Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. L. paracasei MSMC39-1-Derived Conditioned Medium Rescues Kidney Epithelial Cells from Damage
2.2. Attenuation of Kidney Damage in Aged Mice by L. paracasei MSMC39-1
2.3. Reducing Blood Glucose Levels and Enhancement of Kidney Antioxidant Defense by L. paracasei MSMC39-1
2.4. Improving of Kidney Mitochondria DNA (mtDNA) Content in Aged Mice by L. paracasei MSMC39-1
2.5. Anti-Inflammation in Kidney by L. paracasei MSMC39-1
2.6. Positive Effects of L. paracasei MSMC39-1 on Maintained Colon Integrity and Anti-Oxidative Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Vero Cell Culture
4.2. Probiotic Strain, Culture Conditions, and Conditioned Medium Preparation
4.3. In Vitro Cell Damaging Induced by Glucose Experiment
4.4. Mitochondrial DNA Measurement
4.5. Experimental Animals
4.6. Organ Collection and Preparation
4.7. Blood Glucose Evaluation
4.8. Inflammatory Cytokines Evaluation by ELISA
4.9. Lipoperoxidation and Anti-Oxidative Stress Evaluation
4.10. Histopathological Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Koelman, L.; Rodrigues, C.E. Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: A systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, E.N.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, H.D.; Ban, T.H.; Yang, C.W.; Park, C.W.; Choi, B.S. Role of Aberrantly Activated Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Signaling Mediated Inflammation in Renal Aging. Cells 2021, 10, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez-Exposito, L.; Tejedor-Santamaria, L.; Santos-Sanchez, L.; Valentijn, F.A.; Cantero-Navarro, E.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R.; Tejera-Munoz, A.; Marchant, V.; Sanz, A.B.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury is Aggravated in Aged Mice by the Exacerbation of Proinflammatory Processes. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 662020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lin, H.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shu, S.; Luo, T.; Liang, T.; Lai, W.; Rao, J.; et al. Macrophage iron dyshomeostasis promotes aging-related renal fibrosis. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Exposito, L.; Tejedor, L.; Santos-Sanchez, L.; Valentijn, F.A.; Cantero-Navarro, E.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues Diez, R.; Tejera-Muñoz, A.; Marchant, V.; Sanz, A.; et al. MO338 increased inflammatory response is a hallmark of age-related aggravation of experimental AKI. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, gfab084.0011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Huang, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, W.; Chen, X.; Sun, X. Reduction in Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in Aged Male Mice by Intestinal Microbiota Rejuvenation. Gerontology 2024, 70, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Cho, W.Y.; Chung, S.M.; Choi, Y.E.; Fang, Y.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.J.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Altered gut microbiome plays an important role in AKI to CKD transition in aged mice. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1238960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonnaud, E.; Biragyn, A. Gut microbiota as the key controllers of “healthy” aging of elderly people. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, N.; Noti, M. The aging gut microbiome and its impact on host immunity. Genes. Immun. 2021, 22, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, S.T.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Amiri, M.M.; Pourshafie, M.R.; Rohani, M. The impact of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotic cocktail on modulation of gene expression of gap junctions dysregulated by intestinal pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Valan Arasu, M.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Esmail, G.A.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J. Probiotic and Antioxidant Potential of Lactobacillus reuteriLR12 and Lactobacillus lactisLL10 Isolated from Pineapple Puree and Quality Analysis of Pineapple-Flavored Goat Milk Yoghurt during Storage. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarella, L.A.T.; Mari, N.L.; Alcantara, C.C.; Iryioda, T.M.V.; Costa, N.T.; Oliveira, S.R.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Reiche, E.M.V.; Dichi, I.; Simao, A.N.C. Mixture of probiotics reduces inflammatory biomarkers and improves the oxidative/nitrosative profile in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaree, K.K.; Prasanth, M.I.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Tencomnao, T.; Chaiyasut, C.; Prasansuklab, A. Lactobacillus paracasei HII01 enhances lifespan and promotes neuroprotection in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladda, B.; Tangteerawatana, P.; Padungchaichot, P.; Pradidarcheep, W.; Kasorn, A.; Taweechotipatr, M. Anti-inflammatory effect of probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on alcohol-induced hepatitis in rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ladda, B.; Jantararussamee, C.; Pradidarcheep, W.; Kasorn, A.; Matsathit, U.; Taweechotipatr, M. Anti-Inflammatory and Gut Microbiota Modulating Effects of Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujoth, G.C.; Hiona, A.; Pugh, T.D.; Someya, S.; Panzer, K.; Wohlgemuth, S.E.; Hofer, T.; Seo, A.Y.; Sullivan, R.; Jobling, W.A.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutations, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in mammalian aging. Science 2005, 309, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W. Intestinal homeostasis in the gut-lung-kidney axis: A prospective therapeutic target in immune-related chronic kidney diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1266792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaul, E.; Barron, J. Age-Related Diseases and Clinical and Public Health Implications for the 85 Years Old and Over Population. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.O.; Fries, L.R.; Silva-Zolezzi, I.; Thakkar, S.K.; Iroz, A.; Blanchard, C. Effects of Probiotic Intervention on Markers of Inflammation and Health Outcomes in Women of Reproductive Age and Their Children. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 889040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flurkey, K.; Currer, J.M.; Harrison, D.E. Chapter 20—Mouse Models in Aging Research. In The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd ed.; Fox, J.G., Davisson, M.T., Quimby, F.W., Barthold, S.W., Newcomer, C.E., Smith, A.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2007; pp. 637–672. [Google Scholar]
- Adams-Sherrod, G.A.; Brooks, H.L.; Kumar, P. Sex-specific modulation of renal epigenetic and injury markers in aging kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2024, 327, F543–F551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yang, X.; Gong, H.; Li, X. Time- and Gender-Dependent Alterations in Mice during the Aging Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, J.H. Lacticaseibacillus paracsei HY7207 Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Liver Fibrosis in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease-Potential Therapeutic Role of Minerals, Vitamins and Plant-Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Merkling, T.; Metzger, M.; Koppe, L.; Laville, M.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Frimat, L.; Combe, C.; Massy, Z.A.; Stengel, B.; et al. Probiotic Intake and Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Analysis of the CKD-REIN Cohort. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 772596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, K.; Lee, Y.; Chen, M. Preventive Effects of Lactobacillus Mixture against Chronic Kidney Disease Progression through Enhancement of Beneficial Bacteria and Downregulation of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7353–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-K.; Jang, Y.J.; Seo, B.; Han, D.H.; Park, S.; Ko, G. Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei strains improves immunomodulation and changes the composition of gut microbiota leading to improvement of colitis in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoli, R.; Mattace Raso, G.; Lama, A.; Pirozzi, C.; Santoro, A.; Di Guida, F.; Sanges, M.; Aksoy, E.; Calignano, A.; D’Arienzo, A.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus paracasei B21060-based synbiotic treatment on gut inflammation and barrier integrity in colitic mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Q.; Hao, H.; Bu, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, T.; Yi, H. Lactobacillus paracasei X11 Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Kang, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, J.; Du, L.; Zhou, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Mi, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Loss of legumain induces premature senescence and mediates aging-related renal fibrosis. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Yang, Y.; Won Kim, J.; Son, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Im, D.S.; Young Chung, H.; Chung, K.W. Diminished Tubule Epithelial Farnesoid X Receptor Expression Exacerbates Inflammation and Fibrosis Response in Aged Rat Kidney. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntoye, M.A.; Oridupa, O.A.; Ezekiel, O.O. Phenolic, flavonoid, and beta-carotene contents of provitamin A cassava hydrolysate with free and encapsulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves antioxidant biomarkers in kidney, heart and liver of Wistar rats. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.J.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, W.J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, Y. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the improvement of metabolic profiles in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Kuo, Y.W.; Chiang, P.R.; Ho, H.H. Probiotics and their Metabolites Reduce Oxidative Stress in Middle-Aged Mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroijen, M.A.; de Mutsert, R.; Dekker, F.W.; de Vries, A.P.J.; de Koning, E.J.P.; Rabelink, T.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Dekkers, O.M. The association of glucose metabolism and kidney function in middle-aged adults. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dabet, M.M.; Shahzad, K.; Elwakiel, A.; Sulaj, A.; Kopf, S.; Bock, F.; Gadi, I.; Zimmermann, S.; Rana, R.; Krishnan, S.; et al. Reversal of the renal hyperglycemic memory in diabetic kidney disease by targeting sustained tubular p21 expression. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samikkannu, T.; Thomas, J.J.; Bhat, G.J.; Wittman, V.; Thekkumkara, T.J. Acute effect of high glucose on long-term cell growth: A role for transient glucose increase in proximal tubule cell injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 291, F162–F175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsiao, H.Y.; Yen, T.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Cheng, C.M.; Liu, J.W.; Fan, Y.T.; Huang, J.J.; Nien, C.Y. Delivery and Transcriptome Assessment of an In Vitro Three-Dimensional Proximal Tubule Model Established by Human Kidney 2 Cells in Clinical Gelatin Sponges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, V.; Carta, G.; da Costa Pereira, D.; Gupta, R.; Murphy, C.; Feifel, E.; Kern, G.; Lechner, J.; Cavallo, A.L.; Gupta, S.; et al. Generation and characterization of iPSC-derived renal proximal tubule-like cells with extended stability. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawrysh, P.J.; Gao, J.; Tan, S.; Oh, A.; Nodwell, J.; Tompkins, T.A.; McQuibban, G.A. PRKN/parkin-mediated mitophagy is induced by the probiotics Saccharomyces boulardii and Lactococcus lactis. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2094–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, J.F.; Patel, H.V.; Naples, C.J.; Fujioka, H.; Hoppel, C.L. Decreased cytochrome c mediates an age-related decline of oxidative phosphorylation in rat kidney mitochondria. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Liu, J.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Yang, P.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin/RAS signaling mediates age-related renal fibrosis and is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.D.; Lei, Y.; VanPortfliet, J.J.; Winters, A.D.; West, A.P. Assessing Mitochondrial DNA Release into the Cytosol and Subsequent Activation of Innate Immune-related Pathways in Mammalian Cells. Curr. Protoc. 2022, 2, e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.J.; Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Wijers, M.E.; Sieben, C.J.; Zhong, J.; Saltness, R.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Verzosa, G.C.; Pezeshki, A.; et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 2016, 530, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, E.J.; Marshall, J.S. Aging in the absence of TLR2 is associated with reduced IFN-gamma responses in the large intestine and increased severity of induced colitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
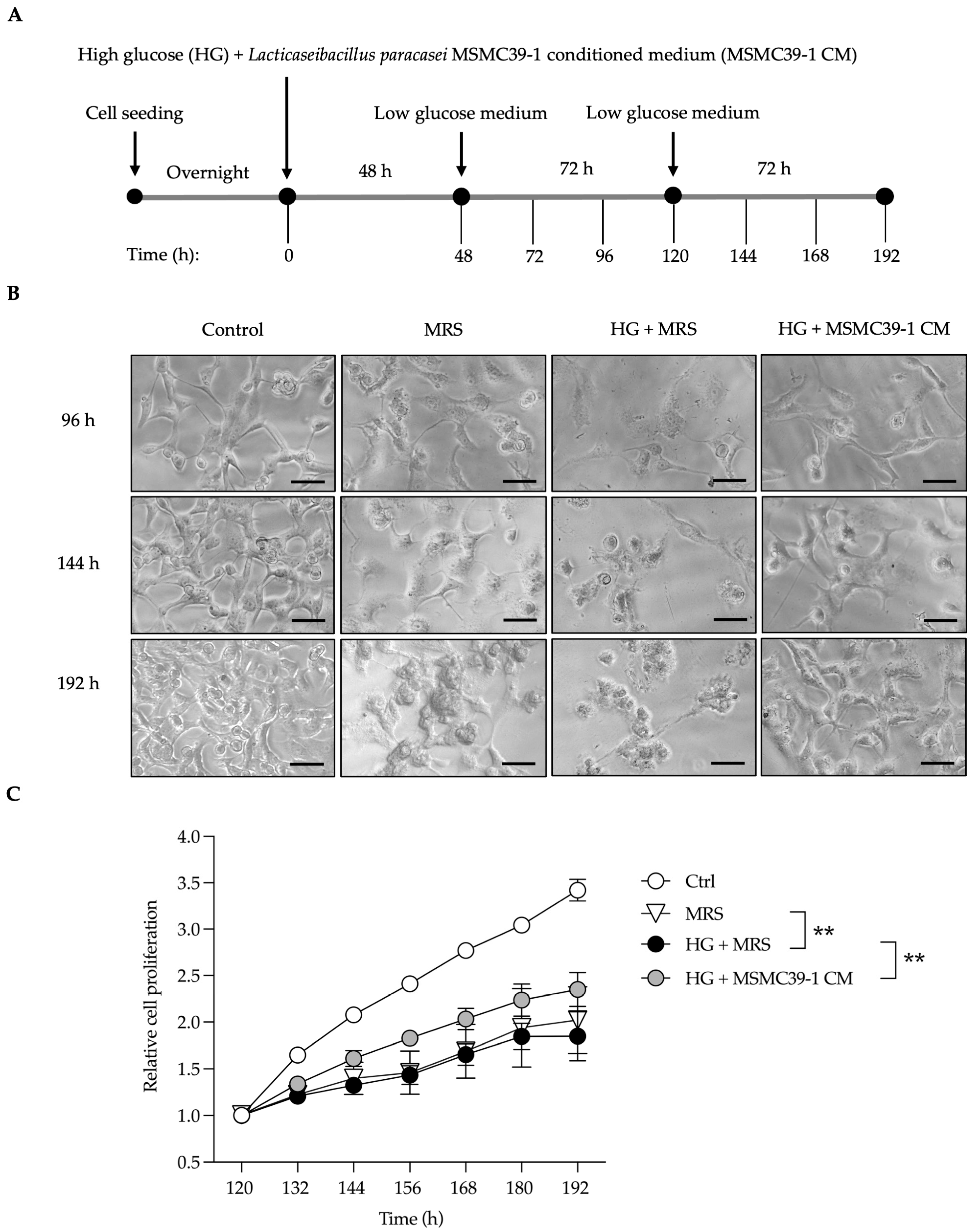

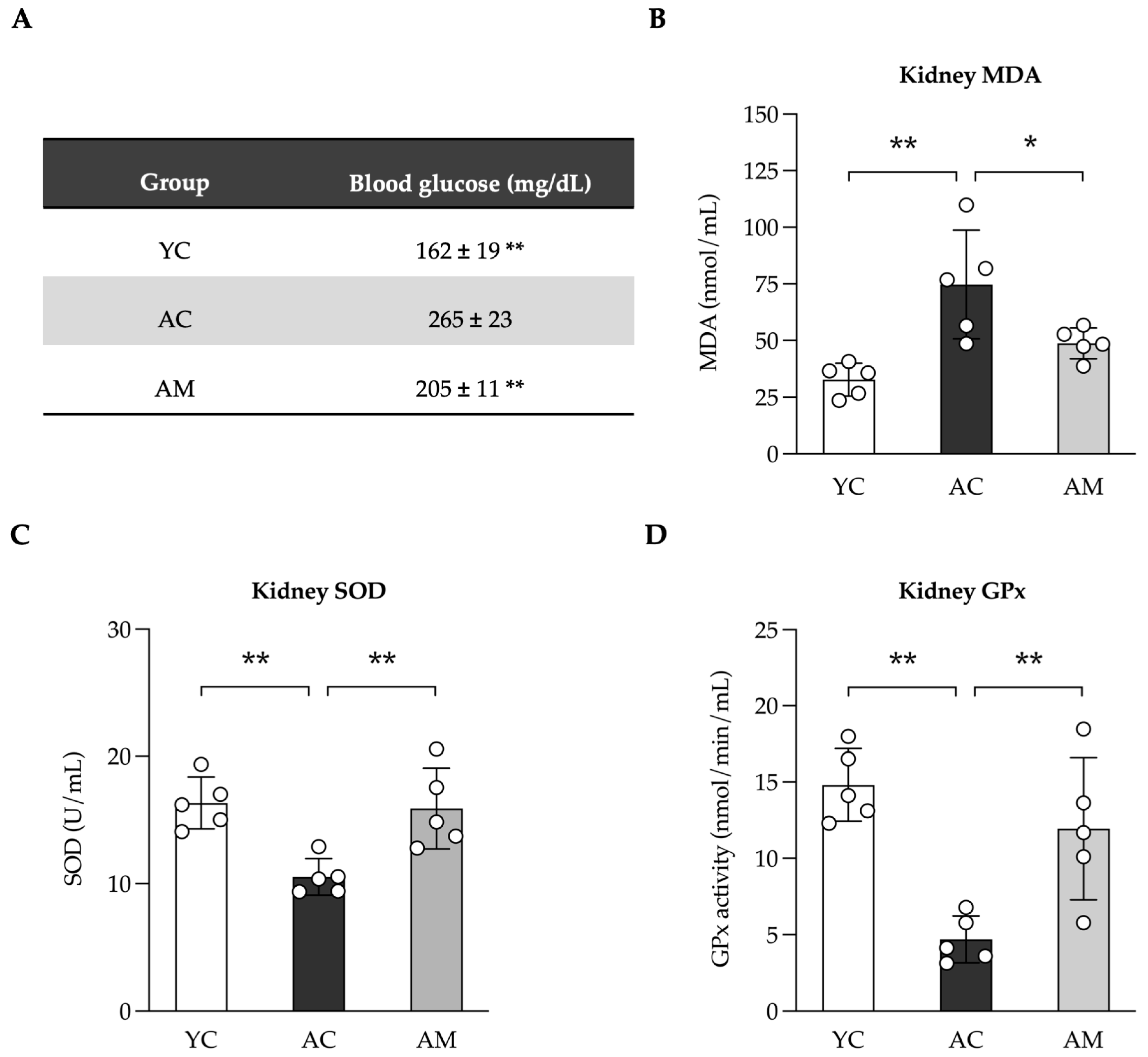

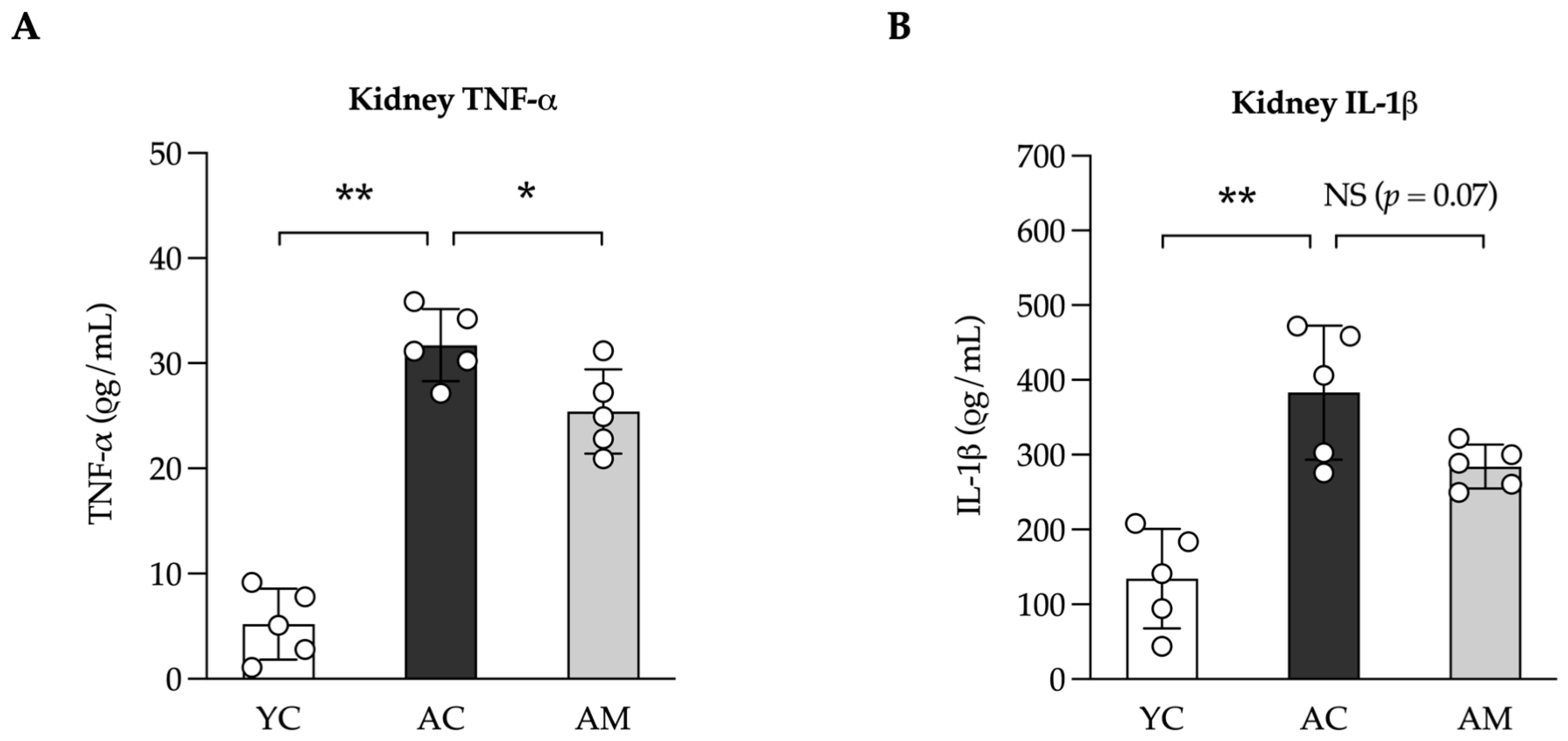
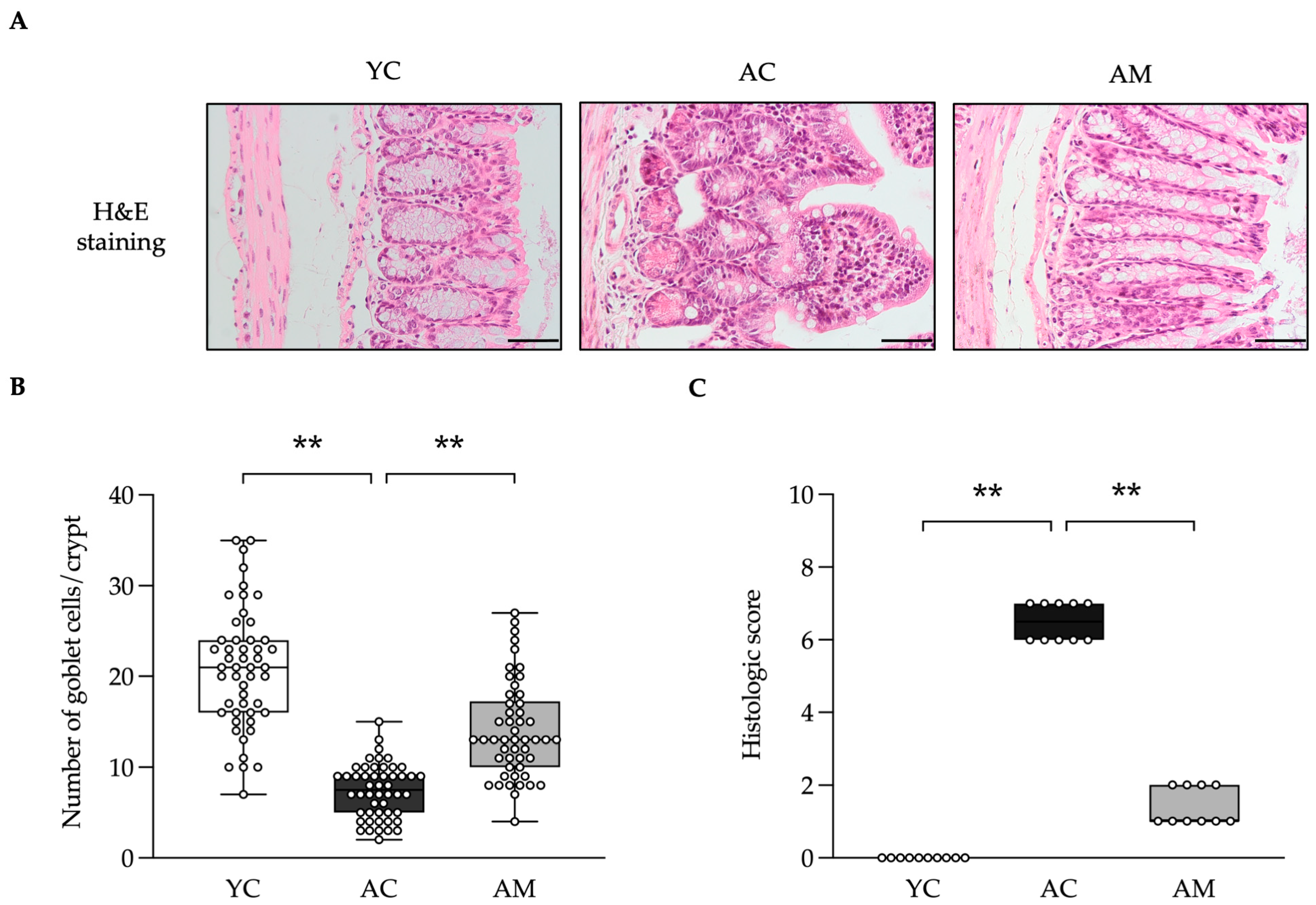
| Feature Graded | Grade | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory cell infiltration (0–3) | 0 | Less than three inflammatory cells per field of view at 40× magnification in the lamina propria |
| 1 | Greater than three inflammatory cells per field of view in the lamina propria | |
| 2 | Confluence of inflammatory cells extending into the submucosa | |
| 3 | Confluence of inflammatory cells present in all tissue layers | |
| Tissue damage (0–5) | 0 | Normal |
| 1 | Damage limited to the epithelium | |
| 2 | Focal ulceration limited to the mucosa | |
| 3 | Focal transmural inflammation and ulceration | |
| 4 | Extensive transmural ulceration and inflammation bordered by normal mucosa | |
| 5 | Extensive transmural inflammation and ulceration involving the entire section | |
| Edema (0–2) | 0 | No edema |
| 1 | Focal submucosal edema | |
| 2 | Extensive submucosal edema involving the entire section |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sookpotarom, P.; Namkaew, J.; Wuttisa, K.; Chantarangkul, C.; Jamjuree, P.; Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Taweechotipatr, M. Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential. Foods 2025, 14, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111874
Sookpotarom P, Namkaew J, Wuttisa K, Chantarangkul C, Jamjuree P, Jaroonwitchawan T, Taweechotipatr M. Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111874
Chicago/Turabian StyleSookpotarom, Pol, Jirapat Namkaew, Kaikwa Wuttisa, Chantanapa Chantarangkul, Praewpannarai Jamjuree, Thiranut Jaroonwitchawan, and Malai Taweechotipatr. 2025. "Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential" Foods 14, no. 11: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111874
APA StyleSookpotarom, P., Namkaew, J., Wuttisa, K., Chantarangkul, C., Jamjuree, P., Jaroonwitchawan, T., & Taweechotipatr, M. (2025). Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential. Foods, 14(11), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111874






