Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Arsenic Concentration Determination in Seaweed Samples
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Calibration Procedure
2.2.3. ICP-MS Analysis
2.2.4. Method Assurance
2.3. Metabolite Extraction
2.4. Non-Targeted Metabolomics by LCMS-QTOF
2.5. Preprocessing of MS Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
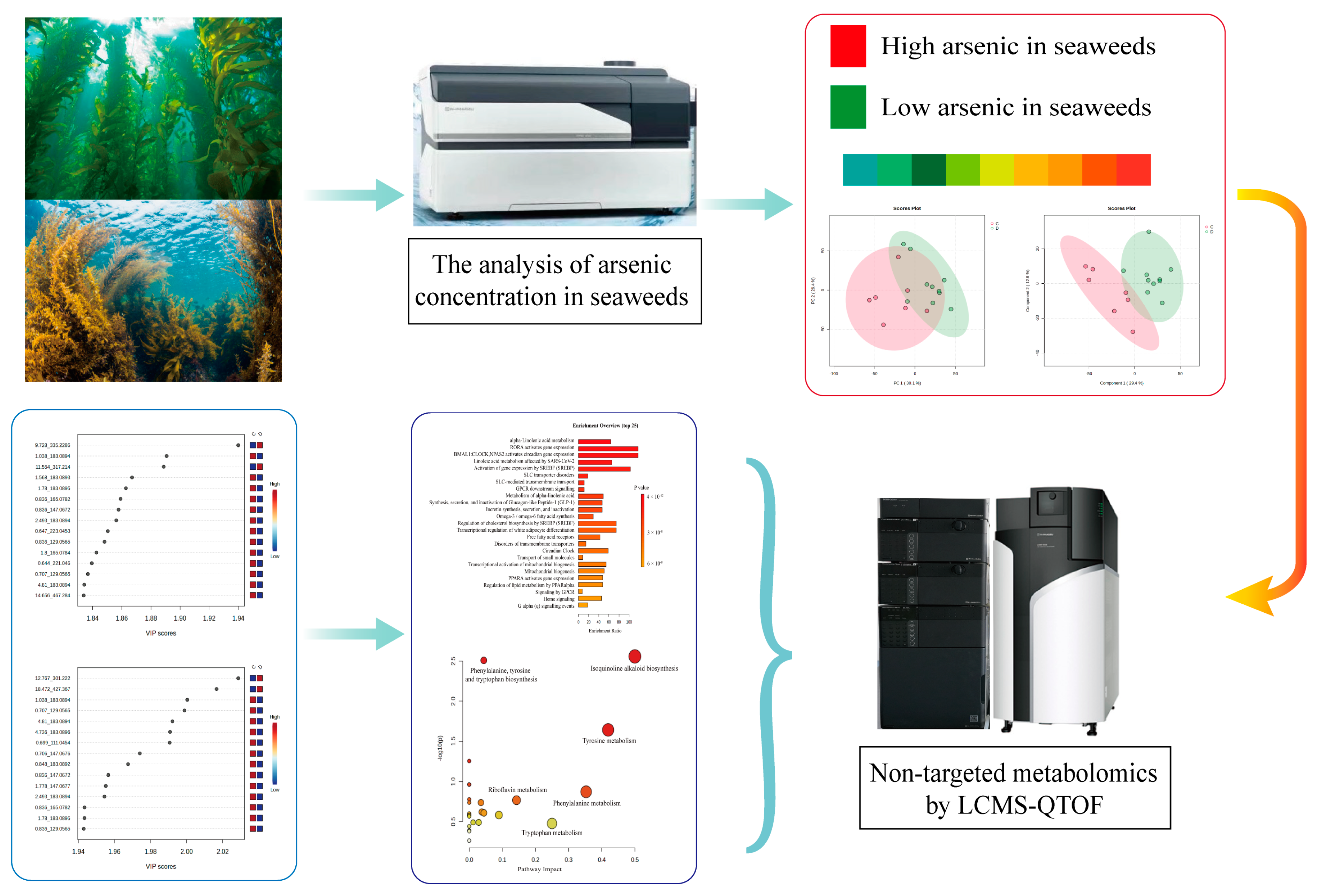
3. Results and Discussion
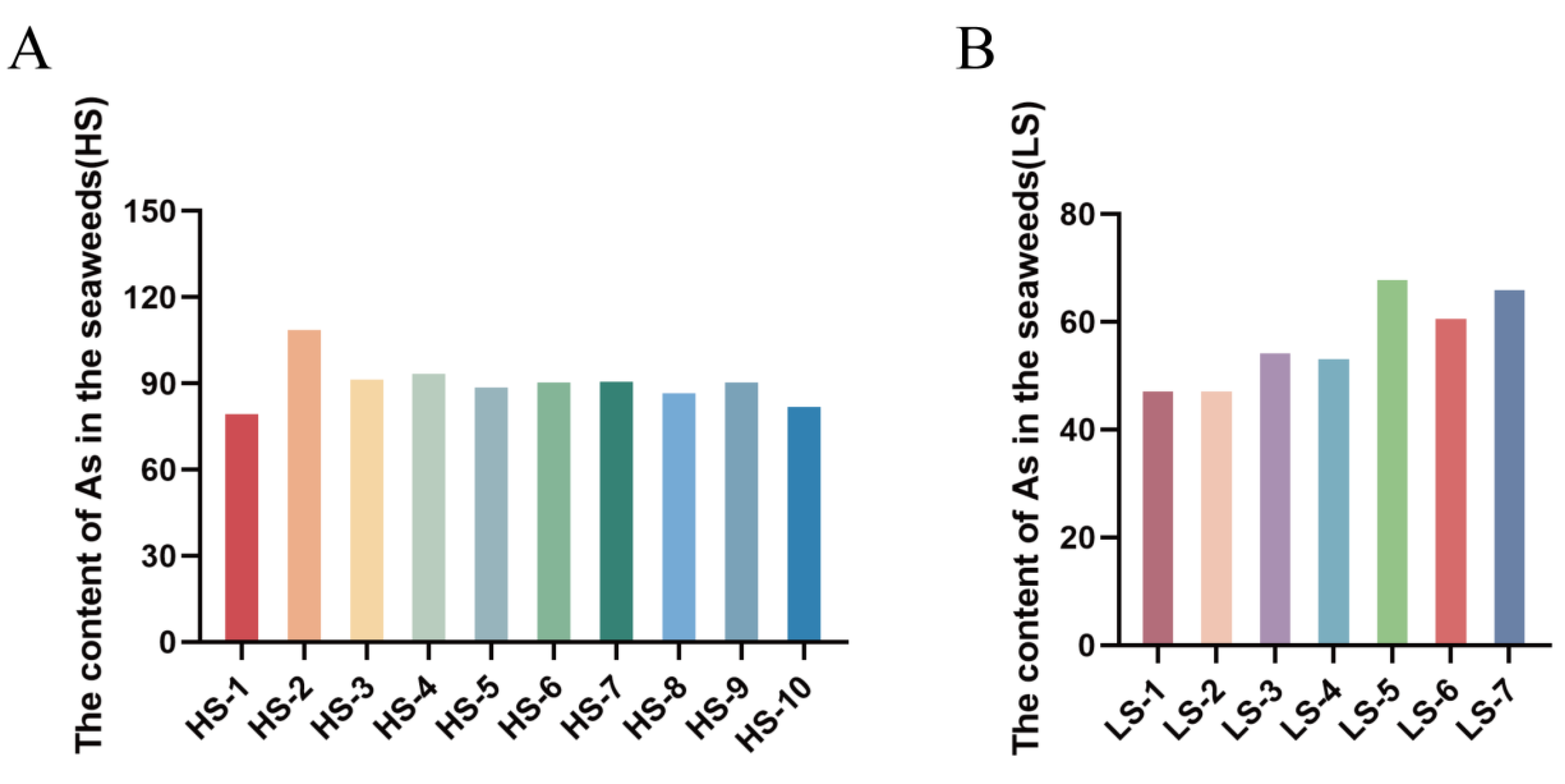
3.1. Arsenic Concentration
3.2. Metabolomic Analysis Based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS
3.2.1. Metabolic Profiles
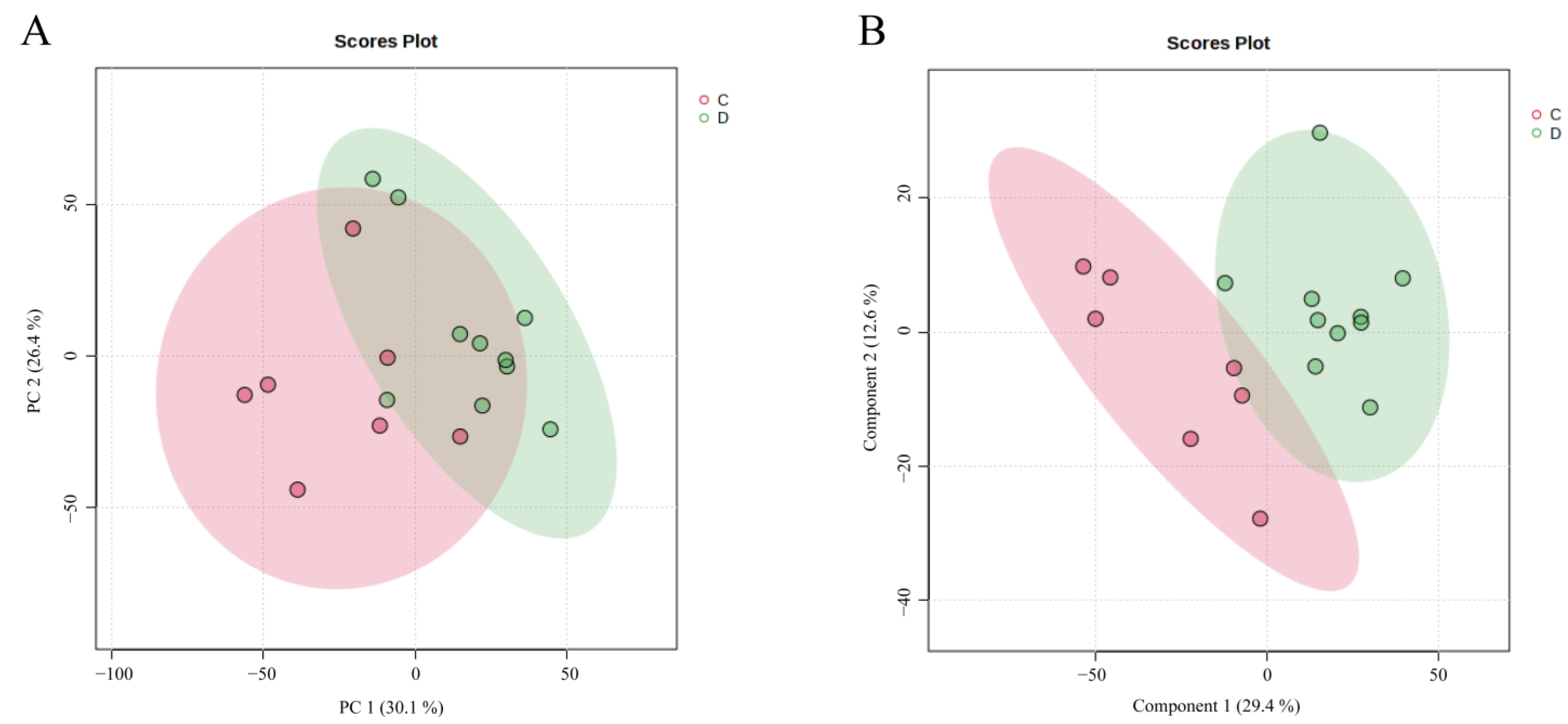
3.2.2. PCA and PLS-DA Models
3.3. Metabolic Pathway
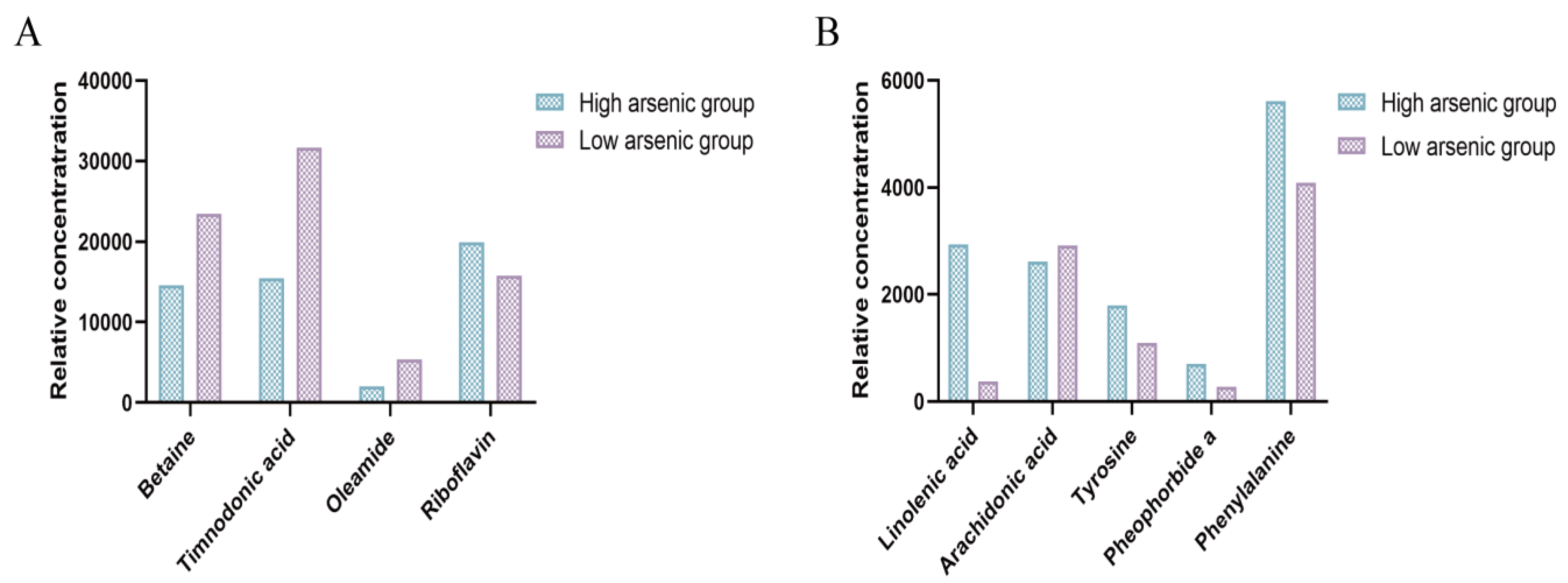
3.4. Targeted Profiles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.Y.; Costa, M. Arsenic: A Global Environmental Challenge. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 61, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Biotransformation and detoxification of inorganic arsenic in Bombay oyster Saccostrea cucullata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, M.; Shi, Y.; Wu, D.; Ye, H.; Feng, D.; Huang, D.; Li, S.; Fang, C. Characteristics of arsenic speciation in mainly cultured shellfish from Sanmen Bay, Zhejiang Province, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnaike, R.N. Acute and chronic arsenic toxicity. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; He, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, H.; Mehmood, K.; Tang, Z.; Hu, L. Toxicity of inorganic arsenic to animals and its treatment strategies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2023, 271, 109654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Moallem, S.A.; Sahebkar, A. Counteracting arsenic toxicity: Curcumin to the rescue? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; He, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Grimi, N.; Xiao, J. Species-specific arsenic species and health risk assessment in seaweeds from tropic coasts of South China Sea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Lourdes, C. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic that are shared with neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive impairment: Role of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, M.S.; Desai, K.P.; Lynch, H.N.; Rhomberg, L.R.; Beck, B.D.; Venditti, F.J. Mechanisms of action for arsenic in cardiovascular toxicity and implications for risk assessment. Toxicology 2015, 331, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.E.; Fahad, S.; Shao, Z.; Sarven, M.S.; Khan, I.A.; Alam, M.; Saeed, M.; Ullah, H.; Adnan, M.; Saud, S.; et al. Arsenic in a groundwater environment in Bangladesh: Occurrence and mobilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, M.H.; Haque, M. Arsenic contamination in groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications and challenges for healthcare policy. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2018, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigra, A.E.; Olmedo, P.; Grau-Perez, M.; O’Leary, R.; O’Leary, M.; Fretts, A.M.; Umans, J.G.; Best, L.G.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; et al. Dietary determinants of inorganic arsenic exposure in the Strong Heart Family Study. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Bi, R.; Musil, S.; Pétursdóttir, Á.H.; Luo, B.; Zhao, P.; Tan, X.; Jia, Y. Arsenic species and their health risks in edible seaweeds collected along the Chinese coastline. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard of Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. National Health Commission of the Peolple’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Luvonga, C.; Rimmer, C.A.; Yu, L.L.; Lee, S.B. Determination of total arsenic and hydrophilic arsenic species in seafood. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 96, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molin, M.; Ulven, S.M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J. Arsenic in the human food chain, biotransformation and toxicology--Review focusing on seafood arsenic. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. (GMS) 2015, 31, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Fu, F. Bio-accessibility and bio-availability evaluation of each arsenic species existing in various edible seaweeds in vitro and in vivo for arsenic risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preetha, J.S.Y.; Arun, M.; Vidya, N.; Kowsalya, K.; Halka, J.; Ondrasek, G. Biotechnology Advances in Bioremediation of Arsenic: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.S. Bioremediation of heavy metals using microalgae: Recent advances and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Liu, R. Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic in water samples by immobilized nanometer titanium dioxide separation and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 602, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Mao, S.W.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, J.Q.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.W.; Duan, J.A. Combining stable isotope, multielement and untargeted metabolomics with chemometrics to discriminate the geographical origins of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, W.; Koidis, A.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H. Untargeted metabolomics by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for food authentication: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2455–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Ren, Q.Q.; Lai, Y.H.; Peng, M.Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.T.; Huang, Z.R.; Chen, L.S. Metabolomics combined with physiology and transcriptomics reveals how Citrus grandis leaves cope with copper-toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.; Poulsen, R.; Langebæk, R.; Jenssen, B.M.; Moe, J.; Ciesielski, T.M.; Dietz, R.; Sonne, C.; Madsen, J.; Hansen, M. The metabolome of pink-footed goose: Heavy metals and lipid metabolism. Environ. Res. 2023, 231 Pt 1, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Chemical elements in Mediterranean macroalgae. A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, K.; Musil, S.; Mikšík, I.; Dědina, J. Investigation of hydride generation from arsenosugars—Is it feasible for speciation analysis? Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1008, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Nam, Y.A.; Kim, H.S.; Hayes, A.W.; Lee, B.M. α-Linolenic acid: Nutraceutical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 70, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.Y.; Song, J. Important roles of linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid in regulating cognitive impairment and neuropsychiatric issues in metabolic-related dementia. Life Sci. 2024, 337, 122356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Aleman, G.H.; Castro, V.; Londaitsbehere, A.; Gutierrez-Rodríguez, M.; Garaigorta, U.; Solano, R.; Gastaminza, P. SARS-CoV-2 Fears Green: The Chlorophyll Catabolite Pheophorbide A Is a Potent Antiviral. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, M.J.; Olivera, V.; Pérez, G.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E.; Carrau, F. Impact of phenylalanine on Hanseniaspora vineae aroma metabolism during wine fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 415, 110631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, P.; Bai, L.; et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals phenylalanine enhance mitochondrial function and hypoxic endurance via LKB1/AMPK activation. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Shi, M.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Lou, D.; Zhang, A.; Hu, Y. LC/MS/MS-Based Liver Metabolomics to Identify Chronic Liver Injury Biomarkers Following Exposure to Arsenic in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4355–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Parida, A.K. Salinity alleviates arsenic stress-induced oxidative damage via antioxidative defense and metabolic adjustment in the root of the halophyte Salvadora persica. Planta 2023, 258, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.C.; Collela, C.F.; Sousa, T.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Seaweed-Based Products and Mushroom β-Glucan as Tomato Plant Immunological Inducers. Vaccines 2020, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasom, N.; Kao, I.; Pruß, A.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, S.; Arora, S. Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3650–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C. Importance of EPA and DHA Blood Levels in Brain Structure and Function. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bito, T.; Teng, F.; Watanabe, F. Bioactive Compounds of Edible Purple Laver Porphyra sp. (Nori). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10685–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, D.K.; Bhushan, S.; Jamwal, A. Mitigating multiple stresses in Pangasianodon hypophthalmus with a novel dietary mixture of selenium nanoparticles and Omega-3-fatty acid. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczuko, M.; Kikut, J.; Komorniak, N.; Bilicki, J.; Celewicz, Z.; Ziętek, M. The Role of Arachidonic and Linoleic Acid Derivatives in Pathological Pregnancies and the Human Reproduction Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, D.; Camera, E.; Póliska, S.; Cavallo, A.; Maiellaro, M.; Dull, K.; Gruber, F.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Szegedi, A.; Törőcsik, D. Linoleic Acid Induced Changes in SZ95 Sebocytes-Comparison with Palmitic Acid and Arachidonic Acid. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghiaty, M.A.; Alqahtani, M.A.; El-Mahrouk, S.R.; Isse, F.A.; Alammari, A.H.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. Alteration of Hepatic Cytochrome P450 Expression and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism by Arsenic Trioxide (ATO) in C57BL/6 Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Díaz, C.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Mascher, D.; Pavón, N.; Regla, I.; Paredes-Carbajal, M.C. Effects of Oleamide on the Vasomotor Responses in the Rat. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrijević, D.; Pastor, K.; Nastić, N.; Özogul, F.; Krulj, J.; Kokić, B.; Bartkiene, E.; Rocha, J.M.; Kojić, J. Betaine as a Functional Ingredient: Metabolism, Health-Promoting Attributes, Food Sources, Applications and Analysis Methods. Molecules 2023, 28, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Yin, N.; Cai, X.; Geng, Z.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y. Effects of foods and food components on the in vitro bioaccessibility of total arsenic and arsenic species from Hizikia fusiforme seaweed. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.; Chen, Q.; Patra, J.K.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Gai, Z. Arachidonic Acid Metabolism and Kidney Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.L.; Pardella, E.; Pranzini, E.; Raugei, G.; Paoli, P. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation in modulating cancer cell metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Schramm, K.W.; Nan, B.; Huang, Q.; Tian, M.; Shen, H. Persistence and reversibility of arsenic-induced gut microbiome and metabolome shifts in male rats after 30-days recovery duration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.A.; Ball, R.O.; Filler, R.M.; Moore, A.M.; Pencharz, P.B. Phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism in neonates receiving parenteral nutrition differing in pattern of amino acids. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Zhu, T.; Hu, X.; Hou, C.; He, J.; Liu, X. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Isoquinoline Alkaloid Biosynthesis of Coptis chinensis in Different Years. Genes 2023, 14, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Batch No. | Location | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HS-1 | Zhejiang | Origin |
| 2 | HS-2 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 3 | HS-3 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 4 | HS-4 | Zhejiang | TCM market |
| 5 | HS-5 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 6 | HS-6 | Zhejiang | TCM market |
| 7 | HS-7 | Zhejiang | TCM market |
| 8 | HS-8 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 9 | HS-9 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 10 | HS-10 | Shandong | TCM market |
| 11 | LS-1 | Shandong | Origin |
| 12 | LS-2 | Zhejiang | Origin |
| 13 | LS-3 | Zhejiang | Origin |
| 14 | LS-4 | Zhejiang | Origin |
| 15 | LS-5 | Zhejiang | Origin |
| 16 | LS-6 | Shandong | Origin |
| 17 | LS-7 | Zhejiang | TCM market |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.-s.; Gong, S.; Xie, S.-m.; Chen, A.-z.; Jin, H.-y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Kang, S.; Li, P.; Wei, F.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure. Foods 2024, 13, 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244055
Guo Y-s, Gong S, Xie S-m, Chen A-z, Jin H-y, Liu J, Wang Q, Kang S, Li P, Wei F, et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure. Foods. 2024; 13(24):4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244055
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yuan-sheng, Shuo Gong, Si-min Xie, An-zhen Chen, Hong-yu Jin, Jing Liu, Qi Wang, Shuai Kang, Ping Li, Feng Wei, and et al. 2024. "Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure" Foods 13, no. 24: 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244055
APA StyleGuo, Y.-s., Gong, S., Xie, S.-m., Chen, A.-z., Jin, H.-y., Liu, J., Wang, Q., Kang, S., Li, P., Wei, F., Zuo, T.-t., & Ma, S.-c. (2024). Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Investigation on Two Different Seaweeds Under Arsenic Exposure. Foods, 13(24), 4055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13244055






