The Impact of Peeling on Highland Barley’s Digestive Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nutritional Components
2.2.1. Total Starch
2.2.2. Dietary Fiber
2.2.3. β-Glucan
2.3. Extraction of Polyphenols
2.4. Total Phenol Content
2.5. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Capacity
2.5.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Capacity
2.5.3. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Capacity
2.6. In Vitro Starch Digestibility Analysis
2.7. Rheological Simulation of Highland Barley Digestion
2.8. Microstructure Analysis
2.9. Animal Experiment
2.10. Gut Microbiota Analysis by 16S rDNA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutritional Composition
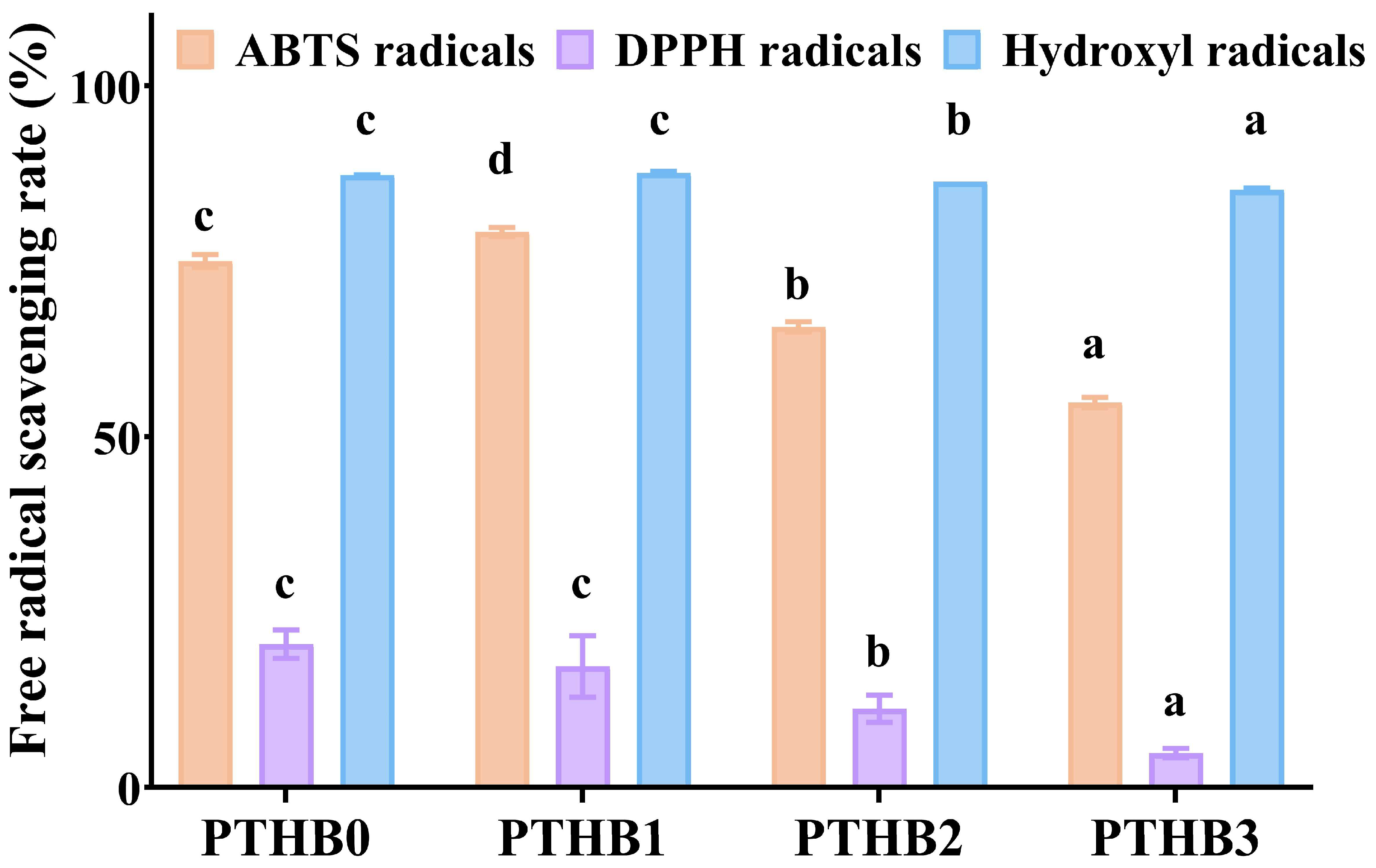
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. In Vitro Starch Digestibility
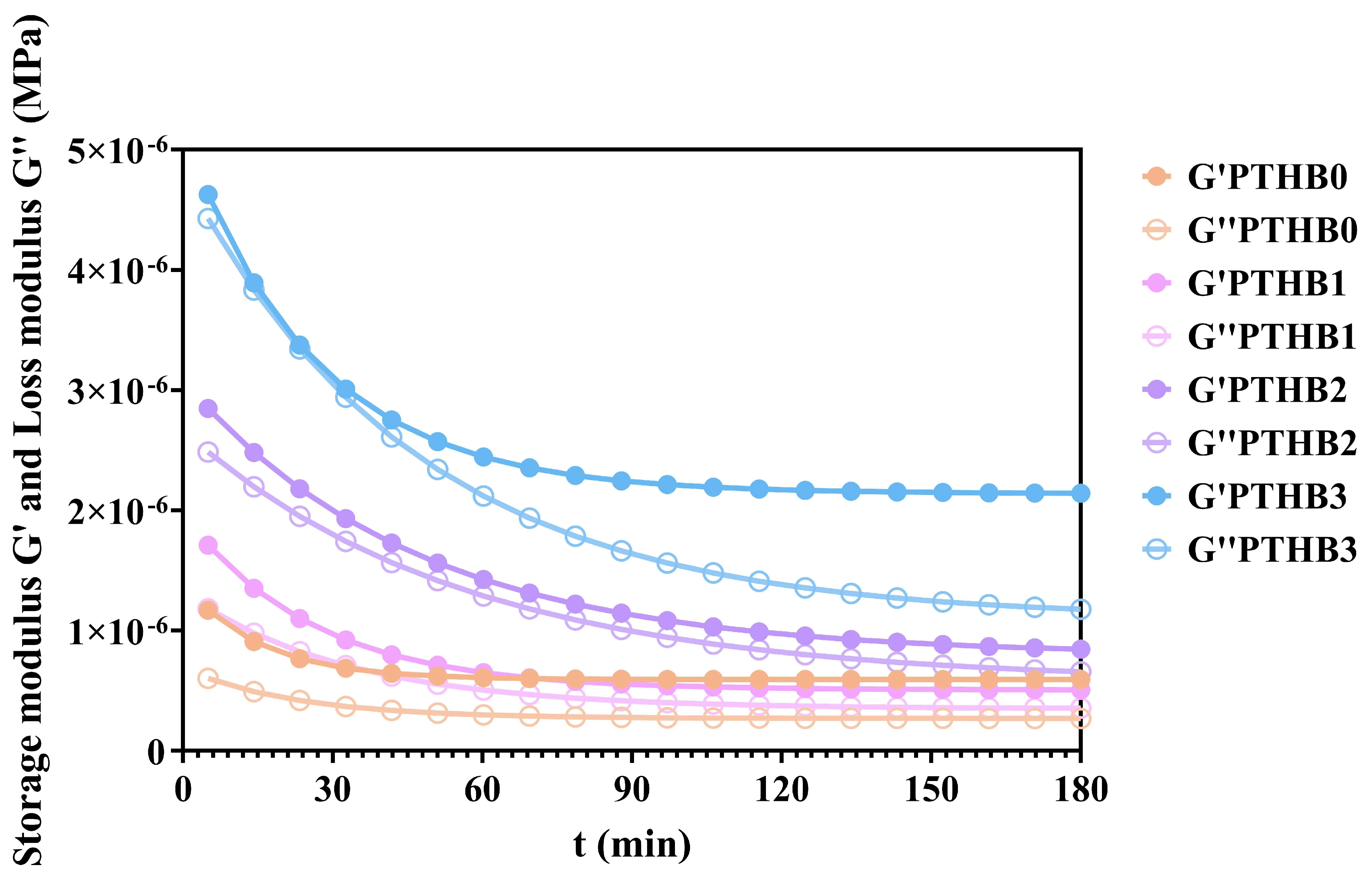
3.4. Rheological Simulation
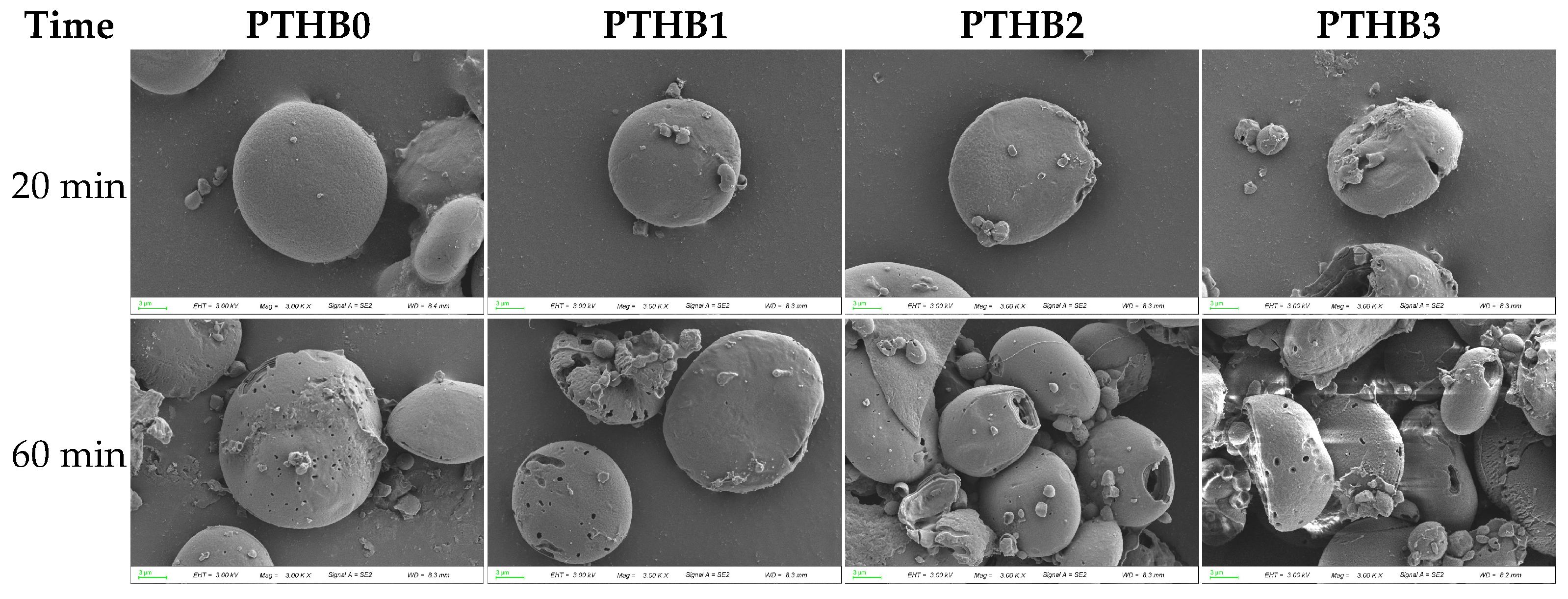
3.5. Microstructure
3.6. Hypoglycemic Activity
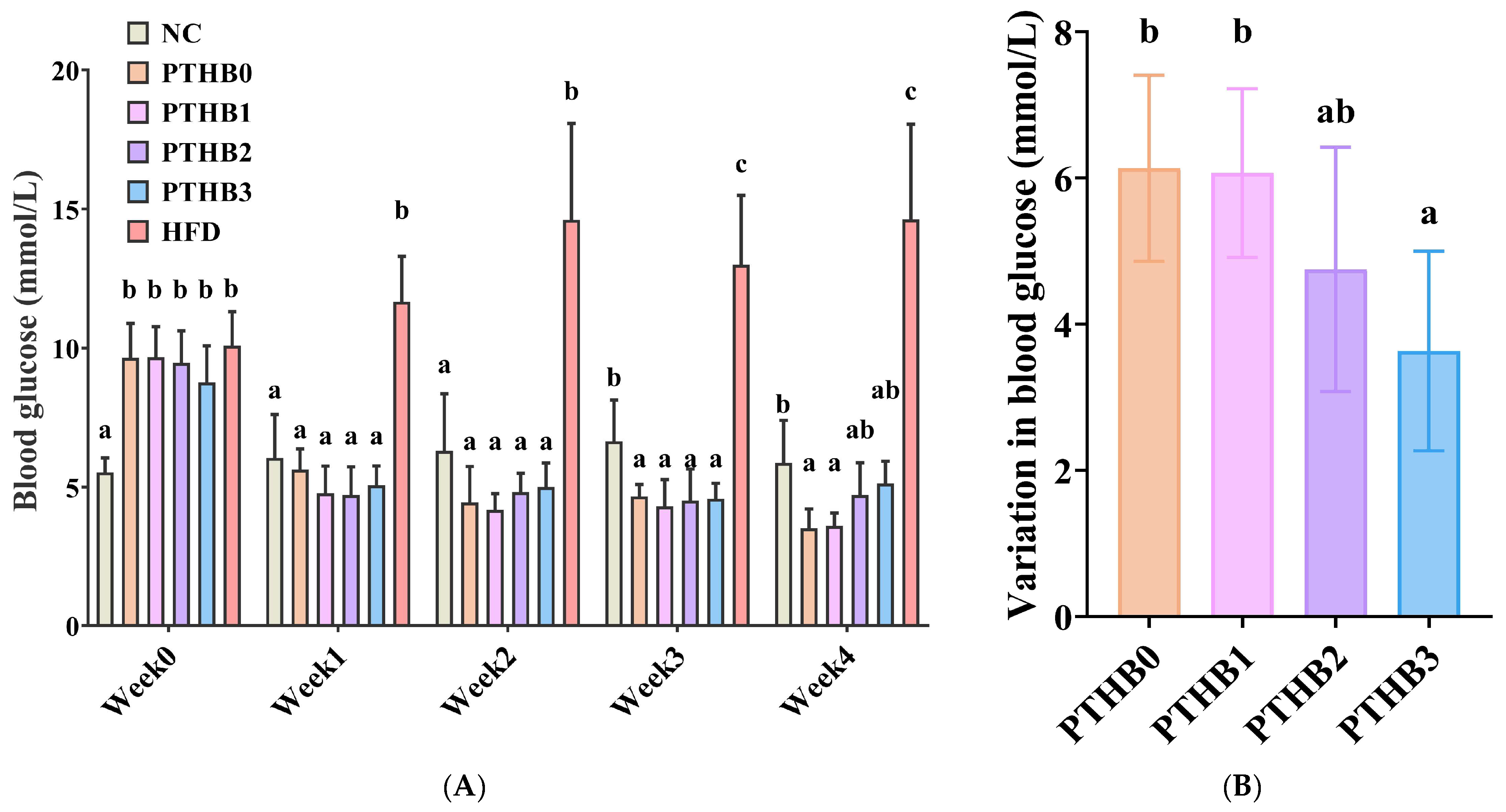
3.6.1. Fasting Blood Glucose in Mice
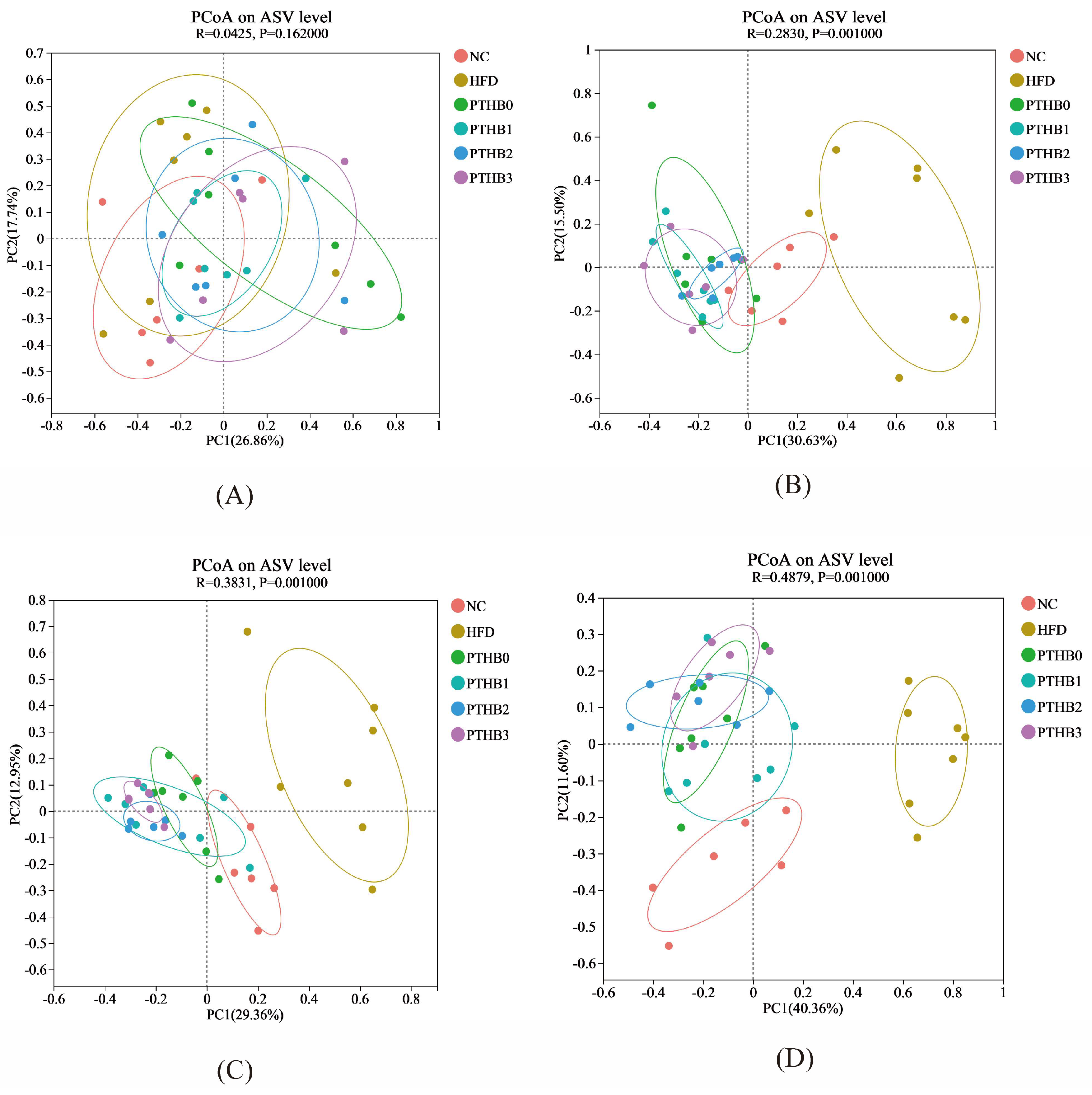
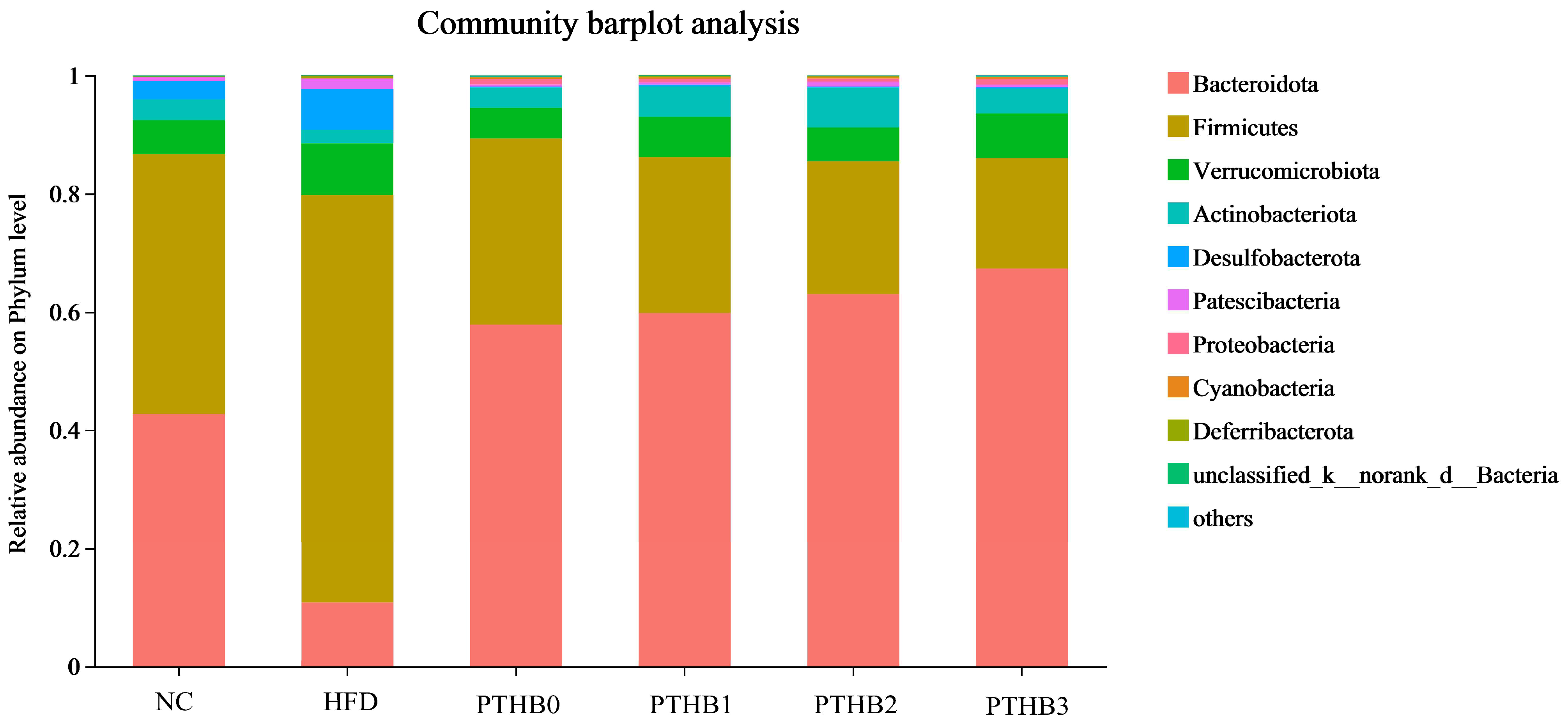
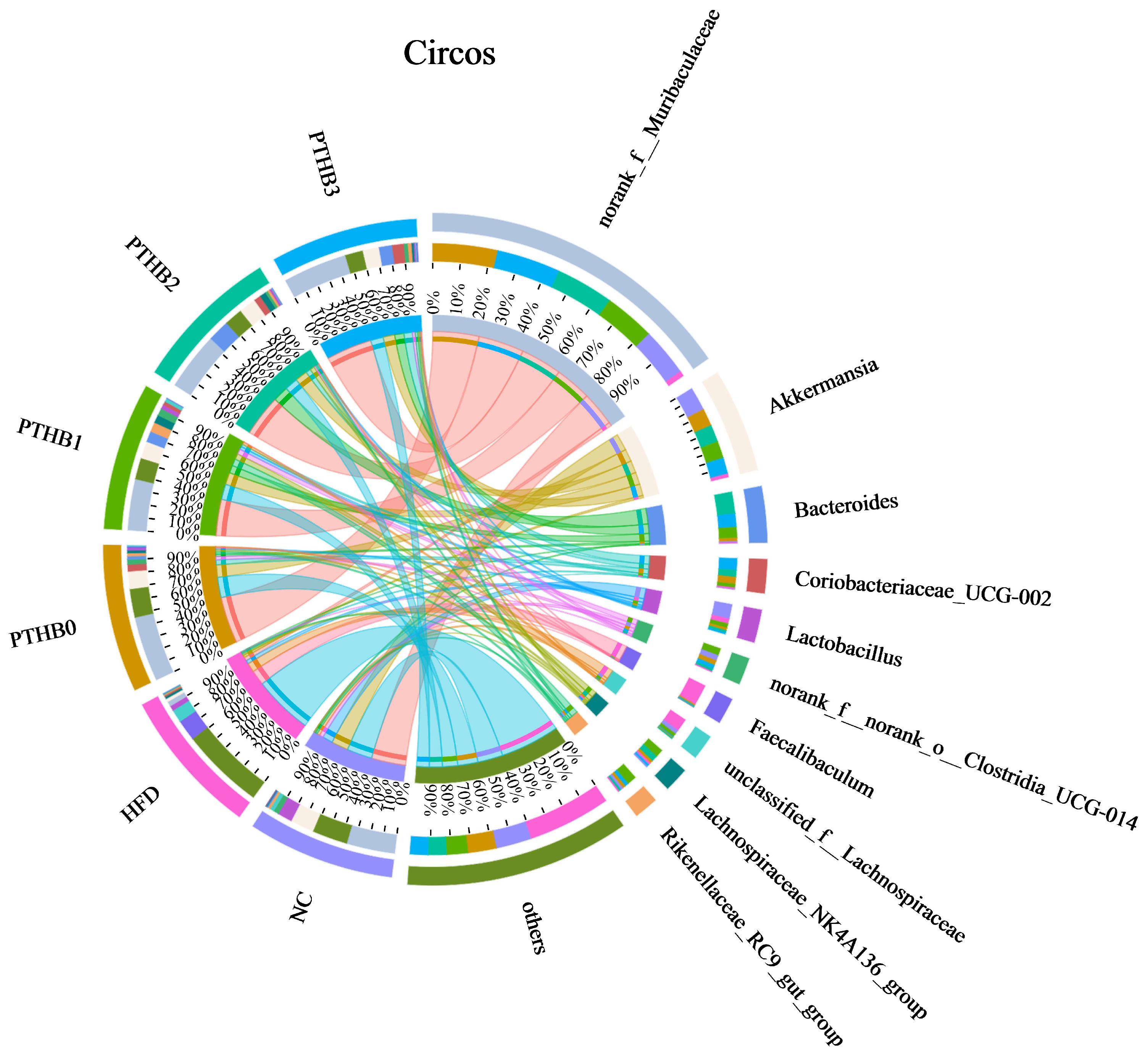
3.6.2. Gut Microbiota in Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PTHB0 | Unpeeled highland barley |
| PTHB1 | Highland barley with one peeling |
| PTHB2 | Highland barley with two peelings |
| PTHB3 | Highland barley with three peelings |
References
- Yin, Y.Y.; Wang, J.A.; Leng, G.Y.; Zhao, J.T.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.D. Future potential distribution and expansion trends of highland barley under climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau (QTP). Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Horvath, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, B. Understanding the nutrient composition and nutritional functions of highland barley (Qingke): A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland barley: Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, health effects, and applications. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.T.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Bioactive compounds of highland barley and their health benefits. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 103, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yue, M.; Jing, H.; Peng, W.J.; Pi, R.B.; Bo, Y.; Zeyu, Z. T-Fiber, A Highland Barley Fiber-Rich Powder, Alleviates Hyperglycemia and Improves Kidney Pathology in Db/db Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2023, 2023, 4165718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.L.; Shen, J. Molecular mechanism of microRNA-mediated hypoglycemic effect of whole grain highland barley. Gene 2024, 895, 148021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiao, A.; Liu, Q.; Ren, X.; Zhu, K.; Jin, Z. The effects of removing endogenous proteins, β-glucan and lipids on the surface microstructure, water migration and glucose diffusion in vitro of starch in highland barley flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H. Methylglyoxal scavenging capacity of fiber-bound polyphenols from highland barley during colonic fermentation and its modulation on methylglyoxal-interfered gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Zang, Y.; Cao, Y. Effects of highland barley β-glucan on gut microbiota composition and metabolism in vitro fermentation. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Gao, N.; Xu, X.; Zhao, R. Ultrafine grinding improves the nutritional, physicochemical, and antioxidant activities of two varieties of whole-grain highland barley. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 1960–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Yang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Zhu, B.; Shi, Z.; Xiang, Z. Distribution of free and bound phenolic compounds, β-glucan, and araboxylan in fractions of milled hulless barley. LWT 2022, 169, 113935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Meng, Q.; Meng, Y.; Ying, J.; Bai, S.; Shen, Q.; Xue, Y. Beneficial Effects of Partly Milled Highland Barley on the Prevention of High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycometabolic Disorder and the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.L.; Hergert, N.; Rompato, G.; Lefevre, M. Whole Grain Oats Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Plasma Cholesterol Profile and Modify Gut Microbiota Composition in C57BL/6J Mice1, 2, 3. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mio, K.; Yamanaka, C.; Kohyama, N.; Ichinose, Y.; Yanagisawa, T.; Aoe, S. Effect of roasted barley flour on lipid metabolism and gut fermentation in mice fed high-fat diets. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis (925); The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Nie, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, J.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Wang, L. Effect of boiling and roasting on phenolic components and their bioaccessibilities of highland barley. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Dong, W.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, H.; Ren, N.; Luo, L.Y.; Li, Y. The bioaccessibility and bioactivity of polyphenols from tsampa prepared from roasted highland barley flour solid-fermented by autochthonous lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Jiao, A.Q.; Zhao, S.N.; Liu, Q.; Fu, X.; Jin, Z.Y. Effect of removal of endogenous non-starch components on the structural, physicochemical properties, and in vitro digestibility of highland barley starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; He, Y.-X.; Wang, H.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhong, Y.-d.; Hu, X.-T.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y.; Hu, J.-L. Impact of eight extruded starchy whole grains on glycemic regulation and fecal microbiota modulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Xing, D.; Wang, W.; Yang, Q.; Liao, S.; Li, E.; Pang, D.; Zou, Y. Effects of Cinnamon Powder on Glucose Metabolism in Diabetic Mice and the Molecular Mechanisms. Foods 2023, 12, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Qi, Y.; Xu, B. Highland barley starch (Qingke): Structures, properties, modifications, and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Deng, N.; Zheng, B.; Cui, C. Effects of milling behavior on the distribution of nutrients and storage properties of highland barley graded powder. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 111, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y.; Dang, B. Study of the effect of milling on nutritional and sensory quality and volatile flavor compounds of cooked highland barley rice. LWT 2024, 198, 115972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of polyphenols extracted from black highland barley. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofuji, K.; Aoki, A.; Tsubaki, K.; Konishi, M.; Isobe, T.; Murata, Y. Antioxidant Activity of beta-Glucan. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 125864. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.D.; Shi, M.M.; Zhao, Y.T.; Chen, B.L.; He, Y.J.; Wang, M.Y. Dietary compounds slow starch enzymatic digestion: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1004966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korompokis, K.; Verbeke, K.; Delcour, J.A. Structural factors governing starch digestion and glycemic responses and how they can be modified by enzymatic approaches: A review and a guide. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5965–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cheng, L.L.; Wu, G.C. Structural barriers governing starch digestibility in intact highland barley cells: A closer insight from cell wall and protein matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.C.; Cheng, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Unraveling cereal physical barriers composed of cell walls and protein matrix: Insights from structural changes and starch digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, A.S.; Bordenave, N. Whole grain chemistry and nutrition from a health perspective: Understanding the fibre-phenolic-starch ménage à trois. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T. Impact of chemical and rheological properties on 3D printability and starch digestibility of potato pastes from different cultivars. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Singh, R.; de Campo, L.; Gilbert, E.P.; Wu, Z.; Hemar, Y. Effect of amyloglucosidase hydrolysis on the multi-scale supramolecular structure of corn starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.W. Multi-scale structural and digestion properties of wheat starches with different amylose contents. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, A.; Wu, K.; Chuang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, C. Effects of highland barley β-glucan on blood glucose and gut microbiota in streptozotocin-induced, diabetic, C57BL/6 mice on a high-fat diet. Nutrition 2023, 107, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Xie, H.F.; Shi, W.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Jiang, D.; Hu, H.; Zheng, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Purification, Preliminary Structural Characterization, and In Vitro Inhibitory Effect on Digestive Enzymes by β-Glucan from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley). Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 2709536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Edwards, M.; Huang, Y.M.; Bilate, A.M.; Araujo, L.P.; Tanoue, T.; Atarashi, K.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Reiner, S.L.; Wang, H.H.; et al. Microbiota imbalance induced by dietary sugar disrupts immune-mediated protection from metabolic syndrome. Cell 2022, 185, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, X.X.; Dai, F.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Tong, X.L. Ameliorative Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei L14 on Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Chang, S.Y.; Jin, Z.Y.; Li, D.X.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Z.B.; Han, S.-Z.; Kang, J.-D.; Quan, L.-H. Lactobacillus reuteri-Enriched Eicosatrienoic Acid Regulates Glucose Homeostasis by Promoting GLP-1 Secretion to Protect Intestinal Barrier Integrity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 73, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huan, M. Fecal microbiota transplantation: Whole grain highland barley improves glucose metabolism by changing gut microbiota. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2014–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | C∞ (%) | k (10−3 min−1) | GI |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTHB0 | 81.44 ± 4.27 a | 8.22 ± 0.92 a | 68.99 ± 1.41 a |
| PTHB1 | 81.62 ± 4.80 a | 8.71 ± 0.18 ab | 70.17 ± 2.14 a |
| PTHB2 | 86.20 ± 0.07 ab | 9.67 ± 0.70 bc | 73.56 ± 1.36 b |
| PTHB3 | 88.81 ± 1.80 b | 10.04 ± 0.62 c | 75.38 ± 0.67 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, F.; Ai, L. The Impact of Peeling on Highland Barley’s Digestive Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Insights. Foods 2025, 14, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101686
Yan Y, Gao X, Zhang Y, Xie F, Ai L. The Impact of Peeling on Highland Barley’s Digestive Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Insights. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101686
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yuting, Xin Gao, Yi Zhang, Fan Xie, and Lianzhong Ai. 2025. "The Impact of Peeling on Highland Barley’s Digestive Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Insights" Foods 14, no. 10: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101686
APA StyleYan, Y., Gao, X., Zhang, Y., Xie, F., & Ai, L. (2025). The Impact of Peeling on Highland Barley’s Digestive Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Insights. Foods, 14(10), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101686






