Integrating Strategy of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Experimental Verification to Investigate the Potential Mechanism of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of Bioactive Components and Gene Targets Related to Alcoholic Liver Injury
2.3. Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.4. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
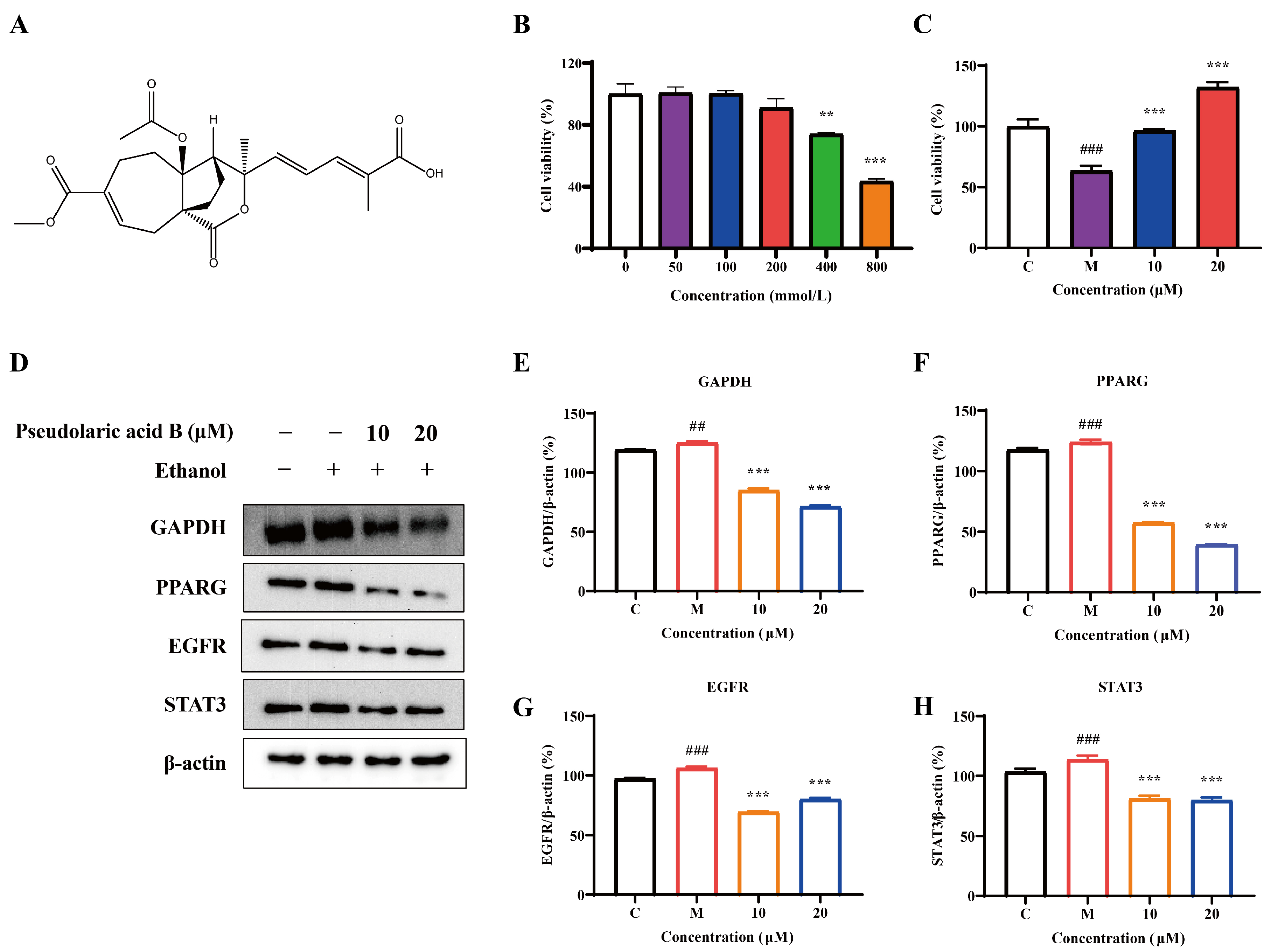
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. MTT Assay
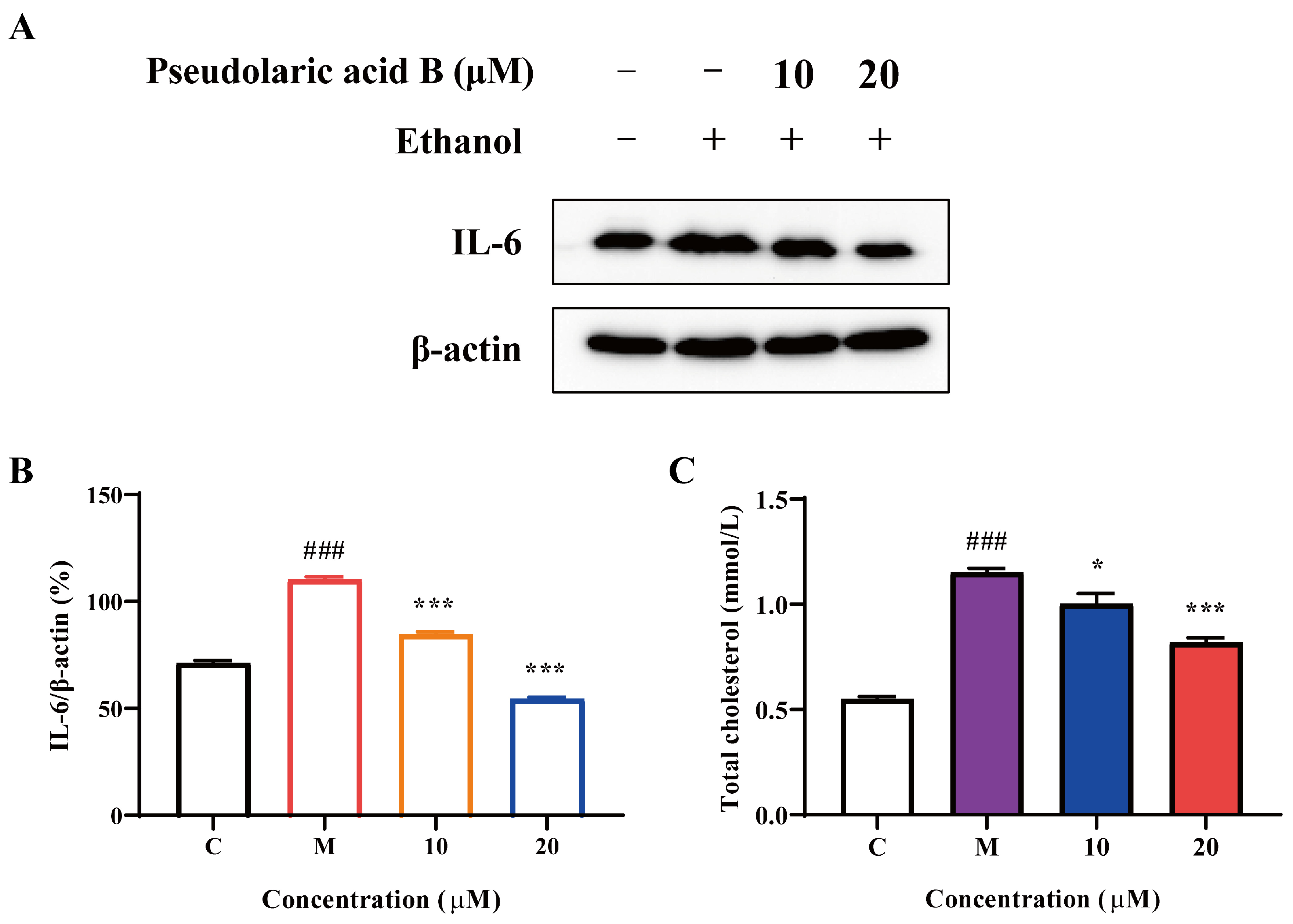
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Detection of Total Cholesterol
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
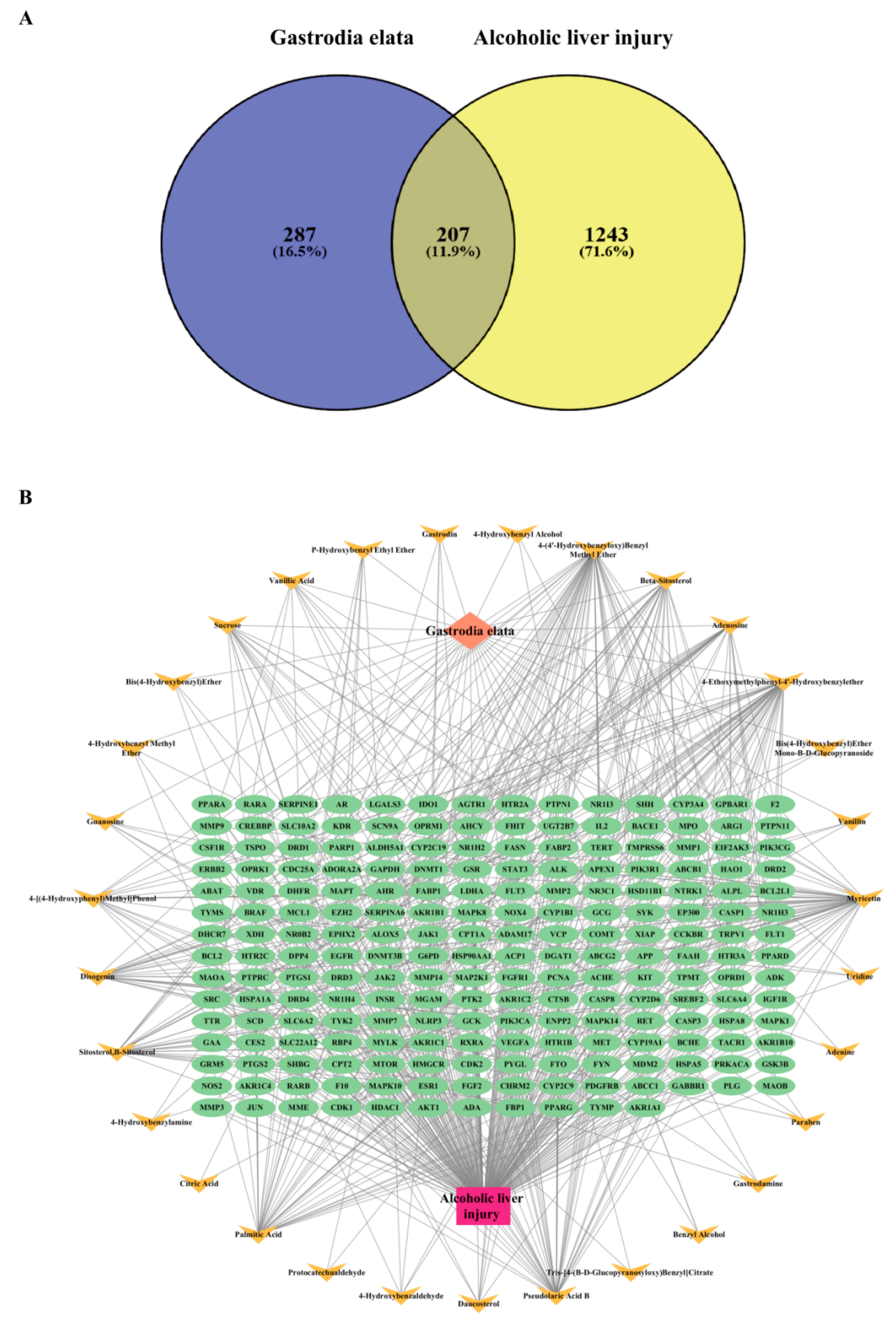
3.1. Construction of Intersection Target Network Between GE and Alcoholic Liver Injury
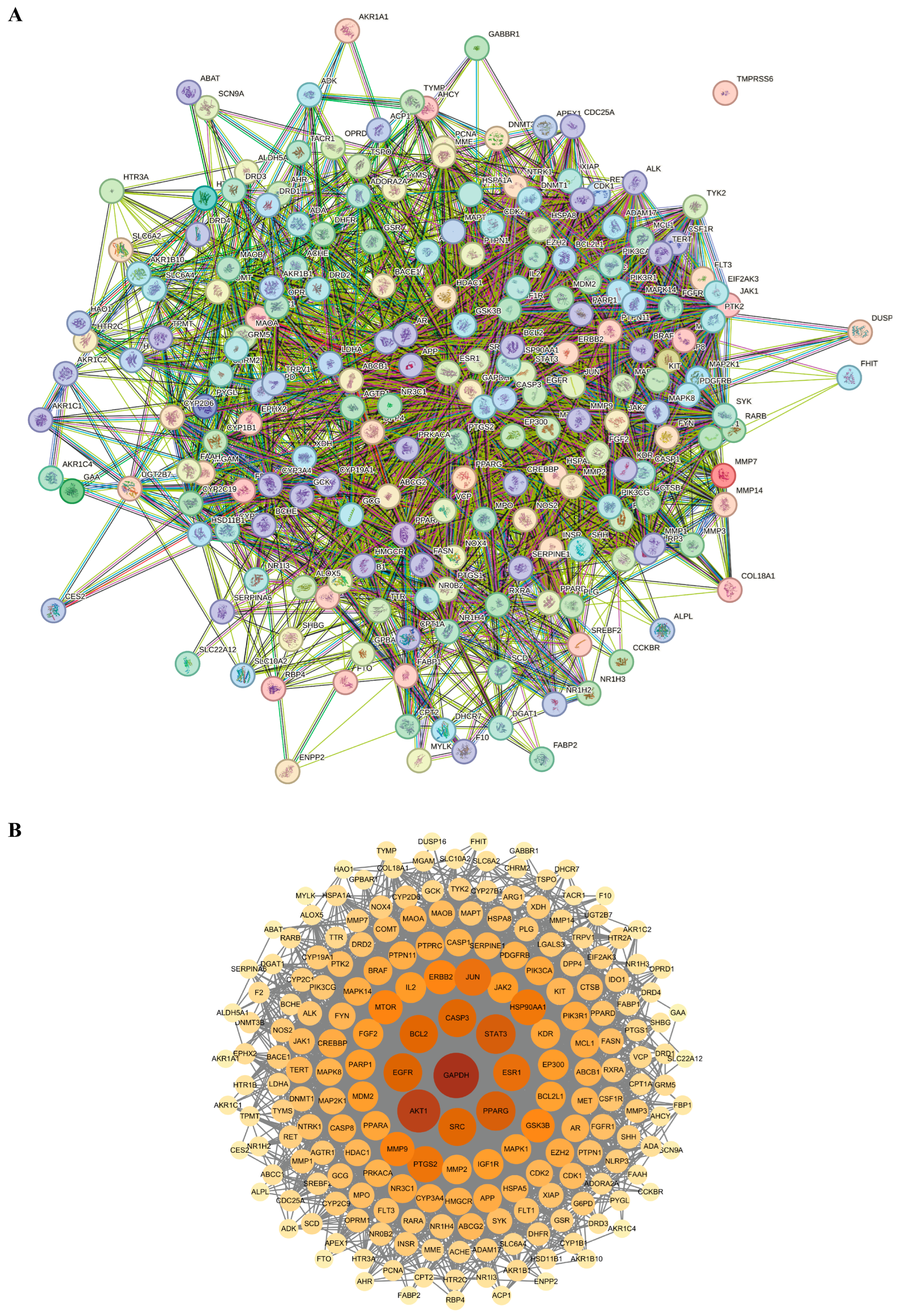
3.2. Analysis of PPI Network of Targets Between Gastrodia elata and Alcoholic Liver Injury
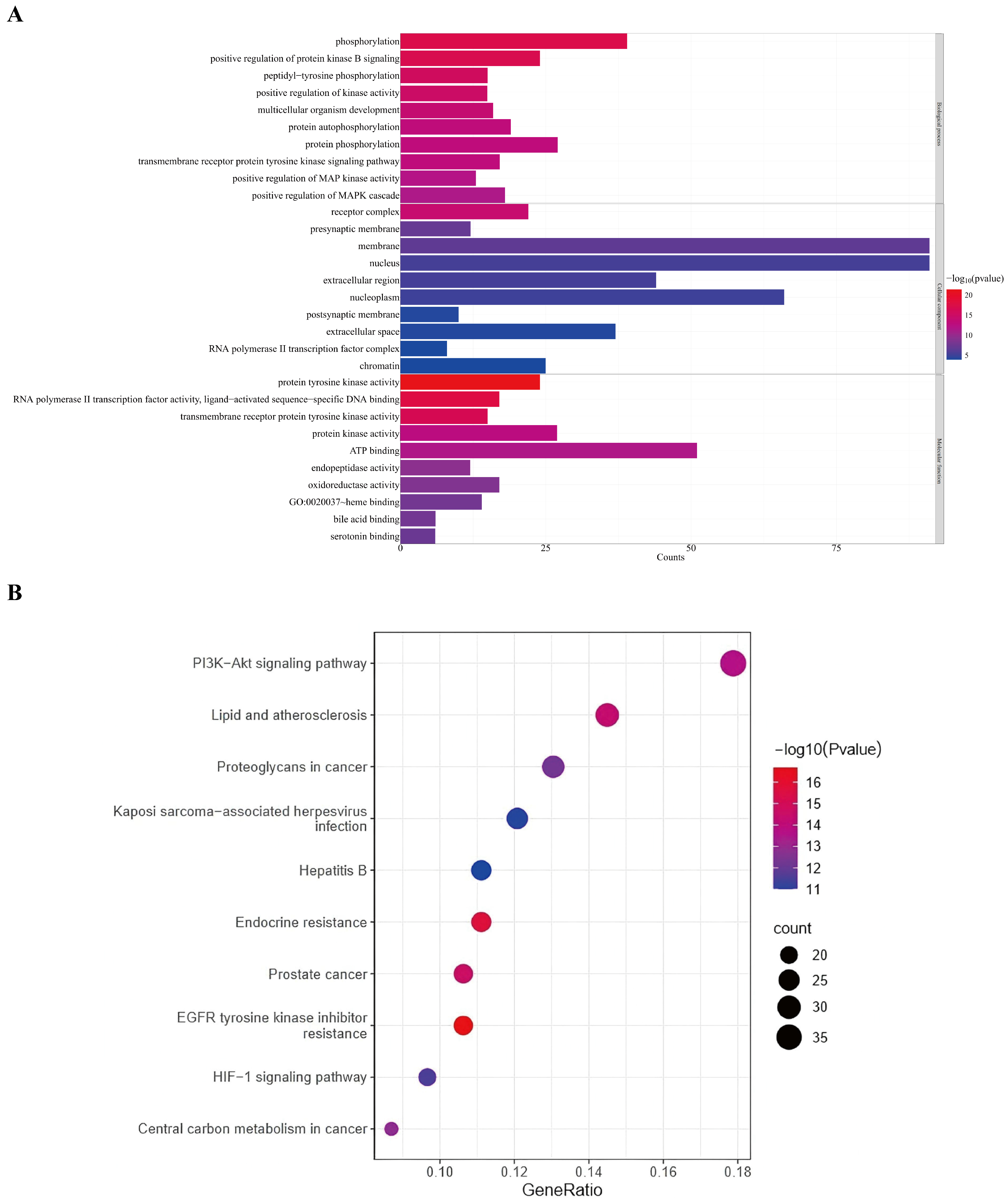
3.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Potential Targets of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury
3.4. Molecular Docking of the Main Bioactive Components Derived from Gastrodia elata to Key Targets
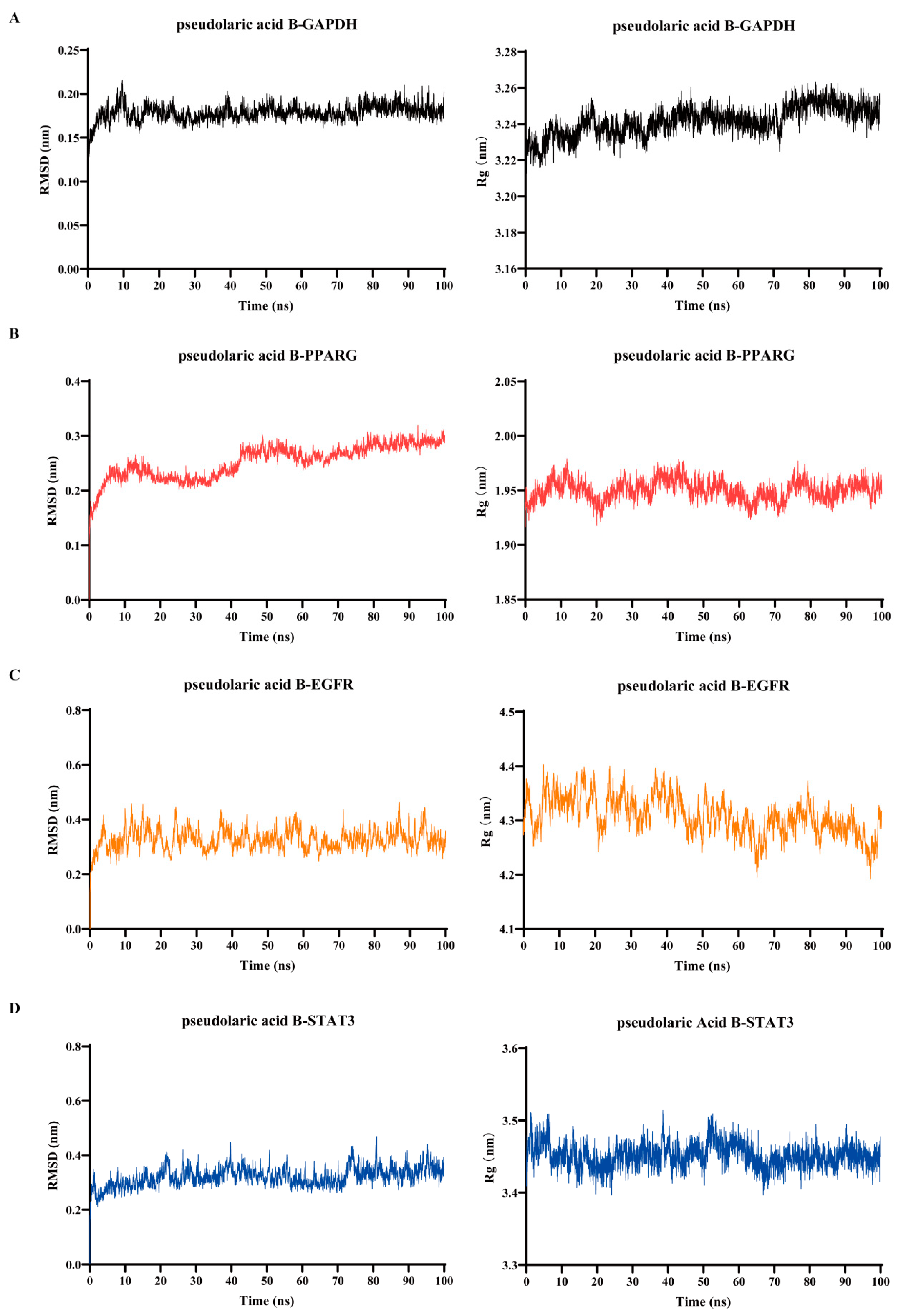
3.5. Verification of Binding of Pseudolaric Acid B to the Key Target Proteins by Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.6. The Effect of Pseudolaric Acid B in Ameliorating Alcoholic Liver Injury via the Regulation of Key Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GE | Gastrodia elata |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ALD | Alcoholic liver disease |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| MTT | Methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| RMSD | Root-mean-square deviation |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
References
- Lai, Y.; Tan, Q.; Xv, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, T.; Mo, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Alleviates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Steatosis, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 616409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Xiao, P.; Xu, H.Q.; Niu, J.Q.; Gao, Y.H. Growing burden of alcoholic liver disease in China: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.M.; Huang, H.; Ding, W.X. Autophagy in alcohol-induced multiorgan injury: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 498491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukić, M.; Radonjić, T.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Todorović, Z.; Kraišnik, N.; Aranđelović, B.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Nikolić, N.; et al. Alcohol, Inflammation, and Microbiota in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Shah, V.H. Current trials and novel therapeutic targets for alcoholic hepatitis. J. Hepatol 2019, 70, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Sheng, J.; Sun, P. The Potential Mechanism of Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus Against Hyperuricemia: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and In Vitro Experiments. Nutrients 2024, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildziukevich, U.; Özdemir, Z.; Wimmer, Z. Recent Achievements in Medicinal and Supramolecular Chemistry of Betulinic Acid and Its Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Yue, Y.; Kan, J.; Wang, Z.; Awad, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Du, M. Biocontrol of Fusarium oxysporum-infested Gastrodia elata Bl. by Lactobacillus curvatus 2768-VOCs and mechanism of inhibition. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, O.; Wang, B.; Ma, K.; Deng, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Lipid Modulating Anti-oxidant Stress Activity of Gastrodin on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Larval Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.L.; Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.X.; Jiang, J.D.; Kong, W.J. Gastrodin Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory Response in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through the AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Lu, X.; Tao, F.; Tukhvatshin, M.; Xiang, F.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y. The Potential Mechanisms of Catechins in Tea for Anti-Hypertension: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Foods 2024, 13, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challapa-Mamani, M.R.; Tomás-Alvarado, E.; Espinoza-Baigorria, A.; León-Figueroa, D.A.; Sah, R.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Barboza, J.J. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Related to Leishmania donovani: An Update and Literature Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xian, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Sheng, J.; Sun, P. α-Mangostin Exhibits Antitumor Activity Against NCI-H1975 Cells via the EGFR/STAT3 Pathway: An Experimental and Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, P.W.; Rose, A.S.; Tiemann, J.K.S. Bringing Molecular Dynamics Simulation Data into View. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Wei, B.; Liu, H.S. The Protective Effect of Panax notoginseng Mixture on Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice via Regulating NR3C2, SRC, and GAPDH. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, D.; Huang, Y.; Sheng, J.; Wang, X. Gallic Acid Can Promote Low-Density Lipoprotein Uptake in HepG2 Cells via Increasing Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Accumulation. Molecules 2024, 29, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, X.; Long, F.; Tian, K.; Wu, L. Lianhua Qingwen exerts anti-liver cancer effects and synergistic efficacy with sorafenib through PI3K/AKT pathway: Integrating network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation. Gene 2024, 912, 148383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Wen, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S.S.; Yang, K.; Liu, D.; Zhao, C.B.; Sun, J. Gastrodia elata BI: A Comprehensive Review of Its Traditional Use, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pharmacokinetics. Evid-Based. Compl. Alt. 2023, 2023, 5606021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, P.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, H.R.; Heo, J.S.; Choi, J.R.; Shin, J.H. Protective effects of Gastrodia elata Blume on acetaminophen-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Rehman, M.U.; Lin, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H. HTR1D regulates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to impact hepatocellular carcinoma development and resistance to sorafenib. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Song, G.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.J.; Hong, S.; Park, J.; Um, J.Y. Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wu, C.; Cheng, G.; Li, B.; et al. Exploring the effect of Yinzhihuang granules on alcoholic liver disease based on pharmacodynamics, network pharmacology and molecular docking. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z. S-allylmercaptocysteine inhibits mucin overexpression and inflammation via MAPKs and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.M.; Chen, W.; Yao, K.T.; Sun, T.; Wang, J.H. Global, regional, and national burdens of alcohol-related cirrhosis among women from 1992 to 2021 and its predictions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanadis, C.; Antoniou, C.K.; Tsiachris, D.; Pietri, P. Coronary Atherosclerotic Vulnerable Plaque: Current Perspectives. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, S.; Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J.; Wang, J. Coccinic acid exhibits anti-tumor efficacy against NSCLC harboring EGFR L858R/T790M mutation via the EGFR/STAT3 pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 154, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Wang, L.T.; Zhang, M.; Nie, Y.; Yang, J.B.; Meng, W.L.; Wang, X.J.; Sheng, J. Caffeine can alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by augmenting LDLR expression via targeting EGFR. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J.; Sun, P. Inhibitory effect of 1,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-7,8-diprenylxanthone against NSCLC with L858R/T790M/C797S mutant EGFR. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Gordillo, K.; Shah, R.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ibrahim, J.; Tuma, P.L. Akt1 and Akt2 Isoforms Play Distinct Roles in Regulating the Development of Inflammation and Fibrosis Associated with Alcoholic Liver Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, N.; Wang, L.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Park, O.; Jeong, W.I.; Lafdil, F.; Osei-Hyiaman, D.; Moh, A.; Fu, X.Y.; Pacher, P.; et al. Cell type-dependent pro- and anti-inflammatory role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in alcoholic liver injury. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus, G. Impact of Autoantibodies against Glycolytic Enzymes on Pathogenicity of Autoimmune Retinopathy and Other Autoimmune Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Xie, H.B.; Huang, M.; Jiang, W.; Ding, B.W.; Zhu, Q.X. TNF-α/TNFR1 regulates the polarization of Kupffer cells to mediate trichloroethylene-induced liver injury. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2022, 230, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No. | Ingredient ID | Component Name | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TCMC4620 | 4-(4′-Hydroxybenzyloxy)benzyl methyl ether | C13H12O2 |
| 2 | TCMC4547 | 4-Ethoxymethylphenyl-4′-hydroxybenzylether | C16H18O3 |
| 3 | TCMC478 | 4-[(4-Hydroxyphenyl)methyl]phenol | C19H20O2 |
| 4 | TCMC495 | 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | C8H6O3 |
| 5 | TCMC2829 | 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol | C7H8O2 |
| 6 | TCMC3279 | 4-Hydroxybenzyl methyl ether | C8H10O2 |
| 7 | TCMC497 | 4-Hydroxybenzylamine | C7H9NO |
| 8 | TCMC631 | Adenine | C5H5N5 |
| 9 | TCMC632 | Adenosine | C10H13N5O4 |
| 10 | TCMC774 | Benzyl alcohol | C7H8O |
| 11 | TCMC801 | Beta-sitosterol | C29H50O |
| 12 | TCMC2223 | Vanillin | C8H8O3 |
| 13 | TCMC4448 | Bis(4-hydroxybenzyl)ether | C14H14O3 |
| 14 | TCMC923 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 |
| 15 | TCMC995 | Daucosterol | C35H60O6 |
| 16 | TCMC1072 | Disogenin | C27H42O4 |
| 17 | TCMC4578 | Gastrodamine | C14H15NO3 |
| 18 | TCMC3409 | Gastrodin | C13H18O7 |
| 19 | TCMC1298 | Guanosine | C10H13N5O5 |
| 20 | TCMC1609 | Myricetin | C15H10O8 |
| 21 | TCMC1830 | Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 |
| 22 | TCMC1839 | Paraben | C7H6O3 |
| 23 | TCMC3338 | P-Hydroxybenzyl ethyl ether | C9H12O2 |
| 24 | TCMC1955 | Protocatechualdehyde | C7H6O3 |
| 25 | TCMC2821 | Pseudolaric acid B | C23H28O8 |
| 26 | TCMC5840 | Bis(4-hydroxybenzyl)ether mono-β-D-glucopyranoside | C6H12O6 |
| 27 | TCMC2111 | Succinic acid | C4H6O2 |
| 28 | TCMC2886 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 |
| 29 | TCMC5445 | Tris-[4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)benzyl]citrate | C45H56O25 |
| 30 | TCMC2209 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 |
| 31 | TCMC2222 | Vanillic acid | C8H8O4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Ji, S.; Peng, L.; Sheng, J.; Wang, J. Integrating Strategy of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Experimental Verification to Investigate the Potential Mechanism of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury. Foods 2025, 14, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122008
Sun P, Zhang R, Li X, Yang D, Ji S, Peng L, Sheng J, Wang J. Integrating Strategy of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Experimental Verification to Investigate the Potential Mechanism of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122008
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Peiyuan, Ruohan Zhang, Xuanyou Li, Dengwang Yang, Shunfeng Ji, Lei Peng, Jun Sheng, and Jing Wang. 2025. "Integrating Strategy of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Experimental Verification to Investigate the Potential Mechanism of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury" Foods 14, no. 12: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122008
APA StyleSun, P., Zhang, R., Li, X., Yang, D., Ji, S., Peng, L., Sheng, J., & Wang, J. (2025). Integrating Strategy of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Experimental Verification to Investigate the Potential Mechanism of Gastrodia elata Against Alcoholic Liver Injury. Foods, 14(12), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122008






