Effective Identification of Variety and Origin of Chenpi Using Hyperspectral Imaging Assisted with Chemometric Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition
2.3. Spectral Preprocessing Methods
2.4. Effective Wavelength Screening Algorithms
2.5. Conventional Machine Learning Model
2.6. Deep Learning Model
2.7. Data Analysis and Model Evaluation
3. Results
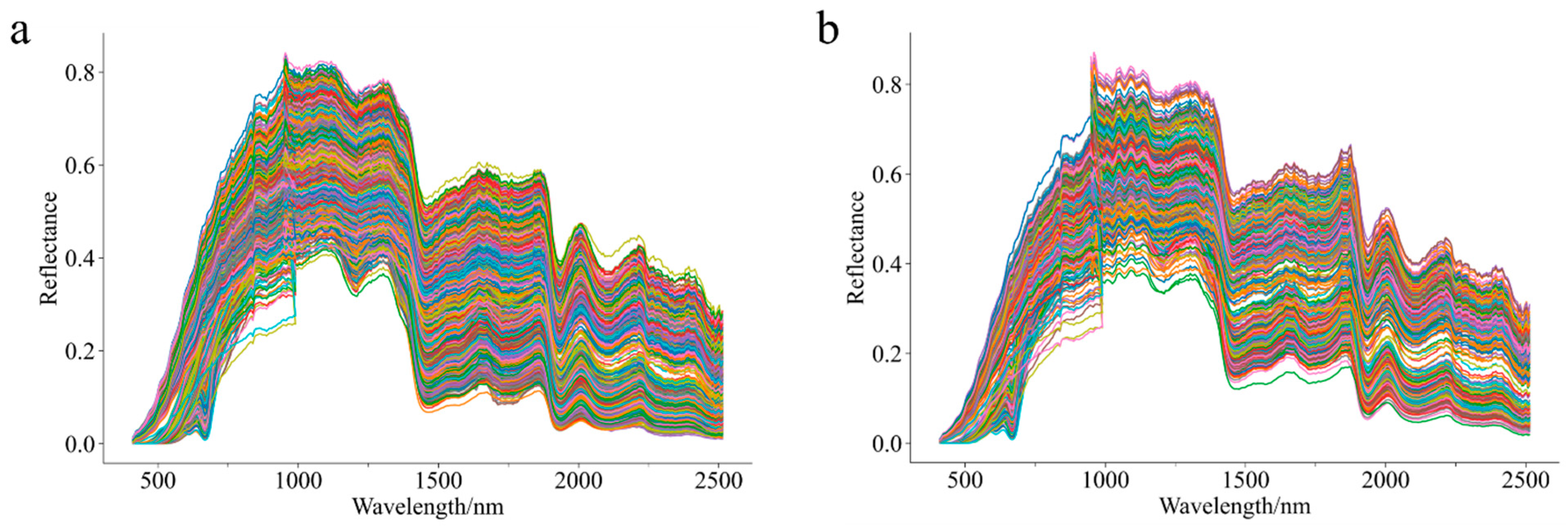
3.1. Raw Spectra of Chenpi Samples from Different Varieties and Origins
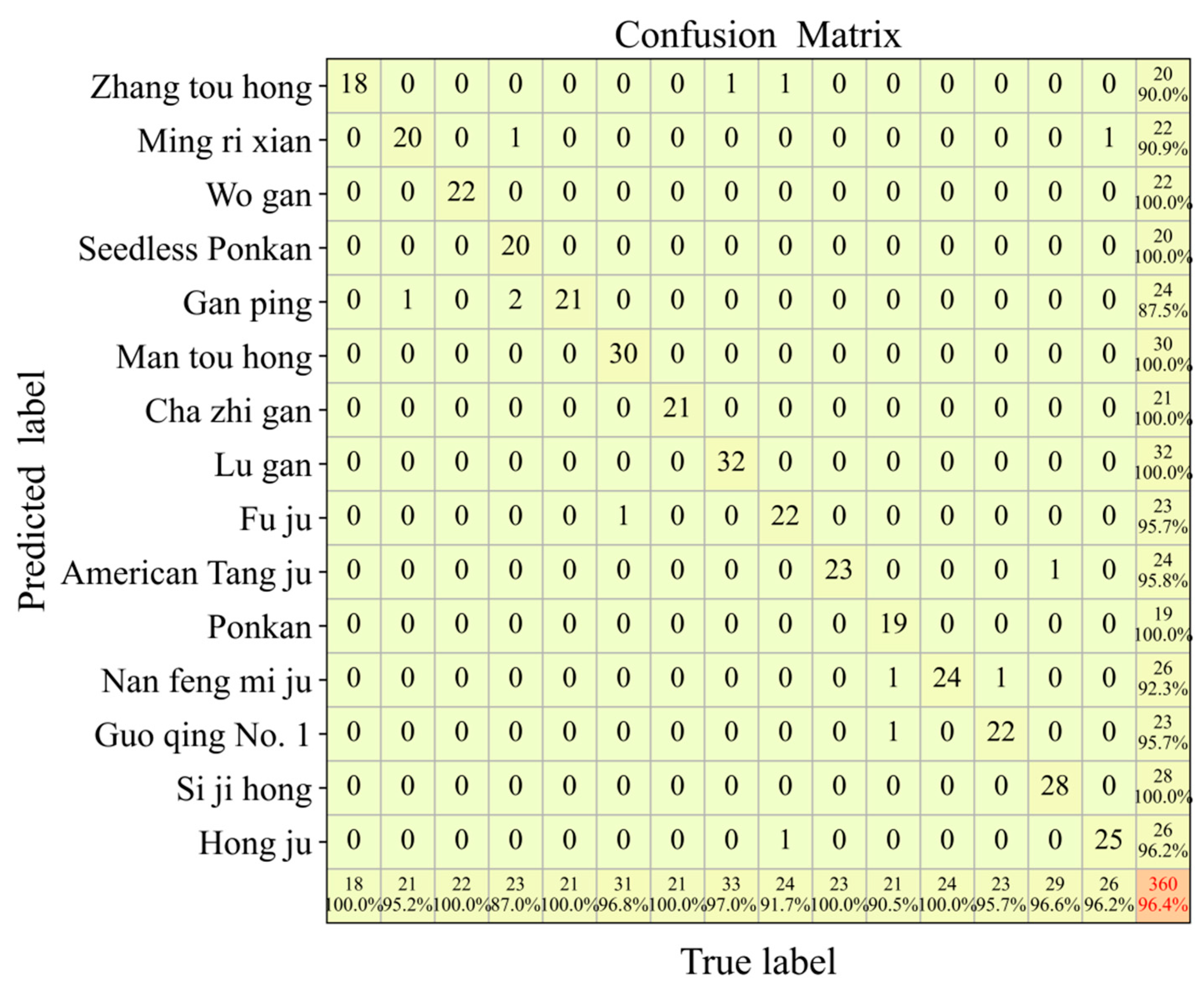
3.2. Discriminant Analysis of Different Chenpi Varieties
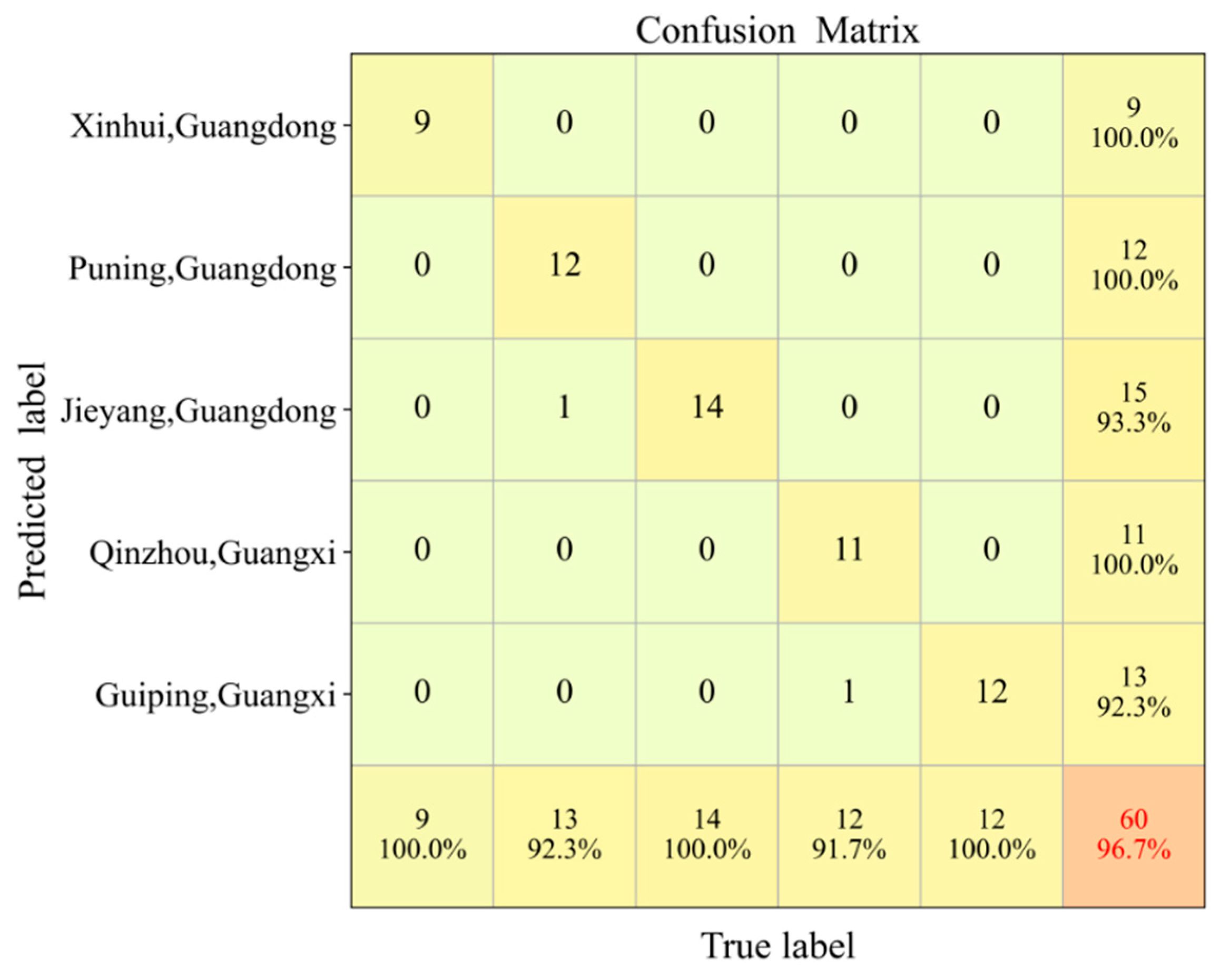
3.3. Discriminant Analysis of Different Chenpi Origins
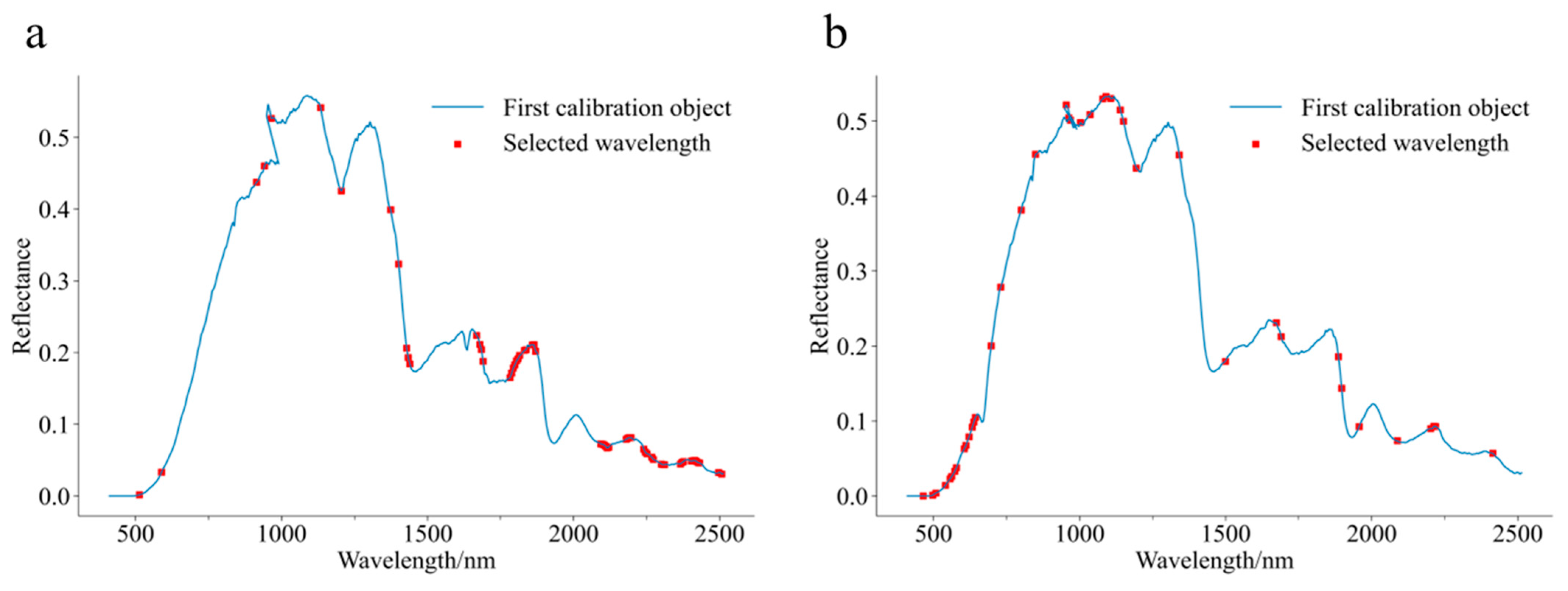
3.4. Extraction of Spectral Feature Wavelength
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsouna, A.B.; Sadaka, C.; Mekinić, I.G.; Garzoli, S.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Morais, S.; Moreira, M.; Ferreira, E.; Spigno, G.; et al. The Chemical Variability, Nutraceutical Value, and Food-Industry and Cosmetic Applications of Citrus Plants: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Mahato, N.; Cho, M.; Lee, Y. Converting Citrus Wastes into Value-Added Products: Economic and Environmently Friendly Approaches. Nutrition 2017, 34, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, D.; Saini, A.; Panesar, P.; Chopra, H. Unraveling the Scientific Perspectives of Citrus By-Products Utilization: Progress towards Circular Economy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anticona, M.; Blesa, J.; Frígola, A.; Esteve, M. High Biological Value Compounds Extraction from Citrus Waste with Non-Conventional Methods. Foods 2020, 9, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shi, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Pan, S. Integrated Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology to Reveal Antioxidant Mechanisms and Potential Pharmacological Ingredients of Citrus Herbs. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.J.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, J.; Qi, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Xie, T.Z.; Tang, Q.; et al. Comparative Investigation of Phytochemicals among Ten Citrus Herbs by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Electrospray Ionization Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Properties. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 1st ed.; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Qiu, X.; Gong, L.; Huang, J.; Bai, J.; Huang, Z.; Xu, W. Chemical and Genetic Discrimination of Commercial Guangchenpi (Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’) by Using UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Based Metabolomics and DNA Barcoding Approaches. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23373–23381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamy, D.; Huang, Y.; Akpabli-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Battino, M.; Chen, X. Valorization of Citrus reticulata Peels for Flavonoids and Antioxidant Enhancement by Solid-State Fermentation Using Aspergillus Niger CGMCC 3.6189. Molecules 2022, 27, 8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, G.; Lü, S. Citri reticulatae Pericarpium (Chenpi): Botany, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of a Frequently Used Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ai, Z.; Li, M.; Lei, D.; Mowafy, S.; Liu, Y. Comparative Analysis of Citri reticulatae Pericarpium: Revealing the Nonvolatile Compounds Transformation and Optimizing Drying Processes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Peng, W.; Wu, Z.; Su, W. Study on the Discrimination between Citri reticulatae Pericarpium Varieties Based on HS-SPME-GC-MS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analyses. Molecules 2018, 23, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Flavonoid Metabolites in Citrus Peels (Citrus reticulata “Dahongpao”) Using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Pan, H.; Jin, D.; Wen, J.; Jin, C.; Sahu, S.K.; Su, J.; Luo, X.; et al. An Integrated Multi-Omics Approach Reveals Polymethoxylated Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Citrus reticulata Cv. Chachiensis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gong, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Li, M. Assessment of Components of Gingko biloba Leaves Collected from Different Regions of China That Contribute to Its Antioxidant Effects for Improved Quality Monitoring. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41 (Suppl. 2), fst.33620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, L.; Song, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Comparative Metabolomics Provides Novel Insights into Correlation Between Dominant Habitat Factors and Constituents of Stellaria Radix (Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1035712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Liao, Y.; Peng, M.; Fu, F.; Li, G.; Su, D.; Guo, J.; Shan, Y. Microbes: Drivers of Chenpi Manufacturing, Biotransformation, and Physiological Effects. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Guo, L.; Dou, L.L.; Zhou, C.L.; Xu, F.G.; Zheng, G.D.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Discrimination of Citrus reticulata Blanco and Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’ by Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics Approach. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Qi, J. Change in Nutrients of Citri reticulatae ‘Chachi’ in Relation to Browning during Aging. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Lin, T.; Ren, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bi, F.; Gu, L.; Hou, H.; He, J. Rapid Discrimination of Citrus reticulata ‘Chachi’ by Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry Fingerprints Combined with Principal Component Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, J. Flavor Characterization of Citri reticulatae Pericarpium (Citrus reticulata ‘Chachiensis’) with Different Aging Years via Sensory and Metabolomic Approaches. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, H. The Study on Food Sensory Evaluation Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. AJFST 2015, 8, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Fu, F.; Guo, J.; Shan, Y. Effects of Different Treatment Methods of Dried Citrus Peel (Chenpi) on Intestinal Microflora and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Healthy Mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.J.; Li, X.K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, B.Q. Accurate and Visualiable Discrimination of Chenpi Age Using 2D-CNN and Grad-CAM++ Based on Infrared Spectral Images. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Chen, T.; Dong, H.; Zhu, L.; Ju, W. Si-Ni-San Prevents Reserpine-Induced Depression by Inhibiting Inflammation and Regulating CYP450 Enzymatic Activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jităreanu, A.; Trifan, A.; Vieriu, M.; Caba, I.C.; Mârțu, I.; Agoroaei, L. Current Trends in Toxicity Assessment of Herbal Medicines: A Narrative Review. Processes 2022, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; An, D. Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology Combined with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network to Predict Oil Content of Single Maize Kernel. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wu, B.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, C. Application of Visible/Infrared Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning Techniques for Identifying Food Varieties and Geographical Origins. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 680357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Li, W.; Du, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Predicting Micronutrients of Wheat Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Bi, S.; Xu, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Hybrid Lightweight Deep-Learning Model for Sensor-Fusion Basketball Shooting-Posture Recognition. Measurement 2022, 189, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Niu, G.; Yan, B.; Chen, C.; Huang, M.; Ying, G. Application of Novel Hybrid Deep Leaning Model for Cleaner Production in a Paper Industrial Wastewater Treatment System. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Q.; Deng, S.; Li, Z.; Yan, Y.; Ying, Z. Coix seed Improves Growth Performance and Productivity in Post-Weaning Pigs by Reducing Gut pH and Modulating Gut Microbiota. AMB Express 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Gouda, M.; Wei, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Hyperspectral Imaging with Shallow Convolutional Neural Networks (SCNN) Predicts the Early Herbicide Stress in Wheat Cultivars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, P.; Nakisa, B.; Rastgoo, M.N.; Jain, R.; Gao, W. Driver Stress Detection via Multimodal Fusion Using Attention-Based CNN-LSTM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 173, 114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yipeng, L.; Wenbing, L.; Kaixuan, H.; Wentao, T.; Ling, Z.; Shizhuang, W.; Linsheng, H. Determination of Wheat Kernels Damaged by Fusarium Head Blight Using Monochromatic Images of Effective Wavelengths from Hyperspectral Imaging Coupled with an Architecture Self-Search Deep Network. Food Control 2022, 135, 108819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Zhao, J.; Bodner, G.; Ali, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Rewald, B. Early Decay Detection in Fruit by Hyperspectral Imaging–Principles and Application Potential. Food Control 2023, 152, 109830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Huang, Z.; He, M.; Li, C.; Qi, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, C. Identification of Geographical Origins of Radix Paeoniae Alba Using Hyperspectral Imaging with Deep Learning-Based Fusion Approaches. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yan, B.; Xiong, F.; Bai, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Yang, J. Tanshinone Content Prediction and Geographical Origin Classification of Salvia miltiorrhiza by Combining Hyperspectral Imaging with Chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, S. Variety Identification of Sweet Maize Seeds Based on Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Deep Learning. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 130, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; He, M.; Li, C.; Qi, H.; Bai, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C. Identification of Chrysanthemum Using Hyperspectral Imaging Based on Few-Shot Class Incremental Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 215, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Huang, Z.; Jin, B.; Tang, Q.; Jia, L.; Zhao, G.; Cao, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C. SAM-GAN: An Improved DCGAN for Rice Seed Viability Determination Using near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 108473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, L. Nondestructive Prediction and Visualization of Total Flavonoids Content in Cerasus Humilis Fruit during Storage Periods Based on Hyperspectral Imaging Technique. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, S.; Fu, H.; He, S.; Yang, B.; Nan, T.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L. Prediction of Chemical Indicators for Quality of Zanthoxylum Spices from Multi-Regions Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Chemometrics. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 1036892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Peng, F.; Liu, J.; Han, G. Non-Destructive Prediction and Visualization of Anthocyanin Content in Mulberry Fruits Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1137198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Hu, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, P.; Luo, H.; Huang, D. Rapid and Nondestructive Detection of Sorghum Adulteration Using Optimization Algorithms and Hyperspectral Imaging. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
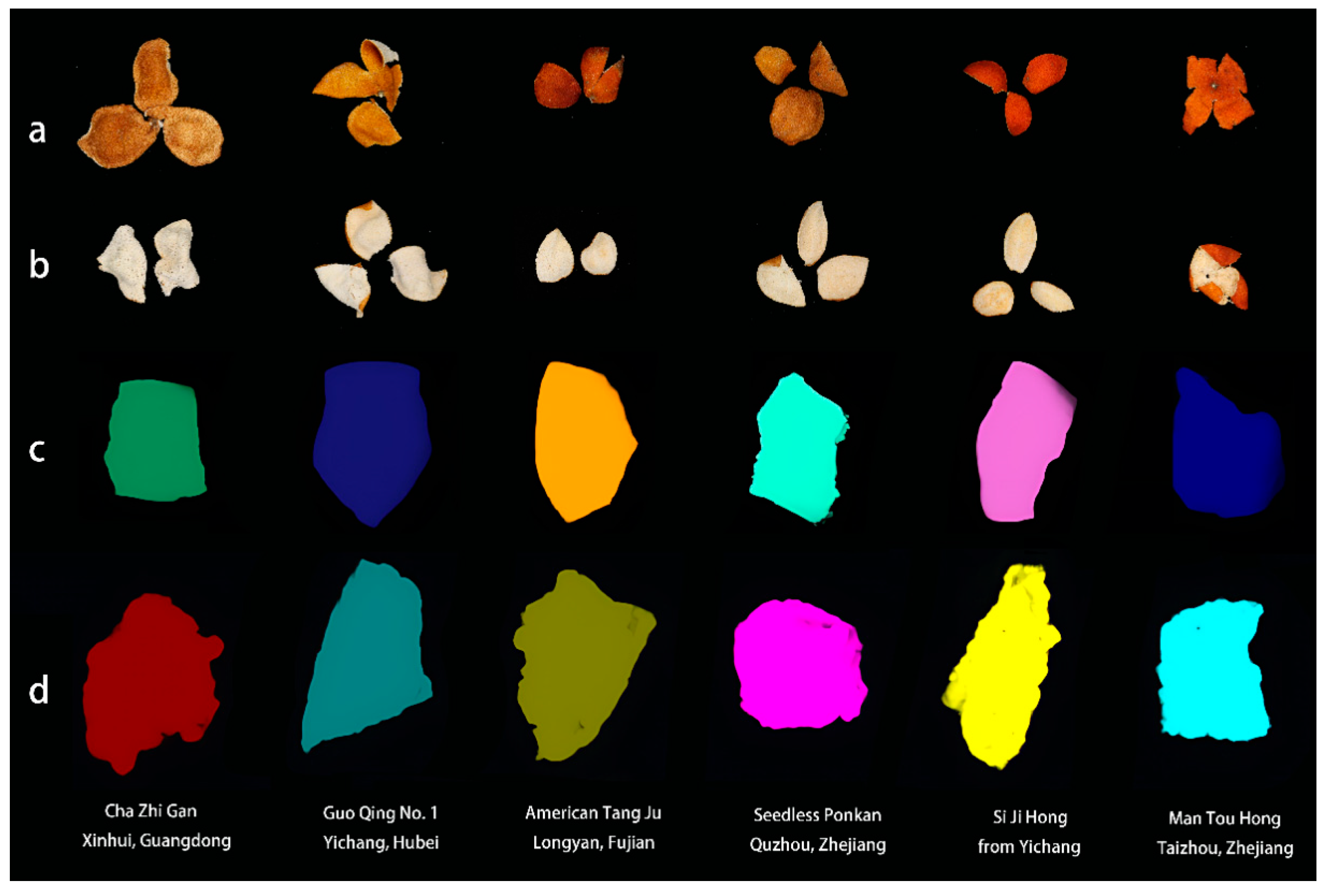
| No. | Chenpi Variety | Geographical Origin |
|---|---|---|
| C-1 | Zhang tou hong | Xingan, Jiangxi |
| C-2 | Ming ri xian | Quzhou, Zhejiang |
| C-3 | Wo gan | Quzhou, Zhejiang |
| C-4 | Seedless Ponkan | Quzhou, Zhejiang |
| C-5 | Gan ping | Quzhou, Zhejiang |
| C-6 | Man tou hong | Taizhou, Zhejiang |
| C-7, C-8, C-9 | Cha zhi gan | Xinhui, Puning and Jieyang, Guangdong |
| C-10, C-11 | Cha zhi gan | Qinzhou and Guiping, Guangxi |
| C-12 | Lu gan | Fuzhou, Fujian |
| C-13 | Fu ju | Fuzhou, Fujian |
| C-14 | American Tang ju | Longyan, Fujian |
| C-15 | Ponkan | Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Hunan |
| C-16 | Nan feng mi ju | Yichang, Hubei |
| C-17 | Guo qing No. 1 | Yichang, Hubei |
| C-18 | Si ji hong | Yichang, Hubei |
| C-19 | Hong ju | Wanzhou, Chongqing |
| Models | Pretreatments | Z | F | ZF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | ||
| PLS-DA | RAW | 86.81 | 85.38 | 79.44 | 90.14 | 89.12 | 90.56 | 86.25 | 86.19 | 85.28 |
| MSC | 90.56 | 86.79 | 85.56 | 91.11 | 91.01 | 91.67 | 87.64 | 84.44 | 84.17 | |
| D1 | 93.33 | 88.23 | 87.78 | 92.36 | 89.24 | 90.56 | 92.57 | 90.28 | 90.28 | |
| D2 | 96.67 | 91.24 | 90.00 | 87.78 | 84.67 | 83.89 | 89.38 | 83.33 | 83.89 | |
| SG | 87.22 | 84.17 | 80.56 | 91.25 | 90.14 | 91.67 | 86.04 | 84.34 | 85.28 | |
| SNV | 90.42 | 86.42 | 85.56 | 90.14 | 90.00 | 87.78 | 88.12 | 85.56 | 85.28 | |
| SVM | RAW | 93.19 | 87.33 | 84.44 | 86.39 | 83.06 | 76.67 | 83.75 | 81.24 | 80.00 |
| MSC | 91.67 | 84.37 | 85.00 | 84.44 | 82.24 | 81.11 | 83.13 | 82.56 | 78.89 | |
| D1 | 96.81 | 90.28 | 88.33 | 98.19 | 93.36 | 92.22 | 97.57 | 93.79 | 94.44 | |
| D2 | 97.64 | 88.67 | 87.22 | 99.44 | 86.34 | 85.56 | 99.03 | 93.04 | 92.22 | |
| SG | 90.83 | 85.00 | 83.33 | 81.81 | 74.56 | 73.33 | 79.58 | 78.56 | 74.44 | |
| SNV | 99.58 | 95.84 | 90.56 | 99.86 | 95.66 | 94.44 | 98.82 | 91.39 | 92.78 | |
| MLP | RAW | 90.00 | 85.76 | 82.78 | 70.96 | 70.12 | 70.56 | 76.60 | 75.67 | 71.94 |
| MSC | 86.11 | 80.12 | 80.56 | 65.28 | 64.36 | 62.78 | 73.82 | 72.22 | 70.28 | |
| D1 | 100.0 | 93.24 | 92.78 | 99.72 | 94.12 | 93.33 | 98.68 | 94.12 | 94.72 | |
| D2 | 97.92 | 93.45 | 92.22 | 81.67 | 80.33 | 77.22 | 84.72 | 83.33 | 81.39 | |
| SG | 81.81 | 75.67 | 73.33 | 65.14 | 63.44 | 62.22 | 61.46 | 60.39 | 54.44 | |
| SNV | 94.31 | 87.42 | 85.00 | 94.44 | 89.33 | 86.11 | 84.31 | 82.12 | 83.06 | |
| CNN | RAW | 99.70 | 85.56 | 83.33 | 98.08 | 90.23 | 88.33 | 99.18 | 98.67 | 96.39 |
| Models | Pretreatments | Z | F | ZF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) | ||
| PLS-DA | RAW | 90.83 | 85.42 | 86.67 | 96.67 | 92.42 | 83.33 | 85.83 | 81.42 | 83.33 |
| MSC | 96.25 | 95.00 | 88.33 | 93.75 | 91.67 | 93.33 | 87.29 | 85.83 | 82.50 | |
| D1 | 98.97 | 98.33 | 93.33 | 95.00 | 93.67 | 91.67 | 96.25 | 91.67 | 90.83 | |
| D2 | 98.75 | 95.75 | 96.67 | 88.33 | 82.50 | 85.00 | 96.04 | 92.42 | 90.83 | |
| SG | 88.33 | 87.29 | 83.33 | 90.42 | 89.33 | 85.00 | 85.42 | 82.50 | 85.00 | |
| SNV | 95.83 | 92.83 | 90.00 | 97.08 | 87.42 | 85.00 | 85.42 | 81.63 | 83.33 | |
| SVM | RAW | 84.17 | 83.67 | 83.33 | 85.83 | 83.33 | 76.67 | 81.04 | 79.58 | 79.17 |
| MSC | 85.00 | 80.00 | 78.33 | 82.92 | 81.67 | 78.33 | 81.87 | 75.00 | 77.50 | |
| D1 | 92.08 | 86.67 | 85.00 | 96.67 | 89.02 | 85.00 | 93.54 | 90.21 | 86.67 | |
| D2 | 92.08 | 88.33 | 91.67 | 95.00 | 84.58 | 87.29 | 93.13 | 84.79 | 85.00 | |
| SG | 82.50 | 80.33 | 78.33 | 82.92 | 76.67 | 75.00 | 76.46 | 74.38 | 75.00 | |
| SNV | 98.75 | 93.75 | 91.67 | 99.17 | 95.42 | 95.00 | 97.92 | 95.63 | 94.17 | |
| MLP | RAW | 78.33 | 75.00 | 76.67 | 73.75 | 72.33 | 70.00 | 92.08 | 90.33 | 85.83 |
| MSC | 78.75 | 73.33 | 70.00 | 90.83 | 90.00 | 80.00 | 95.83 | 90.79 | 87.50 | |
| D1 | 95.00 | 92.75 | 95.00 | 93.33 | 85.83 | 80.00 | 99.38 | 95.75 | 91.67 | |
| D2 | 98.75 | 91.67 | 93.33 | 88.33 | 87.67 | 83.33 | 98.75 | 90.17 | 91.67 | |
| SG | 80.83 | 72.67 | 70.00 | 73.33 | 72.42 | 71.67 | 98.75 | 86.67 | 84.17 | |
| SNV | 81.67 | 78.75 | 76.67 | 92.08 | 85.33 | 78.33 | 95.83 | 82.50 | 83.33 | |
| CNN | RAW | 83.33 | 78.33 | 80.00 | 77.50 | 76.67 | 75.00 | 89.00 | 87.90 | 85.83 |
| Models | Methods | Number | Training Set (%) | Validation Set (%) | Prediction Set (%) |
| ZF-CNN | SPA | 38 | 77.19 | 74.44 | 73.06 |
| CARS | 57 | 88.67 | 86.78 | 85.00 | |
| Z-D2-PLSDA | SPA | 20 | 76.67 | 72.34 | 71.67 |
| CARS | 41 | 92.92 | 92.67 | 91.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, H.; Zhong, X.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, J. Effective Identification of Variety and Origin of Chenpi Using Hyperspectral Imaging Assisted with Chemometric Models. Foods 2025, 14, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111979
Liu H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Hu H, Zhong X, Yuan Q, Yang J. Effective Identification of Variety and Origin of Chenpi Using Hyperspectral Imaging Assisted with Chemometric Models. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111979
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hangxiu, Youyou Wang, Yiheng Wang, Jingyi Wang, Hanqing Hu, Xinyi Zhong, Qingjun Yuan, and Jian Yang. 2025. "Effective Identification of Variety and Origin of Chenpi Using Hyperspectral Imaging Assisted with Chemometric Models" Foods 14, no. 11: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111979
APA StyleLiu, H., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Hu, H., Zhong, X., Yuan, Q., & Yang, J. (2025). Effective Identification of Variety and Origin of Chenpi Using Hyperspectral Imaging Assisted with Chemometric Models. Foods, 14(11), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111979






