Entomophagy: Nutritional Value, Benefits, Regulation and Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Insects as Food
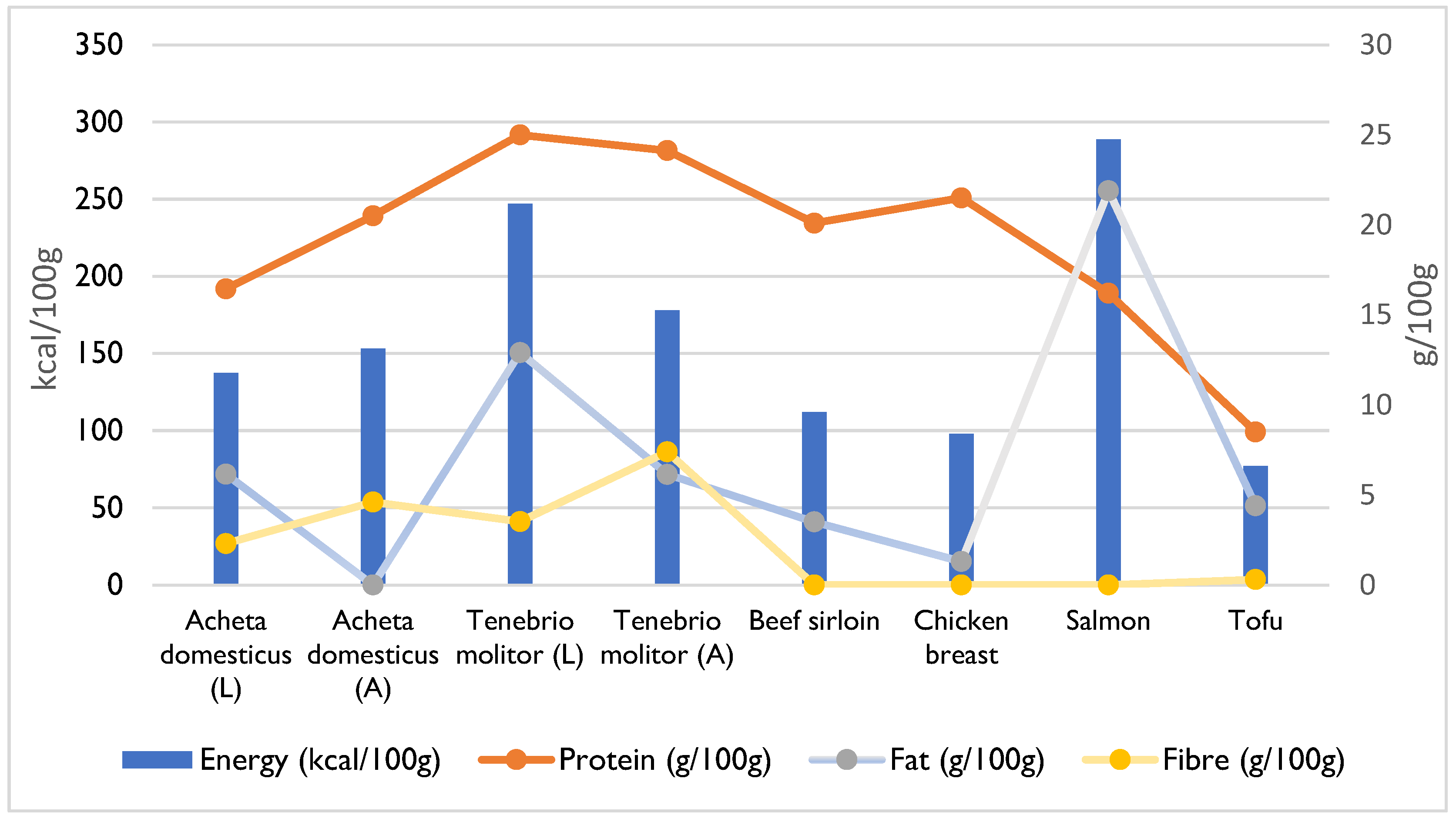
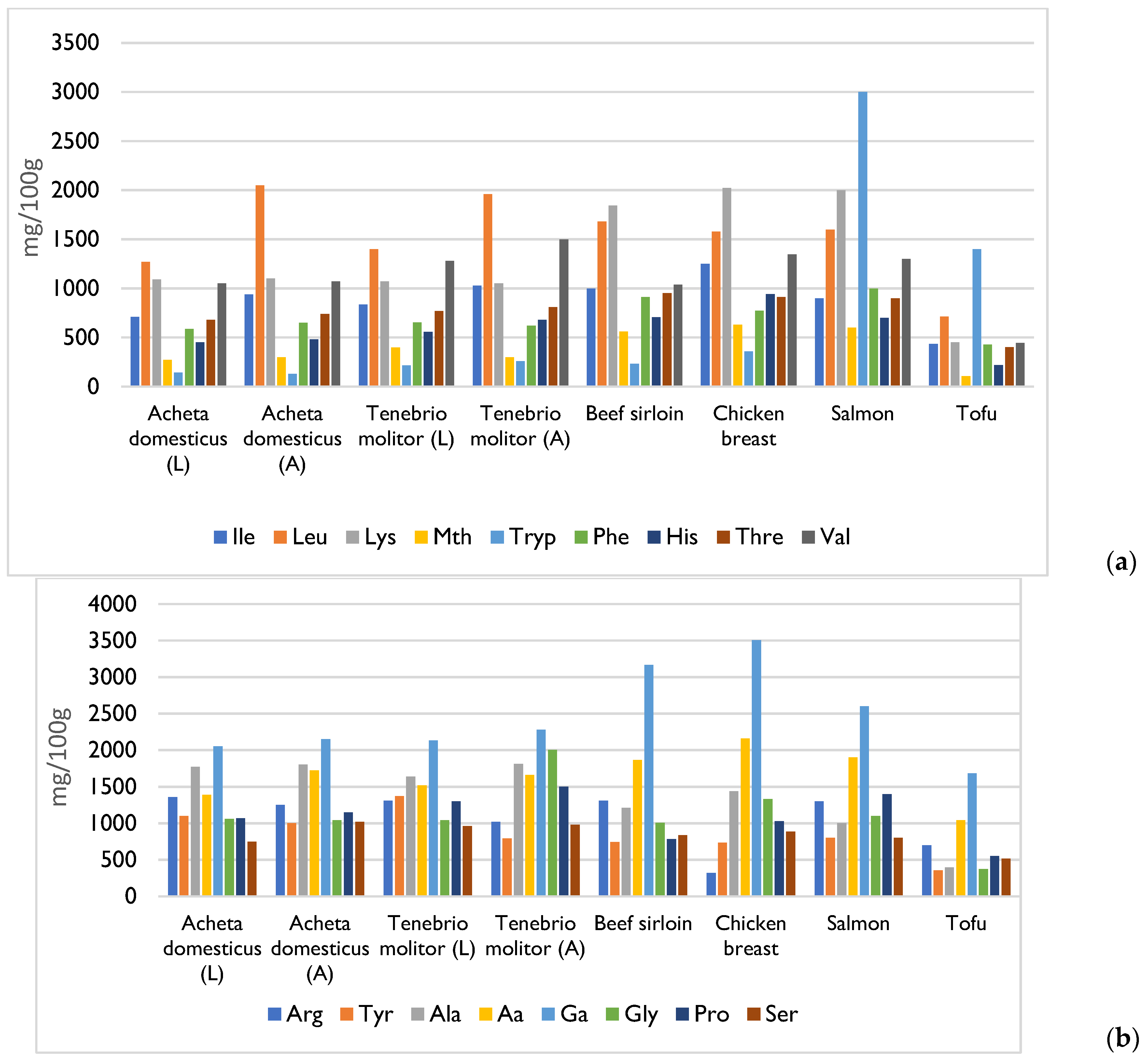
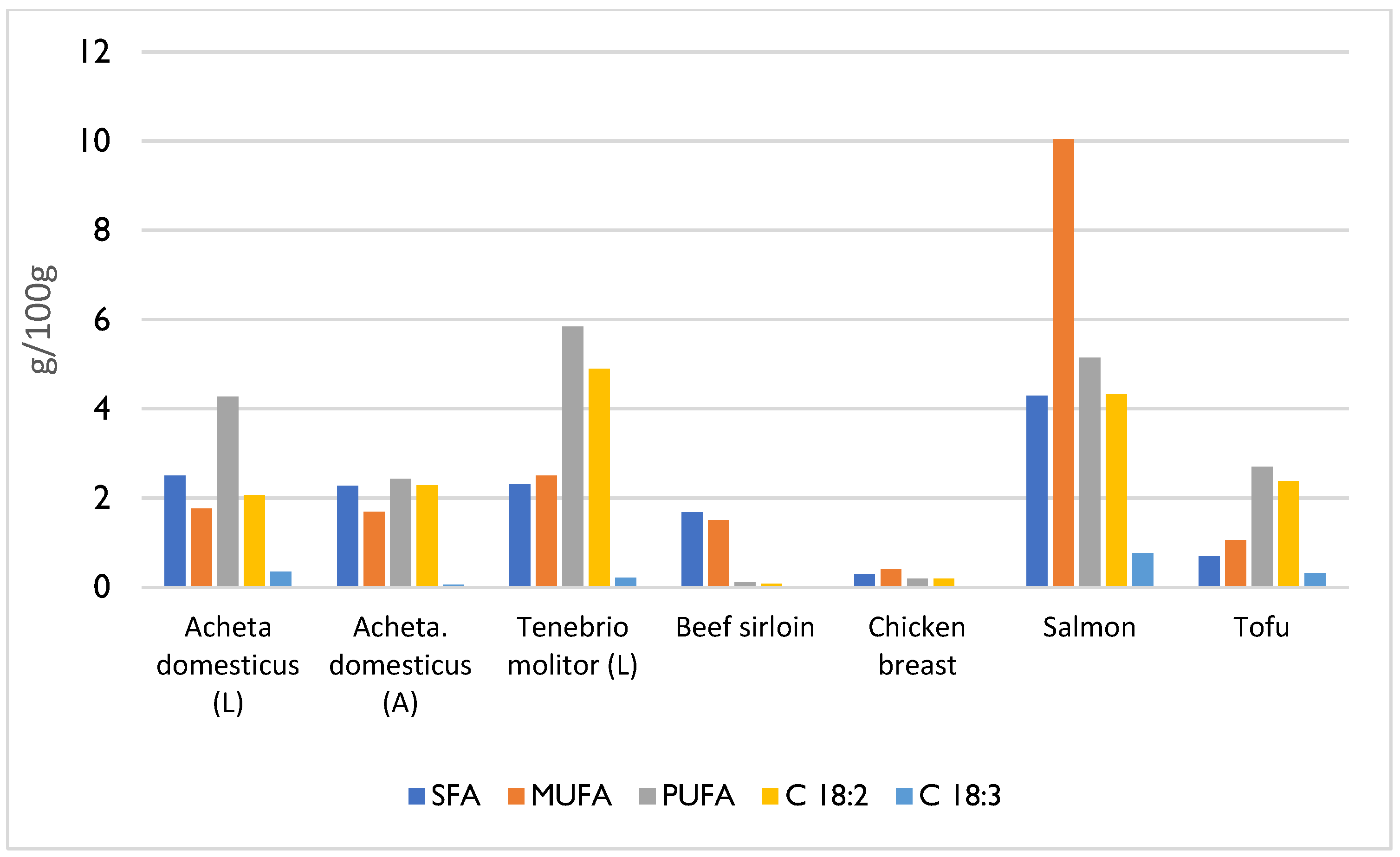
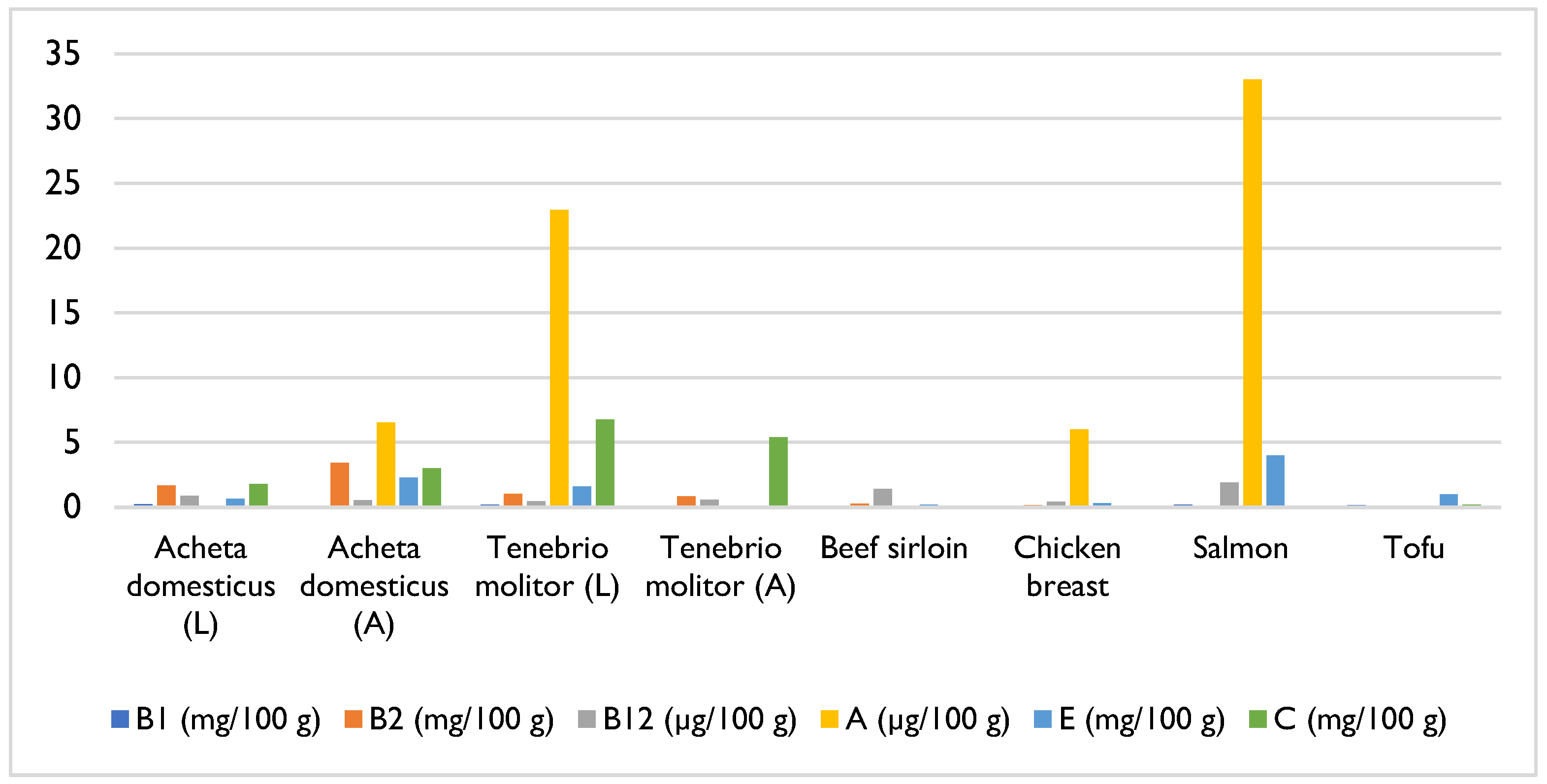
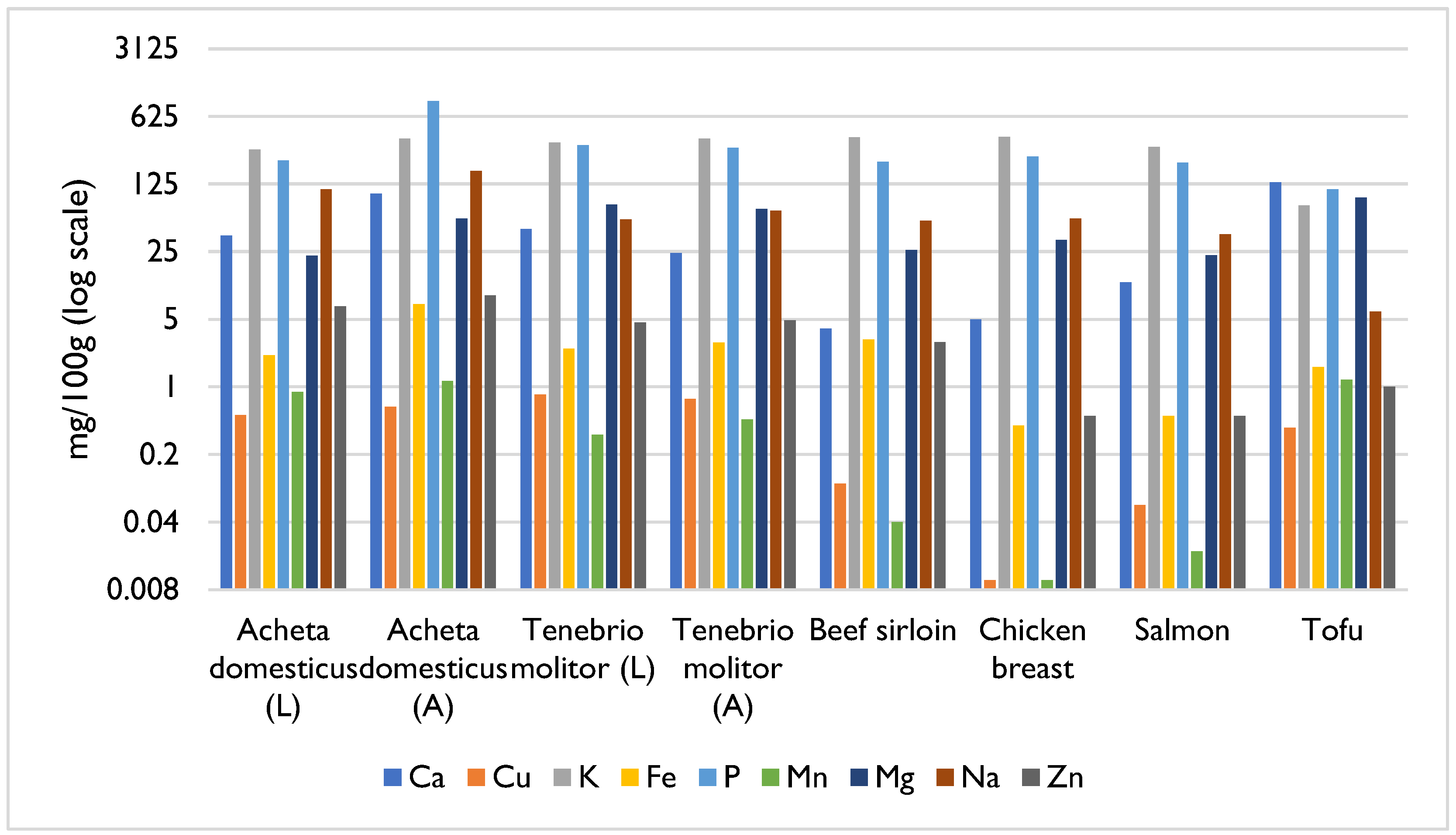
4. Composition and Nutritional Value
5. Entomophagy Benefits
5.1. Health Benefits
5.1.1. Antioxidant Activity
5.1.2. Hypotensive Effects
5.1.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
5.2. Environmental Benefits
5.3. Socioeconomic Benefits
6. Legal and Regulatory Framework
7. Food Safety
7.1. Insect Farming
7.2. Preservation and Storage
7.3. Biological Hazards
7.3.1. Bacteria
7.3.2. Viruses
7.3.3. Fungi
7.3.4. Parasites
7.4. Chemical Hazards
7.4.1. Heavy Metals
7.4.2. Mycotoxins
7.4.3. Veterinary Drugs
7.4.4. Pesticides
7.5. Allergens
7.6. Anti-Nutritional Factors
8. Future Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; Wageningen UR, FAO, Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 9789251075951. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Looking at Edible Insects from a Food Safety Perspective—Challenges and Opportunities for the Sector; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; ISBN 9789251341964. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, C.; Chavez, K.; Jorge, R. Entomofagia—Consumo atual e potencial de futuro. Acta Port. Nutr. 2022, 29, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations-Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results; UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3; United Nations-Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–52. ISBN 978-92-1-148373-4. [Google Scholar]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Correia, P.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C.A. The role of edible insects to mitigate challenges for sustainability. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD-FAO. Chapter 6: Meat. In OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 163–177. ISBN 9789264675377. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, W.D.; Bonysana, R.; Singh, K.D.; Koijam, A.S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Rajashekar, Y. Bio-economic potential of ethno-entomophagy and its therapeutics in India. NPJ Sci. Food 2024, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Tao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Peng, Y. A review on edible insects in China: Nutritional supply, environmental benefits, and potential applications. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, D.; Raposo, A.; Oluwole, O.B.; Nieuwland, M.; Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C. Entomophagy: Nutritional, ecological, safety and legislation aspects. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez-Araque, R.; Quishpillo-Miranda, N.; Ramos-Guerrero, L. Edible Insects for Humans and Animals: Nutritional Composition and an Option for Mitigating Environmental Damage. Insects 2022, 13, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, S.; Duan, H.; Guo, J.; Yan, W. Nutritional Composition, Health Benefits, and Application Value of Edible Insects: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Bekhit, A.E.D.; Grune, T.; Schlüter, O.K. Bioavailability of nutrients from edible insects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 41, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, H.J.O.; Niassy, S.; Ayieko, M.A.; Mukundamago, M.; Egonyu, J.P.; Tanga, C.M.; Kimathi, E.K.; Ongere, J.O.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Hugel, S.; et al. Edible Crickets (Orthoptera) Around the World: Distribution, Nutritional Value, and Other Benefits—A Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 537915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imathiu, S. Benefits and food safety concerns associated with consumption of edible insects. NFS J. 2020, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivadese, M.; Dindo, M.L. Edible Insects: A Historical and Cultural Perspective on Entomophagy with a Focus on Western Societies. Insects 2023, 14, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuse, E.R.; Tonnang, H.E.Z.; Yusuf, A.A.; Machekano, H.; Egonyu, J.P.; Kimathi, E.; Mohamed, S.F.; Kassie, M.; Subramanian, S.; Onditi, J.; et al. The global atlas of edible insects: Analysis of diversity and commonality contributing to food systems and sustainability. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huis, A.; Rumpold, B.; Maya, C.; Roos, N. Nutritional Qualities and Enhancement of Edible Insects. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 551–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abril, S.; Pinzón, M.; Hernández-Carrión, M.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.d.P. Edible Insects in Latin America: A Sustainable Alternative for Our Food Security. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 904812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, W.D.; Bonysana, R.; Kapesa, K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Rajashekar, Y. Edible insects: As traditional medicine for human wellness. Futur. Foods 2023, 7, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efsa Scientific Committee. Risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkusz, A. Edible insects versus meat—Nutritional comparison: Knowledge of their composition is the key to good health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Pankiewicz, U. The Potential for the Use of Edible Insects in the Production of Protein Supplements for Athletes. Foods 2023, 12, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge Tabela da Composição dos Alimentos. Available online: https://portfir-insa.min-saude.pt/# (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Mwangi, M.N.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Stouten, T.; Veenenbos, M.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Dicke, M.; Van Loon, J.J.A. Insects as sources of iron and zinc in human nutrition. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Cruz-Monterrosa, R.G.; Liceaga, A.M. Beyond Human Nutrition of Edible Insects: Health Benefits and Safety Aspects. Insects 2022, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantzen da Silva Lucas, A.; Menegon de Oliveira, L.; da Rocha, M.; Prentice, C. Edible insects: An alternative of nutritional, functional and bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Estrada, B.A.; Reyes, A.; Rosell, C.M.; Rodrigo, D.; Ibarra-Herrera, C.C. Benefits and Challenges in the Incorporation of Insects in Food Products. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 687712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. Metal Ions, Metal Chelators and Metal Chelating Assay as Antioxidant Method. Processes 2022, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalodia, N.; Nariya, P.; Shukla, V.; Acharya, R. In vitro antioxidant activity of hydro alcoholic extract from the fruit pulp of Cassia fistula Linn. AYU (Int. Q. J. Res. Ayurveda) 2013, 34, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Karaś, M.; Baraniak, B.; Jakubczyk, A. Evaluation of ACE, α-glucosidase, and lipase inhibitory activities of peptides obtained by in vitro digestion of selected species of edible insects. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of hydrolysates and peptide fractions obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of selected heat-treated edible insects. Nutrients 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, C.; Michie, C.; Tachtatzis, C.; Andonovic, I.; Bowen, J.; Duthie, C.A. Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) and Performance Group Estimation Based on Predicted Feed Intake for the Optimisation of Beef Production. Sensors 2023, 23, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlu, A.; Ngasakul, N.; Klojdová, I.; Baigts-Allende, D.K. Edible insect-processing techniques: A strategy to develop nutritional food products and novelty food analogs. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 27 January 1997. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1997, L43, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Novel Food-European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/novel_food_en%0Ahttp://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/novel_food_en%5Cnhttp://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/novel_food/index_en.htm (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 25 November 2015. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, L327, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- IPIFF. EU Novel Food Legislation and Other EU Requirements Applying to Insect Food Producers. Available online: https://ipiff.org/insects-novel-food-eu-legislation-2/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- The European Commission. Comission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470, of 20 December 2017. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L351, 72–201. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2469, of 20 December 2017. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L351, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Comission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2468, of 20 December 2017. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L351, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 25 October 2011. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L304, 18–63. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) N. 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 20 December 2006. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L404, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/188, of 10 February 2022. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, L30, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/58, of 5 January 2023. Off. J. Eur. Union 2023, L5, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/5, of 3 January 2023. Off. J. Eur. Union 2023, L2, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1975, of 12 November 2021. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, L402, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/882, of 1 June 2021. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, L194, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/169, of 8 February 2022. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, L28, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Marimuthu, S.B.; Meijer, N. Regulations on insects as food and feed: A global comparison. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, J.; Campbell, B.; Hénault-Éthier, L.; Banks, I.J.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Preyer, C.; Deschamps, M.H.; Vandenberg, G.W. The edible insect sector in Canada and the United States. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, A.; Burns, D.T.; Wu, D.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Elliott, C.T. An analysis of emerging food safety and fraud risks of novel insect proteins within complex supply chains. NPJ Sci. Food 2024, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; Murta, D.d.M.; Magalhães, T.O.N.L.d. Produção, Processamento e Utilização de Insetos em Alimentação Animal; Direção-Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária: Lisboa, Portugal, 2018; Volume 1, ISBN 9789729904486. [Google Scholar]
- Baiano, A. Edible insects: An overview on nutritional characteristics, safety, farming, production technologies, regulatory framework, and socio-economic and ethical implications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar-Lalanne, G.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J.; Salinas-Castro, A. Edible Insects Processing: Traditional and Innovative Technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1166–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunder, H.C.; Wolkers-Rooijackers, J.; Korpela, J.M.; Nout, M.J.R. Microbiological aspects of processing and storage of edible insects. Food Control 2012, 26, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, M.; Mutinelli, F. A systematic review on viruses in mass-reared edible insect species. Viruses 2021, 13, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.M.; Meijer, N.; van den Hil, E.F.H.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Chemical food safety hazards of insects reared for food and feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency KABAM Version 1.0 User’s Guide and Technical Documentation-Appendix F-Description of Equations Used to Calculate the BCF, BAF, BMF, and BSAF Values. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-science-and-assessing-pesticide-risks/kabam-version-10-users-guide-and-technical (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Singapore Food Agency Local Production of Insects for Food and for Animal Feed for Food-Producing Animals. Available online: https://www.sfa.gov.sg/regulatory-standards-frameworks-guidelines/insect-regulatory-framework/local-production-of-insects-for-food-and-for-animal-feed-for-food-producing-animals (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 300, 1–33.
- Regulation 2017/893/EC, 2017 Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/ 893-of 24 May 2017-amending Annexes I and IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Annexes X, XIV and XV to Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as regards the provision. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 60, 92–116.
- Gao, Q.; Deng, W.; Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, F. Effect of sulfonamide pollution on the growth of manure management candidate Hermetia illucens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Fonseca, J.; Fonseca, S.C.; Cunha, L.M. Edible insects and food safety: Allergy. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barre, A.; Pichereaux, C.; Simplicien, M.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Benoist, H.; Rougé, P. A Proteomic- and Bioinformatic-Based Identification of Specific Allergens from Edible Insects: Probes for Future Detection as Food Ingredients. Foods 2021, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunatsa, Y.; Chidewe, C.; Zvidzai, C.J. Phytochemical and anti-nutrient composite from selected marginalized Zimbabwean edible insects and vegetables. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Gahukar, R.T.; Ghosh, S.; Jung, C. Chemical composition, nutrient quality and acceptability of edible insects are affected by species, developmental stage, gender, diet, and processing method. Foods 2021, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Sánchez-Estrada, M.L.; Aguirre-Becerra, H.; Feregrino-Pérez, A.A. Bioactive compounds and biological activity in edible insects: A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO The Contribution of Insects to Food Security, Livelihoods and the Environment. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/i3264e/i3264e00.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Jensen, H.; Elleby, C.; Domínguez, I.P.; Chatzopoulos, T.; Charlebois, P. Insect-based protein feed: From fork to farm. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEDIAF EuropeanPetFood Insect-Based Ingredients in Pet Food. Available online: https://europeanpetfood.org/pet-food-facts/fact-sheets/nutrition/insect-based-ingredients-in-pet-food/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, N.A.; Silva, L.J.G.; Pena, A.; Pereira, A.M.P.T. Entomophagy: Nutritional Value, Benefits, Regulation and Food Safety. Foods 2025, 14, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132380
Pinheiro NA, Silva LJG, Pena A, Pereira AMPT. Entomophagy: Nutritional Value, Benefits, Regulation and Food Safety. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132380
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Noélia A., Liliana J. G. Silva, Angelina Pena, and André M. P. T. Pereira. 2025. "Entomophagy: Nutritional Value, Benefits, Regulation and Food Safety" Foods 14, no. 13: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132380
APA StylePinheiro, N. A., Silva, L. J. G., Pena, A., & Pereira, A. M. P. T. (2025). Entomophagy: Nutritional Value, Benefits, Regulation and Food Safety. Foods, 14(13), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132380









