Development of Soy-Based Meat Analogues via Wet Twin-Screw Extrusion: Enhancing Textural and Structural Properties Through Whole Yeast Powder Supplementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. HME Process
2.3. Microstructure and Visual
2.4. Textural
2.5. LF-NMR Determination
2.6. Intermolecular Interaction Forces
2.7. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.8. Color Measurement
2.9. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Color Analysis
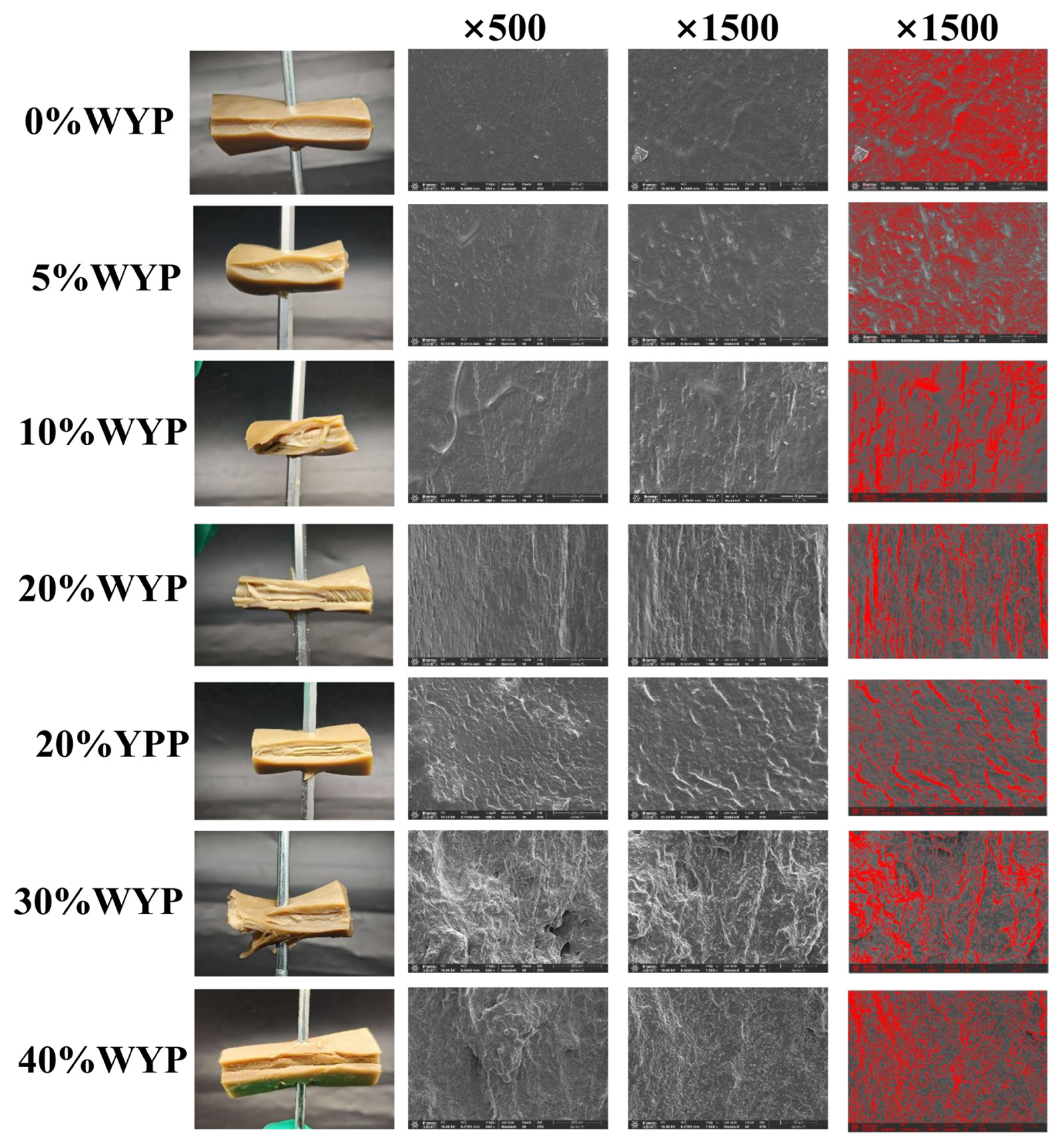
3.2. Microstructure and Visual Analysis
3.3. Texture Analysis
3.4. Low-Field NMR Analysis
3.5. Intermolecular Interaction Analysis
3.6. Surface Hydrophobicity Analysis
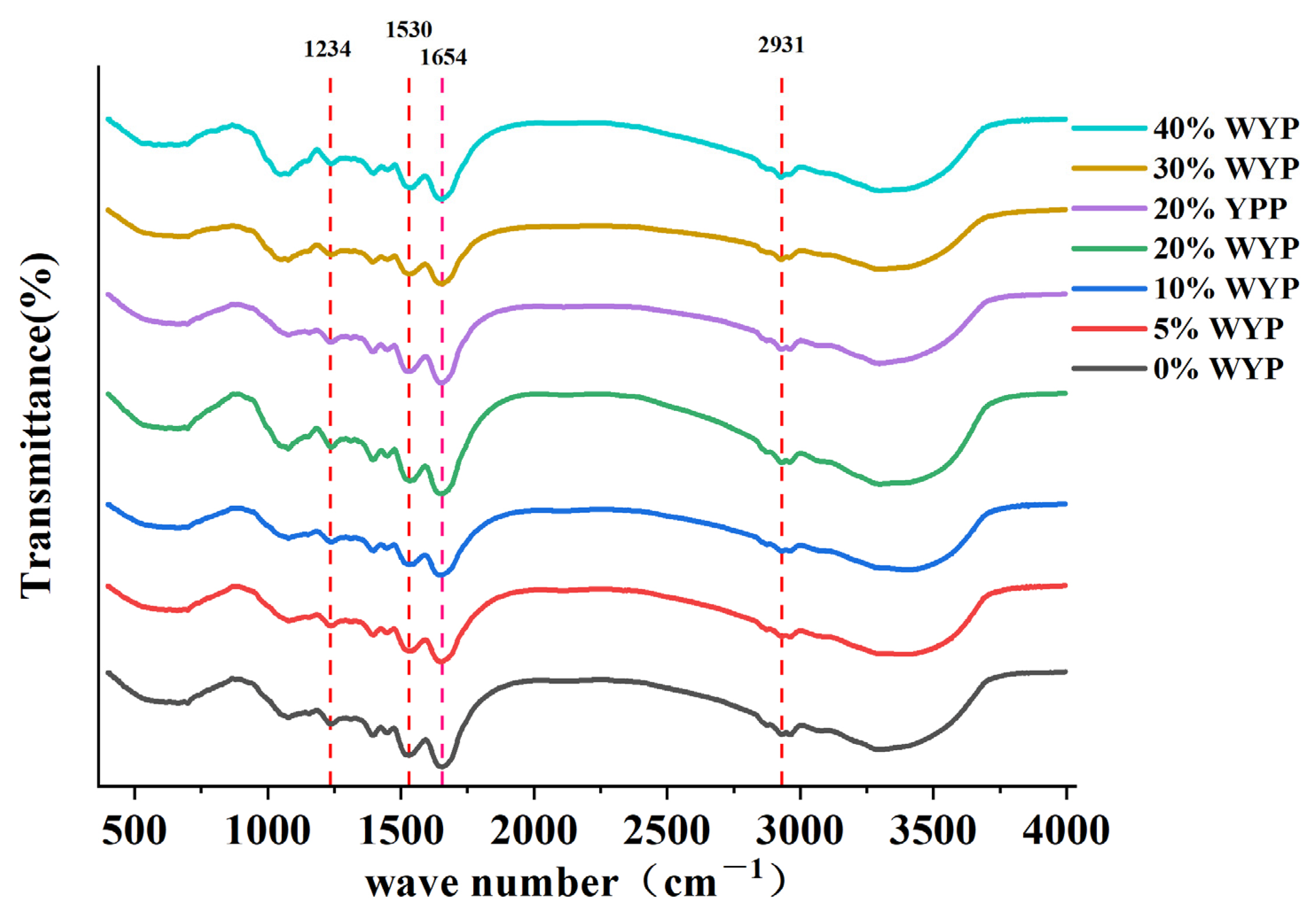
3.7. FTIR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Badar, I.H.; Xia, X.; Kong, B.; Chen, Q. Prospects of artificial meat: Opportunities and challenges around consumer acceptance. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 116, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Trivedi, N.; Enamala, M.K.; Kuppam, C.; Parikh, P.; Nikolova, M.P.; Chavali, M. Plant-based meat analogue (PBMA) as a sustainable food: A concise review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2499–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Evans, N.M.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. A review of research on plant-based meat alternatives: Driving forces, history, manufacturing, and consumer attitudes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2639–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Choi, I.; Han, J. Construction of rice protein-based meat analogues by extruding process: Effect of substitution of soy protein with rice protein on dynamic energy, appearance, physicochemical, and textural properties of meat analogues. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Chao, C.; Che, Q.T.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.J. Development of plant-based meat analogs using 3D printing: Status and opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2023, 132, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xia, S.; Ma, C.; Hao, T.; Shen, S.; Feng, T.; Xue, C.; Jiang, X. Structure and flavor properties of meat analogues from yeast and soy protein prepared via high-moisture extrusion. LWT 2024, 213, 117013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.H.; Loveday, S.M.; Hardacre, A.K.; Parker, M.E. Effects of soy protein to wheat gluten ratio on the physicochemical properties of extruded meat analogues. Food Struct. 2019, 19, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, J.; Li, K.; Hao, T.; Ma, C.; Shen, S.; Jiang, X.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y. Yeast protein-based meat analogues: Konjac glucomannan induces the fibrous structure formation by modifying protein structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, A.; Brennan, M.A.; Morton, J.; Torrico, D.; Brennan, C.S. In-vitro digestibility, protein digestibility corrected amino acid, and sensory properties of banana-cassava gluten-free pasta with soy protein isolate and egg white protein addition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Shen, S.; Song, J.; Li, K.; Qin, X.; Jiang, X.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y. Physicochemical and structural properties of meat analogues from yeast and soy protein prepared via high-moisture extrusion. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timira, V.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, T. Potential use of yeast protein in terms of biorefinery, functionality, and sustainability in food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agboola, J.O.; Lapeña, D.; Øverland, M.; Arntzen, M.Ø.; Mydland, L.T.; Hansen, J.Ø. Yeast as a novel protein source—Effect of species and autolysis on protein and amino acid digestibility in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Protein blend extrusion: Crafting meat analogues with varied textural structures and characteristics. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Fu, L.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. High-moisture extrusion of soy protein: Effects of insoluble dietary fiber on anisotropic extrudates. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. High moisture extrusion of soy protein and wheat gluten blend: An underlying mechanism for the formation of fibrous structures. LWT 2022, 163, 113561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Shao, Y.; Tu, Y. Changes of microstructure characteristics and intermolecular interactions of preserved egg white gel during pickling. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dara, P.K.; Geetha, A.; Mohanty, U.; Raghavankutty, M.; Mathew, S.; Chandragiri Nagarajarao, R.; Rangasamy, A. Extraction and Characterization of Myofibrillar Proteins from Different Meat Sources: A Comparative Study. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Enriquez, E.; Salmeron-Ochoa, I.; Gutierrez-Mendez, N.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Ortega-Rivas, E. Shelf life studies on apple juice pasteurised by ultrahigh hydrostatic pressure. LWT 2015, 62, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Yue, X. Effects of electron beam irradiation and ultrahigh-pressure treatments on the physicochemical properties, active components, and flavor volatiles of jujube jam. LWT 2023, 187, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, S.B.M.; Sutton, K.H.; Newberry, M.P.; Andrews, N.R.; Gerrard, J.A. The impact of Maillard cross-linking on soy proteins and tofu texture. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, I.; Ferawati, F.; Helstad, A.; Ahlstrom, C.; Ostbring, K.; Rayner, M.; Purhagen, J.K. Development of High-Moisture Meat Analogues with Hemp and Soy Protein Using Extrusion Cooking. Foods 2020, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Ren, K.; Cao, X.; Peng, X.; Zheng, L.; Dai, S.; Tong, X.; Zeng, Q.; Qiu, S.; Wang, H.; et al. High moisture extrusion of soybean-wheat co-precipitation protein: Mechanism of fibrosis based on different extrusion energy regulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Advancing molecular understanding in high moisture extrusion for plant-based meat analogs: Challenges and perspectives. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, S.; Wang, Q. Rheological properties of pea protein isolate-amylose/amylopectin mixtures and the application in the high-moisture extruded meat substitutes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, N.; Wang, Q. High-moisture extrusion process of transglutaminase-modified peanut protein: Effect of transglutaminase on the mechanics of the process forming a fibrous structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hsieh, F.-H. Protein–Protein Interactions during High-Moisture Extrusion for Fibrous Meat Analogues and Comparison of Protein Solubility Methods Using Different Solvent Systems. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2008, 56, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osen, R.; Toelstede, S.; Wild, F.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. High moisture extrusion cooking of pea protein isolates: Raw material characteristics, extruder responses, and texture properties. J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, P.; Zhao, D.; Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Effects of adding other protein products on textural properties of soy protein concentrate-based meat analogs. J. Texture Stud. 2023, 54, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Mazlan, M.; Talib, R.A.; Chin, N.L.; Shukri, R.; Taip, F.S.; Mohd Nor, M.Z.; Abdullah, N. Physical and Microstructure Properties of Oyster Mushroom-Soy Protein Meat Analog via Single-Screw Extrusion. Foods 2020, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.X.; Hou, G.G. Effect of Water Migration between Arabinoxylans and Gluten on Baking Quality of Whole Wheat Bread Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 6507–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Luo, Z.; Guan, X.; Huang, K.; Li, Q.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the hydration and physicochemical properties of brewing rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Quantitative characterization of the crosslinking degree of hydroxypropyl guar gum fracturing fluid by low-field NMR. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Li, T.; Zhou, H.; Guo, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Water binding ability changes of different proteins during high-moisture extrusion. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Liu, Y. Investigation on lemon juice gel as food material for 3D printing and optimization of printing parameters. LWT 2018, 87, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cando, D.; Herranz, B.; Borderías, A.J.; Moreno, H.M. Different additives to enhance the gelation of surimi gel with reduced sodium content. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Effect of microbial transglutaminase on NMR relaxometry and microstructure of pork myofibrillar protein gel. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-N.; Gao, F.; Zhu, K.-X. Effect of fresh egg white addition on the quality characteristics and protein aggregation of oat noodles. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.L.; Wei, Y.M.; Zhang, B. Chemical cross-linking and molecular aggregation of soybean protein during extrusion cooking at low and high moisture content. LWT 2011, 44, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrt, M.; Benedik, E.; Podlipnik, Č.; Ulrih, N.P. Interactions of different polyphenols with bovine serum albumin using fluorescence quenching and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, X.; Cui, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, R. The interaction mechanism and the functionality of yeast protein with hydrophilic and hydrophobic bioactive molecules. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Janssen, F.; Verfaillie, D.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A.; Gunes, D.Z.; Cardinaels, R.; Van Royen, G.; Wouters, A.G.B. The interplay between soy proteins and dietary fiber in determining the structure and texture of high moisture extrudates. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huff, H.E.; Hsieh, F. Texture and Chemical Characteristics of Soy Protein Meat Analog Extruded at High Moisture. J. Food Sci. 2008, 65, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Campbell, L.J.; Euston, S.R. Influence of sugars on the characteristics of glucono-δ-lactone-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Shen, S.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Formation mechanism of yeast-soy protein extrudates during high-moisture extrusion and their digestive properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Feng, J.; Huang, G.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Ultrasound driven conformational and physicochemical changes of soy protein hydrolysates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 68, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Su, X.; Xiao, T.; Lu, F.; Xie, T. High moisture extrusion of soybean protein isolate: Effect of β-glucan on physicochemical properties of extrudates. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Ubbink, J. Reversible and irreversible changes in protein secondary structure in the heat- and shear-induced texturization of native pea protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 168, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. High moisture extrusion cooking on soy proteins: Importance influence of gums on promoting the fiber formation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.R.; Wong, Y.X.; Sow, C.W.J.; Halim, F.N.B.A.; Chin, J.T.G.; Taheri, A.; Juan, D. Structuring chicken breast analogs via high moisture extrusion of dairy-plant proteins blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample Number | WYP% | SPI% | YPP% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% WYP | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 5% WYP | 5 | 95 | 0 |
| 10% WYP | 10 | 90 | 0 |
| 20% WYP | 20 | 80 | 0 |
| 20% YPP | 0 | 80 | 20 |
| 30% WYP | 30 | 70 | 0 |
| 40% WYP | 40 | 60 | 0 |
| L* | a* | b* | ΔE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0%WYP | 37.89 ± 0.26 e | 3.17 ± 0.14 b | 14.86 ± 0.45 c | 0.00 |
| 5%WYP | 37.40 ± 0.06 e | 3.17 ± 0.21 b | 15.37 ± 0.62 c | 0.71 ± 0.03 e |
| 10%WYP | 41.11 ± 0.24 d | 3.19 ± 0.96 b | 14.67 ± 0.09 c | 3.23 ± 0.07 d |
| 20%WYP | 47.00 ± 0.45 b | 2.65 ± 0.81 c | 16.39 ± 0.28 b | 9.24 ± 0.06 b |
| 20%YPP | 44.95 ± 0.38 c | 3.20 ± 0.04 b | 16.35 ± 0.37 b | 7.22 ± 0.30 c |
| 30%WYP | 47.47 ± 0.55 b | 3.85 ± 0.21 a | 17.57 ± 0.29 a | 9.04 ± 0.11 b |
| 40%WYP | 49.16 ± 0.70 a | 3.91 ± 0.04 a | 18.22 ± 0.02 a | 11.80 ± 0.24 a |
| Fibrousness (Perpendicular Hardness/Parallel Hardness) | Hardness (N) | Chewiness (N) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel (FL) | Perpendicular (FV) | Parallel | Perpendicular | ||
| 0%WYP | 1.44 ± 0.02 d | 494.31 ± 11.49 d | 698.92 ± 20.18 e | 653.35 ± 21.76 c | 686.44 ± 20.41 d |
| 5%WYP | 1.45 ± 0.02 cd | 522.83 ± 10.40 cd | 760.51 ± 16.96 d | 648.66 ± 15.86 c | 686.21 ± 11.35 d |
| 10%WYP | 1.56 ± 0.04 c | 561.94 ± 16.37 bc | 879.23 ± 15.27 c | 674.74 ± 8.15 bc | 705.91 ± 15.54 cd |
| 20%WYP | 1.84 ± 0.02 a | 574.93 ± 5.84 b | 1054.84 ± 1 6.91 a | 709.51 ± 9.17 abc | 736.12 ± 21.55 bc |
| 20%YPP | 1.81 ± 0.04 ab | 531.18 ± 17.34 cd | 959.53 ± 25.92 b | 653.34 ± 40.12 c | 685.16 ± 20.72 d |
| 30%WYP | 1.73 ± 0.05 b | 582.78 ± 32.73 b | 998.82 ± 10.22 b | 728.30 ± 17.21 ab | 765.10 ± 11.47 ab |
| 40%WYP | 1.69 ± 0.06 b | 627.04 ± 9.58 a | 1062.04 ± 6.60 a | 740.75 ± 27.56 a | 795.61 ± 12.59 a |
| β-Sheet | Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Turn | β-Antiparallel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0%WYP | 0.254 ± 0.001 e | 0.224 ± 0.002 ab | 0.219 ± 0.006 a | 0.191 ± 0.002 a | 0.112 ± 0.002 d |
| 5%WYP | 0.257 ± 0.002 d | 0.230 ± 0.006 a | 0.225 ± 0.003 a | 0.178 ± 0.003 b | 0.116 ± 0.001 bc |
| 10%WYP | 0.263 ± 0.001 bc | 0.227 ± 0.001 ab | 0.224 ± 0.004 a | 0.169 ± 0.001 b | 0.118 ± 0.001 bc |
| 20%WYP | 0.267 ± 0.003 a | 0.229 ± 0.001 ab | 0.219 ± 0.003 a | 0.167 ± 0.002 b | 0.123 ± 0.004 a |
| 20%YPP | 0.260 ± 0.003 c | 0.226 ± 0.002 ab | 0.222 ± 0.001 a | 0.172 ± 0.002 b | 0.119 ± 0.003 b |
| 30%WYP | 0.266 ± 0.002 ab | 0.226 ± 0.001 b | 0.223 ± 0.001 a | 0.169 ± 0.004 c | 0.115 ± 0.003 cd |
| 40%WYP | 0.265 ± 0.001 ab | 0.227 ± 0.002 ab | 0.221 ± 0.001 a | 0.171 ± 0.002 c | 0.115 ± 0.004 cd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Guo, C.; Yi, J. Development of Soy-Based Meat Analogues via Wet Twin-Screw Extrusion: Enhancing Textural and Structural Properties Through Whole Yeast Powder Supplementation. Foods 2025, 14, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142479
Tang S, Li Y, Wang X, Zhou L, Liu Z, Jiang L, Guo C, Yi J. Development of Soy-Based Meat Analogues via Wet Twin-Screw Extrusion: Enhancing Textural and Structural Properties Through Whole Yeast Powder Supplementation. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142479
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shikang, Yidian Li, Xuejiao Wang, Linyan Zhou, Zhijia Liu, Lianzhou Jiang, Chaofan Guo, and Junjie Yi. 2025. "Development of Soy-Based Meat Analogues via Wet Twin-Screw Extrusion: Enhancing Textural and Structural Properties Through Whole Yeast Powder Supplementation" Foods 14, no. 14: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142479
APA StyleTang, S., Li, Y., Wang, X., Zhou, L., Liu, Z., Jiang, L., Guo, C., & Yi, J. (2025). Development of Soy-Based Meat Analogues via Wet Twin-Screw Extrusion: Enhancing Textural and Structural Properties Through Whole Yeast Powder Supplementation. Foods, 14(14), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142479







