Sequence–Activity Relationship of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins, Based on a New Deep Learning Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
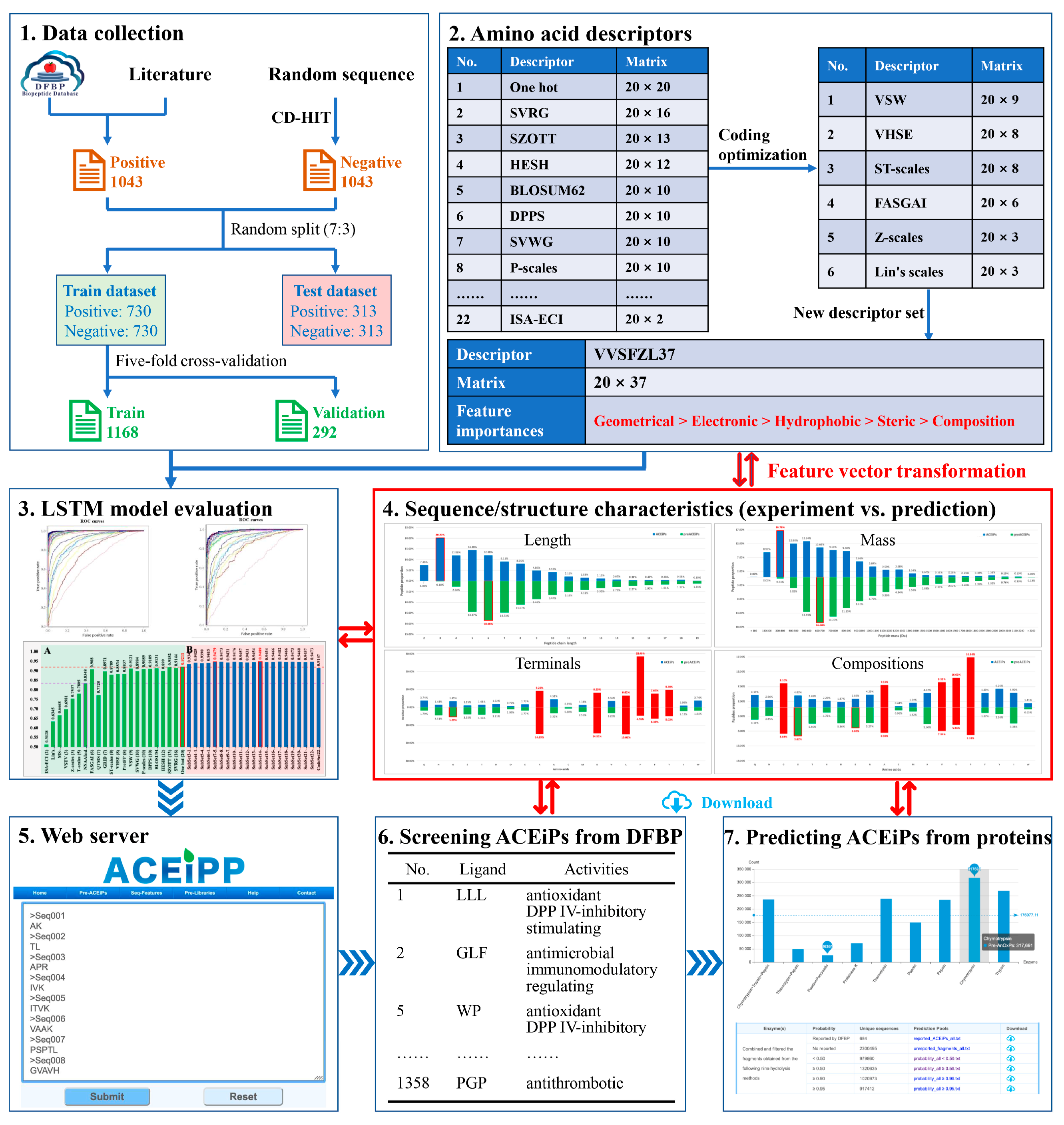
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Benchmark and Independent Dataset
2.2. Sequence Representation
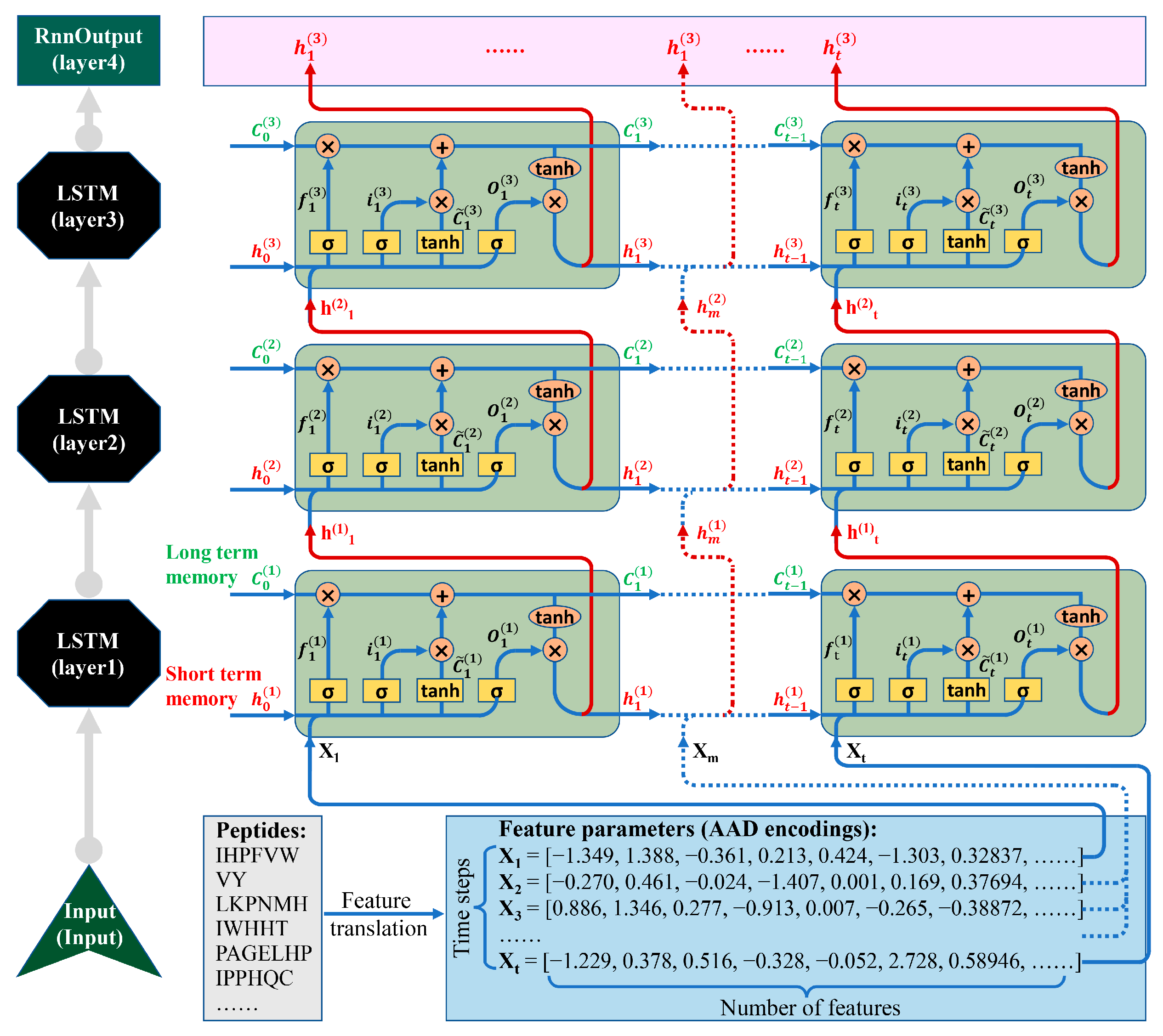
2.3. LSTM Architecture
2.4. Evaluation of Performance
2.5. Webserver Construction
2.6. Theoretical Screening of Food-Derived ACEiPs
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Determination of ACE Inhibitory Activity
3. Results and Discussion
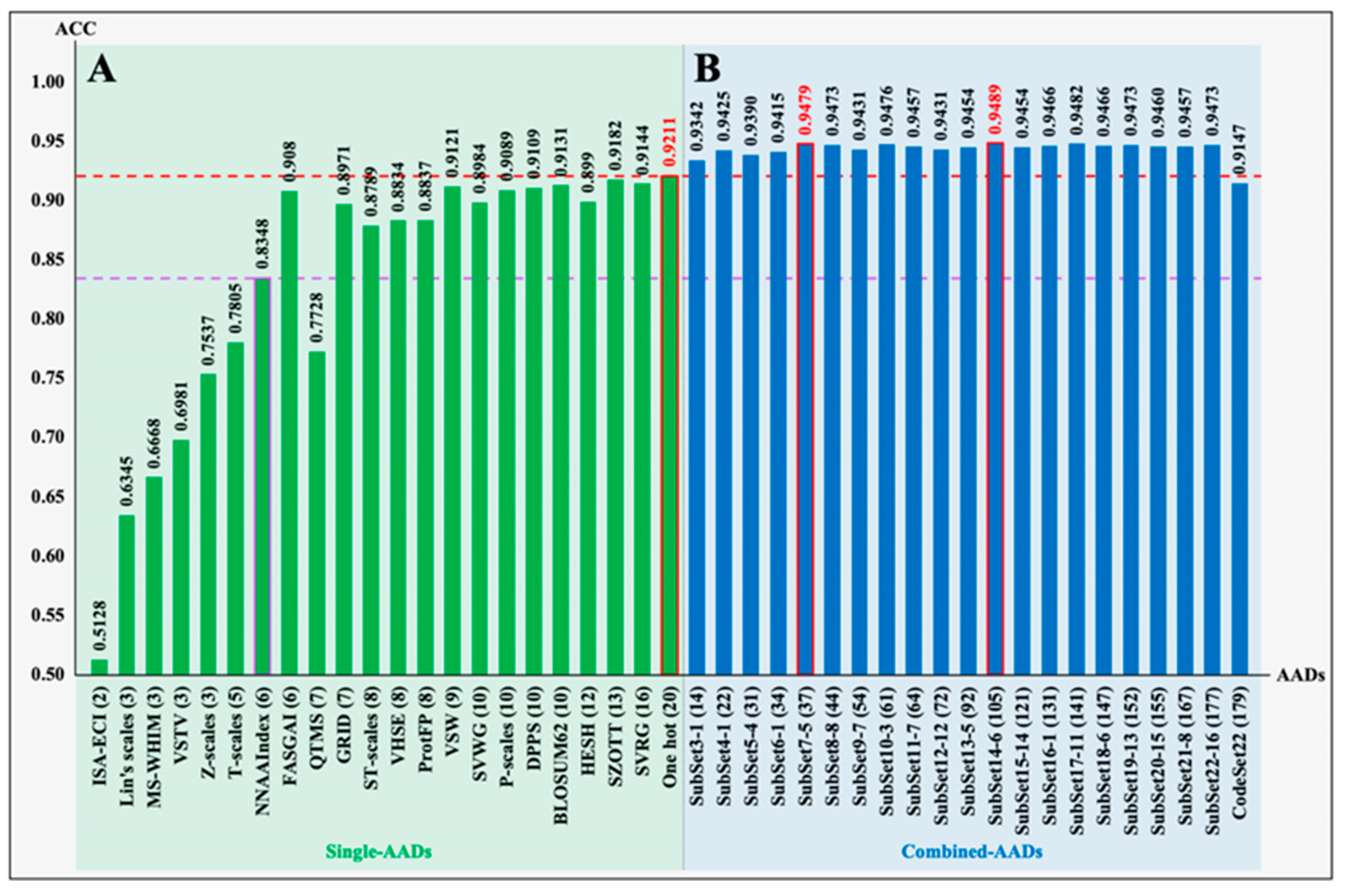
3.1. Performance of Single Coding Models
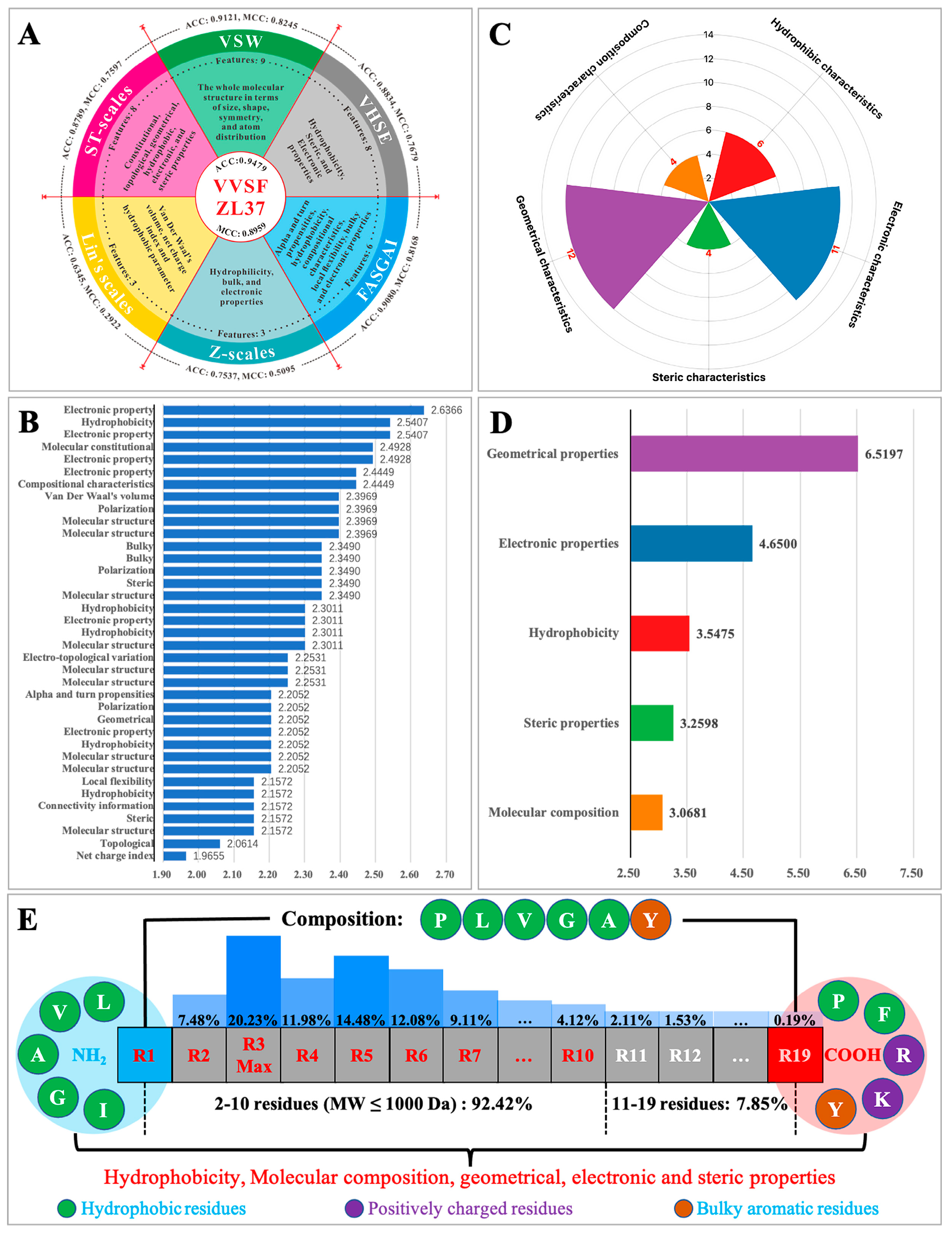
3.2. Performance of Optimized Coding Models
3.3. Comparison with the Existing Predictors
3.4. Key Sequence/Structure Characteristics Learned by ACEiPP
3.5. Web Server Implementation
3.6. Characterization and Screening of Food-Derived ACEiPs with Multi-Activities
3.7. Future Development Trends for ACEiPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from fish as potential cardioprotective compounds. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Deussen, A. Effects of natural peptides from food proteins on angiotensin converting enzyme activity and hypertension. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1264–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Strappe, P.; Shang, W.T.; Zhou, Z.K. Functional peptides derived from rice bran proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, S.; Razavi, S.H. Pulses’ germination and fermentation: Two bioprocessing against hypertension by releasing ACE inhibitory peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2876–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikkam, V.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.N.; Mathai, M.L. A review of potential marine-derived hypotensive and anti-obesity peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.; Miguel, M.; Garcés-Rimón, M. Pseudocereals: A novel source of biologically active peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, S.; Pan, N.; Su, J.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; et al. A novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Mar. Drugs. 2021, 19, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyoung Lee, D.; Ho Kim, J.; Sik Park, J.; Jun Choi, Y.; Soo Lee, J. Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the edible mushroom Tricholoma giganteum. Peptides 2004, 25, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y. Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides identified from walnut glutelin-1 hydrolysates: Molecular interaction, stability, and antihypertensive effects. Nutrients 2021, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Bo, W.; Zheng, X.; Hao, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, J.; Liang, G. DFBP: A comprehensive database of food-derived bioactive peptides for peptidomics research. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3275–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammi, C.; Aiello, G.; Boschin, G.; Arnoldi, A. Multifunctional peptides for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A new concept in the area of bioactive food-derived peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, F.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, Q.; Liu, G.Q. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide: An emerging candidate for vascular dysfunction therapy. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 736–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaioglu, A.S.; Atas, H.; Martin, M.J.; Cetin-Atalay, R.; Atalay, V.; Doğan, T. Recent applications of deep learning and machine intelligence on in silico drug discovery: Methods, tools and databases. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1878–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Chen, L.; Qin, D.; Geng, S.; Li, J.; Mei, H.; Li, B.; Liang, G. Application of quantitative structure-activity relationship to food-derived peptides: Methods, situations, challenges and prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, X. Advancement and prospects of production, transport, functional activity and structure-activity relationship of food-derived angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1437–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Hellberg, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Skagerberg, B.; Wold, S. Peptide quantitative structure-activity relationships, a multivariate approach. J Med Chem. 1987, 30, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Mei, H.; Yang, S.; Liao, L.; Li, Z. Structural parameter characterization and bioactivity simulation based on peptide sequence. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2009, 28, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, Z. Factor analysis scale of generalized amino acid Information as the source of a new set of descriptors for elucidating the structure and activity relationships of cationic antimicrobial peptides. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2007, 26, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Singh Chauhan, J.; Nagpal, G.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Raghava, G.P. An in silico platform for predicting, screening and designing of antihypertensive peptides. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. mAHTPred: A sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of anti-hypertensive peptides using effective feature representation. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Li, S.; Meng, Y.; Suonan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Deep learning drives efficient discovery of novel antihypertensive peptides from soybean protein isolate. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W. sAMP-PFPDeep: Improving accuracy of short antimicrobial peptides prediction using three different sequence encodings and deep neural networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Cui, F.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L. Anticancer peptides prediction with deep representation learning features. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Dai, R.; Yan, W.; Zhang, W.; Bin, Y.; Xia, E.; Xia, J. Identifying multi-functional bioactive peptide functions using multi-label deep learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, B.; Zou, Q. Molecular design in drug discovery: A comprehensive review of deep generative models. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahogue, V.; Réhel, K.; Taupin, L.; Haras, D.; Allaume, P. A HPLC-UV method for the determination of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, D.W.; Cheung, H.S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1971, 20, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UG, Y.; Bhat, I.; Karunasagar, I.; BS, M. Antihypertensive activity of fish protein hydrolysates and its peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A.; Kehinde, B.A.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, D.; Kaur, S. Recently isolated food-derived antihypertensive hydrolysates and peptides: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.-W.; Han, X.; Cheng, D.-Y. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hydrolysates of Qula casein: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço da Costa, E.; Antonio da Rocha Gontijo, J.; Netto, F.M. Effect of heat and enzymatic treatment on the antihypertensive activity of whey protein hydrolysates. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural requirements of Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure-activity relationship study of di- and tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagardia, I.; Roa-Ureta, R.H.; Bald, C. A new QSAR model, for angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory oligopeptides. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurtz, V.I.; Johansen, A.R.; Nielsen, M.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Nielsen, H.; Sønderby, C.K.; Winther, O.; Sønderby, S.K. An introduction to deep learning on biological sequence data: Examples and solutions. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3685–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Lv, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, P. In silico quantitative prediction of peptides binding affinity to human MHC molecule: An intuitive quantitative structure-activity relationship approach. Amino Acids. 2009, 36, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, A.G. Interpretable numerical descriptors of amino acid space. J. Comput. Biol. 2009, 16, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henikoff, S.; Henikoff, J.G. Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10915–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchi, M.; Johansson, E. Amino Acids Characterization by GRID and Multivariate Data Analysis. Quant. Struct. Act. Relatsh. 1993, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantes, E.R.; Dunn, W.J., 3rd. Amino acid side chain descriptors for quantitative structure-activity relationship studies of peptide analogues. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Long, H.X.; Bo, Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.Z. New descriptors of amino acids and their application to peptide QSAR study. Peptides 2008, 29, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaliani, A.; Gancia, E. MS-WHIM scores for amino acids: A new 3D-description for peptide QSAR and QSPR studies. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Liu, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, J. An index for characterization of natural and non-natural amino acids for peptidomimetics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Westen, G.J.; Swier, R.F.; Wegner, J.K.; Ijzerman, A.P.; van Vlijmen, H.W.; Bender, A. Benchmarking of protein descriptor sets in proteochemometric modeling (part 1): Comparative study of 13 amino acid descriptor sets. J. Cheminform. 2013, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmateenejad, B.; Yousefinejad, S.; Mehdipour, A.R. Novel amino acids indices based on quantum topological molecular similarity and their application to QSAR study of peptides. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shu, M.; Ma, K.; Mei, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z. ST-scale as a novel amino acid descriptor and its application in QSAM of peptides and analogues. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Che, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. A descriptor of amino acids: SVRG and its application to peptide quantitative structure-activity relationship. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2011, 22, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Che, T.; Xu, X. A descriptor of amino acids SVWG and its applications in peptide QSAR. J. Chemom. 2012, 26, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.-Z.; Shu, M.; Li, S.-S.Z. A new set of amino acid descriptors for the development of quantitative sequence-activity modelings of HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitopes. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2008, 55, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z. T-scale as a novel vector of topological descriptors for amino acids and its application in QSARs of peptides. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 830, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Liao, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.Z. A new set of amino acid descriptors and its application in peptide QSARs. Biopolymers 2005, 80, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Li, L.; Bai, M.; Li, K. A new descriptor of amino acids-SVGER and its applications in peptide QSAR. Mol. Inform. 2017, 36, 1501023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, P.; Wu, B.; Li, Z. A novel descriptor of amino acids and its application in peptide QSAR. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 253, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z. Predicting the activity of ACE inhibitory peptides with a novel mode of pseudo amino acid composition. Protein Pept. Lett. 2011, 18, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Predictor a | Applicable Length | Independent_ACEiPs | Independent_AHTPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | MCC | Acc | MCC | ||
| AHTpin_AAC | Tetrapeptides | 0.7639 | 0.5168 | - | - |
| Pentapeptides | 0.5429 | 0.0880 | 0.7814 | 0.4121 | |
| Hexapeptides | 0.8507 | 0.7152 | 0.9045 | 0.4354 | |
| Medium peptides (7–12) | 0.7957 | 0.5898 | 0.7622 | 0.5033 | |
| Large peptides (≥13) | 0.9000 | 0.7980 | 0.7761 | 0.2618 | |
| AHTpin_ATC | Tetrapeptides | 0.7639 | 0.5168 | - | - |
| Pentapeptides | 0.5810 | 0.1674 | 0.7705 | 0.3292 | |
| Hexapeptides | 0.7910 | 0.5775 | 0.9045 | 0.3582 | |
| Medium peptides (7–12) | 0.8441 | 0.7053 | 0.7744 | 0.4828 | |
| Large peptides (≥13) | 0.8000 | 0.6162 | 0.8321 | 0.3256 | |
| mAHTPred | ≥5 | 0.8492 | 0.7027 | 0.8834 | 0.7670 |
| ACEiPP | ≥2 | 0.9479 | 0.8959 | 0.8303 | 0.6614 |
| No. | Sequence | IC50 (μM) | Bioactivities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LAF | 4.35 | High ACE-inhibitory activity Antioxidant activity (DFBPANOX1165) |
| 2 | LLL | 17.99 | High ACE-inhibitory activity Antioxidant activity (DFBPANOX0810) DPP IV-inhibitory activity (DFBPDPIV0160) Stimulating activity (DFBPSTPE0004) Multifunctional activity (DFBPMUFU0682) |
| 3 | GLF | 270.93 | Moderate ACE-inhibitory activity Antimicrobial activity (DFBPAMIC0518) Immunomodulatory activity (DFBPIMMU0002) Immunomodulatory activity (DFBPIMMU0093) Regulating activity (DFBPREPE0005) Multifunctional activity (DFBPMUFU0716) |
| 4 | LIV | 330.75 | Moderate ACE-inhibitory activity Antioxidant activity (DFBPANOX0821) |
| 5 | LAL | 1162.34 | Low ACE-inhibitory activity Antioxidant activity (DFBPANOX0812) |
| 6 | AVL | 5093.25 | No ACE-inhibitory activity Antihypertensive activity (DFBPANHY0635) |
| 7 | LE | 28,526.40 | No ACE-inhibitory activity Antiviral activity (DFBPANPE0012) |
| 8 | VLV | No inhibition | No ACE-inhibitory activity Antioxidant activity (DFBPANOX0910) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, D.; Liang, X.; Jiao, L.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, W.; Wang, J.; Liang, G. Sequence–Activity Relationship of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins, Based on a New Deep Learning Model. Foods 2024, 13, 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223550
Qin D, Liang X, Jiao L, Wang R, Zhao Y, Xue W, Wang J, Liang G. Sequence–Activity Relationship of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins, Based on a New Deep Learning Model. Foods. 2024; 13(22):3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223550
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Dongya, Xiao Liang, Linna Jiao, Ruihong Wang, Yi Zhao, Wenjun Xue, Jinhong Wang, and Guizhao Liang. 2024. "Sequence–Activity Relationship of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins, Based on a New Deep Learning Model" Foods 13, no. 22: 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223550
APA StyleQin, D., Liang, X., Jiao, L., Wang, R., Zhao, Y., Xue, W., Wang, J., & Liang, G. (2024). Sequence–Activity Relationship of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins, Based on a New Deep Learning Model. Foods, 13(22), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223550






