.; Shaikh, A.; El-Nashar, H.A.S.; El-Shazly, M.; Islam, M.T. Anticancer Potential of the Plant-Derived Saponin Gracillin: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanistic Approaches. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202300847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Liu, P.; Shi, H.; Fan, W.; Feng, X.; Chen, J.; Jing, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Identification of anti-inflammatory components in Dioscorea nipponica makino based on HPLC-MS/MS, quantitative analysis of multiple components by single marker and chemometric methods. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1213, 123531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukiya, M.; Sato, D.; Kimura, H.; Hirai, Y.; Nishina, A. Tokoronin Contained in Dioscorea tokoro Makino Ex Miyabe Suppressed α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16 Cells via Suppression of Classical MAPK Pathway Activation. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korokin, M.; Gudyrev, O.; Gureev, V.; Korokina, L.; Peresypkina, A.; Pokrovskaia, T.; Lazareva, G.; Soldatov, V.; Zatolokina, M.; Pokrovskii, M. Studies to Elucidate the Effects of Furostanol Glycosides from Dioscorea deltoidea Cell Culture in a Rat Model of Endothelial Dysfunction. Molecules 2019, 25, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.T.; Park, K.-S.; Ryuk, J.A.; Kim, H.J.; Ko, B.S. Development of an Oriental Medicine Discrimination Method through Analysis of Steroidal Saponins in Dioscorea nipponica Makino and Their Anti-Osteosarcoma Effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, M.; Tokiwano, T.; Kawaii, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Oh, K.; Yoshizawa, Y. Protodioscin, Isolated from the Rhizome of Dioscorea tokoro Collected in Northern Japan Is the Major Antiproliferative Compound to HL-60 Leukemic Cells. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2017, 13, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, D.-S.; Jiang, L.-L.; Liu, F.-J.; Wu, Z.-T.; Li, Z.-Q.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhou, J.; Li, P.; et al. Metabolomic-Transcriptomic Landscape of 8-Epidiosbulbin E Acetate -a Major Diterpenoid Lactone from Dioscorea Bulbifera Tuber Induces Hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 135, 110887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Pan, J.; Peng, Y.; et al. Diosbulbin B: An Important Component Responsible for Hepatotoxicity and Protein Covalent Binding Induced by Dioscorea bulbifera L. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severiche-Castro, J.; Wilches Diaz, G.; Combariza Montañez, A.F.; de Almeida Oliveira, M.G.; Rosado Mercado, W. Structural Analysis and Inhibition Capacity of Dioscorin Protein Yam: Theoretical Study by Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulations. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 113, e22025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Fu, Z.; Fu, X.; Han, L. Strategy of Combining Offline 2D LC-MS with LC-DIA-MS/MS to Accurately Identify Chemical Compounds and for Quality Control of Dioscorea septemloba Thunb. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.-N.; Gu, Y.; Guo, Q. Deltonin Enhances Gastric Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis and Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin via Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Signaling. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 15, 1739–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wan, H.; Liu, W.; Kong, F.; Ma, G. Deltonin Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Correlation with Modulation of Autophagy and Inflammation. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaniad, P.; Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Pianwanit, S.; Tewtrakul, S. Anti-HIV-1 Integrase Compounds from Dioscorea bulbifera and Molecular Docking Study. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaniad, P.; Tewtrakul, S.; Sudsai, T.; Langyanai, S.; Kaewdana, K. Anti-Inflammatory, Wound Healing and Antioxidant Potential of Compounds from Dioscorea bulbifera L. Bulbils. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; An, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Bayoude, A.; Fan, X.; Yu, B.; Li, R. Protection Effect of Dioscoreae rhizoma against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Injury in Vitro and in Vivo: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-G.; Guo, X.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Dai, D.-D.; Xu, X.-R.; Ge, X.-J.; Li, Y.-J.; Yang, T.-G. Organ- and Age-Specific Differences of Dioscorea polystachya Compounds Measured by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2000856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wen, L.; Shen, Y.; Shi, N.; Xing, Z.; Xia, Q.; Niu, H.; Huang, W. One Compound of Saponins from Disocorea zingiberensis Protected against Experimental Acute Pancreatitis by Preventing Mitochondria-Mediated Necrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.-L.; Pan, C.-H.; Wang, C.C.-N.; Hsu, K.-C.; Sheu, M.-J.; Chen, H.-F.; Wu, C.-H. Methyl Protodioscin, a Steroidal Saponin, Inhibits Neointima Formation in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.-C.; Shen, T.-S.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, I.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-P.; Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L. Methyl Protodioscin Induces Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Caspase-Dependent and MAPK Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaniad, P.; Mungthin, M.; Payaka, A.; Viriyavejakul, P.; Punsawad, C. Antimalarial Properties and Molecular Docking Analysis of Compounds from Dioscorea bulbifera L. as New Antimalarial Agent Candidates. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, X.; Ren, X.; Qin, Z. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds from Dioscorea (Yam) Leaves. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Młynarz, P. Phytochemicals Containing Biologically Active Polyphenols as an Effective Agent against COVID-19-Inducing Coronavirus. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-L.; Xu, G.-H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, C.-F.; Yi, L.-T. Yamogenin Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects via Inhibition of ER Stress and Microglial Activation in LPS-Induced Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yun, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, X. The Effect of Anthocyanins from Dioscorea alata L. on Antioxidant Properties of Perinatal Hainan Black Goats and Its Possible Mechanism in the Mammary Gland. Animals 2022, 12, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H.; Guan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Dioscorea alata L. Anthocyanins in a TNBS-Induced Colitis Model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, L.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, J. Genome-Wide Methylation, Transcriptome and Characteristic Metabolites Reveal the Balance between Diosgenin and Brassinosteroids in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainasara, M.M.; Abu Bakar, M.F.; Md Akim, A.; Linatoc, A.C.; Abu Bakar, F.I.; Ranneh, Y.K.H. Secondary Metabolites, Antioxidant, and Antiproliferative Activities of Dioscorea bulbifera Leaf Collected from Endau Rompin, Johor, Malaysia. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8826986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, W.; Lu, M.; Liu, X. Rapid Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Dioscorea opposita Thunb Peel Extract by Enzyme Functionalized Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC-MS/MS. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyedun, P.O.; Sonibare, M.A.; Ajiboye, C.O.; Gueye, B.; Paliwal, R.; Albach, D.C.; Nchiozem-Ngnitedem, V.-A.; Schmidt, B. Phytoecdysteroids from Dioscorea dumetorum (Kunth) Pax. and Their Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activities. Fitoterapia 2024, 177, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yang, H.; Ye, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Cui, D. Metabolome and Transcriptome Profiling Reveal Regulatory Network and Mechanism of Flavonoid Biosynthesis during Color Formation of Dioscorea cirrhosa L. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Son, S.-Y.; Jeon, S.-G.; Kim, J.-G.; Lee, C.-H. Metabolite Profiling of Dioscorea (Yam) Leaves to Identify Bioactive Compounds Reveals Their Potential as Renewable Resources. Plants 2021, 10, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-W.; Lee, D.-H.; Nam, I.; Lee, J.-W.; Huh, M.-J.; Roh, G.-H.; Park, I.-K. Acaricidal Activities of Dioscorea japonica Thunb. (Dioscoreales: Dioscoreaceae) Extract and Its Constituents Against the Two-Spotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus Urticae Koch (Trombidiformes: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.S.; Wang, Z.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, S.S. Screening of Korean Natural Products for Anti-Adipogenesis Properties and Isolation of Kaempferol-3-O-Rutinoside as a Potent Anti-Adipogenetic Compound from Solidago virgaurea. Molecules 2016, 21, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirakiattikul, Y.; Rithichai, P.; Boonyeun, T.; Ruangnoo, S.; Itharat, A. Improvement of Dioscorealide B Production by Elicitation in Shoot Cultures of Dioscorea membranacea Pierre Ex Prain & Burkill. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongdeeying, P.; Itharat, A.; Umehara, K.; Ruangnoo, S. A Novel Steroid and Cytotoxic Constituents from Dioscorea membranacea Pierre against Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Cen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Shu, X. Physicochemical Characterizations of Five Dioscorea alata L. Starches from China. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 124225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Teng, H.; An, F.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Song, H. The Beneficial Effects of Purple Yam (Dioscorea alata L.) Resistant Starch on Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat-Fed Hamsters. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Feng, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, P.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B. The structure-glycemic index relationship of Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita thunb.) starch. Food Chem. 2023, 421, 136228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Xie, C.; Wang, Q. Quantitative 1H NMR with Global Spectral Deconvolution Approach for the Determination of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid in Chinese Yam (Dioscorea polystachya Turczaninow). Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Shi, G.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Discovery of an Effective Processing Method for Edible Rhizome to Enhance the Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Content. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Evidence for Adduction of Biologic Amines with Reactive Metabolite of 8-Epidiosbulbin E Acetate In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 365, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Mei, Z. Paeonol Ameliorates Chronic Itch and Spinal Astrocytic Activation via CXCR3 in an Experimental Dry Skin Model in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 805222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adki, K.M.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacology and Recent Novel Drug Delivery Systems of Paeonol. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-C.; Huang, K.-E. The Effects of Phytosterols Extracted from Diascorea alata on the Antioxidant Activity, Plasma Lipids, and Hematological Profiles in Taiwanese Menopausal Women. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ito, Y.; Sun, W. Simultaneous Quantification of Five Steroid Saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. Wright in Rat Plasma by HPLC-MS/MS and Its Application to the Pharmacokinetic Studies. Steroids 2015, 93, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, C.; Hosoya, T.; Agawa, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kozone, I.; Shin-Ya, K.; Terahara, N.; Kumazawa, S. New Acylated Anthocyanins from Purple Yam and Their Antioxidant Activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivichai, S.; Hongsprabhas, P. Profiling Anthocyanins in Thai Purple Yams (Dioscorea alata L.). Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 1594291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, Y.S.; Chung, K.-S.; Lee, H.-W.; Choi, J.-H.; Tapondjou, L.A.; Jang, E.; Lee, K.-T. Pennogenin-3-O-α-L-Rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-L-Rhamnopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-Glucopyranoside (Spiroconazol a) Isolated from Dioscorea bulbifera L. Var. Sativa Induces Autophagic Cell Death by P38 MAPK Activation in NSCLC Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, S.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, W. Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene). Molecules 2021, 26, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, M.; Vehlow, A.; Benka, M.; Lagies, S.; Kammerer, B.; Rieckmann, T.; Cordes, N. Aqueous Extracts from Dioscorea sansibarensis Pax Show Cytotoxic and Radiosensitizing Potential in 3D Growing HPV-Negative and HPV-Positive Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Models. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguansermsri, D.; Sanguansermsri, P.; Buaban, K.; Choommongkol, V.; Akekawatchai, C.; Charoensri, N.; Fraser, I.; Wongkattiya, N. Antibacterial Activity of Dioscorea Bulbifera Linn. Extract and Its Active Component Flavanthrinin against Skin-Associated Bacteria. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narzary, C.; Sarkar, D.; Das, P.; Papi, D. Ethanobotany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activity of Dioscorea bulbifera: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 22, e202401408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Ren, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sui, X.; et al. Diosbulbin C, a Novel Active Ingredient in Dioscorea bulbifera L. Extract, Inhibits Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation by Inducing G0/G1 Phase Cell Cycle Arrest. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, B.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Xia, G.; Shen, Y.; Chen, J.; Shao, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H. Conversion of Dioscorea zingiberensis saponins to prosapogenin A by enzymatic hydrolysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, S.; Puri, M.; Bharath, Y.; Choudhury, U.M.; Mohapatra, D.K.; Muthuswami, R.; Madhubala, R. In Vitro Screening of Natural Product-Based Compounds for Leishmanicidal Activity. J. Parasit. Dis. 2023, 47, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.S.; Iqbal, S.; Lateef, M.; Joseph, N. Preussiate, a New Urease Inhibitory Chalcone from Dioscorea preussii Pax. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, T. Effect and Mechanism of Dioscin from Dioscorea spongiosa on Uric Acid Excretion in Animal Model of Hyperuricemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, C.; Xu, Y.; Gao, H.; Zheng, J. Role of Metabolic Activation in 8-Epidiosbulbin E Acetate-Induced Liver Injury: Mechanism of Action of the Hepatotoxic Furanoid. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Jegal, J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, M.H. Anti-Obesity Effect of Dioscorea oppositifolia Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice and Its Chemical Characterization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, P.; Roy Chowdhuri, S.; Sarkar, M.P.; Chaudhuri, T.K. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Standardisation of Hydro-Methanol Extract of Underground Tuber of Dioscorea alata. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonok, W.; Chaveerach, A.; Siripiyasing, P.; Sudmoon, R.; Tanee, T. The Unique Substance, Lidocaine and Biological Activity of the Dioscorea Species for Potential Application as a Cancer Treatment, Natural Pesticide and Product. Plants 2021, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D.; Nazir, R.; Biswas, P.; Kumar, V.; Nandy, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dey, A.; Pandey, D.K. Endophytic Sources of Diosgenin, a Natural Steroid with Multiple Therapeutic Values. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 134, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, N.; Khaliq, T.; Jan, S.; Nabi, S.; Sultan, P.; Hassan, Q.P.; Mir, F.A. An Overview on Pharmacological Significance, Phytochemical Potential, Traditional Importance and Conservation Strategies of Dioscorea deltoidea: A High Valued Endangered Medicinal Plant. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chu, Z.; Ren, M.; Jia, R.; Zhao, C.; Fei, D.; Su, H.; Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Identification of Anthocyanin Composition and Functional Analysis of an Anthocyanin Activator in Solanum Nigrum Fruits. Molecules 2017, 22, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhan, B.; Nayak, J.K.; Panda, D. Natural Antioxidant Potential of Selected Underutilized Wild Yams (Dioscorea spp.) for Health Benefit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Omari, N.; Guaouguaou, F.-E.; Bouyahya, A. Natural Bioactive Compounds from Medicinal Plants as Antibacterial Drugs: Mechanism Insights and Clinical Perspectives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhu, S.; Du, X.; Wang, X. The Genus Dioscorea L. (Dioscoreaceae), a Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 329, 118069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudjada, A.; Touil, A.; Bensouici, C.; Bendif, H.; Rhouati, S. Phenanthrene and Dihydrophenanthrene Derivatives from Dioscorea communis with Anticholinesterase, and Antioxidant Activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 3278–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangprompo, W.; Aree, K.; Itharat, A.; Hansakul, P. Effects of 5,6-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxy-9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene on G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Lung Carcinoma Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1473–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Gu, M.J.; Lee, J.-G.; Chin, J.; Bae, J.-S.; Hahn, D. Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cao, T.Q.; Yeo, C.-E.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, H.; Hong, D.-H.; Hahn, D. Development and validation of quantitative analysis method for phenanthrenes in peels of the Dioscorea genus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Kongstad, K.T.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Staerk, D. Unraveling the Complexity of Complex Mixtures by Combining High-Resolution Pharmacological, Analytical and Spectroscopic Techniques: Antidiabetic Constituents in Chinese Medicinal Plants. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 218, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.-R.; Dissanayake, A.A.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Nair, M.G. Phenanthrenes in Chinese Yam Peel Exhibit Antiinflammatory Activity, as Shown by Strong In Vitro Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.; Zou, Y.; Liao, S.; Gao, Q.; Li, Q. Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxyphenanthrene from Chinese Yam Modulating NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling Pathway: The Application of Molecular Docking and Gene Silencing. Nutrients 2023, 15, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somteds, A.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Yahuafai, J.; Opanasopit, P.; Patrick, B.O.; Andersen, R.J.; Kanokmedhakul, K. New Norclerodane Diterpenoids from Bulbils of Dioscorea bulbifera L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 38, 2800–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy, G.; Preethi, R.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Diarylheptanoids as Nutraceutical: A Review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Gu, H.; Djukovic, D.; Bettcher, L.; Gong, M.; Zheng, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; et al. Multiplatform Metabolomics Investigation of Antiadipogenic Effects on 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by a Potent Diarylheptanoid. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruan, J.; Li, J.; Chao, L.; Shi, W.; Yu, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, T. Bioactive Diarylheptanoids and Stilbenes from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea septemloba Thunb. Fitoterapia 2017, 117, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Jin, T.; Zhang, R.; Hu, L.; Xing, Z.; Shi, N.; Shen, Y.; Gong, M. Phenolic compounds isolated from Dioscorea zingiberensis protect against pancreatic acinar cells necrosis induced by sodium taurocholate. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xie, H.; Zuo, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, D.; Shu, X. Structural and Functional Properties of Polysaccharides Extracted from Three Dioscorea Species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Xie, J.; Yu, Y.; Shen, M. Recent Progress in the Research of Yam Mucilage Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure and Bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhi, W.; Liu, F.; Qi, L. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Glycoprotein Isolated from the Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb). Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, P.; Zeng, M.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Feng, W. Allantoin Derived from Dioscorea opposita Thunb Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Premature Ovarian Failure in Female Rats by Attenuating Apoptosis, Autophagy and Pyroptosis. Cureus 2023, 15, e50351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Kang, S.Y.; Meng, X.; Kang, A.N.; Park, J.H.; Park, Y.-K.; Jung, H.W. Effects of Rhizome Extract of Dioscorea batatas and Its Active Compound, Allantoin, on the Regulation of Myoblast Differentiation and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in C2C12 Myotubes. Molecules 2018, 23, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and Antioxidant Methods: An Updated Overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zong, A.; Xu, T.; Zhan, P.; Liu, L.; Qiu, B.; Liu, W.; Jia, M.; Du, F.; Tian, H. A Novel Method: Ionic Liquid-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Chinese Purple Yam. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, X. The Effect of Anthocyanin from Dioscorea alata L. after Purification, Identification on Antioxidant Capacity in Mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 6106–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Liu, K.; Xiong, J.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Lu, J.; Yi, J. Extraction Optimization, Purification, and Biological Properties of Polysaccharide from Chinese Yam Peel. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Niu, C.-F.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Ma, B.-J. Preparation, Structural Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide and Its Metal Chelates from the Peel of Dioscorea oppositifolia L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 39, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Yang, T.-L.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.-Z. Isolation, Structure and Activity of a Novel Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Structural and Functional Analyses of Three Purified Polysaccharides Isolated from Chinese Huaishan-Yams. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, P.; Ma, W.; Cen, J.; Liu, X. Characterization, in vitro digestibility, antioxidant activity and intestinal peristalsis in zebrafish of Dioscorea opposita polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegadheeshwari, S.; Velayutham, M.; Gunasekaran, K.; Kesavan, M. DbGTi: Thermostable Trypsin Inhibitor from Dioscorea bulbifera L. Ground Tubers: Assessment of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties and Cytotoxicity Evaluation Using Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegadheeshwari, S.; Santhi, J.J.; Velayutham, M.; Issac, P.K.; Kesavan, M. DbGTi Protein Attenuates Chromium (VI)-Induced Oxidative Stress via Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling Pathway in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Larval Model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 136099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odekanyin, O.O.; Akanni, S.I. Hemagglutinin from the Root Tuber of Dioscorea preussii Pax Exhibit Antioxidative Prowess and Haemolysis Inhibition. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 21, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B.; Naude, R.; Rolka, K.; Tse, R.; Tse, T.F.; Chan, H.; Sze, S.C.W. Tuber Lectins with Potentially Exploitable Bioactivities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5986–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, M.; Yao, C.; Liu, L.; Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Gouty Arthritis: A Protocol for Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e23699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, D.-H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.-M. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Total Saponin Fraction from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on Gouty Arthritis and Its Influence on NALP3 Inflammasome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, H.-J.; Zhang, X.-W. Total Saponin Fraction of Dioscorea nipponica Makino Improves Gouty Arthritis Symptoms in Rats via M1/M2 Polarization of Monocytes and Macrophages Mediated by Arachidonic Acid Signaling. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 29, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, S. Effects of Total Saponins from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on Monosodium Urate-Induced M1-Polarized Macrophages Through Arachidonic Acid Signaling Pathway: An in Vitro Study. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 29, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, H.J.; Liu, S.M.; Jiang, X.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.H. Anti-Inflammation Effects of the Total Saponin Fraction from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on Rats with Gouty Arthritis by Influencing MAPK Signalling Pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Lin, F.F.; Liu, S.M.; Sui, X.F. Influence of the Total Saponin Fraction from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on TLR2/4-IL1R Receptor Singnal Pathway in Rats of Gouty Arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Duan, C.; Li, L.; Chen, G. Total Saponin of Dioscorea collettii Attenuates MSU Crystal-induced Inflammation via Inhibiting the Activation of the NALP3 Inflammasome and Caspase-1 in THP-1 Macrophages. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Na, S.; Han, R.; Wei, C.; Chen, G. Saponins Extracted from Dioscorea collettii Rhizomes Regulate the Expression of Urate Transporters in Chronic Hyperuricemia Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiang, T.; Sun, B.; Luo, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Total Saponins from Dioscorea septemloba Thunb Reduce Serum Uric Acid Levels in Rats with Hyperuricemia Through OATP1A1 Up-Regulation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 2016, 36, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngan, N.T.T.; Hoang, N.H.; Truong, V.V.; Hien, N.T.; Lan, N.N.; Tung, N.V.; Huong, P.T.M.; Oh, H.; Quang, T.H. Anti-Inflammatory Norclerodane Diterpenoids and Tetrahydrophenanthrene from the Leaves and Stems of Dioscorea bulbifera. Fitoterapia 2021, 153, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Oh, J.; Yun, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Hahn, D.; Kim, J.-S. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxy Phenanthrene Isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne Partly Through Suppressing the P38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in BV2 Microglial Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Park, J.-P.; Lim, K.-T.; Lee, S.-J. Phytoglycoprotein Isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne Promotes Intestinal Epithelial Wound Healing. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Jing, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, L. Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of a Polysaccharide from Dioscotea opposita. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Bie, N.; Li, C.; Lian, R.; Qin, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C. The Impact of a Novel Chinese Yam-Derived Polysaccharide on Blood Glucose Control in HFD and STZ-Induced Diabetic C57BL/6 Mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2681–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; He, Q.; Luo, A.; Wang, M.; Luo, A. Characterization and Antihyperglycemic Activity of a Polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb Roots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6391–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashidume, T.; Sasaki, K.; Hirata, J.; Kato, M.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Arai, H.; Miura, S.; Miyoshi, N. Effects of Sanyaku and Its Constituent Diosgenin on the Fasted and Postprandial Hypertriacylglycerolemia in High-Fat-Diet-Fed KK-a y Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9968–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yamaji, A.; Kurosawa, C.; Shinohara, M.; Takayama, I.; Nakagomi, H.; Izumi, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Hariya, N.; Mochizuki, K. Co-Ingestion of Traditional Japanese Barley Mixed Rice (Mugi gohan) with Yam Paste in Healthy Japanese Adults Decreases Postprandial Glucose and Insulin Secretion in a Randomized Crossover Trial. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 32, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Han, B.; Bai, X.; Liu, S.; Xing, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, S. The Cold-Soaking Extract of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Protects against Erectile Dysfunction by Ameliorating Testicular Function in Hydrocortisone-Induced KDS-Yang Rats and in Oxidatively Damaged TM3 Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.L.; Lai, Y.M.; Li, K.W.; Lee, K.F.; Ng, T.B.; Cheung, H.P.; Zhang, Y.B.; Lao, L.; Wong, R.N.-S.; Shaw, P.C.; et al. A Novel, Stable, Estradiol-Stimulating, Osteogenic Yam Protein with Potential for the Treatment of Menopausal Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wong, R.N.S.; Zhang, L.; Wong, R.Y.L.; Ng, T.B.; Lee, K.F.; Zhang, Y.B.; Lao, L.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Sze, S.C.W. Comparative Analysis of Proteins with Stimulating Activity on Ovarian Estradiol Biosynthesis from Four Different Dioscorea Species In Vitro Using Both Phenotypic and Target-Based Approaches: Implication for Treating Menopause. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, N.; Ke, Y.; Feng, W.; Zheng, X. Estrogenic Effects of the Extracts from the Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposite Thunb.) and Its Effective Compounds in Vitro and in Vivo. Molecules 2018, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.J.; Lee, S.; Chang, K.J.; Sohn, E.; Sohn, E.-H.; Kang, S.C.; Pyo, S. Hepatic Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Hexane Extracts of Dioscorea batatas Decne: Possible Suppression of Toll-like Receptor 4-Mediated Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; He, Q.; Li, R.; Lei, F.; Lei, X. Trillin Reduces Liver Chronic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4) Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Shi, N.; Xiong, Q.; Xia, Q.; Xing, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Niu, H.; et al. Dihydrodiosgenin Protects against Experimental Acute Pancreatitis and Associated Lung Injury Through Mitochondrial Protection and PI3Kγ/Akt Inhibition. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, H.; Wan, C.; Yu, X.; Xin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Drug D, a Diosgenin Derive, Inhibits L-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis through Meditating GSDMD in the Endoplasmic Reticulum via the TXNIP/HIF-1α Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, J.; Zhou, S.; Lv, Z.; Wang, B.; Luo, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, A.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Dioscin Modulates Macrophages Polarization and MDSCs Differentiation to Inhibit Tumorigenesis of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Mao, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, Z.; Mao, J.; Sha, R. Insights into Diosgenin Against Inflammatory Bowel Disease as Functional Food Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Cao, X.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, Y. Purple Yam Polyphenol Extracts Exert Anticolitis and Anticolitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer Effects through Inactivation of NF-κB/P65 and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 12177–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, K.; Hu, T.; Liu, F.; Liao, S.; Zou, Y. 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxyphenanthrene from Chinese Yam Peels Alleviates DSS-Induced Intestinal Mucosal Injury in Mice via Modulation of the NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4720–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, P. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Purple Sweet Potato Anthocyanin Extract in DSS-Induced Colitis: Modulation of Commensal Bacteria and Attenuated Bacterial Intestinal Infection. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11503–11514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-F.; Miao, Y.; Yang, D.-W.; Kong, R.; Yuan, B.; Quan, J.-Y.; Bu, W. UPLC-Q TOF-MS-Based Metabolomics and Anti-Myocardial Ischemia Activity of Dioscoreae nipponicae Rhizoma from Different Geographical Origins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-N.; He, X.-C.; Ye, M.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.-L.; Peng, W.-L.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Yi, T.; Chen, H.-B. Cardioprotective Effect of Total Saponins from Three Medicinal Species of Dioscorea against Isoprenaline-Induced Myocardial Ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 175, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, T.; Ma, L.; Liu, B. Effects of the Total Saponins from Dioscorea nipponica on Immunoregulation in Aplastic Anemia Mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Zhang, M.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Ban, L. Protective Effects of Notoginsenoside R1 on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 6012–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Li, X.; Hu, T.; Liang, S.; Xian, M.; Wang, S. Cyclo-(Phe-Tyr) Reduces Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction Through Regulation of Autophagy. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12278–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Xue, Z.; Zhan, G.; Ito, Y.; Guo, Z. Prevention Properties on Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion of Medicine Food Homologous Dioscorea Yam-Derived Diosgenin Based on Mediation of Potential Targets. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Dou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ito, Y.; Guo, Z. New Steroid Saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis Yam and Their Medicinal Use Against I/R via Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8314–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumsuwan, P.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Avula, B.; Walker, L.A.; Shariat-Madar, Z.; Helferich, W.G.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Dasmahapatra, A.K. The Anticancer Potential of Steroidal Saponin, Dioscin, Isolated from Wild Yam (Dioscorea villosa) Root Extract in Invasive Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 in Vitro. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 591, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatoo, G.N.; Banday, J.A. Synthesis, Antioxidant, Antiproliferative Activity, Molecular Docking and DFT Studies of Novel Isoxazole Derivatives of Diosgenin, a Steroidal Sapogenin from Dioscorea deltoidea. Fitoterapia 2023, 170, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Hering, A.; Gucwa, M.; Czerwińska, M.; Ochocka, J.R. Yamogenin-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis in Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Line. Molecules 2022, 27, 8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Wang, G.; He, Y.; Man, S.; Gao, W. Effects of the Polysaccharides Extracted from Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10602–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohda, C.; Yang, X.; Matsui, M.; Inada, Y.; Kadomoto, E.; Nakada, S.; Watari, H.; Shibahara, N. Diosgenin-Rich Yam Extract Enhances Cognitive Function: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study of Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Nomoto, K.; Tohda, C. Diosgenin Content Is a Novel Criterion to Assess Memory Enhancement Effect of Yam Extracts. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iemitsu, K.; Fujie, S.; Uchida, M.; Inoue, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Iemitsu, M. Dioscorea esculenta Intake with Resistance Training Improves Muscle Quantity and Quality in Healthy Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-G.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xiang, L.-H.; Pan, J.-H.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, G.G.; Ju, D.-H. Protective Effect of Rhizoma Dioscoreae Extract Against Alveolar Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Rats via Regulation of IL-6/STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubi, J.A.; Brah, A.S.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Lee, K.-F.; Sze, S.C.W.; Qiao, W.; Yeung, K.W.-K. A New Osteogenic Protein Isolated from Dioscorea opposita Thunb Accelerates Bone Defect Healing Through the mTOR Signaling Axis. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 27, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, K.; Charles, A.L. Fortification Using Grape Extract Polyphenols—A Review on Functional Food Regulations. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3742–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, L.D.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Cámara, M. The Frontier Between Nutrition and Pharma: The International Regulatory Framework of Functional Foods, Food Supplements and Nutraceuticals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, F.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Bi, Y.; Li, M. Management, Safety, and Efficacy Evaluation of Nutraceutical and Functional Food: A Global Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y. Scientific Substantiation of Functional Food Health Claims in China. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1199S–1205S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.Y.-T.; Lai, J.M.C.; Chan, A.W.-K. Regulations and Protection for Functional Food Products in the United States. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, M.T. Functional Foods: Functional Ingredients, Sources and Classification, Health Claims, Food Intolerance, and Allergy. In Functional Food—Upgrading Natural and Synthetic Sources; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-1-83769-088-6. [Google Scholar]
- Intrasook, J.; Tsusaka, T.W.; Anal, A.K. Trends and Current Food Safety Regulations and Policies for Functional Foods and Beverages Containing Botanicals. J. Food Drug Anal. 2024, 32, 118–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sl No. | Phytoconstituents | Nature | Species | Functional Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diosgenin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea bulbifera, Dioscorea nipponica, Dioscorea zingiberensis, Dioscorea esculenta, Dioscorea cirrhosa L., Dioscorea japonica, Dioscorea opposita Thunb. | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antibacterial, anti-hyperlipidemia, anti-myocardial ischemia, regulation of intestinal flora, hypoglycemia, neuroprotection, treatment of thyroid disease, etc. | [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| 2 | Dioscin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea spongiosa, Dioscorea alata L., Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Dioscorea bulbifera, Dioscorea japonica | Hypoglycemic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, treatment of thyroid disease, etc. | [30,31,32,33,34,35] |
| 3 | Allantoin | Alkaloids—Pseudoalkaloids | Dioscorea belophylla, Dioscorea batatas, Dioscorea opposita Thunb, Dioscorea deltoidea | Improve pancreatic islet damage, anti-premature ovarian aging, hypoglycemia, antioxidant, anti-tumor, regulation of intestinal flora, prevention of skeletal muscle dysfunction, etc. | [36,37,38,39,40,41] |
| 4 | Polysaccharides | Carbohydrates | Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Dioscorea bulbifera, Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea polystachya Turcz. | Immune regulation, anti-inflammatory, flora regulation, anti-diabetic and obesity, anti-fatigue, antioxidant, cardioprotection, anti-tumor, digestive system protection, etc. | [42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| 5 | Gracillin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea spongiosa, Dioscorea quinqueloba, Dioscorea tokoro Makino | Anti-allergic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, inhibit melanogenesis, lower uric acid, anti-diabetic | [48,49,50,51] |
| 6 | Protodioscin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea deltoidea, Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea tokoro | Anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-leukemia | [52,53,54] |
| 7 | Diosbulbin B | Terpenoids—Diterpenoids | Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Induces hepatotoxicity | [55,56] |
| 8 | Dioscorin | Alkaloids—Lysine alkaloids | Dioscorea alata, Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Hypoglycemia, insecticide, etc. | [28,57] |
| 9 | Pseudoprotodioscin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea septemloba Thunb., Dioscorea spongiosa, Dioscorea nipponica Makino | Anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory | [53,58] |
| 10 | Deltonin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea zingiberensis | Therapeutic I/R, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective | [59,60] |
| 11 | Myricetin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea alata, Dioscorea bulbifera | Anti-HIV-1 integrase activity, anti-inflammatory, pro-wound healing, antioxidant | [19,61,62] |
| 12 | Adenosine | Carbohydrates—Nucleosides | Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Dioscorea polystachya | Cardioprotection, ex vivo and ex vivo estrogenic effects, anti-inflammatory, etc. | [63,64,65] |
| 13 | Protogracillin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea septemloba Thunb | Anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, uric acid-lowering, anti-diabetic | [31,53,65] |
| 14 | Methyl protodioscin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea villosa, Dioscorea spongiosa | Anti-tumor, inhibits neoplastic endothelial formation | [66,67] |
| 15 | Quercetin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea opposite, Dioscorea alata, Dioscorea bulbifera L., Dioscorea glabra Roxb. | Anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antioxidant, antiviral | [68,69,70] |
| 16 | Yamogenin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea collettii | Anti-tumor, antioxidant, antibacterial, antidepressant | [23,71] |
| 17 | Anthocyanins | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea alata L. | Anti-inflammatory, regulates intestinal flora, antioxidant | [72,73] |
| 18 | Cholesterol | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea bulbifera, Dioscorea zingiberensis | Anti-tumor, antioxidant | [74,75] |
| 19 | batatasin I | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenanthrenoids | Dioscorea opposita Thunb., Dioscorea dumetorum (Kunth) | Antioxidant, anti-diabetic | [76,77] |
| 20 | Epicatechin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea cirrhosa L. | Antioxidant, etc. | [78,79] |
| 21 | Palmitic acid | Fatty acids —Fatty Acids and Conjugates | Dioscorea japonica Thunb., Dioscorea bulbifera | Acaricidal properties, etc. | [75,80] |
| 22 | Rutin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea ploystchya Turcz., Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Antioxidant, etc. | [69,79,81] |
| 23 | Luteolin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea ploystchya Turcz., Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Antioxidant, antiviral | [70,79] |
| 24 | Dioscorealide B | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenanthrenoids | Dioscorea membranacea Pierre | Anti-tumor, etc. | [82,83] |
| 25 | Resistant Starch | Carbohydrates | Dioscorea alata L., Dioscorea opposita Thunb. | Regulate intestinal flora, anti-hyperlipidemia, anti-hyperglycemia and obesity | [84,85,86] |
| 26 | gamma-aminobutyric acid | Amino acids and Peptides —Small peptides | Dioscorea polystachya Turczaninow | Antihypertensive, anti-anxiety, anti-diabetic, etc. | [87,88] |
| 27 | Glutamine | Amino acids and Peptides —Small peptides | Dioscorea polystachya | Antioxidant, etc. | [64,89] |
| 28 | Paeonol | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids | Dioscorea japonica Thunb. | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antioxidant, anti-tumor, etc. | [90,91] |
| 29 | Stigmasterol | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea alata | Antioxidant, anti-hyperlipidemia | [19,92] |
| 30 | Huangjiangsu A | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea zingiberensis, Dioscorea villosa | Antioxidant, liver protection | [36,93] |
| 31 | Taxifolin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea opposita Thunb. | Regulates intestinal flora and synergistically enhances short-chain fatty acid production | [27] |
| 32 | Protodeltonin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea villosa | Antioxidant, liver protection | [36] |
| 33 | Tokoronin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea tokoro Makino | Low cytotoxicity, inhibits melanogenesis | [51] |
| 34 | kaempferol | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea ploystchya Turcz., Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-lipogenic | [62] |
| 35 | Lactulose | Carbohydrates—Saccharides | Dioscorea rhizoma | Synergistic anti-ethanol gastric injury | [63] |
| 36 | Tyramine | Alkaloids—Tyrosine alkaloids | Dioscorea polystachya | Synergistic anti-ethanol gastric injury | |
| 37 | Cycloleucine | Amino acids and Peptides —Small peptides | Dioscorea polystachya | Synergistic anti-ethanol gastric injury | |
| 38 | Rosmarinic acid | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenolic acids (C6-C1) | Dioscorea glabra Roxb., Dioscorea alata | Antioxidant, etc. | [69] |
| 39 | Phytol | Terpenoids—Diterpenoids | Dioscorea bulbifera | Anticancer, antioxidant | [75] |
| 40 | muristerone A | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea dumetorum (Kunth) Pax. | Anti-diabetic, strong α-amylase inhibitory activity | [77] |
| 41 | dihydroresveratrol | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Stilbenoids | Dioscorea dumetorum (Kunth) Pax. | Anti-diabetic, strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | |
| 42 | Kaempferide | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea ploystchya Turcz., Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Antioxidant, etc. | [79] |
| 43 | Octanoic acid | Fatty acids —Fatty Acids and Conjugates | Dioscorea japonica Thunb. | Acaricidal properties, etc. | [80] |
| 44 | Beta-sitosterol | Terpenoids—Steroids | Diascorea alata | Synergistic relief of gout and its complications, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-hyperlipidemia, relief of female menopausal symptoms | [92] |
| 45 | Peonidin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea alata L. | Powerful antioxidant activity | [94] |
| 46 | Cyanidin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea alata L. | Powerful antioxidant activity | [95] |
| 47 | Spiroconazol A | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer | [96] |
| 48 | montroumarin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Coumarins | Dioscorea collettii, Dioscorea septemloba Thunb. | Synergistic relief of gout and its complications, anti-inflammatory, analgesic | [97] |
| 49 | Camptothecin | Alkaloids—Tryptophan alkaloids | Dioscorea sansibarensis Pax. | Anti-head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | [98] |
| 50 | Flavanthrinin | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenanthrenoids | Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Treatment of skin infections, powerful antimicrobial action and low cytotoxicity | [99] |
| 51 | Dioscorine | Alkaloids—Lysine alkaloids | Dioscorea bulbifera | Blockade of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, antibacterial and insecticidal activity | [100] |
| 52 | Diosbulbin C | Terpenoids—Diterpenoids | Dioscorea bulbifera L. | Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer | [101] |
| 53 | Prosapogenin A | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea zingiberensis | Stronger anti-tumor activity, hepatoprotective, low hemolytic effect | [102] |
| 54 | Diospongin B | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Diarylheptanoids | Dioscorea spongiosa | Anti-inflammatory, anti-leishmanial, anti-fungal | [103] |
| 55 | Preussinate | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Flavonoids | Dioscorea preussii Pax. | Antioxidant, urease inhibitory properties | [104] |
| 56 | Tigogenin | Terpenoids—Steroids | Dioscorea spongiosa | Antihyperuricemic activity in vivo | [105] |
| 57 | 2,5,6-Trihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenanthrenoids | Dioscorea bulbifera L. | DPPH free radical scavenging activity comparable to vitamin C | [106] |
| 58 | 3,5-dimethoxy-2,7-phenanthrenediol | Shikimates and Phenylpropanoids—Phenanthrenoids | Dioscorea oppositifolia | Anti-obesity, inhibits eating efficiency and fat absorption | [107] |
| 59 | Methyl Stearate | Fatty acids—Fatty esters | Dioscorea alata, Dioscorea batatas | Anticancer, etc. | [108] |
| 60 | Lidocaine | Alkaloids | Dioscorea depauaperata, Dioscorea glabra | Anticancer, insecticide | [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Yao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Yang, Y. Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development. Foods 2025, 14, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142537
Wang P, Wang Y, Liu S, Wang K, Yao Y, Liu W, Li D, Wang W, Li B, Yang Y. Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142537
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pengcheng, Yashi Wang, Shiqi Liu, Kai Wang, Yuxuan Yao, Weizhen Liu, Donghui Li, Wei Wang, Bin Li, and Yupei Yang. 2025. "Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development" Foods 14, no. 14: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142537
APA StyleWang, P., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Wang, K., Yao, Y., Liu, W., Li, D., Wang, W., Li, B., & Yang, Y. (2025). Bioactive Metabolites of Dioscorea Species and Their Potential Applications in Functional Food Development. Foods, 14(14), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142537







