Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Bacteria Culture Growth
2.2. Screening of Target Gene
2.3. Genomic DNA (gDNA)
2.4. Primer Pair and Hydrolysis Probe Designing
2.5. PCR and qPCR Condition Setup
2.5.1. PCR Base
2.5.2. TaqMan Probe Base
2.6. Primer Pair and Hydrolysis Probe Specificity
2.7. Broth Sample Detection Limit Evaluation
2.8. Artificial Contamination and Natural Milk Sample Experiments
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Screening of Target Gene
3.2. Primer Pair Design and Verification
3.3. qPCR Primer Verification
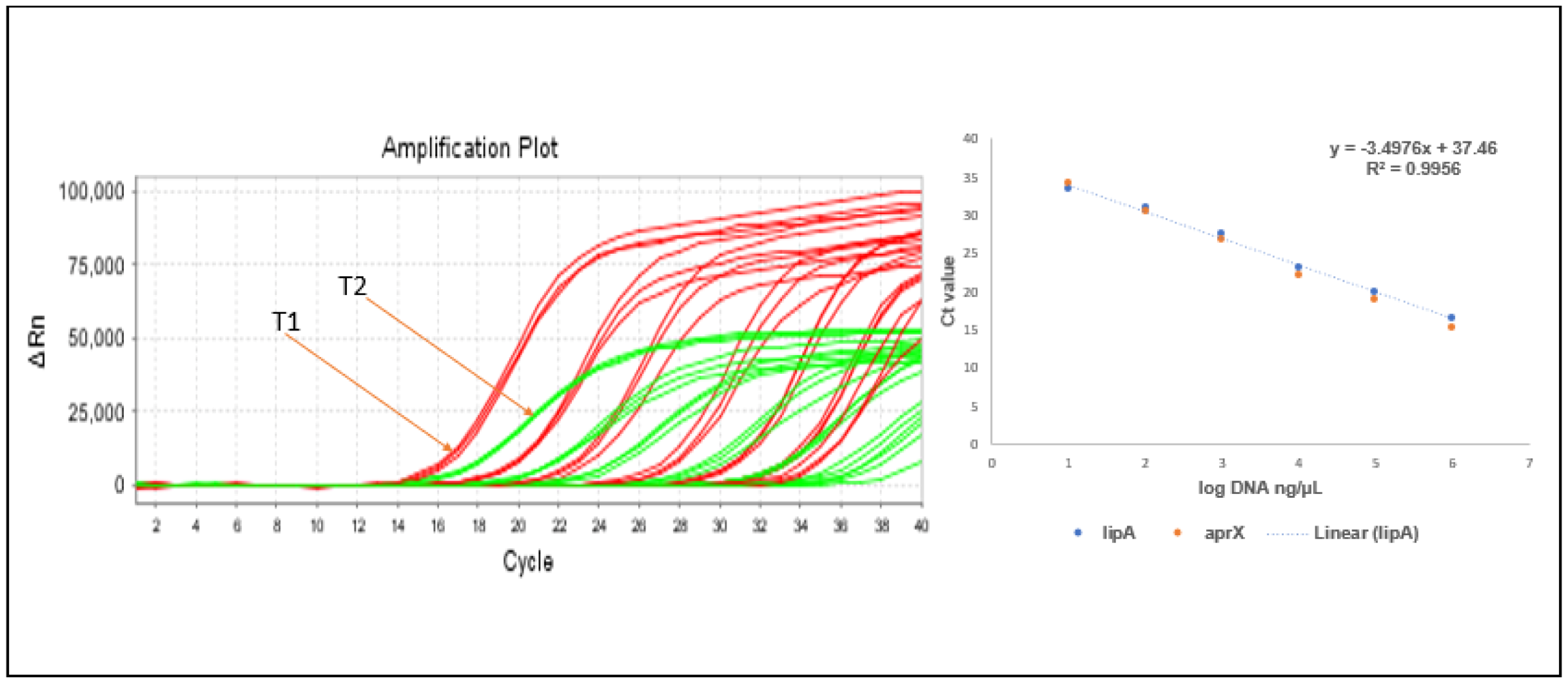
3.4. Taqman Probe-Based Quantification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrimonti, C.; Bottari, B.; Sardaro, M.L.S.; Marmiroli, N. Application of Real-Time PCR (QPCR) for Characterization of Microbial Populations and Type of Milk in Dairy Food Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, N.; Martín, M.C.; Herrero, A.; Fernández, M.; Alvarez, M.A.; Ladero, V. QPCR as a Powerful Tool for Microbial Food Spoilage Quantification: Significance for Food Quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, K.K.; Fayaz, U.; Dar, A.H.; Shams, R.; Manzoor, S.; Sundarsingh, A.; Deka, P.; Khan, S.A. A Comprehensive Review on Heat Treatments and Related Impact on the Quality and Microbial Safety of Milk and Milk-Based Products. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, M.; Bansal, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta, R.K. Molecular Detection of Foodborne Pathogens: A Rapid and Accurate Answer to Food Safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1568–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyaina, M.; Rasco, B.; Sablani, S.S. Rapid Methods of Microbial Detection in Dairy Products. Food Control. 2020, 110, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasca, M.; Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Machado, S.G.; Bagliniére, F.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Psychrotrophic Bacteria. In Microbiology in Dairy Processing: Challenges and Opportunities; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.B. Methods of Assessing the Psychrotrophic Bacterial Content of Milk. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1969, 32, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, M. Psychophilic and Psychrotrophic Microorganisms. Ann. Inst. Pasteur Lille 1965, 16, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Palmer, J.; Teh, K.H.; Flint, S. Identification and Selection of Heat-Stable Protease and Lipase-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria from Fresh and Chilled Raw Milk during up to Five Days Storage. LWT 2020, 134, 110165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C. Screening and Identification of Lipase Producing Bacterium. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, M.A. Presence and Activity of Psychrotrophic Microorganisms in Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. J. Food Prot. 1982, 45, 172–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omiccioli, E.; Amagliani, G.; Brandi, G.; Magnani, M. A New Platform for Real-Time PCR Detection of Salmonella Spp., Listeria Monocytogenes and Escherichia Coli O157 in Milk. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postollec, F.; Falentin, H.; Pavan, S.; Combrisson, J.; Sohier, D. Recent Advances in Quantitative PCR (QPCR) Applications in Food Microbiology. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, C.; Hofmann, K.; Huptas, C.; Scherer, S.; Wenning, M.; Lücking, G. Simultaneous Quantification of the Most Common and Proteolytic Pseudomonas Species in Raw Milk by Multiplex QPCR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rodhan, A.M.; Nasear, H.A. Pcr-Based Detection of Pseudomonas Fluorescens in Cows and Buffaloes. Bas. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 1, 194–208. [Google Scholar]
- Aparna Sudhakaran, V.; Anand, S. Approaches for Detection of Dairy Microorganisms: An Update. In Dairy Processing: Advanced Research to Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlinger, E.; Dorn-In, S.; Beindorf, P.M.; Mang, S.; Kaltner, F.; Gottschalk, C.; Gareis, M.; Schwaiger, K. Development of Two Specific Multiplex QPCRs to Determine Amounts of Pseudomonas, Enterobacteriaceae, Brochothrix Thermosphacta and Staphylococcus in Meat and Heat-Treated Meat Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, K.; Macé, S.; Guilbaud, M.; Jaffrès, E.; Ferchichi, M.; Prévost, H.; Pilet, M.F.; Dousset, X. Quantification of Viable Brochothrix Thermosphacta in Cooked Shrimp and Salmon by Real-Time PCR. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Burke, C.M.; Bolch, C.C.J.; Stanley, R. Seafood Spoilage Microbiota and Associated Volatile Organic Compounds at Different Storage Temperatures and Packaging Conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 280, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azinheiro, S.; Carvalho, J.; Prado, M.; Garrido-Maestu, A. Multiplex Detection of Salmonella spp., E. coli O157 and L. monocytogenes by QPCR Melt Curve Analysis in Spiked Infant Formula. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botaro, B.; Cortinhas, C.; MarÃ, L.; Moreno, J.; Silva, L.; Benites, N.; Santos, M. Detection and Enumeration of Staphylococcus Aureus from Bovine Milk Samples by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Dairy. Sci. 2013, 96, 6955–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.; Chapela, M.J.; Román, B.; Fajardo, P.; Lago, J.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. A New Multiplex Real-Time PCR Developed Method for Salmonella Spp. and Listeria Monocytogenes Detection in Food and Environmental Samples. Food Control. 2013, 30, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, J.; Cronin, U.; Tierney, J.; Piterina, A.V.; O’Meara, E.; Wilkinson, M.G. Gaps in the Assortment of Rapid Assays for Microorganisms of Interest to the Dairy Industry. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortari, A.; Lorenzelli, L. Recent Sensing Technologies for Pathogen Detection in Milk: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; Varlamov, A.; Vaskin, Y.; Efremov, I.; German Grehov, O.G.; Kandrov, D.; Rasputin, K.; Syabro, M.; et al. Unipro UGENE: A Unified Bioinformatics Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genscript Advanced Primer Design. Available online: https://www.genscript.com.cn/tools/pcr-primers-designer/advanced (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Applications Guide Real-Time PCR Applications Guide. Available online: https://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/Bulletin_5279.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Chapela, M.J.; Garrido-Maestu, A.; Cabado, A.G. Detection of Foodborne Pathogens by QPCR: A Practical Approach for Food Industry Applications. Cogent Food Agric. 2015, 1, 1013771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bijl, E.; Svensson, B.; Hettinga, K. The Extracellular Protease AprX from Pseudomonas and Its Spoilage Potential for UHT Milk: A Review. In Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.G.; Burger, M.; Beven, C.A.; Beacham, I.R. The AprX-LipA Operon of Pseudomonas Fluorescens B52: A Molecular Analysis of Metalloprotease and Lipase Production. Microbiology 2001, 147 Pt 2, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.L.; De Araújo, E.F.; Mantovani, H.C.; Moraes, C.A.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Detection of the Apr Gene in Proteolytic Psychrotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Refrigerated Raw Milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 102, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Characterization of Pseudomonas Spp. and Associated Proteolytic Properties in Raw Milk Stored at Low Temperatures. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.G.; Baglinière, F.; Marchand, S.; Van Coillie, E.; Vanetti, M.C.D.; De Block, J.; Heyndrickx, M. The Biodiversity of the Microbiota Producing Heat-Resistant Enzymes Responsible for Spoilage in Processed Bovine Milk and Dairy Products. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmann, M.; Weilmeier, D.; Dineen, S.S.; Ralyea, R.; Boor, K.J. Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Pseudomonas Spp. Isolated from Milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Single Molecule Real-Time Sequencing and Traditional Cultivation Techniques Reveal Complex Community Structures and Regional Variations of Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Raw Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 853263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Russo, F.; Ferrocino, I.; Villani, F. Molecular Identification of Mesophilic and Psychrotrophic Bacteria from Raw Cow’s Milk. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, J.; Shang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, B.; Xiang, X.; Gu, Q.; Pang, R.; et al. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Detection Using Conventional PCR and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Based on Species-Specific Novel Gene Targets Identified by Pangenome Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 820431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, J.; Carleton, H.A.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Lindsey, R.L.; Trees, E. Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies and Their Application to the Study and Control of Bacterial Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 24, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.M.; Srinivasan, V.; Gillespie, B.E.; Murinda, S.E.; Oliver, S.P. Application of SYBR Green Real-Time PCR Assay for Specific Detection of Salmonella Spp. in Dairy Farm Environmental Samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 102, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.N.; Woods, R.G.; Beacham, I.R. Regulation of the AprX–LipA Operon of Pseudomonas Fluorescens B52: Differential Regulation of the Proximal and Distal Genes, Encoding Protease and Lipase, by OmpR–EnvZ. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 241, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorothy, B.; Priya, S. Characterization of Lipase from Lipase-Producing Bacteria and Its Application in the Reduction of Triglyceride Content in Milk Sample. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 17, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, N.; Li, X.; Pang, X.; Lv, J.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of UHT Milk Spoilage Caused by Proteases from Psychrophilic Bacteria Based on Peptidomics. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.A.; Beacham, I.R.; MacRae, I.C.; Free, M.L. Degradation of Triglycerides by a Pseudomonad Isolated from Milk: Molecular Analysis of a Lipase-Encoding Gene and Its Expression in Escherichia Coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Burmølle, M.; Liu, T.; He, G. Insights into Bacterial Milk Spoilage with Particular Emphasis on the Roles of Heat-Stable Enzymes, Biofilms, and Quorum Sensing. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, P.; Qu, T.; Zhao, X.; Ge, Y.; Chen, Y. Detection and Quantification of Bacillus Cereus and Its Spores in Raw Milk by QPCR, and Distinguish Bacillus Cereus from Other Bacteria of the Genus Bacillus. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyab035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Shi, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, D.; Du, L. A Novel QPCR Method for the Detection of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Fermented Milk. Foods 2021, 10, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, M.; Shergill, I.S.; Williamson, M.; Gommersall, L.; Arya, N.; Patel, H.R. Basic Principles of Real-Time Quantitative PCR. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirson, S.N.; Butler, J.N. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction. Circadian Rhythm. Methods Protoc. 2007, 362, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, L.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, N.; Rahman, A.; Wang, J. Multiplex QPCR for Simultaneous Quantification of the Main Psychrotrophic Bacteria and Their Enzymes in Raw Milk. LWT 2025, 222, 117628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.M. Quantification of Pseudomonas Spp. in Raw Milk and Molecular Analysis of Their Proteolytic Potential. Doctoral Dissertation, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
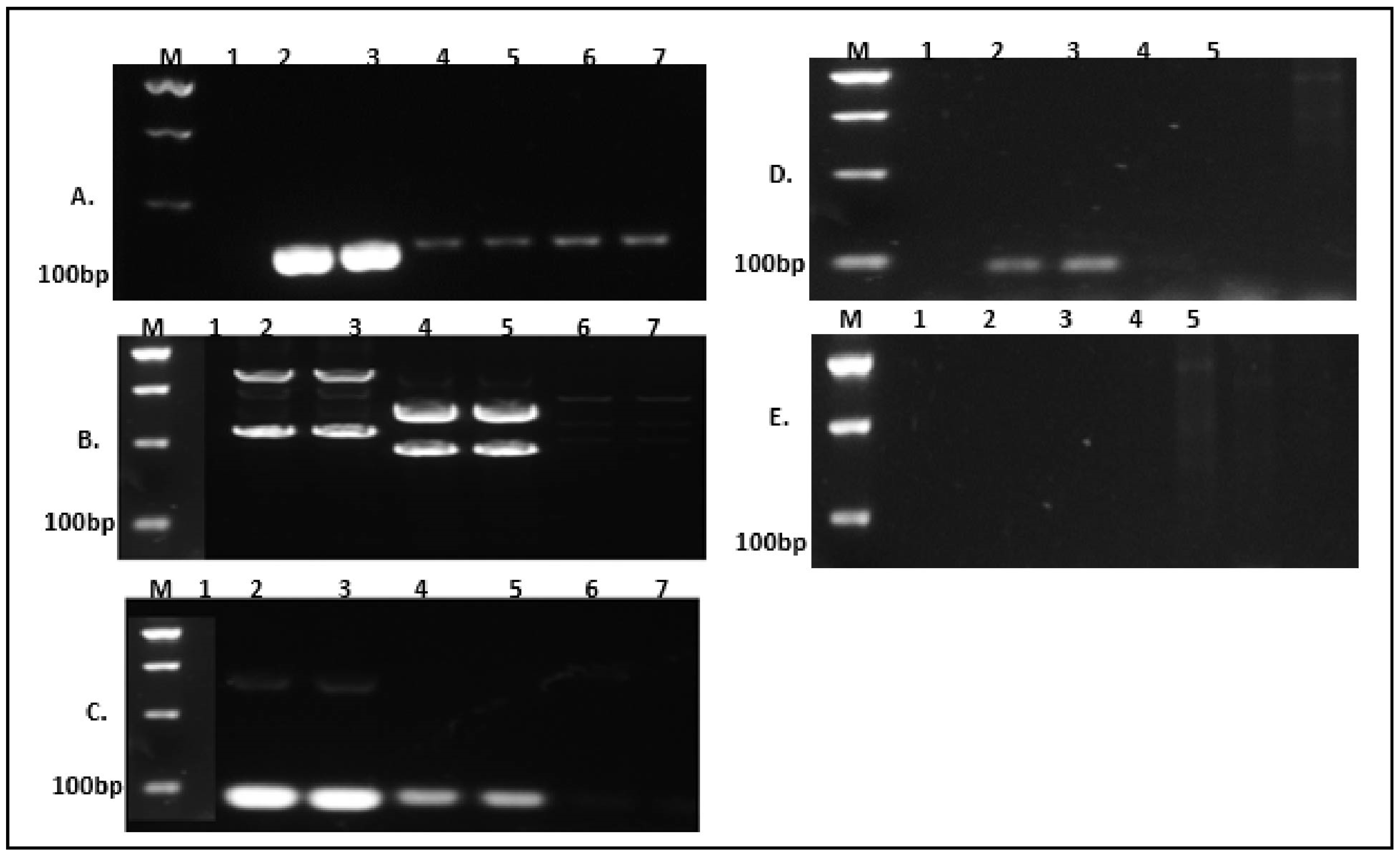


| No | Bacteria | NCBI Acc. No | Lipase/Protease (+Ve/−Ve) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enterococcus hirae | NR_037082 | −ve |
| 2 | Acinetobacter indicus | NZ_CP045198 | +ve |
| 3 | Pseudomonas fluorescens | NZ_LT907842 | +ve |
| 4 | Serratia liquefacients | NZ_MQRG01000035 | +ve |
| 5 | Pseudomonas azotoformans | NZ_LT629702 | +ve |
| 6 | Pseudomonas paralactis | NR_156987 | +ve |
| 7 | Exiguobacterium indicum | NR_042347 | −ve |
| 8 | Pseudomonas putida | NC_021505 | +ve |
| Primer | 5′ to 3′ | Annealed Bases | bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| lipA 3 | F- ACGTGGTGATCACTTCGGTA | 20 | 73 |
| R-CGAATGCAGTCGGCAAAGTG | 20 | ||
| P-FAM-CCGTCACGCAGGTCGTCGCG-TAMRA | 20 | ||
| lipA 6 | F-CTCAGCACTTTGCCGACTG | 19 | 72 |
| R-GAACCAGGGTTTCGAGCATC | 20 | ||
| P-FAM-CCGCAAGCTGTCGCCGAACGT-MGB | 21 | ||
| aprX 1 | F-AACGGCAACCCGACCTATAA | 20 | 85 |
| R-TGTTGCTCTCGCTCCAGTAA | 20 | ||
| P-Cy5-CGCAACCTATGGACAGGACACGCG-BHQ2 | 24 | ||
| aprX 2 | F-CGGACCTGAACAACTATGGC | 20 | 109 |
| R-TTATAGGTCGGGTTGCCGTT | 20 | ||
| P-Cy5-TCGGCCACACCCTGGGCCTG-BHQ1 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yalew, K.; Zhang, S.; Gebreyowhans, S.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, X.; Pang, X. Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria. Foods 2025, 14, 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111975
Yalew K, Zhang S, Gebreyowhans S, Xie N, Wang Y, Lv J, Li X, Pang X. Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111975
Chicago/Turabian StyleYalew, Kidane, Shuwen Zhang, Solomon Gebreyowhans, Ning Xie, Yunna Wang, Jiaping Lv, Xu Li, and Xiaoyang Pang. 2025. "Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria" Foods 14, no. 11: 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111975
APA StyleYalew, K., Zhang, S., Gebreyowhans, S., Xie, N., Wang, Y., Lv, J., Li, X., & Pang, X. (2025). Development of Multiplex qPCR Method for Accurate Detection of Enzyme-Producing Psychrotrophic Bacteria. Foods, 14(11), 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111975








