Non-Destructive Detection of Pomegranate Blackheart Disease via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Soft X-ray Imaging Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation
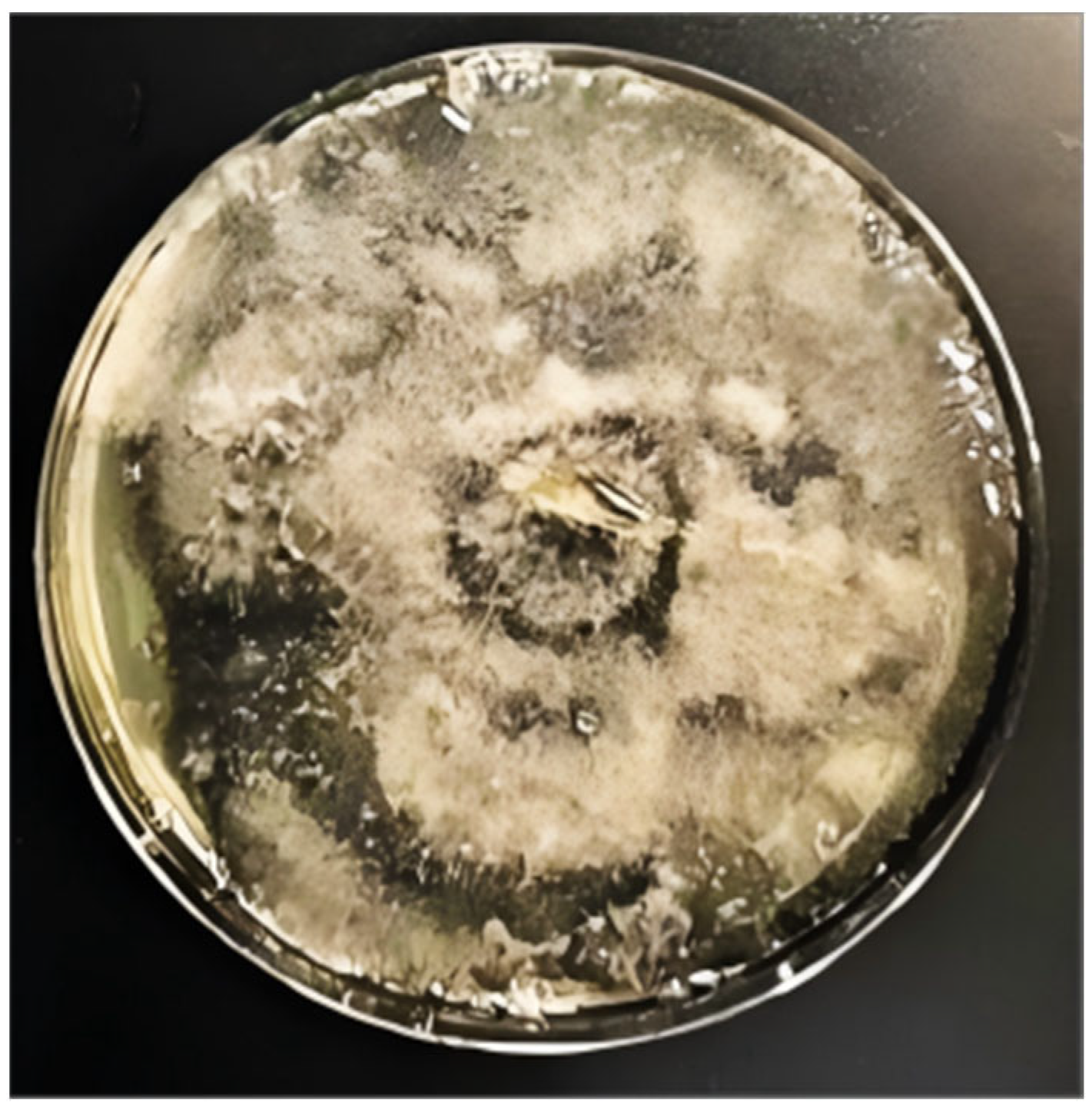
2.1.1. Fungal Cultivation
2.1.2. Fungal Inoculation
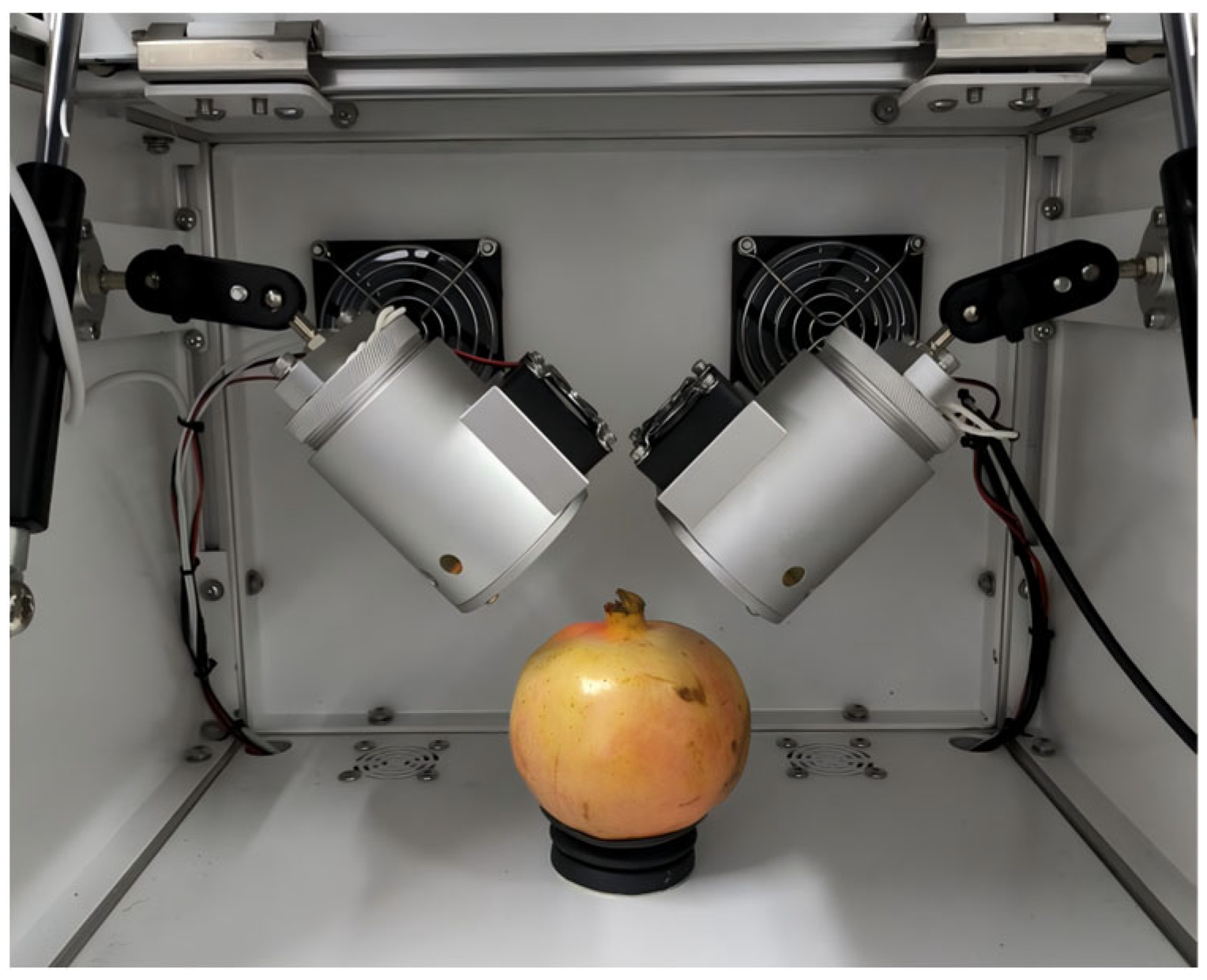
2.2. NIR Spectroscopy Acquisition
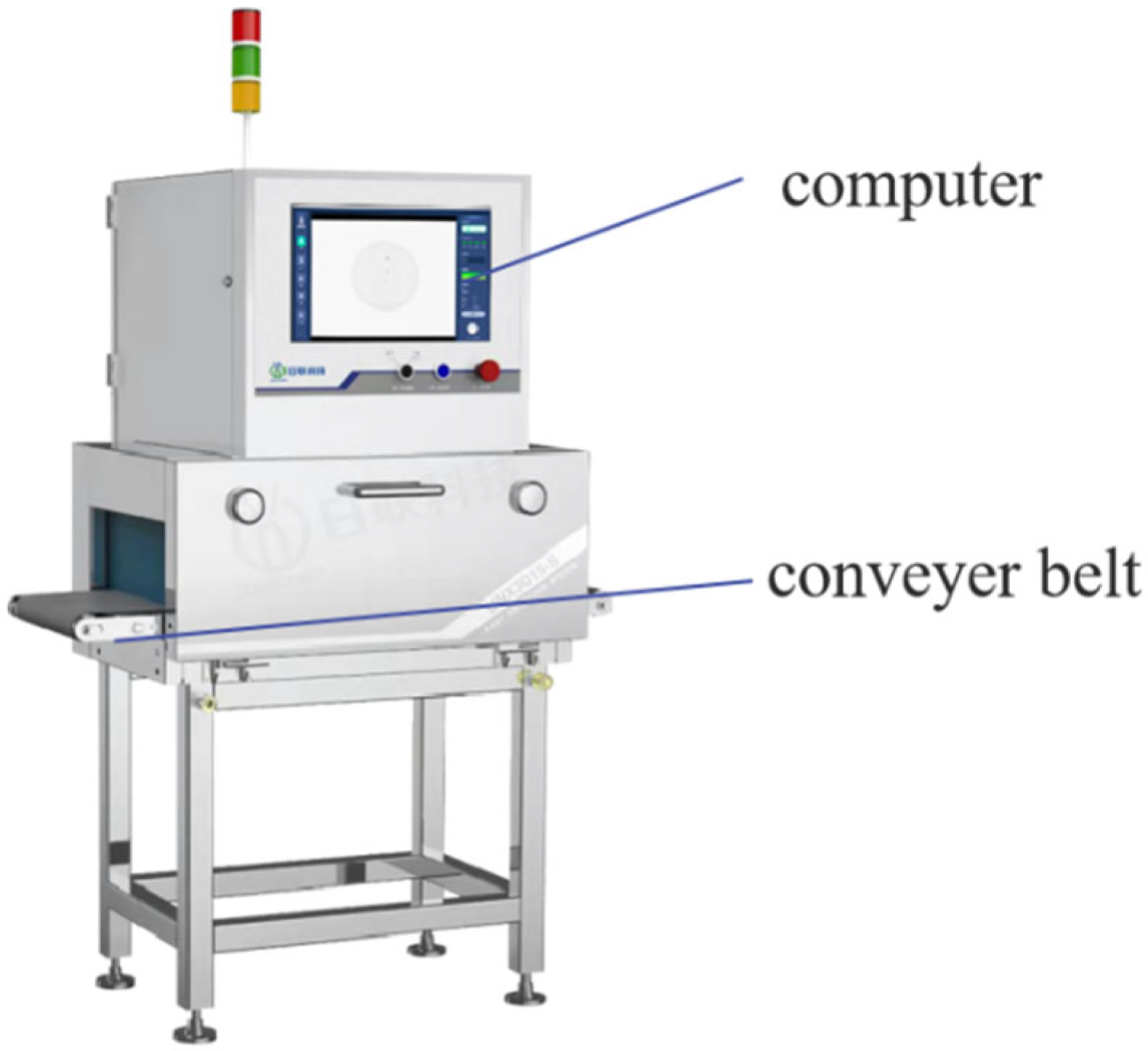
2.3. Soft X-Ray Image Acquisition
2.4. Destructive Verification
2.5. Preprocessing of NIR Spectroscopy
2.6. Preprocessing of Soft X-Ray Image
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Destructive Testing Results of Pomegranate Disease Severity
3.2. Descriptive Analysis of Healthy and Infected Pomegranate Samples
3.3. NIR Spectroscopy-Based Discriminant Model
3.3.1. Outlier Elimination
3.3.2. Spectral Denoising
3.3.3. Feature Wavelength Selection
3.4. Soft X-Ray Imaging-Based Discriminant Model
3.5. NIR Spectroscopy vs. Soft X-Ray Imaging
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahramanoglu, I.; Usanmaz, S.; Nizam, I. Incidence of heart rot at pomegranate fruits caused by Alternaria spp. in Cyprus. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 9, 905–907. [Google Scholar]
- Tziros, G.T.; Lagopodi, A.L.; Tzavella-Klonari, K. Alternaria alternata fruit rot of pomegranate (Punica granatum) in Greece. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, D.; Kirshner, B.; Gat, T.; Shteinberg, D.; Kosto, I. Heart rot of pomegranate, when and how does the pathogen cause the disease? Acta Hortic. 2015, 1089, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, A.; Moreno, M.; Sisterna, M.; Tziros, G.T.; Lagopodi, A.L.; Tzavella-Klonari, K. Alternaria infectoria species-group associated with black point of wheat in Argentina. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.R.; Antúnez, L.; Ares, G.; Johnston, J.W.; Hall, M.; Harker, F.R. Consumers’ visual attention to fruit defects and disorders: A case study with apple images. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 116, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicent, A.; Bartual, J.; Mira, J.L. Notas preeliminares sobre el corazón negro de la granada causado por Alternaria. Agrícola Vergel Frutic. Hortic. Floric. 2015, 34, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, B.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Rafiee, S. Quality detection of pomegranate fruit infected with fungal disease. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; McCarthy, M.J. Black heart characterization and detection in pomegranate using NMR relaxometry and MR imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 67, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, E. Estimation of the density of pomegranate fruit and their fractions using X-ray computed tomography calibrated with polymeric materials. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 148, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myresiotis, C.K.; Testempasis, S.; Vryzas, Z.; Karaoglanidis, G.S.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Determination of mycotoxins in pomegranate fruits and juices using a QuEChERS-based method. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera, S.; Rodríguez-Ortega, A.; Cubero, S.; Aleixos, N.; Blasco, J. Automatic detection of pomegranate fruit affected by blackheart disease using X-ray imaging. LWT 2025, 215, 117248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.J.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, H.R.; Fu, X.P.; Ying, Y.B. Applications of near-infrared systems for quality evaluation of fruits: A review. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 399–419. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ge, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, N.; Ouyang, A.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, M. Non-destructive online detection of early moldy core apples based on Vis/NIR transmission spectroscopy. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.Q.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wu, J.Z.; Li, J.B. Detection of pears with moldy core using online full-transmittance spectroscopy combined with supervised classifier comparison and variable optimization. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.H.; Cao, C.M.; Wang, S.S.; Zhang, X.C.; Ding, W.Y. Non-destructive identification of moldy walnut based on NIR. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, B. Ability of near-infrared spectroscopy for non-destructive detection of internal insect infestation in fruits: Meta-analysis of spectral ranges and optical measurement modes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 225, 117479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Dai, C.; Huang, X. Visualization of Moisture Content, Reducing Sugars, and Chewiness in Bread During Oral Processing Based on Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Foods 2024, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, F.; Ren, Y.; Dai, C.; Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Production monitoring and quality characterization of black garlic using Vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging integrated with chemometrics strategies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 326, 125182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Jayan, H.; Majeed, U.; Watson, N.J.; Zou, X. Dynamic Nondestructive Detection Models of Apple Quality in Critical Harvest Period Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Intelligent Algorithms. Foods 2024, 13, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Harrington Aheto, J.; Xu, F.; Dai, C.; Ren, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, S. Rapid non-destructive monitoring and quality assessment of the fumigation process of Shanxi aged vinegar based on Vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging combined with multiple chemometric algorithms. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 320, 124539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teye, E.; Huang, X.; Sam-Amoah, L.K.; Takrama, J.; Boison, D.; Botchway, F.; Kumi, F. Estimating cocoa bean parameters by FT-NIRS and chemometrics analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanti, N.K.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Ishwarya, S.P.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Cozzolino, D. Emerging non-destructive imaging techniques for fruit damage detection: Image processing and analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Kamata, T.; Koseki, S.; Koyama, K. Development of automatic detection model for stem-end rots of ‘Hass’ avocado fruit using X-ray imaging and image processing. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 192, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dael, M.; Lebotsa, S.; Herremans, E.; Verboven, P.; Sijbers, J.; Opara, U.L.; Cronje, P.J.; Nicolaï, B.M. A segmentation and classification algorithm for online detection of internal disorders in citrus using X-ray radiographs. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 112, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempelaere, A.; Van Doorselaer, L.; He, J.; Verboven, P.; Nicolai, B.M. BraeNet: Internal disorder detection in ‘Braeburn’ apple using X-ray imaging data. Food Control. 2024, 155, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, D.; Shulhani, R.; Shtienberg, D. A method for quantifying the response of asymptomatic pomegranate fruit to Alternaria alternata, the causal agent of black heart disease of pomegranate. Acta Hortic. 2019, 1254, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Nie, F.; Zhang, C. Learning a Mahalanobis distance metric for data clustering and classification. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 3600–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, X. Outlier detection using local density and global structure. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 157, 110947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhr, D.; Affenzeller, M. Little data is often enough for distance-based outlier detection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Lin, L. Blood species identification using Near-Infrared diffuse transmitted spectra and PLS-DA method. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hu, J. Combination of interactance and transmittance modes of Vis/NIR spectroscopy improved the performance of PLS-DA model for moldy apple core. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 126, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Guo, C.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Shi, J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X. Classification for Penicillium expansum Spoilage and Defect in Apples by Electronic Nose Combined with Chemometrics. Sensors 2020, 20, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Wang, C.; Ernest, B.; Tian, X.; He, P.; Chang, X.; Wang, C. Application of volatile and spectral profiling together with multimode data fusion strategy for the discrimination of preserved eggs. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization and quantification of the taste profiles of black garlic via a novel multi-channel colorimetric sensor array and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 138, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, T.D.O.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Fletcher, M.T.; Fox, G. Near Infrared Spectrometry for Rapid Non-Invasive Modelling of Aspergillus-Contaminated Maturing Kernels of Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture 2017, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z. Analysis of Nutritional Content in Rice Seeds Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Photonics 2025, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, P.; Lv, W. An efficient nondestructive detection method of rapeseed varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology. Microchem. J. 2025, 210, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yin, C.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z. Rapid detection of three quality parameters and classification of wine based on Vis-NIR spectroscopy with wavelength selection by ACO and CARS algorithms. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 205, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, A.M.; Raharjo, S.; Utami, E.; Ariatmanto, D. Analysis for diagnosis of pneumonia symptoms using chest X-ray based on MobileNetV2 models with image enhancement using white balance and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE). Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2024, 90, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tat, T.B.; Hung, T.Q.; Nam, P.T.; Ngo, V.M. Evaluating pre-processing and deep learning methods in medical imaging: Combined effectiveness across multiple modalities. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 558–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Tian, Y.; Song, P.; He, K.; Song, S. Analysis and detection of decayed blueberry by low field nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru, D.S.; Nandini, D. Mango Internal Defect Detection using NIR Spectroscopy Data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 258, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyasulu, C.; Diattara, A.; Traore, A.; Ba, C.; Diedhiou, P.M.; Sy, Y.; Raki, H.; Peluffo-Ordóñez, D.H. A comparative study of Machine Learning-based classification of Tomato fungal diseases: Application of GLCM texture features. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Fungal Inoculation Time Point | Harvest Time Point | Infection Time | Quantity | Storage Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | 0 day | 96 | Ambient temperature and humidity |
| Day 3 | Day 4 | 1 day | 32 | 20 °C, 90% RH |
| Day 2 | Day 4 | 2 days | 32 | 20 °C, 90% RH |
| Day 1 | Day 4 | 3 days | 32 | 20 °C, 90% RH |
| No. | Texture Feature | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Angular Second Moment | |
| 2 | Correlation | |
| 3 | Entropy | |
| 4 | Contrast | |
| 5 | Homogeneity | |
| 6 | Variance | |
| 7 | Small Gradient Advantage | |
| 8 | Large Gradient Advantage | |
| 9 | Gray Non-uniformity | |
| 10 | Gradient Non-uniformity | |
| 11 | Energy | |
| 12 | Gray Mean | |
| 13 | Gradient Mean | |
| 14 | Gray Variance | |
| 15 | Gradient Variance | |
| 16 | Correlation | |
| 17 | Gray Entropy | |
| 18 | Gradient Entropy | |
| 19 | Hybrid Entropy | |
| 20 | Inertia | |
| 21 | Inverse Difference Moment |
| Disease Severity (Grade) | Infection Time | Disease Severity (%) | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 day | 0 | 96 |
| 1 | 1 day | 3.2–7.8 | 32 |
| 2 | 2 days | 7.9–18.6 | 32 |
| 3 | 3 days | 18.7–30.4 | 32 |
| Algorithms | Test Set Accuracy | F1-Score | Five-Fold Cross-Validation Mean Accuracy | Five-Fold Cross- Validation Mean F1-Score | Number of Correct Classifications | Number of Incorrect Classifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOF | 52.11% | 45.33% | 66.71% | 65.38% | 95 | 86 |
| Mahalanobis distance | 54.54% | 44.91% | 73.72% | 67.11% | 99 | 82 |
| Models | Training Set Accuracy | Training Set F1-Score | Test Set Accuracy | Test Set F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 87.17% | 93.75% | 56.00% | 78.57% |
| SNV-RF | 94.01% | 95.72% | 56.00% | 77.41% |
| MSC-RF | 93.16% | 96.72% | 68.00% | 89.65% |
| SG-RF | 83.76% | 92.53% | 62.00% | 83.33% |
| D1-RF | 99.14% | 100.0% | 82.00% | 100.0% |
| D2-RF | 99.14% | 100.0% | 84.00% | 98.11% |
| SVM | 89.74% | 100.0% | 80.00% | 96.29% |
| SNV-SVM | 78.63% | 98.30% | 74.00% | 98.24% |
| MSC-SVM | 79.48% | 97.71% | 70.00% | 87.50% |
| SG-SVM | 88.03% | 100.0% | 82.00% | 100.0% |
| D1-SVM | 89.74% | 98.38% | 66.00% | 100.0% |
| D2-SVM | 90.50% | 99.13% | 72.00% | 90.90% |
| Models | Wavelength Number | Training Set Accuracy | Training Set F1-Score | Test Set Accuracy | Test Set F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-RF | 958 | 99.14% | 100.0% | 84.00% | 98.11% |
| D2-CARS-RF | 62 | 97.43% | 99.13% | 86.00% | 89.33% |
| D2-SPA-RF | 50 | 95.21% | 98.26% | 80.00% | 83.33% |
| D2-PCA-RF | 8 | 79.48% | 77.71% | 74.00% | 78.24% |
| No. | Texture Feature | Grade 0 (Healthy) | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Angular second Moment | 0.3862 | 0.4371 | 0.3998 | 0.4066 |
| 2 | Correlation | −33.20 | −23.31 | −32.92 | −30.41 |
| 3 | Entropy | 7.151 | 6.732 | 6.969 | 6.695 |
| 4 | Contrast | 2.913 × 106 | 2.542 × 106 | 2.791 × 106 | 2.526 × 106 |
| 5 | Homogeneity | 1.707 | 1.745 | 1.721 | 1.745 |
| 6 | Variance | 6.158 | 5.764 | 6.066 | 5.778 |
| 7 | Small gradient Advantage | 0.7523 | 0.7217 | 0.7694 | 0.8144 |
| 8 | Large gradient Advantage | 0.6349 | 0.6978 | 0.6011 | 0.5316 |
| 9 | Gray non-uniformity | 4742 | 5231 | 4830 | 4405 |
| 10 | Gradient Non-uniformity | 3.476 × 104 | 3.241 × 104 | 3.625 × 104 | 4.035 × 104 |
| 11 | Energy | 0.0663 | 0.0733 | 0.0676 | 0.0616 |
| 12 | Gray mean | 48.72 | 43.48 | 48.33 | 45.43 |
| 13 | Gradient mean | 0.6349 | 0.5779 | 0.6011 | 0.5316 |
| 14 | Gray variance | 37.62 | 36.03 | 37.14 | 34.45 |
| 15 | Gradient variance | 2.176 | 2.072 | 2.174 | 2.106 |
| 16 | Correlation | 22.42 | 22.46 | 20.94 | 19.34 |
| 17 | Gray entropy | 1.718 | 1.666 | 1.702 | 1.692 |
| 18 | Gradient entropy | 0.3972 | 0.3372 | 0.3787 | 0.3451 |
| 19 | Hybrid entropy | 1.989 | 1.896 | 1.962 | 1.929 |
| 20 | Inertia | 3705 | 3093 | 3629 | 3178 |
| 21 | Inverse difference moment | 0.2483 | 0.2694 | 0.2504 | 0.2349 |
| Models | Grade | Number of Samples | Number of Errors | Accuracy | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0 | 28 | 0 | 93.10% | 98.11% |
| 1 | 10 | 2 | |||
| 2 | 8 | 0 | |||
| 3 | 12 | 2 | |||
| SVM | 0 | 31 | 0 | 81.03% | 67.91% |
| 1 | 11 | 11 | |||
| 2 | 7 | 0 | |||
| 3 | 9 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, R.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Yu, S.; Dai, C.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Q. Non-Destructive Detection of Pomegranate Blackheart Disease via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Soft X-ray Imaging Systems. Foods 2025, 14, 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142454
Nie R, Huang X, Tian X, Yu S, Dai C, Zhang X, Fang Q. Non-Destructive Detection of Pomegranate Blackheart Disease via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Soft X-ray Imaging Systems. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142454
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Rongke, Xingyi Huang, Xiaoyu Tian, Shanshan Yu, Chunxia Dai, Xiaorui Zhang, and Qin Fang. 2025. "Non-Destructive Detection of Pomegranate Blackheart Disease via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Soft X-ray Imaging Systems" Foods 14, no. 14: 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142454
APA StyleNie, R., Huang, X., Tian, X., Yu, S., Dai, C., Zhang, X., & Fang, Q. (2025). Non-Destructive Detection of Pomegranate Blackheart Disease via Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Soft X-ray Imaging Systems. Foods, 14(14), 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142454







