Moving Beyond Indices: A Systematic Approach Integrating Food System Performance and Characteristics for Comprehensive Food Security Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
Existing Weighting Methods
- Food security indices using input-based models, focusing on resource availability, do not relate the composite index to the food system outputs. In other words, these models do not clearly show how efficiently these resources are utilized. To overcome this limitation, this study introduces an input–output model that incorporates nutritional status as an output indicator. This output indicator is important to measure people’s accessibility to enough nutrition and the availability of their daily dietary needs.
- Interpreting composite indices is critical to highlighting specific areas of strength and weakness in food systems. However, stakeholders and decision-makers may encounter serious difficulties interpreting the results when many indicators are involved. To mitigate this, elastic-net regression is employed to reduce the dimension of the impact matrix and include only the indicators relevant to the food system’s performance. This step will help understand the contribution of each indicator (or factor) and effectively address the root causes of food insecurity.
- Using single-score-based rankings in food security assessments often disregards critical contextual factors, such as geographic location, food system typology, economic development levels, etc. The involvement of such characteristics is essential for conducting realistic benchmarking and developing short- and long-term solutions. This study proposes a two-stage clustering method to enhance food security analysis. First, entities (countries) are grouped based on their overall food security score. Following this, each cluster is further analyzed through a second round of clustering, considering key food system characteristics like typology and economic status. By creating more nuanced groupings, this approach aims to provide stakeholders with actionable insights for targeted interventions instead of relying solely on a single-score list.
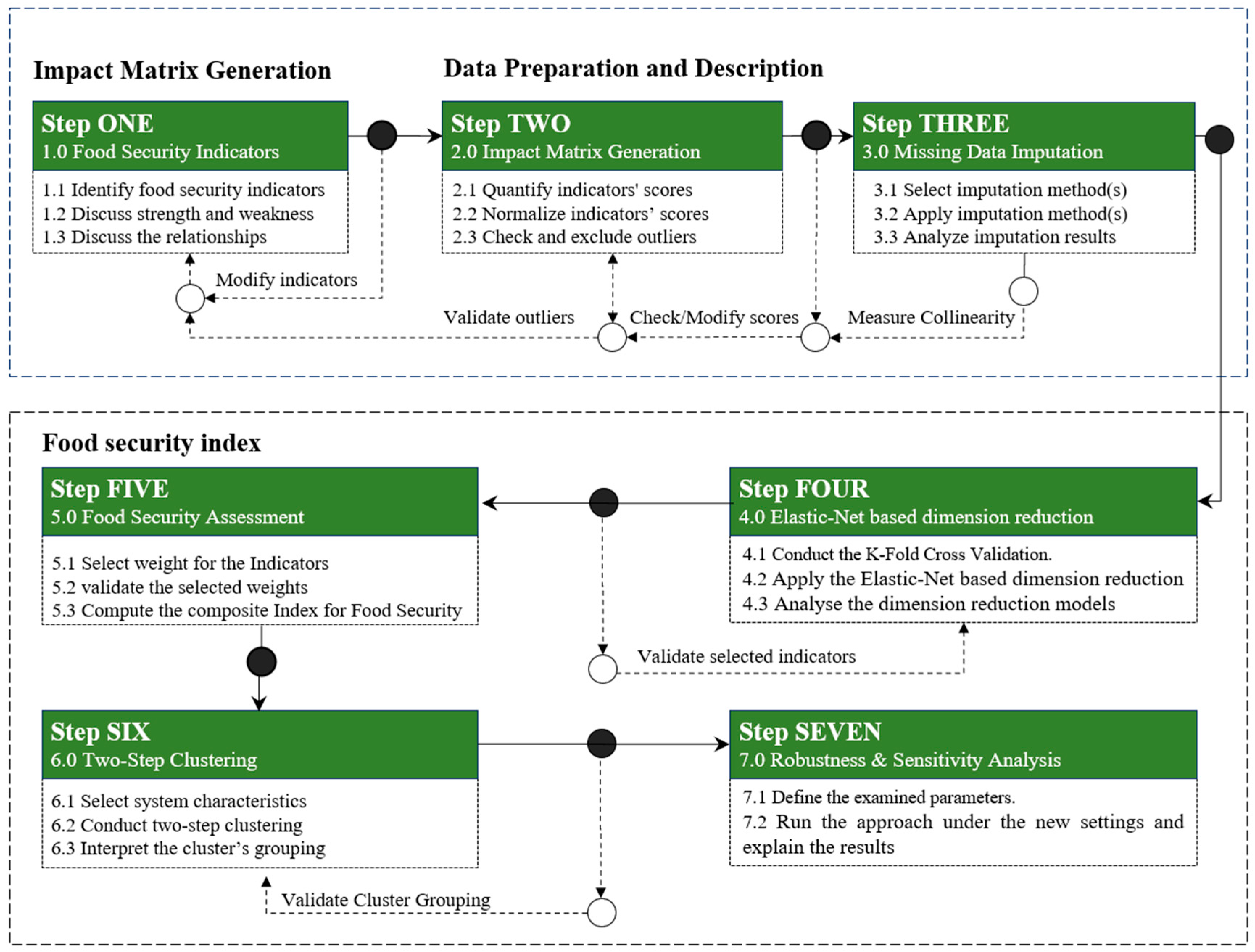
3. Methodology
4. Illustrative Example
4.1. Food Security Indicators
4.2. Impact Matrix Generation
4.3. Outliers Detection and Imputation
4.4. Elastic-Net-Based Dimension Reduction
4.5. Food Security Score Calculation
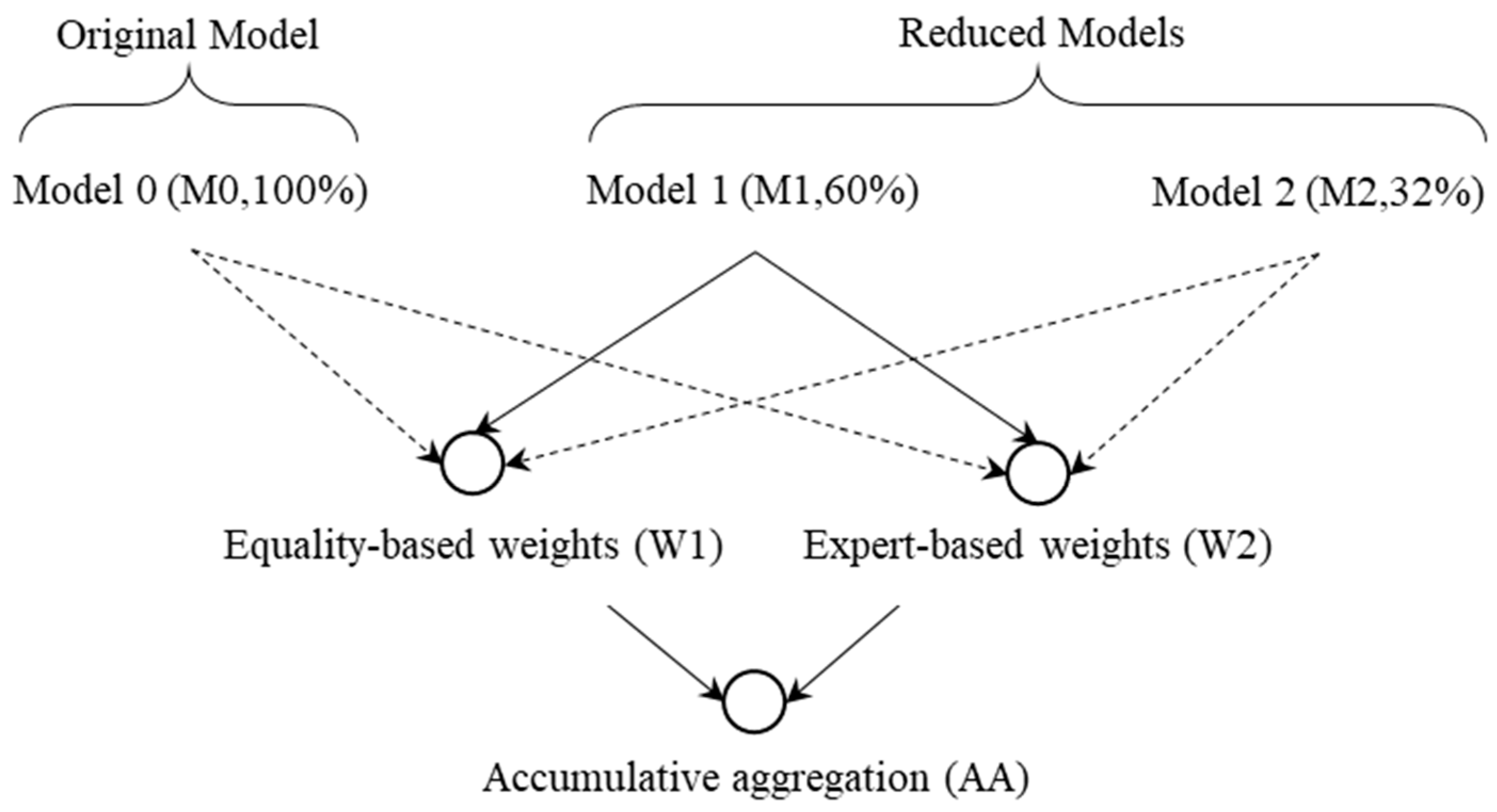
4.5.1. Testing the Impact of the Weighting Method
4.5.2. Testing the Impact of the Dimension Reduction
5. Two-Step Cluster Analysis
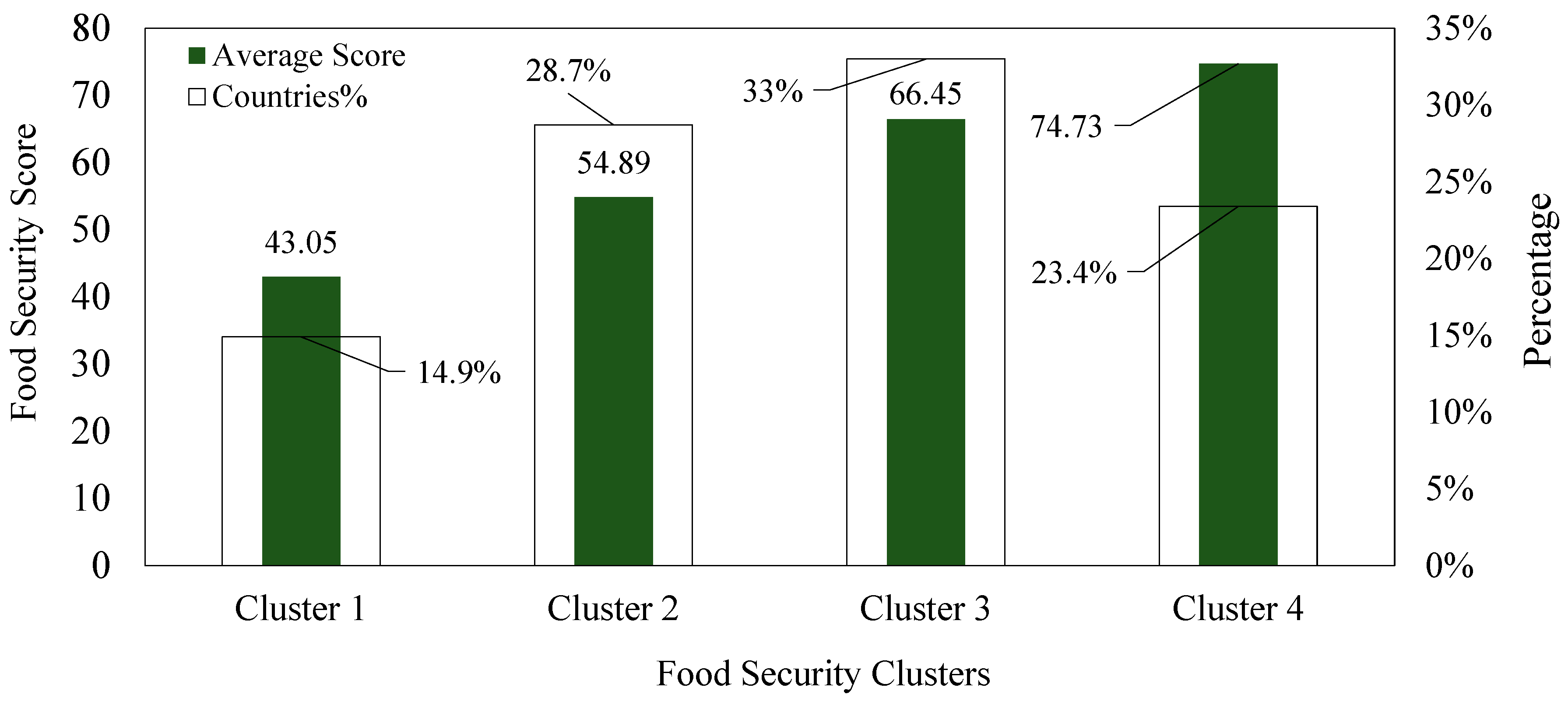
5.1. Step One: Food Security Score-Based Clustering
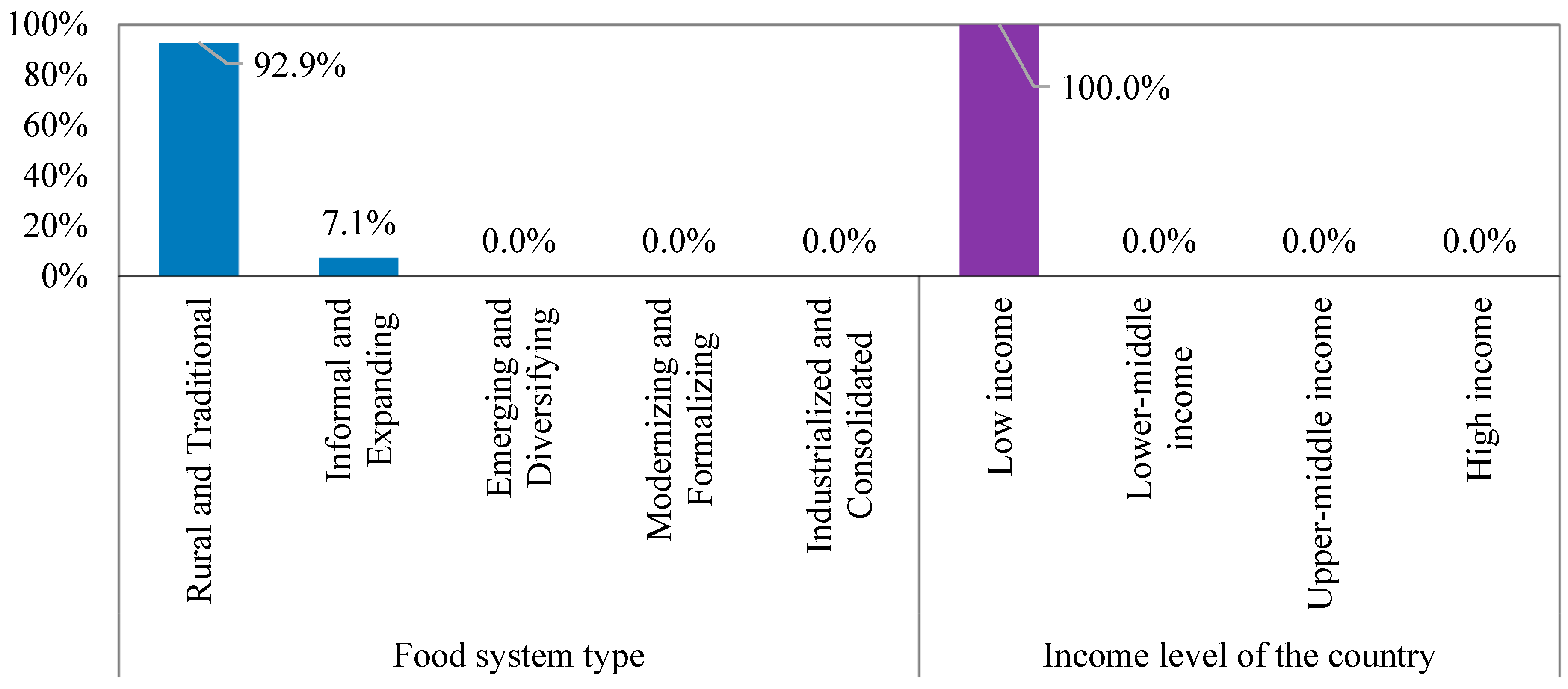
5.2. Step Two: Characteristic-Based Clustering
6. Conclusions and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| AHP | Analytical Hierarchy Process |
| CV | Cross-Validation |
| DEA | Data Envelope Analysis |
| EIU | Economist Intelligence Unit |
| FA | Factor Analysis |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| FIES | Food Insecurity Experience Scale |
| GFSI | Global Food Security Index |
| GHI | Global Hunger Index |
| GNI | Gross national income |
| IFPRI | International Food Policy Research Institute |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Squared Shrinkage Operator |
| NR&R | Natural resources and resilience |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| SE | Standard error |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TOPSIS | Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution |
- List of Mathematical Notations/Abbreviations
| Symbol | Description |
| y | The dependent variable for the elastic-net regression |
| x | The independent variables for the elastic-net regression |
| The coefficients of the regression model | |
| Normally distributed random error term | |
| Penalty function | |
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient | |
| and | Penalty functions 1 and 2 |
| and | Shrinkage parameters |
| The original score of the th country under the indicator | |
| Mmax,j and Mmin,j | Represent the maximum and minimum scores of the jth indicator |
Appendix A
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Difference ( | −0.630 |
| Observed t | −0.658 |
| Critical |t| | 2.074 |
| Degrees of freedom | 22 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | 0.517 |
| Significance level (α) | 0.05 |
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food Security: Concepts and Measurement. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/y4671e/y4671e06.htm (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Stringer, R. Food Security Global Overview. In Food Poverty and Insecurity: International Food Inequalities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, J.B.; Denno Cissé, J.; Barrett, C.B. Food Security as Resilience: Reconciling definition and measurement. Agric. Econ. 2016, 47, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.; Murphy, B.; Cowie, A. Sustainable Land Management for Environmental Benefits and Food Security; A Synthesis Report for the GEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, M.S.; Bhavani, R.V. Food production & availability—Essential prerequisites for sustainable food security. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamdimba, O.Y.; Ortmann, G.F.; Wale, E. Resilience to shocks and food insecurity: Determinants, and the impact of smallholder Jatropha curcas cultivation in Southern Malawi. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2021, 13, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwalla, N.; El Labban, S.; Bahn, R.A. Nutrition security is an integral component of food security. Front. Life Sci. 2016, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, N.; Lashgarara, F.; Hosseini, S.J.F.; Mirdamadi, S.M.; Rezaei-Moghaddam, K. Determining the Resilience of Rural Households to Food Insecurity during Drought Conditions in Fars Province, Iran. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, K.; Robinson, S.; Cattaneo, A. Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security: Impacts and the Potential for Adaptation and Mitigation. In Sustainable Food and Agriculture—An Integrated Approach; Campanhola, C., Pandey, S., Eds.; The Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2019; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Zeng, M.; Luo, K. How does climate change affect food security? Evidence from China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, S.; Anand, A.; Lairenjam, G.; Mohan, G.; Sharma, N.; Khare, A.; Bhargavi, A. Climate Change Impacts on Agricultural Systems Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies: A Review. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Tieu, A.; Huynh, H. Water scarcity impacts on global food production. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 23, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasek, M. Threats To Food Security And Common Agricultural Policy. Econ. Agric. 2013, 59, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.M.; Dhanjal-Adams, K.L.; Milne, A.; Oliver, T.H.; Todman, L.C.; Whitmore, A.P.; Pywell, R.F. Resilience and food security: Rethinking an ecological concept. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Vermeulen, S.J.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Corner-Dolloff, C.; Girvetz, E.; Loboguerrero, A.M.; Ramirez-Villegas, J.; Rosenstock, T.; Sebastian, L.; Thornton, P.K.; et al. Reducing risks to food security from climate change. Glob. Food Secur. 2016, 11, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneiko, O.V.; Rogaleva, N.L. The threats to food security. Amazon. Investig. 2018, 7, 232–242. Available online: https://amazoniainvestiga.info/index.php/amazonia/article/view/398 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Nechifor, V.; Ramos, M.P.; Ferrari, E.; Laichena, J.; Kihiu, E.; Omanyo, D.; Musamali, R.; Kiriga, B. Food security and welfare changes under COVID-19 in Sub-Saharan Africa: Impacts and responses in Kenya. Glob. Food Secur. 2021, 28, 100514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.C.; Boidya, P.; Haque, I.-M.; Hossain, A.; Shams, Z.; Mamun, A.-A. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on fish consumption and household food security in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Glob. Food Secur. 2021, 29, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erezi, E.; Ehi, O.E.; Ayodeji, O.T. Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Resilience in African Nations. Int. J. Agric. Earth Sci. 2023, 9, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muqdadi, S.W.; Abdalwahab, N.S.; Almallah, I.A.; Hussein, S.F.; Yassin, A.; Salim, S.O.; Alfarraji, M.J.; Mishbak, H.H.; Altuma, L.R.; Ab-Dulrahman, B. The complex system of climate change security and the ripple effect of water–food–socioeconomic nexus. J. Infrastruct. Policy Dev. 2024, 8, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuei, C.-H.; Lu, M.H. Integrating quality management principles into sustainability management. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2013, 24, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, B.; Thome, K. International Food Security Assessment, 2017–2027. In Amber Waves: The Economics of Food, Farming, Natural Resources, and Rural America; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.B.; Augustin, M.A.; Robertson, M.J.; Manners, J.M. The science of food security. NPJ Sci. Food 2018, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irtyshcheva, I.; Ponomarova, M.; Dolzhykova, I. Conceptual Fundamentals of Development of the Food Security System. Balt. J. Econ. Stud. 2019, 5, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, S.; Meade, B.; Fuglie, K.; Rada, N.E. International Food Security Assessment, 2014–2024; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Gubert, M.B.; Rogers, B.; Hromi-Fiedler, A. Food security measurement and governance: Assessment of the usefulness of diverse food insecurity indicators for policy makers. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 14, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, V.; Blakley, J.; Loring, P. A framework to assess food security in regional strategic environmental assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 91, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Grebmer, K.; Bernstein, J.; Hossain, N.; Brown, T.; Prasai, N.; Yohannes, Y.; Patterson, F.; Sonntag, A.; Zimmerman, S.-M.; Towey, O. 2017 Global Hunger Index: The Inequalities of Hunger; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/b/fpr/ifprib/9780896292710.html (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Thomas, A.-C.; Dhombres, B.; Casubolo, C.; Saisana, M.; Kayitakire, F. The Use of the Global Food Security Index to Inform the Situation in Food Insecure Countries; EUR 28885 EN; The Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricic, M.; Bulajic, M.; Dobrota, M.; Jeremic, V. Redesigning The Global Food Security Index: A Multivariate Composite I-Distance Indicator Approach. Int. J. Food Agric. Econ. 2016, 4, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booysen, F. An Overview and Evaluation of Composite Indices of Development. Soc. Indic. Res. 2002, 59, 115–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, D.; Gopinath, M. Exploring the disparity in global food security indicators. Glob. Food Secur. 2021, 29, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangaribowo, E.H.; Gerber, N.; Torero, M.A. Food and Nutrition Security Indicators: A Review. SSRN 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiero, C.; Gheri, F.; Viviani, S. Validating the Food Insecurity Experience Scale for Use In Analyses of Recent Food Insecurity. Glob. Food Secur. 2024, 42, 100783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, T.O.; Westengen, O.; Jerven, M. Measuring the end of hunger: Knowledge politics in the selection of SDG food security indicators. Agric. Hum. Values 2023, 40, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, G.M.; Kucukvar, M.; Kutty, A.A.; Abdelsalam, A.G.; Sen, B.; Bulak, M.E.; Onat, N.C. A novel approach for developing composite eco-efficiency indicators: The case for US food consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Christodoulou, A. Review of sustainability indices and indicators: Towards a new City Sustainability Index (CSI). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2012, 32, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Fernandez, I.C.; Guo, J.; Wilson, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J. When to use what: Methods for weighting and aggregating sustainability indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, M.A.; Nabeel, H.; Abdella, G.M.; El Mekkawy, T.; Kutty, A.A. A Non-Parametric Approach-Based Trade-Off between Food System Efficiency and Robustness. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Huang, C.M. Sustainability index for Taipei. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2007, 27, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberg, M. Composite Indicators of Country Performance: A Critical Assessment; OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers: Paris, France, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, M.; Aye, L.; Rajabifard, A.; Ngo, T. Transport sustainability index: Melbourne case study. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, A.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Abdella, G.M.; Bulak, M.E.; Onat, N.C. Sustainability Performance of European Smart Cities: A Novel DEA Approach with Double Frontiers. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 81, 103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tversky, A.; Kahneman, D. Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science 1974, 185, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montibeller, G.; von Winterfeldt, D. Individual and Group Biases in Value and Uncertainty Judgments. In International Series in Operations Research and Management Science; Dias, L., Morton, A., Quigley, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Grisar, C.; Kuhnert, F. The impact of biases on simulation-based risk aggregation: Modeling cognitive influences on risk assessment. J. Manag. Control 2011, 22, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, V.; Hanea, A.M.; Burgman, M.A. What is a Good Calibration Question? Risk Anal. 2021, 42, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmarathne, G.; Nane, G.F.; Robinson, A.; Hanea, A.M. Shrinking the Variance in Experts’ “Classical” Weights Used in Expert Judgment Aggregation. Forecasting 2023, 5, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, F.; Rowe, G. There is Data, and then there is Data: Only Experimental Evidence will Determine the Utility of Differential Weighting of Expert Judgment. Risk Anal. 2015, 35, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Austin, S.; Glass, J.; Mills, G. Toward collective organizational values: A case study in UK construction. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2008, 26, 1009–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, G.M.; Kucukvar, M.; Ismail, R.; Abdelsalam, A.G.; Onat, N.C.; Dawoud, O. A mixed model-based Johnson’s relative weights for eco-efficiency assessment: The case for global food consumption. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 89, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, G.M.; Kim, J.; Al-Khalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.M. Penalized Conway-Maxwell-Poisson regression for modelling dispersed discrete data: The case study of motor vehicle crash frequency. Saf. Sci. 2019, 120, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Egilmez, G.; Kucukvar, M. Emergy and end-point impact assessment of agricultural and food production in the United States: A supply chain-linked Ecologically-based Life Cycle Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, A.A.; Wakjira, T.G.; Kucukvar, M.; Abdella, G.M.; Onat, N.C. Urban resilience and livability performance of European smart cities: A novel machine learning approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, A.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.C.; Ayvaz, B.; Abdella, G.M. Measuring sustainability, resilience and livability performance of European smart cities: A novel fuzzy expert-based multi-criteria decision support model. Cities 2023, 137, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajana, S.; Acar, N.; Bretillon, L.; Hejblum, B.P.; Jacqmin-Gadda, H.; Delcourt, C.; BLISAR Study Group. Benefits of dimension reduction in penalized regression methods for high-dimensional grouped data: A case study in low sample size. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepina, I. Comparative analysis of modern concepts in modeling global food security. Sci. Notes 2024, 37, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, K.A.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Manikas, I. Agricultural big data and methods and models for food security analysis—A mini-review. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herteux, J.; Räth, C.; Martini, G.; Baha, A.; Koupparis, K.; Lauzana, I.; Piovani, D. Forecasting Trends in Food Security: A Reservoir Computing Approach. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofa, A.; Zewotir, T. A bayesian spatio-temporal dynamic analysis of food security in Africa. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asim, H.; Rehman, H.U. Panel Quantile Approach towards Exigent Determinants of Food Security in the Selected Developing Countries. Pak. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2024, 12, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Chandra, H. Measuring disaggregate level food insecurity via multivariate small area modelling: Evidence from rural districts of Uttar Pradesh, India. Food Secur. 2021, 13, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilema, S.A.; Shiferaw, Y.A.; Zewotir, T.; Muluneh, E.K. Multivariate small area estimation of undernutrition for children under five using official statistics. Stat. J. IAOS 2022, 38, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtsiyarava, M.; Williams, T.G.; Verdin, A.; Guikema, S.D. A nonparametric analysis of household-level food insecurity and its determinant factors: Exploratory study in Ethiopia and Nigeria. Food Secur. 2021, 13, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, H.; Alansari, M.; Abdella, G.M.; Kutty, A.A.; Al Mohannadi, I.M. An Input-Output-Based Assessment of the Global Food Security Index. In Proceedings of the 6th European International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Lisbon, Portugal, 18–20 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruolo, P.; Saisana, M.; Saltelli, A. Ratings and rankings: Voodoo or science? J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2013, 176, 609–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurra, A.; Massimiliano, A.; Angela, M. Measuring sustainable food consumption: A case study on organic food. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukvar, M.; Alawi, K.A.; Abdella, G.M.; Bulak, M.E.; Onat, N.C.; Bulu, M.; Yalçıntaş, M. A frontier-based managerial approach for relative sustainability performance assessment of the world’s airports. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 29, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, G.M.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.C.; Al-Yafay, H.M.; Bulak, M.E. Sustainability assessment and modeling based on supervised machine learning techniques: The case for food consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Cantor, G.; Ribal, J.; Sanjuán, N. Measuring regional differences in food security from access and stability dimensions: A methodological proposal based on elasticities. Agric. Econ. 2020, 66, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Taylor, J.; Tibshirani, R.; Walther, G. Stagewise algorithms and lasso-type problems. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0705.0269. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeyemi, G.M.; Ogunjobi, E.O.; Folorunsho, A.I. On Performance of Shrinkage Methods—A Monte Carlo Study. Int. J. Stat. Appl. 2015, 5, 72–76. Available online: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.statistics.20150502.04.html (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Global Food Security Index (GFSI). Available online: https://impact.economist.com/sustainability/project/food-security-index/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Kutty, A.A.; Abdella, G.M.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.C.; Bulu, M. A system thinking approach for harmonizing smart and sustainable city initiatives with United Nations sustainable development goals. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, A.A.; Yetiskin, Z.; Abraham, M.M.; Nooh, M.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Abdella, G.M. An Empirical Assessment on the Transportation Sustainability Indicators and their Impact on Economic Productivity, 2020. Available online: http://qspace.qu.edu.qa/handle/10576/31868 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Majeed, W.A.; Hamad, M.M. Exploring High-Dimensional Outlier Detection: A Comprehensive Study on Methods and Applications Using PCA and k-NN Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 21st International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices (SSD), Erbil, Iraq, 22–25 April 2024; pp. 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A Study of Cross-Validation and Bootstrap for Accuracy Estimation and Model Selection. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QB, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Available online: https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/95-2/Papers/016.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Wong, T.T. Performance evaluation of classification algorithms by k-fold and leave-one-out cross validation. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Systems Dashboard. Available online: https://www.foodsystemsdashboard.org/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- World Bank, WDI—The World by Income and Region. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/the-world-by-income-and-region.html (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- von Grebmer, K.; Bernstein, J.; Patterson, F.; Wiemers, M.; Chéilleachair, R.N.; Foley, C.; Ekstrom, K.; Fritschel, H. 2019 Global Hunger Index: The Challenge of Hunger and Climate Change; Concern Worldwide: Dublin, Ireland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
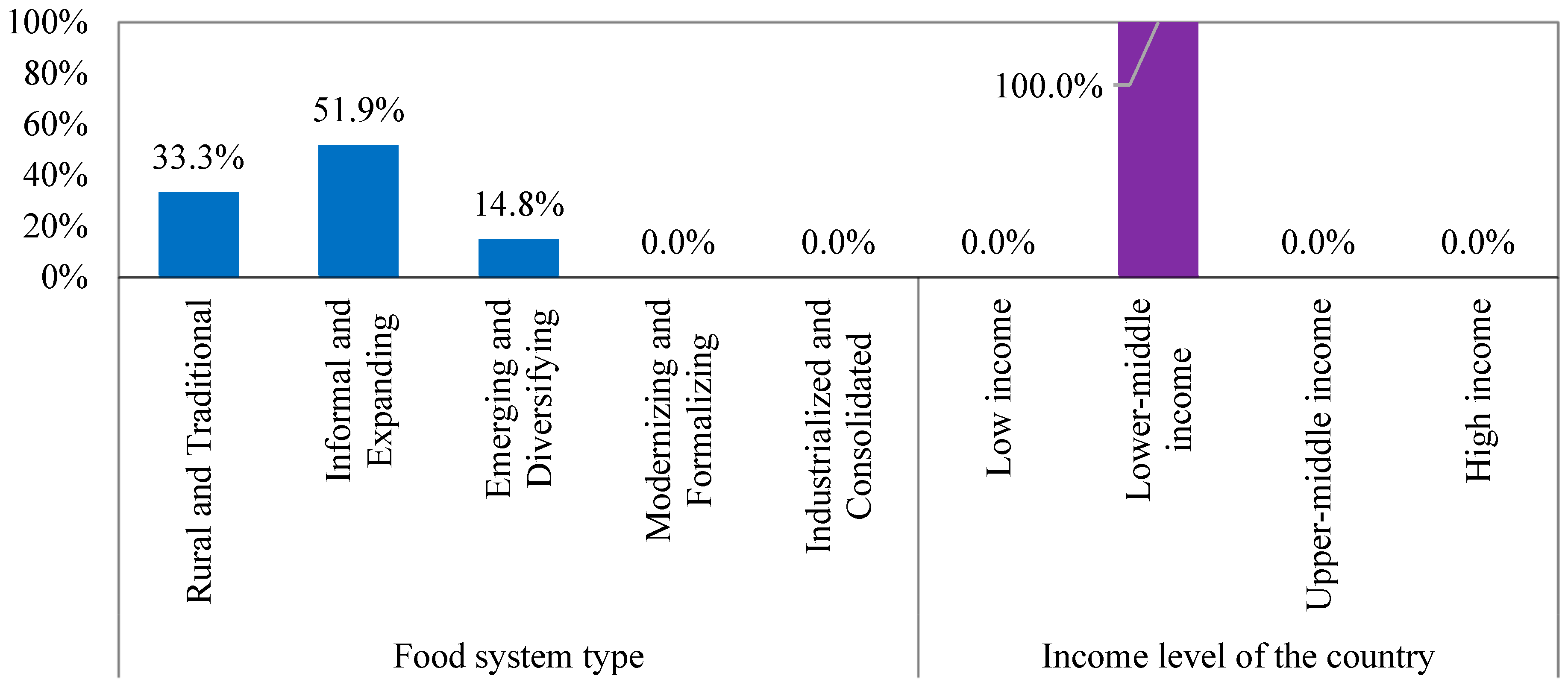
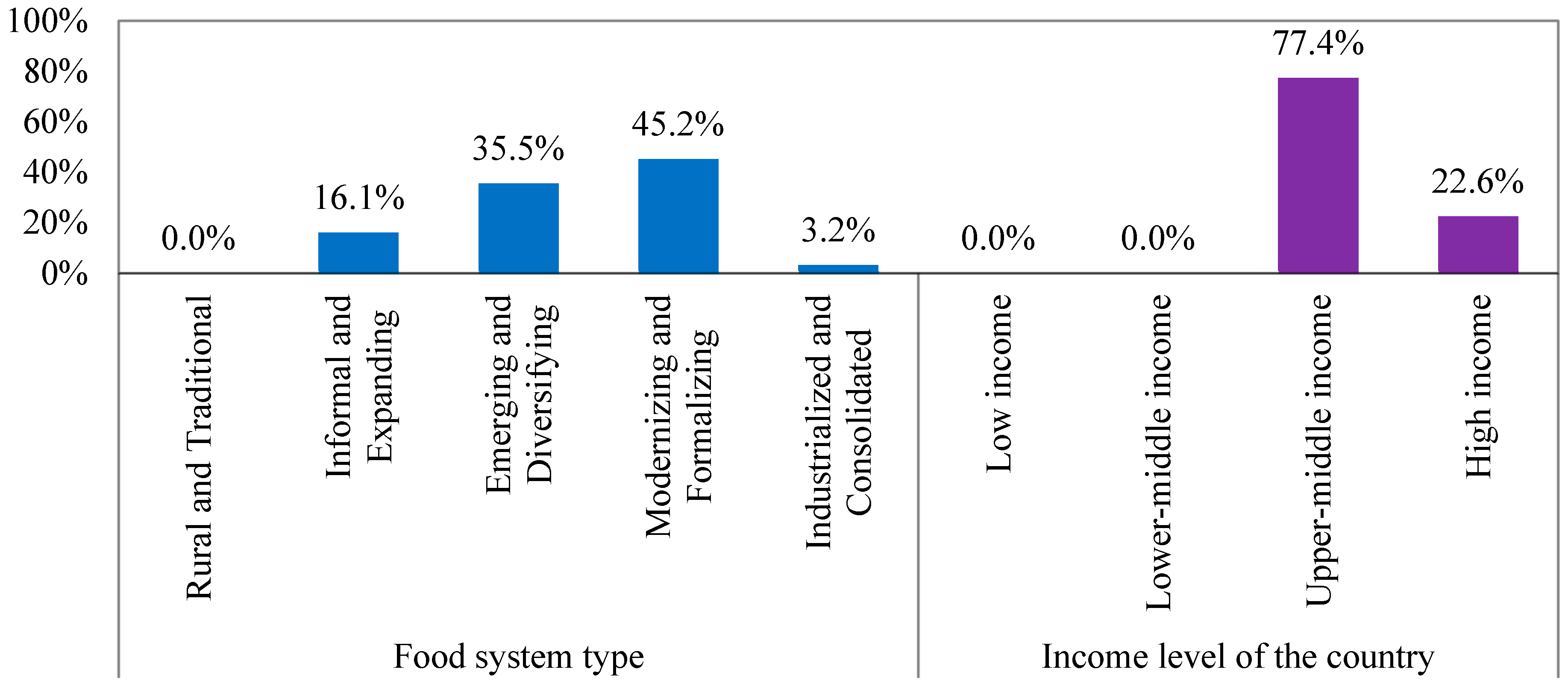
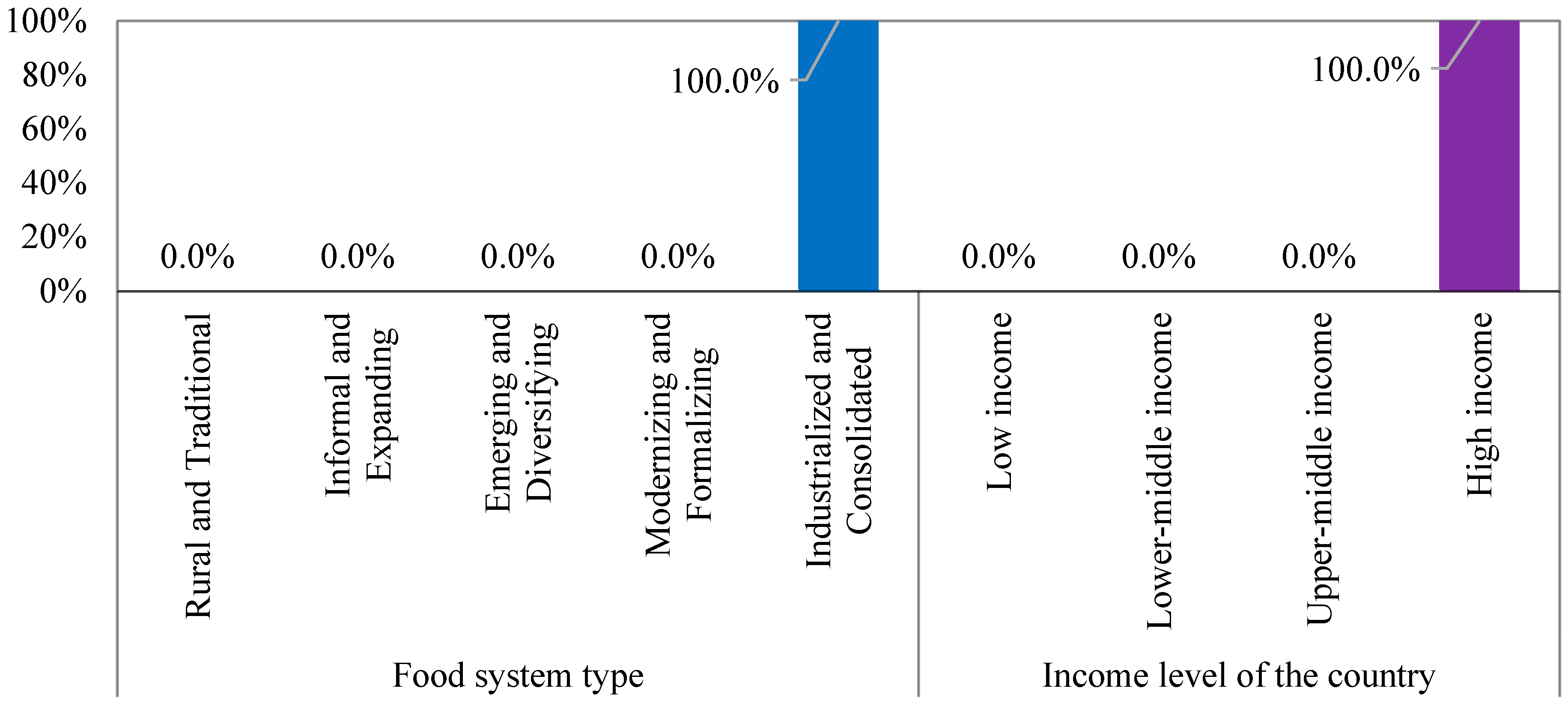
| Category | No. | Indicators | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affordability (AFF) | 1 | Change in the food costs | CFC |
| 2 | Proportion of population under the global poverty line | PPUGP | |
| 3 | Inequality-adjusted income index | IAII | |
| 4 | Agricultural import tariffs | AIT | |
| 5 | Food safety net programs | FSNP | |
| 6 | Market access and agricultural financial services | MAAFS | |
| Availability (AVA) | 7 | Sufficiency of supply | SOS |
| 8 | Agricultural research and development | ARAD | |
| 9 | Agricultural infrastructure | AIS | |
| 10 | Volatility of agricultural production | VOAP | |
| 11 | Political and social barriers to access | PASBA | |
| 12 | Food loss | FL | |
| 13 | Food security and access policy commitments | FSAAPC | |
| Quality and safety (QAS) | 14 | Dietary diversity | DD |
| 15 | Nutritional standards | NS | |
| 16 | Micronutrient availability | MA | |
| 17 | Protein quality | PQ | |
| 18 | Food safety | FS | |
| Natural resources and resilience (NR&R) | 19 | Exposure | E |
| 20 | Water | W | |
| 21 | Land | L | |
| 22 | Oceans, rivers, and lakes | ORL | |
| 23 | Sensitivity | S | |
| 24 | Political commitment to adoption | PCTA | |
| 25 | Demographic stress | DS |
| Variable | GFSI | NR&R | E | W | L | ORL | S | PCTA | DS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFSI | 1.000 | 0.684 | −0.036 | 0.531 | 0.315 | −0.352 | 0.243 | 0.535 | 0.803 |
| NR&R | 0.684 | 1.000 | 0.135 | 0.694 | 0.428 | −0.158 | 0.399 | 0.796 | 0.571 |
| E | −0.036 | 0.135 | 1.000 | −0.061 | 0.064 | −0.083 | −0.016 | −0.028 | −0.199 |
| W | 0.531 | 0.694 | −0.061 | 1.000 | 0.271 | −0.098 | 0.038 | 0.390 | 0.385 |
| L | 0.315 | 0.428 | 0.064 | 0.271 | 1.000 | −0.051 | −0.075 | 0.094 | 0.227 |
| ORL | −0.352 | −0.158 | −0.083 | −0.098 | −0.051 | 1.000 | −0.386 | −0.306 | −0.401 |
| S | 0.243 | 0.399 | −0.016 | 0.038 | −0.075 | −0.386 | 1.000 | 0.317 | 0.426 |
| PCTA | 0.535 | 0.796 | −0.028 | 0.390 | 0.094 | −0.306 | 0.317 | 1.000 | 0.406 |
| DS | 0.803 | 0.571 | −0.199 | 0.385 | 0.227 | −0.401 | 0.426 | 0.406 | 1.000 |
| Rank Change | Number of Countries | Percentage, % |
|---|---|---|
| No change | 70 | 75 |
| +/− 1 rank | 17 | 18 |
| +/− 2 ranks | 6 | 6 |
| +/− 3 ranks | 1 | 1 |
| +/− ≥4 ranks | 0 | 0 |
| Category | Indicator | Coefficient Estimators | Reduction, % | Average Reduction, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M1 | M2 | |||
| Affordability | CFC | - | 50.00 | 66.67 | 58.34 | |
| PPUGP | 0.06 | 0.004 | ||||
| AIT | −0.02 | - | ||||
| FSNP | 0.45 | 0.35 | ||||
| Availability | SOS | −0.03 | - | 57.14 | 70.14 | 63.64 |
| ARAD | −0.05 | - | ||||
| PASBA | - | −0.003 | ||||
| FL | - | - | ||||
| FSAAPC | 0.09 | 0.15 | ||||
| Quality and safety | DD | - | - | 40.00 | 60.00 | 50.00 |
| NS | −0.02 | - | ||||
| MA | −0.13 | −0.07 | ||||
| PQ | 0.05 | 0.01 | ||||
| FS | - | - | ||||
| Natural resources and resilience | E | 0.06 | 0.08 | 28.57 | 57.14 | 42.86 |
| L | −0.34 | −0.27 | ||||
| ORL | 0.02 | - | ||||
| S | −0.06 | −0.01 | ||||
| PCTA | −0.05 | - | ||||
| DS | 0.06 | - | ||||
| Rank Change | Number of Countries | Percentage, % |
|---|---|---|
| No change | 18 | 19.15 |
| +/− 1 rank | 9 | 9.57 |
| +/− 2 ranks | 14 | 14.89 |
| +/− 3 ranks | 8 | 8.51 |
| +/− ≥4 ranks | 45 | 47.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
A. Al-Ansari, M.; Nabeel, H.; Abdella, G.M.; El Mekkawy, T. Moving Beyond Indices: A Systematic Approach Integrating Food System Performance and Characteristics for Comprehensive Food Security Assessment. Foods 2025, 14, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101834
A. Al-Ansari M, Nabeel H, Abdella GM, El Mekkawy T. Moving Beyond Indices: A Systematic Approach Integrating Food System Performance and Characteristics for Comprehensive Food Security Assessment. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101834
Chicago/Turabian StyleA. Al-Ansari, Muna, Hamad Nabeel, Galal M. Abdella, and Tarek El Mekkawy. 2025. "Moving Beyond Indices: A Systematic Approach Integrating Food System Performance and Characteristics for Comprehensive Food Security Assessment" Foods 14, no. 10: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101834
APA StyleA. Al-Ansari, M., Nabeel, H., Abdella, G. M., & El Mekkawy, T. (2025). Moving Beyond Indices: A Systematic Approach Integrating Food System Performance and Characteristics for Comprehensive Food Security Assessment. Foods, 14(10), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101834






