Evaluation of Prebiotic and Health-Promoting Functions of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides and Their Maillard Reaction Conjugates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Processing of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides (HBb-Bps) Preparation
2.3. Preparation of HBb-Bps Conjugated Products Using the Moist-Dry Heating Method with Spontaneous Aging Technique
2.4. Characterization of HBb-Bps and HBb-Bp Conjugated Products
2.4.1. Degree of Protein Hydrolysis
2.4.2. Molecular Weight Distribution Using Size-Exclusion HPLC
2.4.3. Determination of Amino Acid Composition by HPLC
2.5. Biological Properties of HBb-Bps Interaction with Sugar and Honey
2.5.1. Antioxidant Activities of HBb-Bps Interaction with Sugar and Honey
2.5.2. Inhibition of α-Amylase Activity
2.5.3. Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase Activity
2.5.4. Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity (ACE)
2.6. Prebiotic Properties of HBb-Bps Interaction with Sugar and Honey
2.6.1. Prebiotic Effect on Selected Lactobacillus spp. Growth
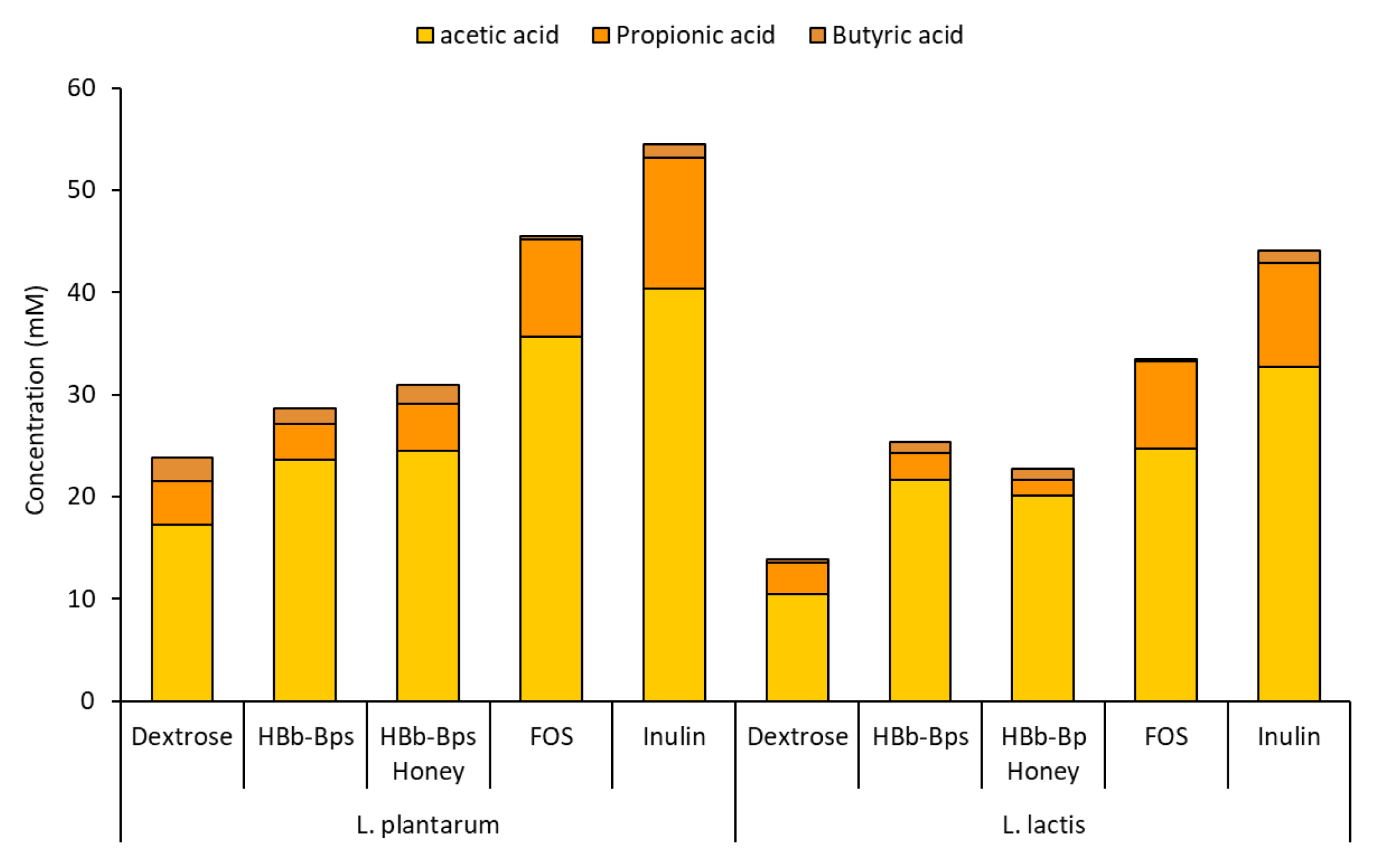
2.6.2. Quantification of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
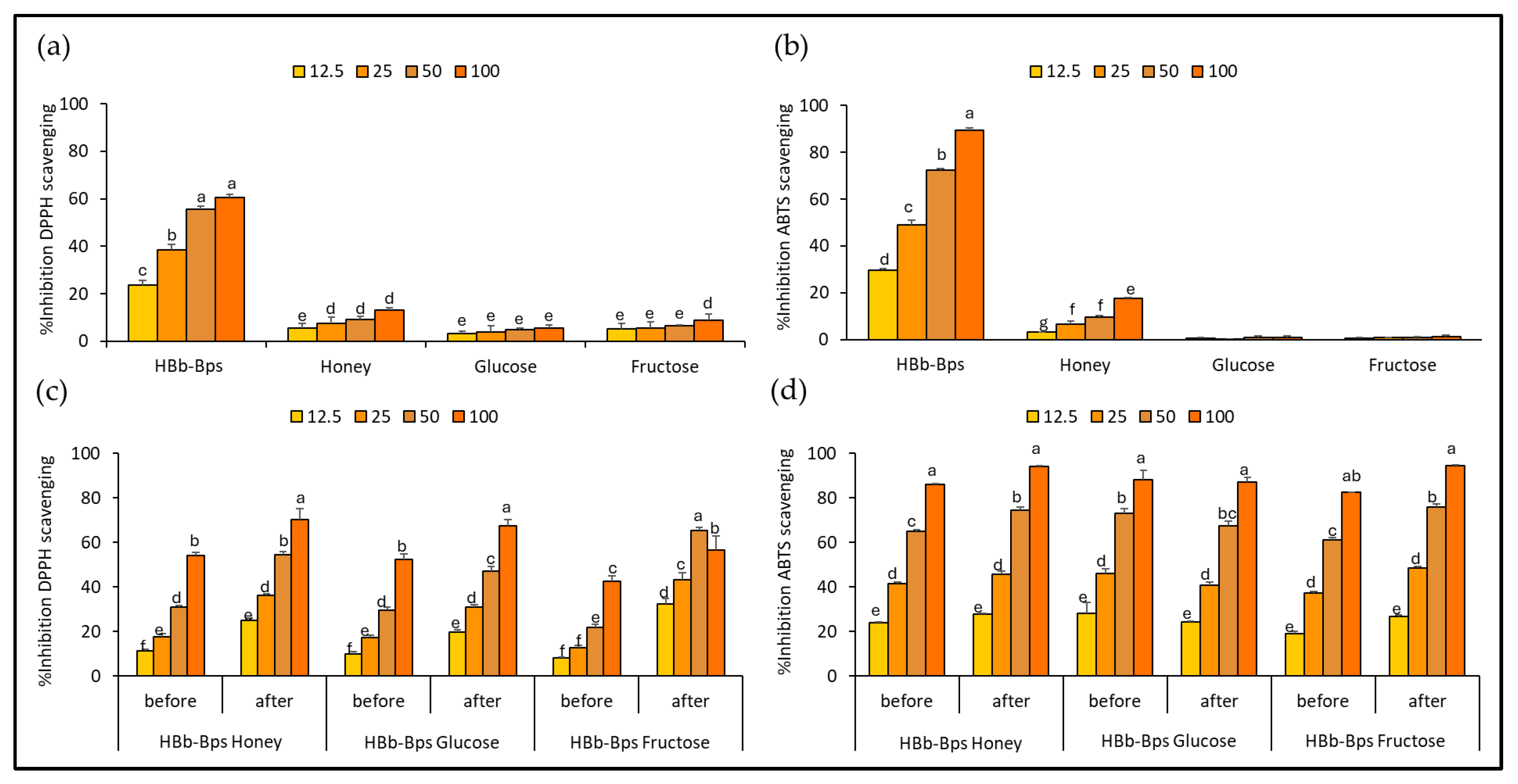
3.1. Antioxidant Activities of HBb-Bps, Honey, and Sugar and Their Conjugating Products before and after the Moist-Dry Heating Process
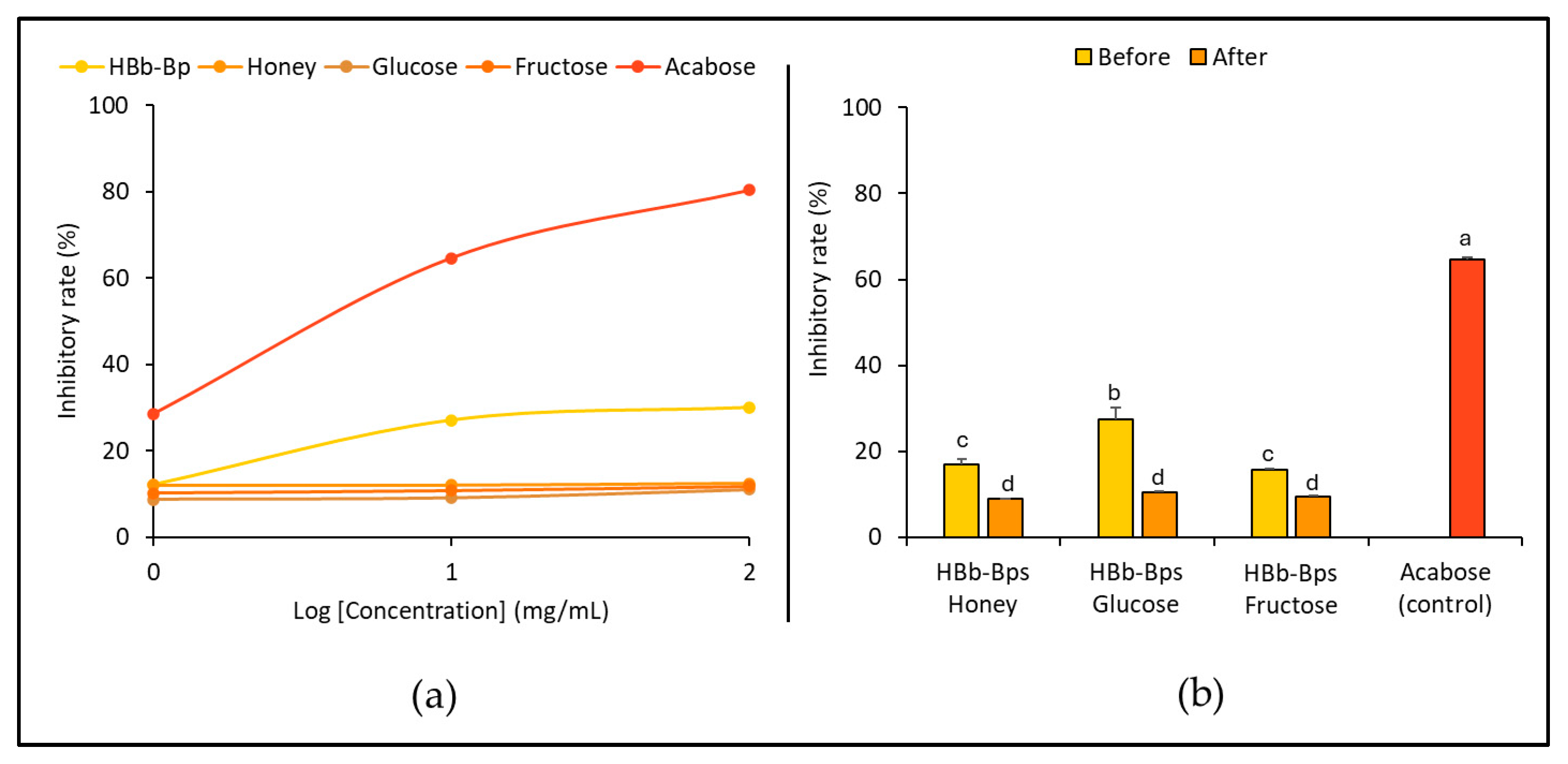
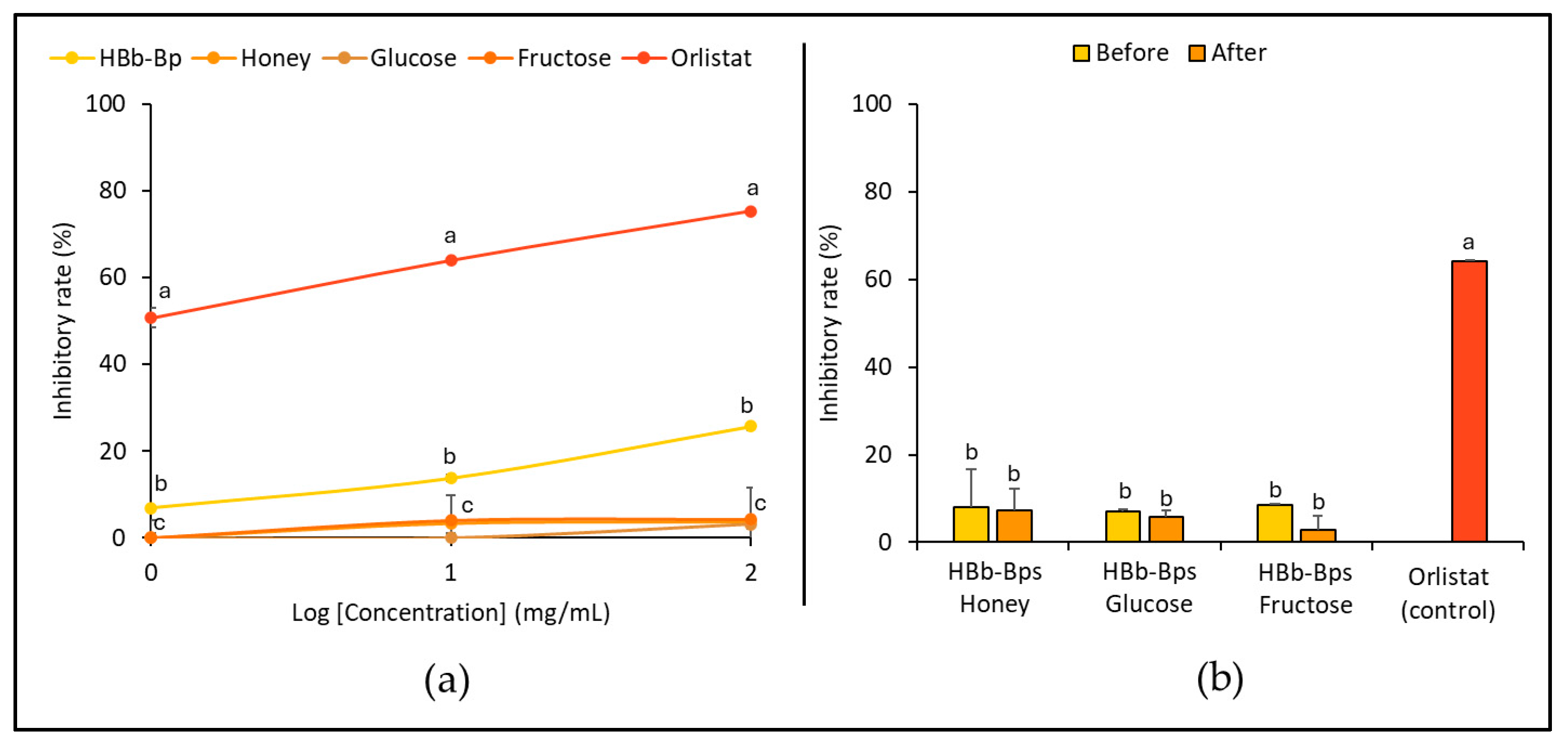
3.2. Anti-Obesity Activities of HBb-Bps, Honey, and Sugar and Their Conjugating Products before and after the Moist-Dry Heating Process
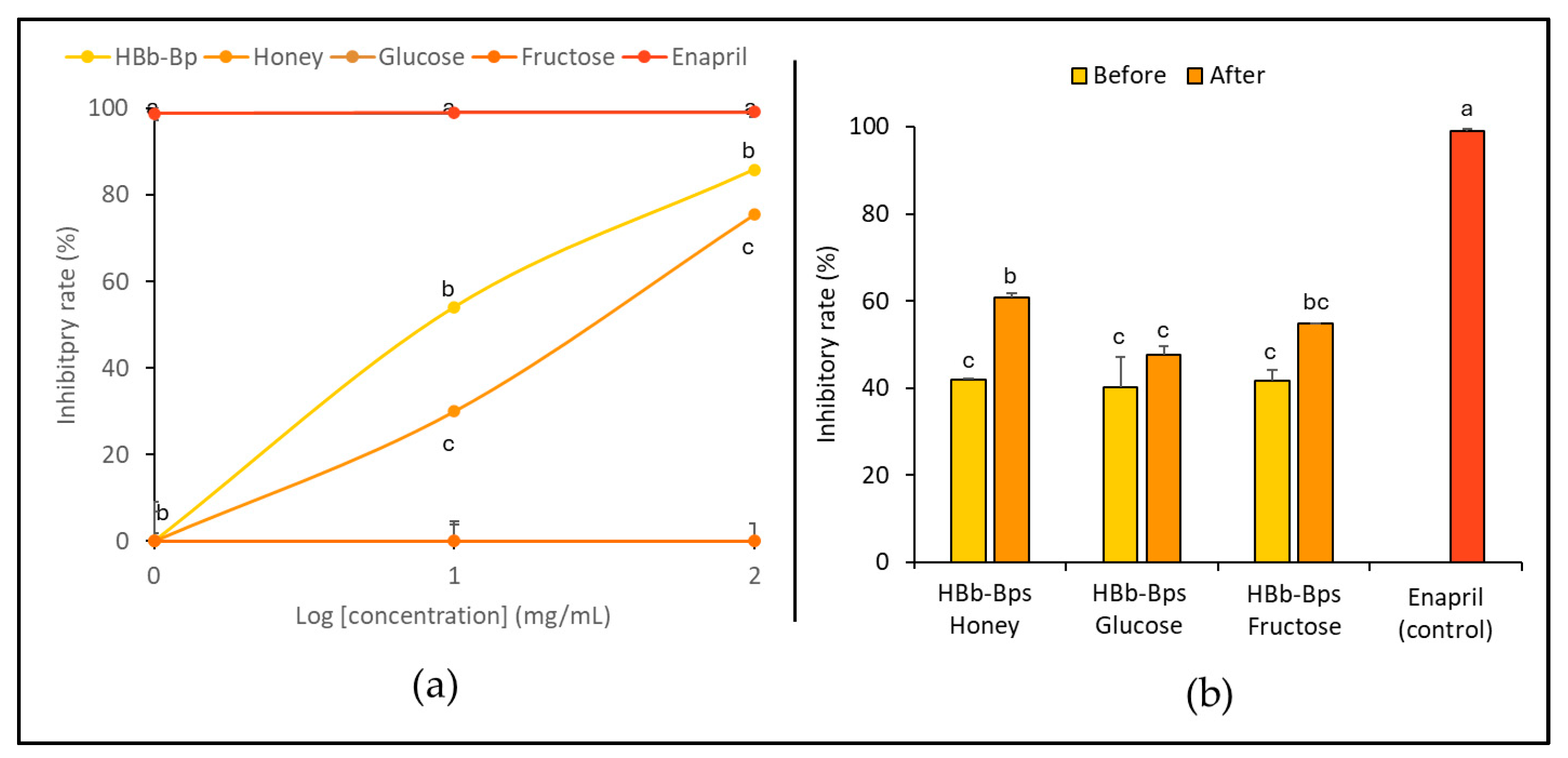
3.3. Anti-Hypertensive Activity of HBb-Bps, Honey, and Sugar and Their Conjugating Products before and after the Moist-Dry Heating Process
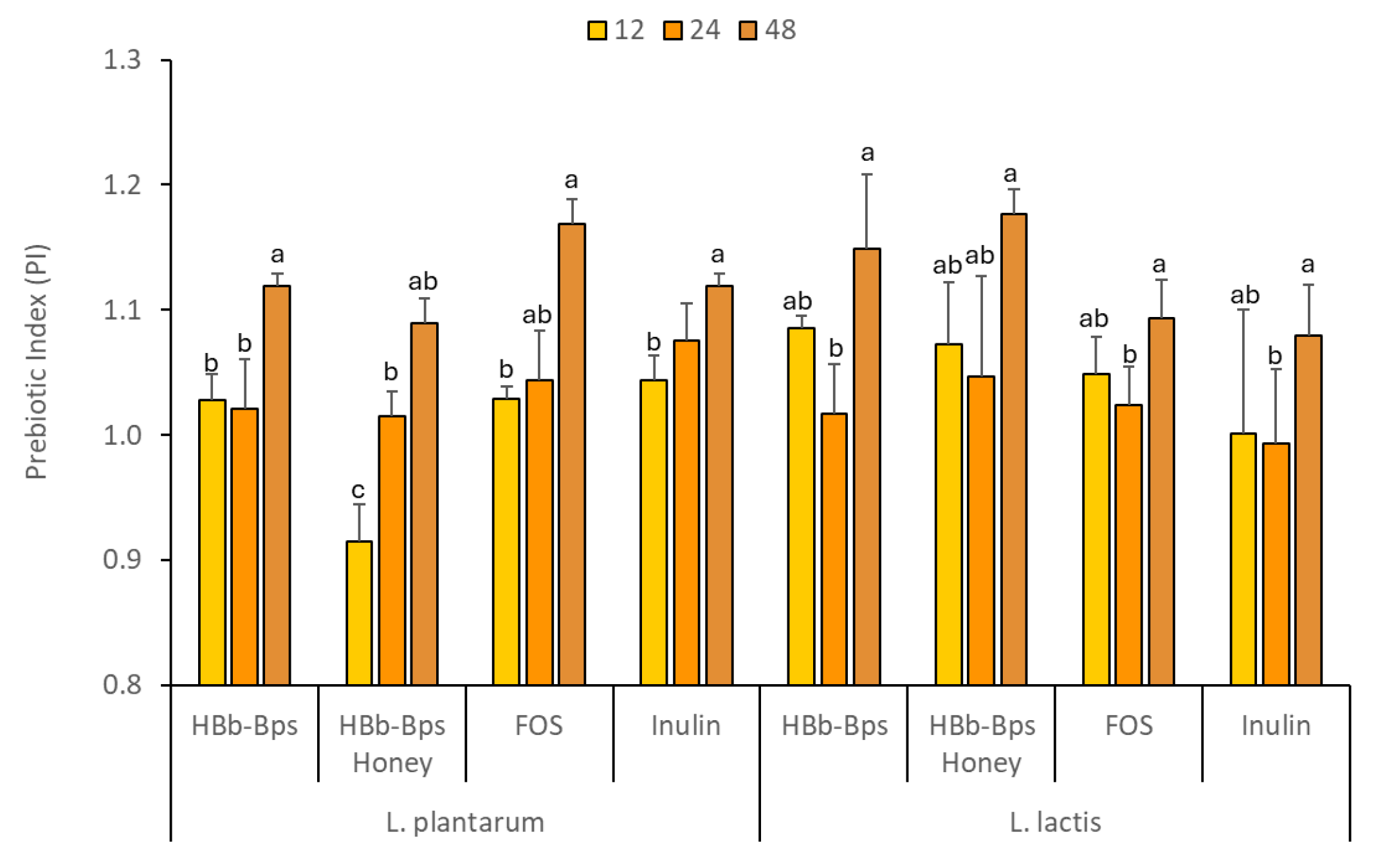
3.4. Prebiotic Properties of HBb-BPs, HBb-Bp Honey, and Commercial Prebiotic Substances
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nasri, M. Protein Hydrolysates and Biopeptides: Production, Biological Activities, and Applications in Foods and Health Benefits. A Review. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 109–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, S.; Saari, N.; Anwar, F.; Abdul Hamid, A.; Ghazali, H.M. Recent Advances in Food Biopeptides: Production, Biological Functionalities and Therapeutic Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 80–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouria, G.; Khashayar, S.; Zahra, A. Insights into Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Exploring Effects on Antioxidant and Functional Properties of Bioactive Peptides from Chlorella Proteins. J. Agri. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.B.; Je, J.Y.; Cho, Y.S. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Fraction from Salmon Byproduct Protein Hydrolysates by Peptic Hydrolysis. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhumen, A.T.; Jose, P.P.; Encarnacion Emilia, S.Y.; Yu-Wei, C. Bioactivities of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates Derived from Chlorella sorokiniana. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, C.; Priyadarshini, P. Whey Protein Hydrolysates Improve High-fat-diet-induced Obesity by Modulating the Brain-Peripheral Axis of GLP-1 through Inhibition of DPP-4 Function in Mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2489–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini Sarteshnizi, R.; Sahari, M.A.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Nikoo, M.; Udenigwe, C.C. Influence of Fish Protein Hydrolysate-Pistachio Green Hull Extract Interactions on Antioxidant Activity and Inhibition of α-Glucosidase, α-Amylase, and DPP-IV Enzymes. LWT 2021, 142, 111019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Rafiq, S.; Gat, Y.; Gat, P.; Waghmare, R.; Kumar, V. A Review on Bioactive Peptides: Physiological Functions, Bioavailability and Safety. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, D.F. Nutrient Composition of Bee Brood and its Potential as Human Food. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2005, 44, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Jung, C. Honeybees and Their Brood: A Potentially Valuable Resource of Food, Worthy of Greater Appreciation and Scientific Attention. J. Ecology Environ. 2021, 45, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, C.; Mazumder, I.; Marrazzo, P. Revolutionizing the Use of Honeybee Products in Healthcare: A Focused Review on Using Bee Pollen as a Potential Adjunct Material for Biomaterial Functionalization. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Florença, S.G.; Correia, P.M.R.; Anjos, O.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C.A. Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Broods: Composition, Technology, and Gastronomic Applicability. Foods 2022, 11, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuraphan, P.; Suang, S.; Bunrod, A.; Kanjanakawinkul, W.; Chaiyana, W. Potential of Bioactive Protein and Protein Hydrolysate from Apis mellifera Larvae as Cosmeceutical Active Ingredients for Anti-Skin Aging. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishyna, M.; Martinez, J.I.; Chen, J.; Benjamin, O. Extraction, Characterization and Functional Properties of Soluble Proteins from Edible Grasshopper (Schistocerca gregaria) and Honeybee (Apis mellifera). Food Res. Inter. 2019, 116, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S. Nutrition, Safety, Health Functional Effects, and Availability of Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Drone Pupae. Insects 2021, 12, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawczuk, R.; Karpinska, J.; Filipowska, D.; Bajguz, A.; Hryniewicka, M. Evaluation of Total Phenols Content, anti-DPPH Activity and the Content of Selected Antioxidants in the Honeybee Drone Brood Homogenate. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y. Purification and Identification of Peptides with High Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity from Honeybee Pupae (Apis mellifera) Hydrolysates with in silico Gastrointestinal Digestion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Woo, S.O.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, H.M.; Moon, H.J.; Han, S.M. Antioxidant and Antihyperglycemic Effects of Honeybee Drone Pupae (Apis mellifera L.) Extracts. J. Apic. 2020, 35, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, M.C.; Cudic, M. Optimization of Physicochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Peptide Drugs by Glycosylation. Methods. Mol. Biol. 2013, 1081, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phongphisutthinant, R.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Boonyapranai, K.; Ounjaijean, S.; Taya, S.; Pitchakarn, P.; Pathomrungsiyounggul, P.; Utarat, P.; Wongwatcharayothin, W.; Somjai, C.; et al. Effect of Conventional Humid–Dry Heating through the Maillard Reaction on Chemical Changes and Enhancement of In Vitro Bioactivities from Soy Protein Isolate Hydrolysate–Yeast Cell Extract Conjugates. Foods 2024, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooshkam, M.; Varidi, M.; Verma, D.K. Functional and Biological Properties of Maillard Conjugates and Their Potential Application in Medical and Food: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjai, C.; Siriwoharn, T.; Kulprachakarn, K.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Wiriyacharee, P. Utilization of Maillard Reaction in Moist-Dry-Heating System to Enhance Physicochemical and Antioxidative Properties of Dried Whole Longan Fruit. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Puangmanee, S.; Izumori, K. Chemical Properties and Antioxidative Activity of Glycated α-lactalbumin with a Rare Rugar, d-Allose, by Maillard Reaction. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Morales, F.J. Microtiter Plate-based Assay for Screening Antimicrobial Activity of Melanoidins Against E. Coli and S. Aureus. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Morales, F.J. Functional Properties of Melanoidins: In Vitro Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antihypertensive Activities. Food Res. Inter. 2007, 40, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Martínez, M.; Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Villamiel, M.; Rastall, R.A.; Moreno, F.J. In vitro bifidogenic effect of Maillard-type milk protein–galactose conjugates on the human intestinal microbiota. Int. Dairy. J. 2013, 31, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, D.; Habermeyer, M.; Kemény, M.; Weyand, U.; Niederberger, E.; Frank, O.; Hofmann, T. Maillard Reaction Products Modulating the Growth of Human Tumor Cells In Vitro. Chemical Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikasari, L.; Mitchell, D.A. Protease Production by Rhizopus oligosporus in Solid-State Fermentation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 10, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.; Xu, Y.; AL-Bukhaiti, W.Q.; Abed, S.M.; Ali, A.H.; Ramadhan, A.H.; Xia, W. Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions on the degree of hydrolysis and functional properties of protein hydrolysate obtained from Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) by using papain enzyme. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaipoot, S.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Buadoktoom, S.; Srisuwun, A.; Somjai, C.; Srinuanpan, S. Changes in physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities of dried shiitake mushroom in dry-moist-heat aging process. Foods 2023, 12, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjai, C.; Siriwoharn, T.; Kulprachakarn, K.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Chaiyana, W.; Srinuanpan, S.; Wiriyacharee, P. Effect of drying process and long-term storage on characterization of Longan pulps and their biological aspects: Antioxidant and cholinesterase inhibition activities. LWT 2022, 154, 112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaipoot, S.; Punfa, W.; Ounjaijean, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Kulprachakarn, K.; Parklak, W.; Phaworn, L.; Rotphet, P.; Boonyapranai, K. Antioxidant, Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Obesity, and Antihypertensive Properties of Protein Hydrolysate and Peptide Fractions from Black Sesame Cake. Molecules 2023, 28, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, N.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, M.; Cui, X.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, X. In vitro Prebiotic Properties of Garlic Polysaccharides and Its Oligosaccharide Mixtures Obtained by Acid Hydrolysis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 798450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, C.; González, A.; Ballesteros, I.; Gullón, B.; Negro, M.J. In Vitro Assessment of the Prebiotic Potential of Xylooligosaccharides from Barley Straw. Foods 2023, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peighambardoust, S.H.; Karami, Z.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Review on Health-Promoting, Biological, and Functional Aspects of Bioactive Peptides in Food Applications. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Chen, G.; Liu, H. Antioxidative Categorization of Twenty Amino Acids Based on Experimental Evaluation. Mol. A J. Synth. Chem. Nat. Product. Chem. 2017, 22, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongchai, P.; Yadoung, S.; Sutan, K.; Kawichai, S.; Danmek, K.; Maitip, J.; Ghosh, S.; Jung, C.; Chuttong, B.; Hongsibsong, S. Antioxidant Capacity, Phytochemicals, Minerals, and Chemical Pollutants in Worker Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Broods from Northern Thailand: A Safe and Sustainable Food Source. Foods 2024, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, M.D.; Tchorbanov, B.P. Preparation of Antioxidant Enzymatic Hydrolysates from Honeybee-Collected Pollen Using Plant Enzymes. Enzym. Res. 2010, 2010, 415949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Abdul, Q.; Jiang, Z. Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Products Derived from Xylose–Bovine Casein Hydrolysate Maillard Reaction: Impact of Reaction Time. Foods 2019, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Guo, A.; Zhang, R.; Shi, L. Mechanism of Natural Antioxidants Regulating Advanced Glycosylation End Products of Maillard Reaction. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hang, F.; Wei, T.; Xie, C.; Niu, D. Modification of Ovalbumin by Maillard Reaction: Effect of Heating Temperature and Different Monosaccharides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 914416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbizo-Reyes, U.; Liceaga, A.M.; Reddivari, L.; Kim, K.; Anderson, J.M. Enzyme Kinetics, Molecular Docking, and in silico Characterization of Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides with ACE and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 88, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Khani, A.; Eghbalpour, S.; Uversky, V.N. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Virtual Screening Technology for Two Novel Peptides in Soybean as Inhibitors of α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase. Foods 2023, 12, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, R.; Seidu, I.; Willmore, W.; Tsopmo, A. Antioxidant, Pancreatic Lipase, and α-Amylase Inhibitory Properties of Oat Bran Hydrolyzed Proteins and Peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Wang, Y.; Selomulya, C. Improvements of plant protein functionalities by Maillard conjugation and Maillard reaction products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7036–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, H.; Khan, H.; Haque, S.; Ahmad, S.; Srivastava, N.; Khan, A. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Hypertension: A Systemic Analysis of Various ACE Inhibitors, Their Side Effects, and Bioactive Peptides as a Putative Therapy for Hypertension. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. JRAAS 2023, 2023, 7890188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskaya-Dikmen, C.; Yucetepe, A.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F.; Daskaya, H.; Ozcelik, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Plants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Chai, Y.U.; Tu, C.C.; Cheng, M.C.; Tseng, C.Y.; Chang, C.Y. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory activity of bee pupae protein hydrolysates. Acad. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Mureşan, C.I.; Dezmirean, D.S.; Marc, B.D.; Suharoschi, R.; Pop, O.L.; Buttstedt, A. Biological Properties and Activities of Major Royal Jelly Proteins and Their Derived Peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 98, 105286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, R.A.; Bashir, A.; Yousaf, M.N.; Ahmed, A.; Dali, Y.; Khan, S.; Sehgal, S.A. In Silico Identification of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from MRJP1. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, Y.; Meenu, M.; Yu, X.; Xu, B. Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids Profiles of Commercial Honey from Different Floral Sources and Geographic Sources. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamigbade, G.B.; Subhash, A.J.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Nyström, L.; Ayyash, M. An Updated Review on Prebiotics: Insights on Potentials of Food Seeds Waste as Source of Potential Prebiotics. Molecules 2022, 27, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, H. Potential Prebiotic Activities of Soybean Peptides Maillard Reaction Products on Modulating Gut Microbiota to Alleviate Aging-Related Disorders in D-Galactose-Induced ICR Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. The growth-promoting effects of protein hydrolysates and their derived peptides on probiotics: Structure-activity relationships, mechanisms and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 2387328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacteria/ Analysis | Carbon Source | Incubation Time (hours) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | ||
| L. plantarum | |||||||||
| Growth (OD620) | Dextrose | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.15 + 0.01 a | 1.47 ± 0.12 b | 2.58 ± 0.12 b | 2.71 ± 0.09 a | 2.79 ± 0.08 a | 2.85 ± 0.08 b | 2.76 ± 0.04 c |
| HBb-Bps | 0.05 ± 0.09 a | 0.22 + 0.11 a | 1.87 ± 0.02 a | 3.04 ± 0.24 a | 2.91 ± 0.03 a | 2.98 ± 0.09 a | 3.21 ± 0.00 a | 3.22 ± 0.02 a | |
| HBb-Bp honey | 0.05 ± 0.02 a | 0.22 + 0.04 a | 1.80 ± 0.04 a | 2.68 ± 0.21 b | 2.47 ± 0.17 b | 2.83 ± 0.11 a | 2.92 ± 0.02 b | 3.01 ± 0.04 b | |
| FOS | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.15 + 0.01 a | 1.55 ± 0.11 b | 2.45 ± 0.11 b | 2.78 ± 0.05 a | 2.91 ± 0.06 a | 3.20 ± 0.10 a | 3.23 ± 0.06 a | |
| Inulin | 0.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 + 0.01 a | 1.53 ± 0.04 b | 2.53 ± 0.06 b | 2.82 ± 0.06 a | 3.00 ± 0.13 a | 3.05 ± 0.20 a | 3.09 ± 0.04 b | |
| pH | Dextrose | 5.30 ± 0.04 a | 5.22 ± 0.05 a | 4.63 ± 0.07 a | 4.34 ± 0.02 a | 4.32 ± 0.08 a | 4.25 ± 0.03 a | 4.26 ± 0.04 a | 4.32 ± 0.09 b |
| HBb-Bps | 5.42 ± 0.04 a | 5.32 ± 0.10 a | 4.79 ± 0.04 a | 4.53 ± 0.07 a | 4.38 ± 0.04 a | 4.16 ± 0.04 a | 4.16 ± 0.06 a | 4.13 ± 0.07 a | |
| HBb-Bps honey | 5.33 ± 0.05 a | 5.26 ± 0.03 a | 4.84 ± 0.04 a | 4.65 ± 0.11 a | 4.33 ± 0.05 a | 4.21 ± 0.07 a | 4.22 ± 0.10 a | 4.28 ± 0.02 b | |
| FOS | 5.38 ± 0.03 a | 5.32 ± 0.08 a | 4.68 ± 0.10 a | 4.42 ± 0.12 a | 4.27 ± 0.02 a | 4.12 ± 0.00 a | 4.19 ± 0.05 a | 4.14 ± 0.10 a | |
| Inulin | 5.31 ± 0.03 a | 5.34 ± 0.03 a | 4.73 ± 0.06 a | 4.45 ± 0.07 a | 4.22 ± 0.06 a | 4.08 ± 0.17 a | 4.06 ± 0.08 a | 4.08 ± 0.07 a | |
| L. lactis | |||||||||
| Growth (OD620) | Dextrose | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.34 ± 0.08 b | 1.13 ± 0.06 c | 2.12 ± 0.06 b | 2.65 ± 0.08 b | 2.98 ± 0.11 a | 2.75 ± 0.05 b | 2.56 ± 0.06 c |
| HBb-Bps | 0.10 ± 0.00 a | 0.41 ± 0.08 b | 1.39 ± 0.06 b | 2.57 ± 0.06 a | 2.93 ± 0.08 a | 3.10 ± 0.11 a | 3.02 ± 0.05 a | 3.00 ± 0.06 a | |
| HBb-Bps honey | 0.05 ± 0.04 a | 0.56 ± 0.04 a | 1.71 ± 0.10 a | 2.42 ± 0.03 a | 2.84 ± 0.10 a | 3.13 ± 0.09 a | 2.98 ± 0.10 a | 3.01 ± 0.10 a | |
| FOS | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.31 ± 0.05 b | 1.18 ± 0.10 c | 2.13 ± 0.06 b | 2.76 ± 0.07 a | 3.04 ± 0.08 a | 2.85 ± 0.07 a | 2.79 ± 0.06 b | |
| Inulin | 0.06 ± 0.05 a | 0.36 ± 0.05 b | 1.20 ± 0.10 c | 2.19 ± 0.06 b | 2.67 ± 0.07 b | 2.98 ± 0.08 a | 2.85 ± 0.07 a | 2.78 ± 0.06 b | |
| pH | Dextrose | 5.33 ± 0.03 a | 5.26 ± 0.07 a | 4.89 ± 0.05 a | 4.51 ± 0.03 a | 4.50 ± 0.12 a | 4.41 ± 0.09 a | 4.34 ± 0.04 a | 4.37 ± 0.06 a |
| HBb-Bps | 5.38 ± 0.04 a | 5.20 ± 0.05 a | 4.68 ± 0.07 a | 4.53 ± 0.05 a | 4.37 ± 0.06 a | 4.23 ± 0.07 b | 4.07 ± 0.05 b | 4.02 ± 0.10 b | |
| HBb-Bps honey | 5.36 ± 0.05 a | 5.17 ± 0.02 a | 4.76 ± 0.10 a | 4.63 ± 0.06 a | 4.41 ± 0.07 a | 4.24 ± 0.11 b | 4.18 ± 0.09 b | 4.15 ± 0.08 b | |
| FOS | 5.29 ± 0.05 a | 5.22 ± 0.04 a | 4.69 ± 0.12 a | 4.52 ± 0.04 a | 4.44 ± 0.01 a | 4.29 ± 0.11 a | 4.20 ± 0.05 b | 4.18 ± 0.10 b | |
| Inulin | 5.28 ± 0.04 a | 5.18 ± 0.07 a | 4.73 ± 0.03 a | 4.50 ± 0.08 a | 4.32 ± 0.01 a | 4.24 ± 0.02 b | 4.17 ± 0.10 b | 4.14 ± 0.05 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ounjaijean, S.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Kanthakat, G.; Taya, S.; Pathomrungsiyounggul, P.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Boonyapranai, K. Evaluation of Prebiotic and Health-Promoting Functions of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides and Their Maillard Reaction Conjugates. Foods 2024, 13, 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172847
Ounjaijean S, Chaipoot S, Phongphisutthinant R, Kanthakat G, Taya S, Pathomrungsiyounggul P, Wiriyacharee P, Boonyapranai K. Evaluation of Prebiotic and Health-Promoting Functions of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides and Their Maillard Reaction Conjugates. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172847
Chicago/Turabian StyleOunjaijean, Sakaewan, Supakit Chaipoot, Rewat Phongphisutthinant, Gochakorn Kanthakat, Sirinya Taya, Pattavara Pathomrungsiyounggul, Pairote Wiriyacharee, and Kongsak Boonyapranai. 2024. "Evaluation of Prebiotic and Health-Promoting Functions of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides and Their Maillard Reaction Conjugates" Foods 13, no. 17: 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172847
APA StyleOunjaijean, S., Chaipoot, S., Phongphisutthinant, R., Kanthakat, G., Taya, S., Pathomrungsiyounggul, P., Wiriyacharee, P., & Boonyapranai, K. (2024). Evaluation of Prebiotic and Health-Promoting Functions of Honeybee Brood Biopeptides and Their Maillard Reaction Conjugates. Foods, 13(17), 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172847







