Rapid Kinetic Fluorogenic Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Ground Beef
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MDA and TBA Solutions
2.3. Preparation of TBA–MDA Adduct
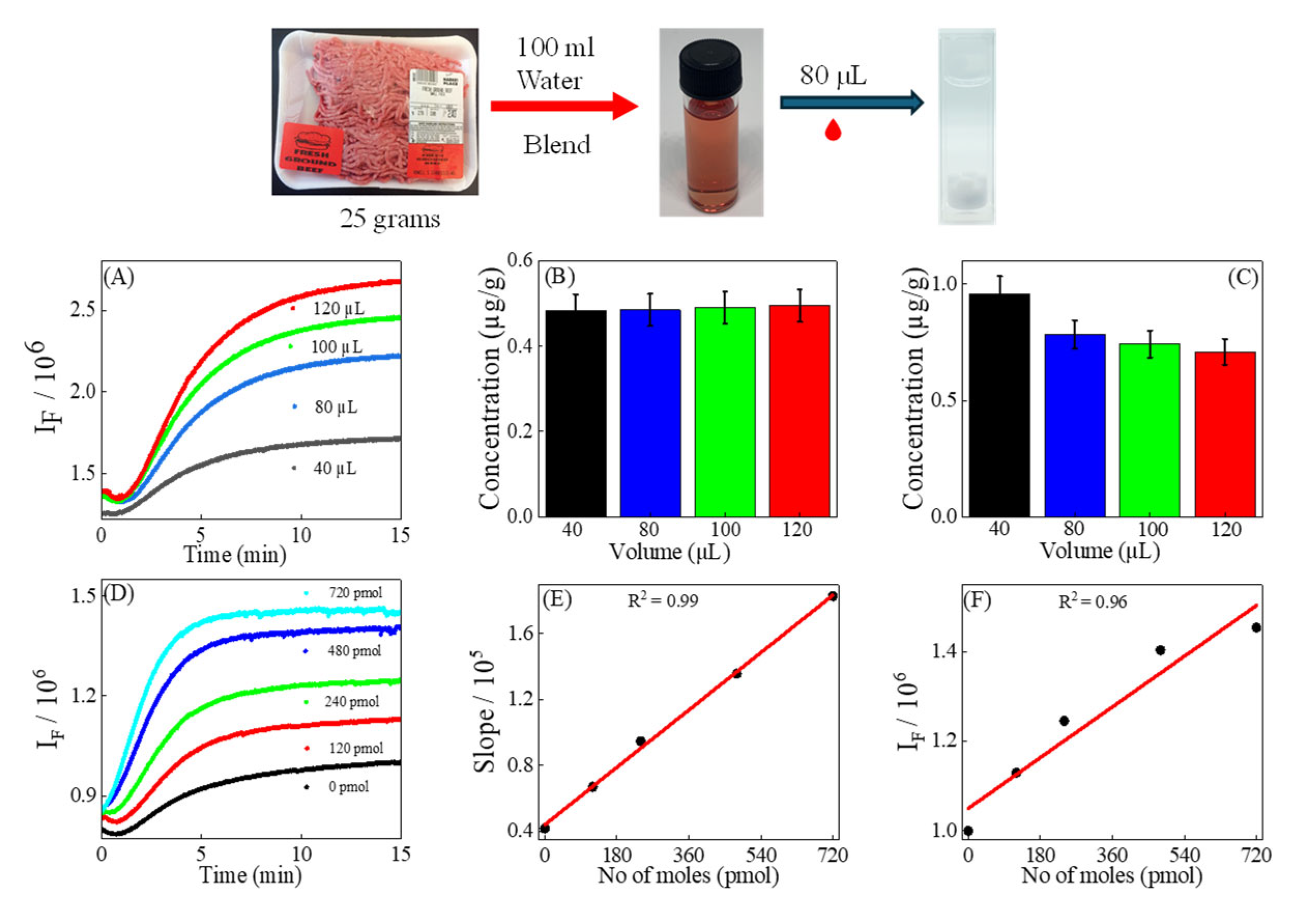
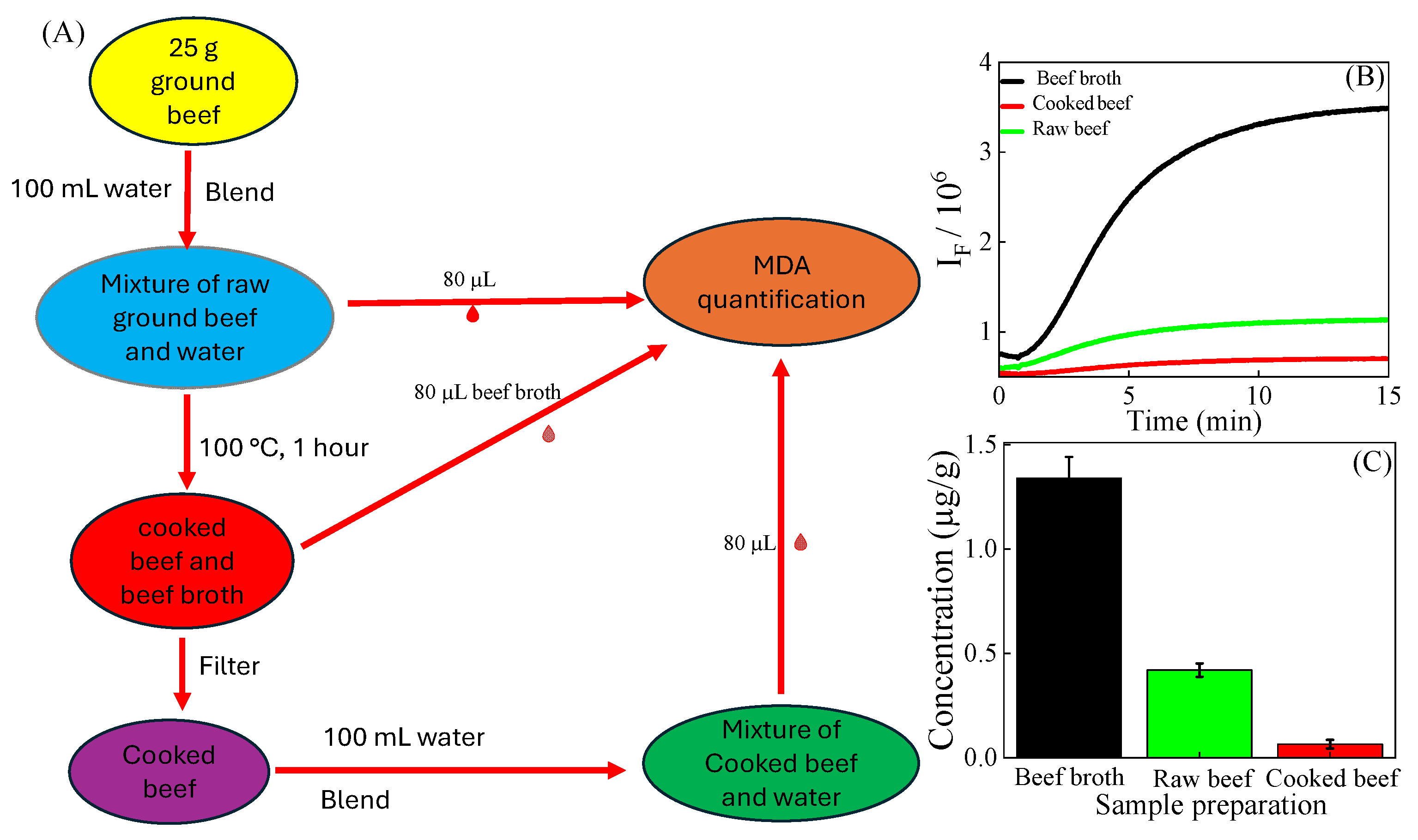
2.4. Preparation of Extracts of Ground Beef
2.5. Sample Volume Variation
2.6. Preparation of Sample for Standard Addition Method
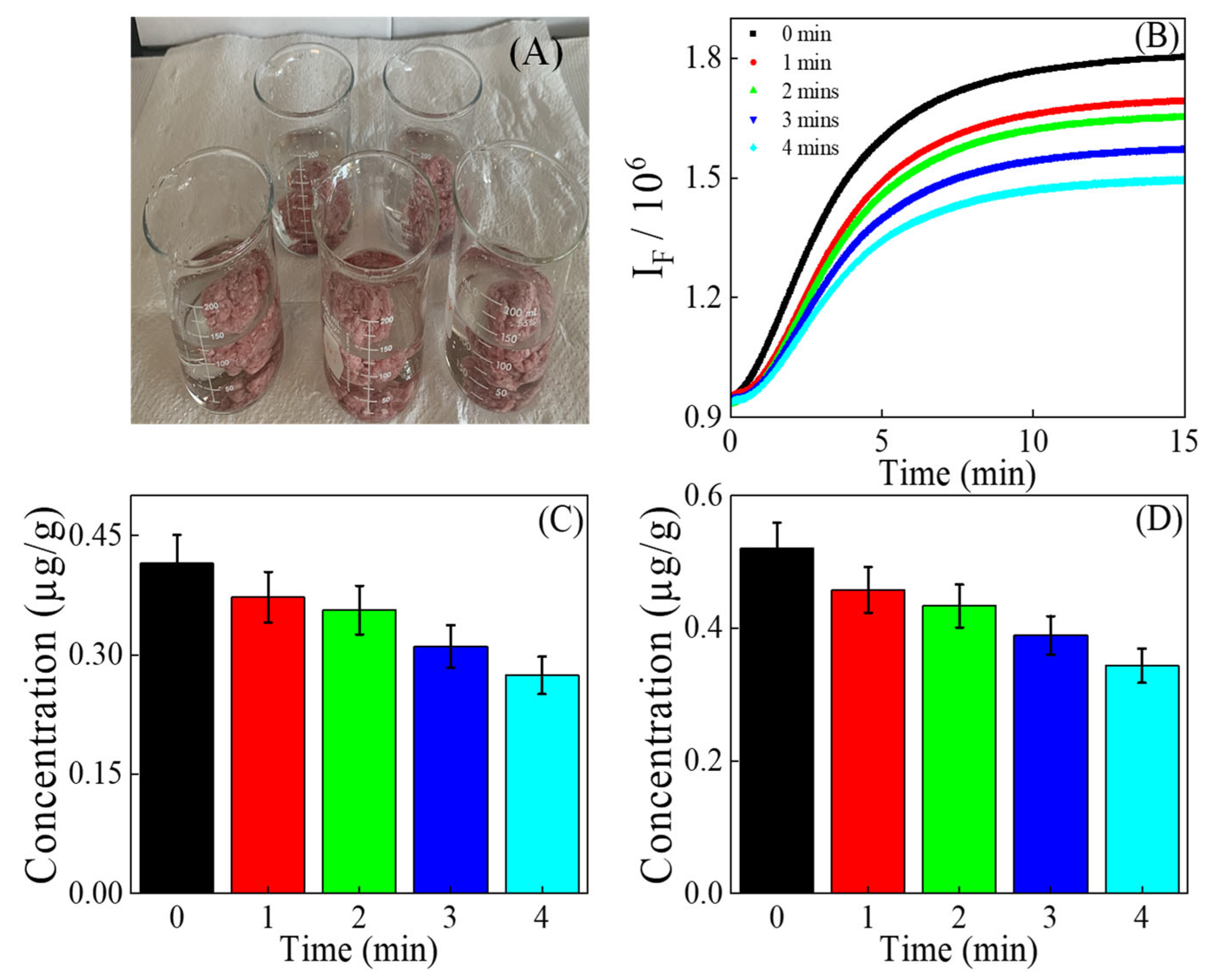
2.7. Preparation of Extracts of Ground Beef Exposed to Air
2.8. Preparation of the Extracts of Washed Ground Beef
2.9. Preparation of Extracts of the Cooked Ground Beef
2.10. Fluorescence Measurements
2.11. Savitsky-Golay Derivatization
2.12. Analytical Characteristics
2.13. Statistical Method
3. Results and Discussion
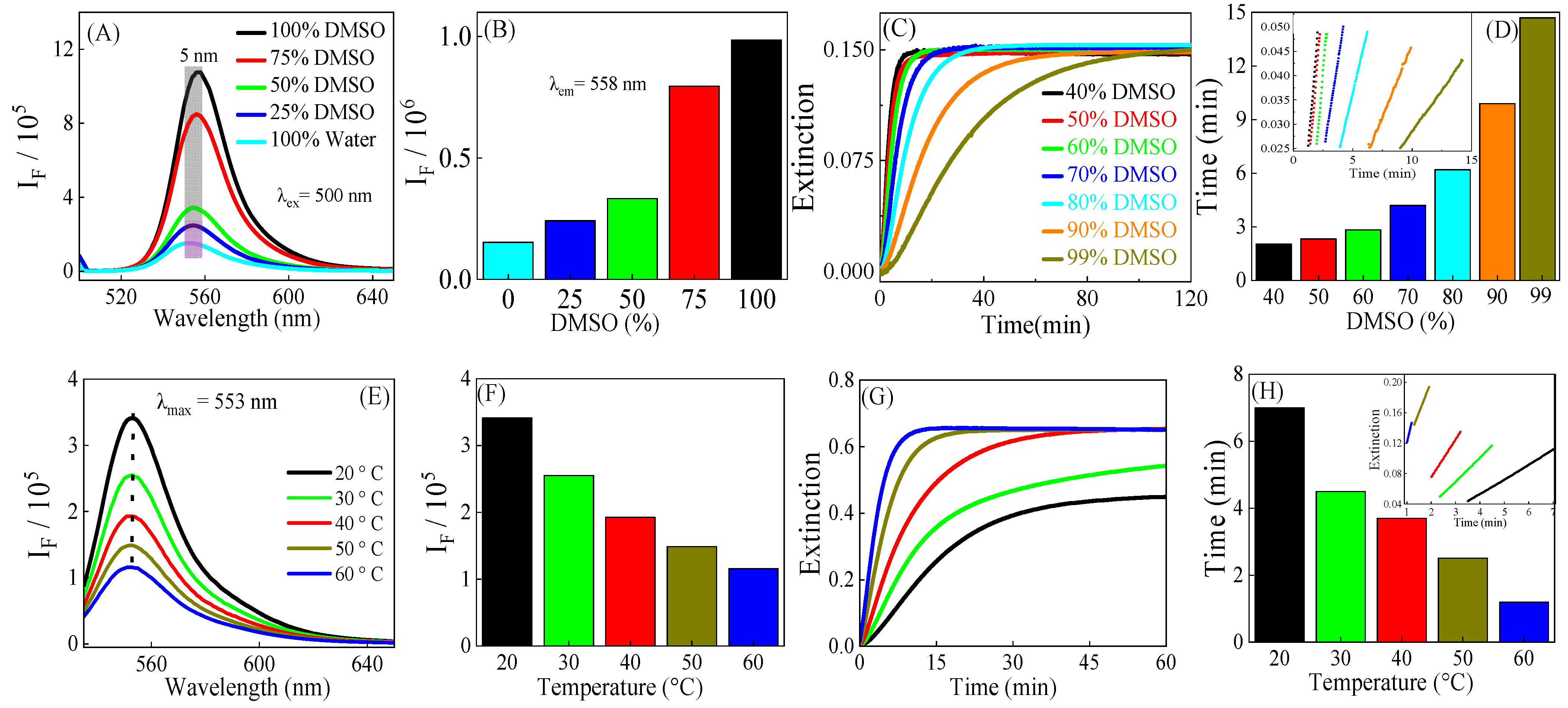
3.1. Solvent and Temperature Effects on FG MDA Quantification
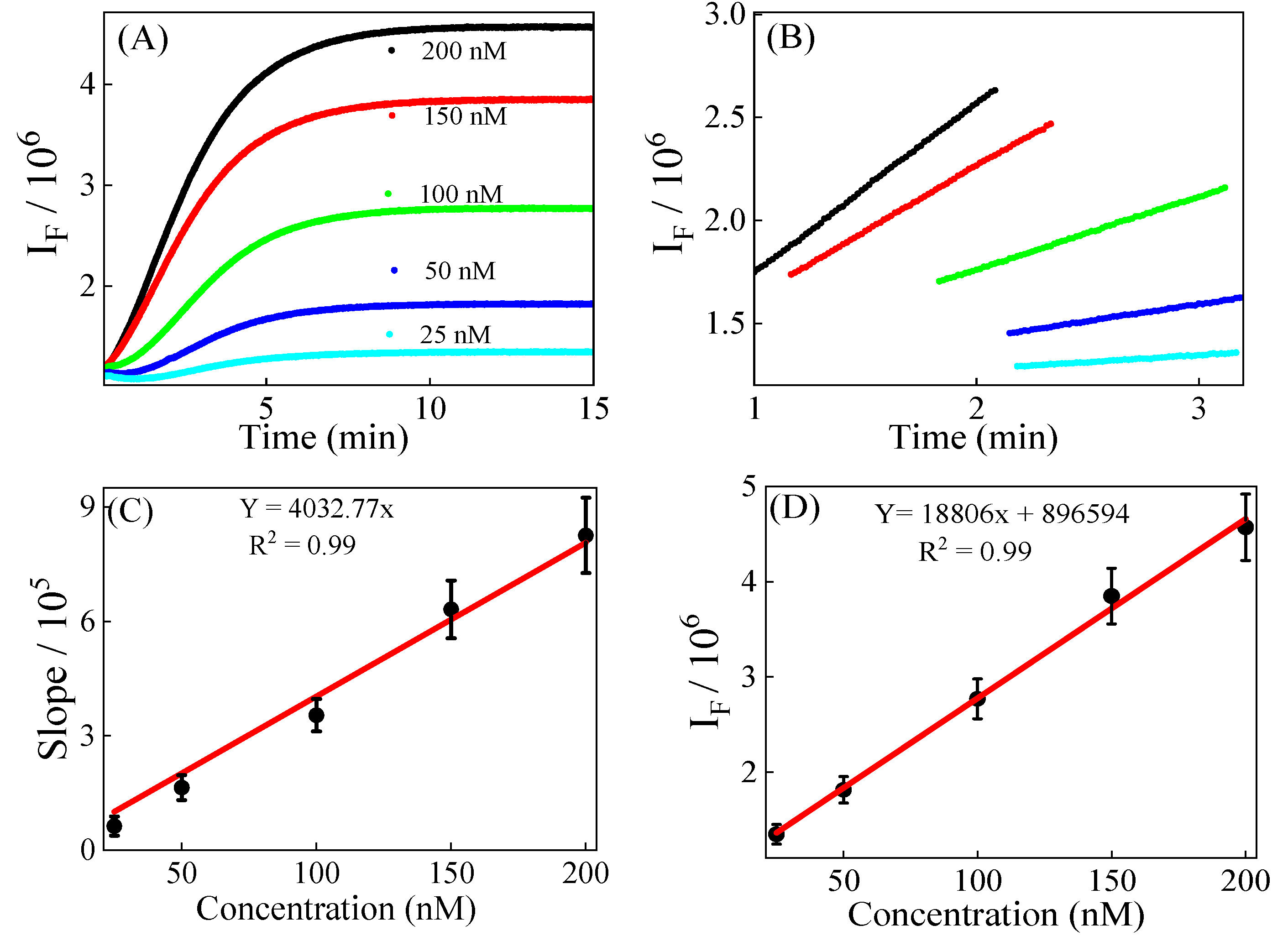
3.2. Calibration, Precision, and Recovery
3.3. Method Validation
3.4. Quantification of MDA in Ground Beef Exposed to Air
3.5. Quantification of MDA in Extracts of Washed Beef
3.6. Quantification of MDA in Cooked Ground Beef
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| TBA | 2-thiobarbituric acid |
| CG | chromogenic |
| FG | fluorogenic |
| TBARS | TBA-reactive substances |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| TEP | tetraethoxypropane |
| SERS | surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMF | dimethylformamide |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| LOQ | limit of quantification |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
References
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Porter, N.A. Free radical lipid peroxidation: Mechanisms and analysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5944–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, M.; Gruffat, D.; Habeanu, M.; Parafita, E.; Bauchart, D.; Durand, D. Plant extracts combined with vitamin E in PUFA-rich diets of cull cows protect processed beef against lipid oxidation. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.I.; Gomaa, E.A.; Buckley, D.J. Oxidative quality and shelf life of meats. Meat Sci. 1996, 43, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A.; Baron, G.; Gianazza, E.; Banfi, C.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Lipid peroxidation derived reactive carbonyl species in free and conjugated forms as an index of lipid peroxidation: Limits and perspectives. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, M.M.; Nute, G.R.; Hughes, S.I.; Enser, M.; Wood, J.D.; Richardson, R.I. Flavour perception of oxidation in beef. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.; Pearson, A. Lipid-derived off-flavours in meat—Formation and inhibition. In Flavor of Meat and Meat Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 116–143. [Google Scholar]
- Miller III, E.R.; Appel, L.J.; Risby, T.H. Effect of dietary patterns on measures of lipid peroxidation: Results from a randomized clinical trial. Circulation 1998, 98, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Wu, M. Effects of glutelin and lipid oxidation on the physicochemical properties of rice starch. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.V.; Dikalov, S.I. Cardiolipin, perhydroxyl radicals, and lipid peroxidation in mitochondrial dysfunctions and aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1323028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnett, L.J. Oxy radicals, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage. Toxicology 2002, 181, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalding, J. Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of malondialdehyde sodium salt (3-hydroxy-2-propenal, sodium salt) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. NTP Tech. Rep. 1988, 331, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.K.; Marnett, L.J. Unequivocal demonstration that malondialdehyde is a mutagen. Carcinogenesis 1983, 4, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutteridge, J.M. Thiobarbituric acid-reactivity following iron-dependent free-radical damage to amino acids and carbohydrates. FEBS Lett. 1981, 128, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leon, J.A.D.; Borges, C.R. Evaluation of oxidative stress in biological samples using the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances assay. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, F.; Bernheim, M.L.; Wilbur, K.M. The reaction between thiobarbituric acid and the oxidation products of certain lipides. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 174, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Haputhanthri, R.; Ansar, S.M.; Vangala, K.; De Silva, H.I.; Sygula, A.; Saebo, S.; Pittman, C.U. Ultrasensitive detection of malondialdehyde with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Athukorale, S.; Hu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, D. Kinetic spectroscopic quantification using two-step chromogenic and fluorogenic reactions: From theoretical modeling to experimental quantification of biomarkers in practical samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1153, 338293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingle Jr, J.D.; Ryan, M.A. Reaction Rate Methods in Fluorescence Analysis. In Modern Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 95–142. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.A.; Abdelmageed, O.H.; Attia, T.Z. Kinetic spectrophotometric determination of certain cephalosporins in pharmaceutical formulations. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2009, 596379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Abdel-Wadood, H.M.; Mohamed, N.A. Kinetic spectrophotometric method for determination of amlodipine besylate in its pharmaceutical tablets. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-S.; Kor, C.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Liu, K.-H.; Shih, K.-L.; Su, W.-W.; Wu, H.-M. Relationships between serum uric acid, malondialdehyde levels, and carotid intima-media thickness in the patients with metabolic syndrome. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6859757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasayar, S.; Orhan, H.; Özgüneş, H. Malondialdehyde quantification in blood plasma of tobacco smokers and non-smokers. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci 2004, 29, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Lakowicz, J.R. Introduction to fluorescence. In Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ben-Amotz, D. Enhanced chemical classification of Raman images in the presence of strong fluorescence interference. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Melavanki, R.; Thipperudrappa, J.; Afi, U.O. Effect of temperature on the fluorescence emission of ENCTTTC in different nonpolar solvents. Can. J. Phys. 2013, 91, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Finegan, T.Μ.; Mohsen, P.; Hatton, T.A.; Laibinis, P.E. Fluorescence-based thermometry: Principles and applications. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 235–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, I.; Ferreira, J.; Thomaz, M. Intramolecular heavy-atom effect and intersystem-crossing in monohalogenated pyrenes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2 Mol. Chem. Phys. 1973, 69, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, G.; Draper, H. A survey of the malonaldehyde content of retail meats and fish. J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamsley, M.; Nawalage, S.; Hu, J.; Collier, W.E.; Zhang, D. Back to the Drawing Board: A Unifying First-Principle Model for Correlating Sample UV–Vis Absorption and Fluorescence Emission. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7123–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Gong, J.; Han, H.; He, L.; Teng, Y.; Tetley, T.; Sinharay, R.; Chung, K.F.; Islam, T.; Gilliland, F. Relationship between free and total malondialdehyde, a well-established marker of oxidative stress, in various types of human biospecimens. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitznerová, A.; Šuleková, M.; Nagy, J.; Marcinčák, S.; Semjon, B.; Čertík, M.; Klempová, T. Lipid peroxidation process in meat and meat products: A comparison study of malondialdehyde determination between modified 2-thiobarbituric acid spectrophotometric method and reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Molecules 2017, 22, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raines, C.R.; Hunt, M.C.; Unruh, J.A. Contributions of muscles of various color stabilities to the overall color stability of ground beef. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C85–C89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formanek, Z.; Kerry, J.P.; Buckley, D.J.; Morrissey, P.A.; Farkas, J. Effects of Dietary Vitamin E Supplementation and Packaging on the Quality of Minced Beef. Meat Sci. 1998, 50, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferioli, F.; Dutta, P.C.; Caboni, M.F. Cholesterol and lipid oxidation in raw and pan-fried minced beef stored under aerobic packaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolín, J.R.; Joy, M.; Blanco, M. Malondialdehyde determination in raw and processed meat products by UPLC-DAD and UPLC-FLD. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cai, J.; Feng, F.; Xing, L.; Zhang, W. Effect of Malondialdehyde on the Digestibility of Beef Myofibrillar Protein: Potential Mechanisms from Structure to Modification Site. Foods 2022, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.B.; Silva, M.V.d.; Lannes, S.C.d.S. Lipid oxidation in meat: Mechanisms and protective factors—A review. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Gómez, M.; Fonseca, S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of different cooking methods on lipid oxidation and formation of volatile compounds in foal meat. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Shin, J.; Kang, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, J.J.; Kim, H.J. Effect of different cooking method on vitamin E and K content and true retention of legumes and vegetables commonly consumed in Korea. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaia, C.M.M.; Alves, S.P.; Lopes, A.F.; Fernandes, M.J.E.; Costa, A.S.H.; Fontes, C.M.G.A.; Castro, M.L.F.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Prates, J.A.M. Effect of cooking methods on fatty acids, conjugated isomers of linoleic acid and nutritional quality of beef intramuscular fat. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aşçıoğlu, Ç.; Şevik, R. The effects of cooking methods on the properties of beef longissimus dorsi. Gıda 2019, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, C.; Flamigni, F.; Caldarera, C.M. Role of oxygen in the cellular damage induced by re-oxygenation of hypoxic heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1980, 12, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöttker, B.; Saum, K.-U.; Jansen, E.H.; Boffetta, P.; Trichopoulou, A.; Holleczek, B.; Dieffenbach, A.K.; Brenner, H. Oxidative stress markers and all-cause mortality at older age: A population-based cohort study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analysis Method | LOD (nM) | LOQ (nM) | R2 | Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | Recovery Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetic | 0.87 | 2.61 | 0.99 | 0.59% | 2.84% | 95.00–104.70% |
| Equilibrium | 2.28 | 6.84 | 0.99 | 0.30% | 2.56% | 95.24–124.50% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhandari, K.R.; Wamsley, M.; Nanduri, B.; Collier, W.E.; Zhang, D. Rapid Kinetic Fluorogenic Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Ground Beef. Foods 2025, 14, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142525
Bhandari KR, Wamsley M, Nanduri B, Collier WE, Zhang D. Rapid Kinetic Fluorogenic Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Ground Beef. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142525
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhandari, Keshav Raj, Max Wamsley, Bindu Nanduri, Willard E. Collier, and Dongmao Zhang. 2025. "Rapid Kinetic Fluorogenic Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Ground Beef" Foods 14, no. 14: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142525
APA StyleBhandari, K. R., Wamsley, M., Nanduri, B., Collier, W. E., & Zhang, D. (2025). Rapid Kinetic Fluorogenic Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Ground Beef. Foods, 14(14), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142525






