Magnetic Particle-Based Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Determination of Hydrocortisone Residues in Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of Streptavidin-Coated MP
2.3. Preparation of AE-Labeled Antibody
2.4. Preparation of Biotinylated Antigen
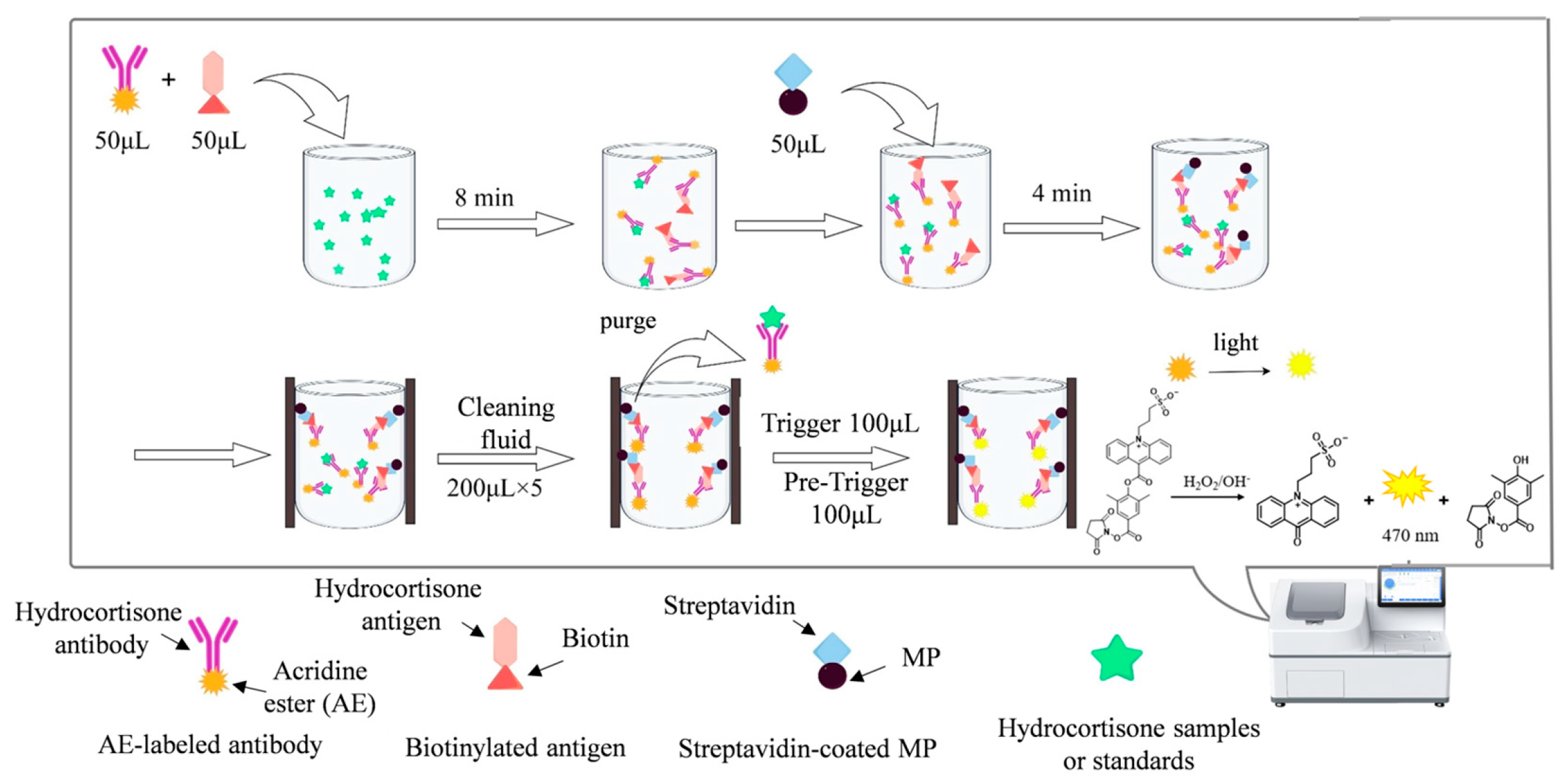
2.5. Development of MP-DCLIA for Hydrocortisone Detection
2.6. MP-DCLIA Performance Evaluation
2.7. Detection of Hydrocortisone
3. Results and Discussion
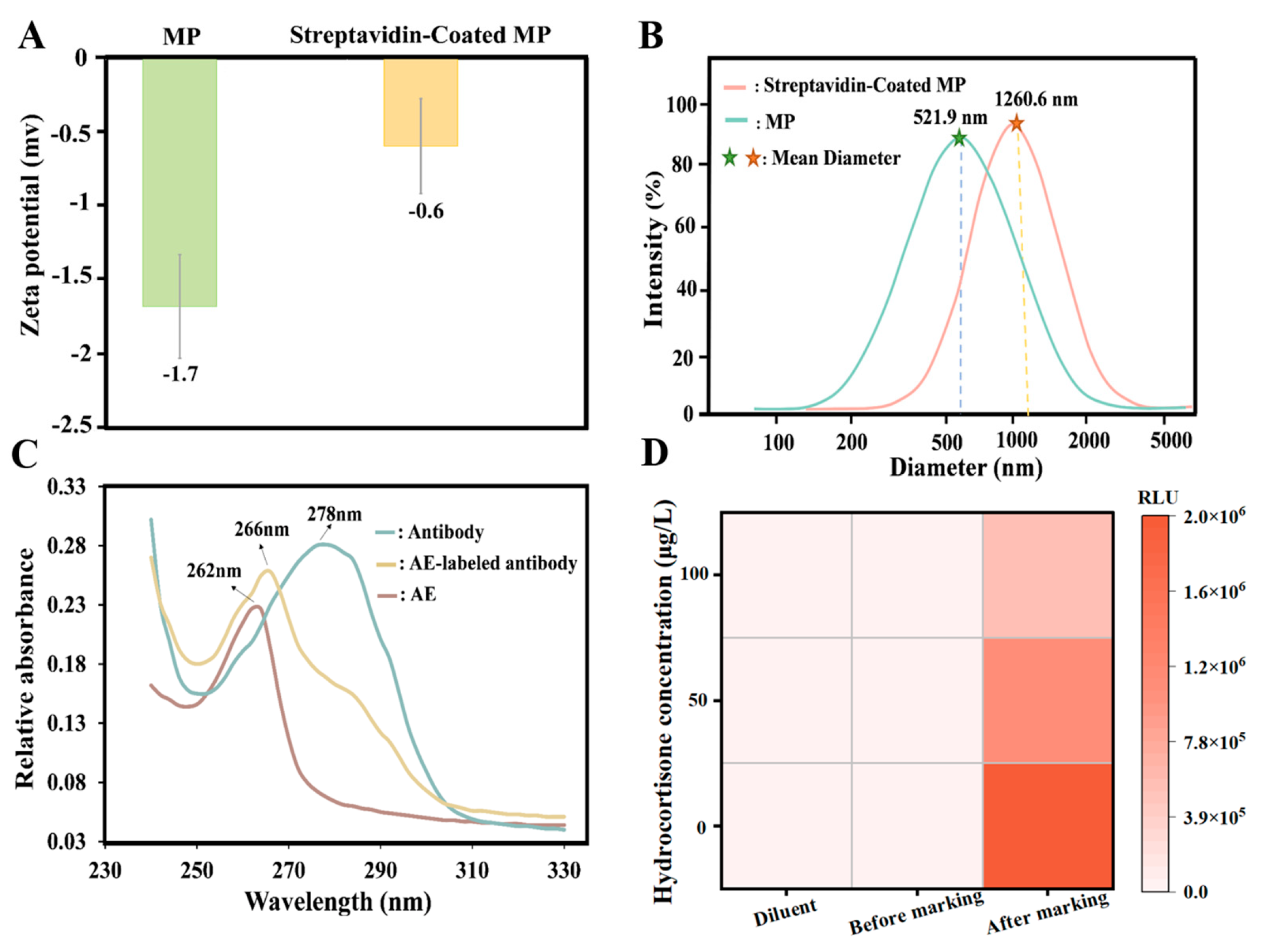
3.1. Characterization of Streptavidin-MP, AE-Labeled Antibody, and Biotinylated Antigen
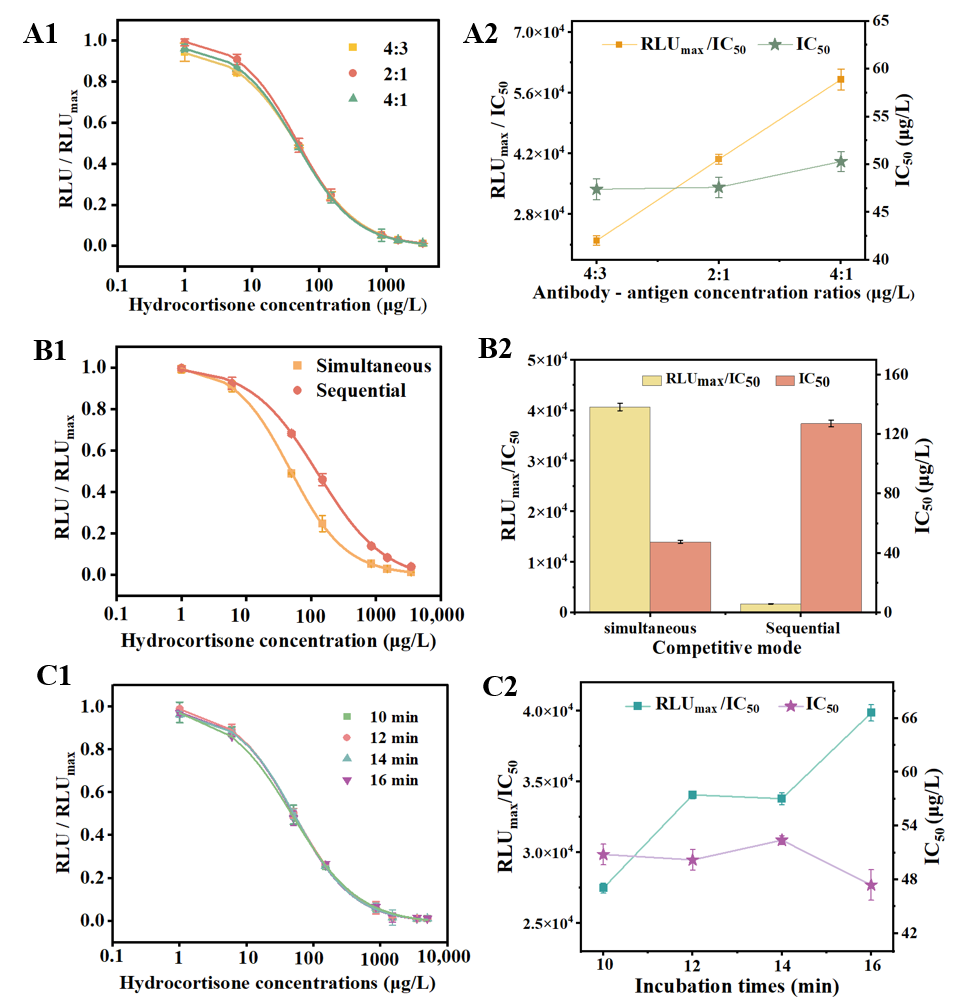
3.2. Optimization of the MP-DCLIA
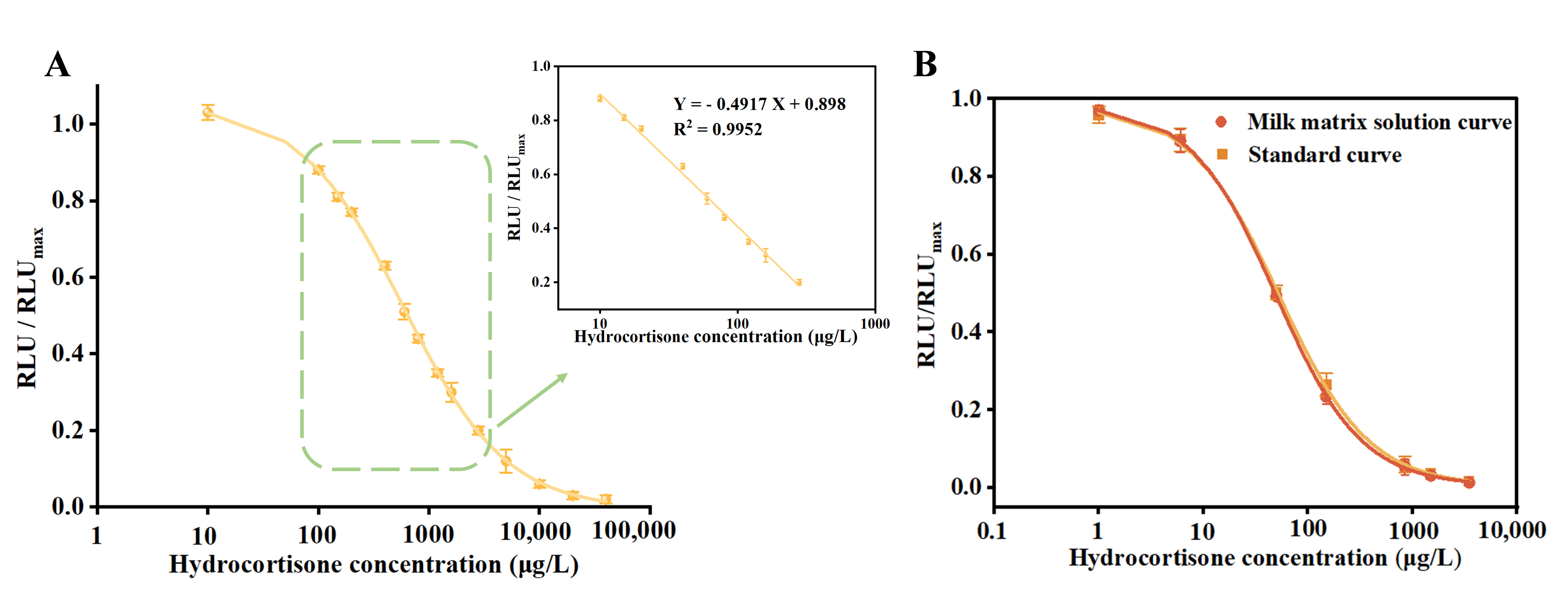
3.3. Performance of MP-DCLIA
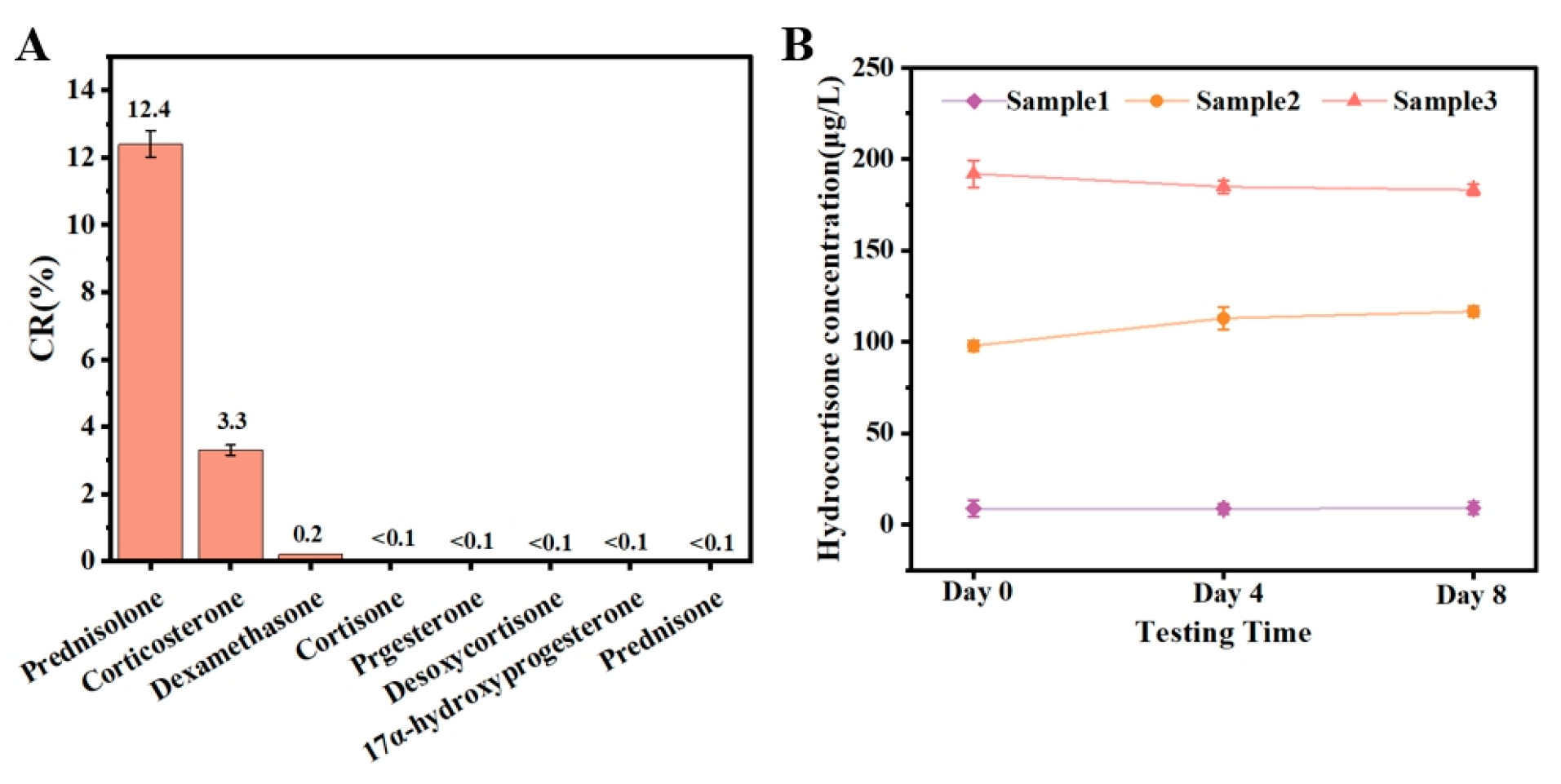
3.4. Recovery Tests
3.5. Detection of Hydrocortisone in Commercial Milk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, G. Simultaneous determination of 58 glucocorticoid residues in milk by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1719, 464734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, R.; Chiesa, L.; Soncin, S.; Panseri, S.; Cannizzo, F.T.; Biolatti, B.; Biondi, P.A. Determination of cortisol, cortisone, prednisolone and prednisone in bovine urine by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation single quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefnawy, M.; Al-Majed, A.; Alrabiah, H.; Algrain, N.; Mohammed, M.; Jardan, Y.B. Rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the enantioanalysis of verapamil in rat plasma using superficially porous silica isopropyl-cyclofructan 6 chiral stationary phase after SPE: Application to a stereoselective pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 201, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Li, W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Yuan, B.; Xu, H. Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Three First-Line Oral Antituberculosis Drug in Plasma. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spies, C.M.; Strehl, C.; van der Goes, M.C.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Buttgereit, F. Glucocorticoids. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devansh, D.; Aditya, P.; Vishvajit, G.; Vinayak, P. Hormones Used in Dairy Products and Their Impact on Public Health. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 2, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoj, T. Hormones in food as a potential risk for human reproductive and health disorders. Acta Vet.-Beogr. 2019, 69, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Kang, K.; Li, N.; An, J.; Lian, K.; Kang, W. Simultaneous Determination of Five Hormones in Milk by Automated Online Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Meng, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ge, S. Determination of eight kinds of glucocorticoids residues in chicken muscle with on-line clean up combined HPLC-MS/MS. Acta Chromatogr. 2022, 34, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W.; Xie, Y. Establishment of the thin-layer chromatography-surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics method for simultaneous identification of eleven illegal drugs in anti-rheumatic health food. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Song, S.; Tao, H.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H. Development of Indirect Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent and Immunochromatographic Strip Assays for Tiamulin Detection in Chicken. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piponski, M.; Stoimenova, T.B.; Stefov, S.; Balkanov, T.; Serafimovska, G.T.; Logoyda, L. Development of a novel, fast, simple, nonderivative HPLC method with direct UV measurement for quantification of memantine hydrochloride in tablets. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3482–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manful, C.F.; Vidal, N.P.; Pham, T.H.; Nadeem, M.; Wheeler, E.; Hamilton, M.C.; Doody, K.M.; Thomas, R.H. Rapid determination of heterocyclic amines in ruminant meats using accelerated solvent extraction and ultra-high performance liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometry. MethodsX 2019, 6, 2686–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Xia, B.; Zhou, Y. A novel functionalized covalent organic framework/carbon nanotube composite as an effective online solid-phase extraction sorbent for simultaneous detection of 33 steroid hormones in pork. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Development, optimization and validation of modified QuEChERS based UPLC-MS/MS for simultaneous determination of nine steroid hormones in milk powder and milk. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 14597–14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinsunthorn, N.; Petsom, A.; Nhujak, T. Determination of steroids adulterated in liquid herbal medicines using QuEChERS sample preparation and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Duan, H.; Bu, Q.; Dong, X. Recent advances of optical sensors for point-of-care detection of phthalic acid esters. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1474831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, A.; He, L.; Cai, C.; You, T. Recent advances in foodborne pathogen detection using photoelectrochemical biosensors: From photoactive material to sensing strategy. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1432555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zong, C.; Xu, J.; Ju, H.-X. Chemiluminescent Immunoassay and its Applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, X.H.; Xie, L.; Han, G.Q.; Zhang, J.; An, W.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Xue, C.H.; Lin, H. Application and prospect of chemiluminescence immunoassay in food safety detection. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 7603–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Lin, J.-M. Advances and Applications of Chemiluminescence Immunoassay in Clinical Diagnosis and Foods Safety. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Ferra, B.; Czechowska, J.; Serdiuk, I.E.; Krzymiński, K. A novel chemiluminescent immunoassay based on original acridinium ester labels as better solution for diagnosis of human toxoplasmosis than conventional ELISA test. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 91, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, C. Research progress on chemiluminescence immunoassay combined with novel technologies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Q. Microplate magnetic chemiluminescence immunoassay for detecting urinary survivin in bladder cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4043–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.S.; Godoy, B.B.R.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Martins, L.C.; Rocha, F.R.P. Novel approach for screening milk based on fast and environmentally friendly determination of protein and fat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 104, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, B. Effect of dietary cortisol administration on growth and reproductive success of channel catfish. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, X.; Tan, S.; Zhong, C.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Determination of Amantadine and Chloramphenicol Residues in Poultry Meat by Indirect Competitive Chemiluminescence Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Xie, S.; Petti, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, F. Specific binding of antigen-antibody in physiological environments: Measurement, force characteristics and analysis. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 104, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Zhou, K.; Luo, L.; Xu, Z.-L. Development of a competitive indirect ELISA for high-throughput screening of hydrocortisone in cosmetic sample. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Jin, E.; Lee, M.-H. Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum. Biosensors 2021, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; He, N.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Ma, Y.; Cui, X.; Xu, J.; Zeng, A. Development of Poly(L-arginine)/PSSA/QDs Modified Biosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Different Glucocorticoids in Wastewater. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 077516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. Molecularly imprinted Monolithic column-based SERS sensor for selective detection of cortisol in dog saliva. Talanta 2022, 249, 123609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, P.; Sun, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, H.; Lu, Y.; Fu, Q. Multi-residue analysis of eight veterinary drugs in buffalo milk using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2023, 63, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measurement Methods | Linear Range (μg/L) | LOD (μg/L) | Reaction Time (min) | Detect the Object | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 0.10~2.00. | 0.04 | >90 | cosmetic | [30] |
| Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform | 0.78~12.5 | 0.342 | 13 | Serum | [31] |
| Electrochemical biosensing platform | * | 13.41 | ≥7 | Wastewater | [32] |
| SERS sensor | 36.25~3.63 × 105 | 36.25 | * | Saliva | [33] |
| LC-MS/MS | 10~1000 | 10 | ≥11 | Buffalo milk | [34] |
| Magnetic particles direct chemiluminescence immunoassay | 13.08~261.71 | 5.45 | 12 | Milk | This work |
| Addition (μg/L) | LC-MS/MS (μg/L) | MP-DCLIA (μg/L) | CV (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10.72 ± 0.91 | 8.75 ± 0.84 | 9.64 | 87.53 |
| 100 | 105.72 ± 0.74 | 100.30 ± 2.19 | 2.19 | 100.30 |
| 200 | 191.50 ± 1.93 | 171.71 ± 4.24 | 2.47 | 85.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-Y.; Jia, B.-Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Liu, Y.-X.; Luo, L. Magnetic Particle-Based Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Determination of Hydrocortisone Residues in Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122105
Yang Y-Y, Jia B-Z, Xu Z-L, Liu Y-X, Luo L. Magnetic Particle-Based Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Determination of Hydrocortisone Residues in Milk. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122105
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuan-Yuan, Bao-Zhu Jia, Zhen-Lin Xu, Yi-Xian Liu, and Lin Luo. 2025. "Magnetic Particle-Based Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Determination of Hydrocortisone Residues in Milk" Foods 14, no. 12: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122105
APA StyleYang, Y.-Y., Jia, B.-Z., Xu, Z.-L., Liu, Y.-X., & Luo, L. (2025). Magnetic Particle-Based Automated Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for the Determination of Hydrocortisone Residues in Milk. Foods, 14(12), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122105






