Garlic Origin Traceability and Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Spectral Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
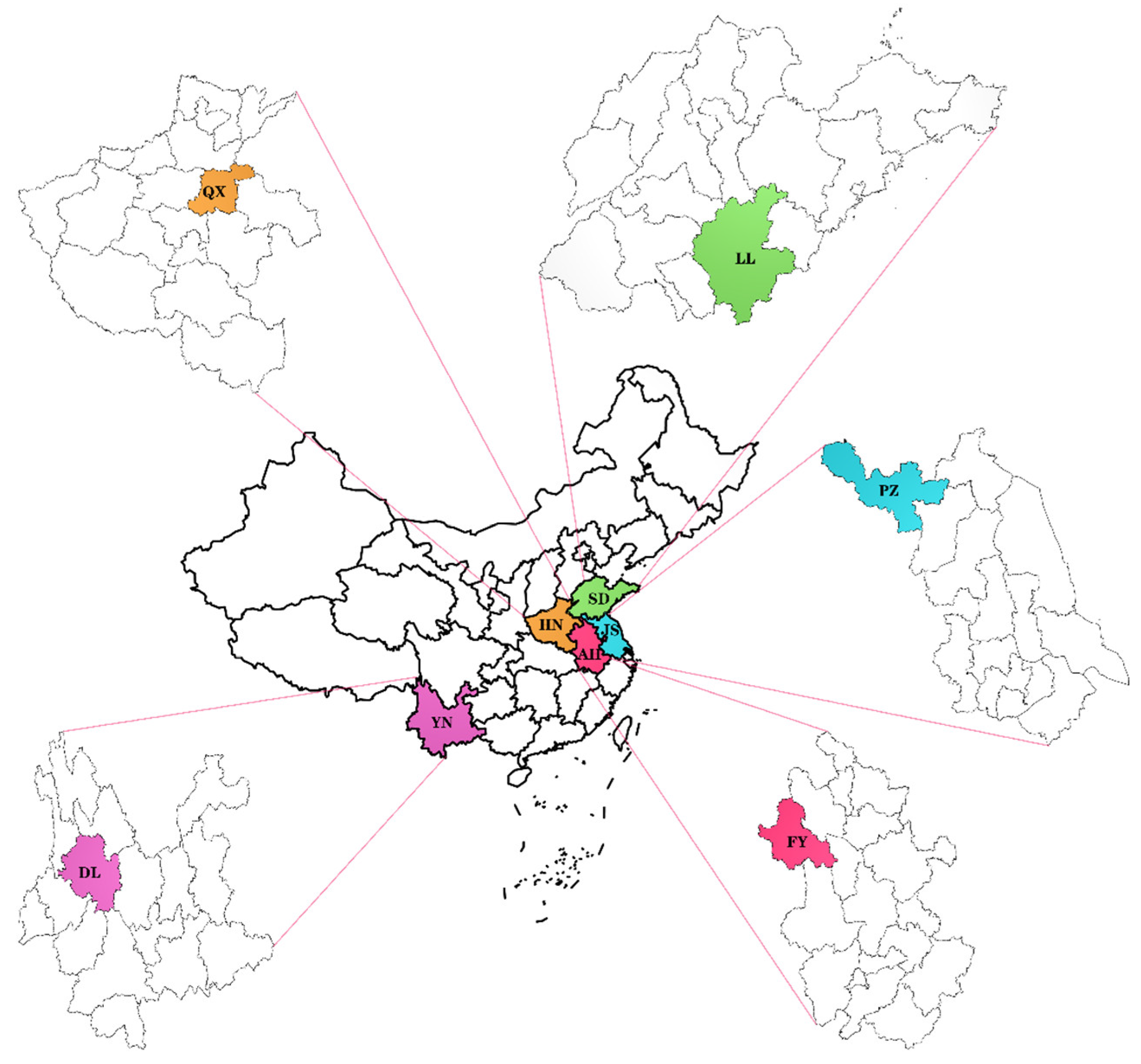
2.1. Sample Material
2.2. Spectra Acquisition
2.3. Spectral Pretreatment
2.4. Data Fusion
2.5. Modeling of Origin Classification
3. Results and Discussion
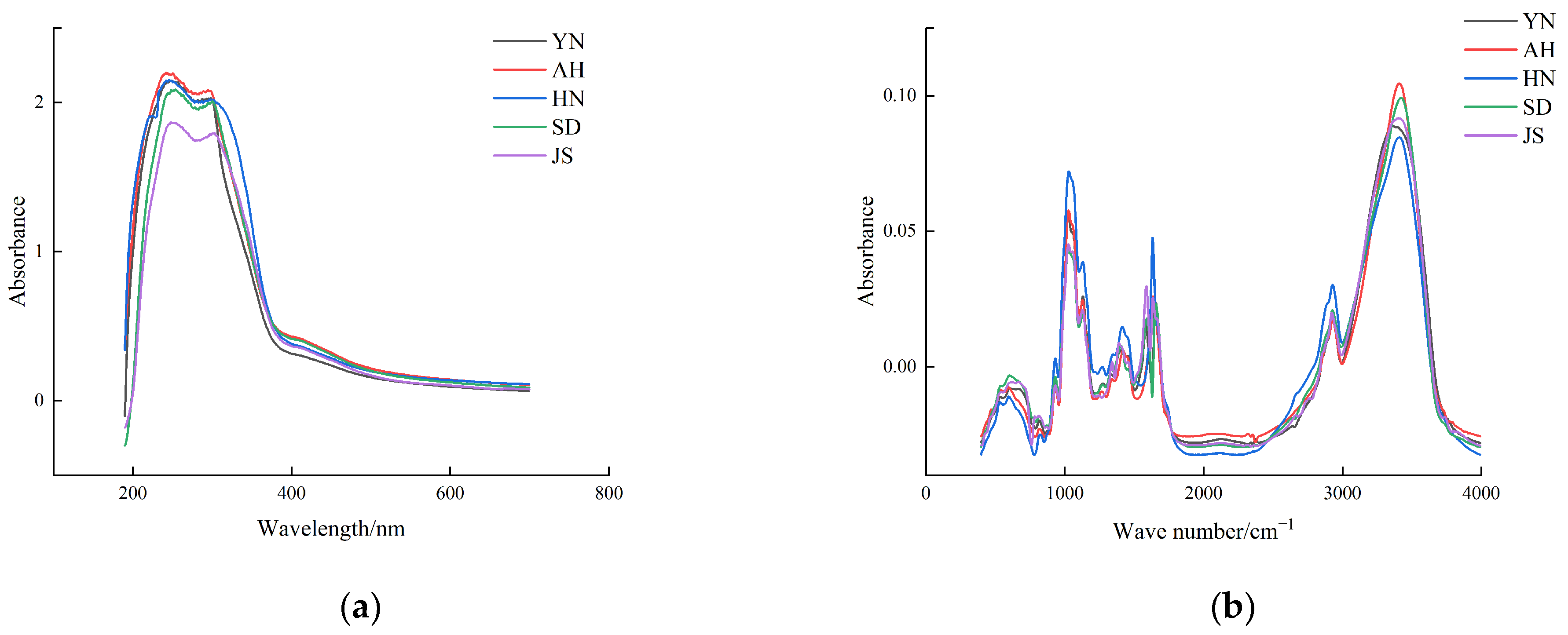
3.1. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Spectral Preprocessing
3.3. Extraction of Characteristics
3.4. Spectral Data Fusion
3.5. Model Evaluation Metrics
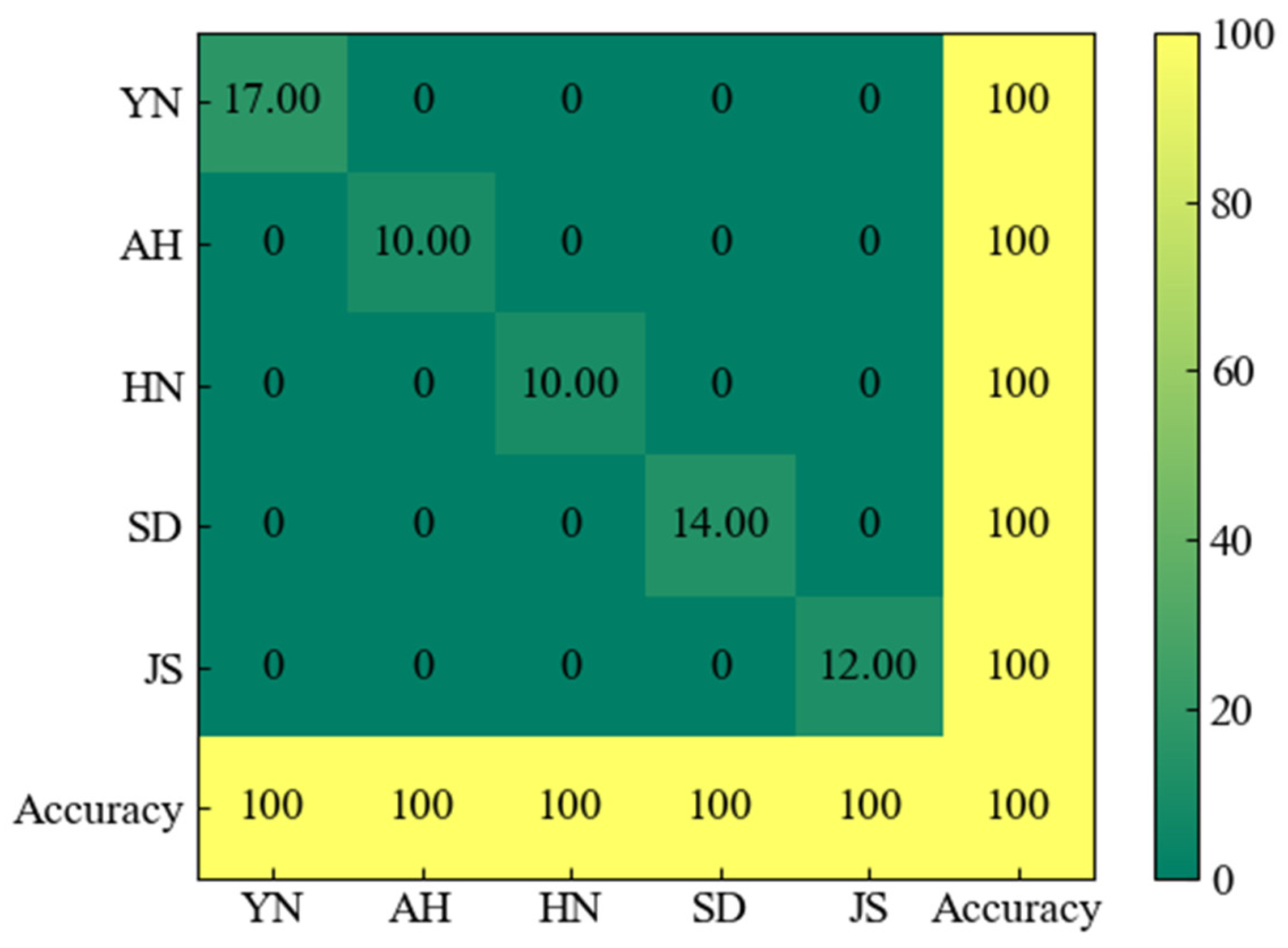
3.6. Confusion Matrix
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nie, J.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Rogers, K.M.; Wu, M.; Lee, C.; Yuan, Y. Discriminating protected geographical indication Chinese Jinxiang garlic from other origins using stable isotopes and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 99, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Petropoulos, S.; Ferreira, I.C. Chemical composition and bioactive compounds of garlic (Allium sativum L.) as affected by pre- and post-harvest conditions: A review. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, V.M.; Orgaz, F.; Mansilla, F.; Montaño, A. Changes in Phenolic Compounds in Garlic (Allium sativum L.) Owing to the Cultivar and Location of Growth. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunanta, P.; Kontogiorgos, V.; Pankasemsuk, T.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rachtanapun, P.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Sommano, S.R. The nutritional value, bioactive availability and functional properties of garlic and its related products during processing. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1142784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C. Anti-inflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of bioactive small molecule garlic polysaccharide. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1092873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, A.; Azimi, H.; Rahimi, R. A Comprehensive Review on Pharmacotherapeutics of Three Phytochemicals, Curcumin, Quercetin, and Allicin, in the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Archivio, A.A.; Foschi, M.; Aloia, R.; Maggi, M.A.; Rossi, L.; Ruggieri, F. Geographical discrimination of red garlic (Allium sativum L.) produced in Italy by means of multivariate statistical analysis of ICP-OES data. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teresita Velarde-Mendivil, A.; Maria Camarena-Gomez, D.; Salgado-Beltran, L. Preferences towards the brand and origin of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Rev. Fac. Agron. Luz. 2021, 38, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F.; D’Archivio, A.A. Geographical discrimination of red garlic (Allium sativum L.) using fast and non-invasive Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transformed Infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 86, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Sang, Y.; Gong, H.; Wang, X. Geographical discrimination and authentication of Chinese garlic based on multi-element, volatile and metabolomics profiling combined with chemometrics. Food Control 2021, 130, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S. NIR Spectroscopy Oranges Origin Identification Framework Based on Machine Learning. Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst. 2022, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Yin, J.; Gu, H.; Yu, X. Rapid On-site identification of geographical origin and storage age of tangerine peel by Near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A 2022, 271, 120936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peijin, T.; Kevin, L.J.; Tingting, W.; Elejalde, U.; Hongchao, Z.; Yuanrong, J.; Wenming, C. Rapid identification of the variety and geographical origin of Wuyou No.4 rice by fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritota, M.; Casciani, L.; Han, B.Z.; Cozzolino, S.; Leita, L.; Sequi, P.; Valentini, M. Traceability of Italian garlic (Allium sativum L.) by means of HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallini, N.; Savorani, F.; Bro, R.; Cocchi, M. Fused adjacency matrices to enhance information extraction: The beer benchmark. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1061, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Huang, Y.; Huo, D.; Luo, X.; Hou, C. Identification of liquors from the same brand based on ultraviolet, near-infrared and fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, X.; Zhai, C.; An, H.; Qian, C.; Shi, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, L. Applications of Molecular Spectral Information Fusion to Distinguish the Rice from Different Growing Regions. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2023, 43, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Abdullah, N.A.; Ait-Kaddour, A.; Ghellam, M.; Besir, A.; Zannou, O.; Onal, B.; Aadil, R.M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Khaneghah, A.M.; et al. Food traceability 4.0 as part of the fourth industrial revolution: Key enabling technologies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, Q.; Ying, Z.; Chen, R.; Chen, H. Design of feature selection algorithm for high-dimensional network data based on supervised discriminant projection. Peerj Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Fu, J.; Yun, Y. Application Progress of Data Fusion Strategy in Food Origin Traceability. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Bureau, S.; Chen, S.; Leca, A.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Jaillais, B. Visible, near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy coupled with an innovative chemometric strategy to control apple puree quality. Food Control 2021, 120, 107546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, C. Geographical traceability of Eucommia ulmoides leaves using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy combined with chemometrics and data fusion. Ind. Crop Prod. 2021, 160, 113090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Application of Two-Dimensional Correlation UV-Vis Spectroscopy in Chinese Liquor Moutai Discrimination. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 6, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. FT-MIR and NIR spectral data fusion: A synergetic strategy for the geographical traceability of Panax notoginseng. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ma, F.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S. Analysis and identification of wild and cultivated Paridis Rhizoma by infrared spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1165, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Data Fusion of Fourier Transform Mid-Infrared (MIR) and Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopies to Identify Geographical Origin of Wild Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Molecules 2019, 24, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. Classification of Tea Quality Levels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Based on CLPSO-SVM. Foods 2022, 11, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Shi, S.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Research on Coal Dust Wettability Identification Based on GA-BP Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Xu, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zong, J.; Cai, H.; Ning, J.; Wei, C.; Hou, R. Rapid identification of the geographic origin of Taiping Houkui green tea using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with a variable selection method. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2022, 102, 6123–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.K.; de Castro, E.V.R.; Romão, W.; Filgueiras, P.R. Data fusion applied in near and mid infrared spectroscopy for crude oil classification. Fuel 2023, 340, 127580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhong, L.; Xue, J.; Lv, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, A. Data fusion based on near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging technology for rapid adulteration detection of Ganoderma lucidum spore powder. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Preprocessing | Ultraviolet Spectrum | Mid-Infrared Spectrum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train (%) | Test (%) | Train (%) | Test (%) | ||
| SVC | None | 100 | 87.31 | 100 | 40.00 |
| SG | 100 | 100 | 100 | 40.00 | |
| MSC | 100 | 92.41 | 100 | 19.31 | |
| SNV | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94 | |
| RF | None | 100 | 89.44 | 100 | 94.67 |
| SG | 100 | 92.46 | 100 | 95.44 | |
| MSC | 100 | 94.44 | 100 | 97.59 | |
| SNV | 100 | 91.42 | 100 | 96.00 | |
| ANN | None | 100 | 93.45 | 26.84 | 18.66 |
| SG | 100 | 100 | 26.84 | 18.66 | |
| MSC | 100 | 97.32 | 26.84 | 18.66 | |
| SNV | 100 | 97.65 | 92.44 | 84.00 | |
| XGboost | None | 100 | 92.67 | 100 | 90.67 |
| SG | 96.32 | 93.29 | 100 | 85.33 | |
| MSC | 100 | 95.34 | 100 | 91.43 | |
| SNV | 100 | 93.52 | 100 | 90.67 | |
| Model | Preprocessing | Ultraviolet Spectrum | Mid-Infrared Spectrum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train (%) | Test (%) | Train (%) | Test (%) | ||
| SVC | None | 100 | 87.31 | 100 | 40.00 |
| SG-GA | 100 | 96.05 | 100 | 26.66 | |
| MSC-GA | 100 | 96.68 | 100 | 28.45 | |
| SNV-GA | 100 | 98.54 | 100 | 97.33 | |
| RF | None | 100 | 89.44 | 100 | 94.67 |
| SG-GA | 100 | 98.56 | 100 | 97.34 | |
| MSC-GA | 100 | 93.47 | 100 | 94.67 | |
| SNV-GA | 100 | 99.16 | 100 | 97.34 | |
| ANN | None | 100 | 93.45 | 26.84 | 18.66 |
| SG-GA | 100 | 96.54 | 26.74 | 18.43 | |
| MSC-GA | 97.62 | 95.65 | 26.74 | 18.66 | |
| SNV-GA | 100 | 99.73 | 87.28 | 80.00 | |
| XGBoost | None | 100 | 92.67 | 100 | 90.67 |
| SG-GA | 100 | 97.92 | 100 | 90.56 | |
| MSC-GA | 100 | 96.38 | 100 | 85.34 | |
| SNV-GA | 100 | 97.41 | 100 | 89.33 | |
| Model | Preprocessing | Fusion Spectrum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train (%) | Test (%) | ||
| SVC | SNV-GA | 100 | 100 |
| RF | SNV-GA | 100 | 100 |
| ANN | SNV-GA | 100 | 100 |
| XGBoost | SNV-GA | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Sha, R.; Dai, J.; Wang, Z.; Mao, J.; Cai, M. Garlic Origin Traceability and Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Spectral Information. Foods 2024, 13, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071016
Han H, Sha R, Dai J, Wang Z, Mao J, Cai M. Garlic Origin Traceability and Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Spectral Information. Foods. 2024; 13(7):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071016
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Hao, Ruyi Sha, Jing Dai, Zhenzhen Wang, Jianwei Mao, and Min Cai. 2024. "Garlic Origin Traceability and Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Spectral Information" Foods 13, no. 7: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071016
APA StyleHan, H., Sha, R., Dai, J., Wang, Z., Mao, J., & Cai, M. (2024). Garlic Origin Traceability and Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Spectral Information. Foods, 13(7), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13071016








