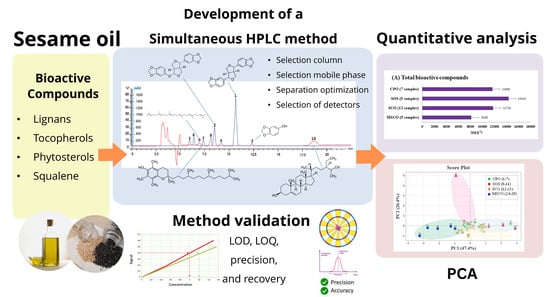
Development of a Simultaneous Normal-Phase HPLC Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene in Sesame Oil Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sesame Oil Samples
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. HPLC-DAD-FLD Analysis
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of Simultaneous Determination of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene
3.2. Method Validation
3.2.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
3.2.2. Precision and Accuracy
3.2.3. Recovery
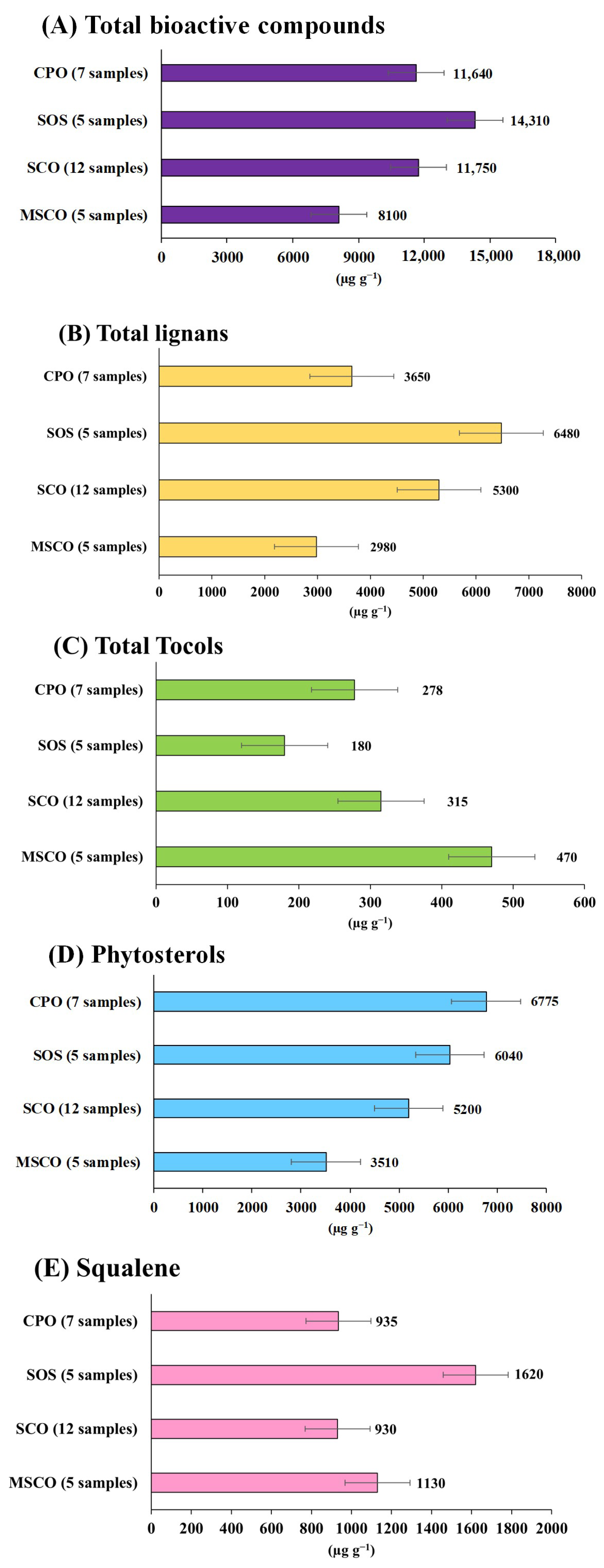
3.3. Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Squalene, and Phytosterol in Sesame Oil Samples
3.4. Statistical Analysis of Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPO | Cold-pressed sesame oil |
| DAD | Diode array detector |
| FLD | Fluorescence detector |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MSCO | Sesame cooking oil mixed with other oil |
| NP | Normal-phase |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| RP | Reverse-phase |
| RSDs | Relative standard deviations |
| SCO | Sesame cooking oil |
| SOS | Sesame oil supplement |
References
- Pathak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Kumari, R.; Thapa, A.; Bhat, K.V.; Srinivasan, R. Variation in biochemical components in black (Sesamum indicum L.) and white (Sesamum indicum L.) sesame seeds collected from different regions of India. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, S.C.; Cho, Y.J.; Oh, J.H.; Kwon, K.; Kim, B.H. A triple isotope approach for discriminating the geographic origin of Asian sesame oils. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Man, Y.B.; Liu, J. Quality characteristics of cold-pressed sesame oil obtained from different methods. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C739–C746. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Kumari, R. Quality characteristics of sesame oil extracted from some Indian varieties. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Langyan, S.; Yadava, P.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, N.C.; Bansal, R.; Yadav, R.; Kalia, S.; Kumar, A. Food and nutraceutical functions of Sesame oil: An underutilized crop for nutritional and health benefits. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 132990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.S. Sesame oil. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 6th ed.; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 547–552. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, K.; Krishnakumari, S. Phytochemical analysis of Achyranthes aspera and its activity on sesame oil induced lipid peroxi-dation. Anc. Sci. Life. 2007, 27, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Elleuch, M.; Bedigian, D.; Zitoun, A. Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds in food, nutrition, and health. In Nuts and Seeds in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1029–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Moazzami, A.A.; Haese, S.L.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Lignan contents in sesame seeds and products. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Bhaduri, A.; Rai, A.K. Sesame: Bioactive Compounds and Health Benefits; Bioactive Molecules in Food; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fort Wayne, M.; Ro, J. Squalene: A potential chemopreventive agent. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010, 10, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.V.; Newmark, H.L.; Reddy, B.S. Chemopreventive effect of squalene on colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; Galvin, K.; O’Connor, T.P.; Maguire, A.R.; O’Brien, N.M. Phytosterol, squalene, tocopherol content and fatty acid profile of selected seeds, grains, and legumes. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M.; Sherma, J. (Eds.) High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Phytochemical Analysis; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Finn, C.E. Determination of lignans in flaxseed by HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8126–8131. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, R.A.; Hicks, K.B. The in vitro hydrolysis and fermentation of squalene and phytosterols by human fecal inoculum. Lipids 2004, 39, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, H. Determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in cereals by HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4689–4694. [Google Scholar]
- Pokkanta, P.; Sookwong, P.; Tanang, M.; Setchaiyan, S.; Boontakham, P.; Mahatheeranont, S. Simultaneous determination of tocols, γ-oryzanols, phytosterols, squalene, cholecalciferol and phylloquinone in rice bran and vegetable oil samples. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Ellison, S.L.; Fajgelj, A.; Willetts, P.; Wood, R. Harmonized guidelines for the use of recovery information in analytical measurement. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G. Chemometrics: Data Analysis for the Laboratory and Chemical Plant; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2003; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Brereton, R.G. Chemometrics for Pattern Recognition; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.Y.; Yun, C.I.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, Y.J. Determination and daily intake estimation of lignans in sesame seeds and sesame oil products in Korea. Foods 2020, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Cao, L.; Zheng, D.; Lei, Z.; Ge, Y.; Cheng, J.; Cao, L. Simultaneous detection of lignans and tocopherols in sesame oil by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Authorea 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.K.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, Y.F.; Liu, R.J.; Chang, M.; Jin, Q.Z.; Wang, X.G. A rapid method for simultaneous analysis of lignan and γ-tocopherol in sesame oil by using normal-phase liquid chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Bi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, D. Simultaneous determination of α-tocopherol, β-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, δ-tocopherol, sesamin, sesamolin, sesamol, and asarinin in sesame oil by normal-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2021, 104, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, A.A.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Sesame seed is a rich source of dietary lignans. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Chen, S.; Wu, T.S. The facile reversed-phase HPLC resolution of tetrahydrofurofuran nucleus lignans in traditional Chinese medicine: Quantitative analysis of asarinin and sesamin in Asari radix. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2003, 50, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Saarinen, N.M.; Thompson, L.U. Sesamin is one of the major precursors of mammalian lignans in sesame seed (Sesamum indicum) as observed in vitro and in rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.R.; Lee, J.S. Determination of sesamin and sesamolin in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds using UV spectrophotometer and HPLC. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2006, 51, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. HPLC analysis of seed sesamin and sesamolin variation in a sesame germplasm collection in China. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangkadilok, N.; Pholphana, N.; Mahidol, C.; Wongyai, W.; Saengsooksree, K.; Nookabkaew, S.; Satayavivad, J. Variation of sesamin, sesamolin and tocopherols in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds and oil products in Thailand. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, K.S.; Morris, J.B.; Pye, Q.N.; Kamat, C.D.; Hensley, K. A survey of sesamin and composition of tocopherol variability from seeds of eleven diverse sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes using HPLC-PAD-ECD. Phytochem. Anal. 2008, 19, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.M.A.; Awatif, I.I. The use of sesame oil unsaponifiable matter as a natural antioxidant. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuenyong, J.; Pokkanta, P.; Phuangsaijai, N.; Kittiwachana, S.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Sookwong, P. GC-MS and HPLC-DAD analysis of fatty acid profile and functional phytochemicals in fifty cold-pressed plant oils in Thailand. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, F.; Qamar, A.; Nadeem, M.T.; Ahmed, R.S.; Arshad, M.S.; Afzaal, M. Nutritional composition and fatty acid profile of some promising sesame cultivars. Pak. J. Food Sci. 2015, 25, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Tenyang, N.; Ponka, R.; Tiencheu, B.; Djikeng, F.T.; Azmeera, T.; Karuna, M.S.; Prasad, R.B.; Womeni, H.M. Effects of boiling and roasting on proximate composition, lipid oxidation, fatty acid profile and mineral content of two sesame varieties commercialized and consumed in Far-North Region of Cameroon. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
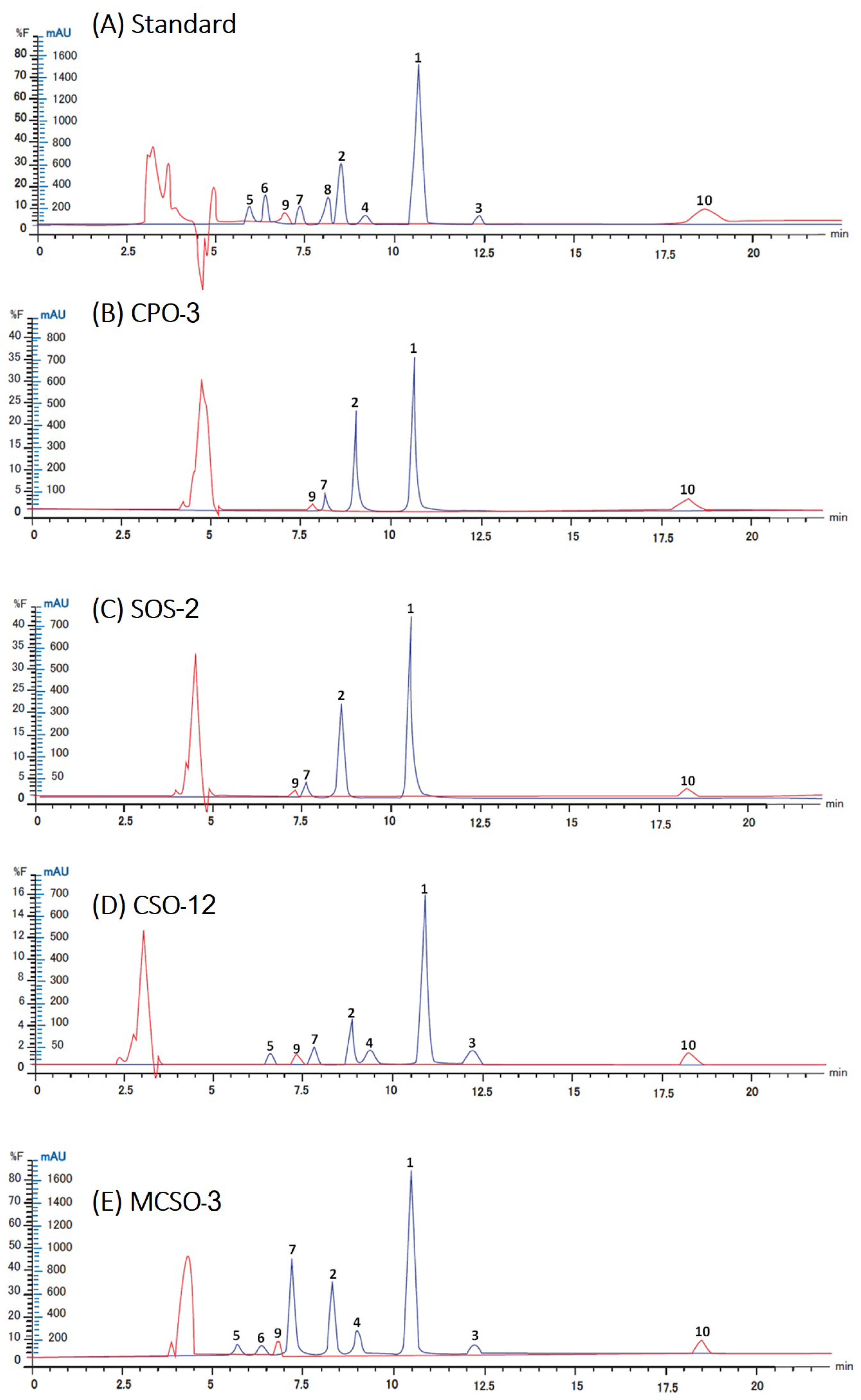

| Compounds | Retention Time (min) | Regression Equation | Correlation (R2) | LOD a (µg mL−1) | LOQ b (µg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sesamin | 10.34 | y = 36.705x − 2.918 | 0.9982 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Sesamolin | 8.94 | y =26.738x + 19.573 | 0.9901 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Sesamol | 11.73 | y = 46.016x + 13.691 | 0.9975 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Asarinin | 9.08 | y = 30.685x + 5.4833 | 0.9947 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| α-Tocopherol | 6.31 | y = 21.621x − 6.6543 | 0.9996 | 0.41 | 0.43 |
| β-Tocopherol | 6.97 | y = 41.061x + 3.1872 | 0.9998 | 0.35 | 0.42 |
| γ-Tocopherol | 7.52 | y = 44.828x + 3.2547 | 0.9999 | 0.40 | 0.42 |
| δ-Tocopherol | 8.44 | y = 43.128x + 15.908 | 0.9995 | 0.21 | 0.40 |
| Phytosterols | 18.17 | y = 6.2278x + 60.16 | 0.9992 | 10.04 | 10.34 |
| Squalene | 7.38 | y = 0.0453x − 5.2587 | 0.9986 | 307.07 | 326.23 |
| Compounds | Concentration (µg mL−1) | Intra-Day %RSD (n = 6) | Inter-Day %RSD (n = 3) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sesamin | Con 1 | 0.18 | 0.61 | 107.2 |
| Con 2 | 1.09 | 3.07 | 100.4 | |
| Con 3 | 0.78 | 3.02 | 104.8 | |
| Sesamolin | Con 1 | 0.14 | 0.66 | 99.3 |
| Con 2 | 0.35 | 1.39 | 100.2 | |
| Con 3 | 0.27 | 3.32 | 97.8 | |
| Sesamol | Con 1 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 91.6 |
| Con 2 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 102.8 | |
| Con 3 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 88.4 | |
| Asarinin | Con 1 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 101.1 |
| Con 2 | 0.42 | 1.46 | 99.7 | |
| Con 3 | 0.46 | 2.65 | 93.5 | |
| α-Tocopherol | Con 1 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 92.5 |
| Con 2 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 88.9 | |
| Con 3 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 96.7 | |
| β-Tocopherol | Con 1 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 102.0 |
| Con 2 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 109.4 | |
| Con 3 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 113.5 | |
| γ-Tocopherol | Con 1 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 100.0 |
| Con 2 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 98.5 | |
| Con 3 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 107.6 | |
| δ-Tocopherol | Con 1 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 102.6 |
| Con 2 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 90.6 | |
| Con 3 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 91.4 | |
| Squalene | Con 1 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 99.7 |
| Con 2 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 100.9 | |
| Con 3 | 0.22 | 0.46 | 104.7 | |
| Phytosterol | Con 1 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 91.0 |
| Con 2 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 92.5 | |
| Con 3 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 94.6 |
| Sample | Tocopherol | Lignan | Squalene | Phytosterols | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-T a | β-T | γ-T | δ-T | Sesamolin | Asarinin | Sesamin | Sesamol | |||
| CPO-1 | ND b | ND | 293.8 | ND | 2240 | ND | 2315 | ND | 875 | 6640 |
| CPO-2 | ND | ND | 286.6 | ND | 1275 | ND | 1260 | ND | 935 | 6385 |
| CPO-3 | ND | ND | 377.5 | ND | 1540 | ND | 1480 | ND | 1005 | 6690 |
| CPO-4 | ND | ND | 298.9 | ND | 1300 | ND | 1280 | ND | 960 | 6530 |
| CPO-5 | ND | ND | 324.8 | ND | 1645 | ND | 1620 | ND | 1030 | 6610 |
| CPO-6 | ND | ND | 194.2 | ND | 2800 | ND | 2990 | ND | 845 | 9500 |
| CPO-7 | ND | ND | 169.4 | ND | 1820 | ND | 1940 | ND | 910 | 5065 |
| SOS-1 | ND | ND | 162.0 | 1.3 | 1630 | ND | 1630 | ND | 4030 | 4885 |
| SOS-2 | ND | ND | 249.4 | ND | 3330 | ND | 3840 | ND | 995 | 5490 |
| SOS-3 | ND | ND | 29.7 | ND | 3000 | ND | 3540 | ND | 245 | 7055 |
| SOS-4 | ND | ND | 266.9 | ND | 4240 | ND | 4725 | ND | 1195 | 6725 |
| SCO-1 | 38.3 | 5.4 | 298.8 | ND | 2130 | 92.8 | 2495 | 7.6 | 875 | 4120 |
| SCO-2 | ND | ND | 391.6 | ND | 2615 | 122.8 | 3215 | 25.1 | 965 | 7020 |
| SCO-3 | ND | ND | 329.2 | ND | 2365 | 115.2 | 2690 | 9.5 | 990 | 6900 |
| SCO-4 | ND | ND | 250.9 | ND | 2175 | 168.9 | 2740 | 7.9 | 815 | 4560 |
| SCO-5 | ND | ND | 254.1 | ND | 2500 | 41.8 | 2900 | 5.5 | 905 | 5850 |
| SCO-6 | ND | ND | 275.3 | ND | 2850 | 132.9 | 3360 | 121.5 | 1040 | 5210 |
| SCO-7 | 147.8 | ND | 226.4 | ND | 1730 | 323.8 | 4360 | 30.5 | 620 | 3930 |
| SCO-8 | ND | ND | 400.7 | ND | 2300 | 157.8 | 2740 | 30.0 | 990 | 5495 |
| SCO-9 | ND | ND | 307.5 | ND | 1500 | 18.0 | 2980 | 42.8 | 1260 | 4610 |
| SCO-10 | ND | ND | 270.0 | ND | 2140 | 126.1 | 2440 | 20.4 | 990 | 4835 |
| SCO-11 | ND | ND | 283.0 | ND | 2860 | 60.3 | 3180 | 105.3 | 1050 | 5895 |
| SCO-12 | 80.0 | 18.9 | 206.7 | ND | 1490 | 12.7 | 2115 | ND | 705 | 4000 |
| MSCO-1 | 100.3 | 12.6 | 343.9 | ND | 420 | 145.2 | 1210 | ND | 1160 | 2640 |
| MSCO-2 | 53.2 | 14.1 | 311.9 | ND | 1390 | 104.5 | 1765 | 32.0 | 1115 | 4195 |
| MSCO-3 | 139.4 | 18.8 | 529.7 | ND | 685 | 213.1 | 1555 | 1.7 | 1175 | 3640 |
| MSCO-4 | 57.2 | 21.8 | 308.7 | ND | 1800 | 150.4 | 2525 | 7.8 | 1070 | 3995 |
| MSCO-5 | 67.8 | 14.7 | 357.9 | ND | 1215 | 183.5 | 1515 | 30.6 | 1130 | 3090 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuenyong, J.; Bennett, C.; Jiamyangyuen, S.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Sookwong, P. Development of a Simultaneous Normal-Phase HPLC Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene in Sesame Oil Samples. Foods 2024, 13, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091368
Yuenyong J, Bennett C, Jiamyangyuen S, Mahatheeranont S, Sookwong P. Development of a Simultaneous Normal-Phase HPLC Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene in Sesame Oil Samples. Foods. 2024; 13(9):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091368
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuenyong, Jitkunya, Chonlada Bennett, Sudarat Jiamyangyuen, Sugunya Mahatheeranont, and Phumon Sookwong. 2024. "Development of a Simultaneous Normal-Phase HPLC Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene in Sesame Oil Samples" Foods 13, no. 9: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091368
APA StyleYuenyong, J., Bennett, C., Jiamyangyuen, S., Mahatheeranont, S., & Sookwong, P. (2024). Development of a Simultaneous Normal-Phase HPLC Analysis of Lignans, Tocopherols, Phytosterols, and Squalene in Sesame Oil Samples. Foods, 13(9), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091368